User login
Home Modifications for Rural Veterans With Disabilities
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) created the Home Improvements and Structural Alterations (HISA) program to help provide necessary home modifications (HMs) to veterans with disabilities (VWDs) that will facilitate the provision of medical services at home and improve home accessibility and functional independence. The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has more than 9 million veteran enrollees; of those, 2.7 million are classified as rural or highly rural.1 Rural veterans (RVs) possess higher rate of disability compared with that of urban veterans.2-5 RVs have unequal access to screening of ambulatory care sensitive conditions (eg, hypertension, diabetes mellitus).6 Furthermore, RVs are at risk of poor medical outcomes due to distance from health care facilities and specialist care, which can be a barrier to emergency care when issues arise. These barriers, among others, are associated with compromised health quality of life and health outcomes for RVs.3,6 The HISA program may be key to decreasing falls and other serious mishaps in the home. Therefore, understanding use of the HISA program by RVs is important. However, to date little information has been available regarding use of HISA benefits by RVs or characteristics of RVs who receive HISA benefits.
HISA Alterations Program
HISA was initially developed by VA to improve veterans’ transition from acute medical care to home.7,8 However, to obtain HISA grants currently, there is an average 3 to 6 months application process.7 Through the HISA program, VWDs can be prescribed the following HMs, including (but not limited to): flooring replacement, permanent ramps, roll-in showers, installation of central air-conditioning systems, improved lighting, kitchen/bathroom modifications, and home inspections. The HMs prescribed depend on an assessment of medical need by health care providers (HCPs).8
As time passed and the veteran population aged, the program now primarily helps ensure the ability to enter into essential areas and safety in the home.5 The amount of a HISA payment is based on whether a veteran’s health condition is related to military service as defined by the VHA service connection medical evaluation process. Barriers to obtaining a HISA HM can include difficulty in navigating the evaluation process and difficulty in finding a qualified contractor or builder to do the HM.7
This article aims to: (1) Detail the sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of rural HISA users (RHUs); (2) report on HISA usage patterns in number, types, and cost of HMs; (3) compare use amid the diverse VA medical centers (VAMCs) and related complexity levels and Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs); and (4) examine the relationship between travel time/distance and HISA utilization. The long-term goal is to provide accurate information to researchers, HM administrators, health care providers and policy makers on HISA program utilization by rural VWDs, which may help improve its use and bring awareness of its users. This study was approved by the affiliate University of Florida Institutional Review Board and VA research and development committee at the North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System.
Methods
Data were obtained from 3 VA sources: the National Prosthetics Patient Database (NPPD), the VHA Medical Inpatient Dataset, and the VHA Outpatient Dataset.7 The NPPD is a national administrative database that contains information on prosthetic-associated products ordered by HCPs for patients, such as portable ramps, handrails, home oxygen equipment, and orthotic and prosthetic apparatus. Data obtained from the NPPD included cost of HMs, clinical characteristics, VISN, and VAMC. VA facilities are categorized into complexity levels 1a, 1b, 1c, 2, and 3. Complexity level 1a to 1c VAMCs address medical cases that entail “heightening involvedness,” meaning a larger number of patients presented with medical concerns needing medical specialists. Complexity levels 2 and 3 have fewer resources, lower patient numbers, and less medically complex patients. Finally, the VHA Medical Inpatient and Outpatient Datasets administrated by VA Informatics and Computing Infrastructure, consist of in-depth health services national data on inpatient and outpatient encounters and procedures.
The study cohort was divided into those with service-connected conditions (Class 1) or those with conditions not related to military service (Class 2). If veterans were identified in both classes, they were assigned to Class 1. The cost variable is determined by using the veterans’ classification. Class 1 veterans receive a lifetime limit of $6800, and Class 2 veterans receive a lifetime limit of $2000. A Class 2 veteran with ≥ 50% disability rating is eligible for a HISA lifetime limit of $6800. Whenever a value exceeds allowed limit of $6800 or $2000, due to data entry error or other reasons, the study team reassigned the cost value to the maximum allowed value.
Travel distance and time were derived by loading patient zip codes and HISA facility locations into the geographical information system program and using the nearest facility and find-route tools. These tools used a road network that simulates real-world driving conditions to calculate distance.
Study Variables
VWDs of any age, gender, and race/ethnicity who qualified for HISA and received HMs from fiscal year ( FY) 2015 through FY 2018 were identified (N = 30,823). Most VWDs were nonrural subjects (n = 19,970), and 43 had no Federal Information Processing System data. The final study cohort consisted of 10,810 HISA recipients. The NPPD, inpatient and outpatient data were merged by scrambled social security numbers to retrieve the following data: age, gender, race, ethnicity, marital status, Class (1 or 2), mean and total number of inpatient days, and type of HMs prescribed.
We also recorded rurality using the VA Rural-Urban Commuting Areas (RUCA) system, but we combined the rural and highly rural designation.1 Census tracts with a RUCA score of 10.0 are deemed highly rural, the remainder are considered rural except those with a RUCA score of 1.0 or 1.1. Travel time and distance from a veteran’s home to the VA facility that provided the HISA prescription were determined from zip codes. The current study focuses on VAMCs prescribing stations (affiliated sites of administrative parent medical facilities) where the HISA users obtained the HM, not the parent station (administrative parent medical facilities).
HISA Utilization
To characterize HISA utilization geographically and over time, the number of users were mapped by county. Areas where users were increasing (hot spots) or decreasing (cold spots) also were mapped. The maps were created using Environmental Systems Research Institute ArcGIS Pro 2.2.1 software. We chose to use natural breaks (Jenks) data classification method in a choropleth to symbolize the change over time map. We then used the Getis Ord GI* optimized hot spot analysis tool in the ArcGIS Pro spatial statistics tool set to generate the hot/cold spot maps. This tool identifies clusters of high values (hot spots) and low values (cold spots) creating a new output layer, RHUs by county, with a Z score, P value, and CI for each county. The Gi Bin field classifies statistically significant hot and cold spots. Counties sorted into the ± 3 category (bin) have a clustering characteristic (eg, with neighboring counties) that is statistically significant with a 99% CI; the ± 2 bin indicates a 95% CI for those county clustering sorted therein; ± 1 reflects a 90% CI; and 0 bin contains county features that have no statistical significant clustering with neighboring counties.
Data Analysis
Data were cleaned and analyzed using SAS 9.4 and R 3.5.3. Descriptive statistics are provided for sociodemographic characteristics, clinical characteristics, and class. ANOVA and t tests were used to compare continuous variables between groups, while χ2 and Fisher exact tests were used for dichotomous and categorical outcome variables. The threshold for statistical significance for these tests was set at α = .001.
Results
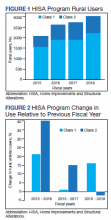
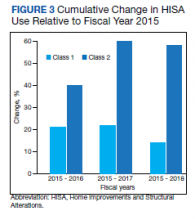
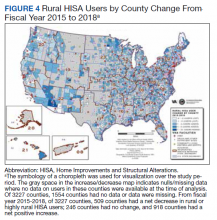
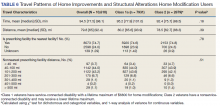
There were 10,810 RHUs from FY 2015 through FY 2018 and HISA utilization increased each year (Figure 1). Although some years may show usage decreases relative to previous fiscal years, the cumulative trends showed an increase relative to FY 2015 for both Classes of RVs (Figure 2). There was a 45.4% increase from FY 2015 to FY 2018 with a mean 13.6% yearly increase. Class 1 increased 21.0% and Class 2 increased 39.5% from FY 2015 to FY 2016 (Figure 3).
Most RHUs were male, White, and married. Class 1 and Class 2 RHUs differed significantly by age, race, marital status, and disability conditions: Class 1 RHUs were aged 6.6 years younger with a mean age of 69.1 years compared with 75.7 years for Class 2 users. For Class 1 RHUs, a plurality (29.4%) were aged 65 to 69 years; while a plurality (41.4%) of Class 2 users were aged ≥ 80 years. Musculoskeletal was the most common identified type of condition for all RHUs (Table 1).
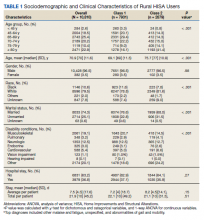
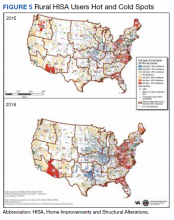
To better understand HISA utilization patterns and net RHUs per county, we used a map to detail RHUs by county and change over time (Figure 4). Additionally, we compared US counties by RHUs from FY 2015 to FY 2018 and determined how clusters of high numbers of RHUs (hot spots) and low numbers of RHUs (cold spots) shifted over this period (Figure 5). While HISA utilization grew over the study period, the net count of RHUs per county varied by 9 to 20 persons/county. The population of RHUs increased over time in the Southwest, Southeast, and over much of the East/Northeast, while in the Central and Midwest regions, number of RHUs seems to decrease in population and/or use of the system. The cold spots in the Midwest and South Central US seem to increase with a significant relationship to neighboring counties having a low number of RHUs.
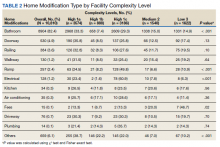
There were 11,166 HM prescribed to RHUs (Table 2). Bathroom HMs also were the dominant HM type for all facilities regardless of complexity levels (Table 3). The San Antonio, Texas, VAMC demonstrated the highest Class 1 vs Class 2 difference in HISA use (Class 1: 87.7% and Class 2: 12.3%). Except for the Des Moines VAMC, all other VAMCs showed HISA use > 60% by Class 1.
Cost Data
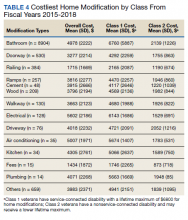
Air-conditioning installation ($5007) was the costliest HM overall (Table 4), closely followed by bathroom ($4978) and kitchen modifications ($4305). Bathroom renovations were the costliest HM type for both Class 1 and Class 2, closely followed by electrical repair and air-conditioning installation for Class 1 and driveway reconstruction and wooden ramp construction for Class 2.
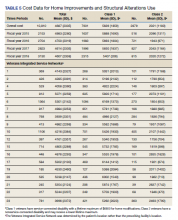
The mean award received for HM was $4687 (Table 5). While the number of RHUs increased from FY 2015 to FY 2016, the average cost decreased, both overall ($280) and for Class 1 ($195) and Class 2 ($153). Except for a small decline in the number of Class 2 HISA recipients from FY 2017 to FY 2018, overall, the number of RHUs continuously grew from FY 2015 to FY 2018: 977 for the overall cohort, 678 for Class 1 and 299 for Class 2. Despite the obvious gain in the number of RHUs, the average costs did not notably change over time. VISN 21 had the highest mean cost, followed by VISNs 17, 6, 22, and 20.
Travel
Travel time and distance to the HISA prescribing facility differed significantly between Class 1 and Class 2 HISA users. RHUs had to travel about 95 minutes from their place of residence to access the HISA benefits program. There were no statistically significant differences between Class 1 and 2 users with respect to travel time and distance traveled (Table 6).
The majority of Class 1 and Class 2 veterans accessed the HISA from their nearest facility. However, nearly one-quarter of both Class 1 and 2 RHUs (24% each) did not. Among the 2598 who accessed the nonnearest facility, 97 (3.7%) accessed a facility that is ≤ 40 miles. Many (44%) users traveled 40 to 100 miles, and another 43.2% traveled 100 to 200 miles from their residence to access a HM prescription. Some 2598 users (1.1%) traveled > 500 miles to access a facility.
Discussion
Although utilization of the HISA program has steadily increased, overall participation by subpopulations such as RHUs can still be improved significantly. Veterans aged ≤ 46 years who have a disability that is common to those receiving HISA benefits have low HISA utilization. Similarly, veterans with sensory disabilities also have low use. These subpopulations are among those in great need of attention and services.
A study by Lucas and Zelaya, using the 2016 National Health Interview Survey data with an aim to measure degree of vision problems, dual sensory impairment, and hearing trouble in male veterans aged ≥ 18 years, found that veterans were more likely to report dual sensory impairment and balance difficulties when compared with nonveterans.9 The number of female veterans is growing but had very low representation in this study.10 This emerging VHA population requires information and education on their HM benefits.
Home Modifications
The most common HM prescribed for RHUs was for the bathroom. Further investigation is warranted as to why, given the diversity of HM types that the grant covers, low prescription rates exist across most of the HM types. There may be a lack of knowledge by providers and VWD as to the range of HMs that can be awarded under the grant. It is important that HCPs and veterans receive education on HISA HM options.
Semeah and colleagues pointed out the need for an assessment of the HISA HM ordering system to ensure that multiple HMs items (eg, kitchen, air conditioning, fees, driveway, and plumbing) are listed among the forced choices shown to clinicians to select from.7 Poor housing in rural America is widespread: 63% of rural dwellings need renovations and/or repairs to be accessible to individuals with disabilities, with > 6.7 million rural homes having no or faulty plumbing or kitchens; yet in this study, prescriptions for these HMs accounted for < 1%.11,12
VISN 6 had the most HISA awards with 1364, while VISN 21 had the fewest (245). Across all VISNs, Class 1 RHUs received more prescriptions than did Class 2 RHUs. Future research may seek to examine whether prescribers are fully aware of the eligibility of HM prescription to Class 2 veterans. VISN 21 ($5354); VISN 17 ($5302); and VISN 6 ($5301) had the highest mean HM expenditures. The national mean cost for HISA HMs were $4978 for bathrooms and $4305 for kitchens; for non-HISA HMs in FY 2017, the mean costs were $6362 and $12,255, respectively. A noteworthy concern is whether the maximum grant limit awards are sufficient to perform more expensive and complex HMs, such as the kitchen or major bathroom alternations.13
Facilities categorized as 1a, 1b, or 1c provided
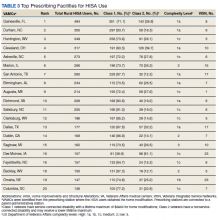
North Florida/Sough Georgia was the highest-prescribing VAMC with 39% more HM prescriptions than the second highest prescribing facility (Durham, NC). Unfortunately, the data presented here cannot establish causality for the large variance difference between the top facilities, and the skewed distribution of total RHUs across VAMCs.
Travel-Related Variables
HISA beneficiaries face significant travel-related challenges. Just 3.6% of RHUs could access a facility within 40 miles of their home and 43.2% traveled 100 to 200 miles from their home to access a HM prescription. Further exploration is warranted to understand how travel patterns impact access to or the uptake of HISA.
RVs already have problems with accessing care because of long travel time.14,15 The choice or necessity to travel to a farther facility for HISA prescription is problematic for RVs, especially when transportation is often reported in the literature as a barrier to resources for people living in rural communities.15-17 When patients have travel barriers, they wait longer to obtain medical services and often wait for their conditions to worsen before seeking services.15,18 Once HM is completed, telerehabilitation is an effective delivery method used for delivering health care services to people in remote places.18,19 Considering that HISA use has the potential to improve quality of life, afford comfort, facilitate the accomplishment of activities of daily living for RVs, it is important that future studies examine how existing telehealth technologies can be used to improve HISA access.
Future Directions
County-level analyses is warranted in future studies exploring potential variables associated with HISA use; for example, county-level rates of primary care physicians and other HCPs. Future research should explore how long distance travel impacts the HISA application process and HM implementation. Further research also should focus on the HISA application structure and process to identify causes of delays. The HISA application process takes a mean 6 months to complete, yet the duration of hospital stays is 1 to 3 weeks, thus it is impossible to connect HISA to hospital discharge, which was the original intent of the program. Future research can examine how telehealth services can expedite HISA obtainment and coordination of the application process. Future research also may study the possible causes of the wide variations in HM prescriptions per facility. It is also important that educational programs provide information on the array of HM items that veterans can obtain.
Conclusions
In our previous study of the HISA cohort (2011-2017), we documented that an increase in utilization of the HISA program was warranted based on the low national budgetary appropriation and identification of significant low participation by vulnerable subpopulations, including veterans residing in rural areas or having returned from recent conflicts.7 The present study documents national utilization patterns, demographic profiles, and clinical characteristics of RHUs from FY 2015 through FY 2018, data that may be useful to policy makers and HISA administrators in predicting future use and users. It is important to note that the data and information presented in this article identify trends. The work in no way establishes a gold standard or any targeted goal of utilization. Future research could focus on conceptualizing or theorizing what steps are necessary to set such a gold standard of utilization rate and steps toward achievement.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grant 15521 from the US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health . Furthermore, the research was supported in part by grant K12 HD055929 from the National Institutes of Health.
1. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veteran Health Administration, Office of Rural Health. Rural veteran health care challenges. Updated February 9, 2021. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
2. Holder, K.A. Veterans in rural America, 2011–2015. Published January 2017. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2017/acs/acs-36.pdf
3. Pezzin LE, Bogner HR, Kurichi JE, et al. Preventable hospitalizations, barriers to care, and disability. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(19):e0691. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000010691
4. Rosenbach ML. Access and satisfaction within the disabled Medicare population. Health Care Financ Rev. 1995;17(2):147-167.
5. Semeah LM, Ganesh SP, Wang X, et al. Home modification and health services utilization in rural and urban veterans with disabilities. Housing Policy Debate. 2021. Published online: March 4, 2021. doi:10.1080/10511482.2020.1858923
6. Spoont M, Greer N, Su J, Fitzgerald P, Rutks I, and Wilt TJ. Rural vs. urban ambulatory health care: A Systematic Review. Published May 2011. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/esp/ambulatory.pdf
7. Semeah LM, Wang X, Cowper Ripley DC, et al. Improving health through a home modification service for veterans. In: Fiedler BA, ed. Three Facets of Public Health and Paths to Improvements. Academic Press; 2020:381-416.
8. Semeah LM, Ahrentzen S, Jia H, Cowper-Ripley DC, Levy CE, Mann WC. The home improvements and structural alterations benefits program: veterans with disabilities and home accessibility. J Disability Policy Studies. 2017;28(1):43-51. doi:10.1177/1044207317696275
9. Lucas, JW, Zelaya, CE. Hearing difficulty, vision trouble, and balance problems among male veterans and nonveterans. Published June 12, 2020. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhsr/nhsr142-508.pdf
10. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Women veterans report: the past, present, and future of women veterans. Published February 2017. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/docs/SpecialReports/Women_Veterans_2015_Final.pdf
11. US Department of Housing and Urban Development, Office of Policy Development and Research. Housing challenges of rural seniors. Published 2017. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.huduser.gov/portal/periodicals/em/summer17/highlight1.html
12. Pendall R, Goodman L, Zhu J, Gold A. The future of rural housing. Published October 2016. Accessed June 11, 202.1 https://www.urban.org/sites/default/files/publication/85101/2000972-the-future-of-rural-housing_6.pdf
13. Joint Center for Housing Studies at Harvard University. Improving America’s housing 2019. Published 2019. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.jchs.harvard.edu/sites/default/files/reports/files/Harvard_JCHS_Improving_Americas_Housing_2019.pdf
14. Schooley BL, Horan TA, Lee PW, West PA. Rural veteran access to healthcare services: investigating the role of information and communication technologies in overcoming spatial barriers. Perspect Health Inf Manag. 2010;7(Spring):1f. Published 2010 Apr 1.
15. Ripley DC, Kwong PL, Vogel WB, Kurichi JE, Bates BE, Davenport C. How does geographic access affect in-hospital mortality for veterans with acute ischemic stroke?. Med Care. 2015;53(6):501-509. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000366
16. Cowper-Ripley DC, Reker DM, Hayes J, et al. Geographic access to VHA rehabilitation services for traumatically injured veterans. Fed Pract. 2009;26(10):28-39.
17. Smith M, Towne S, Herrera-Venson A, Cameron K, Horel S, Ory M, et al. Delivery of fall prevention interventions for at-risk older adults in rural areas: Findings from a national dissemination. International journal of environmental research and public health. 2018;15:2798. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15122798
18. Hale-Gallardo JL, Kreider CM, Jia H, et al. Telerehabilitation for Rural Veterans: A Qualitative Assessment of Barriers and Facilitators to Implementation. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2020;13:559-570. doi:10.2147/JMDH.S247267
19. Sarfo FS, Akassi J, Kyem G, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Stroke in a Ghanaian Outpatient Clinic. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018;27(4):1090-1099. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.11.017
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) created the Home Improvements and Structural Alterations (HISA) program to help provide necessary home modifications (HMs) to veterans with disabilities (VWDs) that will facilitate the provision of medical services at home and improve home accessibility and functional independence. The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has more than 9 million veteran enrollees; of those, 2.7 million are classified as rural or highly rural.1 Rural veterans (RVs) possess higher rate of disability compared with that of urban veterans.2-5 RVs have unequal access to screening of ambulatory care sensitive conditions (eg, hypertension, diabetes mellitus).6 Furthermore, RVs are at risk of poor medical outcomes due to distance from health care facilities and specialist care, which can be a barrier to emergency care when issues arise. These barriers, among others, are associated with compromised health quality of life and health outcomes for RVs.3,6 The HISA program may be key to decreasing falls and other serious mishaps in the home. Therefore, understanding use of the HISA program by RVs is important. However, to date little information has been available regarding use of HISA benefits by RVs or characteristics of RVs who receive HISA benefits.
HISA Alterations Program
HISA was initially developed by VA to improve veterans’ transition from acute medical care to home.7,8 However, to obtain HISA grants currently, there is an average 3 to 6 months application process.7 Through the HISA program, VWDs can be prescribed the following HMs, including (but not limited to): flooring replacement, permanent ramps, roll-in showers, installation of central air-conditioning systems, improved lighting, kitchen/bathroom modifications, and home inspections. The HMs prescribed depend on an assessment of medical need by health care providers (HCPs).8
As time passed and the veteran population aged, the program now primarily helps ensure the ability to enter into essential areas and safety in the home.5 The amount of a HISA payment is based on whether a veteran’s health condition is related to military service as defined by the VHA service connection medical evaluation process. Barriers to obtaining a HISA HM can include difficulty in navigating the evaluation process and difficulty in finding a qualified contractor or builder to do the HM.7
This article aims to: (1) Detail the sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of rural HISA users (RHUs); (2) report on HISA usage patterns in number, types, and cost of HMs; (3) compare use amid the diverse VA medical centers (VAMCs) and related complexity levels and Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs); and (4) examine the relationship between travel time/distance and HISA utilization. The long-term goal is to provide accurate information to researchers, HM administrators, health care providers and policy makers on HISA program utilization by rural VWDs, which may help improve its use and bring awareness of its users. This study was approved by the affiliate University of Florida Institutional Review Board and VA research and development committee at the North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System.
Methods
Data were obtained from 3 VA sources: the National Prosthetics Patient Database (NPPD), the VHA Medical Inpatient Dataset, and the VHA Outpatient Dataset.7 The NPPD is a national administrative database that contains information on prosthetic-associated products ordered by HCPs for patients, such as portable ramps, handrails, home oxygen equipment, and orthotic and prosthetic apparatus. Data obtained from the NPPD included cost of HMs, clinical characteristics, VISN, and VAMC. VA facilities are categorized into complexity levels 1a, 1b, 1c, 2, and 3. Complexity level 1a to 1c VAMCs address medical cases that entail “heightening involvedness,” meaning a larger number of patients presented with medical concerns needing medical specialists. Complexity levels 2 and 3 have fewer resources, lower patient numbers, and less medically complex patients. Finally, the VHA Medical Inpatient and Outpatient Datasets administrated by VA Informatics and Computing Infrastructure, consist of in-depth health services national data on inpatient and outpatient encounters and procedures.
The study cohort was divided into those with service-connected conditions (Class 1) or those with conditions not related to military service (Class 2). If veterans were identified in both classes, they were assigned to Class 1. The cost variable is determined by using the veterans’ classification. Class 1 veterans receive a lifetime limit of $6800, and Class 2 veterans receive a lifetime limit of $2000. A Class 2 veteran with ≥ 50% disability rating is eligible for a HISA lifetime limit of $6800. Whenever a value exceeds allowed limit of $6800 or $2000, due to data entry error or other reasons, the study team reassigned the cost value to the maximum allowed value.
Travel distance and time were derived by loading patient zip codes and HISA facility locations into the geographical information system program and using the nearest facility and find-route tools. These tools used a road network that simulates real-world driving conditions to calculate distance.
Study Variables
VWDs of any age, gender, and race/ethnicity who qualified for HISA and received HMs from fiscal year ( FY) 2015 through FY 2018 were identified (N = 30,823). Most VWDs were nonrural subjects (n = 19,970), and 43 had no Federal Information Processing System data. The final study cohort consisted of 10,810 HISA recipients. The NPPD, inpatient and outpatient data were merged by scrambled social security numbers to retrieve the following data: age, gender, race, ethnicity, marital status, Class (1 or 2), mean and total number of inpatient days, and type of HMs prescribed.
We also recorded rurality using the VA Rural-Urban Commuting Areas (RUCA) system, but we combined the rural and highly rural designation.1 Census tracts with a RUCA score of 10.0 are deemed highly rural, the remainder are considered rural except those with a RUCA score of 1.0 or 1.1. Travel time and distance from a veteran’s home to the VA facility that provided the HISA prescription were determined from zip codes. The current study focuses on VAMCs prescribing stations (affiliated sites of administrative parent medical facilities) where the HISA users obtained the HM, not the parent station (administrative parent medical facilities).
HISA Utilization
To characterize HISA utilization geographically and over time, the number of users were mapped by county. Areas where users were increasing (hot spots) or decreasing (cold spots) also were mapped. The maps were created using Environmental Systems Research Institute ArcGIS Pro 2.2.1 software. We chose to use natural breaks (Jenks) data classification method in a choropleth to symbolize the change over time map. We then used the Getis Ord GI* optimized hot spot analysis tool in the ArcGIS Pro spatial statistics tool set to generate the hot/cold spot maps. This tool identifies clusters of high values (hot spots) and low values (cold spots) creating a new output layer, RHUs by county, with a Z score, P value, and CI for each county. The Gi Bin field classifies statistically significant hot and cold spots. Counties sorted into the ± 3 category (bin) have a clustering characteristic (eg, with neighboring counties) that is statistically significant with a 99% CI; the ± 2 bin indicates a 95% CI for those county clustering sorted therein; ± 1 reflects a 90% CI; and 0 bin contains county features that have no statistical significant clustering with neighboring counties.
Data Analysis
Data were cleaned and analyzed using SAS 9.4 and R 3.5.3. Descriptive statistics are provided for sociodemographic characteristics, clinical characteristics, and class. ANOVA and t tests were used to compare continuous variables between groups, while χ2 and Fisher exact tests were used for dichotomous and categorical outcome variables. The threshold for statistical significance for these tests was set at α = .001.
Results
There were 10,810 RHUs from FY 2015 through FY 2018 and HISA utilization increased each year (Figure 1). Although some years may show usage decreases relative to previous fiscal years, the cumulative trends showed an increase relative to FY 2015 for both Classes of RVs (Figure 2). There was a 45.4% increase from FY 2015 to FY 2018 with a mean 13.6% yearly increase. Class 1 increased 21.0% and Class 2 increased 39.5% from FY 2015 to FY 2016 (Figure 3).
Most RHUs were male, White, and married. Class 1 and Class 2 RHUs differed significantly by age, race, marital status, and disability conditions: Class 1 RHUs were aged 6.6 years younger with a mean age of 69.1 years compared with 75.7 years for Class 2 users. For Class 1 RHUs, a plurality (29.4%) were aged 65 to 69 years; while a plurality (41.4%) of Class 2 users were aged ≥ 80 years. Musculoskeletal was the most common identified type of condition for all RHUs (Table 1).
To better understand HISA utilization patterns and net RHUs per county, we used a map to detail RHUs by county and change over time (Figure 4). Additionally, we compared US counties by RHUs from FY 2015 to FY 2018 and determined how clusters of high numbers of RHUs (hot spots) and low numbers of RHUs (cold spots) shifted over this period (Figure 5). While HISA utilization grew over the study period, the net count of RHUs per county varied by 9 to 20 persons/county. The population of RHUs increased over time in the Southwest, Southeast, and over much of the East/Northeast, while in the Central and Midwest regions, number of RHUs seems to decrease in population and/or use of the system. The cold spots in the Midwest and South Central US seem to increase with a significant relationship to neighboring counties having a low number of RHUs.
There were 11,166 HM prescribed to RHUs (Table 2). Bathroom HMs also were the dominant HM type for all facilities regardless of complexity levels (Table 3). The San Antonio, Texas, VAMC demonstrated the highest Class 1 vs Class 2 difference in HISA use (Class 1: 87.7% and Class 2: 12.3%). Except for the Des Moines VAMC, all other VAMCs showed HISA use > 60% by Class 1.
Cost Data
Air-conditioning installation ($5007) was the costliest HM overall (Table 4), closely followed by bathroom ($4978) and kitchen modifications ($4305). Bathroom renovations were the costliest HM type for both Class 1 and Class 2, closely followed by electrical repair and air-conditioning installation for Class 1 and driveway reconstruction and wooden ramp construction for Class 2.
The mean award received for HM was $4687 (Table 5). While the number of RHUs increased from FY 2015 to FY 2016, the average cost decreased, both overall ($280) and for Class 1 ($195) and Class 2 ($153). Except for a small decline in the number of Class 2 HISA recipients from FY 2017 to FY 2018, overall, the number of RHUs continuously grew from FY 2015 to FY 2018: 977 for the overall cohort, 678 for Class 1 and 299 for Class 2. Despite the obvious gain in the number of RHUs, the average costs did not notably change over time. VISN 21 had the highest mean cost, followed by VISNs 17, 6, 22, and 20.
Travel
Travel time and distance to the HISA prescribing facility differed significantly between Class 1 and Class 2 HISA users. RHUs had to travel about 95 minutes from their place of residence to access the HISA benefits program. There were no statistically significant differences between Class 1 and 2 users with respect to travel time and distance traveled (Table 6).
The majority of Class 1 and Class 2 veterans accessed the HISA from their nearest facility. However, nearly one-quarter of both Class 1 and 2 RHUs (24% each) did not. Among the 2598 who accessed the nonnearest facility, 97 (3.7%) accessed a facility that is ≤ 40 miles. Many (44%) users traveled 40 to 100 miles, and another 43.2% traveled 100 to 200 miles from their residence to access a HM prescription. Some 2598 users (1.1%) traveled > 500 miles to access a facility.
Discussion
Although utilization of the HISA program has steadily increased, overall participation by subpopulations such as RHUs can still be improved significantly. Veterans aged ≤ 46 years who have a disability that is common to those receiving HISA benefits have low HISA utilization. Similarly, veterans with sensory disabilities also have low use. These subpopulations are among those in great need of attention and services.
A study by Lucas and Zelaya, using the 2016 National Health Interview Survey data with an aim to measure degree of vision problems, dual sensory impairment, and hearing trouble in male veterans aged ≥ 18 years, found that veterans were more likely to report dual sensory impairment and balance difficulties when compared with nonveterans.9 The number of female veterans is growing but had very low representation in this study.10 This emerging VHA population requires information and education on their HM benefits.
Home Modifications
The most common HM prescribed for RHUs was for the bathroom. Further investigation is warranted as to why, given the diversity of HM types that the grant covers, low prescription rates exist across most of the HM types. There may be a lack of knowledge by providers and VWD as to the range of HMs that can be awarded under the grant. It is important that HCPs and veterans receive education on HISA HM options.
Semeah and colleagues pointed out the need for an assessment of the HISA HM ordering system to ensure that multiple HMs items (eg, kitchen, air conditioning, fees, driveway, and plumbing) are listed among the forced choices shown to clinicians to select from.7 Poor housing in rural America is widespread: 63% of rural dwellings need renovations and/or repairs to be accessible to individuals with disabilities, with > 6.7 million rural homes having no or faulty plumbing or kitchens; yet in this study, prescriptions for these HMs accounted for < 1%.11,12
VISN 6 had the most HISA awards with 1364, while VISN 21 had the fewest (245). Across all VISNs, Class 1 RHUs received more prescriptions than did Class 2 RHUs. Future research may seek to examine whether prescribers are fully aware of the eligibility of HM prescription to Class 2 veterans. VISN 21 ($5354); VISN 17 ($5302); and VISN 6 ($5301) had the highest mean HM expenditures. The national mean cost for HISA HMs were $4978 for bathrooms and $4305 for kitchens; for non-HISA HMs in FY 2017, the mean costs were $6362 and $12,255, respectively. A noteworthy concern is whether the maximum grant limit awards are sufficient to perform more expensive and complex HMs, such as the kitchen or major bathroom alternations.13
Facilities categorized as 1a, 1b, or 1c provided
North Florida/Sough Georgia was the highest-prescribing VAMC with 39% more HM prescriptions than the second highest prescribing facility (Durham, NC). Unfortunately, the data presented here cannot establish causality for the large variance difference between the top facilities, and the skewed distribution of total RHUs across VAMCs.
Travel-Related Variables
HISA beneficiaries face significant travel-related challenges. Just 3.6% of RHUs could access a facility within 40 miles of their home and 43.2% traveled 100 to 200 miles from their home to access a HM prescription. Further exploration is warranted to understand how travel patterns impact access to or the uptake of HISA.
RVs already have problems with accessing care because of long travel time.14,15 The choice or necessity to travel to a farther facility for HISA prescription is problematic for RVs, especially when transportation is often reported in the literature as a barrier to resources for people living in rural communities.15-17 When patients have travel barriers, they wait longer to obtain medical services and often wait for their conditions to worsen before seeking services.15,18 Once HM is completed, telerehabilitation is an effective delivery method used for delivering health care services to people in remote places.18,19 Considering that HISA use has the potential to improve quality of life, afford comfort, facilitate the accomplishment of activities of daily living for RVs, it is important that future studies examine how existing telehealth technologies can be used to improve HISA access.
Future Directions
County-level analyses is warranted in future studies exploring potential variables associated with HISA use; for example, county-level rates of primary care physicians and other HCPs. Future research should explore how long distance travel impacts the HISA application process and HM implementation. Further research also should focus on the HISA application structure and process to identify causes of delays. The HISA application process takes a mean 6 months to complete, yet the duration of hospital stays is 1 to 3 weeks, thus it is impossible to connect HISA to hospital discharge, which was the original intent of the program. Future research can examine how telehealth services can expedite HISA obtainment and coordination of the application process. Future research also may study the possible causes of the wide variations in HM prescriptions per facility. It is also important that educational programs provide information on the array of HM items that veterans can obtain.
Conclusions
In our previous study of the HISA cohort (2011-2017), we documented that an increase in utilization of the HISA program was warranted based on the low national budgetary appropriation and identification of significant low participation by vulnerable subpopulations, including veterans residing in rural areas or having returned from recent conflicts.7 The present study documents national utilization patterns, demographic profiles, and clinical characteristics of RHUs from FY 2015 through FY 2018, data that may be useful to policy makers and HISA administrators in predicting future use and users. It is important to note that the data and information presented in this article identify trends. The work in no way establishes a gold standard or any targeted goal of utilization. Future research could focus on conceptualizing or theorizing what steps are necessary to set such a gold standard of utilization rate and steps toward achievement.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grant 15521 from the US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health . Furthermore, the research was supported in part by grant K12 HD055929 from the National Institutes of Health.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) created the Home Improvements and Structural Alterations (HISA) program to help provide necessary home modifications (HMs) to veterans with disabilities (VWDs) that will facilitate the provision of medical services at home and improve home accessibility and functional independence. The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has more than 9 million veteran enrollees; of those, 2.7 million are classified as rural or highly rural.1 Rural veterans (RVs) possess higher rate of disability compared with that of urban veterans.2-5 RVs have unequal access to screening of ambulatory care sensitive conditions (eg, hypertension, diabetes mellitus).6 Furthermore, RVs are at risk of poor medical outcomes due to distance from health care facilities and specialist care, which can be a barrier to emergency care when issues arise. These barriers, among others, are associated with compromised health quality of life and health outcomes for RVs.3,6 The HISA program may be key to decreasing falls and other serious mishaps in the home. Therefore, understanding use of the HISA program by RVs is important. However, to date little information has been available regarding use of HISA benefits by RVs or characteristics of RVs who receive HISA benefits.
HISA Alterations Program
HISA was initially developed by VA to improve veterans’ transition from acute medical care to home.7,8 However, to obtain HISA grants currently, there is an average 3 to 6 months application process.7 Through the HISA program, VWDs can be prescribed the following HMs, including (but not limited to): flooring replacement, permanent ramps, roll-in showers, installation of central air-conditioning systems, improved lighting, kitchen/bathroom modifications, and home inspections. The HMs prescribed depend on an assessment of medical need by health care providers (HCPs).8
As time passed and the veteran population aged, the program now primarily helps ensure the ability to enter into essential areas and safety in the home.5 The amount of a HISA payment is based on whether a veteran’s health condition is related to military service as defined by the VHA service connection medical evaluation process. Barriers to obtaining a HISA HM can include difficulty in navigating the evaluation process and difficulty in finding a qualified contractor or builder to do the HM.7
This article aims to: (1) Detail the sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of rural HISA users (RHUs); (2) report on HISA usage patterns in number, types, and cost of HMs; (3) compare use amid the diverse VA medical centers (VAMCs) and related complexity levels and Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs); and (4) examine the relationship between travel time/distance and HISA utilization. The long-term goal is to provide accurate information to researchers, HM administrators, health care providers and policy makers on HISA program utilization by rural VWDs, which may help improve its use and bring awareness of its users. This study was approved by the affiliate University of Florida Institutional Review Board and VA research and development committee at the North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System.
Methods
Data were obtained from 3 VA sources: the National Prosthetics Patient Database (NPPD), the VHA Medical Inpatient Dataset, and the VHA Outpatient Dataset.7 The NPPD is a national administrative database that contains information on prosthetic-associated products ordered by HCPs for patients, such as portable ramps, handrails, home oxygen equipment, and orthotic and prosthetic apparatus. Data obtained from the NPPD included cost of HMs, clinical characteristics, VISN, and VAMC. VA facilities are categorized into complexity levels 1a, 1b, 1c, 2, and 3. Complexity level 1a to 1c VAMCs address medical cases that entail “heightening involvedness,” meaning a larger number of patients presented with medical concerns needing medical specialists. Complexity levels 2 and 3 have fewer resources, lower patient numbers, and less medically complex patients. Finally, the VHA Medical Inpatient and Outpatient Datasets administrated by VA Informatics and Computing Infrastructure, consist of in-depth health services national data on inpatient and outpatient encounters and procedures.
The study cohort was divided into those with service-connected conditions (Class 1) or those with conditions not related to military service (Class 2). If veterans were identified in both classes, they were assigned to Class 1. The cost variable is determined by using the veterans’ classification. Class 1 veterans receive a lifetime limit of $6800, and Class 2 veterans receive a lifetime limit of $2000. A Class 2 veteran with ≥ 50% disability rating is eligible for a HISA lifetime limit of $6800. Whenever a value exceeds allowed limit of $6800 or $2000, due to data entry error or other reasons, the study team reassigned the cost value to the maximum allowed value.
Travel distance and time were derived by loading patient zip codes and HISA facility locations into the geographical information system program and using the nearest facility and find-route tools. These tools used a road network that simulates real-world driving conditions to calculate distance.
Study Variables
VWDs of any age, gender, and race/ethnicity who qualified for HISA and received HMs from fiscal year ( FY) 2015 through FY 2018 were identified (N = 30,823). Most VWDs were nonrural subjects (n = 19,970), and 43 had no Federal Information Processing System data. The final study cohort consisted of 10,810 HISA recipients. The NPPD, inpatient and outpatient data were merged by scrambled social security numbers to retrieve the following data: age, gender, race, ethnicity, marital status, Class (1 or 2), mean and total number of inpatient days, and type of HMs prescribed.
We also recorded rurality using the VA Rural-Urban Commuting Areas (RUCA) system, but we combined the rural and highly rural designation.1 Census tracts with a RUCA score of 10.0 are deemed highly rural, the remainder are considered rural except those with a RUCA score of 1.0 or 1.1. Travel time and distance from a veteran’s home to the VA facility that provided the HISA prescription were determined from zip codes. The current study focuses on VAMCs prescribing stations (affiliated sites of administrative parent medical facilities) where the HISA users obtained the HM, not the parent station (administrative parent medical facilities).
HISA Utilization
To characterize HISA utilization geographically and over time, the number of users were mapped by county. Areas where users were increasing (hot spots) or decreasing (cold spots) also were mapped. The maps were created using Environmental Systems Research Institute ArcGIS Pro 2.2.1 software. We chose to use natural breaks (Jenks) data classification method in a choropleth to symbolize the change over time map. We then used the Getis Ord GI* optimized hot spot analysis tool in the ArcGIS Pro spatial statistics tool set to generate the hot/cold spot maps. This tool identifies clusters of high values (hot spots) and low values (cold spots) creating a new output layer, RHUs by county, with a Z score, P value, and CI for each county. The Gi Bin field classifies statistically significant hot and cold spots. Counties sorted into the ± 3 category (bin) have a clustering characteristic (eg, with neighboring counties) that is statistically significant with a 99% CI; the ± 2 bin indicates a 95% CI for those county clustering sorted therein; ± 1 reflects a 90% CI; and 0 bin contains county features that have no statistical significant clustering with neighboring counties.
Data Analysis
Data were cleaned and analyzed using SAS 9.4 and R 3.5.3. Descriptive statistics are provided for sociodemographic characteristics, clinical characteristics, and class. ANOVA and t tests were used to compare continuous variables between groups, while χ2 and Fisher exact tests were used for dichotomous and categorical outcome variables. The threshold for statistical significance for these tests was set at α = .001.
Results
There were 10,810 RHUs from FY 2015 through FY 2018 and HISA utilization increased each year (Figure 1). Although some years may show usage decreases relative to previous fiscal years, the cumulative trends showed an increase relative to FY 2015 for both Classes of RVs (Figure 2). There was a 45.4% increase from FY 2015 to FY 2018 with a mean 13.6% yearly increase. Class 1 increased 21.0% and Class 2 increased 39.5% from FY 2015 to FY 2016 (Figure 3).
Most RHUs were male, White, and married. Class 1 and Class 2 RHUs differed significantly by age, race, marital status, and disability conditions: Class 1 RHUs were aged 6.6 years younger with a mean age of 69.1 years compared with 75.7 years for Class 2 users. For Class 1 RHUs, a plurality (29.4%) were aged 65 to 69 years; while a plurality (41.4%) of Class 2 users were aged ≥ 80 years. Musculoskeletal was the most common identified type of condition for all RHUs (Table 1).
To better understand HISA utilization patterns and net RHUs per county, we used a map to detail RHUs by county and change over time (Figure 4). Additionally, we compared US counties by RHUs from FY 2015 to FY 2018 and determined how clusters of high numbers of RHUs (hot spots) and low numbers of RHUs (cold spots) shifted over this period (Figure 5). While HISA utilization grew over the study period, the net count of RHUs per county varied by 9 to 20 persons/county. The population of RHUs increased over time in the Southwest, Southeast, and over much of the East/Northeast, while in the Central and Midwest regions, number of RHUs seems to decrease in population and/or use of the system. The cold spots in the Midwest and South Central US seem to increase with a significant relationship to neighboring counties having a low number of RHUs.
There were 11,166 HM prescribed to RHUs (Table 2). Bathroom HMs also were the dominant HM type for all facilities regardless of complexity levels (Table 3). The San Antonio, Texas, VAMC demonstrated the highest Class 1 vs Class 2 difference in HISA use (Class 1: 87.7% and Class 2: 12.3%). Except for the Des Moines VAMC, all other VAMCs showed HISA use > 60% by Class 1.
Cost Data
Air-conditioning installation ($5007) was the costliest HM overall (Table 4), closely followed by bathroom ($4978) and kitchen modifications ($4305). Bathroom renovations were the costliest HM type for both Class 1 and Class 2, closely followed by electrical repair and air-conditioning installation for Class 1 and driveway reconstruction and wooden ramp construction for Class 2.
The mean award received for HM was $4687 (Table 5). While the number of RHUs increased from FY 2015 to FY 2016, the average cost decreased, both overall ($280) and for Class 1 ($195) and Class 2 ($153). Except for a small decline in the number of Class 2 HISA recipients from FY 2017 to FY 2018, overall, the number of RHUs continuously grew from FY 2015 to FY 2018: 977 for the overall cohort, 678 for Class 1 and 299 for Class 2. Despite the obvious gain in the number of RHUs, the average costs did not notably change over time. VISN 21 had the highest mean cost, followed by VISNs 17, 6, 22, and 20.
Travel
Travel time and distance to the HISA prescribing facility differed significantly between Class 1 and Class 2 HISA users. RHUs had to travel about 95 minutes from their place of residence to access the HISA benefits program. There were no statistically significant differences between Class 1 and 2 users with respect to travel time and distance traveled (Table 6).
The majority of Class 1 and Class 2 veterans accessed the HISA from their nearest facility. However, nearly one-quarter of both Class 1 and 2 RHUs (24% each) did not. Among the 2598 who accessed the nonnearest facility, 97 (3.7%) accessed a facility that is ≤ 40 miles. Many (44%) users traveled 40 to 100 miles, and another 43.2% traveled 100 to 200 miles from their residence to access a HM prescription. Some 2598 users (1.1%) traveled > 500 miles to access a facility.
Discussion
Although utilization of the HISA program has steadily increased, overall participation by subpopulations such as RHUs can still be improved significantly. Veterans aged ≤ 46 years who have a disability that is common to those receiving HISA benefits have low HISA utilization. Similarly, veterans with sensory disabilities also have low use. These subpopulations are among those in great need of attention and services.
A study by Lucas and Zelaya, using the 2016 National Health Interview Survey data with an aim to measure degree of vision problems, dual sensory impairment, and hearing trouble in male veterans aged ≥ 18 years, found that veterans were more likely to report dual sensory impairment and balance difficulties when compared with nonveterans.9 The number of female veterans is growing but had very low representation in this study.10 This emerging VHA population requires information and education on their HM benefits.
Home Modifications
The most common HM prescribed for RHUs was for the bathroom. Further investigation is warranted as to why, given the diversity of HM types that the grant covers, low prescription rates exist across most of the HM types. There may be a lack of knowledge by providers and VWD as to the range of HMs that can be awarded under the grant. It is important that HCPs and veterans receive education on HISA HM options.
Semeah and colleagues pointed out the need for an assessment of the HISA HM ordering system to ensure that multiple HMs items (eg, kitchen, air conditioning, fees, driveway, and plumbing) are listed among the forced choices shown to clinicians to select from.7 Poor housing in rural America is widespread: 63% of rural dwellings need renovations and/or repairs to be accessible to individuals with disabilities, with > 6.7 million rural homes having no or faulty plumbing or kitchens; yet in this study, prescriptions for these HMs accounted for < 1%.11,12
VISN 6 had the most HISA awards with 1364, while VISN 21 had the fewest (245). Across all VISNs, Class 1 RHUs received more prescriptions than did Class 2 RHUs. Future research may seek to examine whether prescribers are fully aware of the eligibility of HM prescription to Class 2 veterans. VISN 21 ($5354); VISN 17 ($5302); and VISN 6 ($5301) had the highest mean HM expenditures. The national mean cost for HISA HMs were $4978 for bathrooms and $4305 for kitchens; for non-HISA HMs in FY 2017, the mean costs were $6362 and $12,255, respectively. A noteworthy concern is whether the maximum grant limit awards are sufficient to perform more expensive and complex HMs, such as the kitchen or major bathroom alternations.13
Facilities categorized as 1a, 1b, or 1c provided
North Florida/Sough Georgia was the highest-prescribing VAMC with 39% more HM prescriptions than the second highest prescribing facility (Durham, NC). Unfortunately, the data presented here cannot establish causality for the large variance difference between the top facilities, and the skewed distribution of total RHUs across VAMCs.
Travel-Related Variables
HISA beneficiaries face significant travel-related challenges. Just 3.6% of RHUs could access a facility within 40 miles of their home and 43.2% traveled 100 to 200 miles from their home to access a HM prescription. Further exploration is warranted to understand how travel patterns impact access to or the uptake of HISA.
RVs already have problems with accessing care because of long travel time.14,15 The choice or necessity to travel to a farther facility for HISA prescription is problematic for RVs, especially when transportation is often reported in the literature as a barrier to resources for people living in rural communities.15-17 When patients have travel barriers, they wait longer to obtain medical services and often wait for their conditions to worsen before seeking services.15,18 Once HM is completed, telerehabilitation is an effective delivery method used for delivering health care services to people in remote places.18,19 Considering that HISA use has the potential to improve quality of life, afford comfort, facilitate the accomplishment of activities of daily living for RVs, it is important that future studies examine how existing telehealth technologies can be used to improve HISA access.
Future Directions
County-level analyses is warranted in future studies exploring potential variables associated with HISA use; for example, county-level rates of primary care physicians and other HCPs. Future research should explore how long distance travel impacts the HISA application process and HM implementation. Further research also should focus on the HISA application structure and process to identify causes of delays. The HISA application process takes a mean 6 months to complete, yet the duration of hospital stays is 1 to 3 weeks, thus it is impossible to connect HISA to hospital discharge, which was the original intent of the program. Future research can examine how telehealth services can expedite HISA obtainment and coordination of the application process. Future research also may study the possible causes of the wide variations in HM prescriptions per facility. It is also important that educational programs provide information on the array of HM items that veterans can obtain.
Conclusions
In our previous study of the HISA cohort (2011-2017), we documented that an increase in utilization of the HISA program was warranted based on the low national budgetary appropriation and identification of significant low participation by vulnerable subpopulations, including veterans residing in rural areas or having returned from recent conflicts.7 The present study documents national utilization patterns, demographic profiles, and clinical characteristics of RHUs from FY 2015 through FY 2018, data that may be useful to policy makers and HISA administrators in predicting future use and users. It is important to note that the data and information presented in this article identify trends. The work in no way establishes a gold standard or any targeted goal of utilization. Future research could focus on conceptualizing or theorizing what steps are necessary to set such a gold standard of utilization rate and steps toward achievement.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grant 15521 from the US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health . Furthermore, the research was supported in part by grant K12 HD055929 from the National Institutes of Health.
1. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veteran Health Administration, Office of Rural Health. Rural veteran health care challenges. Updated February 9, 2021. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
2. Holder, K.A. Veterans in rural America, 2011–2015. Published January 2017. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2017/acs/acs-36.pdf
3. Pezzin LE, Bogner HR, Kurichi JE, et al. Preventable hospitalizations, barriers to care, and disability. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(19):e0691. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000010691
4. Rosenbach ML. Access and satisfaction within the disabled Medicare population. Health Care Financ Rev. 1995;17(2):147-167.
5. Semeah LM, Ganesh SP, Wang X, et al. Home modification and health services utilization in rural and urban veterans with disabilities. Housing Policy Debate. 2021. Published online: March 4, 2021. doi:10.1080/10511482.2020.1858923
6. Spoont M, Greer N, Su J, Fitzgerald P, Rutks I, and Wilt TJ. Rural vs. urban ambulatory health care: A Systematic Review. Published May 2011. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/esp/ambulatory.pdf
7. Semeah LM, Wang X, Cowper Ripley DC, et al. Improving health through a home modification service for veterans. In: Fiedler BA, ed. Three Facets of Public Health and Paths to Improvements. Academic Press; 2020:381-416.
8. Semeah LM, Ahrentzen S, Jia H, Cowper-Ripley DC, Levy CE, Mann WC. The home improvements and structural alterations benefits program: veterans with disabilities and home accessibility. J Disability Policy Studies. 2017;28(1):43-51. doi:10.1177/1044207317696275
9. Lucas, JW, Zelaya, CE. Hearing difficulty, vision trouble, and balance problems among male veterans and nonveterans. Published June 12, 2020. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhsr/nhsr142-508.pdf
10. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Women veterans report: the past, present, and future of women veterans. Published February 2017. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/docs/SpecialReports/Women_Veterans_2015_Final.pdf
11. US Department of Housing and Urban Development, Office of Policy Development and Research. Housing challenges of rural seniors. Published 2017. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.huduser.gov/portal/periodicals/em/summer17/highlight1.html
12. Pendall R, Goodman L, Zhu J, Gold A. The future of rural housing. Published October 2016. Accessed June 11, 202.1 https://www.urban.org/sites/default/files/publication/85101/2000972-the-future-of-rural-housing_6.pdf
13. Joint Center for Housing Studies at Harvard University. Improving America’s housing 2019. Published 2019. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.jchs.harvard.edu/sites/default/files/reports/files/Harvard_JCHS_Improving_Americas_Housing_2019.pdf
14. Schooley BL, Horan TA, Lee PW, West PA. Rural veteran access to healthcare services: investigating the role of information and communication technologies in overcoming spatial barriers. Perspect Health Inf Manag. 2010;7(Spring):1f. Published 2010 Apr 1.
15. Ripley DC, Kwong PL, Vogel WB, Kurichi JE, Bates BE, Davenport C. How does geographic access affect in-hospital mortality for veterans with acute ischemic stroke?. Med Care. 2015;53(6):501-509. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000366
16. Cowper-Ripley DC, Reker DM, Hayes J, et al. Geographic access to VHA rehabilitation services for traumatically injured veterans. Fed Pract. 2009;26(10):28-39.
17. Smith M, Towne S, Herrera-Venson A, Cameron K, Horel S, Ory M, et al. Delivery of fall prevention interventions for at-risk older adults in rural areas: Findings from a national dissemination. International journal of environmental research and public health. 2018;15:2798. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15122798
18. Hale-Gallardo JL, Kreider CM, Jia H, et al. Telerehabilitation for Rural Veterans: A Qualitative Assessment of Barriers and Facilitators to Implementation. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2020;13:559-570. doi:10.2147/JMDH.S247267
19. Sarfo FS, Akassi J, Kyem G, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Stroke in a Ghanaian Outpatient Clinic. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018;27(4):1090-1099. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.11.017
1. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veteran Health Administration, Office of Rural Health. Rural veteran health care challenges. Updated February 9, 2021. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
2. Holder, K.A. Veterans in rural America, 2011–2015. Published January 2017. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2017/acs/acs-36.pdf
3. Pezzin LE, Bogner HR, Kurichi JE, et al. Preventable hospitalizations, barriers to care, and disability. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(19):e0691. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000010691
4. Rosenbach ML. Access and satisfaction within the disabled Medicare population. Health Care Financ Rev. 1995;17(2):147-167.
5. Semeah LM, Ganesh SP, Wang X, et al. Home modification and health services utilization in rural and urban veterans with disabilities. Housing Policy Debate. 2021. Published online: March 4, 2021. doi:10.1080/10511482.2020.1858923
6. Spoont M, Greer N, Su J, Fitzgerald P, Rutks I, and Wilt TJ. Rural vs. urban ambulatory health care: A Systematic Review. Published May 2011. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/publications/esp/ambulatory.pdf
7. Semeah LM, Wang X, Cowper Ripley DC, et al. Improving health through a home modification service for veterans. In: Fiedler BA, ed. Three Facets of Public Health and Paths to Improvements. Academic Press; 2020:381-416.
8. Semeah LM, Ahrentzen S, Jia H, Cowper-Ripley DC, Levy CE, Mann WC. The home improvements and structural alterations benefits program: veterans with disabilities and home accessibility. J Disability Policy Studies. 2017;28(1):43-51. doi:10.1177/1044207317696275
9. Lucas, JW, Zelaya, CE. Hearing difficulty, vision trouble, and balance problems among male veterans and nonveterans. Published June 12, 2020. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhsr/nhsr142-508.pdf
10. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Women veterans report: the past, present, and future of women veterans. Published February 2017. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/docs/SpecialReports/Women_Veterans_2015_Final.pdf
11. US Department of Housing and Urban Development, Office of Policy Development and Research. Housing challenges of rural seniors. Published 2017. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.huduser.gov/portal/periodicals/em/summer17/highlight1.html
12. Pendall R, Goodman L, Zhu J, Gold A. The future of rural housing. Published October 2016. Accessed June 11, 202.1 https://www.urban.org/sites/default/files/publication/85101/2000972-the-future-of-rural-housing_6.pdf
13. Joint Center for Housing Studies at Harvard University. Improving America’s housing 2019. Published 2019. Accessed June 11, 2021. https://www.jchs.harvard.edu/sites/default/files/reports/files/Harvard_JCHS_Improving_Americas_Housing_2019.pdf
14. Schooley BL, Horan TA, Lee PW, West PA. Rural veteran access to healthcare services: investigating the role of information and communication technologies in overcoming spatial barriers. Perspect Health Inf Manag. 2010;7(Spring):1f. Published 2010 Apr 1.
15. Ripley DC, Kwong PL, Vogel WB, Kurichi JE, Bates BE, Davenport C. How does geographic access affect in-hospital mortality for veterans with acute ischemic stroke?. Med Care. 2015;53(6):501-509. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000366
16. Cowper-Ripley DC, Reker DM, Hayes J, et al. Geographic access to VHA rehabilitation services for traumatically injured veterans. Fed Pract. 2009;26(10):28-39.
17. Smith M, Towne S, Herrera-Venson A, Cameron K, Horel S, Ory M, et al. Delivery of fall prevention interventions for at-risk older adults in rural areas: Findings from a national dissemination. International journal of environmental research and public health. 2018;15:2798. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15122798
18. Hale-Gallardo JL, Kreider CM, Jia H, et al. Telerehabilitation for Rural Veterans: A Qualitative Assessment of Barriers and Facilitators to Implementation. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2020;13:559-570. doi:10.2147/JMDH.S247267
19. Sarfo FS, Akassi J, Kyem G, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Stroke in a Ghanaian Outpatient Clinic. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018;27(4):1090-1099. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.11.017