User login
and is associated with various predisposing factors, including HLA genes, comorbidities, aging, and trigger factors such as drugs, trauma, radiation, chemotherapy, and infections. The autoimmune reaction is mediated by a dysregulation of T cells in which IgG and IgE autoantibodies form against hemidesmosomal proteins (BP180 and BP230). These autoantibodies induce neutrophil activation, recruitment, and degradation in the basement membrane of the skin.
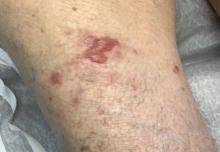
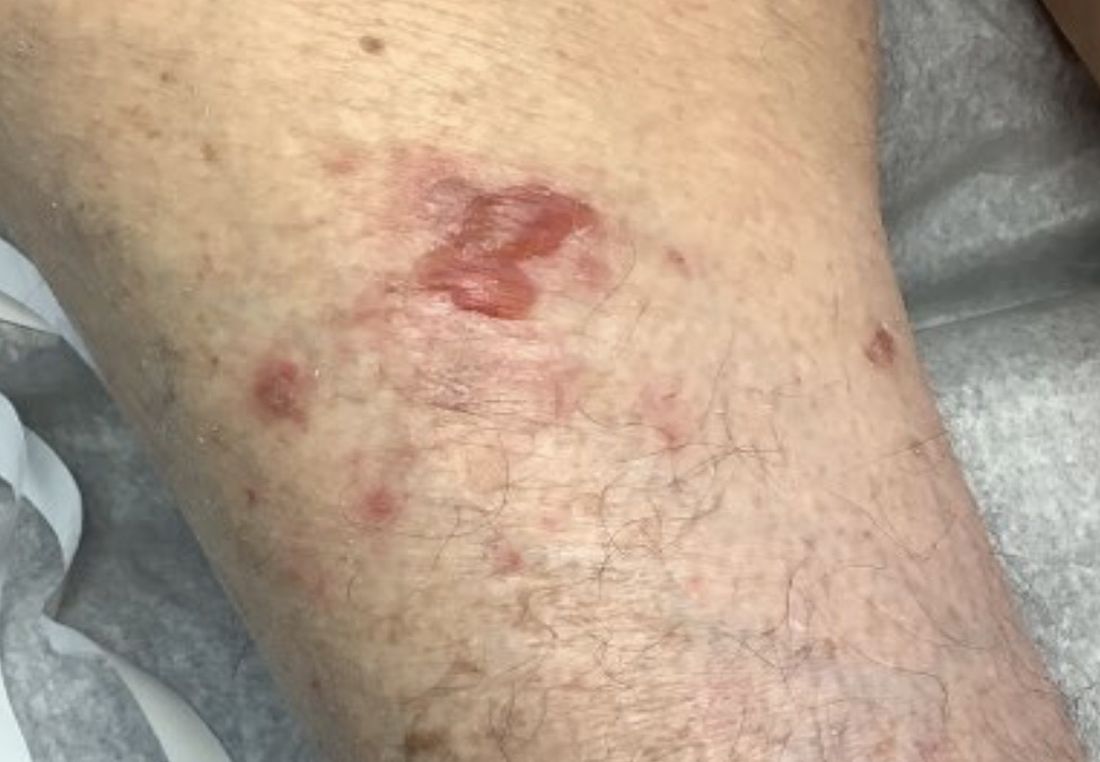
Typically, patients present with intense pruritus followed by an urticarial or eczematous eruption. Tense blisters and bullae occur commonly on the trunk and extremities. Drug-associated bullous pemphigoid (DABP) is a common manifestation of the disease with histologic and immunologic features similar to those of the idiopathic version. Eruptions can be triggered by systemic or topical medications, and incidence of these reactions may be related to a genetic predisposition for the disease.
Some research suggests that drug-induced changes to the antigenic properties of the epidermal basement membrane result in an augmented immune response, while others point to structural modification in these zones that stimulate the immune system. Thiol- and phenol-based drugs have been largely implicated in the development of DABP because they are capable of structural modification and disruption of the dermo-epidermal junction in the basement membrane.
DABP often presents with patients taking multiple medications. Some of the most common medications are gliptins, PD-1 inhibitors, diuretics, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and ACE-inhibitors, and other cardiovascular drugs. DABP may present with mucosal eruptions unlike its idiopathic counterpart that is mostly contained to the skin.
On this patient, two punch biopsies were taken. Histopathology revealed an eosinophil-rich subepidermal blister with a smooth epidermal undersurface consistent with bullous pemphigoid. Direct immunofluorescence was positive with a deposition of IgG and C3 at the epidermal side of salt split basement membrane zone.
Treatment for BP includes high potency topical and systemic steroids. Tetracyclines and niacinamide have been reported to improve the condition. Treatment is tailored to allow for cutaneous healing and control pruritus, but the physician must be mindful of the patient’s comorbidities and capacity for self-care. Prognosis is often better for DABP as withdrawal of the medication greatly accelerates clearance of the lesions. Worse prognosis is related to increased number of comorbidities and older age. Our patient’s BP is controlled currently with topical steroids and oral doxycycline.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Tampa, and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Miyamoto D et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2019 Mar-Apr;94(2):133-46.
2. Moro et al. Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 10;10(10):1432.
3. Verheyden M et al. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020 Aug 17;100(15):adv00224.
and is associated with various predisposing factors, including HLA genes, comorbidities, aging, and trigger factors such as drugs, trauma, radiation, chemotherapy, and infections. The autoimmune reaction is mediated by a dysregulation of T cells in which IgG and IgE autoantibodies form against hemidesmosomal proteins (BP180 and BP230). These autoantibodies induce neutrophil activation, recruitment, and degradation in the basement membrane of the skin.
Typically, patients present with intense pruritus followed by an urticarial or eczematous eruption. Tense blisters and bullae occur commonly on the trunk and extremities. Drug-associated bullous pemphigoid (DABP) is a common manifestation of the disease with histologic and immunologic features similar to those of the idiopathic version. Eruptions can be triggered by systemic or topical medications, and incidence of these reactions may be related to a genetic predisposition for the disease.
Some research suggests that drug-induced changes to the antigenic properties of the epidermal basement membrane result in an augmented immune response, while others point to structural modification in these zones that stimulate the immune system. Thiol- and phenol-based drugs have been largely implicated in the development of DABP because they are capable of structural modification and disruption of the dermo-epidermal junction in the basement membrane.
DABP often presents with patients taking multiple medications. Some of the most common medications are gliptins, PD-1 inhibitors, diuretics, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and ACE-inhibitors, and other cardiovascular drugs. DABP may present with mucosal eruptions unlike its idiopathic counterpart that is mostly contained to the skin.
On this patient, two punch biopsies were taken. Histopathology revealed an eosinophil-rich subepidermal blister with a smooth epidermal undersurface consistent with bullous pemphigoid. Direct immunofluorescence was positive with a deposition of IgG and C3 at the epidermal side of salt split basement membrane zone.
Treatment for BP includes high potency topical and systemic steroids. Tetracyclines and niacinamide have been reported to improve the condition. Treatment is tailored to allow for cutaneous healing and control pruritus, but the physician must be mindful of the patient’s comorbidities and capacity for self-care. Prognosis is often better for DABP as withdrawal of the medication greatly accelerates clearance of the lesions. Worse prognosis is related to increased number of comorbidities and older age. Our patient’s BP is controlled currently with topical steroids and oral doxycycline.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Tampa, and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Miyamoto D et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2019 Mar-Apr;94(2):133-46.
2. Moro et al. Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 10;10(10):1432.
3. Verheyden M et al. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020 Aug 17;100(15):adv00224.
and is associated with various predisposing factors, including HLA genes, comorbidities, aging, and trigger factors such as drugs, trauma, radiation, chemotherapy, and infections. The autoimmune reaction is mediated by a dysregulation of T cells in which IgG and IgE autoantibodies form against hemidesmosomal proteins (BP180 and BP230). These autoantibodies induce neutrophil activation, recruitment, and degradation in the basement membrane of the skin.
Typically, patients present with intense pruritus followed by an urticarial or eczematous eruption. Tense blisters and bullae occur commonly on the trunk and extremities. Drug-associated bullous pemphigoid (DABP) is a common manifestation of the disease with histologic and immunologic features similar to those of the idiopathic version. Eruptions can be triggered by systemic or topical medications, and incidence of these reactions may be related to a genetic predisposition for the disease.
Some research suggests that drug-induced changes to the antigenic properties of the epidermal basement membrane result in an augmented immune response, while others point to structural modification in these zones that stimulate the immune system. Thiol- and phenol-based drugs have been largely implicated in the development of DABP because they are capable of structural modification and disruption of the dermo-epidermal junction in the basement membrane.
DABP often presents with patients taking multiple medications. Some of the most common medications are gliptins, PD-1 inhibitors, diuretics, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and ACE-inhibitors, and other cardiovascular drugs. DABP may present with mucosal eruptions unlike its idiopathic counterpart that is mostly contained to the skin.
On this patient, two punch biopsies were taken. Histopathology revealed an eosinophil-rich subepidermal blister with a smooth epidermal undersurface consistent with bullous pemphigoid. Direct immunofluorescence was positive with a deposition of IgG and C3 at the epidermal side of salt split basement membrane zone.
Treatment for BP includes high potency topical and systemic steroids. Tetracyclines and niacinamide have been reported to improve the condition. Treatment is tailored to allow for cutaneous healing and control pruritus, but the physician must be mindful of the patient’s comorbidities and capacity for self-care. Prognosis is often better for DABP as withdrawal of the medication greatly accelerates clearance of the lesions. Worse prognosis is related to increased number of comorbidities and older age. Our patient’s BP is controlled currently with topical steroids and oral doxycycline.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Tampa, and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Miyamoto D et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2019 Mar-Apr;94(2):133-46.
2. Moro et al. Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 10;10(10):1432.
3. Verheyden M et al. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020 Aug 17;100(15):adv00224.