User login
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Committee on Immunization Practices voted unanimously in support of three recommendations for the use of hepatitis A vaccines.
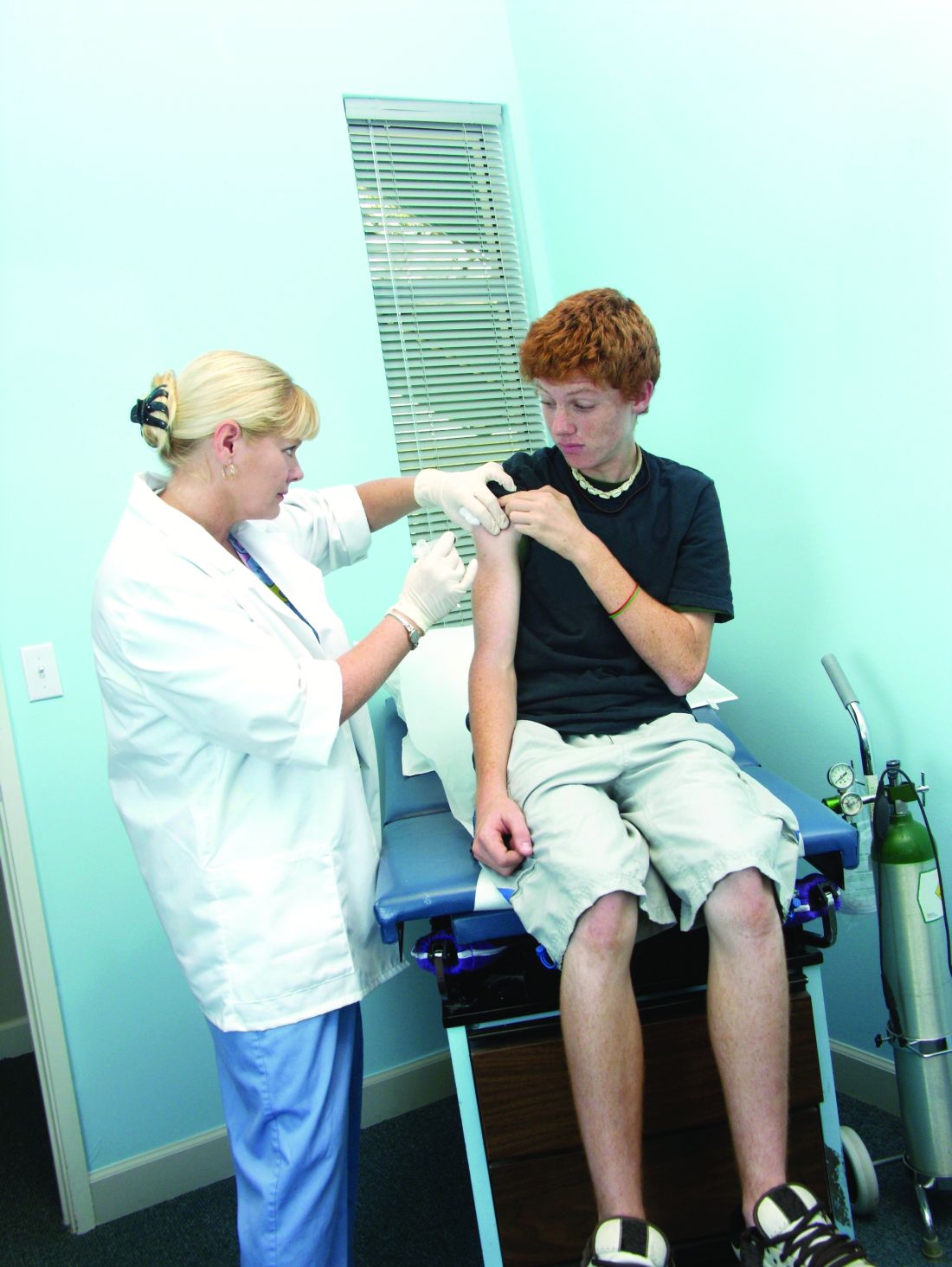
The committee recommended catch-up vaccination at any age for all children aged 2-18 years who had not previously received hepatitis A vaccination, recommended that all persons with HIV aged 1 year and older should be vaccinated with the hepatitis A vaccine, and approved updating the language in the full hepatitis A vaccine statement, “Prevention of Hepatitis A Virus Infection in The United States: Recommendations of The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.”
Catch-up vaccination will expand coverage to adolescents who might have missed it, and data show that the vaccine effectiveness is high, and the rates of adverse events are low in the child and adolescent population, said Noele Nelson, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention, who presented the recommendations to the committee. “Recent outbreaks are occurring primarily among adults,” and many cases are among persons who use drugs or are homeless, she added.
Several committee members noted that the specific recommendations for catch-up in children and teens and for vaccination of HIV patients offer more opportunities for protection than risk-based recommendations. Catching up with vaccinating adolescents is “more effective than tracking down high-risk adults later in life,” noted Grace Lee, MD, of Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford, Calif.
The committee also recommended that all persons with HIV aged 1 year and older should be vaccinated with the hepatitis A vaccine. Data on persons with HIV show that approximately 60% have at least one risk factor for hepatitis A, such as men who have sex with men or individuals engaged in intravenous drug use, said Dr. Nelson. Data also show that individuals with HIV are at increased risk for complications if they get hepatitis A.
The committee’s approval of the full hepatitis A vaccine statement included one notable change – the removal of clotting factor disorders as a high-risk group. The risk has decreased over time based on improvements such as better screening of source plasma, and this group is now at no greater risk than the general population, according to work group chair Kelly Moore, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Committee on Immunization Practices voted unanimously in support of three recommendations for the use of hepatitis A vaccines.
The committee recommended catch-up vaccination at any age for all children aged 2-18 years who had not previously received hepatitis A vaccination, recommended that all persons with HIV aged 1 year and older should be vaccinated with the hepatitis A vaccine, and approved updating the language in the full hepatitis A vaccine statement, “Prevention of Hepatitis A Virus Infection in The United States: Recommendations of The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.”
Catch-up vaccination will expand coverage to adolescents who might have missed it, and data show that the vaccine effectiveness is high, and the rates of adverse events are low in the child and adolescent population, said Noele Nelson, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention, who presented the recommendations to the committee. “Recent outbreaks are occurring primarily among adults,” and many cases are among persons who use drugs or are homeless, she added.
Several committee members noted that the specific recommendations for catch-up in children and teens and for vaccination of HIV patients offer more opportunities for protection than risk-based recommendations. Catching up with vaccinating adolescents is “more effective than tracking down high-risk adults later in life,” noted Grace Lee, MD, of Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford, Calif.
The committee also recommended that all persons with HIV aged 1 year and older should be vaccinated with the hepatitis A vaccine. Data on persons with HIV show that approximately 60% have at least one risk factor for hepatitis A, such as men who have sex with men or individuals engaged in intravenous drug use, said Dr. Nelson. Data also show that individuals with HIV are at increased risk for complications if they get hepatitis A.
The committee’s approval of the full hepatitis A vaccine statement included one notable change – the removal of clotting factor disorders as a high-risk group. The risk has decreased over time based on improvements such as better screening of source plasma, and this group is now at no greater risk than the general population, according to work group chair Kelly Moore, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Committee on Immunization Practices voted unanimously in support of three recommendations for the use of hepatitis A vaccines.
The committee recommended catch-up vaccination at any age for all children aged 2-18 years who had not previously received hepatitis A vaccination, recommended that all persons with HIV aged 1 year and older should be vaccinated with the hepatitis A vaccine, and approved updating the language in the full hepatitis A vaccine statement, “Prevention of Hepatitis A Virus Infection in The United States: Recommendations of The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.”
Catch-up vaccination will expand coverage to adolescents who might have missed it, and data show that the vaccine effectiveness is high, and the rates of adverse events are low in the child and adolescent population, said Noele Nelson, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention, who presented the recommendations to the committee. “Recent outbreaks are occurring primarily among adults,” and many cases are among persons who use drugs or are homeless, she added.
Several committee members noted that the specific recommendations for catch-up in children and teens and for vaccination of HIV patients offer more opportunities for protection than risk-based recommendations. Catching up with vaccinating adolescents is “more effective than tracking down high-risk adults later in life,” noted Grace Lee, MD, of Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford, Calif.
The committee also recommended that all persons with HIV aged 1 year and older should be vaccinated with the hepatitis A vaccine. Data on persons with HIV show that approximately 60% have at least one risk factor for hepatitis A, such as men who have sex with men or individuals engaged in intravenous drug use, said Dr. Nelson. Data also show that individuals with HIV are at increased risk for complications if they get hepatitis A.
The committee’s approval of the full hepatitis A vaccine statement included one notable change – the removal of clotting factor disorders as a high-risk group. The risk has decreased over time based on improvements such as better screening of source plasma, and this group is now at no greater risk than the general population, according to work group chair Kelly Moore, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
REPORTING FROM AN ACIP MEETING