User login
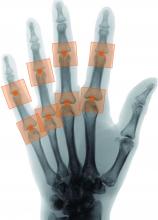
A novel program that aims to automate the Sharp-van der Heijde scoring of radiographs of patients with rheumatoid arthritis has shown good reliability in identifying regions of interest and matching human reader scoring for joint-space narrowing, according to a report given at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year because of COVID-19.
First author and presenter Thomas Deimel, MD, and colleagues at the Medical University of Vienna said their program, called autoscoRA, may be a solution to the problem of readers having to make subjective calls on the severity of damage seen on radiographs.
Although the work continues to be validated, Dr. Deimel, a resident at the university, is confident in the system as is. “I think for joint space narrowing, we’re there at the point where this could be used and could be as good as a human reader in terms of reliability,” he said in an interview. To find out, the group plans to compare the variability between autoscoRA and a gold-standard human reader against the variability seen between human readers. If the two measures of variability are similar, it would provide a strong endorsement.
The effort is far from the first to develop an automatic scoring system for RA images, but no fully automated system has emerged as reliable, according to Dr. Deimel. He thinks one main issue for others has been lack of access to a sufficient data set to train systems. It can be difficult to find enough training images because many types of joint damage are comparatively uncommon. The problem is made even worse because images can be hard to interpret: The shapes that the system must decipher can be misleading, especially in positions of tendon insertion or ligament attachment that can resemble damage. Differing angles of view between various training images can also complicate matters.
The autoscoRA program is based on modifications of a form of convolutional neural network called the VGG16 architecture. The team used 2,207 images from 270 patients to train autoscoRA, 1,150 images from 133 patients for validation, and 1,834 images from 237 patients to test it.
The group had access to a high-quality data set of almost 6,000 hand radiographs from their institution, the result of foresight of principal investigator Daniel Aletaha, MD, and his predecessor Josef Smolen, MD. They “thought ahead and started collecting data and had all of it scored,” Dr. Deimel said. The work wasn’t all completed ahead of time, though. Dr. Deimel had to pull images from the hospital’s system sort through them manually.
The group also benefited from close proximity to computer scientists, including coauthor Georg Langs from the Medical University of Vienna’s computational imaging research lab. “We were lucky that we have a computer science department that is very much involved in medical imaging,” Dr. Deimel said.
The trained system successfully identified regions of interest in 96% of joints. It calculated the same score as the human reader in 80.5% of metacarpophalangeal joints and 72.3% of proximal interphalangeal joints. It deviated by more than 1 point from the gold-standard score in just 1.8% of metacarpophalangeal joints and 1.7% of proximal interphalangeal joints.
The researchers aim next to extend the program to bone erosions and also to images of the wrists and feet. They also hope to use scores from the program in clinical trials to measure a treatment’s effect, in registries of routine patient visits where thousands of such images along with clinical data could form the basis of informative observational studies, and in clinical practice, though likely with human oversight.
The study received no outside financial support. Dr. Deimel had no relevant financial disclosures. Mr. Langs reported being cofounder and shareholder of contextflow and receiving grants from Novartis, Siemens Healthineers, and NVIDIA. Dr. Aletaha reported financial relationships with many companies marketing drugs for rheumatoid arthritis.
SOURCE: Deimel T et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79(suppl 1):39-40.
A novel program that aims to automate the Sharp-van der Heijde scoring of radiographs of patients with rheumatoid arthritis has shown good reliability in identifying regions of interest and matching human reader scoring for joint-space narrowing, according to a report given at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year because of COVID-19.
First author and presenter Thomas Deimel, MD, and colleagues at the Medical University of Vienna said their program, called autoscoRA, may be a solution to the problem of readers having to make subjective calls on the severity of damage seen on radiographs.
Although the work continues to be validated, Dr. Deimel, a resident at the university, is confident in the system as is. “I think for joint space narrowing, we’re there at the point where this could be used and could be as good as a human reader in terms of reliability,” he said in an interview. To find out, the group plans to compare the variability between autoscoRA and a gold-standard human reader against the variability seen between human readers. If the two measures of variability are similar, it would provide a strong endorsement.
The effort is far from the first to develop an automatic scoring system for RA images, but no fully automated system has emerged as reliable, according to Dr. Deimel. He thinks one main issue for others has been lack of access to a sufficient data set to train systems. It can be difficult to find enough training images because many types of joint damage are comparatively uncommon. The problem is made even worse because images can be hard to interpret: The shapes that the system must decipher can be misleading, especially in positions of tendon insertion or ligament attachment that can resemble damage. Differing angles of view between various training images can also complicate matters.
The autoscoRA program is based on modifications of a form of convolutional neural network called the VGG16 architecture. The team used 2,207 images from 270 patients to train autoscoRA, 1,150 images from 133 patients for validation, and 1,834 images from 237 patients to test it.
The group had access to a high-quality data set of almost 6,000 hand radiographs from their institution, the result of foresight of principal investigator Daniel Aletaha, MD, and his predecessor Josef Smolen, MD. They “thought ahead and started collecting data and had all of it scored,” Dr. Deimel said. The work wasn’t all completed ahead of time, though. Dr. Deimel had to pull images from the hospital’s system sort through them manually.
The group also benefited from close proximity to computer scientists, including coauthor Georg Langs from the Medical University of Vienna’s computational imaging research lab. “We were lucky that we have a computer science department that is very much involved in medical imaging,” Dr. Deimel said.
The trained system successfully identified regions of interest in 96% of joints. It calculated the same score as the human reader in 80.5% of metacarpophalangeal joints and 72.3% of proximal interphalangeal joints. It deviated by more than 1 point from the gold-standard score in just 1.8% of metacarpophalangeal joints and 1.7% of proximal interphalangeal joints.
The researchers aim next to extend the program to bone erosions and also to images of the wrists and feet. They also hope to use scores from the program in clinical trials to measure a treatment’s effect, in registries of routine patient visits where thousands of such images along with clinical data could form the basis of informative observational studies, and in clinical practice, though likely with human oversight.
The study received no outside financial support. Dr. Deimel had no relevant financial disclosures. Mr. Langs reported being cofounder and shareholder of contextflow and receiving grants from Novartis, Siemens Healthineers, and NVIDIA. Dr. Aletaha reported financial relationships with many companies marketing drugs for rheumatoid arthritis.
SOURCE: Deimel T et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79(suppl 1):39-40.
A novel program that aims to automate the Sharp-van der Heijde scoring of radiographs of patients with rheumatoid arthritis has shown good reliability in identifying regions of interest and matching human reader scoring for joint-space narrowing, according to a report given at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year because of COVID-19.
First author and presenter Thomas Deimel, MD, and colleagues at the Medical University of Vienna said their program, called autoscoRA, may be a solution to the problem of readers having to make subjective calls on the severity of damage seen on radiographs.
Although the work continues to be validated, Dr. Deimel, a resident at the university, is confident in the system as is. “I think for joint space narrowing, we’re there at the point where this could be used and could be as good as a human reader in terms of reliability,” he said in an interview. To find out, the group plans to compare the variability between autoscoRA and a gold-standard human reader against the variability seen between human readers. If the two measures of variability are similar, it would provide a strong endorsement.
The effort is far from the first to develop an automatic scoring system for RA images, but no fully automated system has emerged as reliable, according to Dr. Deimel. He thinks one main issue for others has been lack of access to a sufficient data set to train systems. It can be difficult to find enough training images because many types of joint damage are comparatively uncommon. The problem is made even worse because images can be hard to interpret: The shapes that the system must decipher can be misleading, especially in positions of tendon insertion or ligament attachment that can resemble damage. Differing angles of view between various training images can also complicate matters.
The autoscoRA program is based on modifications of a form of convolutional neural network called the VGG16 architecture. The team used 2,207 images from 270 patients to train autoscoRA, 1,150 images from 133 patients for validation, and 1,834 images from 237 patients to test it.
The group had access to a high-quality data set of almost 6,000 hand radiographs from their institution, the result of foresight of principal investigator Daniel Aletaha, MD, and his predecessor Josef Smolen, MD. They “thought ahead and started collecting data and had all of it scored,” Dr. Deimel said. The work wasn’t all completed ahead of time, though. Dr. Deimel had to pull images from the hospital’s system sort through them manually.
The group also benefited from close proximity to computer scientists, including coauthor Georg Langs from the Medical University of Vienna’s computational imaging research lab. “We were lucky that we have a computer science department that is very much involved in medical imaging,” Dr. Deimel said.
The trained system successfully identified regions of interest in 96% of joints. It calculated the same score as the human reader in 80.5% of metacarpophalangeal joints and 72.3% of proximal interphalangeal joints. It deviated by more than 1 point from the gold-standard score in just 1.8% of metacarpophalangeal joints and 1.7% of proximal interphalangeal joints.
The researchers aim next to extend the program to bone erosions and also to images of the wrists and feet. They also hope to use scores from the program in clinical trials to measure a treatment’s effect, in registries of routine patient visits where thousands of such images along with clinical data could form the basis of informative observational studies, and in clinical practice, though likely with human oversight.
The study received no outside financial support. Dr. Deimel had no relevant financial disclosures. Mr. Langs reported being cofounder and shareholder of contextflow and receiving grants from Novartis, Siemens Healthineers, and NVIDIA. Dr. Aletaha reported financial relationships with many companies marketing drugs for rheumatoid arthritis.
SOURCE: Deimel T et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79(suppl 1):39-40.
FROM THE EULAR 2020 E-CONGRESS