User login
Perianal squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCCIS) is an intraepidermal neoplasm with human papillomavirus implicated in its etiology.1 It can present as a raised, scaly, erythematous, fissured, ulcerated, or pigmented lesion; however, perianal SCCIS often is subclinical and therefore requires a high level of suspicion in individuals with risk factors (eg, history of genital or perianal human papillomavirus infection, other sexually transmitted diseases, or cervical dysplasia).2 Although relatively rare, perianal SCCIS is believed to be increasing in frequency and has the potential to progress to invasive squamous cell carcinoma.1,3 The rarity of this neoplasm and its uncertain natural history has made the development of a definitive, evidence-based management strategy difficult and controversial.1,4,5 We present the case of a 61-year-old woman with perianal SCCIS who was treated with a novel combination of 5-aminolevulinic acid–based photodynamic therapy (ALA-PDT) and topical imiquimod cream 5% following 2 unsuccessful surgical excisions. Using this treatment regimen, the neoplasm resolved completely with no evidence of recurrence at 2 years’ follow-up.
Case Report
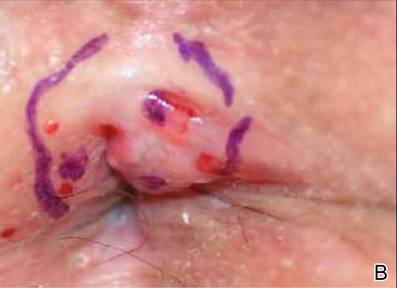
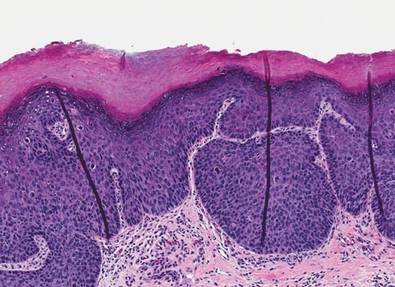
A 61-year-old woman was referred to our dermatology clinic for management of persistent SCCIS of the perianal region. A colorectal surgeon performed 2 unsuccessful excisions of the neoplasm at 6 months and 1 month prior to presentation. Biopsy results from the second excision demonstrated persistent perianal SCCIS with positive margins (Figure 1). The patient was referred to our clinic to discuss Mohs micrographic surgery versus nonsurgical treatment options. The patient’s medical history was remarkable for an abnormal Papanicolaou test 10 years prior, which resulted in cervical cryotherapy.
 |
|
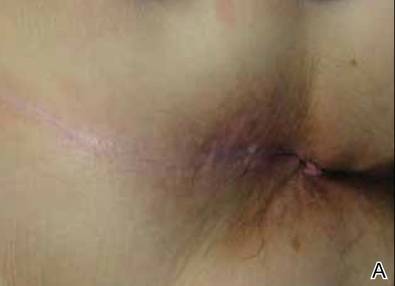
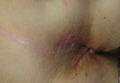
Physical examination revealed a 2×1-cm pink scar with peripheral scaling on the right anal verge (Figure 2A). Potential therapies discussed with the patient included Mohs surgery, ablative laser treatment, and nonsurgical treatment with ALA-PDT in combination with topical imiquimod cream 5%. To avoid further invasive treatments, we decided to administer a 3-week course of topical imiquimod cream 5% applied 3 times weekly to the entire affected area, followed 1 week later with a treatment of ALA-PDT. The incubation time was 6 hours. After completing 4 cycles of this therapeutic regimen, the erythema and scaling resolved (Figure 2B). The patient did not note any remarkable side effects associated with imiquimod but reported progressively resolving pain in the week following each ALA-PDT treatment, with the worst pain occurring during the first 48 hours after treatment. Three posttreatment scout biopsies revealed no evidence of residual perianal SCCIS. Two years after the negative biopsies, ongoing physical examinations demonstrated no evidence of clinical recurrence. Physicians in the dermatology and gynecology departments are following her closely.
Comment
Wide surgical excision is currently recommended as first-line therapy for perianal SCCIS.1,3,4 Unfortunately, surgical excision has been associated with difficulty in achieving disease-free margins, recurrence rates as high as 31%, and substantial morbidity.1,4 Other nonsurgical treatment modalities have been investigated for treating this neoplasm to simultaneously reduce recurrence rates while minimizing structural and functional damage to the treatment area, including radiotherapy, imiquimod, laser ablation, and ALA-PDT.1,3,4,5
In particular, imiquimod and ALA-PDT have shown promise as monotherapies for the treatment of perianal SCCIS, with several case reports describing complete resolution, low rates of recurrence, and preserved structure and function of the surrounding tissue after therapy1,3,4; however, recurrence of perianal SCCIS is still known to occur after monotherapy with either ALA-PDT or imiquimod.5,6
In contrast to noninvasive monotherapies, the literature is largely devoid of reports of noninvasive combination treatments used for perianal SCCIS. Our case represents successful use of a combination of imiquimod and ALA-PDT to treat persistent perianal SCCIS.
Conclusion
Although further research is necessary, the therapeutic success presented in our case suggests noninvasive combination therapy with imiquimod and ALA-PDT may represent a viable alternative to both surgical excision and noninvasive monotherapies for the treatment of perianal SCCIS.
Acknowledgement—The authors would like to thank Alejandro Gru, MD, Columbus, Ohio, for his review of the pathology slides for this case.
1. van Egmond S, Hoedemaker C, Sinclair R. Successful treatment of perianal Bowen’s disease with imiquimod. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:318-319.
2. Abbasakoor F, Boulos PB. Anal intraepithelial neoplasia. Br J Surg. 2005;92:277-290.
3. Petrelli NJ, Cebollero JA, Rodriguez-Bigas M, et al. Photodynamic therapy in the management of neoplasms of the perianal skin. Arch Surg. 1992;127:1436-1438.
4. Wietfeldt E, Thiele J. Malignancies of the anal margin and perianal skin. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009;22:127-135.
5. Pineda C, Welton M. Management of anal squamous intraepithelial lesions. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009;22:94-101.
6. Runfola MA, Weber TK, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, et al. Photodynamic therapy for residual neoplasms of the perianal skin. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000;43:499-502.
Perianal squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCCIS) is an intraepidermal neoplasm with human papillomavirus implicated in its etiology.1 It can present as a raised, scaly, erythematous, fissured, ulcerated, or pigmented lesion; however, perianal SCCIS often is subclinical and therefore requires a high level of suspicion in individuals with risk factors (eg, history of genital or perianal human papillomavirus infection, other sexually transmitted diseases, or cervical dysplasia).2 Although relatively rare, perianal SCCIS is believed to be increasing in frequency and has the potential to progress to invasive squamous cell carcinoma.1,3 The rarity of this neoplasm and its uncertain natural history has made the development of a definitive, evidence-based management strategy difficult and controversial.1,4,5 We present the case of a 61-year-old woman with perianal SCCIS who was treated with a novel combination of 5-aminolevulinic acid–based photodynamic therapy (ALA-PDT) and topical imiquimod cream 5% following 2 unsuccessful surgical excisions. Using this treatment regimen, the neoplasm resolved completely with no evidence of recurrence at 2 years’ follow-up.
Case Report
A 61-year-old woman was referred to our dermatology clinic for management of persistent SCCIS of the perianal region. A colorectal surgeon performed 2 unsuccessful excisions of the neoplasm at 6 months and 1 month prior to presentation. Biopsy results from the second excision demonstrated persistent perianal SCCIS with positive margins (Figure 1). The patient was referred to our clinic to discuss Mohs micrographic surgery versus nonsurgical treatment options. The patient’s medical history was remarkable for an abnormal Papanicolaou test 10 years prior, which resulted in cervical cryotherapy.
 |
|
Physical examination revealed a 2×1-cm pink scar with peripheral scaling on the right anal verge (Figure 2A). Potential therapies discussed with the patient included Mohs surgery, ablative laser treatment, and nonsurgical treatment with ALA-PDT in combination with topical imiquimod cream 5%. To avoid further invasive treatments, we decided to administer a 3-week course of topical imiquimod cream 5% applied 3 times weekly to the entire affected area, followed 1 week later with a treatment of ALA-PDT. The incubation time was 6 hours. After completing 4 cycles of this therapeutic regimen, the erythema and scaling resolved (Figure 2B). The patient did not note any remarkable side effects associated with imiquimod but reported progressively resolving pain in the week following each ALA-PDT treatment, with the worst pain occurring during the first 48 hours after treatment. Three posttreatment scout biopsies revealed no evidence of residual perianal SCCIS. Two years after the negative biopsies, ongoing physical examinations demonstrated no evidence of clinical recurrence. Physicians in the dermatology and gynecology departments are following her closely.
Comment
Wide surgical excision is currently recommended as first-line therapy for perianal SCCIS.1,3,4 Unfortunately, surgical excision has been associated with difficulty in achieving disease-free margins, recurrence rates as high as 31%, and substantial morbidity.1,4 Other nonsurgical treatment modalities have been investigated for treating this neoplasm to simultaneously reduce recurrence rates while minimizing structural and functional damage to the treatment area, including radiotherapy, imiquimod, laser ablation, and ALA-PDT.1,3,4,5
In particular, imiquimod and ALA-PDT have shown promise as monotherapies for the treatment of perianal SCCIS, with several case reports describing complete resolution, low rates of recurrence, and preserved structure and function of the surrounding tissue after therapy1,3,4; however, recurrence of perianal SCCIS is still known to occur after monotherapy with either ALA-PDT or imiquimod.5,6
In contrast to noninvasive monotherapies, the literature is largely devoid of reports of noninvasive combination treatments used for perianal SCCIS. Our case represents successful use of a combination of imiquimod and ALA-PDT to treat persistent perianal SCCIS.
Conclusion
Although further research is necessary, the therapeutic success presented in our case suggests noninvasive combination therapy with imiquimod and ALA-PDT may represent a viable alternative to both surgical excision and noninvasive monotherapies for the treatment of perianal SCCIS.
Acknowledgement—The authors would like to thank Alejandro Gru, MD, Columbus, Ohio, for his review of the pathology slides for this case.
Perianal squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCCIS) is an intraepidermal neoplasm with human papillomavirus implicated in its etiology.1 It can present as a raised, scaly, erythematous, fissured, ulcerated, or pigmented lesion; however, perianal SCCIS often is subclinical and therefore requires a high level of suspicion in individuals with risk factors (eg, history of genital or perianal human papillomavirus infection, other sexually transmitted diseases, or cervical dysplasia).2 Although relatively rare, perianal SCCIS is believed to be increasing in frequency and has the potential to progress to invasive squamous cell carcinoma.1,3 The rarity of this neoplasm and its uncertain natural history has made the development of a definitive, evidence-based management strategy difficult and controversial.1,4,5 We present the case of a 61-year-old woman with perianal SCCIS who was treated with a novel combination of 5-aminolevulinic acid–based photodynamic therapy (ALA-PDT) and topical imiquimod cream 5% following 2 unsuccessful surgical excisions. Using this treatment regimen, the neoplasm resolved completely with no evidence of recurrence at 2 years’ follow-up.
Case Report
A 61-year-old woman was referred to our dermatology clinic for management of persistent SCCIS of the perianal region. A colorectal surgeon performed 2 unsuccessful excisions of the neoplasm at 6 months and 1 month prior to presentation. Biopsy results from the second excision demonstrated persistent perianal SCCIS with positive margins (Figure 1). The patient was referred to our clinic to discuss Mohs micrographic surgery versus nonsurgical treatment options. The patient’s medical history was remarkable for an abnormal Papanicolaou test 10 years prior, which resulted in cervical cryotherapy.
 |
|
Physical examination revealed a 2×1-cm pink scar with peripheral scaling on the right anal verge (Figure 2A). Potential therapies discussed with the patient included Mohs surgery, ablative laser treatment, and nonsurgical treatment with ALA-PDT in combination with topical imiquimod cream 5%. To avoid further invasive treatments, we decided to administer a 3-week course of topical imiquimod cream 5% applied 3 times weekly to the entire affected area, followed 1 week later with a treatment of ALA-PDT. The incubation time was 6 hours. After completing 4 cycles of this therapeutic regimen, the erythema and scaling resolved (Figure 2B). The patient did not note any remarkable side effects associated with imiquimod but reported progressively resolving pain in the week following each ALA-PDT treatment, with the worst pain occurring during the first 48 hours after treatment. Three posttreatment scout biopsies revealed no evidence of residual perianal SCCIS. Two years after the negative biopsies, ongoing physical examinations demonstrated no evidence of clinical recurrence. Physicians in the dermatology and gynecology departments are following her closely.
Comment
Wide surgical excision is currently recommended as first-line therapy for perianal SCCIS.1,3,4 Unfortunately, surgical excision has been associated with difficulty in achieving disease-free margins, recurrence rates as high as 31%, and substantial morbidity.1,4 Other nonsurgical treatment modalities have been investigated for treating this neoplasm to simultaneously reduce recurrence rates while minimizing structural and functional damage to the treatment area, including radiotherapy, imiquimod, laser ablation, and ALA-PDT.1,3,4,5
In particular, imiquimod and ALA-PDT have shown promise as monotherapies for the treatment of perianal SCCIS, with several case reports describing complete resolution, low rates of recurrence, and preserved structure and function of the surrounding tissue after therapy1,3,4; however, recurrence of perianal SCCIS is still known to occur after monotherapy with either ALA-PDT or imiquimod.5,6
In contrast to noninvasive monotherapies, the literature is largely devoid of reports of noninvasive combination treatments used for perianal SCCIS. Our case represents successful use of a combination of imiquimod and ALA-PDT to treat persistent perianal SCCIS.
Conclusion
Although further research is necessary, the therapeutic success presented in our case suggests noninvasive combination therapy with imiquimod and ALA-PDT may represent a viable alternative to both surgical excision and noninvasive monotherapies for the treatment of perianal SCCIS.
Acknowledgement—The authors would like to thank Alejandro Gru, MD, Columbus, Ohio, for his review of the pathology slides for this case.
1. van Egmond S, Hoedemaker C, Sinclair R. Successful treatment of perianal Bowen’s disease with imiquimod. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:318-319.
2. Abbasakoor F, Boulos PB. Anal intraepithelial neoplasia. Br J Surg. 2005;92:277-290.
3. Petrelli NJ, Cebollero JA, Rodriguez-Bigas M, et al. Photodynamic therapy in the management of neoplasms of the perianal skin. Arch Surg. 1992;127:1436-1438.
4. Wietfeldt E, Thiele J. Malignancies of the anal margin and perianal skin. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009;22:127-135.
5. Pineda C, Welton M. Management of anal squamous intraepithelial lesions. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009;22:94-101.
6. Runfola MA, Weber TK, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, et al. Photodynamic therapy for residual neoplasms of the perianal skin. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000;43:499-502.
1. van Egmond S, Hoedemaker C, Sinclair R. Successful treatment of perianal Bowen’s disease with imiquimod. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:318-319.
2. Abbasakoor F, Boulos PB. Anal intraepithelial neoplasia. Br J Surg. 2005;92:277-290.
3. Petrelli NJ, Cebollero JA, Rodriguez-Bigas M, et al. Photodynamic therapy in the management of neoplasms of the perianal skin. Arch Surg. 1992;127:1436-1438.
4. Wietfeldt E, Thiele J. Malignancies of the anal margin and perianal skin. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009;22:127-135.
5. Pineda C, Welton M. Management of anal squamous intraepithelial lesions. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009;22:94-101.
6. Runfola MA, Weber TK, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, et al. Photodynamic therapy for residual neoplasms of the perianal skin. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000;43:499-502.
Practice Points
- Perianal squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCCIS) is an uncommon malignancy with most cases related to human papillomavirus infection.
- Treatment of perianal SCCIS is important to prevent progression to invasive squamous cell carcinoma.
- Treatment usually is surgical, but nonsurgical modalities such as combination therapy with imiquimod and 5-aminolevulinic acid–based photodynamic therapy should be considered in patients who are poor surgical candidates or in cases of recurrences after excisional surgery.