User login
THE COMPARISON
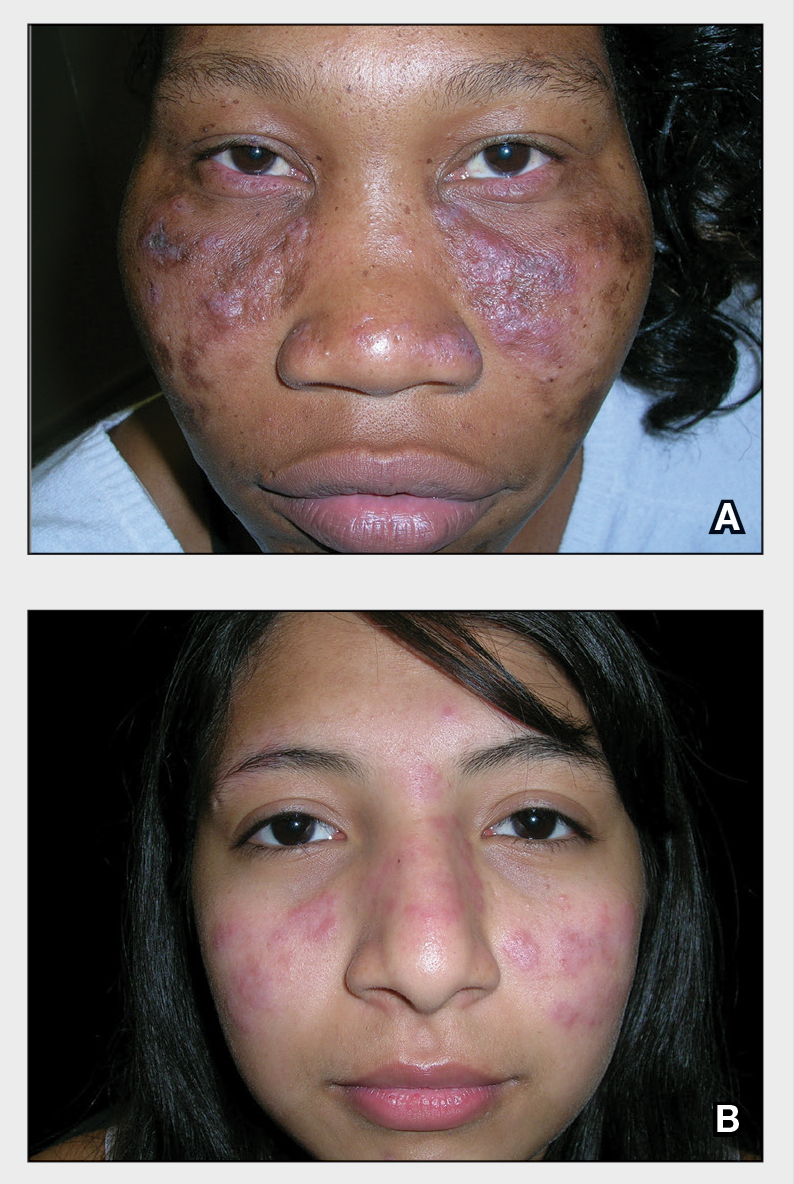
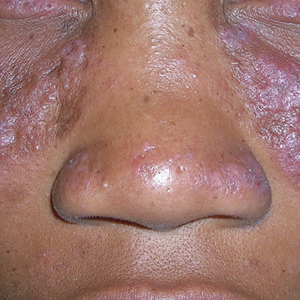
A Multicolored (pink, brown, and white) indurated plaques in a butterfly distribution on the face of a 30-year-old woman with a darker skin tone.
B Pink, elevated, indurated plaques with hypopigmentation in a butterfly distribution on the face of a 19-year-old woman with a lighter skin tone.
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus may occur with or without systemic lupus erythematosus. Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE), a form of chronic cutaneous lupus, is most commonly found on the scalp, face, and ears.1
Epidemiology
Discoid lupus erythematosus is most common in adult women (age range, 20–40 years).2 It occurs more frequently in women of African descent.3,4
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones:
Clinical features of DLE lesions include erythema, induration, follicular plugging, dyspigmentation, and scarring alopecia.1 In patients of African descent, lesions may be annular and hypopigmented to depigmented centrally with a border of hyperpigmentation. Active lesions may be painful and/or pruritic.2
Discoid lupus erythematosus lesions occur in photodistributed areas, although not exclusively. Photoprotective clothing and sunscreen are an important part of the treatment plan.1 Although sunscreen is recommended for patients with DLE, those with darker skin tones may find some sunscreens cosmetically unappealing due to a mismatch with their normal skin color.5 Tinted sunscreens may be beneficial additions.
Worth noting
Approximately 5% to 25% of patients with cutaneous lupus go on to develop systemic lupus erythematosus.6
Health disparity highlight
Discoid lesions may cause cutaneous scars that are quite disfiguring and may negatively impact quality of life. Some patients may have a few scattered lesions, whereas others have extensive disease covering most of the scalp. Discoid lupus erythematosus lesions of the scalp have classic clinical features including hair loss, erythema, hypopigmentation, and hyperpigmentation. The clinician’s comfort with performing a scalp examination with cultural humility is an important acquired skill and is especially important when the examination is performed on patients with more tightly coiled hair.7 For example, physicians may adopt the “compliment, discuss, and suggest” method when counseling patients.8
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JJ, Schaffer JV, et al. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2012.
- Otberg N, Wu W-Y, McElwee KJ, et al. Diagnosis and management of primary cicatricial alopecia: part I. Skinmed. 2008;7:19-26. doi:10.1111/j.1540-9740.2007.07163.x
- Callen JP. Chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus. clinical, laboratory, therapeutic, and prognostic examination of 62 patients. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:412-416. doi:10.1001/archderm.118.6.412
- McCarty DJ, Manzi S, Medsger TA Jr, et al. Incidence of systemic lupus erythematosus. race and gender differences. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:1260-1270. doi:10.1002/art.1780380914
- Morquette AJ, Waples ER, Heath CR. The importance of cosmetically elegant sunscreen in skin of color populations. J Cosmet Dermatol. In press.
- Zhou W, Wu H, Zhao M, et al. New insights into the progression from cutaneous lupus to systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020;16:829-837. doi:10.1080/17446 66X.2020.1805316
- Grayson C, Heath C. An approach to examining tightly coiled hair among patients with hair loss in race-discordant patientphysician interactions. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:505-506. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0338
- Grayson C, Heath CR. Counseling about traction alopecia: a “compliment, discuss, and suggest” method. Cutis. 2021;108:20-22.
THE COMPARISON
A Multicolored (pink, brown, and white) indurated plaques in a butterfly distribution on the face of a 30-year-old woman with a darker skin tone.
B Pink, elevated, indurated plaques with hypopigmentation in a butterfly distribution on the face of a 19-year-old woman with a lighter skin tone.
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus may occur with or without systemic lupus erythematosus. Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE), a form of chronic cutaneous lupus, is most commonly found on the scalp, face, and ears.1
Epidemiology
Discoid lupus erythematosus is most common in adult women (age range, 20–40 years).2 It occurs more frequently in women of African descent.3,4
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones:
Clinical features of DLE lesions include erythema, induration, follicular plugging, dyspigmentation, and scarring alopecia.1 In patients of African descent, lesions may be annular and hypopigmented to depigmented centrally with a border of hyperpigmentation. Active lesions may be painful and/or pruritic.2
Discoid lupus erythematosus lesions occur in photodistributed areas, although not exclusively. Photoprotective clothing and sunscreen are an important part of the treatment plan.1 Although sunscreen is recommended for patients with DLE, those with darker skin tones may find some sunscreens cosmetically unappealing due to a mismatch with their normal skin color.5 Tinted sunscreens may be beneficial additions.
Worth noting
Approximately 5% to 25% of patients with cutaneous lupus go on to develop systemic lupus erythematosus.6
Health disparity highlight
Discoid lesions may cause cutaneous scars that are quite disfiguring and may negatively impact quality of life. Some patients may have a few scattered lesions, whereas others have extensive disease covering most of the scalp. Discoid lupus erythematosus lesions of the scalp have classic clinical features including hair loss, erythema, hypopigmentation, and hyperpigmentation. The clinician’s comfort with performing a scalp examination with cultural humility is an important acquired skill and is especially important when the examination is performed on patients with more tightly coiled hair.7 For example, physicians may adopt the “compliment, discuss, and suggest” method when counseling patients.8
THE COMPARISON
A Multicolored (pink, brown, and white) indurated plaques in a butterfly distribution on the face of a 30-year-old woman with a darker skin tone.
B Pink, elevated, indurated plaques with hypopigmentation in a butterfly distribution on the face of a 19-year-old woman with a lighter skin tone.
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus may occur with or without systemic lupus erythematosus. Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE), a form of chronic cutaneous lupus, is most commonly found on the scalp, face, and ears.1
Epidemiology
Discoid lupus erythematosus is most common in adult women (age range, 20–40 years).2 It occurs more frequently in women of African descent.3,4
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones:
Clinical features of DLE lesions include erythema, induration, follicular plugging, dyspigmentation, and scarring alopecia.1 In patients of African descent, lesions may be annular and hypopigmented to depigmented centrally with a border of hyperpigmentation. Active lesions may be painful and/or pruritic.2
Discoid lupus erythematosus lesions occur in photodistributed areas, although not exclusively. Photoprotective clothing and sunscreen are an important part of the treatment plan.1 Although sunscreen is recommended for patients with DLE, those with darker skin tones may find some sunscreens cosmetically unappealing due to a mismatch with their normal skin color.5 Tinted sunscreens may be beneficial additions.
Worth noting
Approximately 5% to 25% of patients with cutaneous lupus go on to develop systemic lupus erythematosus.6
Health disparity highlight
Discoid lesions may cause cutaneous scars that are quite disfiguring and may negatively impact quality of life. Some patients may have a few scattered lesions, whereas others have extensive disease covering most of the scalp. Discoid lupus erythematosus lesions of the scalp have classic clinical features including hair loss, erythema, hypopigmentation, and hyperpigmentation. The clinician’s comfort with performing a scalp examination with cultural humility is an important acquired skill and is especially important when the examination is performed on patients with more tightly coiled hair.7 For example, physicians may adopt the “compliment, discuss, and suggest” method when counseling patients.8
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JJ, Schaffer JV, et al. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2012.
- Otberg N, Wu W-Y, McElwee KJ, et al. Diagnosis and management of primary cicatricial alopecia: part I. Skinmed. 2008;7:19-26. doi:10.1111/j.1540-9740.2007.07163.x
- Callen JP. Chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus. clinical, laboratory, therapeutic, and prognostic examination of 62 patients. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:412-416. doi:10.1001/archderm.118.6.412
- McCarty DJ, Manzi S, Medsger TA Jr, et al. Incidence of systemic lupus erythematosus. race and gender differences. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:1260-1270. doi:10.1002/art.1780380914
- Morquette AJ, Waples ER, Heath CR. The importance of cosmetically elegant sunscreen in skin of color populations. J Cosmet Dermatol. In press.
- Zhou W, Wu H, Zhao M, et al. New insights into the progression from cutaneous lupus to systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020;16:829-837. doi:10.1080/17446 66X.2020.1805316
- Grayson C, Heath C. An approach to examining tightly coiled hair among patients with hair loss in race-discordant patientphysician interactions. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:505-506. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0338
- Grayson C, Heath CR. Counseling about traction alopecia: a “compliment, discuss, and suggest” method. Cutis. 2021;108:20-22.
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JJ, Schaffer JV, et al. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2012.
- Otberg N, Wu W-Y, McElwee KJ, et al. Diagnosis and management of primary cicatricial alopecia: part I. Skinmed. 2008;7:19-26. doi:10.1111/j.1540-9740.2007.07163.x
- Callen JP. Chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus. clinical, laboratory, therapeutic, and prognostic examination of 62 patients. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:412-416. doi:10.1001/archderm.118.6.412
- McCarty DJ, Manzi S, Medsger TA Jr, et al. Incidence of systemic lupus erythematosus. race and gender differences. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:1260-1270. doi:10.1002/art.1780380914
- Morquette AJ, Waples ER, Heath CR. The importance of cosmetically elegant sunscreen in skin of color populations. J Cosmet Dermatol. In press.
- Zhou W, Wu H, Zhao M, et al. New insights into the progression from cutaneous lupus to systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020;16:829-837. doi:10.1080/17446 66X.2020.1805316
- Grayson C, Heath C. An approach to examining tightly coiled hair among patients with hair loss in race-discordant patientphysician interactions. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:505-506. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0338
- Grayson C, Heath CR. Counseling about traction alopecia: a “compliment, discuss, and suggest” method. Cutis. 2021;108:20-22.