User login
“No matter who the patient is, whether a child, adolescent, or adult, the key to figuring out hair disease is getting a good history,” Maria Hordinsky, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said at the Medscape Live Women’s and Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
. She also urged physicians and other health care providers to use the electronic medical record and to be thorough in documenting information – noting nutrition, hair care habits, supplement use, and other details.
Lab tests should be selected based on that history, she said. For instance, low iron stores can be associated with hair shedding; and thyroid function studies might be needed.
Other highlights of her presentation included comments on different types of alopecia, and some new treatment approaches:
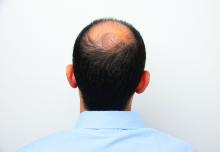
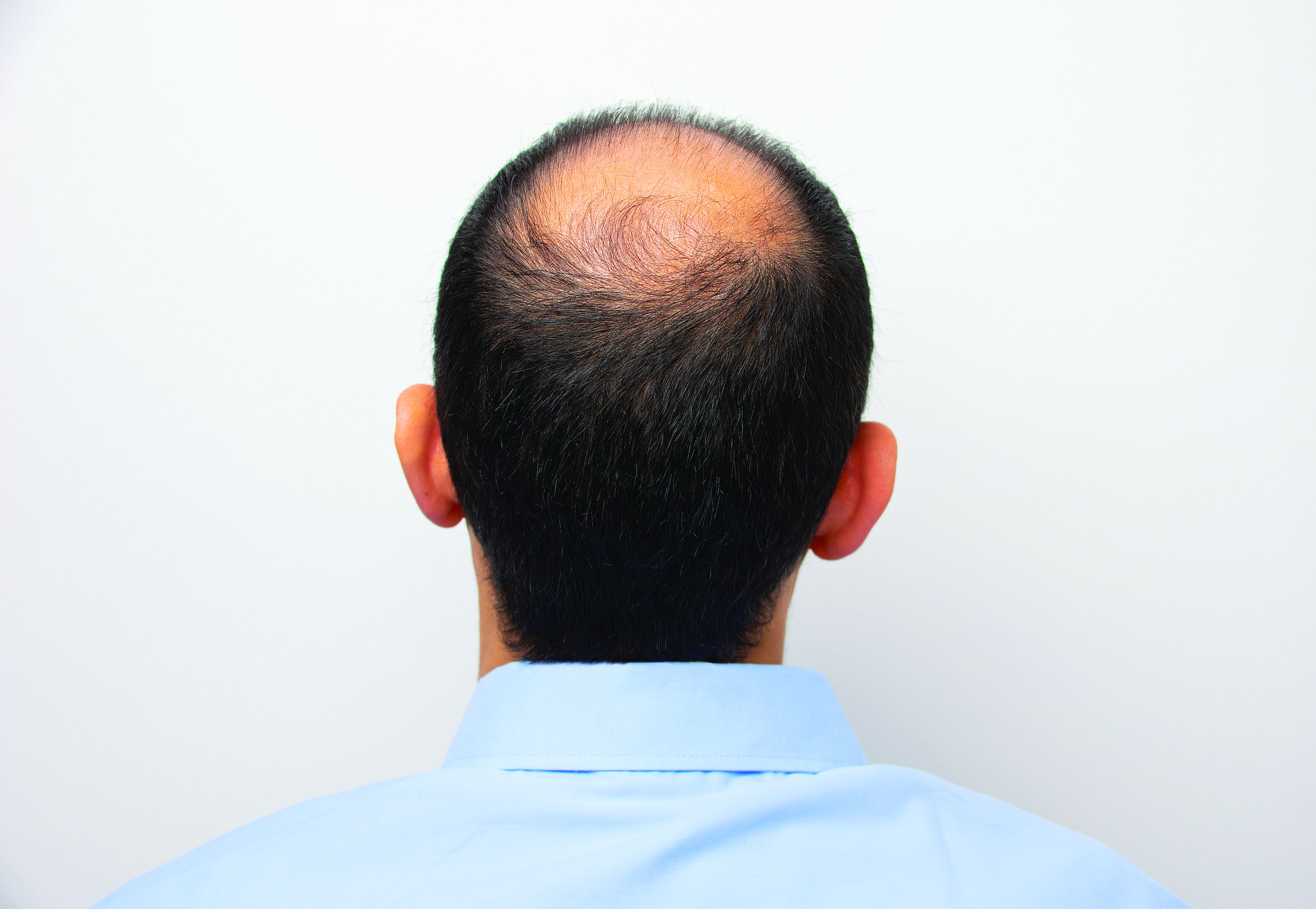
Androgenetic alopecia. In a meta-analysis and systematic review published in 2017, all treatments tested (2% and 5% minoxidil in men, 1 mg finasteride in men, 2% minoxidil in women, and low-level laser light therapy in men) were superior to placebo. Several photobiomodulation (PBM) devices (also known as low-level laser light) for home use have been cleared for androgenetic alopecia by the Food and Drug Administration; a clinician’s guide, published in 2018, provides information on these devices.
Hair and hormones. Combination therapy for female-pattern hair loss – low-dose minoxidil and spironolactone – is important to know about, she said, adding there are data from an observational pilot study supporting this treatment. Women should not become pregnant while on this treatment, Dr. Hordinsky cautioned.
PRP (platelet rich plasma). This treatment for hair loss can be costly, she cautioned, as it’s viewed as a cosmetic technique, “but it actually can work rather well.”
Hair regrowth measures. Traditionally, measures center on global assessment, the patient’s self-assessment, investigator assessment, and an independent photo review. Enter the dermatoscope. “We can now get pictures as a baseline. Patients can see, and also see the health of their scalp,” and if treatments make it look better or worse, she noted.
Alopecia areata (AA). Patients and families need to be made aware that this is an autoimmune disease that can recur, and if it does recur, the extent of hair loss is not predictable. According to Dr. Hordinsky, the most widely used tool to halt disease activity has been treatment with a corticosteroid (topical, intralesional, oral, or even intravenous corticosteroids).
Clinical trials and publications from 2018 to 2020 have triggered interest in off-label use and further studies of JAK inhibitors for treating AA, which include baricitinib, ruxolitinib, and tofacitinib. At the American Academy of Dermatology meeting in March 2022, results of the ALLEGRO phase 2b/3 trial found that the JAK inhibitor ritlecitinib (50 mg or 20 mg daily, with or without a 200-mg loading dose), was efficacious in adults and adolescents with AA, compared with placebo, with no safety concerns noted. “This looks to be very, very promising,” she said, “and also very safe.” Two phase 3 trials of baricitinib also presented at the same meeting found it was superior to placebo for hair regrowth in adults with severe AA at 36 weeks. (On June 13, shortly after Dr. Hordinsky spoke at the meeting, the FDA approved baricitinib for treating AA in adults, making this the first systemic treatment to be approved for AA).
Research on topical JAK inhibitors for AA has been disappointing, Dr. Hordinsky said.
Alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis. For patients with both AA and AD, dupilumab may provide relief, she said. She referred to a recently published phase 2a trial in patients with AA (including some with both AA and AD), which found that Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) scores improved after 48 weeks of treatment, with higher response rates among those with baseline IgE levels of 200 IU/mL or higher. “If your patient has both, and their immunoglobulin-E level is greater than 200, then they may be a good candidate for dupilumab and both diseases may respond,” she said.
Scalp symptoms. It can be challenging when patients complain of itch, pain, or burning on the scalp, but have no obvious skin disease, Dr. Hordinsky said. Her tips: Some of these patients may be experiencing scalp symptoms secondary to a neuropathy; others may have mast cell degranulation, but for others, the basis of the symptoms may be unclear. Special nerve studies may be needed. For relief, a trial of antihistamines or topical or oral gabapentin may be needed, she said.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA). This condition, first described in postmenopausal women, is now reported in men and in younger women. While sunscreen has been suspected, there are no good data that have proven that link, she said. Cosmetics are also considered a possible culprit. For treatment, “the first thing we try to do is treat the inflammation,” Dr. Hordinsky said. Treatment options include topical high-potency corticosteroids, intralesional steroids, and topical nonsteroid anti-inflammatory creams (tier 1); hydroxychloroquine, low-dose antibiotics, and acitretin (tier 2); and cyclosporin and mycophenolate mofetil (tier 3).
In an observational study of mostly women with FFA, she noted, treatment with dutasteride was more effective than commonly used systemic treatments.
“Don’t forget to address the psychosocial needs of the hair loss patient,” Dr. Hordinsky advised. “Hair loss patients are very distressed, and you have to learn how to be fast and nimble and address those needs.” Working with a behavioral health specialist or therapist can help, she said.
She also recommended directing patients to appropriate organizations such as the National Alopecia Areata Foundation and the Scarring Alopecia Foundation, as well as conferences, such as the upcoming NAAF conference in Washington. “These organizations do give good information that should complement what you are doing.”
Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Hordinsky reported no disclosures.
“No matter who the patient is, whether a child, adolescent, or adult, the key to figuring out hair disease is getting a good history,” Maria Hordinsky, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said at the Medscape Live Women’s and Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
. She also urged physicians and other health care providers to use the electronic medical record and to be thorough in documenting information – noting nutrition, hair care habits, supplement use, and other details.
Lab tests should be selected based on that history, she said. For instance, low iron stores can be associated with hair shedding; and thyroid function studies might be needed.
Other highlights of her presentation included comments on different types of alopecia, and some new treatment approaches:
Androgenetic alopecia. In a meta-analysis and systematic review published in 2017, all treatments tested (2% and 5% minoxidil in men, 1 mg finasteride in men, 2% minoxidil in women, and low-level laser light therapy in men) were superior to placebo. Several photobiomodulation (PBM) devices (also known as low-level laser light) for home use have been cleared for androgenetic alopecia by the Food and Drug Administration; a clinician’s guide, published in 2018, provides information on these devices.
Hair and hormones. Combination therapy for female-pattern hair loss – low-dose minoxidil and spironolactone – is important to know about, she said, adding there are data from an observational pilot study supporting this treatment. Women should not become pregnant while on this treatment, Dr. Hordinsky cautioned.
PRP (platelet rich plasma). This treatment for hair loss can be costly, she cautioned, as it’s viewed as a cosmetic technique, “but it actually can work rather well.”
Hair regrowth measures. Traditionally, measures center on global assessment, the patient’s self-assessment, investigator assessment, and an independent photo review. Enter the dermatoscope. “We can now get pictures as a baseline. Patients can see, and also see the health of their scalp,” and if treatments make it look better or worse, she noted.
Alopecia areata (AA). Patients and families need to be made aware that this is an autoimmune disease that can recur, and if it does recur, the extent of hair loss is not predictable. According to Dr. Hordinsky, the most widely used tool to halt disease activity has been treatment with a corticosteroid (topical, intralesional, oral, or even intravenous corticosteroids).
Clinical trials and publications from 2018 to 2020 have triggered interest in off-label use and further studies of JAK inhibitors for treating AA, which include baricitinib, ruxolitinib, and tofacitinib. At the American Academy of Dermatology meeting in March 2022, results of the ALLEGRO phase 2b/3 trial found that the JAK inhibitor ritlecitinib (50 mg or 20 mg daily, with or without a 200-mg loading dose), was efficacious in adults and adolescents with AA, compared with placebo, with no safety concerns noted. “This looks to be very, very promising,” she said, “and also very safe.” Two phase 3 trials of baricitinib also presented at the same meeting found it was superior to placebo for hair regrowth in adults with severe AA at 36 weeks. (On June 13, shortly after Dr. Hordinsky spoke at the meeting, the FDA approved baricitinib for treating AA in adults, making this the first systemic treatment to be approved for AA).
Research on topical JAK inhibitors for AA has been disappointing, Dr. Hordinsky said.
Alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis. For patients with both AA and AD, dupilumab may provide relief, she said. She referred to a recently published phase 2a trial in patients with AA (including some with both AA and AD), which found that Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) scores improved after 48 weeks of treatment, with higher response rates among those with baseline IgE levels of 200 IU/mL or higher. “If your patient has both, and their immunoglobulin-E level is greater than 200, then they may be a good candidate for dupilumab and both diseases may respond,” she said.
Scalp symptoms. It can be challenging when patients complain of itch, pain, or burning on the scalp, but have no obvious skin disease, Dr. Hordinsky said. Her tips: Some of these patients may be experiencing scalp symptoms secondary to a neuropathy; others may have mast cell degranulation, but for others, the basis of the symptoms may be unclear. Special nerve studies may be needed. For relief, a trial of antihistamines or topical or oral gabapentin may be needed, she said.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA). This condition, first described in postmenopausal women, is now reported in men and in younger women. While sunscreen has been suspected, there are no good data that have proven that link, she said. Cosmetics are also considered a possible culprit. For treatment, “the first thing we try to do is treat the inflammation,” Dr. Hordinsky said. Treatment options include topical high-potency corticosteroids, intralesional steroids, and topical nonsteroid anti-inflammatory creams (tier 1); hydroxychloroquine, low-dose antibiotics, and acitretin (tier 2); and cyclosporin and mycophenolate mofetil (tier 3).
In an observational study of mostly women with FFA, she noted, treatment with dutasteride was more effective than commonly used systemic treatments.
“Don’t forget to address the psychosocial needs of the hair loss patient,” Dr. Hordinsky advised. “Hair loss patients are very distressed, and you have to learn how to be fast and nimble and address those needs.” Working with a behavioral health specialist or therapist can help, she said.
She also recommended directing patients to appropriate organizations such as the National Alopecia Areata Foundation and the Scarring Alopecia Foundation, as well as conferences, such as the upcoming NAAF conference in Washington. “These organizations do give good information that should complement what you are doing.”
Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Hordinsky reported no disclosures.
“No matter who the patient is, whether a child, adolescent, or adult, the key to figuring out hair disease is getting a good history,” Maria Hordinsky, MD, professor and chair of the department of dermatology at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said at the Medscape Live Women’s and Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
. She also urged physicians and other health care providers to use the electronic medical record and to be thorough in documenting information – noting nutrition, hair care habits, supplement use, and other details.
Lab tests should be selected based on that history, she said. For instance, low iron stores can be associated with hair shedding; and thyroid function studies might be needed.
Other highlights of her presentation included comments on different types of alopecia, and some new treatment approaches:
Androgenetic alopecia. In a meta-analysis and systematic review published in 2017, all treatments tested (2% and 5% minoxidil in men, 1 mg finasteride in men, 2% minoxidil in women, and low-level laser light therapy in men) were superior to placebo. Several photobiomodulation (PBM) devices (also known as low-level laser light) for home use have been cleared for androgenetic alopecia by the Food and Drug Administration; a clinician’s guide, published in 2018, provides information on these devices.
Hair and hormones. Combination therapy for female-pattern hair loss – low-dose minoxidil and spironolactone – is important to know about, she said, adding there are data from an observational pilot study supporting this treatment. Women should not become pregnant while on this treatment, Dr. Hordinsky cautioned.
PRP (platelet rich plasma). This treatment for hair loss can be costly, she cautioned, as it’s viewed as a cosmetic technique, “but it actually can work rather well.”
Hair regrowth measures. Traditionally, measures center on global assessment, the patient’s self-assessment, investigator assessment, and an independent photo review. Enter the dermatoscope. “We can now get pictures as a baseline. Patients can see, and also see the health of their scalp,” and if treatments make it look better or worse, she noted.
Alopecia areata (AA). Patients and families need to be made aware that this is an autoimmune disease that can recur, and if it does recur, the extent of hair loss is not predictable. According to Dr. Hordinsky, the most widely used tool to halt disease activity has been treatment with a corticosteroid (topical, intralesional, oral, or even intravenous corticosteroids).
Clinical trials and publications from 2018 to 2020 have triggered interest in off-label use and further studies of JAK inhibitors for treating AA, which include baricitinib, ruxolitinib, and tofacitinib. At the American Academy of Dermatology meeting in March 2022, results of the ALLEGRO phase 2b/3 trial found that the JAK inhibitor ritlecitinib (50 mg or 20 mg daily, with or without a 200-mg loading dose), was efficacious in adults and adolescents with AA, compared with placebo, with no safety concerns noted. “This looks to be very, very promising,” she said, “and also very safe.” Two phase 3 trials of baricitinib also presented at the same meeting found it was superior to placebo for hair regrowth in adults with severe AA at 36 weeks. (On June 13, shortly after Dr. Hordinsky spoke at the meeting, the FDA approved baricitinib for treating AA in adults, making this the first systemic treatment to be approved for AA).
Research on topical JAK inhibitors for AA has been disappointing, Dr. Hordinsky said.
Alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis. For patients with both AA and AD, dupilumab may provide relief, she said. She referred to a recently published phase 2a trial in patients with AA (including some with both AA and AD), which found that Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) scores improved after 48 weeks of treatment, with higher response rates among those with baseline IgE levels of 200 IU/mL or higher. “If your patient has both, and their immunoglobulin-E level is greater than 200, then they may be a good candidate for dupilumab and both diseases may respond,” she said.
Scalp symptoms. It can be challenging when patients complain of itch, pain, or burning on the scalp, but have no obvious skin disease, Dr. Hordinsky said. Her tips: Some of these patients may be experiencing scalp symptoms secondary to a neuropathy; others may have mast cell degranulation, but for others, the basis of the symptoms may be unclear. Special nerve studies may be needed. For relief, a trial of antihistamines or topical or oral gabapentin may be needed, she said.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA). This condition, first described in postmenopausal women, is now reported in men and in younger women. While sunscreen has been suspected, there are no good data that have proven that link, she said. Cosmetics are also considered a possible culprit. For treatment, “the first thing we try to do is treat the inflammation,” Dr. Hordinsky said. Treatment options include topical high-potency corticosteroids, intralesional steroids, and topical nonsteroid anti-inflammatory creams (tier 1); hydroxychloroquine, low-dose antibiotics, and acitretin (tier 2); and cyclosporin and mycophenolate mofetil (tier 3).
In an observational study of mostly women with FFA, she noted, treatment with dutasteride was more effective than commonly used systemic treatments.
“Don’t forget to address the psychosocial needs of the hair loss patient,” Dr. Hordinsky advised. “Hair loss patients are very distressed, and you have to learn how to be fast and nimble and address those needs.” Working with a behavioral health specialist or therapist can help, she said.
She also recommended directing patients to appropriate organizations such as the National Alopecia Areata Foundation and the Scarring Alopecia Foundation, as well as conferences, such as the upcoming NAAF conference in Washington. “These organizations do give good information that should complement what you are doing.”
Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Hordinsky reported no disclosures.
FROM MEDSCAPELIVE WOMEN’S & PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR