User login
Take-Home Points
- Hockey is a high-speed collision sport with one of the highest injury rates among all sports.
- Use of a helmet with visors or full-face shields significantly reduces the risk for eye injury.
- Broken portions of teeth should be found and placed in a protective medium such as saline, saliva, or milk for transport.
- A player with unresolved concussion symptoms should not be allowed to return to the ice.
- Shoulder dominance, which determines stick grip, is an important consideration in the treatment of shoulder instability in an ice hockey player.
On a surface of ice in Windsor, Nova Scotia in the middle of the 19th century, the modern game of ice hockey evolved.1 A blend of hurley, a Gaelic sport, and lacrosse, from the native Mi’kmaq culture, the sport of ice hockey gained rapidly in popularity throughout Canada and is now the country’s national sport. Hockey quickly spread to the United States and then Europe. It is presently played in 77 countries across the world.2
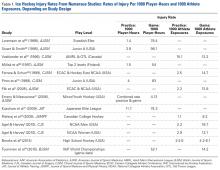
Hockey players can reach speeds of up to 48 km (~30 miles) per hour on razor-sharp skates on an ice surface surrounded by rigid plastic composite boards topped with plexiglass.3 They use sticks made of wood, aluminum, or a composite material to advance a 6-ounce vulcanized rubber puck on the opposing goal, and this puck sometimes reaches speeds over 160 km (~100 miles) per hour. Older, male players are allowed to make physical contact with their opposing counterparts to separate them from the puck (body-checking). Not surprisingly, the potential risk for injury in hockey is high. At the 2010 Winter Olympics, men’s ice hockey players had the highest rate of injury of any other competitors there—more than 30% were affected.4
Hockey is played and enjoyed by athletes ranging widely in age. Youth hockey leagues accept players as young as 5 years. Hockey can become a lifelong recreational activity. In North America, old timers’ leagues have many players up to age 70 years.6 According to International Ice Hockey Federation data for 2016, more than 543,000 and 639,500 people play hockey in the United States and Canada, respectively.2 Most of the rules, protective equipment, skates, ice surfaces, and goal sizes are the same in men’s and women’s hockey.7 The major difference is in body-checking—this practice is not allowed at any age in women’s ice hockey.
In this article, we review the evaluation and management of common head, neck, and shoulder hockey injuries for physicians who provide medical support and coverage for youth, amateur, and senior hockey teams.
Evaluation and Management of Common Hockey Injuries
Eye Injuries
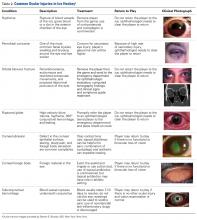
Although eye injuries are less common than musculoskeletal injuries and concussions in hockey, they are a serious risk for recreational and competitive players alike. Furthermore, recovery may be difficult, and eye injuries can have serious lifelong consequences.8 In hockey, the most commonly reported eye injuries are periorbital contusions and lacerations, hyphema, corneal and conjunctival abrasions, orbital fractures, and ruptured globes (Table 2).9,10
As a contact sport, hockey often involves high-impact, blunt-force trauma. The trauma in hockey results from collisions with other players, the boards, hockey sticks, and pucks. It is therefore not surprising that the most common ocular injuries in this sport are periorbital contusions. Although most contusions cause only mild swelling and ecchymosis of the soft tissues around the eye, there is potential for serious consequences. In a Scandinavia study, Leivo and colleagues10 found that 9% of patients who sustained a periocular contusion also had a clinically significant secondary diagnosis, such as retinal tear or hemorrhage, eyelid laceration, vitreous hemorrhage, or retinal detachment. Although the study was hospital-based, and therefore biased toward more severe cases, its findings highlight the potential severity of eye injuries in hockey. Furthermore, the study found that the majority of players who sustained blunt trauma to the eye itself required lifelong follow-up because of increased risk for glaucoma. This is particularly true for hyphema, as this finding indicates significant damage to intraocular tissues.10Players can also sustain fractures of the orbital bones, including orbital blowout fractures. Typical signs and symptoms of blowout fractures include diplopia, proptosis or enophthalmos, infraorbital hypoesthesia, painful and decreased extraocular movement (particularly upgaze), and palpable crepitance caused by sinus air entering the lower eyelid.11 If orbital fracture is suspected, as it should be in any case in which the injured player experiences pain with eye movement or diplopia, the player should be referred to the ED for computed tomography (CT) and ophthalmologic evaluation.12 Continued participation seriously risks making the injury much worse, particularly should another impact occur. In addition, given the impact needed to cause orbital fractures, consideration must be given to the potential for a coexisting concussion injury.
Severe direct trauma to the eye—from a puck, a stick, or a fist—can result in a ruptured globe, a particularly serious injury that requires immediate surgical attention. Signs and symptoms of a ruptured globe are rarely subtle, but associated eyelid swelling or laceration may obscure the injury, delaying proper diagnosis and treatment. More obvious signs include severely reduced vision, hemorrhagic chemosis (swelling) of the conjunctiva, and an irregular or peaked pupil. If a rupture or any significant intraocular injury is suspected, it is crucial to avoid applying any pressure to the globe, as this can significantly worsen the damage to the intraocular tissues. Use of a helmet with protective shields and cages attached markedly reduces the risk for such injuries.13All eye injuries require prompt assessment, which allows for appropriate management and prevention of secondary damage.14 Initial evaluation of a patient with ocular trauma should begin with external examination for lacerations, swelling, or orbital rim step-off deformity. The physician should also check visual acuity in order to assess for significant vision impairment (counting fingers or reading a sign in the arena; confrontation visual fields). This should be done before attending to any periocular injuries, with the uninjured side serving as a control. Next, the physician should assess the extraocular eye movements as well as the size, shape, and reactivity of the pupils. Particular attention should be paid to detecting any deficit in extraocular movement or irregularity in pupil size, shape, or reactivity, as such findings are highly suggestive of serious injury to the globe.13 Hyphema (blood in anterior chamber of eye anterior to pupil) should be suspected if vision is reduced and the pupil cannot be clearly visualized. However, a bright red clot is not always apparent at time of injury or if the amount of blood is small. An irregular pupil, or a pupil that does not constrict well to light, is also a red flag for serious contusion injury to the eye, and requires ophthalmologic evaluation. It is important to keep in mind that blunt trauma severe enough to produce hyphema or an irregular and poorly reactive pupil is often associated with retinal damage as well, including retinal edema or detachment.
Minor injuries (eg, small foreign bodies, minor periocular contusions and lacerations) can often be managed rink-side. Foreign bodies not embedded in the cornea, but lodged under the upper eyelid, can sometimes be removed by everting the eyelid and sweeping with a moistened cotton swab or using diffuse, sterile saline irrigation.11 Corneal abrasions generally cause severe pain, photophobia, and tearing and are easily diagnosed with use of topical fluorescein and a blue light. A topical anesthetic can be extremely helpful in this setting, as it allows for proper pain-free evaluation, but should never be used in an ongoing manner for pain relief. Small lacerations of the brow can be sutured with 5-0 or 6-0 nylon or closed with 2-Octyl cyanoacrylate tissue adhesive (Dermabond). Eyelid lacerations, unless very small, are best managed by an ophthalmologist; care must be taken to rule out injury to the deeper orbital tissues and eye. If serious injury is suspected, or the eye cannot be appropriately evaluated, it should be stabilized and protected with a protective shield or plastic cup, and the player should be transferred to an ED for appropriate ophthalmologic evaluation.13Most eye injuries are accidental, caused by sticks or deflected pucks, but 18% are acquired in fights.8 Use of visors or full-face cages effectively minimizes the rate of eye injuries.8,13,15,16 In a cohort study of 282 elite amateur ice hockey players, the risk of eye injury was 4.7 times higher in players without face protection than in players who used half-face shields; there were no eye injuries in players who used full-face protection.13 For visors to prevent eye injury, they must be positioned to cover the eyes and the lower edge of the nose in all projections.10
Dental Injuries
The incidence and type of facial and dental injuries depend directly on the type of face protection used.11,17,18 In a study of face, head, and neck injuries in elite amateur ice hockey players, Stuart and colleagues13 found game-related injury rates of 158.9 per 1000 player-hours in players without face protection, 73.5 in players who used half-face shields, and 23.2 in players who used full-face shields. Players who wore full-face shields had facial, head, and neck injury rates of only 23.2 per 1000 player-game hours.13 Other studies clearly support the important role face shields play in lowering injury risk in hockey. Face and head injuries account for 20% to 40% of all hockey-related injuries,3,16,19 and dental injuries up to 11.5%.20 In a study from Finland, Lahti and colleagues19 found that over a 2-year period, 479 hockey players sustained injuries, including 650 separate dental injuries. The most commonly diagnosed dental injury was an uncomplicated crown fracture, and the most common cause was a hit with a hockey stick, which accounted for 52.7% and 40.3% of dental injuries in games and practices, respectively.19
In the management of dental fractures, the broken portions of teeth should be found and placed in a transportation-protective medium, such as saline, saliva, or milk,16 which can improve functional and esthetic replacement outcomes.21,22 Loose pieces of teeth should not be left in the player’s mouth. The residual tooth should be stabilized and exposure to air and occlusion limited. Dental fractures can affect the enamel, the enamel and dentin structures (uncomplicated fracture), or enamel, dentin, and pulp (complicated).23 Fractures involving only the enamel do not require urgent dental evaluation. Dentin or pulp involvement may cause temperature and air sensitivity.23 If a tooth is air-sensitive, the player should be referred to a specialist immediately.11
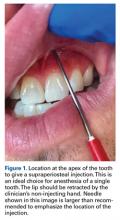
Direct trauma can cause instability without displacement (subluxation) or complete displacement of the tooth from its alveolar socket (avulsion).23 An avulsed tooth should be handled by the crown to avoid further damage to the root and periodontal ligament.16,24 The tooth should be rinsed gently with saline and reimplanted in its socket, ideally within 5 to 10 minutes,23with the athlete biting down gently on gauze to hold the tooth in place. A 1-mL supraperiosteal infiltration of 1% or 2% lidocaine hydrochloride (1:100,000 epinephrine) can be given into the apex of the tooth being anesthetized (Figure 1).
Concussions
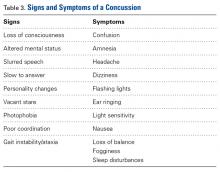
A concussion is a “complex pathophysiological process affecting the brain, induced by traumatic biomechanical forces.”25 Concussion is largely a functional disturbance instead of a structural injury, owing to the rotational and/or shearing forces involved. Many studies have identified concussion as the most common type of injury in all of youth hockey.26 Concussions account for up to 19% of all injuries in men’s collegiate hockey.3
Concussion can be challenging to diagnose on the ice. The most important factor in concussion management is symptom reporting by the athlete.27 Despite significant efforts in education and awareness, student athletes, especially hockey players, withhold reporting a possible concussion.28 Reasons for underreporting include fear of letting down other players and coaches, thinking the injury is not severe enough to warrant evaluation, and fear of losing standing with the current team or future teams.28
As postinjury concussion assessments are ideal when comparisons can be made with preseason (baseline) scores, preseason testing is becoming standard in professional, college, junior, and high school hockey. This testing involves the Sport Concussion Assessment Tool, 3rd edition (SCAT3), and the King-Devick (K-D) test.30,31 Some youth leagues have baseline testing as well, though the frequency of baseline testing in their players is controversial,32 as the adolescent mind’s processing speed and memory increase exponentially.33 For these younger athletes, it may be necessary to perform baseline testing more frequently than annually.32 A physician can use baseline test results to help diagnose a concussion at the rink and then track the athlete’s recovery and help with return-to-play decisions.29 Vision involves almost half of the brain’s circuits,34 including areas vulnerable to head impact. A neuro-ophthalmologic test can assess for irregularities in accommodation, convergence, ocular muscle balance, pursuit, and saccades.29 The K-D test is a visual performance examination that allows easy and objective assessment of eye movements. Use of both the K-D test and the SCAT3 at the rink may increase the number of concussions detected.29,35 We recommend that physicians use both tests to assess for concussion at the hockey rink.
Initial treatment involves a period of physical rest and relative cognitive rest. Acute worsening of symptoms warrants urgent imaging to rule out a subdural or subarachnoid bleed. Once a player is symptom-free, a graded return-to-play protocol should be followed (Table 4).
On the prevention side, great efforts have been made to improve hockey helmets. (Some manufacturers claim to have made concussion-proof helmets, but there is no evidence supporting this claim.6) Numerous investigators have reported a lower overall injury rate in players who wear a helmet and a full-face shield.6,13 In addition, rule changes aimed at decreasing head contact have been implemented to decrease the incidence of sport-related concussions.36 Moreover, education on proper helmet use and wear should be emphasized. A study of the effects of hockey helmet fit on cervical motion found that 7 (39%) of 18 players wore a game or competition helmet so loosely that it could be removed without unbuttoning its chinstrap.37 Improperly worn helmets cannot prevent injury as well as properly worn helmets can.
Cervical Spine Injuries
Whereas American football is associated with a higher annual number of nonfatal catastrophic neck injuries, hockey has a 3 to 6 times higher incidence of cervical spine injuries and spinal cord damage.38,39 A Canadian Ice Hockey Spinal Injuries Registry review of the period 2006 to 2011 identified 44 cervical spine injuries, 7.3 per year on average.40 Severe injury, defined as complete motor and sensory loss, complete motor loss and incomplete sensory, or complete motor loss, occurred in 4 (9.1%) of the 44 injured players. In hockey, a major mechanism of cervical spine injury is an axial load to the slightly flexed spine.39 Of 355 hockey-related cervical spine injuries in a Canada study, 95 (35.5%) were caused by a check from behind.40,41 The Canadian neurosurgeons’ work led to rule changes prohibiting checks from behind, and this prohibition has reduced the incidence of cervical spine injuries in ice hockey.38,40
Team physicians should be comfortable managing serious neck and spine injuries on the ice. Initial evaluation should follow the standard ABCs (airway, breathing, circulation). The physician places a hand on each side of the head to stabilize the neck until the initial examination is complete. The goal is to minimize cervical spine motion until transportation to the hospital for advanced imaging and definitive treatment.37 The decision to remove or leave on the helmet is now controversial. Hockey helmets differ from football helmets in that their chinstraps do not afford significant cervical stabilization, and the helmets have less padding and cover less of the head; in addition, a shockingly high percentage of hockey players do not wear properly fitting helmets.37 In one study, 3-dimensional motion analysis of a hockey player during the logroll technique showed less transverse and sagittal cervical plane motion with the helmet removed than with the helmet (properly fitting or not) in place; the authors recommended removing the helmet to limit extraneous cervical spine motion during the technique.37 However, 2 other studies found that helmet removal can result in significantly increased cervical spine motion of the immobilized hockey player.42,43Recommendation 4 of the recently released interassociation consensus statement of the National Athletic Trainers’ Association reads, “Protective athletic equipment should be removed before transport to an emergency facility for an athlete-patient with suspected cervical spine instability.”44 This represents a shift from leaving the helmet and shoulder pads in place. For ice hockey players with suspected cervical spine injury, more research is needed on cervical motion during the entire sequence—partial logrolls, spine-boarding, placement of cervical collar before or after logroll, and different immobilization techniques for transport.37
The athlete must be carefully transferred to a spine board with either logroll or lift-and-slide. Although an extrication cervical collar can be placed before the spine board is placed, the effectiveness of this collar in executing the spine-board transfer is not proven.45 When the player is on the spine board, the head can be secured with pads and straps en route to the hospital.
Return-to-Play Criteria for Cervical Spine Injuries There is no clear consensus on return-to-play guidelines for cervical spine injuries in athletes.46
Shoulder Injuries
For hockey players, the upper extremity traditionally has been considered a well-protected area.48 However, shoulder pads are considerably more flexible in hockey than in football and other collision sports. In addition, hockey gloves allow a fair amount of motion for stick handling, and the wrist may be in maximal flexion or extension when a hit against the boards or the ice occurs. Open-ice checking, board collisions, and hockey stick use have been postulated as reasons for the high incidence of upper extremity injuries in hockey. Researchers in Finland found that upper extremity injuries accounted for up to 31% of all hockey injuries.49 More than 50% of these injuries resulted from checking or board collisions. Furthermore, study findings highlighted a low rate of injury in younger players and indicated the rate increases with age.49,50
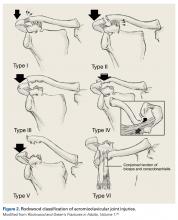
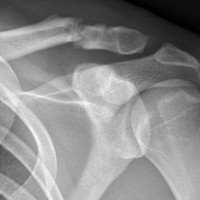
In hockey players, the acromioclavicular (AC) joint is the most commonly injured shoulder structure.51 The mechanism of injury can be a board collision or an open-ice hit, but most often is a direct blow to the shoulder. The collision disrupts the AC joint and can sprain or tear the coracoclavicular ligaments. The Rockwood classification is used to categorize AC joint injuries (Figure 2).
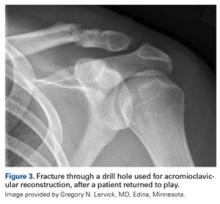
Initial management involves icing the AC joint and placing a sling for comfort. Type I and type II injuries can be managed with progressive range-of-motion (ROM) exercises, strengthening, cryotherapy, and a period of rest. Treatment of type III injuries remains controversial,52 but in hockey players these injuries are almost always treated nonoperatively. Return to play requires full motion, normal strength, and minimal discomfort. Players return a few days to 2 weeks after a grade I injury; recovery from grade II injuries may take 2 to 3 weeks, and recovery from grade III injuries, 6 to 12 weeks. Surgical treatment is usually required in type IV and type V injuries, but we have had experience treating these injuries nonoperatively in high-level players. AC joint reinjury in hockey players is common, and surgical treatment should be approached cautiously, as delayed fracture after return to sport has been reported.53 Special precautions should be taken in collision athletes who undergo AC joint reconstruction. In the anatomical reconstruction described by Carofino and Mazzocca,54 2 holes are drilled in the clavicle; these holes are a potential source of fracture when the collision athlete returns to sport (Figure 3).
Clavicle fracture is another common hockey injury.55 Studies have shown clavicle fractures proportionally occur most often in people 15 to 19 years old.49 The injury presents with pain and deformity over the clavicle; in more severe fractures, skin tenting is identified. Initial management of suspected clavicle fracture includes cryotherapy, sling, and radiographs. Radiographs should include an AP view and then a 45° cephalad view, which eliminates overshadowing from the ribs. Most clavicle fractures are successfully managed nonoperatively, though there is evidence that significantly displaced or comminuted fractures have better union rates and shoulder function when treated with open reduction and internal fixation.56 After a clavicle fracture, return to skating and noncontact practice usually takes 8 weeks, with return to full contact occurring around 12 weeks.
Sternoclavicular injuries are relatively uncommon, but potentially serious. Special attention should also be given to adolescent athletes with sternoclavicular pain. Although sternoclavicular dislocations have been reported in hockey players, instead these likely are fractures involving the medial clavicle physis.57
The shoulder is the most commonly dislocated major joint, and the incidence of shoulder dislocation in elite hockey players is 8% to 21%.50,58 Anterior shoulder instability occurs from a fall with the shoulder in an abducted, externally rotated and extended position or from a direct anteriorly placed impact to the posterior shoulder. We recommend taking players off the ice for evaluation. Depending on physician comfort, the shoulder can be reduced in the training room, and the athlete sent for radiographs after reduction. If resources or support for closed reduction is not available at the rink, the athlete should be sent to the ED. Initial radiographic evaluation of a player with shoulder injury begins with plain radiographs, including a true AP (Grashey) view with the humerus in neutral, internal, and external rotation and an axillary view. The axillary radiograph is crucial in determining anterior or posterior dislocation. If the patient cannot tolerate the pain associated with having an axillary radiograph taken, a Velpeau radiograph can be used. This radiograph is taken with the patient’s arm in a sling and with the patient leaning back 30° while the x-ray beam is directed superior to inferior.
CT is performed for a suspected osseous injury. CT is more accurate than plain radiographs in showing glenoid and humeral fractures in the acute setting as well as the amount of bone loss in the case of chronic instability. Magnetic resonance arthrography is the imaging modality of choice for the diagnoses of capsulolabral injury.
After shoulder reduction, treatment with a sling, cryotherapy, and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug is initiated. In a Minnesota study of nonoperative management of shoulder instability, 9 of 10 hockey players were able to return to play the same season, and 6 of the 10 required surgery at the end of the season.59
Compared with noncontact athletes, hockey players and other collision athletes are at increased risk for recurrence.60-62 For collision athletes who want to continue playing their sport after recurrent instability, surgery is recommended. A shoulder instability study in Toronto found that more than 54% of 24 professional hockey players had associated Hill-Sachs lesions, but only 3 shoulders (12.5%) had glenoid defects.50 Arthroscopic and open techniques both demonstrate good results, and identification of bone loss can help determine which surgery to recommend.63 Hockey players can usually return to sport 6 months after shoulder stabilization.
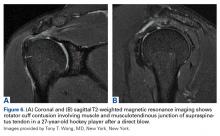
Another important consideration in managing shoulder instability in hockey players is shoulder dominance, which determines stick grip. A left-handed player places the right hand on top of the stick for support, but most of the motion associated with shooting the puck—including abduction and external rotation—occurs with the left shoulder. Thus, a left-handed player with a history of previous left-side shoulder dislocation may dislocate with each shot, but a right-handed player with left shoulder instability may have considerably less trouble on the ice.58Shoulder and rotator cuff contusions (RCCs) occur in hockey and other collision sports.49,64 RCCs almost always result from a direct blow to the shoulder, and present with shoulder function loss, weakness, and pain.
Summary
Hockey is a high-speed collision sport with one of the highest injury rates among all sports. Physicians caring for youth, amateur, and senior hockey teams see a range of acute head, neck, and shoulder injuries. Although treatment of eye injuries, dental injuries, and concussions is not always considered orthopedic care, an orthopedic surgeon who is covering hockey needs to be comfortable managing these injuries acutely. Quality rink-side care minimizes the impact of the injury, maximizes the functional result, and expedites the safe return of the injured player back to the ice.
Am J Orthop. 2017;46(3):123-134. Copyright Frontline Medical Communications Inc. 2017. All rights reserved.
1. Vaughan G. The Puck Starts Here: The Origin of Canada’s Great Winter Game, Ice Hockey. Fredericton, Canada: Goose Lane Editions; 1996.
2. IIHF member national associations. International Ice Hockey Federation website. http://www.iihf.com/iihf-home/the-iihf/members. Accessed April 6, 2017.
3. Flik K, Lyman S, Marx RG. American collegiate men’s ice hockey: an analysis of injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(2):183-187.
4. Engebretsen L, Steffen K, Alonso JM, et al. Sports injuries and illnesses during the Winter Olympic Games 2010. Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(11):772-780.
5. Deits J, Yard EE, Collins CL, Fields SK, Comstock RD. Patients with ice hockey injuries presenting to US emergency departments, 1990-2006. J Athl Train. 2010;45(5):467-474.
6. Brooks A, Loud KJ, Brenner JS, et al. Reducing injury risk from body checking in boys’ youth ice hockey. Pediatrics. 2014;133(6):1151-1157.
7. Agel J, Harvey EJ. A 7-year review of men’s and women’s ice hockey injuries in the NCAA. Can J Surg. 2010;53(5):319-323.
8. Micieli JA, Zurakowski D, Ahmed, II. Impact of visors on eye and orbital injuries in the National Hockey League. Can J Ophthalmol. 2014;49(3):243-248.
9. Pashby TJ. Ocular injuries in hockey. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1988;28(3):228-231.
10. Leivo T, Haavisto AK, Sahraravand A. Sports-related eye injuries: the current picture. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015;93(3):224-231.
11. Cohn RM, Alaia MJ, Strauss EJ, Feldman AF. Rink-side management of ice hockey related injuries to the face, neck, and chest. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2013;71(4):253-256.
12. Reehal P. Facial injury in sport. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010;9(1):27-34.
13. Stuart MJ, Smith AM, Malo-Ortiguera SA, Fischer TL, Larson DR. A comparison of facial protection and the incidence of head, neck, and facial injuries in Junior A hockey players. A function of individual playing time. Am J Sports Med. 2002;30(1):39-44.
14. MacEwen CJ, McLatchie GR. Eye injuries in sport. Scott Med J. 2010;55(2):22-24.
15. Stevens ST, Lassonde M, de Beaumont L, Keenan JP. The effect of visors on head and facial injury in National Hockey League players. J Sci Med Sport. 2006;9(3):238-242.
16. Moslener MD, Wadsworth LT. Ice hockey: a team physician’s perspective. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010;9(3):134-138.
17. LaPrade RF, Burnett QM, Zarzour R, Moss R. The effect of the mandatory use of face masks on facial lacerations and head and neck injuries in ice hockey. A prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(6):773-775.
18. Benson BW, Mohtadi NG, Rose MS, Meeuwisse WH. Head and neck injuries among ice hockey players wearing full face shields vs half face shields. JAMA. 1999;282(24):2328-2332.
19. Lahti H, Sane J, Ylipaavalniemi P. Dental injuries in ice hockey games and training. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002;34(3):400-402.
20. Sane J, Ylipaavalniemi P, Leppanen H. Maxillofacial and dental ice hockey injuries. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1988;20(2):202-207.
21. Emerich K, Kaczmarek J. First aid for dental trauma caused by sports activities: state of knowledge, treatment and prevention. Sports Med. 2010;40(5):361-366.
22. Rosenberg H, Rosenberg H, Hickey M. Emergency management of a traumatic tooth avulsion. Ann Emerg Med. 2011;57(4):375-377.
23. Young EJ, Macias CR, Stephens L. Common dental injury management in athletes. Sports Health. 2015;7(3):250-255.
24. Andersson L, Andreasen JO, Day P, et al. International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth. Dent Traumatol. 2012;28(2):88-96.
25. McCrory P, Meeuwisse W, Johnston K, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport 3rd International Conference on Concussion in Sport held in Zurich, November 2008. Clin J Sport Med. 2009;19(3):185-200.
26. Schneider KJ, Meeuwisse WH, Kang J, Schneider GM, Emery CA. Preseason reports of neck pain, dizziness, and headache as risk factors for concussion in male youth ice hockey players. Clin J Sport Med. 2013;23(4):267-272.
27. McCrory P, Meeuwisse WH, Aubry M, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport: the 4th International Conference on Concussion in Sport held in Zurich, November 2012. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):250-258.
28. Delaney JS, Lamfookon C, Bloom GA, Al-Kashmiri A, Correa JA. Why university athletes choose not to reveal their concussion symptoms during a practice or game. Clin J Sport Med. 2015;25(2):113-125.
29. Ventura RE, Balcer LJ, Galetta SL. The concussion toolbox: the role of vision in the assessment of concussion. Semin Neurol. 2015;35(5):599-606.
30. Vartiainen MV, Holm A, Peltonen K, Luoto TM, Iverson GL, Hokkanen L. King-Devick test normative reference values for professional male ice hockey players. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25(3):e327-e330.
31. Galetta MS, Galetta KM, McCrossin J, et al. Saccades and memory: baseline associations of the King-Devick and SCAT2 SAC tests in professional ice hockey players. J Neurol Sci. 2013;328(1-2):28-31.
32. Vernau BT, Grady MF, Goodman A, et al. Oculomotor and neurocognitive assessment of youth ice hockey players: baseline associations and observations after concussion. Dev Neuropsychol. 2015;40(1):7-11.
33. Fry AF, Hale S. Relationships among processing speed, working memory, and fluid intelligence in children. Biol Psychol. 2000;54(1-3):1-34.
34. Felleman DJ, Van Essen DC. Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 1991;1(1):1-47.
35. Guskiewicz KM, Register-Mihalik J, McCrory P, et al. Evidence-based approach to revising the SCAT2: introducing the SCAT3. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):289-293.
36. Smith AM, Stuart MJ, Dodick DW, et al. Ice Hockey Summit II: zero tolerance for head hits and fighting. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2015;14(2):135-144.
37. Mihalik JP, Beard JR, Petschauer MA, Prentice WE, Guskiewicz KM. Effect of ice hockey helmet fit on cervical spine motion during an emergency log roll procedure. Clin J Sport Med. 2008;18(5):394-398.
38. Banerjee R, Palumbo MA, Fadale PD. Catastrophic cervical spine injuries in the collision sport athlete, part 1: epidemiology, functional anatomy, and diagnosis. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(4):1077-1087.
39. Reynen PD, Clancy WG Jr. Cervical spine injury, hockey helmets, and face masks. Am J Sports Med. 1994;22(2):167-170.
40. Tator CH, Provvidenza C, Cassidy JD. Update and overview of spinal injuries in Canadian ice hockey, 1943 to 2011: the continuing need for injury prevention and education. Clin J Sport Med. 2016;26(3):232-238.
41. Tator CH, Edmonds VE, Lapczak L, Tator IB. Spinal injuries in ice hockey players, 1966-1987. Can J Surg. 1991;34(1):63-69.
42. Laprade RF, Schnetzler KA, Broxterman RJ, Wentorf F, Gilbert TJ. Cervical spine alignment in the immobilized ice hockey player. A computed tomographic analysis of the effects of helmet removal. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28(6):800-803.
43. Metz CM, Kuhn JE, Greenfield ML. Cervical spine alignment in immobilized hockey players: radiographic analysis with and without helmets and shoulder pads. Clin J Sport Med. 1998;8(2):92-95.
44. National Athletic Trainers’ Association. Appropriate prehospital management of the spine-injured athlete: updated from 1998 document. http://www.nata.org/sites/default/files/Executive-Summary-Spine-Injury-updated.pdf. Updated August 5, 2015. Accessed April 6, 2017.
45. Del Rossi G, Heffernan TP, Horodyski M, Rechtine GR. The effectiveness of extrication collars tested during the execution of spine-board transfer techniques. Spine J. 2004;4(6):619-623.
46. Morganti C, Sweeney CA, Albanese SA, Burak C, Hosea T, Connolly PJ. Return to play after cervical spine injury. Spine. 2001;26(10):1131-1136.
47. Huang P, Anissipour A, McGee W, Lemak L. Return-to-play recommendations after cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine injuries: a comprehensive review. Sports Health. 2016;8(1):19-25.
48. Shindle MK, Marx RG, Kelly BT, Bisson L, Burke CJ 3rd. Hockey injuries: a pediatric sport update. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010;22(1):54-60.
49. Molsa J, Kujala U, Myllynen P, Torstila I, Airaksinen O. Injuries to the upper extremity in ice hockey: analysis of a series of 760 injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31(5):751-757.
50. Dwyer T, Petrera M, Bleakney R, Theodoropoulos JS. Shoulder instability in ice hockey players: incidence, mechanism, and MRI findings. Clin Sports Med. 2013;32(4):803-813.
51. LaPrade RF, Wijdicks CA, Griffith CJ. Division I intercollegiate ice hockey team coverage. Br J Sports Med. 2009;43(13):1000-1005.
52. Willimon SC, Gaskill TR, Millett PJ. Acromioclavicular joint injuries: anatomy, diagnosis, and treatment. Phys Sportsmed. 2011;39(1):116-122.
53. Martetschlager F, Horan MP, Warth RJ, Millett PJ. Complications after anatomic fixation and reconstruction of the coracoclavicular ligaments. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(12):2896-2903.
54. Carofino BC, Mazzocca AD. The anatomic coracoclavicular ligament reconstruction: surgical technique and indications. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(2 suppl):37-46.
55. Laprade RF, Surowiec RK, Sochanska AN, et al. Epidemiology, identification, treatment and return to play of musculoskeletal-based ice hockey injuries. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(1):4-10.
56. Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(1):1-10.
57. Lee JT, Nasreddine AY, Black EM, Bae DS, Kocher MS. Posterior sternoclavicular joint injuries in skeletally immature patients. J Pediatr Orthop. 2014;34(4):369-375.
58. Hovelius L. Shoulder dislocation in Swedish ice hockey players. Am J Sports Med. 1978;6(6):373-377.
59. Buss DD, Lynch GP, Meyer CP, Huber SM, Freehill MQ. Nonoperative management for in-season athletes with anterior shoulder instability. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(6):1430-1433.
60. Mazzocca AD, Brown FM Jr, Carreira DS, Hayden J, Romeo AA. Arthroscopic anterior shoulder stabilization of collision and contact athletes. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(1):52-60.
61. Harris JD, Romeo AA. Arthroscopic management of the contact athlete with instability. Clin Sports Med. 2013;32(4):709-730.
62. Cho NS, Hwang JC, Rhee YG. Arthroscopic stabilization in anterior shoulder instability: collision athletes versus noncollision athletes. Arthroscopy. 2006;22(9):947-953.
63. Griffin JW, Brockmeier SF. Shoulder instability with concomitant bone loss in the athlete. Orthop Clin North Am. 2015;46(1):89-103.
64. Cohen SB, Towers JD, Bradley JP. Rotator cuff contusions of the shoulder in professional football players: epidemiology and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(3):442-447.
65. Lorentzon R, Wedrèn H, Pietilä T. Incidence, nature, and causes of ice hockey injuries. A three-year prospective study of a Swedish elite ice hockey team. Am J Sports Med. 1988;16(4):392-396.
66. Stuart MJ, Smith A. Injuries in Junior A ice hockey. A three-year prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(4):458-461.
67. Voaklander DC, Saunders LD, Quinney HA, Macnab RB. Epidemiology of recreational and old-timer ice hockey injuries. Clin J Sport Med. 1996;6(1):15-21.
68. Mölsä J, Airaksinen O, Näsman O, Torstila I. Ice hockey injuries in Finland. A prospective epidemiologic study. Am J Sports Med. 1997;25(4):495-499.
69. Ferrara MS, Schurr KT. Intercollegiate ice hockey injuries: a casual analysis. Clin J Sport Med. 1999;9(1):30-33.
70. Pinto M, Kuhn JE, Greenfield ML, Hawkins RJ. Prospective analysis of ice hockey injuries at the Junior A level over the course of one season. Clin J Sport Med. 1999;9(2):70-74.
71. Emery CA, Meeuwisse WH. Injury rates, risk factors, and mechanisms of injury in minor hockey. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(12):1960-1969.
72. Kuzuhara K, Shimamoto H, Mase Y. Ice hockey injuries in a Japanese elite team: a 3-year prospective study. J Athl Train. 2009;44(2):208-214.
73. Rishiraj N, Lloyd-Smith R, Lorenz T, Niven B, Michel M. University men’s ice hockey: rates and risk of injuries over 6-years. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2009;49(2):159-166.
74. Tuominen M, Stuart MJ, Aubry M, Kannus P, Parkkari J. Injuries in men’s international ice hockey: a 7-year study of the International Ice Hockey Federation Adult World Championship Tournaments and Olympic Winter Games. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(1):30-36.
75. Heckman JD, Bucholz RW. In: Rockwood CA, Green DP, Heckman JD, Bucholz RW, eds. Rockwood and Green’s Fractures in Adults, Volume 1. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001.
Take-Home Points
- Hockey is a high-speed collision sport with one of the highest injury rates among all sports.
- Use of a helmet with visors or full-face shields significantly reduces the risk for eye injury.
- Broken portions of teeth should be found and placed in a protective medium such as saline, saliva, or milk for transport.
- A player with unresolved concussion symptoms should not be allowed to return to the ice.
- Shoulder dominance, which determines stick grip, is an important consideration in the treatment of shoulder instability in an ice hockey player.
On a surface of ice in Windsor, Nova Scotia in the middle of the 19th century, the modern game of ice hockey evolved.1 A blend of hurley, a Gaelic sport, and lacrosse, from the native Mi’kmaq culture, the sport of ice hockey gained rapidly in popularity throughout Canada and is now the country’s national sport. Hockey quickly spread to the United States and then Europe. It is presently played in 77 countries across the world.2
Hockey players can reach speeds of up to 48 km (~30 miles) per hour on razor-sharp skates on an ice surface surrounded by rigid plastic composite boards topped with plexiglass.3 They use sticks made of wood, aluminum, or a composite material to advance a 6-ounce vulcanized rubber puck on the opposing goal, and this puck sometimes reaches speeds over 160 km (~100 miles) per hour. Older, male players are allowed to make physical contact with their opposing counterparts to separate them from the puck (body-checking). Not surprisingly, the potential risk for injury in hockey is high. At the 2010 Winter Olympics, men’s ice hockey players had the highest rate of injury of any other competitors there—more than 30% were affected.4
Hockey is played and enjoyed by athletes ranging widely in age. Youth hockey leagues accept players as young as 5 years. Hockey can become a lifelong recreational activity. In North America, old timers’ leagues have many players up to age 70 years.6 According to International Ice Hockey Federation data for 2016, more than 543,000 and 639,500 people play hockey in the United States and Canada, respectively.2 Most of the rules, protective equipment, skates, ice surfaces, and goal sizes are the same in men’s and women’s hockey.7 The major difference is in body-checking—this practice is not allowed at any age in women’s ice hockey.
In this article, we review the evaluation and management of common head, neck, and shoulder hockey injuries for physicians who provide medical support and coverage for youth, amateur, and senior hockey teams.
Evaluation and Management of Common Hockey Injuries
Eye Injuries
Although eye injuries are less common than musculoskeletal injuries and concussions in hockey, they are a serious risk for recreational and competitive players alike. Furthermore, recovery may be difficult, and eye injuries can have serious lifelong consequences.8 In hockey, the most commonly reported eye injuries are periorbital contusions and lacerations, hyphema, corneal and conjunctival abrasions, orbital fractures, and ruptured globes (Table 2).9,10
As a contact sport, hockey often involves high-impact, blunt-force trauma. The trauma in hockey results from collisions with other players, the boards, hockey sticks, and pucks. It is therefore not surprising that the most common ocular injuries in this sport are periorbital contusions. Although most contusions cause only mild swelling and ecchymosis of the soft tissues around the eye, there is potential for serious consequences. In a Scandinavia study, Leivo and colleagues10 found that 9% of patients who sustained a periocular contusion also had a clinically significant secondary diagnosis, such as retinal tear or hemorrhage, eyelid laceration, vitreous hemorrhage, or retinal detachment. Although the study was hospital-based, and therefore biased toward more severe cases, its findings highlight the potential severity of eye injuries in hockey. Furthermore, the study found that the majority of players who sustained blunt trauma to the eye itself required lifelong follow-up because of increased risk for glaucoma. This is particularly true for hyphema, as this finding indicates significant damage to intraocular tissues.10Players can also sustain fractures of the orbital bones, including orbital blowout fractures. Typical signs and symptoms of blowout fractures include diplopia, proptosis or enophthalmos, infraorbital hypoesthesia, painful and decreased extraocular movement (particularly upgaze), and palpable crepitance caused by sinus air entering the lower eyelid.11 If orbital fracture is suspected, as it should be in any case in which the injured player experiences pain with eye movement or diplopia, the player should be referred to the ED for computed tomography (CT) and ophthalmologic evaluation.12 Continued participation seriously risks making the injury much worse, particularly should another impact occur. In addition, given the impact needed to cause orbital fractures, consideration must be given to the potential for a coexisting concussion injury.
Severe direct trauma to the eye—from a puck, a stick, or a fist—can result in a ruptured globe, a particularly serious injury that requires immediate surgical attention. Signs and symptoms of a ruptured globe are rarely subtle, but associated eyelid swelling or laceration may obscure the injury, delaying proper diagnosis and treatment. More obvious signs include severely reduced vision, hemorrhagic chemosis (swelling) of the conjunctiva, and an irregular or peaked pupil. If a rupture or any significant intraocular injury is suspected, it is crucial to avoid applying any pressure to the globe, as this can significantly worsen the damage to the intraocular tissues. Use of a helmet with protective shields and cages attached markedly reduces the risk for such injuries.13All eye injuries require prompt assessment, which allows for appropriate management and prevention of secondary damage.14 Initial evaluation of a patient with ocular trauma should begin with external examination for lacerations, swelling, or orbital rim step-off deformity. The physician should also check visual acuity in order to assess for significant vision impairment (counting fingers or reading a sign in the arena; confrontation visual fields). This should be done before attending to any periocular injuries, with the uninjured side serving as a control. Next, the physician should assess the extraocular eye movements as well as the size, shape, and reactivity of the pupils. Particular attention should be paid to detecting any deficit in extraocular movement or irregularity in pupil size, shape, or reactivity, as such findings are highly suggestive of serious injury to the globe.13 Hyphema (blood in anterior chamber of eye anterior to pupil) should be suspected if vision is reduced and the pupil cannot be clearly visualized. However, a bright red clot is not always apparent at time of injury or if the amount of blood is small. An irregular pupil, or a pupil that does not constrict well to light, is also a red flag for serious contusion injury to the eye, and requires ophthalmologic evaluation. It is important to keep in mind that blunt trauma severe enough to produce hyphema or an irregular and poorly reactive pupil is often associated with retinal damage as well, including retinal edema or detachment.
Minor injuries (eg, small foreign bodies, minor periocular contusions and lacerations) can often be managed rink-side. Foreign bodies not embedded in the cornea, but lodged under the upper eyelid, can sometimes be removed by everting the eyelid and sweeping with a moistened cotton swab or using diffuse, sterile saline irrigation.11 Corneal abrasions generally cause severe pain, photophobia, and tearing and are easily diagnosed with use of topical fluorescein and a blue light. A topical anesthetic can be extremely helpful in this setting, as it allows for proper pain-free evaluation, but should never be used in an ongoing manner for pain relief. Small lacerations of the brow can be sutured with 5-0 or 6-0 nylon or closed with 2-Octyl cyanoacrylate tissue adhesive (Dermabond). Eyelid lacerations, unless very small, are best managed by an ophthalmologist; care must be taken to rule out injury to the deeper orbital tissues and eye. If serious injury is suspected, or the eye cannot be appropriately evaluated, it should be stabilized and protected with a protective shield or plastic cup, and the player should be transferred to an ED for appropriate ophthalmologic evaluation.13Most eye injuries are accidental, caused by sticks or deflected pucks, but 18% are acquired in fights.8 Use of visors or full-face cages effectively minimizes the rate of eye injuries.8,13,15,16 In a cohort study of 282 elite amateur ice hockey players, the risk of eye injury was 4.7 times higher in players without face protection than in players who used half-face shields; there were no eye injuries in players who used full-face protection.13 For visors to prevent eye injury, they must be positioned to cover the eyes and the lower edge of the nose in all projections.10
Dental Injuries
The incidence and type of facial and dental injuries depend directly on the type of face protection used.11,17,18 In a study of face, head, and neck injuries in elite amateur ice hockey players, Stuart and colleagues13 found game-related injury rates of 158.9 per 1000 player-hours in players without face protection, 73.5 in players who used half-face shields, and 23.2 in players who used full-face shields. Players who wore full-face shields had facial, head, and neck injury rates of only 23.2 per 1000 player-game hours.13 Other studies clearly support the important role face shields play in lowering injury risk in hockey. Face and head injuries account for 20% to 40% of all hockey-related injuries,3,16,19 and dental injuries up to 11.5%.20 In a study from Finland, Lahti and colleagues19 found that over a 2-year period, 479 hockey players sustained injuries, including 650 separate dental injuries. The most commonly diagnosed dental injury was an uncomplicated crown fracture, and the most common cause was a hit with a hockey stick, which accounted for 52.7% and 40.3% of dental injuries in games and practices, respectively.19
In the management of dental fractures, the broken portions of teeth should be found and placed in a transportation-protective medium, such as saline, saliva, or milk,16 which can improve functional and esthetic replacement outcomes.21,22 Loose pieces of teeth should not be left in the player’s mouth. The residual tooth should be stabilized and exposure to air and occlusion limited. Dental fractures can affect the enamel, the enamel and dentin structures (uncomplicated fracture), or enamel, dentin, and pulp (complicated).23 Fractures involving only the enamel do not require urgent dental evaluation. Dentin or pulp involvement may cause temperature and air sensitivity.23 If a tooth is air-sensitive, the player should be referred to a specialist immediately.11
Direct trauma can cause instability without displacement (subluxation) or complete displacement of the tooth from its alveolar socket (avulsion).23 An avulsed tooth should be handled by the crown to avoid further damage to the root and periodontal ligament.16,24 The tooth should be rinsed gently with saline and reimplanted in its socket, ideally within 5 to 10 minutes,23with the athlete biting down gently on gauze to hold the tooth in place. A 1-mL supraperiosteal infiltration of 1% or 2% lidocaine hydrochloride (1:100,000 epinephrine) can be given into the apex of the tooth being anesthetized (Figure 1).
Concussions
A concussion is a “complex pathophysiological process affecting the brain, induced by traumatic biomechanical forces.”25 Concussion is largely a functional disturbance instead of a structural injury, owing to the rotational and/or shearing forces involved. Many studies have identified concussion as the most common type of injury in all of youth hockey.26 Concussions account for up to 19% of all injuries in men’s collegiate hockey.3
Concussion can be challenging to diagnose on the ice. The most important factor in concussion management is symptom reporting by the athlete.27 Despite significant efforts in education and awareness, student athletes, especially hockey players, withhold reporting a possible concussion.28 Reasons for underreporting include fear of letting down other players and coaches, thinking the injury is not severe enough to warrant evaluation, and fear of losing standing with the current team or future teams.28
As postinjury concussion assessments are ideal when comparisons can be made with preseason (baseline) scores, preseason testing is becoming standard in professional, college, junior, and high school hockey. This testing involves the Sport Concussion Assessment Tool, 3rd edition (SCAT3), and the King-Devick (K-D) test.30,31 Some youth leagues have baseline testing as well, though the frequency of baseline testing in their players is controversial,32 as the adolescent mind’s processing speed and memory increase exponentially.33 For these younger athletes, it may be necessary to perform baseline testing more frequently than annually.32 A physician can use baseline test results to help diagnose a concussion at the rink and then track the athlete’s recovery and help with return-to-play decisions.29 Vision involves almost half of the brain’s circuits,34 including areas vulnerable to head impact. A neuro-ophthalmologic test can assess for irregularities in accommodation, convergence, ocular muscle balance, pursuit, and saccades.29 The K-D test is a visual performance examination that allows easy and objective assessment of eye movements. Use of both the K-D test and the SCAT3 at the rink may increase the number of concussions detected.29,35 We recommend that physicians use both tests to assess for concussion at the hockey rink.
Initial treatment involves a period of physical rest and relative cognitive rest. Acute worsening of symptoms warrants urgent imaging to rule out a subdural or subarachnoid bleed. Once a player is symptom-free, a graded return-to-play protocol should be followed (Table 4).
On the prevention side, great efforts have been made to improve hockey helmets. (Some manufacturers claim to have made concussion-proof helmets, but there is no evidence supporting this claim.6) Numerous investigators have reported a lower overall injury rate in players who wear a helmet and a full-face shield.6,13 In addition, rule changes aimed at decreasing head contact have been implemented to decrease the incidence of sport-related concussions.36 Moreover, education on proper helmet use and wear should be emphasized. A study of the effects of hockey helmet fit on cervical motion found that 7 (39%) of 18 players wore a game or competition helmet so loosely that it could be removed without unbuttoning its chinstrap.37 Improperly worn helmets cannot prevent injury as well as properly worn helmets can.
Cervical Spine Injuries
Whereas American football is associated with a higher annual number of nonfatal catastrophic neck injuries, hockey has a 3 to 6 times higher incidence of cervical spine injuries and spinal cord damage.38,39 A Canadian Ice Hockey Spinal Injuries Registry review of the period 2006 to 2011 identified 44 cervical spine injuries, 7.3 per year on average.40 Severe injury, defined as complete motor and sensory loss, complete motor loss and incomplete sensory, or complete motor loss, occurred in 4 (9.1%) of the 44 injured players. In hockey, a major mechanism of cervical spine injury is an axial load to the slightly flexed spine.39 Of 355 hockey-related cervical spine injuries in a Canada study, 95 (35.5%) were caused by a check from behind.40,41 The Canadian neurosurgeons’ work led to rule changes prohibiting checks from behind, and this prohibition has reduced the incidence of cervical spine injuries in ice hockey.38,40
Team physicians should be comfortable managing serious neck and spine injuries on the ice. Initial evaluation should follow the standard ABCs (airway, breathing, circulation). The physician places a hand on each side of the head to stabilize the neck until the initial examination is complete. The goal is to minimize cervical spine motion until transportation to the hospital for advanced imaging and definitive treatment.37 The decision to remove or leave on the helmet is now controversial. Hockey helmets differ from football helmets in that their chinstraps do not afford significant cervical stabilization, and the helmets have less padding and cover less of the head; in addition, a shockingly high percentage of hockey players do not wear properly fitting helmets.37 In one study, 3-dimensional motion analysis of a hockey player during the logroll technique showed less transverse and sagittal cervical plane motion with the helmet removed than with the helmet (properly fitting or not) in place; the authors recommended removing the helmet to limit extraneous cervical spine motion during the technique.37 However, 2 other studies found that helmet removal can result in significantly increased cervical spine motion of the immobilized hockey player.42,43Recommendation 4 of the recently released interassociation consensus statement of the National Athletic Trainers’ Association reads, “Protective athletic equipment should be removed before transport to an emergency facility for an athlete-patient with suspected cervical spine instability.”44 This represents a shift from leaving the helmet and shoulder pads in place. For ice hockey players with suspected cervical spine injury, more research is needed on cervical motion during the entire sequence—partial logrolls, spine-boarding, placement of cervical collar before or after logroll, and different immobilization techniques for transport.37
The athlete must be carefully transferred to a spine board with either logroll or lift-and-slide. Although an extrication cervical collar can be placed before the spine board is placed, the effectiveness of this collar in executing the spine-board transfer is not proven.45 When the player is on the spine board, the head can be secured with pads and straps en route to the hospital.
Return-to-Play Criteria for Cervical Spine Injuries There is no clear consensus on return-to-play guidelines for cervical spine injuries in athletes.46
Shoulder Injuries
For hockey players, the upper extremity traditionally has been considered a well-protected area.48 However, shoulder pads are considerably more flexible in hockey than in football and other collision sports. In addition, hockey gloves allow a fair amount of motion for stick handling, and the wrist may be in maximal flexion or extension when a hit against the boards or the ice occurs. Open-ice checking, board collisions, and hockey stick use have been postulated as reasons for the high incidence of upper extremity injuries in hockey. Researchers in Finland found that upper extremity injuries accounted for up to 31% of all hockey injuries.49 More than 50% of these injuries resulted from checking or board collisions. Furthermore, study findings highlighted a low rate of injury in younger players and indicated the rate increases with age.49,50
In hockey players, the acromioclavicular (AC) joint is the most commonly injured shoulder structure.51 The mechanism of injury can be a board collision or an open-ice hit, but most often is a direct blow to the shoulder. The collision disrupts the AC joint and can sprain or tear the coracoclavicular ligaments. The Rockwood classification is used to categorize AC joint injuries (Figure 2).
Initial management involves icing the AC joint and placing a sling for comfort. Type I and type II injuries can be managed with progressive range-of-motion (ROM) exercises, strengthening, cryotherapy, and a period of rest. Treatment of type III injuries remains controversial,52 but in hockey players these injuries are almost always treated nonoperatively. Return to play requires full motion, normal strength, and minimal discomfort. Players return a few days to 2 weeks after a grade I injury; recovery from grade II injuries may take 2 to 3 weeks, and recovery from grade III injuries, 6 to 12 weeks. Surgical treatment is usually required in type IV and type V injuries, but we have had experience treating these injuries nonoperatively in high-level players. AC joint reinjury in hockey players is common, and surgical treatment should be approached cautiously, as delayed fracture after return to sport has been reported.53 Special precautions should be taken in collision athletes who undergo AC joint reconstruction. In the anatomical reconstruction described by Carofino and Mazzocca,54 2 holes are drilled in the clavicle; these holes are a potential source of fracture when the collision athlete returns to sport (Figure 3).
Clavicle fracture is another common hockey injury.55 Studies have shown clavicle fractures proportionally occur most often in people 15 to 19 years old.49 The injury presents with pain and deformity over the clavicle; in more severe fractures, skin tenting is identified. Initial management of suspected clavicle fracture includes cryotherapy, sling, and radiographs. Radiographs should include an AP view and then a 45° cephalad view, which eliminates overshadowing from the ribs. Most clavicle fractures are successfully managed nonoperatively, though there is evidence that significantly displaced or comminuted fractures have better union rates and shoulder function when treated with open reduction and internal fixation.56 After a clavicle fracture, return to skating and noncontact practice usually takes 8 weeks, with return to full contact occurring around 12 weeks.
Sternoclavicular injuries are relatively uncommon, but potentially serious. Special attention should also be given to adolescent athletes with sternoclavicular pain. Although sternoclavicular dislocations have been reported in hockey players, instead these likely are fractures involving the medial clavicle physis.57
The shoulder is the most commonly dislocated major joint, and the incidence of shoulder dislocation in elite hockey players is 8% to 21%.50,58 Anterior shoulder instability occurs from a fall with the shoulder in an abducted, externally rotated and extended position or from a direct anteriorly placed impact to the posterior shoulder. We recommend taking players off the ice for evaluation. Depending on physician comfort, the shoulder can be reduced in the training room, and the athlete sent for radiographs after reduction. If resources or support for closed reduction is not available at the rink, the athlete should be sent to the ED. Initial radiographic evaluation of a player with shoulder injury begins with plain radiographs, including a true AP (Grashey) view with the humerus in neutral, internal, and external rotation and an axillary view. The axillary radiograph is crucial in determining anterior or posterior dislocation. If the patient cannot tolerate the pain associated with having an axillary radiograph taken, a Velpeau radiograph can be used. This radiograph is taken with the patient’s arm in a sling and with the patient leaning back 30° while the x-ray beam is directed superior to inferior.
CT is performed for a suspected osseous injury. CT is more accurate than plain radiographs in showing glenoid and humeral fractures in the acute setting as well as the amount of bone loss in the case of chronic instability. Magnetic resonance arthrography is the imaging modality of choice for the diagnoses of capsulolabral injury.
After shoulder reduction, treatment with a sling, cryotherapy, and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug is initiated. In a Minnesota study of nonoperative management of shoulder instability, 9 of 10 hockey players were able to return to play the same season, and 6 of the 10 required surgery at the end of the season.59
Compared with noncontact athletes, hockey players and other collision athletes are at increased risk for recurrence.60-62 For collision athletes who want to continue playing their sport after recurrent instability, surgery is recommended. A shoulder instability study in Toronto found that more than 54% of 24 professional hockey players had associated Hill-Sachs lesions, but only 3 shoulders (12.5%) had glenoid defects.50 Arthroscopic and open techniques both demonstrate good results, and identification of bone loss can help determine which surgery to recommend.63 Hockey players can usually return to sport 6 months after shoulder stabilization.
Another important consideration in managing shoulder instability in hockey players is shoulder dominance, which determines stick grip. A left-handed player places the right hand on top of the stick for support, but most of the motion associated with shooting the puck—including abduction and external rotation—occurs with the left shoulder. Thus, a left-handed player with a history of previous left-side shoulder dislocation may dislocate with each shot, but a right-handed player with left shoulder instability may have considerably less trouble on the ice.58Shoulder and rotator cuff contusions (RCCs) occur in hockey and other collision sports.49,64 RCCs almost always result from a direct blow to the shoulder, and present with shoulder function loss, weakness, and pain.
Summary
Hockey is a high-speed collision sport with one of the highest injury rates among all sports. Physicians caring for youth, amateur, and senior hockey teams see a range of acute head, neck, and shoulder injuries. Although treatment of eye injuries, dental injuries, and concussions is not always considered orthopedic care, an orthopedic surgeon who is covering hockey needs to be comfortable managing these injuries acutely. Quality rink-side care minimizes the impact of the injury, maximizes the functional result, and expedites the safe return of the injured player back to the ice.
Am J Orthop. 2017;46(3):123-134. Copyright Frontline Medical Communications Inc. 2017. All rights reserved.
Take-Home Points
- Hockey is a high-speed collision sport with one of the highest injury rates among all sports.
- Use of a helmet with visors or full-face shields significantly reduces the risk for eye injury.
- Broken portions of teeth should be found and placed in a protective medium such as saline, saliva, or milk for transport.
- A player with unresolved concussion symptoms should not be allowed to return to the ice.
- Shoulder dominance, which determines stick grip, is an important consideration in the treatment of shoulder instability in an ice hockey player.
On a surface of ice in Windsor, Nova Scotia in the middle of the 19th century, the modern game of ice hockey evolved.1 A blend of hurley, a Gaelic sport, and lacrosse, from the native Mi’kmaq culture, the sport of ice hockey gained rapidly in popularity throughout Canada and is now the country’s national sport. Hockey quickly spread to the United States and then Europe. It is presently played in 77 countries across the world.2
Hockey players can reach speeds of up to 48 km (~30 miles) per hour on razor-sharp skates on an ice surface surrounded by rigid plastic composite boards topped with plexiglass.3 They use sticks made of wood, aluminum, or a composite material to advance a 6-ounce vulcanized rubber puck on the opposing goal, and this puck sometimes reaches speeds over 160 km (~100 miles) per hour. Older, male players are allowed to make physical contact with their opposing counterparts to separate them from the puck (body-checking). Not surprisingly, the potential risk for injury in hockey is high. At the 2010 Winter Olympics, men’s ice hockey players had the highest rate of injury of any other competitors there—more than 30% were affected.4
Hockey is played and enjoyed by athletes ranging widely in age. Youth hockey leagues accept players as young as 5 years. Hockey can become a lifelong recreational activity. In North America, old timers’ leagues have many players up to age 70 years.6 According to International Ice Hockey Federation data for 2016, more than 543,000 and 639,500 people play hockey in the United States and Canada, respectively.2 Most of the rules, protective equipment, skates, ice surfaces, and goal sizes are the same in men’s and women’s hockey.7 The major difference is in body-checking—this practice is not allowed at any age in women’s ice hockey.
In this article, we review the evaluation and management of common head, neck, and shoulder hockey injuries for physicians who provide medical support and coverage for youth, amateur, and senior hockey teams.
Evaluation and Management of Common Hockey Injuries
Eye Injuries
Although eye injuries are less common than musculoskeletal injuries and concussions in hockey, they are a serious risk for recreational and competitive players alike. Furthermore, recovery may be difficult, and eye injuries can have serious lifelong consequences.8 In hockey, the most commonly reported eye injuries are periorbital contusions and lacerations, hyphema, corneal and conjunctival abrasions, orbital fractures, and ruptured globes (Table 2).9,10
As a contact sport, hockey often involves high-impact, blunt-force trauma. The trauma in hockey results from collisions with other players, the boards, hockey sticks, and pucks. It is therefore not surprising that the most common ocular injuries in this sport are periorbital contusions. Although most contusions cause only mild swelling and ecchymosis of the soft tissues around the eye, there is potential for serious consequences. In a Scandinavia study, Leivo and colleagues10 found that 9% of patients who sustained a periocular contusion also had a clinically significant secondary diagnosis, such as retinal tear or hemorrhage, eyelid laceration, vitreous hemorrhage, or retinal detachment. Although the study was hospital-based, and therefore biased toward more severe cases, its findings highlight the potential severity of eye injuries in hockey. Furthermore, the study found that the majority of players who sustained blunt trauma to the eye itself required lifelong follow-up because of increased risk for glaucoma. This is particularly true for hyphema, as this finding indicates significant damage to intraocular tissues.10Players can also sustain fractures of the orbital bones, including orbital blowout fractures. Typical signs and symptoms of blowout fractures include diplopia, proptosis or enophthalmos, infraorbital hypoesthesia, painful and decreased extraocular movement (particularly upgaze), and palpable crepitance caused by sinus air entering the lower eyelid.11 If orbital fracture is suspected, as it should be in any case in which the injured player experiences pain with eye movement or diplopia, the player should be referred to the ED for computed tomography (CT) and ophthalmologic evaluation.12 Continued participation seriously risks making the injury much worse, particularly should another impact occur. In addition, given the impact needed to cause orbital fractures, consideration must be given to the potential for a coexisting concussion injury.
Severe direct trauma to the eye—from a puck, a stick, or a fist—can result in a ruptured globe, a particularly serious injury that requires immediate surgical attention. Signs and symptoms of a ruptured globe are rarely subtle, but associated eyelid swelling or laceration may obscure the injury, delaying proper diagnosis and treatment. More obvious signs include severely reduced vision, hemorrhagic chemosis (swelling) of the conjunctiva, and an irregular or peaked pupil. If a rupture or any significant intraocular injury is suspected, it is crucial to avoid applying any pressure to the globe, as this can significantly worsen the damage to the intraocular tissues. Use of a helmet with protective shields and cages attached markedly reduces the risk for such injuries.13All eye injuries require prompt assessment, which allows for appropriate management and prevention of secondary damage.14 Initial evaluation of a patient with ocular trauma should begin with external examination for lacerations, swelling, or orbital rim step-off deformity. The physician should also check visual acuity in order to assess for significant vision impairment (counting fingers or reading a sign in the arena; confrontation visual fields). This should be done before attending to any periocular injuries, with the uninjured side serving as a control. Next, the physician should assess the extraocular eye movements as well as the size, shape, and reactivity of the pupils. Particular attention should be paid to detecting any deficit in extraocular movement or irregularity in pupil size, shape, or reactivity, as such findings are highly suggestive of serious injury to the globe.13 Hyphema (blood in anterior chamber of eye anterior to pupil) should be suspected if vision is reduced and the pupil cannot be clearly visualized. However, a bright red clot is not always apparent at time of injury or if the amount of blood is small. An irregular pupil, or a pupil that does not constrict well to light, is also a red flag for serious contusion injury to the eye, and requires ophthalmologic evaluation. It is important to keep in mind that blunt trauma severe enough to produce hyphema or an irregular and poorly reactive pupil is often associated with retinal damage as well, including retinal edema or detachment.
Minor injuries (eg, small foreign bodies, minor periocular contusions and lacerations) can often be managed rink-side. Foreign bodies not embedded in the cornea, but lodged under the upper eyelid, can sometimes be removed by everting the eyelid and sweeping with a moistened cotton swab or using diffuse, sterile saline irrigation.11 Corneal abrasions generally cause severe pain, photophobia, and tearing and are easily diagnosed with use of topical fluorescein and a blue light. A topical anesthetic can be extremely helpful in this setting, as it allows for proper pain-free evaluation, but should never be used in an ongoing manner for pain relief. Small lacerations of the brow can be sutured with 5-0 or 6-0 nylon or closed with 2-Octyl cyanoacrylate tissue adhesive (Dermabond). Eyelid lacerations, unless very small, are best managed by an ophthalmologist; care must be taken to rule out injury to the deeper orbital tissues and eye. If serious injury is suspected, or the eye cannot be appropriately evaluated, it should be stabilized and protected with a protective shield or plastic cup, and the player should be transferred to an ED for appropriate ophthalmologic evaluation.13Most eye injuries are accidental, caused by sticks or deflected pucks, but 18% are acquired in fights.8 Use of visors or full-face cages effectively minimizes the rate of eye injuries.8,13,15,16 In a cohort study of 282 elite amateur ice hockey players, the risk of eye injury was 4.7 times higher in players without face protection than in players who used half-face shields; there were no eye injuries in players who used full-face protection.13 For visors to prevent eye injury, they must be positioned to cover the eyes and the lower edge of the nose in all projections.10
Dental Injuries
The incidence and type of facial and dental injuries depend directly on the type of face protection used.11,17,18 In a study of face, head, and neck injuries in elite amateur ice hockey players, Stuart and colleagues13 found game-related injury rates of 158.9 per 1000 player-hours in players without face protection, 73.5 in players who used half-face shields, and 23.2 in players who used full-face shields. Players who wore full-face shields had facial, head, and neck injury rates of only 23.2 per 1000 player-game hours.13 Other studies clearly support the important role face shields play in lowering injury risk in hockey. Face and head injuries account for 20% to 40% of all hockey-related injuries,3,16,19 and dental injuries up to 11.5%.20 In a study from Finland, Lahti and colleagues19 found that over a 2-year period, 479 hockey players sustained injuries, including 650 separate dental injuries. The most commonly diagnosed dental injury was an uncomplicated crown fracture, and the most common cause was a hit with a hockey stick, which accounted for 52.7% and 40.3% of dental injuries in games and practices, respectively.19
In the management of dental fractures, the broken portions of teeth should be found and placed in a transportation-protective medium, such as saline, saliva, or milk,16 which can improve functional and esthetic replacement outcomes.21,22 Loose pieces of teeth should not be left in the player’s mouth. The residual tooth should be stabilized and exposure to air and occlusion limited. Dental fractures can affect the enamel, the enamel and dentin structures (uncomplicated fracture), or enamel, dentin, and pulp (complicated).23 Fractures involving only the enamel do not require urgent dental evaluation. Dentin or pulp involvement may cause temperature and air sensitivity.23 If a tooth is air-sensitive, the player should be referred to a specialist immediately.11
Direct trauma can cause instability without displacement (subluxation) or complete displacement of the tooth from its alveolar socket (avulsion).23 An avulsed tooth should be handled by the crown to avoid further damage to the root and periodontal ligament.16,24 The tooth should be rinsed gently with saline and reimplanted in its socket, ideally within 5 to 10 minutes,23with the athlete biting down gently on gauze to hold the tooth in place. A 1-mL supraperiosteal infiltration of 1% or 2% lidocaine hydrochloride (1:100,000 epinephrine) can be given into the apex of the tooth being anesthetized (Figure 1).
Concussions
A concussion is a “complex pathophysiological process affecting the brain, induced by traumatic biomechanical forces.”25 Concussion is largely a functional disturbance instead of a structural injury, owing to the rotational and/or shearing forces involved. Many studies have identified concussion as the most common type of injury in all of youth hockey.26 Concussions account for up to 19% of all injuries in men’s collegiate hockey.3
Concussion can be challenging to diagnose on the ice. The most important factor in concussion management is symptom reporting by the athlete.27 Despite significant efforts in education and awareness, student athletes, especially hockey players, withhold reporting a possible concussion.28 Reasons for underreporting include fear of letting down other players and coaches, thinking the injury is not severe enough to warrant evaluation, and fear of losing standing with the current team or future teams.28
As postinjury concussion assessments are ideal when comparisons can be made with preseason (baseline) scores, preseason testing is becoming standard in professional, college, junior, and high school hockey. This testing involves the Sport Concussion Assessment Tool, 3rd edition (SCAT3), and the King-Devick (K-D) test.30,31 Some youth leagues have baseline testing as well, though the frequency of baseline testing in their players is controversial,32 as the adolescent mind’s processing speed and memory increase exponentially.33 For these younger athletes, it may be necessary to perform baseline testing more frequently than annually.32 A physician can use baseline test results to help diagnose a concussion at the rink and then track the athlete’s recovery and help with return-to-play decisions.29 Vision involves almost half of the brain’s circuits,34 including areas vulnerable to head impact. A neuro-ophthalmologic test can assess for irregularities in accommodation, convergence, ocular muscle balance, pursuit, and saccades.29 The K-D test is a visual performance examination that allows easy and objective assessment of eye movements. Use of both the K-D test and the SCAT3 at the rink may increase the number of concussions detected.29,35 We recommend that physicians use both tests to assess for concussion at the hockey rink.
Initial treatment involves a period of physical rest and relative cognitive rest. Acute worsening of symptoms warrants urgent imaging to rule out a subdural or subarachnoid bleed. Once a player is symptom-free, a graded return-to-play protocol should be followed (Table 4).
On the prevention side, great efforts have been made to improve hockey helmets. (Some manufacturers claim to have made concussion-proof helmets, but there is no evidence supporting this claim.6) Numerous investigators have reported a lower overall injury rate in players who wear a helmet and a full-face shield.6,13 In addition, rule changes aimed at decreasing head contact have been implemented to decrease the incidence of sport-related concussions.36 Moreover, education on proper helmet use and wear should be emphasized. A study of the effects of hockey helmet fit on cervical motion found that 7 (39%) of 18 players wore a game or competition helmet so loosely that it could be removed without unbuttoning its chinstrap.37 Improperly worn helmets cannot prevent injury as well as properly worn helmets can.
Cervical Spine Injuries
Whereas American football is associated with a higher annual number of nonfatal catastrophic neck injuries, hockey has a 3 to 6 times higher incidence of cervical spine injuries and spinal cord damage.38,39 A Canadian Ice Hockey Spinal Injuries Registry review of the period 2006 to 2011 identified 44 cervical spine injuries, 7.3 per year on average.40 Severe injury, defined as complete motor and sensory loss, complete motor loss and incomplete sensory, or complete motor loss, occurred in 4 (9.1%) of the 44 injured players. In hockey, a major mechanism of cervical spine injury is an axial load to the slightly flexed spine.39 Of 355 hockey-related cervical spine injuries in a Canada study, 95 (35.5%) were caused by a check from behind.40,41 The Canadian neurosurgeons’ work led to rule changes prohibiting checks from behind, and this prohibition has reduced the incidence of cervical spine injuries in ice hockey.38,40
Team physicians should be comfortable managing serious neck and spine injuries on the ice. Initial evaluation should follow the standard ABCs (airway, breathing, circulation). The physician places a hand on each side of the head to stabilize the neck until the initial examination is complete. The goal is to minimize cervical spine motion until transportation to the hospital for advanced imaging and definitive treatment.37 The decision to remove or leave on the helmet is now controversial. Hockey helmets differ from football helmets in that their chinstraps do not afford significant cervical stabilization, and the helmets have less padding and cover less of the head; in addition, a shockingly high percentage of hockey players do not wear properly fitting helmets.37 In one study, 3-dimensional motion analysis of a hockey player during the logroll technique showed less transverse and sagittal cervical plane motion with the helmet removed than with the helmet (properly fitting or not) in place; the authors recommended removing the helmet to limit extraneous cervical spine motion during the technique.37 However, 2 other studies found that helmet removal can result in significantly increased cervical spine motion of the immobilized hockey player.42,43Recommendation 4 of the recently released interassociation consensus statement of the National Athletic Trainers’ Association reads, “Protective athletic equipment should be removed before transport to an emergency facility for an athlete-patient with suspected cervical spine instability.”44 This represents a shift from leaving the helmet and shoulder pads in place. For ice hockey players with suspected cervical spine injury, more research is needed on cervical motion during the entire sequence—partial logrolls, spine-boarding, placement of cervical collar before or after logroll, and different immobilization techniques for transport.37
The athlete must be carefully transferred to a spine board with either logroll or lift-and-slide. Although an extrication cervical collar can be placed before the spine board is placed, the effectiveness of this collar in executing the spine-board transfer is not proven.45 When the player is on the spine board, the head can be secured with pads and straps en route to the hospital.
Return-to-Play Criteria for Cervical Spine Injuries There is no clear consensus on return-to-play guidelines for cervical spine injuries in athletes.46
Shoulder Injuries
For hockey players, the upper extremity traditionally has been considered a well-protected area.48 However, shoulder pads are considerably more flexible in hockey than in football and other collision sports. In addition, hockey gloves allow a fair amount of motion for stick handling, and the wrist may be in maximal flexion or extension when a hit against the boards or the ice occurs. Open-ice checking, board collisions, and hockey stick use have been postulated as reasons for the high incidence of upper extremity injuries in hockey. Researchers in Finland found that upper extremity injuries accounted for up to 31% of all hockey injuries.49 More than 50% of these injuries resulted from checking or board collisions. Furthermore, study findings highlighted a low rate of injury in younger players and indicated the rate increases with age.49,50
In hockey players, the acromioclavicular (AC) joint is the most commonly injured shoulder structure.51 The mechanism of injury can be a board collision or an open-ice hit, but most often is a direct blow to the shoulder. The collision disrupts the AC joint and can sprain or tear the coracoclavicular ligaments. The Rockwood classification is used to categorize AC joint injuries (Figure 2).
Initial management involves icing the AC joint and placing a sling for comfort. Type I and type II injuries can be managed with progressive range-of-motion (ROM) exercises, strengthening, cryotherapy, and a period of rest. Treatment of type III injuries remains controversial,52 but in hockey players these injuries are almost always treated nonoperatively. Return to play requires full motion, normal strength, and minimal discomfort. Players return a few days to 2 weeks after a grade I injury; recovery from grade II injuries may take 2 to 3 weeks, and recovery from grade III injuries, 6 to 12 weeks. Surgical treatment is usually required in type IV and type V injuries, but we have had experience treating these injuries nonoperatively in high-level players. AC joint reinjury in hockey players is common, and surgical treatment should be approached cautiously, as delayed fracture after return to sport has been reported.53 Special precautions should be taken in collision athletes who undergo AC joint reconstruction. In the anatomical reconstruction described by Carofino and Mazzocca,54 2 holes are drilled in the clavicle; these holes are a potential source of fracture when the collision athlete returns to sport (Figure 3).
Clavicle fracture is another common hockey injury.55 Studies have shown clavicle fractures proportionally occur most often in people 15 to 19 years old.49 The injury presents with pain and deformity over the clavicle; in more severe fractures, skin tenting is identified. Initial management of suspected clavicle fracture includes cryotherapy, sling, and radiographs. Radiographs should include an AP view and then a 45° cephalad view, which eliminates overshadowing from the ribs. Most clavicle fractures are successfully managed nonoperatively, though there is evidence that significantly displaced or comminuted fractures have better union rates and shoulder function when treated with open reduction and internal fixation.56 After a clavicle fracture, return to skating and noncontact practice usually takes 8 weeks, with return to full contact occurring around 12 weeks.
Sternoclavicular injuries are relatively uncommon, but potentially serious. Special attention should also be given to adolescent athletes with sternoclavicular pain. Although sternoclavicular dislocations have been reported in hockey players, instead these likely are fractures involving the medial clavicle physis.57
The shoulder is the most commonly dislocated major joint, and the incidence of shoulder dislocation in elite hockey players is 8% to 21%.50,58 Anterior shoulder instability occurs from a fall with the shoulder in an abducted, externally rotated and extended position or from a direct anteriorly placed impact to the posterior shoulder. We recommend taking players off the ice for evaluation. Depending on physician comfort, the shoulder can be reduced in the training room, and the athlete sent for radiographs after reduction. If resources or support for closed reduction is not available at the rink, the athlete should be sent to the ED. Initial radiographic evaluation of a player with shoulder injury begins with plain radiographs, including a true AP (Grashey) view with the humerus in neutral, internal, and external rotation and an axillary view. The axillary radiograph is crucial in determining anterior or posterior dislocation. If the patient cannot tolerate the pain associated with having an axillary radiograph taken, a Velpeau radiograph can be used. This radiograph is taken with the patient’s arm in a sling and with the patient leaning back 30° while the x-ray beam is directed superior to inferior.
CT is performed for a suspected osseous injury. CT is more accurate than plain radiographs in showing glenoid and humeral fractures in the acute setting as well as the amount of bone loss in the case of chronic instability. Magnetic resonance arthrography is the imaging modality of choice for the diagnoses of capsulolabral injury.
After shoulder reduction, treatment with a sling, cryotherapy, and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug is initiated. In a Minnesota study of nonoperative management of shoulder instability, 9 of 10 hockey players were able to return to play the same season, and 6 of the 10 required surgery at the end of the season.59
Compared with noncontact athletes, hockey players and other collision athletes are at increased risk for recurrence.60-62 For collision athletes who want to continue playing their sport after recurrent instability, surgery is recommended. A shoulder instability study in Toronto found that more than 54% of 24 professional hockey players had associated Hill-Sachs lesions, but only 3 shoulders (12.5%) had glenoid defects.50 Arthroscopic and open techniques both demonstrate good results, and identification of bone loss can help determine which surgery to recommend.63 Hockey players can usually return to sport 6 months after shoulder stabilization.
Another important consideration in managing shoulder instability in hockey players is shoulder dominance, which determines stick grip. A left-handed player places the right hand on top of the stick for support, but most of the motion associated with shooting the puck—including abduction and external rotation—occurs with the left shoulder. Thus, a left-handed player with a history of previous left-side shoulder dislocation may dislocate with each shot, but a right-handed player with left shoulder instability may have considerably less trouble on the ice.58Shoulder and rotator cuff contusions (RCCs) occur in hockey and other collision sports.49,64 RCCs almost always result from a direct blow to the shoulder, and present with shoulder function loss, weakness, and pain.
Summary
Hockey is a high-speed collision sport with one of the highest injury rates among all sports. Physicians caring for youth, amateur, and senior hockey teams see a range of acute head, neck, and shoulder injuries. Although treatment of eye injuries, dental injuries, and concussions is not always considered orthopedic care, an orthopedic surgeon who is covering hockey needs to be comfortable managing these injuries acutely. Quality rink-side care minimizes the impact of the injury, maximizes the functional result, and expedites the safe return of the injured player back to the ice.
Am J Orthop. 2017;46(3):123-134. Copyright Frontline Medical Communications Inc. 2017. All rights reserved.
1. Vaughan G. The Puck Starts Here: The Origin of Canada’s Great Winter Game, Ice Hockey. Fredericton, Canada: Goose Lane Editions; 1996.
2. IIHF member national associations. International Ice Hockey Federation website. http://www.iihf.com/iihf-home/the-iihf/members. Accessed April 6, 2017.
3. Flik K, Lyman S, Marx RG. American collegiate men’s ice hockey: an analysis of injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(2):183-187.
4. Engebretsen L, Steffen K, Alonso JM, et al. Sports injuries and illnesses during the Winter Olympic Games 2010. Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(11):772-780.
5. Deits J, Yard EE, Collins CL, Fields SK, Comstock RD. Patients with ice hockey injuries presenting to US emergency departments, 1990-2006. J Athl Train. 2010;45(5):467-474.
6. Brooks A, Loud KJ, Brenner JS, et al. Reducing injury risk from body checking in boys’ youth ice hockey. Pediatrics. 2014;133(6):1151-1157.
7. Agel J, Harvey EJ. A 7-year review of men’s and women’s ice hockey injuries in the NCAA. Can J Surg. 2010;53(5):319-323.
8. Micieli JA, Zurakowski D, Ahmed, II. Impact of visors on eye and orbital injuries in the National Hockey League. Can J Ophthalmol. 2014;49(3):243-248.
9. Pashby TJ. Ocular injuries in hockey. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1988;28(3):228-231.
10. Leivo T, Haavisto AK, Sahraravand A. Sports-related eye injuries: the current picture. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015;93(3):224-231.
11. Cohn RM, Alaia MJ, Strauss EJ, Feldman AF. Rink-side management of ice hockey related injuries to the face, neck, and chest. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2013;71(4):253-256.
12. Reehal P. Facial injury in sport. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010;9(1):27-34.
13. Stuart MJ, Smith AM, Malo-Ortiguera SA, Fischer TL, Larson DR. A comparison of facial protection and the incidence of head, neck, and facial injuries in Junior A hockey players. A function of individual playing time. Am J Sports Med. 2002;30(1):39-44.
14. MacEwen CJ, McLatchie GR. Eye injuries in sport. Scott Med J. 2010;55(2):22-24.
15. Stevens ST, Lassonde M, de Beaumont L, Keenan JP. The effect of visors on head and facial injury in National Hockey League players. J Sci Med Sport. 2006;9(3):238-242.
16. Moslener MD, Wadsworth LT. Ice hockey: a team physician’s perspective. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010;9(3):134-138.
17. LaPrade RF, Burnett QM, Zarzour R, Moss R. The effect of the mandatory use of face masks on facial lacerations and head and neck injuries in ice hockey. A prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(6):773-775.
18. Benson BW, Mohtadi NG, Rose MS, Meeuwisse WH. Head and neck injuries among ice hockey players wearing full face shields vs half face shields. JAMA. 1999;282(24):2328-2332.
19. Lahti H, Sane J, Ylipaavalniemi P. Dental injuries in ice hockey games and training. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002;34(3):400-402.
20. Sane J, Ylipaavalniemi P, Leppanen H. Maxillofacial and dental ice hockey injuries. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1988;20(2):202-207.
21. Emerich K, Kaczmarek J. First aid for dental trauma caused by sports activities: state of knowledge, treatment and prevention. Sports Med. 2010;40(5):361-366.
22. Rosenberg H, Rosenberg H, Hickey M. Emergency management of a traumatic tooth avulsion. Ann Emerg Med. 2011;57(4):375-377.
23. Young EJ, Macias CR, Stephens L. Common dental injury management in athletes. Sports Health. 2015;7(3):250-255.
24. Andersson L, Andreasen JO, Day P, et al. International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth. Dent Traumatol. 2012;28(2):88-96.
25. McCrory P, Meeuwisse W, Johnston K, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport 3rd International Conference on Concussion in Sport held in Zurich, November 2008. Clin J Sport Med. 2009;19(3):185-200.
26. Schneider KJ, Meeuwisse WH, Kang J, Schneider GM, Emery CA. Preseason reports of neck pain, dizziness, and headache as risk factors for concussion in male youth ice hockey players. Clin J Sport Med. 2013;23(4):267-272.
27. McCrory P, Meeuwisse WH, Aubry M, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport: the 4th International Conference on Concussion in Sport held in Zurich, November 2012. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):250-258.
28. Delaney JS, Lamfookon C, Bloom GA, Al-Kashmiri A, Correa JA. Why university athletes choose not to reveal their concussion symptoms during a practice or game. Clin J Sport Med. 2015;25(2):113-125.
29. Ventura RE, Balcer LJ, Galetta SL. The concussion toolbox: the role of vision in the assessment of concussion. Semin Neurol. 2015;35(5):599-606.
30. Vartiainen MV, Holm A, Peltonen K, Luoto TM, Iverson GL, Hokkanen L. King-Devick test normative reference values for professional male ice hockey players. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25(3):e327-e330.
31. Galetta MS, Galetta KM, McCrossin J, et al. Saccades and memory: baseline associations of the King-Devick and SCAT2 SAC tests in professional ice hockey players. J Neurol Sci. 2013;328(1-2):28-31.
32. Vernau BT, Grady MF, Goodman A, et al. Oculomotor and neurocognitive assessment of youth ice hockey players: baseline associations and observations after concussion. Dev Neuropsychol. 2015;40(1):7-11.
33. Fry AF, Hale S. Relationships among processing speed, working memory, and fluid intelligence in children. Biol Psychol. 2000;54(1-3):1-34.
34. Felleman DJ, Van Essen DC. Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 1991;1(1):1-47.
35. Guskiewicz KM, Register-Mihalik J, McCrory P, et al. Evidence-based approach to revising the SCAT2: introducing the SCAT3. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):289-293.
36. Smith AM, Stuart MJ, Dodick DW, et al. Ice Hockey Summit II: zero tolerance for head hits and fighting. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2015;14(2):135-144.
37. Mihalik JP, Beard JR, Petschauer MA, Prentice WE, Guskiewicz KM. Effect of ice hockey helmet fit on cervical spine motion during an emergency log roll procedure. Clin J Sport Med. 2008;18(5):394-398.
38. Banerjee R, Palumbo MA, Fadale PD. Catastrophic cervical spine injuries in the collision sport athlete, part 1: epidemiology, functional anatomy, and diagnosis. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(4):1077-1087.
39. Reynen PD, Clancy WG Jr. Cervical spine injury, hockey helmets, and face masks. Am J Sports Med. 1994;22(2):167-170.
40. Tator CH, Provvidenza C, Cassidy JD. Update and overview of spinal injuries in Canadian ice hockey, 1943 to 2011: the continuing need for injury prevention and education. Clin J Sport Med. 2016;26(3):232-238.
41. Tator CH, Edmonds VE, Lapczak L, Tator IB. Spinal injuries in ice hockey players, 1966-1987. Can J Surg. 1991;34(1):63-69.
42. Laprade RF, Schnetzler KA, Broxterman RJ, Wentorf F, Gilbert TJ. Cervical spine alignment in the immobilized ice hockey player. A computed tomographic analysis of the effects of helmet removal. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28(6):800-803.
43. Metz CM, Kuhn JE, Greenfield ML. Cervical spine alignment in immobilized hockey players: radiographic analysis with and without helmets and shoulder pads. Clin J Sport Med. 1998;8(2):92-95.
44. National Athletic Trainers’ Association. Appropriate prehospital management of the spine-injured athlete: updated from 1998 document. http://www.nata.org/sites/default/files/Executive-Summary-Spine-Injury-updated.pdf. Updated August 5, 2015. Accessed April 6, 2017.
45. Del Rossi G, Heffernan TP, Horodyski M, Rechtine GR. The effectiveness of extrication collars tested during the execution of spine-board transfer techniques. Spine J. 2004;4(6):619-623.
46. Morganti C, Sweeney CA, Albanese SA, Burak C, Hosea T, Connolly PJ. Return to play after cervical spine injury. Spine. 2001;26(10):1131-1136.
47. Huang P, Anissipour A, McGee W, Lemak L. Return-to-play recommendations after cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine injuries: a comprehensive review. Sports Health. 2016;8(1):19-25.
48. Shindle MK, Marx RG, Kelly BT, Bisson L, Burke CJ 3rd. Hockey injuries: a pediatric sport update. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010;22(1):54-60.
49. Molsa J, Kujala U, Myllynen P, Torstila I, Airaksinen O. Injuries to the upper extremity in ice hockey: analysis of a series of 760 injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31(5):751-757.
50. Dwyer T, Petrera M, Bleakney R, Theodoropoulos JS. Shoulder instability in ice hockey players: incidence, mechanism, and MRI findings. Clin Sports Med. 2013;32(4):803-813.
51. LaPrade RF, Wijdicks CA, Griffith CJ. Division I intercollegiate ice hockey team coverage. Br J Sports Med. 2009;43(13):1000-1005.
52. Willimon SC, Gaskill TR, Millett PJ. Acromioclavicular joint injuries: anatomy, diagnosis, and treatment. Phys Sportsmed. 2011;39(1):116-122.
53. Martetschlager F, Horan MP, Warth RJ, Millett PJ. Complications after anatomic fixation and reconstruction of the coracoclavicular ligaments. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(12):2896-2903.
54. Carofino BC, Mazzocca AD. The anatomic coracoclavicular ligament reconstruction: surgical technique and indications. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(2 suppl):37-46.
55. Laprade RF, Surowiec RK, Sochanska AN, et al. Epidemiology, identification, treatment and return to play of musculoskeletal-based ice hockey injuries. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(1):4-10.
56. Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(1):1-10.
57. Lee JT, Nasreddine AY, Black EM, Bae DS, Kocher MS. Posterior sternoclavicular joint injuries in skeletally immature patients. J Pediatr Orthop. 2014;34(4):369-375.
58. Hovelius L. Shoulder dislocation in Swedish ice hockey players. Am J Sports Med. 1978;6(6):373-377.
59. Buss DD, Lynch GP, Meyer CP, Huber SM, Freehill MQ. Nonoperative management for in-season athletes with anterior shoulder instability. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(6):1430-1433.
60. Mazzocca AD, Brown FM Jr, Carreira DS, Hayden J, Romeo AA. Arthroscopic anterior shoulder stabilization of collision and contact athletes. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(1):52-60.
61. Harris JD, Romeo AA. Arthroscopic management of the contact athlete with instability. Clin Sports Med. 2013;32(4):709-730.
62. Cho NS, Hwang JC, Rhee YG. Arthroscopic stabilization in anterior shoulder instability: collision athletes versus noncollision athletes. Arthroscopy. 2006;22(9):947-953.
63. Griffin JW, Brockmeier SF. Shoulder instability with concomitant bone loss in the athlete. Orthop Clin North Am. 2015;46(1):89-103.
64. Cohen SB, Towers JD, Bradley JP. Rotator cuff contusions of the shoulder in professional football players: epidemiology and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(3):442-447.
65. Lorentzon R, Wedrèn H, Pietilä T. Incidence, nature, and causes of ice hockey injuries. A three-year prospective study of a Swedish elite ice hockey team. Am J Sports Med. 1988;16(4):392-396.
66. Stuart MJ, Smith A. Injuries in Junior A ice hockey. A three-year prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(4):458-461.
67. Voaklander DC, Saunders LD, Quinney HA, Macnab RB. Epidemiology of recreational and old-timer ice hockey injuries. Clin J Sport Med. 1996;6(1):15-21.
68. Mölsä J, Airaksinen O, Näsman O, Torstila I. Ice hockey injuries in Finland. A prospective epidemiologic study. Am J Sports Med. 1997;25(4):495-499.
69. Ferrara MS, Schurr KT. Intercollegiate ice hockey injuries: a casual analysis. Clin J Sport Med. 1999;9(1):30-33.
70. Pinto M, Kuhn JE, Greenfield ML, Hawkins RJ. Prospective analysis of ice hockey injuries at the Junior A level over the course of one season. Clin J Sport Med. 1999;9(2):70-74.
71. Emery CA, Meeuwisse WH. Injury rates, risk factors, and mechanisms of injury in minor hockey. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(12):1960-1969.
72. Kuzuhara K, Shimamoto H, Mase Y. Ice hockey injuries in a Japanese elite team: a 3-year prospective study. J Athl Train. 2009;44(2):208-214.
73. Rishiraj N, Lloyd-Smith R, Lorenz T, Niven B, Michel M. University men’s ice hockey: rates and risk of injuries over 6-years. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2009;49(2):159-166.
74. Tuominen M, Stuart MJ, Aubry M, Kannus P, Parkkari J. Injuries in men’s international ice hockey: a 7-year study of the International Ice Hockey Federation Adult World Championship Tournaments and Olympic Winter Games. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(1):30-36.
75. Heckman JD, Bucholz RW. In: Rockwood CA, Green DP, Heckman JD, Bucholz RW, eds. Rockwood and Green’s Fractures in Adults, Volume 1. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001.
1. Vaughan G. The Puck Starts Here: The Origin of Canada’s Great Winter Game, Ice Hockey. Fredericton, Canada: Goose Lane Editions; 1996.
2. IIHF member national associations. International Ice Hockey Federation website. http://www.iihf.com/iihf-home/the-iihf/members. Accessed April 6, 2017.
3. Flik K, Lyman S, Marx RG. American collegiate men’s ice hockey: an analysis of injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(2):183-187.
4. Engebretsen L, Steffen K, Alonso JM, et al. Sports injuries and illnesses during the Winter Olympic Games 2010. Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(11):772-780.
5. Deits J, Yard EE, Collins CL, Fields SK, Comstock RD. Patients with ice hockey injuries presenting to US emergency departments, 1990-2006. J Athl Train. 2010;45(5):467-474.
6. Brooks A, Loud KJ, Brenner JS, et al. Reducing injury risk from body checking in boys’ youth ice hockey. Pediatrics. 2014;133(6):1151-1157.
7. Agel J, Harvey EJ. A 7-year review of men’s and women’s ice hockey injuries in the NCAA. Can J Surg. 2010;53(5):319-323.
8. Micieli JA, Zurakowski D, Ahmed, II. Impact of visors on eye and orbital injuries in the National Hockey League. Can J Ophthalmol. 2014;49(3):243-248.
9. Pashby TJ. Ocular injuries in hockey. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1988;28(3):228-231.
10. Leivo T, Haavisto AK, Sahraravand A. Sports-related eye injuries: the current picture. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015;93(3):224-231.
11. Cohn RM, Alaia MJ, Strauss EJ, Feldman AF. Rink-side management of ice hockey related injuries to the face, neck, and chest. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2013;71(4):253-256.
12. Reehal P. Facial injury in sport. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010;9(1):27-34.
13. Stuart MJ, Smith AM, Malo-Ortiguera SA, Fischer TL, Larson DR. A comparison of facial protection and the incidence of head, neck, and facial injuries in Junior A hockey players. A function of individual playing time. Am J Sports Med. 2002;30(1):39-44.
14. MacEwen CJ, McLatchie GR. Eye injuries in sport. Scott Med J. 2010;55(2):22-24.
15. Stevens ST, Lassonde M, de Beaumont L, Keenan JP. The effect of visors on head and facial injury in National Hockey League players. J Sci Med Sport. 2006;9(3):238-242.
16. Moslener MD, Wadsworth LT. Ice hockey: a team physician’s perspective. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010;9(3):134-138.
17. LaPrade RF, Burnett QM, Zarzour R, Moss R. The effect of the mandatory use of face masks on facial lacerations and head and neck injuries in ice hockey. A prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(6):773-775.
18. Benson BW, Mohtadi NG, Rose MS, Meeuwisse WH. Head and neck injuries among ice hockey players wearing full face shields vs half face shields. JAMA. 1999;282(24):2328-2332.
19. Lahti H, Sane J, Ylipaavalniemi P. Dental injuries in ice hockey games and training. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002;34(3):400-402.
20. Sane J, Ylipaavalniemi P, Leppanen H. Maxillofacial and dental ice hockey injuries. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1988;20(2):202-207.
21. Emerich K, Kaczmarek J. First aid for dental trauma caused by sports activities: state of knowledge, treatment and prevention. Sports Med. 2010;40(5):361-366.
22. Rosenberg H, Rosenberg H, Hickey M. Emergency management of a traumatic tooth avulsion. Ann Emerg Med. 2011;57(4):375-377.
23. Young EJ, Macias CR, Stephens L. Common dental injury management in athletes. Sports Health. 2015;7(3):250-255.
24. Andersson L, Andreasen JO, Day P, et al. International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth. Dent Traumatol. 2012;28(2):88-96.
25. McCrory P, Meeuwisse W, Johnston K, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport 3rd International Conference on Concussion in Sport held in Zurich, November 2008. Clin J Sport Med. 2009;19(3):185-200.
26. Schneider KJ, Meeuwisse WH, Kang J, Schneider GM, Emery CA. Preseason reports of neck pain, dizziness, and headache as risk factors for concussion in male youth ice hockey players. Clin J Sport Med. 2013;23(4):267-272.
27. McCrory P, Meeuwisse WH, Aubry M, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport: the 4th International Conference on Concussion in Sport held in Zurich, November 2012. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):250-258.
28. Delaney JS, Lamfookon C, Bloom GA, Al-Kashmiri A, Correa JA. Why university athletes choose not to reveal their concussion symptoms during a practice or game. Clin J Sport Med. 2015;25(2):113-125.
29. Ventura RE, Balcer LJ, Galetta SL. The concussion toolbox: the role of vision in the assessment of concussion. Semin Neurol. 2015;35(5):599-606.
30. Vartiainen MV, Holm A, Peltonen K, Luoto TM, Iverson GL, Hokkanen L. King-Devick test normative reference values for professional male ice hockey players. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25(3):e327-e330.
31. Galetta MS, Galetta KM, McCrossin J, et al. Saccades and memory: baseline associations of the King-Devick and SCAT2 SAC tests in professional ice hockey players. J Neurol Sci. 2013;328(1-2):28-31.
32. Vernau BT, Grady MF, Goodman A, et al. Oculomotor and neurocognitive assessment of youth ice hockey players: baseline associations and observations after concussion. Dev Neuropsychol. 2015;40(1):7-11.
33. Fry AF, Hale S. Relationships among processing speed, working memory, and fluid intelligence in children. Biol Psychol. 2000;54(1-3):1-34.
34. Felleman DJ, Van Essen DC. Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 1991;1(1):1-47.
35. Guskiewicz KM, Register-Mihalik J, McCrory P, et al. Evidence-based approach to revising the SCAT2: introducing the SCAT3. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):289-293.
36. Smith AM, Stuart MJ, Dodick DW, et al. Ice Hockey Summit II: zero tolerance for head hits and fighting. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2015;14(2):135-144.
37. Mihalik JP, Beard JR, Petschauer MA, Prentice WE, Guskiewicz KM. Effect of ice hockey helmet fit on cervical spine motion during an emergency log roll procedure. Clin J Sport Med. 2008;18(5):394-398.
38. Banerjee R, Palumbo MA, Fadale PD. Catastrophic cervical spine injuries in the collision sport athlete, part 1: epidemiology, functional anatomy, and diagnosis. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(4):1077-1087.
39. Reynen PD, Clancy WG Jr. Cervical spine injury, hockey helmets, and face masks. Am J Sports Med. 1994;22(2):167-170.
40. Tator CH, Provvidenza C, Cassidy JD. Update and overview of spinal injuries in Canadian ice hockey, 1943 to 2011: the continuing need for injury prevention and education. Clin J Sport Med. 2016;26(3):232-238.
41. Tator CH, Edmonds VE, Lapczak L, Tator IB. Spinal injuries in ice hockey players, 1966-1987. Can J Surg. 1991;34(1):63-69.
42. Laprade RF, Schnetzler KA, Broxterman RJ, Wentorf F, Gilbert TJ. Cervical spine alignment in the immobilized ice hockey player. A computed tomographic analysis of the effects of helmet removal. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28(6):800-803.
43. Metz CM, Kuhn JE, Greenfield ML. Cervical spine alignment in immobilized hockey players: radiographic analysis with and without helmets and shoulder pads. Clin J Sport Med. 1998;8(2):92-95.
44. National Athletic Trainers’ Association. Appropriate prehospital management of the spine-injured athlete: updated from 1998 document. http://www.nata.org/sites/default/files/Executive-Summary-Spine-Injury-updated.pdf. Updated August 5, 2015. Accessed April 6, 2017.
45. Del Rossi G, Heffernan TP, Horodyski M, Rechtine GR. The effectiveness of extrication collars tested during the execution of spine-board transfer techniques. Spine J. 2004;4(6):619-623.
46. Morganti C, Sweeney CA, Albanese SA, Burak C, Hosea T, Connolly PJ. Return to play after cervical spine injury. Spine. 2001;26(10):1131-1136.
47. Huang P, Anissipour A, McGee W, Lemak L. Return-to-play recommendations after cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine injuries: a comprehensive review. Sports Health. 2016;8(1):19-25.
48. Shindle MK, Marx RG, Kelly BT, Bisson L, Burke CJ 3rd. Hockey injuries: a pediatric sport update. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010;22(1):54-60.
49. Molsa J, Kujala U, Myllynen P, Torstila I, Airaksinen O. Injuries to the upper extremity in ice hockey: analysis of a series of 760 injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31(5):751-757.
50. Dwyer T, Petrera M, Bleakney R, Theodoropoulos JS. Shoulder instability in ice hockey players: incidence, mechanism, and MRI findings. Clin Sports Med. 2013;32(4):803-813.
51. LaPrade RF, Wijdicks CA, Griffith CJ. Division I intercollegiate ice hockey team coverage. Br J Sports Med. 2009;43(13):1000-1005.
52. Willimon SC, Gaskill TR, Millett PJ. Acromioclavicular joint injuries: anatomy, diagnosis, and treatment. Phys Sportsmed. 2011;39(1):116-122.
53. Martetschlager F, Horan MP, Warth RJ, Millett PJ. Complications after anatomic fixation and reconstruction of the coracoclavicular ligaments. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(12):2896-2903.
54. Carofino BC, Mazzocca AD. The anatomic coracoclavicular ligament reconstruction: surgical technique and indications. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(2 suppl):37-46.
55. Laprade RF, Surowiec RK, Sochanska AN, et al. Epidemiology, identification, treatment and return to play of musculoskeletal-based ice hockey injuries. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(1):4-10.
56. Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(1):1-10.
57. Lee JT, Nasreddine AY, Black EM, Bae DS, Kocher MS. Posterior sternoclavicular joint injuries in skeletally immature patients. J Pediatr Orthop. 2014;34(4):369-375.
58. Hovelius L. Shoulder dislocation in Swedish ice hockey players. Am J Sports Med. 1978;6(6):373-377.
59. Buss DD, Lynch GP, Meyer CP, Huber SM, Freehill MQ. Nonoperative management for in-season athletes with anterior shoulder instability. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(6):1430-1433.
60. Mazzocca AD, Brown FM Jr, Carreira DS, Hayden J, Romeo AA. Arthroscopic anterior shoulder stabilization of collision and contact athletes. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(1):52-60.
61. Harris JD, Romeo AA. Arthroscopic management of the contact athlete with instability. Clin Sports Med. 2013;32(4):709-730.
62. Cho NS, Hwang JC, Rhee YG. Arthroscopic stabilization in anterior shoulder instability: collision athletes versus noncollision athletes. Arthroscopy. 2006;22(9):947-953.
63. Griffin JW, Brockmeier SF. Shoulder instability with concomitant bone loss in the athlete. Orthop Clin North Am. 2015;46(1):89-103.
64. Cohen SB, Towers JD, Bradley JP. Rotator cuff contusions of the shoulder in professional football players: epidemiology and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(3):442-447.
65. Lorentzon R, Wedrèn H, Pietilä T. Incidence, nature, and causes of ice hockey injuries. A three-year prospective study of a Swedish elite ice hockey team. Am J Sports Med. 1988;16(4):392-396.
66. Stuart MJ, Smith A. Injuries in Junior A ice hockey. A three-year prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(4):458-461.
67. Voaklander DC, Saunders LD, Quinney HA, Macnab RB. Epidemiology of recreational and old-timer ice hockey injuries. Clin J Sport Med. 1996;6(1):15-21.
68. Mölsä J, Airaksinen O, Näsman O, Torstila I. Ice hockey injuries in Finland. A prospective epidemiologic study. Am J Sports Med. 1997;25(4):495-499.
69. Ferrara MS, Schurr KT. Intercollegiate ice hockey injuries: a casual analysis. Clin J Sport Med. 1999;9(1):30-33.
70. Pinto M, Kuhn JE, Greenfield ML, Hawkins RJ. Prospective analysis of ice hockey injuries at the Junior A level over the course of one season. Clin J Sport Med. 1999;9(2):70-74.
71. Emery CA, Meeuwisse WH. Injury rates, risk factors, and mechanisms of injury in minor hockey. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(12):1960-1969.
72. Kuzuhara K, Shimamoto H, Mase Y. Ice hockey injuries in a Japanese elite team: a 3-year prospective study. J Athl Train. 2009;44(2):208-214.
73. Rishiraj N, Lloyd-Smith R, Lorenz T, Niven B, Michel M. University men’s ice hockey: rates and risk of injuries over 6-years. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2009;49(2):159-166.
74. Tuominen M, Stuart MJ, Aubry M, Kannus P, Parkkari J. Injuries in men’s international ice hockey: a 7-year study of the International Ice Hockey Federation Adult World Championship Tournaments and Olympic Winter Games. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(1):30-36.
75. Heckman JD, Bucholz RW. In: Rockwood CA, Green DP, Heckman JD, Bucholz RW, eds. Rockwood and Green’s Fractures in Adults, Volume 1. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001.