User login
Medical Complications and Outcomes After Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Nationwide Analysis
ABSTRACT
There is a paucity of evidence describing the types and rates of postoperative complications following total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA). We sought to analyze the complications following TSA and determine their effects on described outcome measures.
Using discharge data from the weighted Nationwide Inpatient Sample from 2006 to 2010, patients who underwent primary TSA were identified. The prevalence of specific complications was identified using the International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) codes. The data from this database represent events occurring during admission, prior to discharge. The associations between patient characteristics, complications, and outcomes of TSA were evaluated. The specific outcomes analyzed in this study were mortality and length of stay (LOS).
A total of 125,766 patients were identified. The rate of complication after TSA was 6.7% (8457 patients). The most frequent complications were respiratory, renal, and cardiac, occurring in 2.9%, 0.8%, and 0.8% of cases, respectively. Increasing age and total number of preoperative comorbidities significantly increased the likelihood of having a complication. The prevalence of postoperative shock and central nervous system, cardiac, vascular, and respiratory complications was significantly higher in patients who suffered postoperative mortality (88 patients; 0.07% mortality rate) than in those who survived surgery (P < 0.0001). In terms of LOS, shock and infectious and vascular complications most significantly increased the length of hospitalization.
Postoperative complications following TSA are not uncommon and occur in >6% of patients. Older patients and certain comorbidities are associated with complications after surgery. These complications are associated with postoperative mortality and increased LOS.
Continue to: Total shoulder arthroplasty...
Total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) provides a predictably high level of satisfaction with survival as high as 92% at 15 years.1 As implant instrumentation and surgical technique and understanding have improved, the frequency of TSAs being performed has also increased.2 Although there are enough data on long-term surgical complications following TSA,1,3-6 there is a paucity of evidence delineating the incidence and types of postoperative complications during hospitalization. Several current issues motivate the improved understanding of TSA, including the increasing number of TSAs being performed, the desire to improve quality of care, and the desire to create financially efficient healthcare.
The purpose of this study is to detail the postoperative complications that occur following TSA using a large national database. Specifically, our goals are to determine the incidence and types of complications after shoulder arthroplasty, determine the patient factors that are associated with these complications, and evaluate the effects of these complications on postoperative in-hospital mortality and length of stay (LOS). Our hypothesis is that there would be a correlation between specific patient factors and complications and that these complications would adversely correlate to patient postoperative outcomes.
METHODS
DESIGN
We conducted a retrospective analysis of TSAs captured by the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS) database between 2006 and 2010. The NIS is the largest all-payer inpatient database that is currently available to the public in the United States.7
The NIS is a part of the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) and the US Department of Health and Human Services. The NIS database is designed to approximate a 20% sample of US hospitals and the patients they serve, including community, academic, general, and specialty-specific hospitals such as orthopedic hospitals.7 The 2010 update of the NIS database contains discharge data from 1051 hospitals across 45 states, with a representative sample of >39 million inpatient hospital stays.7 The NIS database and its data sources have been independently validated and assessed for quality each year since 1988.8Furthermore, comparative analysis of multiple database elements and distributions has been validated against standard norms, including the National Hospital Discharge Survey.9 The NIS database has been used in numerous published studies.2,10,11
PATIENT SELECTION
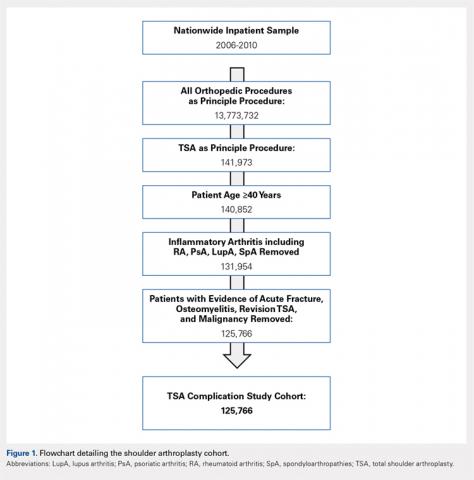
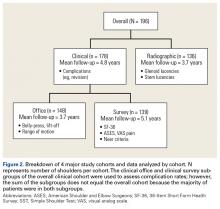
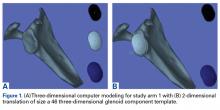
The yearly NIS databases from 2006 to 2010 were compiled. Patients aged ≥40 years who underwent a TSA were identified using the International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision (ICD-9), procedural code 81.80. Exclusion criteria were patients with a primary or a secondary diagnosis of humeral or scapular fracture, chronic osteomyelitis, rheumatologic diseases, or evidence of concurrent malignancy (Figure 1).
Native to NIS are patient demographics, including age, sex, and race. Patient comorbidities as described by Elixhauser and colleagues12 are also included in the database.
Continue to: OUTCOMES...
OUTCOMES
The primary outcome of this study was a description of the type and frequency of postoperative complications of TSA. To conduct this analysis, we queried the TSA cohort for specific ICD-9 codes representing acute cardiac, central nervous system, infectious, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, postoperative shock, renal, respiratory, surgical, vascular, and wound complications. The ICD-9 codes used to identify complications were modeled according to previous literature on various surgical applications and were further parsed to reflect only acute postoperative diagnoses13-15(see the Appendix for the comprehensive list of ICD-9 codes).
Two additional outcomes were analyzed, including postoperative mortality and LOS. Postoperative mortality was defined as death occurring prior to discharge. We calculated the average LOS among the complication and the noncomplication cohort.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Patient demographics and target outcomes of the study were analyzed by frequency distribution. Where applicable, the chi-square and the Student’s t tests were used to confirm the statistical difference for dichotomous and continuous variables, respectively. Multivariate regressions were performed after controlling for possible clustering of the data using a generalized estimating equation following a previous analytical methodology.16-20 The results are reported with odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals where applicable, all statistical tests with P ≤ 0.05 were considered to be significant, and all statistical tests were two-sided. We conducted all analyses using SAS, version 9.2 (SAS Institute).
RESULTS
From 2006 to 2010, a weighted sample of 141,973 patients was found to undergo a TSA. After applying our inclusion and exclusion criteria, our study cohort consisted of 125,766 patients (Figure 1).
Continue to: OVERALL TSA COHORT DEMOGRAPHICS...
OVERALL TSA COHORT DEMOGRAPHICS
The average age of the TSA cohort was 69.4 years (standard deviation [SD], 21.20), and 54.1% were females. The cohort had significant comorbidities, with 83.3% of them having at least 1 comorbidity at the time of surgery. Specifically, 31.3% of the patients had 1 comorbidity, 26.5% had 2 comorbidities, and 25.4% had ≥3 comorbidities. Hypertension was the most common comorbidity present in 66.2% of patients, and diabetes was the second most common comorbidity with a prevalence of 16.8%.
COMPLICATION COHORT DEMOGRAPHICS
An overall postoperative complication rate of 6.7% (weighted sample of 8457 patients) was noted in the overall TSA cohort. The TSA cohort was dichotomized into patients who suffered at least 1 complication (weighted, n = 8457) and patients undergoing routine TSAs (weighted, n = 117,308). The average age was significantly higher in the complication vs routine cohort (71.38 vs 69.27 years, P < 0.0001). Similarly, there were significantly more comorbidities (2.51 vs 1.71, P < 0.0001) in the complication cohort.
COMPLICATIONS
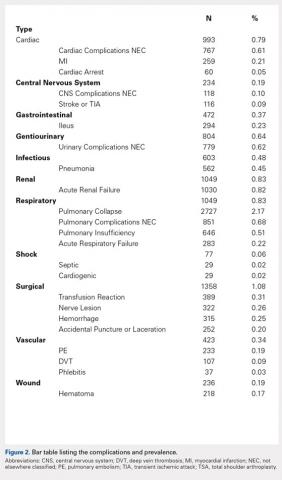
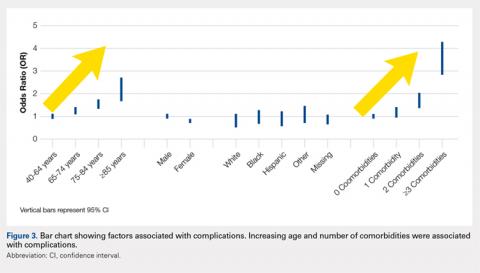
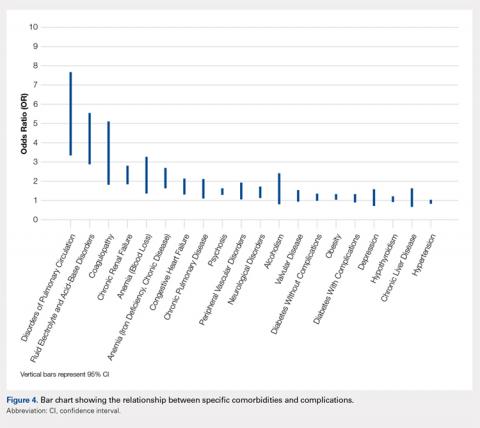
We noted a complication rate of 6.7% (weighted sample of 8457 patients). A single complication was noted in 5% of these patients, whereas 1.3% and 0.4% of the patients had 2 and ≥3 complications, respectively. Respiratory abnormalities (2.9%), acute renal failure (0.8%), and cardiac complications (0.8%) were the most prevalent complications after TSA. The list of complications is detailed in Figure 2. Logistic regression analysis of patient characteristics predicting complications showed that advanced age (odds ratio [OR], 2.1 in those aged ≥85 years) and increasing number of comorbidities (≥3; OR, 3.5) were most significant in predicting complications (all P < 0.0001) (Figure 3). Despite the ubiquity of hypertension in this patient population, it was not a significant predictor of complication (OR, 0.9); in contrast, pulmonary disorders (OR, 5.1) and fluid and electrolyte disorders (4.0) were most strongly associated with the development of a postoperative complication after surgery (Figure 4).
EFFECT OF COMPLICATIONS ON LOS
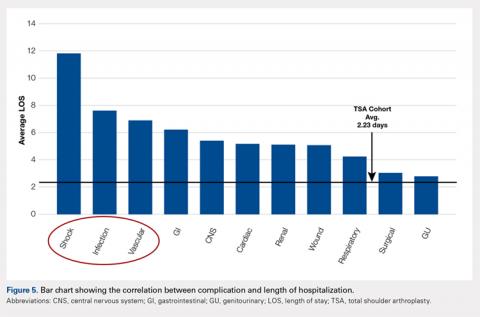
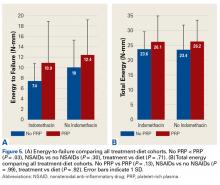
The average length of hospitalization was 2.3 days (95% confidence interval, 2.22-2.25) among the entire cohort. The average LOS was longer in the complication cohort (3.9 days) than in patients who did not have a complication (2.1 days, P < 0.0001). Of the specific complications noted, hemodynamic shock (11.8 days); infectious, most commonly pneumonia (7.6 days); and vascular complications (6.9 days) were associated with the longest hospitalizations. This result is summarized in Figure 5.
MORTALITY
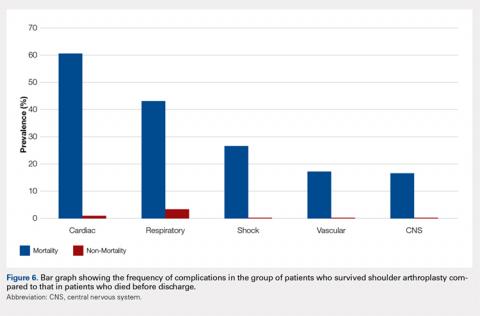
An overall postoperative (in-house) mortality rate of 0.07% was noted (weighted, n = 88). Comparison between the patient cohort that died vs those who survived TSA resulted in significant differences in the rates of complications. Complications that were most significantly different between the cohorts included cardiac (60.47% vs 0.75%, P < 0.0001), postoperative shock (26.61% vs 0.04%, P < 0.0001), and respiratory complications (43.1% vs 2.8%, P < 0.0001). It is important to note that the overall rate of postoperative shock was exceedingly low in the TSA cohort, but it was highly prevalent in the mortality cohort, occurring in 26.61% of patients. A summary of the mortality statistics is presented in Figure 6.
Continue to: DISCUSSION...
DISCUSSION
TSA continues to be associated with high levels of satisfaction;1 as a result, its incidence is increasing.2 As our understanding and efficiency improves nationally, it is imperative that we determine the short-term and longer-term outcomes and complications. In addition, the factors that may affect prognosis must be elucidated to provide a more individualized and effective standard of care. To date, most of the outcome studies of TSA have evaluated long-term outcomes and specific implant-related complications.1,5,6,21,22 Our intent was to evaluate the complications that occur in the postoperative period and their effect on unique “patient care” outcomes. With knowledge of these complications and the predisposing factors, we can better assess patients, risk-stratify, and provide appropriate guidelines.
We noted that complications occurring after TSA are not uncommon, with >6% of patients suffering a postoperative complication. In this study, the number of complications noted was associated with worse patient outcomes. In addition, we noted that patients undergoing a TSA have a significant burden of comorbidities; however, hematologic and fluid disorders (eg, iron deficiency anemia, pulmonary circulatory disorders, and fluid imbalances) were most important in predicting postoperative complications.
Increased LOS in the hospital after TSA was associated with the occurrence of complications. Of all noted complications, shock and infectious and vascular complications led to the longest hospitalizations. Hospital-acquired pneumonia was the most common infectious etiology, while pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis were the most consistent vascular complications. Although seldom studied in the TSA population, a similar finding has been noted in patients after THA. O’Malley and colleagues,23 using the American College of Surgeon’s National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database, identified independent factors that were associated with complications and average prolonged LOS. They noted that the occurrence of major complications was associated with a prolonged LOS. Some, but not all the major complications, included organ space infection, cardiac events, pneumonia, and venous thromboembolic events.23 Therefore, attempts to limit the amount of time spent in hospitals and control the associated costs must focus on managing the incidence of complications.
Postoperative mortality after TSA was uncommon, occurring in 0.07% of the patients in this study. The low incidence of mortality noted in this study is probably related to the fact that our data represent mortality, whereas in the hospital and, unlike most mortality studies, it does not account for patient demise that may occur in the months after surgery. Other reports have noted that mortality occurs in <1.5% of these patients.24-28 Singh and colleagues25 observed in their evaluation of perioperative mortality after TSA a mortality rate of 0.8% with 90 days after 4380 shoulder replacements performed at their institution. Using multivariate analysis, they were able to identify associations between mortality and increasing American Society of Anesthesiology (ASA) class and Charlson Comorbidity Index. These results in relation to ours would indicate that the majority of patients who die after shoulder arthroplasty do so after initial discharge. Although we could not determine a causal relationship between mortality and patient comorbidities, we noted that certain complications strongly correlated with mortality. In patients who died, there was a relatively high incidence of cardiac (60.5%) and respiratory (43.1%) complications. Similarly, although postoperative shock was almost nonexistent in the patients who survived surgery (0.04%), it was much more common in the patients who suffered mortality (26.6%).
This study is not without limitations. Data were extracted from a national database, therefore precluding the inclusion of specific details of surgery and functional assessment. Inherent to ICD-9 coding, we were unable to assess the exact detail and severity of complications. For instance, we cannot be certain what criteria were used to define “acute renal failure” for each patient. This study is retrospective in nature and therefore adequate randomization and standardization of patients is not possible. Similarly, the nature of the database may not allow for exacting our inclusion and exclusion criteria. However, the large sample size of the patient population lessens the chance of potential biases and type 2 errors. Prior to October 2010, reverse shoulder arthroplasty was coded under the ICD-9procedural code 81.80 as TSA. Therefore, there is some overlap between TSA and reverse shoulder arthroplasty in our data. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty is now coded under ICD-9 procedural code 81.88. It is possible that results may differ if reverse shoulder arthroplasty were excluded from our patient cohort. This can be an area of future research.
CONCLUSION
Although much is known about the long-term hardware and functional complications after TSA, in this study, we have attempted to broaden the understanding of perioperative complications and the associated sequelae. Complications are common after TSA surgery and are related to adverse outcomes. In the setting of healthcare changes, the surgeon and the patient must understand the cause, types, incidence, and outcomes of medical and surgical complications after surgery. This allows for more accurate “standard of care” metrics. Further large-volume multicenter studies are needed to gain further insight into the short- and long-term outcomes of TSA.
1. Fox TJ, Cil A, Sperling JW, Sanchez-Sotelo J, Schleck CD, Cofield RH. Survival of the glenoid component in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18(6):859-863. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2008.11.020.
2. Kim SH, Wise BL, Zhang Y, Szabo RM. Increasing incidence of shoulder arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(24):2249-2254. doi:10.2106/JBJS.J.01994.
3. Ahmadi S, Lawrence TM, Sahota S, et al. The incidence and risk factors for blood transfusion in revision shoulder arthroplasty: our institution's experience and review of the literature. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(1):43–48. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2013.03.010.
4. Boyd AD Jr, Aliabadi P, Thornhill TS. Postoperative proximal migration in total shoulder arthroplasty. Incidence and significance. J Arthroplasty. 1991;6(1):31-37. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(06)80154-3.
5. Choi T, Horodyski M, Struk AM, Sahajpal DT, Wright TW. Incidence of early radiolucent lines after glenoid component insertion for total shoulder arthroplasty: a radiographic study comparing pressurized and unpressurized cementing techniques. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(3):403-408. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2012.05.041.
6. Favard L, Katz D, Colmar M, Benkalfate T, Thomazeau H, Emily S. Total shoulder arthroplasty - arthroplasty for glenohumeral arthropathies: results and complications after a minimum follow-up of 8 years according to the type of arthroplasty and etiology. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(4 Suppl):S41-S47. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2012.04.003.
7. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Introduction to the HCUP national inpatient sample (NIS) 2012. https://hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/nation/nis/NISIntroduction2012.pdf 2012. Accessed June 9, 2013.
8. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. HCUP quality control procedures. https://hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/quality.pdf. Accessed June 15, 2013.
9. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Comparative analysis of HCUP and NHDS inpatient discharge data: technical supplement 13. https://archive.ahrq.gov/research/data/hcup/nhds/niscomp.html. Accessed June 15, 2013.
10. Rajaee SS, Trofa D, Matzkin E, Smith E. National trends in primary total hip arthroplasty in extremely young patients: a focus on bearing surface usage. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(10):1870-1878. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2012.04.006.
11. Bozic KJ, Kurtz S, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of bearing surface usage in total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(7):1614-1620. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.01220.
12. Elixhauser A, Steiner C, Harris DR, Coffey RM. Comorbidity measures for use with administrative data. Med Care. 1998;36(1):8-27. doi:10.1097/00005650-199801000-00004.
13. Cahill KS, Chi JH, Day A, Claus EB. Prevalence, complications, and hospital charges associated with use of bone-morphogenetic proteins in spinal fusion procedures. JAMA. 2009;302(1):58-66. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.956.
14. Lin CA, Kuo AC, Takemoto S. Comorbidities and perioperative complications in HIV-positive patients undergoing primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(11):1028-1036. doi:10.2106/JBJS.L.00269.
15. Rasouli MR, Maltenfort MG, Ross D, Hozack WJ, Memtsoudis SG, Parvizi J. Perioperative morbidity and mortality following bilateral total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(1):142-148. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2013.04.001.
16. Begg CB, Riedel ER, Bach PB, et al. Variations in morbidity after radical prostatectomy. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(15):1138-1144. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa011788.
17. Hu JC, Gold KF, Pashos CL, Mehta SS, Litwin MS. Temporal trends in radical prostatectomy complications from 1991 to 1998. J Urol. 2003;169(4):1443-1448. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000056046.16588.e4.
18. Abdollah F, Sun M, Schmitges J, et al. Surgical caseload is an important determinant of continent urinary diversion rate at radical cystectomy: a population-based study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(9):2680-2687. doi:10.1245/s10434-011-1618-2.
19. Panageas KS, Schrag D, Riedel E, Bach PB, Begg CB. The effect of clustering of outcomes on the association of procedure volume and surgical outcomes. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139(8):658-665. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-139-8-200310210-00009.
20. Joice GA, Deibert CM, Kates M, Spencer BA, McKiernan JM. "Never events”: centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services complications after radical cystectomy. Urology. 2013;81(3):527-532. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2012.09.050.
21. Taunton MJ, McIntosh AL, Sperling JW, Cofield RH. Total shoulder arthroplasty with a metal-backed, bone-ingrowth glenoid component. Medium to long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(10):2180-2188. doi:10.2106/JBJS.G.00966.
22. Raiss P, Schmitt M, Bruckner T, et al. Results of cemented total shoulder replacement with a minimum follow-up of ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(23):e1711-e1710. doi:10.2106/JBJS.K.00580.
23. O'Malley NT, Fleming FJ, Gunzler DD, Messing SP, Kates SL. Factors independently associated with complications and length of stay after hip arthroplasty: analysis of the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(10):1832-1837. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2012.04.025.
24. White CB, Sperling JW, Cofield RH, Rowland CM. Ninety-day mortality after shoulder arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(7):886-888. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(03)00269-9.
25. Singh JA, Sperling JW, Cofield RH. Ninety day mortality and its predictors after primary shoulder arthroplasty: an analysis of 4,019 patients from 1976-2008. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:231. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-12-231.
26. Fehringer EV, Mikuls TR, Michaud KD, Henderson WG, O'Dell JR. Shoulder arthroplasties have fewer complications than hip or knee arthroplasties in US veterans. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(3):717-722. doi:10.1007/s11999-009-0996-2.
27. Farmer KW, Hammond JW, Queale WS, Keyurapan E, McFarland EG. Shoulder arthroplasty versus hip and knee arthroplasties: a comparison of outcomes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;455:183-189. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000238839.26423.8d.
28. Farng E, Zingmond D, Krenek L, Soohoo NF. Factors predicting complication rates after primary shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(4):557-563. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2010.11.005.
ABSTRACT
There is a paucity of evidence describing the types and rates of postoperative complications following total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA). We sought to analyze the complications following TSA and determine their effects on described outcome measures.
Using discharge data from the weighted Nationwide Inpatient Sample from 2006 to 2010, patients who underwent primary TSA were identified. The prevalence of specific complications was identified using the International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) codes. The data from this database represent events occurring during admission, prior to discharge. The associations between patient characteristics, complications, and outcomes of TSA were evaluated. The specific outcomes analyzed in this study were mortality and length of stay (LOS).
A total of 125,766 patients were identified. The rate of complication after TSA was 6.7% (8457 patients). The most frequent complications were respiratory, renal, and cardiac, occurring in 2.9%, 0.8%, and 0.8% of cases, respectively. Increasing age and total number of preoperative comorbidities significantly increased the likelihood of having a complication. The prevalence of postoperative shock and central nervous system, cardiac, vascular, and respiratory complications was significantly higher in patients who suffered postoperative mortality (88 patients; 0.07% mortality rate) than in those who survived surgery (P < 0.0001). In terms of LOS, shock and infectious and vascular complications most significantly increased the length of hospitalization.
Postoperative complications following TSA are not uncommon and occur in >6% of patients. Older patients and certain comorbidities are associated with complications after surgery. These complications are associated with postoperative mortality and increased LOS.
Continue to: Total shoulder arthroplasty...
Total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) provides a predictably high level of satisfaction with survival as high as 92% at 15 years.1 As implant instrumentation and surgical technique and understanding have improved, the frequency of TSAs being performed has also increased.2 Although there are enough data on long-term surgical complications following TSA,1,3-6 there is a paucity of evidence delineating the incidence and types of postoperative complications during hospitalization. Several current issues motivate the improved understanding of TSA, including the increasing number of TSAs being performed, the desire to improve quality of care, and the desire to create financially efficient healthcare.
The purpose of this study is to detail the postoperative complications that occur following TSA using a large national database. Specifically, our goals are to determine the incidence and types of complications after shoulder arthroplasty, determine the patient factors that are associated with these complications, and evaluate the effects of these complications on postoperative in-hospital mortality and length of stay (LOS). Our hypothesis is that there would be a correlation between specific patient factors and complications and that these complications would adversely correlate to patient postoperative outcomes.
METHODS
DESIGN
We conducted a retrospective analysis of TSAs captured by the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS) database between 2006 and 2010. The NIS is the largest all-payer inpatient database that is currently available to the public in the United States.7
The NIS is a part of the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) and the US Department of Health and Human Services. The NIS database is designed to approximate a 20% sample of US hospitals and the patients they serve, including community, academic, general, and specialty-specific hospitals such as orthopedic hospitals.7 The 2010 update of the NIS database contains discharge data from 1051 hospitals across 45 states, with a representative sample of >39 million inpatient hospital stays.7 The NIS database and its data sources have been independently validated and assessed for quality each year since 1988.8Furthermore, comparative analysis of multiple database elements and distributions has been validated against standard norms, including the National Hospital Discharge Survey.9 The NIS database has been used in numerous published studies.2,10,11
PATIENT SELECTION
The yearly NIS databases from 2006 to 2010 were compiled. Patients aged ≥40 years who underwent a TSA were identified using the International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision (ICD-9), procedural code 81.80. Exclusion criteria were patients with a primary or a secondary diagnosis of humeral or scapular fracture, chronic osteomyelitis, rheumatologic diseases, or evidence of concurrent malignancy (Figure 1).
Native to NIS are patient demographics, including age, sex, and race. Patient comorbidities as described by Elixhauser and colleagues12 are also included in the database.
Continue to: OUTCOMES...
OUTCOMES
The primary outcome of this study was a description of the type and frequency of postoperative complications of TSA. To conduct this analysis, we queried the TSA cohort for specific ICD-9 codes representing acute cardiac, central nervous system, infectious, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, postoperative shock, renal, respiratory, surgical, vascular, and wound complications. The ICD-9 codes used to identify complications were modeled according to previous literature on various surgical applications and were further parsed to reflect only acute postoperative diagnoses13-15(see the Appendix for the comprehensive list of ICD-9 codes).
Two additional outcomes were analyzed, including postoperative mortality and LOS. Postoperative mortality was defined as death occurring prior to discharge. We calculated the average LOS among the complication and the noncomplication cohort.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Patient demographics and target outcomes of the study were analyzed by frequency distribution. Where applicable, the chi-square and the Student’s t tests were used to confirm the statistical difference for dichotomous and continuous variables, respectively. Multivariate regressions were performed after controlling for possible clustering of the data using a generalized estimating equation following a previous analytical methodology.16-20 The results are reported with odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals where applicable, all statistical tests with P ≤ 0.05 were considered to be significant, and all statistical tests were two-sided. We conducted all analyses using SAS, version 9.2 (SAS Institute).
RESULTS
From 2006 to 2010, a weighted sample of 141,973 patients was found to undergo a TSA. After applying our inclusion and exclusion criteria, our study cohort consisted of 125,766 patients (Figure 1).
Continue to: OVERALL TSA COHORT DEMOGRAPHICS...
OVERALL TSA COHORT DEMOGRAPHICS
The average age of the TSA cohort was 69.4 years (standard deviation [SD], 21.20), and 54.1% were females. The cohort had significant comorbidities, with 83.3% of them having at least 1 comorbidity at the time of surgery. Specifically, 31.3% of the patients had 1 comorbidity, 26.5% had 2 comorbidities, and 25.4% had ≥3 comorbidities. Hypertension was the most common comorbidity present in 66.2% of patients, and diabetes was the second most common comorbidity with a prevalence of 16.8%.
COMPLICATION COHORT DEMOGRAPHICS
An overall postoperative complication rate of 6.7% (weighted sample of 8457 patients) was noted in the overall TSA cohort. The TSA cohort was dichotomized into patients who suffered at least 1 complication (weighted, n = 8457) and patients undergoing routine TSAs (weighted, n = 117,308). The average age was significantly higher in the complication vs routine cohort (71.38 vs 69.27 years, P < 0.0001). Similarly, there were significantly more comorbidities (2.51 vs 1.71, P < 0.0001) in the complication cohort.
COMPLICATIONS
We noted a complication rate of 6.7% (weighted sample of 8457 patients). A single complication was noted in 5% of these patients, whereas 1.3% and 0.4% of the patients had 2 and ≥3 complications, respectively. Respiratory abnormalities (2.9%), acute renal failure (0.8%), and cardiac complications (0.8%) were the most prevalent complications after TSA. The list of complications is detailed in Figure 2. Logistic regression analysis of patient characteristics predicting complications showed that advanced age (odds ratio [OR], 2.1 in those aged ≥85 years) and increasing number of comorbidities (≥3; OR, 3.5) were most significant in predicting complications (all P < 0.0001) (Figure 3). Despite the ubiquity of hypertension in this patient population, it was not a significant predictor of complication (OR, 0.9); in contrast, pulmonary disorders (OR, 5.1) and fluid and electrolyte disorders (4.0) were most strongly associated with the development of a postoperative complication after surgery (Figure 4).
EFFECT OF COMPLICATIONS ON LOS
The average length of hospitalization was 2.3 days (95% confidence interval, 2.22-2.25) among the entire cohort. The average LOS was longer in the complication cohort (3.9 days) than in patients who did not have a complication (2.1 days, P < 0.0001). Of the specific complications noted, hemodynamic shock (11.8 days); infectious, most commonly pneumonia (7.6 days); and vascular complications (6.9 days) were associated with the longest hospitalizations. This result is summarized in Figure 5.
MORTALITY
An overall postoperative (in-house) mortality rate of 0.07% was noted (weighted, n = 88). Comparison between the patient cohort that died vs those who survived TSA resulted in significant differences in the rates of complications. Complications that were most significantly different between the cohorts included cardiac (60.47% vs 0.75%, P < 0.0001), postoperative shock (26.61% vs 0.04%, P < 0.0001), and respiratory complications (43.1% vs 2.8%, P < 0.0001). It is important to note that the overall rate of postoperative shock was exceedingly low in the TSA cohort, but it was highly prevalent in the mortality cohort, occurring in 26.61% of patients. A summary of the mortality statistics is presented in Figure 6.
Continue to: DISCUSSION...
DISCUSSION
TSA continues to be associated with high levels of satisfaction;1 as a result, its incidence is increasing.2 As our understanding and efficiency improves nationally, it is imperative that we determine the short-term and longer-term outcomes and complications. In addition, the factors that may affect prognosis must be elucidated to provide a more individualized and effective standard of care. To date, most of the outcome studies of TSA have evaluated long-term outcomes and specific implant-related complications.1,5,6,21,22 Our intent was to evaluate the complications that occur in the postoperative period and their effect on unique “patient care” outcomes. With knowledge of these complications and the predisposing factors, we can better assess patients, risk-stratify, and provide appropriate guidelines.
We noted that complications occurring after TSA are not uncommon, with >6% of patients suffering a postoperative complication. In this study, the number of complications noted was associated with worse patient outcomes. In addition, we noted that patients undergoing a TSA have a significant burden of comorbidities; however, hematologic and fluid disorders (eg, iron deficiency anemia, pulmonary circulatory disorders, and fluid imbalances) were most important in predicting postoperative complications.
Increased LOS in the hospital after TSA was associated with the occurrence of complications. Of all noted complications, shock and infectious and vascular complications led to the longest hospitalizations. Hospital-acquired pneumonia was the most common infectious etiology, while pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis were the most consistent vascular complications. Although seldom studied in the TSA population, a similar finding has been noted in patients after THA. O’Malley and colleagues,23 using the American College of Surgeon’s National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database, identified independent factors that were associated with complications and average prolonged LOS. They noted that the occurrence of major complications was associated with a prolonged LOS. Some, but not all the major complications, included organ space infection, cardiac events, pneumonia, and venous thromboembolic events.23 Therefore, attempts to limit the amount of time spent in hospitals and control the associated costs must focus on managing the incidence of complications.
Postoperative mortality after TSA was uncommon, occurring in 0.07% of the patients in this study. The low incidence of mortality noted in this study is probably related to the fact that our data represent mortality, whereas in the hospital and, unlike most mortality studies, it does not account for patient demise that may occur in the months after surgery. Other reports have noted that mortality occurs in <1.5% of these patients.24-28 Singh and colleagues25 observed in their evaluation of perioperative mortality after TSA a mortality rate of 0.8% with 90 days after 4380 shoulder replacements performed at their institution. Using multivariate analysis, they were able to identify associations between mortality and increasing American Society of Anesthesiology (ASA) class and Charlson Comorbidity Index. These results in relation to ours would indicate that the majority of patients who die after shoulder arthroplasty do so after initial discharge. Although we could not determine a causal relationship between mortality and patient comorbidities, we noted that certain complications strongly correlated with mortality. In patients who died, there was a relatively high incidence of cardiac (60.5%) and respiratory (43.1%) complications. Similarly, although postoperative shock was almost nonexistent in the patients who survived surgery (0.04%), it was much more common in the patients who suffered mortality (26.6%).
This study is not without limitations. Data were extracted from a national database, therefore precluding the inclusion of specific details of surgery and functional assessment. Inherent to ICD-9 coding, we were unable to assess the exact detail and severity of complications. For instance, we cannot be certain what criteria were used to define “acute renal failure” for each patient. This study is retrospective in nature and therefore adequate randomization and standardization of patients is not possible. Similarly, the nature of the database may not allow for exacting our inclusion and exclusion criteria. However, the large sample size of the patient population lessens the chance of potential biases and type 2 errors. Prior to October 2010, reverse shoulder arthroplasty was coded under the ICD-9procedural code 81.80 as TSA. Therefore, there is some overlap between TSA and reverse shoulder arthroplasty in our data. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty is now coded under ICD-9 procedural code 81.88. It is possible that results may differ if reverse shoulder arthroplasty were excluded from our patient cohort. This can be an area of future research.
CONCLUSION
Although much is known about the long-term hardware and functional complications after TSA, in this study, we have attempted to broaden the understanding of perioperative complications and the associated sequelae. Complications are common after TSA surgery and are related to adverse outcomes. In the setting of healthcare changes, the surgeon and the patient must understand the cause, types, incidence, and outcomes of medical and surgical complications after surgery. This allows for more accurate “standard of care” metrics. Further large-volume multicenter studies are needed to gain further insight into the short- and long-term outcomes of TSA.
ABSTRACT
There is a paucity of evidence describing the types and rates of postoperative complications following total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA). We sought to analyze the complications following TSA and determine their effects on described outcome measures.
Using discharge data from the weighted Nationwide Inpatient Sample from 2006 to 2010, patients who underwent primary TSA were identified. The prevalence of specific complications was identified using the International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) codes. The data from this database represent events occurring during admission, prior to discharge. The associations between patient characteristics, complications, and outcomes of TSA were evaluated. The specific outcomes analyzed in this study were mortality and length of stay (LOS).
A total of 125,766 patients were identified. The rate of complication after TSA was 6.7% (8457 patients). The most frequent complications were respiratory, renal, and cardiac, occurring in 2.9%, 0.8%, and 0.8% of cases, respectively. Increasing age and total number of preoperative comorbidities significantly increased the likelihood of having a complication. The prevalence of postoperative shock and central nervous system, cardiac, vascular, and respiratory complications was significantly higher in patients who suffered postoperative mortality (88 patients; 0.07% mortality rate) than in those who survived surgery (P < 0.0001). In terms of LOS, shock and infectious and vascular complications most significantly increased the length of hospitalization.
Postoperative complications following TSA are not uncommon and occur in >6% of patients. Older patients and certain comorbidities are associated with complications after surgery. These complications are associated with postoperative mortality and increased LOS.
Continue to: Total shoulder arthroplasty...
Total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) provides a predictably high level of satisfaction with survival as high as 92% at 15 years.1 As implant instrumentation and surgical technique and understanding have improved, the frequency of TSAs being performed has also increased.2 Although there are enough data on long-term surgical complications following TSA,1,3-6 there is a paucity of evidence delineating the incidence and types of postoperative complications during hospitalization. Several current issues motivate the improved understanding of TSA, including the increasing number of TSAs being performed, the desire to improve quality of care, and the desire to create financially efficient healthcare.
The purpose of this study is to detail the postoperative complications that occur following TSA using a large national database. Specifically, our goals are to determine the incidence and types of complications after shoulder arthroplasty, determine the patient factors that are associated with these complications, and evaluate the effects of these complications on postoperative in-hospital mortality and length of stay (LOS). Our hypothesis is that there would be a correlation between specific patient factors and complications and that these complications would adversely correlate to patient postoperative outcomes.
METHODS
DESIGN
We conducted a retrospective analysis of TSAs captured by the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS) database between 2006 and 2010. The NIS is the largest all-payer inpatient database that is currently available to the public in the United States.7
The NIS is a part of the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) and the US Department of Health and Human Services. The NIS database is designed to approximate a 20% sample of US hospitals and the patients they serve, including community, academic, general, and specialty-specific hospitals such as orthopedic hospitals.7 The 2010 update of the NIS database contains discharge data from 1051 hospitals across 45 states, with a representative sample of >39 million inpatient hospital stays.7 The NIS database and its data sources have been independently validated and assessed for quality each year since 1988.8Furthermore, comparative analysis of multiple database elements and distributions has been validated against standard norms, including the National Hospital Discharge Survey.9 The NIS database has been used in numerous published studies.2,10,11
PATIENT SELECTION
The yearly NIS databases from 2006 to 2010 were compiled. Patients aged ≥40 years who underwent a TSA were identified using the International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision (ICD-9), procedural code 81.80. Exclusion criteria were patients with a primary or a secondary diagnosis of humeral or scapular fracture, chronic osteomyelitis, rheumatologic diseases, or evidence of concurrent malignancy (Figure 1).
Native to NIS are patient demographics, including age, sex, and race. Patient comorbidities as described by Elixhauser and colleagues12 are also included in the database.
Continue to: OUTCOMES...
OUTCOMES
The primary outcome of this study was a description of the type and frequency of postoperative complications of TSA. To conduct this analysis, we queried the TSA cohort for specific ICD-9 codes representing acute cardiac, central nervous system, infectious, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, postoperative shock, renal, respiratory, surgical, vascular, and wound complications. The ICD-9 codes used to identify complications were modeled according to previous literature on various surgical applications and were further parsed to reflect only acute postoperative diagnoses13-15(see the Appendix for the comprehensive list of ICD-9 codes).
Two additional outcomes were analyzed, including postoperative mortality and LOS. Postoperative mortality was defined as death occurring prior to discharge. We calculated the average LOS among the complication and the noncomplication cohort.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Patient demographics and target outcomes of the study were analyzed by frequency distribution. Where applicable, the chi-square and the Student’s t tests were used to confirm the statistical difference for dichotomous and continuous variables, respectively. Multivariate regressions were performed after controlling for possible clustering of the data using a generalized estimating equation following a previous analytical methodology.16-20 The results are reported with odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals where applicable, all statistical tests with P ≤ 0.05 were considered to be significant, and all statistical tests were two-sided. We conducted all analyses using SAS, version 9.2 (SAS Institute).
RESULTS
From 2006 to 2010, a weighted sample of 141,973 patients was found to undergo a TSA. After applying our inclusion and exclusion criteria, our study cohort consisted of 125,766 patients (Figure 1).
Continue to: OVERALL TSA COHORT DEMOGRAPHICS...
OVERALL TSA COHORT DEMOGRAPHICS
The average age of the TSA cohort was 69.4 years (standard deviation [SD], 21.20), and 54.1% were females. The cohort had significant comorbidities, with 83.3% of them having at least 1 comorbidity at the time of surgery. Specifically, 31.3% of the patients had 1 comorbidity, 26.5% had 2 comorbidities, and 25.4% had ≥3 comorbidities. Hypertension was the most common comorbidity present in 66.2% of patients, and diabetes was the second most common comorbidity with a prevalence of 16.8%.
COMPLICATION COHORT DEMOGRAPHICS
An overall postoperative complication rate of 6.7% (weighted sample of 8457 patients) was noted in the overall TSA cohort. The TSA cohort was dichotomized into patients who suffered at least 1 complication (weighted, n = 8457) and patients undergoing routine TSAs (weighted, n = 117,308). The average age was significantly higher in the complication vs routine cohort (71.38 vs 69.27 years, P < 0.0001). Similarly, there were significantly more comorbidities (2.51 vs 1.71, P < 0.0001) in the complication cohort.
COMPLICATIONS
We noted a complication rate of 6.7% (weighted sample of 8457 patients). A single complication was noted in 5% of these patients, whereas 1.3% and 0.4% of the patients had 2 and ≥3 complications, respectively. Respiratory abnormalities (2.9%), acute renal failure (0.8%), and cardiac complications (0.8%) were the most prevalent complications after TSA. The list of complications is detailed in Figure 2. Logistic regression analysis of patient characteristics predicting complications showed that advanced age (odds ratio [OR], 2.1 in those aged ≥85 years) and increasing number of comorbidities (≥3; OR, 3.5) were most significant in predicting complications (all P < 0.0001) (Figure 3). Despite the ubiquity of hypertension in this patient population, it was not a significant predictor of complication (OR, 0.9); in contrast, pulmonary disorders (OR, 5.1) and fluid and electrolyte disorders (4.0) were most strongly associated with the development of a postoperative complication after surgery (Figure 4).
EFFECT OF COMPLICATIONS ON LOS
The average length of hospitalization was 2.3 days (95% confidence interval, 2.22-2.25) among the entire cohort. The average LOS was longer in the complication cohort (3.9 days) than in patients who did not have a complication (2.1 days, P < 0.0001). Of the specific complications noted, hemodynamic shock (11.8 days); infectious, most commonly pneumonia (7.6 days); and vascular complications (6.9 days) were associated with the longest hospitalizations. This result is summarized in Figure 5.
MORTALITY
An overall postoperative (in-house) mortality rate of 0.07% was noted (weighted, n = 88). Comparison between the patient cohort that died vs those who survived TSA resulted in significant differences in the rates of complications. Complications that were most significantly different between the cohorts included cardiac (60.47% vs 0.75%, P < 0.0001), postoperative shock (26.61% vs 0.04%, P < 0.0001), and respiratory complications (43.1% vs 2.8%, P < 0.0001). It is important to note that the overall rate of postoperative shock was exceedingly low in the TSA cohort, but it was highly prevalent in the mortality cohort, occurring in 26.61% of patients. A summary of the mortality statistics is presented in Figure 6.
Continue to: DISCUSSION...
DISCUSSION
TSA continues to be associated with high levels of satisfaction;1 as a result, its incidence is increasing.2 As our understanding and efficiency improves nationally, it is imperative that we determine the short-term and longer-term outcomes and complications. In addition, the factors that may affect prognosis must be elucidated to provide a more individualized and effective standard of care. To date, most of the outcome studies of TSA have evaluated long-term outcomes and specific implant-related complications.1,5,6,21,22 Our intent was to evaluate the complications that occur in the postoperative period and their effect on unique “patient care” outcomes. With knowledge of these complications and the predisposing factors, we can better assess patients, risk-stratify, and provide appropriate guidelines.
We noted that complications occurring after TSA are not uncommon, with >6% of patients suffering a postoperative complication. In this study, the number of complications noted was associated with worse patient outcomes. In addition, we noted that patients undergoing a TSA have a significant burden of comorbidities; however, hematologic and fluid disorders (eg, iron deficiency anemia, pulmonary circulatory disorders, and fluid imbalances) were most important in predicting postoperative complications.
Increased LOS in the hospital after TSA was associated with the occurrence of complications. Of all noted complications, shock and infectious and vascular complications led to the longest hospitalizations. Hospital-acquired pneumonia was the most common infectious etiology, while pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis were the most consistent vascular complications. Although seldom studied in the TSA population, a similar finding has been noted in patients after THA. O’Malley and colleagues,23 using the American College of Surgeon’s National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database, identified independent factors that were associated with complications and average prolonged LOS. They noted that the occurrence of major complications was associated with a prolonged LOS. Some, but not all the major complications, included organ space infection, cardiac events, pneumonia, and venous thromboembolic events.23 Therefore, attempts to limit the amount of time spent in hospitals and control the associated costs must focus on managing the incidence of complications.
Postoperative mortality after TSA was uncommon, occurring in 0.07% of the patients in this study. The low incidence of mortality noted in this study is probably related to the fact that our data represent mortality, whereas in the hospital and, unlike most mortality studies, it does not account for patient demise that may occur in the months after surgery. Other reports have noted that mortality occurs in <1.5% of these patients.24-28 Singh and colleagues25 observed in their evaluation of perioperative mortality after TSA a mortality rate of 0.8% with 90 days after 4380 shoulder replacements performed at their institution. Using multivariate analysis, they were able to identify associations between mortality and increasing American Society of Anesthesiology (ASA) class and Charlson Comorbidity Index. These results in relation to ours would indicate that the majority of patients who die after shoulder arthroplasty do so after initial discharge. Although we could not determine a causal relationship between mortality and patient comorbidities, we noted that certain complications strongly correlated with mortality. In patients who died, there was a relatively high incidence of cardiac (60.5%) and respiratory (43.1%) complications. Similarly, although postoperative shock was almost nonexistent in the patients who survived surgery (0.04%), it was much more common in the patients who suffered mortality (26.6%).
This study is not without limitations. Data were extracted from a national database, therefore precluding the inclusion of specific details of surgery and functional assessment. Inherent to ICD-9 coding, we were unable to assess the exact detail and severity of complications. For instance, we cannot be certain what criteria were used to define “acute renal failure” for each patient. This study is retrospective in nature and therefore adequate randomization and standardization of patients is not possible. Similarly, the nature of the database may not allow for exacting our inclusion and exclusion criteria. However, the large sample size of the patient population lessens the chance of potential biases and type 2 errors. Prior to October 2010, reverse shoulder arthroplasty was coded under the ICD-9procedural code 81.80 as TSA. Therefore, there is some overlap between TSA and reverse shoulder arthroplasty in our data. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty is now coded under ICD-9 procedural code 81.88. It is possible that results may differ if reverse shoulder arthroplasty were excluded from our patient cohort. This can be an area of future research.
CONCLUSION
Although much is known about the long-term hardware and functional complications after TSA, in this study, we have attempted to broaden the understanding of perioperative complications and the associated sequelae. Complications are common after TSA surgery and are related to adverse outcomes. In the setting of healthcare changes, the surgeon and the patient must understand the cause, types, incidence, and outcomes of medical and surgical complications after surgery. This allows for more accurate “standard of care” metrics. Further large-volume multicenter studies are needed to gain further insight into the short- and long-term outcomes of TSA.
1. Fox TJ, Cil A, Sperling JW, Sanchez-Sotelo J, Schleck CD, Cofield RH. Survival of the glenoid component in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18(6):859-863. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2008.11.020.
2. Kim SH, Wise BL, Zhang Y, Szabo RM. Increasing incidence of shoulder arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(24):2249-2254. doi:10.2106/JBJS.J.01994.
3. Ahmadi S, Lawrence TM, Sahota S, et al. The incidence and risk factors for blood transfusion in revision shoulder arthroplasty: our institution's experience and review of the literature. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(1):43–48. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2013.03.010.
4. Boyd AD Jr, Aliabadi P, Thornhill TS. Postoperative proximal migration in total shoulder arthroplasty. Incidence and significance. J Arthroplasty. 1991;6(1):31-37. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(06)80154-3.
5. Choi T, Horodyski M, Struk AM, Sahajpal DT, Wright TW. Incidence of early radiolucent lines after glenoid component insertion for total shoulder arthroplasty: a radiographic study comparing pressurized and unpressurized cementing techniques. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(3):403-408. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2012.05.041.
6. Favard L, Katz D, Colmar M, Benkalfate T, Thomazeau H, Emily S. Total shoulder arthroplasty - arthroplasty for glenohumeral arthropathies: results and complications after a minimum follow-up of 8 years according to the type of arthroplasty and etiology. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(4 Suppl):S41-S47. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2012.04.003.
7. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Introduction to the HCUP national inpatient sample (NIS) 2012. https://hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/nation/nis/NISIntroduction2012.pdf 2012. Accessed June 9, 2013.
8. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. HCUP quality control procedures. https://hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/quality.pdf. Accessed June 15, 2013.
9. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Comparative analysis of HCUP and NHDS inpatient discharge data: technical supplement 13. https://archive.ahrq.gov/research/data/hcup/nhds/niscomp.html. Accessed June 15, 2013.
10. Rajaee SS, Trofa D, Matzkin E, Smith E. National trends in primary total hip arthroplasty in extremely young patients: a focus on bearing surface usage. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(10):1870-1878. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2012.04.006.
11. Bozic KJ, Kurtz S, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of bearing surface usage in total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(7):1614-1620. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.01220.
12. Elixhauser A, Steiner C, Harris DR, Coffey RM. Comorbidity measures for use with administrative data. Med Care. 1998;36(1):8-27. doi:10.1097/00005650-199801000-00004.
13. Cahill KS, Chi JH, Day A, Claus EB. Prevalence, complications, and hospital charges associated with use of bone-morphogenetic proteins in spinal fusion procedures. JAMA. 2009;302(1):58-66. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.956.
14. Lin CA, Kuo AC, Takemoto S. Comorbidities and perioperative complications in HIV-positive patients undergoing primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(11):1028-1036. doi:10.2106/JBJS.L.00269.
15. Rasouli MR, Maltenfort MG, Ross D, Hozack WJ, Memtsoudis SG, Parvizi J. Perioperative morbidity and mortality following bilateral total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(1):142-148. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2013.04.001.
16. Begg CB, Riedel ER, Bach PB, et al. Variations in morbidity after radical prostatectomy. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(15):1138-1144. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa011788.
17. Hu JC, Gold KF, Pashos CL, Mehta SS, Litwin MS. Temporal trends in radical prostatectomy complications from 1991 to 1998. J Urol. 2003;169(4):1443-1448. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000056046.16588.e4.
18. Abdollah F, Sun M, Schmitges J, et al. Surgical caseload is an important determinant of continent urinary diversion rate at radical cystectomy: a population-based study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(9):2680-2687. doi:10.1245/s10434-011-1618-2.
19. Panageas KS, Schrag D, Riedel E, Bach PB, Begg CB. The effect of clustering of outcomes on the association of procedure volume and surgical outcomes. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139(8):658-665. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-139-8-200310210-00009.
20. Joice GA, Deibert CM, Kates M, Spencer BA, McKiernan JM. "Never events”: centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services complications after radical cystectomy. Urology. 2013;81(3):527-532. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2012.09.050.
21. Taunton MJ, McIntosh AL, Sperling JW, Cofield RH. Total shoulder arthroplasty with a metal-backed, bone-ingrowth glenoid component. Medium to long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(10):2180-2188. doi:10.2106/JBJS.G.00966.
22. Raiss P, Schmitt M, Bruckner T, et al. Results of cemented total shoulder replacement with a minimum follow-up of ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(23):e1711-e1710. doi:10.2106/JBJS.K.00580.
23. O'Malley NT, Fleming FJ, Gunzler DD, Messing SP, Kates SL. Factors independently associated with complications and length of stay after hip arthroplasty: analysis of the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(10):1832-1837. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2012.04.025.
24. White CB, Sperling JW, Cofield RH, Rowland CM. Ninety-day mortality after shoulder arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(7):886-888. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(03)00269-9.
25. Singh JA, Sperling JW, Cofield RH. Ninety day mortality and its predictors after primary shoulder arthroplasty: an analysis of 4,019 patients from 1976-2008. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:231. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-12-231.
26. Fehringer EV, Mikuls TR, Michaud KD, Henderson WG, O'Dell JR. Shoulder arthroplasties have fewer complications than hip or knee arthroplasties in US veterans. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(3):717-722. doi:10.1007/s11999-009-0996-2.
27. Farmer KW, Hammond JW, Queale WS, Keyurapan E, McFarland EG. Shoulder arthroplasty versus hip and knee arthroplasties: a comparison of outcomes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;455:183-189. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000238839.26423.8d.
28. Farng E, Zingmond D, Krenek L, Soohoo NF. Factors predicting complication rates after primary shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(4):557-563. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2010.11.005.
1. Fox TJ, Cil A, Sperling JW, Sanchez-Sotelo J, Schleck CD, Cofield RH. Survival of the glenoid component in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18(6):859-863. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2008.11.020.
2. Kim SH, Wise BL, Zhang Y, Szabo RM. Increasing incidence of shoulder arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(24):2249-2254. doi:10.2106/JBJS.J.01994.
3. Ahmadi S, Lawrence TM, Sahota S, et al. The incidence and risk factors for blood transfusion in revision shoulder arthroplasty: our institution's experience and review of the literature. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(1):43–48. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2013.03.010.
4. Boyd AD Jr, Aliabadi P, Thornhill TS. Postoperative proximal migration in total shoulder arthroplasty. Incidence and significance. J Arthroplasty. 1991;6(1):31-37. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(06)80154-3.
5. Choi T, Horodyski M, Struk AM, Sahajpal DT, Wright TW. Incidence of early radiolucent lines after glenoid component insertion for total shoulder arthroplasty: a radiographic study comparing pressurized and unpressurized cementing techniques. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(3):403-408. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2012.05.041.
6. Favard L, Katz D, Colmar M, Benkalfate T, Thomazeau H, Emily S. Total shoulder arthroplasty - arthroplasty for glenohumeral arthropathies: results and complications after a minimum follow-up of 8 years according to the type of arthroplasty and etiology. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(4 Suppl):S41-S47. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2012.04.003.
7. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Introduction to the HCUP national inpatient sample (NIS) 2012. https://hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/nation/nis/NISIntroduction2012.pdf 2012. Accessed June 9, 2013.
8. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. HCUP quality control procedures. https://hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/quality.pdf. Accessed June 15, 2013.
9. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Comparative analysis of HCUP and NHDS inpatient discharge data: technical supplement 13. https://archive.ahrq.gov/research/data/hcup/nhds/niscomp.html. Accessed June 15, 2013.
10. Rajaee SS, Trofa D, Matzkin E, Smith E. National trends in primary total hip arthroplasty in extremely young patients: a focus on bearing surface usage. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(10):1870-1878. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2012.04.006.
11. Bozic KJ, Kurtz S, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of bearing surface usage in total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(7):1614-1620. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.01220.
12. Elixhauser A, Steiner C, Harris DR, Coffey RM. Comorbidity measures for use with administrative data. Med Care. 1998;36(1):8-27. doi:10.1097/00005650-199801000-00004.
13. Cahill KS, Chi JH, Day A, Claus EB. Prevalence, complications, and hospital charges associated with use of bone-morphogenetic proteins in spinal fusion procedures. JAMA. 2009;302(1):58-66. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.956.
14. Lin CA, Kuo AC, Takemoto S. Comorbidities and perioperative complications in HIV-positive patients undergoing primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(11):1028-1036. doi:10.2106/JBJS.L.00269.
15. Rasouli MR, Maltenfort MG, Ross D, Hozack WJ, Memtsoudis SG, Parvizi J. Perioperative morbidity and mortality following bilateral total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(1):142-148. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2013.04.001.
16. Begg CB, Riedel ER, Bach PB, et al. Variations in morbidity after radical prostatectomy. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(15):1138-1144. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa011788.
17. Hu JC, Gold KF, Pashos CL, Mehta SS, Litwin MS. Temporal trends in radical prostatectomy complications from 1991 to 1998. J Urol. 2003;169(4):1443-1448. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000056046.16588.e4.
18. Abdollah F, Sun M, Schmitges J, et al. Surgical caseload is an important determinant of continent urinary diversion rate at radical cystectomy: a population-based study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(9):2680-2687. doi:10.1245/s10434-011-1618-2.
19. Panageas KS, Schrag D, Riedel E, Bach PB, Begg CB. The effect of clustering of outcomes on the association of procedure volume and surgical outcomes. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139(8):658-665. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-139-8-200310210-00009.
20. Joice GA, Deibert CM, Kates M, Spencer BA, McKiernan JM. "Never events”: centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services complications after radical cystectomy. Urology. 2013;81(3):527-532. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2012.09.050.
21. Taunton MJ, McIntosh AL, Sperling JW, Cofield RH. Total shoulder arthroplasty with a metal-backed, bone-ingrowth glenoid component. Medium to long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(10):2180-2188. doi:10.2106/JBJS.G.00966.
22. Raiss P, Schmitt M, Bruckner T, et al. Results of cemented total shoulder replacement with a minimum follow-up of ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(23):e1711-e1710. doi:10.2106/JBJS.K.00580.
23. O'Malley NT, Fleming FJ, Gunzler DD, Messing SP, Kates SL. Factors independently associated with complications and length of stay after hip arthroplasty: analysis of the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(10):1832-1837. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2012.04.025.
24. White CB, Sperling JW, Cofield RH, Rowland CM. Ninety-day mortality after shoulder arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(7):886-888. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(03)00269-9.
25. Singh JA, Sperling JW, Cofield RH. Ninety day mortality and its predictors after primary shoulder arthroplasty: an analysis of 4,019 patients from 1976-2008. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:231. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-12-231.
26. Fehringer EV, Mikuls TR, Michaud KD, Henderson WG, O'Dell JR. Shoulder arthroplasties have fewer complications than hip or knee arthroplasties in US veterans. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(3):717-722. doi:10.1007/s11999-009-0996-2.
27. Farmer KW, Hammond JW, Queale WS, Keyurapan E, McFarland EG. Shoulder arthroplasty versus hip and knee arthroplasties: a comparison of outcomes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;455:183-189. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000238839.26423.8d.
28. Farng E, Zingmond D, Krenek L, Soohoo NF. Factors predicting complication rates after primary shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(4):557-563. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2010.11.005.
TAKE HOME POINTS
- Medical complications are common (6.7%) after total shoulder arthroplasty.
- Age and preoperative medical comorbidities increased the risk of a postoperative complication.
- The most frequent medical complications are respiratory, renal, and cardiac.
- Length of stay was effected most by shock, infections, and vascular complications.
- Mortality was associated with major complications such as, shock, central nervous system, cardiac, vascular, and respiratory complications.
Outcomes After Peripheral Nerve Block in Hip Arthroscopy
ABSTRACT
Pain control following hip arthroscopy presents a significant clinical challenge, with postoperative pain requiring considerable opioid use. Peripheral nerve blocks (PNBs) have emerged as one option to improve pain and limit the consequences of opioid use. The purpose of this study is to provide a comprehensive review of outcomes associated with PNB in hip arthroscopy. We hypothesize that the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy leads to improved outcomes and is associated with few complications. A systematic review of PubMed, Medline, Scopus, and Embase databases was conducted through January 2015 for English-language articles reporting outcome data, with 2 reviewers independently reviewing studies for inclusion. When available, similar outcomes were combined to generate frequency-weighted means. Six studies met the inclusion criteria for this review, reporting on 710 patients undergoing hip arthroscopy. The mean ages were 37.0 and 37.7 years for the PNB and comparator groups, respectively, with a reported total of 281 (40.5%) male and 412 (59.5%) female patients. Postoperative post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) pain was consistently reduced in the PNB group, with the use of a lower morphine equivalent dose and lower rates of inpatient admission, compared with that in the control groups. Postoperative nausea and/or vomiting as well as PACU discharge time showed mixed results. High satisfaction and few complications were reported. In conclusion, PNB is associated with reductions in postoperative pain, analgesic use, and the rate of inpatient admissions, though similar rates of nausea/vomiting and time to discharge were reported. Current PNB techniques are varied, and future research efforts should focus on examining which of these methods provides the optimal risk-benefit profile in hip arthroscopy.
Continue to: Hip arthroscopy has emerged...
Hip arthroscopy has emerged as a useful procedure in the diagnosis and treatment of hip pathology,1-8 experiencing a substantial rise in popularity in recent years, with the number of procedures growing by a factor of 18 from 1999 to 20099 and 25 from 2006 to 2013.10 Though hip arthroscopy is beneficial in many cases, marked postoperative pain has presented a substantial challenge, with patients requiring considerable doses of opiate-based medications in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU).11,12 Increased narcotic use carries increased side effects, including postoperative nausea and vomiting,13 and poorly managed pain leads to increased unplanned admissions.14 Furthermore, patients with chronic hip pain and long-term opioid use may experience heightened and prolonged pain following the procedure, owing to medication tolerance and reduced opioid efficacy in this setting.15
Several pain control strategies have been employed in patients undergoing hip arthroscopy. General anesthesia16,17 and combined spinal epidural (CSE)18 are commonly used. However, such techniques rely heavily on opioids for postoperative pain control,11 and epidural anesthesia commonly requires adjunctive treatments (eg, neuromuscular blockade) to ensure muscle relaxation for joint distraction.19 One technique that has been employed recently is peripheral nerve block (PNB), which has been associated with a significant decrease in postoperative opioid use and nausea and vomiting.13,20 This method has proven successful in other fields of arthroscopy, including shoulder arthroscopy, in which it resulted in faster recovery, reduced opioid consumption,21 and demonstrated cost-effectiveness22 compared with general anesthesia and knee arthroscopy.23-26 As it is a relatively new field, little is known about the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy.
The goal of this systematic review was to comprehensively review the studies reporting on PNB in hip arthroscopy. We specifically focused on outcomes, including postoperative pain; analgesic use; nausea, vomiting, and antiemetic use; discharge time; inpatient admission; and patient satisfaction, as well as the complications associated with the use of PNB. Our knowledge of outcomes associated with PNB in hip arthroscopy is based on a few individual studies that have reported on small groups of patients using a variety of outcome measures and other findings. Furthermore, each of these studies commonly reflects the experience of an individual surgeon at a single institution and, when taken alone, may not be an accurate representation of the more general outcomes associated with PNB. A comprehensive review of such studies will provide surgeons, anesthesiologists, and patients with a better understanding of the anticipated outcomes of using PNB in hip arthroscopy. We hypothesize that the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy leads to improved outcomes and is associated with few complications.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A systematic review of outcomes associated with PNB in hip arthroscopy was performed using the available English-language literature in accordance with the guidelines laid out by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses statement and included studies retrieved from the PubMed, Medline, Scopus, and Embase computerized literature databases. Searches were executed comprising all years from database inception through January 2015. Articles were retrieved by an electronic search of medical subject headings and keyword terms and their respective combinations (Table 1). The inclusion criteria for studies in this systematic review were studies that (1) were written in the English language and (2) reported explicit outcome data. The exclusion criteria were (1) review articles, meta-analyses, case reports, abstracts/conference papers, comments/letters, or technique articles without reported patient data and (2) basic research, biomechanics, or animal/cadaveric studies without reported patient data.
Table 1. Search Terms Entered to Identify English-Language Studies Through January 2015
Database | Search terms |
PubMed, Scopus | Keyword: (hip AND arthroscopy) AND (pain control OR pain management OR pain regimen OR nerve block OR spinal anesthesia OR regional anesthesia OR general anesthesia) |
Medline | MeSH (includes both MeSH terms and keywords): (Hip) AND (Arthroscopy) AND (“Pain Management” OR “Anesthesia, General” OR “Anesthesia” OR “Anesthesia, Inhalation”, OR “Balanced Anesthesia” OR “Anesthesia, Local” OR “Anesthesia, Spinal” OR “Anesthesia, Conduction” OR “Nerve Block”) |
Embase | MeSH (includes both MeSH terms and keywords): (Hip) AND (Arthroscopy) AND (“Pain Management” OR “General Anesthesia” OR “Anesthesia” OR “Inhalation Anesthesia”, OR “Balanced Anesthesia” OR “Local Anesthesia” OR “Spinal Anesthesia” OR “Regional Anesthesia” OR “Nerve Block”) |
The literature search strategy is outlined in the Figure. The initial title search yielded a subset of possible articles that were then further included or excluded on the basis of the contents of the article’s abstract, wherein articles were again selected on the basis of the aforementioned inclusion and exclusion criteria. Articles selected in both the title and abstract phases underwent full-text review, during which the full text of each qualifying article was reviewed. In addition, the reference sections from articles undergoing full-text review were scanned to identify any additional studies that had not been identified in the original literature search. Appropriate studies for final inclusion were then selected at this stage. The title, abstract, and full-text selection process were performed by 2 of the study authors (Dr. Steinhaus and Dr. Lynch), with any discrepancies being discussed and resolved by mutual agreement.
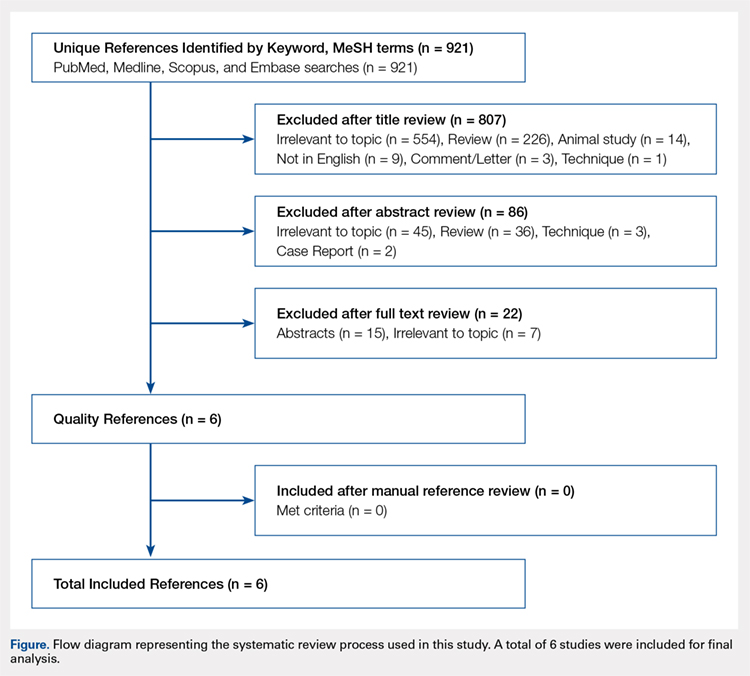
Continue to: For all 6 included studies...
For all 6 included studies,16-18,27-29 data were collected regarding the study specifics, patients included, and outcomes measured in the study. The journal of publication, type of study, level of evidence, and type of PNB, as well as the presence of a comparator group were noted (Table 2). Patient information included the number of patients at baseline and follow-up, mean age, gender, weight, height, body mass index, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) status, and the specific procedures performed. In addition, data were collected on outcomes, including postoperative pain, as well as secondary outcomes and additional findings reported by the studies (Table 3). Where possible, weighted averages were calculated across all studies to obtain aggregate data.
RESULTS
STUDY INCLUSION
Six studies, all published between 2012 and 2014, were included in this systematic review (Table 2). Three studies involved lumbar plexus block, 2 studies involved femoral nerve block, and 1 study evaluated fascia iliaca block. Two studies used a control group of patients who received only general anesthesia (compared with the treatment group who received both general anesthesia and PNB); another study compared intravenous morphine with PNB; and 1 study compared CSE alone with PNB in addition to epidural.
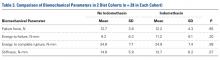
DEMOGRAPHIC DATA
Demographic data from the included studies are presented in Table 2. In total, 710 and 549 patients were evaluated at baseline and final follow-up, respectively, which represents a follow-up rate of 77%. The frequency-weighted mean age of patients receiving PNB was 37.0 years compared with 37.7 years in the comparison groups, and the studies reported a total of 281 (40.5%) male and 412 (59.5%) female patients. The procedures performed were heterogeneously reported; therefore, totals were not tabulated, although the reported procedures included osteochondroplasty, labral débridement, labral and/or capsular repair, gluteus minimus repair, and synovectomy.
POSTOPERATIVE PAIN
Four studies reported on postoperative pain, and these data are presented in Table 3. In a retrospective study of patients receiving femoral nerve block in addition to general anesthesia, Dold and colleagues16 noted postoperative pain at 0, 15, 30, 45, and 60 minutes following arrival in the PACU, and discovered a statistically significantly lower level of pain at 60 minutes compared with inpatients receiving general anesthesia alone. YaDeau and colleagues18 found a significantly lower level of pain at rest in the PACU for those receiving CSE and lumbar plexus blockade compared with those receiving CSE alone. This significant difference did not persist at 24 hours or 6 months after the procedure, nor did it exist for pain with movement at any time point. Similarly, Schroeder and colleagues17 examined patients receiving general anesthesia and lumbar plexus block and found a significant reduction in pain immediately postoperatively in the PACU, though these effects disappeared the day following the procedure. Krych and colleagues27 also reported on postoperative pain in patients undergoing fascia iliaca blockade, although they did not include a comparator group. Outcome comparison between patients who received PNB and controls in the PACU and 1 day following the procedure are presented in Table 4.
ANALGESIC USE
Four studies reported on analgesic use after PNB, and these data are presented in Table 3. Dold and colleagues16 noted analgesic use intraoperatively, in the PACU, and in the surgical day care unit (SDCU). These authors found a significant reduction in morphine equivalent dose given in the operating room and in the PACU in the group receiving PNB, with a nonsignificant trend toward lower use of oxycodone in the SDCU. Schroeder and colleagues17 similarly reported significant reductions in morphine equivalent dose intraoperatively and in Phase I recovery for patients receiving PNB, and these differences disappeared in Phase II recovery as well as intraoperatively if the block dose was considered. In addition, these authors found a significant reduction in the use of fentanyl and hydromorphone in the operating room in the PNB group, as well as a significant reduction in the proportion of patients receiving ketorolac in the operating room or PACU. Finally, YaDeau and colleagues18 reported total analgesic usage in the PACU among PNB patients compared with those receiving CSE alone and showed a strong trend toward reduced use in the PNB group, although this difference was not significant (P = .051). PACU analgesic use is presented in Table 4.
Continue to: Postoperative nausea...
POSTOPERATIVE NAUSEA/VOMITING AND ANTIEMETIC USE
Five studies presented data on nausea, vomiting, or antiemetic use following PNB and are shown in Table 3. YaDeau and colleagues18 reported nausea among 34% of patients in the PNB group, compared with 20% in the control group, vomiting in 2% and 7%, respectively, and antiemetic use in 12% of both groups. Dold and colleagues16 identified a similar trend, with 41.1% of patients in the PNB group and 32.5% of patients in the control group experiencing postoperative nausea or vomiting, while Krych and colleagues27 noted only 10% of PNB patients with mild nausea and none requiring antiemetic use. In their study of patients receiving PNB, Schroeder and colleagues17 found a significant reduction in antiemetic use among PNB patients compared with those receiving general anesthesia alone. Similarly, Ward and colleagues29 noted a significant difference in postoperative nausea, with 10% of patients in the PNB group experiencing postoperative nausea compared with 75% of those in the comparator group who received intravenous morphine. The mean percentage of patients experiencing postoperative nausea and/or vomiting is shown in Table 4.
DISCHARGE TIME
Four studies presented data on discharge time from the PACU and are summarized in Table 3. Three of these studies included a comparator group. Both Dold and colleagues16 and YaDeau and colleagues18 reported an increase in the time to discharge for patients receiving PNB, although these differences were not significant. The study by Ward and colleagues,29 on the other hand, noted a significant reduction in the time to discharge for the PNB group. In addition to these studies, Krych and colleagues27 examined the time from skin closure to discharge for patients receiving PNB, noting a mean 199 minutes for the patients in their study. Mean times to discharge for the PNB and control groups are presented in Table 4.
INPATIENT ADMISSION
Four studies presented data on the proportion of study participants who were admitted as inpatients, and these data are shown in Table 3. Dold and colleagues16 reported no inpatient admissions in their PNB group compared with 5.0% for the control group (both cases of pain control), while YaDeau and colleagues18 found that 3 admissions occurred, with 2 in the control group (1 for oxygen desaturation and the other for intractable pain and nausea) and 1 from the PNB group (epidural spread and urinary retention). Two additional studies reported data on PNB groups alone. Krych and colleagues27 observed no overnight admissions in their study, while Nye and colleagues28 reported 1 readmission for bilateral leg numbness and weakness due to epidural spread, which resolved following discontinuation of the block. The mean proportion of inpatient admissions is presented in Table 4.
SATISFACTION
A total of 3 studies examined patient satisfaction, and these data are presented in Table 3. In their study, Ward and colleagues29 reported a significantly greater rate of satisfaction at 1 day postoperatively among the patients in the PNB group (90%) than among patients who received intravenous morphine (25%) (P < .0001). Similarly, YaDeau and colleagues18 noted greater satisfaction among the PNB group than among the control group, with PNB patients rating their satisfaction at a mean of 8.6 and control patients at a mean of 7.9 on a 10-point scale (0-10) 24 hours postoperatively, although this difference was not significant. Finally, Krych and colleagues27 found that 67% of patients were “very satisfied” and 33% were “satisfied”, based on a Likert scale.
COMPLICATIONS
Four studies presented data on complications, and these findings are summarized in Table 3. In their work, Nye and colleagues28 reported most extensively on complications associated with PNB. Overall, the authors found a rate of significant complications of 3.8%. In terms of specific complications, they noted local anesthetic systemic toxicity (0.9%), epidural spread (0.5%), sensory or motor deficits (9.4%), falls (0.5%), and catheter issues. In their study of patients receiving PNB and CSE, YaDeau and colleagues18 identified 1 patient in the PNB group with epidural spread and urinary retention, while they noted 1 case of oxygen desaturation and another case of intractable pain and nausea in the group receiving CSE alone, all 3 of which required inpatient admission. They found no permanent adverse events attributable to the PNB. In another study, Dold and colleagues16 observed no complications in patients receiving PNB compared with those in 2 admissions in the control group for inadequate pain control. Similarly, Krych and colleagues27 identified no complications in patients who received PNB in their study.
DISCUSSION
Hip arthroscopy has experienced a substantial gain in popularity in recent years, emerging as a beneficial technique for both the diagnosis and treatment of diverse hip pathologies in patients spanning a variety of demographics. Nevertheless, postoperative pain control, as well as medication side effects and unwanted patient admissions, present major challenges to the treating surgeon. As an adjuvant measure, peripheral nerve block represents one option to improve postoperative pain management, while at the same time addressing the adverse effects of considerable opioid use, which is commonly seen in these patients. Early experience with this method in hip arthroscopy was reported in a case series by Lee and colleagues.12 In an attempt to reduce postoperative pain, as well as limit the adverse effects and delay in discharge associated with considerable opioid use in the PACU, the authors used preoperative paravertebral blocks of L1 and L2 in 2 patients requiring hip arthroscopy with encouraging results. Since then, a number of studies have attempted the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy.16-18,27-29 However, we were unable to identify any prior reviews reporting on peripheral nerve blockade in hip arthroscopy, and thus this study is unique in providing a greater understanding of the outcomes associated with PNB use.
In general, we found that PNB was associated with improved outcomes. Based on the studies included in this review, there was a statistically significantly lower level of pain in the PACU for femoral nerve block (compared with general anesthesia alone)16 and lumbar plexus blockade (compared with general anesthesia17 and CSE18 alone). Nevertheless, these effects are likely short-lived, with differences disappearing the day following the procedure. In terms of analgesic use, 2 studies report significant reductions in analgesic use intraoperatively and in the PACU/Phase I recovery,16,17 with a third reporting a strong trend toward reduced analgesic use in the PACU (P = .051).18 Finally, we report fewer admissions for the PNB group, as well as high rates of satisfaction and few complications across these studies.
Continue to: Unlike these measures...
Unlike these measures, postoperative nausea, vomiting, and antiemetic use, as well as time to discharge, showed more mixed results. With regard to nausea/vomiting, 2 studies16,18 reported nonsignificantly increased rates in the PNB group, whereas others reported significant reductions in nausea/vomiting29 and in the proportion of patients receiving antiemetics.17 Similarly, mixed results were seen in terms of patient discharge time from the PACU. Two studies16,18 reported a nonsignificant increase in time to discharge for the PNB group, while another29 noted a significant reduction for the PNB group compared with those receiving intravenous morphine. These mixed results were surprising, as we expected reductions in opioid use to result in fewer instances of nausea/vomiting and a quicker time to discharge. The reasons underlying these findings are not clear, although it has been suggested that current discharge guidelines and clinical pathways limit the ability to take advantage of the accelerated timeline offered by regional anesthesia.16,30 As experience with PNB grows, our guidelines and pathways are likely to adapt to capitalize on these advantages, and future studies may show more reliable improvements in these measures.
While rare, the risk of bleeding requiring blood transfusion following hip arthroscopy is one of the most common complications of this procedure. Though the studies included in this review did not report on the need for transfusion, a recent study by Cvetanovich and colleagues10 used a national database and found that, of patients undergoing hip arthroscopy (n = 1338), 0.4% (n = 5) had bleeding requiring a transfusion, with 0.3% (n = 4) requiring return to the operating room, similar to an earlier study by Clarke and colleagues,31 who noted bleeding from the portal site in 0.4% of hip arthroscopy patients. In terms of risk factors, Cvetanovich and colleagues10 found that ASA class, older age, and prior cardiac surgery were significantly associated with minor and overall complications, whereas both regional anesthesia/monitored anesthesia care and alcohol consumption of >2 drinks a day were significantly associated with minor complications, including bleeding requiring transfusions. They noted, however, that these risk factors accounted for only 5% of the variance in complication rates, indicating that other unidentified variables better explained the variance in complication rates. These authors concluded that complications associated with hip arthroscopy are so rare that we may not be able to predict which risk factors or anesthesia types are more likely to cause them. Further characterization of bleeding following hip arthroscopy and its associated risk factors is a valuable area for future research.
LIMITATIONS
Our study contains a number of limitations. This review included studies whose level of evidence varied from I to IV; therefore, our study is limited by any bias or heterogeneity introduced in patient recruitment, selection, variability of technique, data collection, and analysis used in these studies. This heterogeneity is most apparent in the block types and comparator groups. Furthermore, several different outcome measures were reported across the 6 studies used in this review, which decreased the relevance of any one of these individual outcomes. Finally, given the limited data that currently exist for the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy, we are unable to note meaningful differences between various types of PNBs, such as differences in postoperative pain or other measures such as quadriceps weakness, which can accompany femoral nerve block.12 While it is important to read our work with these limitations in mind, this systematic review is, to our knowledge, the only comprehensive review to date of studies reporting on PNB in hip arthroscopy, providing clinicians and patients with a greater understanding of the associated outcomes across these studies.
CONCLUSION
This systematic review shows improved outcomes and few complications with PNB use in hip arthroscopy, with reductions in postoperative pain, analgesic use, and the rate of inpatient admissions. Although opioid use was reduced in these studies, we found similar rates of postoperative nausea/vomiting as well as similar time to discharge from the PACU, which may reflect our continued reliance on outdated discharge guidelines and clinical pathways. Current attempts to provide peripheral nerve blockade are quite varied, with studies targeting femoral nerve, fascia iliaca, L1/L2 paravertebral, and lumbar plexus blockade. Future research efforts with a large prospective trial investigating these techniques should focus on which of these PNBs presents the optimal risk-benefit profile for hip arthroscopy patients and thus appropriately address the clinical questions at hand.
This paper will be judged for the Resident Writer’s Award.
- Baber YF, Robinson AH, Villar RN. Is diagnostic arthroscopy of the hip worthwhile? A prospective review of 328 adults investigated for hip pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81:600-603.
- Byrd JW, Jones KS. Arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement: minimum 2-year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2011;27:1379-1388.
- Larson CM, Giveans MR. Arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement: early outcomes measures. Arthroscopy. 2008;24:540-546.
- O'Leary JA, Berend K, Vail TP. The relationship between diagnosis and outcome in arthroscopy of the hip. Arthroscopy. 2001;17:181-188.
- Philippon M, Schenker M, Briggs K, Kuppersmith D. Femoroacetabular impingement in 45 professional athletes: associated pathologies and return to sport following arthroscopic decompression. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007;15:908-914.
- Potter BK, Freedman BA, Andersen RC, Bojescul JA, Kuklo TR, Murphy KP. Correlation of Short Form-36 and disability status with outcomes of arthroscopic acetabular labral debridement. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33:864-870.
- Robertson WJ, Kadrmas WR, Kelly BT. Arthroscopic management of labral tears in the hip: a systematic review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;455:88-92.
- Yusaf MA, Hame SL. Arthroscopy of the hip. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2008;7:269-274.
- Colvin AC, Harrast J, Harner C. Trends in hip arthroscopy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94:e23.
- Cvetanovich GL, Chalmers PN, Levy DM, et al. Hip arthroscopy surgical volume trends and 30-day postoperative complications. Arthroscopy. 2016 Apr 8. [Epub before print].
- Baker JF, Byrne DP, Hunter K, Mulhall KJ. Post-operative opiate requirements after hip arthroscopy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19:1399-1402.
- Lee EM, Murphy KP, Ben-David B. Postoperative analgesia for hip arthroscopy: combined L1 and L2 paravertebral blocks. J Clin Anesth. 2008;20:462-465.
- Ganesh A, Rose JB, Wells L, et al. Continuous peripheral nerve blockade for inpatient and outpatient postoperative analgesia in children. Anesth Analg. 2007;105:1234-1242.
- Williams BA, Kentor ML, Vogt MT, et al. Femoral-sciatic nerve blocks for complex outpatient knee surgery are associated with less postoperative pain before same-day discharge: a review of 1,200 consecutive cases from the period 1996-1999. Anesthesiology. 2003;98:1206-1213.
- Zywiel MG, Stroh DA, Lee SY, Bonutti PM, Mont MA. Chronic opioid use prior to total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93:1988-1993.
- Dold AP, Murnaghan L, Xing J, Abdallah FW, Brull R, Whelan DB. Preoperative femoral nerve block in hip arthroscopic surgery: a retrospective review of 108 consecutive cases. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42:144-149.
- Schroeder KM, Donnelly MJ, Anderson BM, Ford MP, Keene JS. The analgesic impact of preoperative lumbar plexus blocks for hip arthroscopy. A retrospective review. Hip Int. 2013;23:93-98.
- YaDeau JT, Tedore T, Goytizolo EA, et al. Lumbar plexus blockade reduces pain after hip arthroscopy: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Anesth Analg. 2012;115:968-972.
- Smart LR, Oetgen M, Noonan B, Medvecky M. Beginning hip arthroscopy: indications, positioning, portals, basic techniques, and complications. Arthroscopy. 2007;23:1348-1353.
- Stevens M, Harrison G, McGrail M. A modified fascia iliaca compartment block has significant morphine-sparing effect after total hip arthroplasty. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2007;35:949-952.
- Lehmann LJ, Loosen G, Weiss C, Schmittner MD. Interscalene plexus block versus general anaesthesia for shoulder surgery: a randomized controlled study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25:255-261.
- Gonano C, Kettner SC, Ernstbrunner M, Schebesta K, Chiari A, Marhofer P. Comparison of economical aspects of interscalene brachial plexus blockade and general anaesthesia for arthroscopic shoulder surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2009;103:428-433.
- Hadzic A, Karaca PE, Hobeika P, et al. Peripheral nerve blocks result in superior recovery profile compared with general anesthesia in outpatient knee arthroscopy. Anesth Analg. 2005;100:976-981.
- Hsu LP, Oh S, Nuber GW, et al. Nerve block of the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve in knee arthroscopy: a prospective, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95:1465-1472.
- Montes FR, Zarate E, Grueso R, et al. Comparison of spinal anesthesia with combined sciatic-femoral nerve block for outpatient knee arthroscopy. J Clin Anesth. 2008;20:415-420.
- Wulf H, Lowe J, Gnutzmann KH, Steinfeldt T. Femoral nerve block with ropivacaine or bupivacaine in day case anterior crucial ligament reconstruction. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2010;54:414-420.
- Krych AJ, Baran S, Kuzma SA, Smith HM, Johnson RL, Levy BA. Utility of multimodal analgesia with fascia iliaca blockade for acute pain management following hip arthroscopy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22:843-847.
- Nye ZB, Horn JL, Crittenden W, Abrahams MS, Aziz MF. Ambulatory continuous posterior lumbar plexus blocks following hip arthroscopy: a review of 213 cases. J Clin Anesth. 2013;25:268-274.
- Ward JP, Albert DB, Altman R, Goldstein RY, Cuff G, Youm T. Are femoral nerve blocks effective for early postoperative pain management after hip arthroscopy? Arthroscopy. 2012;28:1064-1069.
- Liu SS, Strodtbeck WM, Richman JM, Wu CL. A comparison of regional versus general anesthesia for ambulatory anesthesia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesth Analg. 2005;101:1634-1642.
- Clarke MT, Arora A, Villar RN. Hip arthroscopy: complications in 1054 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;406:84-88.
ABSTRACT
Pain control following hip arthroscopy presents a significant clinical challenge, with postoperative pain requiring considerable opioid use. Peripheral nerve blocks (PNBs) have emerged as one option to improve pain and limit the consequences of opioid use. The purpose of this study is to provide a comprehensive review of outcomes associated with PNB in hip arthroscopy. We hypothesize that the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy leads to improved outcomes and is associated with few complications. A systematic review of PubMed, Medline, Scopus, and Embase databases was conducted through January 2015 for English-language articles reporting outcome data, with 2 reviewers independently reviewing studies for inclusion. When available, similar outcomes were combined to generate frequency-weighted means. Six studies met the inclusion criteria for this review, reporting on 710 patients undergoing hip arthroscopy. The mean ages were 37.0 and 37.7 years for the PNB and comparator groups, respectively, with a reported total of 281 (40.5%) male and 412 (59.5%) female patients. Postoperative post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) pain was consistently reduced in the PNB group, with the use of a lower morphine equivalent dose and lower rates of inpatient admission, compared with that in the control groups. Postoperative nausea and/or vomiting as well as PACU discharge time showed mixed results. High satisfaction and few complications were reported. In conclusion, PNB is associated with reductions in postoperative pain, analgesic use, and the rate of inpatient admissions, though similar rates of nausea/vomiting and time to discharge were reported. Current PNB techniques are varied, and future research efforts should focus on examining which of these methods provides the optimal risk-benefit profile in hip arthroscopy.
Continue to: Hip arthroscopy has emerged...
Hip arthroscopy has emerged as a useful procedure in the diagnosis and treatment of hip pathology,1-8 experiencing a substantial rise in popularity in recent years, with the number of procedures growing by a factor of 18 from 1999 to 20099 and 25 from 2006 to 2013.10 Though hip arthroscopy is beneficial in many cases, marked postoperative pain has presented a substantial challenge, with patients requiring considerable doses of opiate-based medications in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU).11,12 Increased narcotic use carries increased side effects, including postoperative nausea and vomiting,13 and poorly managed pain leads to increased unplanned admissions.14 Furthermore, patients with chronic hip pain and long-term opioid use may experience heightened and prolonged pain following the procedure, owing to medication tolerance and reduced opioid efficacy in this setting.15
Several pain control strategies have been employed in patients undergoing hip arthroscopy. General anesthesia16,17 and combined spinal epidural (CSE)18 are commonly used. However, such techniques rely heavily on opioids for postoperative pain control,11 and epidural anesthesia commonly requires adjunctive treatments (eg, neuromuscular blockade) to ensure muscle relaxation for joint distraction.19 One technique that has been employed recently is peripheral nerve block (PNB), which has been associated with a significant decrease in postoperative opioid use and nausea and vomiting.13,20 This method has proven successful in other fields of arthroscopy, including shoulder arthroscopy, in which it resulted in faster recovery, reduced opioid consumption,21 and demonstrated cost-effectiveness22 compared with general anesthesia and knee arthroscopy.23-26 As it is a relatively new field, little is known about the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy.
The goal of this systematic review was to comprehensively review the studies reporting on PNB in hip arthroscopy. We specifically focused on outcomes, including postoperative pain; analgesic use; nausea, vomiting, and antiemetic use; discharge time; inpatient admission; and patient satisfaction, as well as the complications associated with the use of PNB. Our knowledge of outcomes associated with PNB in hip arthroscopy is based on a few individual studies that have reported on small groups of patients using a variety of outcome measures and other findings. Furthermore, each of these studies commonly reflects the experience of an individual surgeon at a single institution and, when taken alone, may not be an accurate representation of the more general outcomes associated with PNB. A comprehensive review of such studies will provide surgeons, anesthesiologists, and patients with a better understanding of the anticipated outcomes of using PNB in hip arthroscopy. We hypothesize that the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy leads to improved outcomes and is associated with few complications.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A systematic review of outcomes associated with PNB in hip arthroscopy was performed using the available English-language literature in accordance with the guidelines laid out by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses statement and included studies retrieved from the PubMed, Medline, Scopus, and Embase computerized literature databases. Searches were executed comprising all years from database inception through January 2015. Articles were retrieved by an electronic search of medical subject headings and keyword terms and their respective combinations (Table 1). The inclusion criteria for studies in this systematic review were studies that (1) were written in the English language and (2) reported explicit outcome data. The exclusion criteria were (1) review articles, meta-analyses, case reports, abstracts/conference papers, comments/letters, or technique articles without reported patient data and (2) basic research, biomechanics, or animal/cadaveric studies without reported patient data.
Table 1. Search Terms Entered to Identify English-Language Studies Through January 2015
Database | Search terms |
PubMed, Scopus | Keyword: (hip AND arthroscopy) AND (pain control OR pain management OR pain regimen OR nerve block OR spinal anesthesia OR regional anesthesia OR general anesthesia) |
Medline | MeSH (includes both MeSH terms and keywords): (Hip) AND (Arthroscopy) AND (“Pain Management” OR “Anesthesia, General” OR “Anesthesia” OR “Anesthesia, Inhalation”, OR “Balanced Anesthesia” OR “Anesthesia, Local” OR “Anesthesia, Spinal” OR “Anesthesia, Conduction” OR “Nerve Block”) |
Embase | MeSH (includes both MeSH terms and keywords): (Hip) AND (Arthroscopy) AND (“Pain Management” OR “General Anesthesia” OR “Anesthesia” OR “Inhalation Anesthesia”, OR “Balanced Anesthesia” OR “Local Anesthesia” OR “Spinal Anesthesia” OR “Regional Anesthesia” OR “Nerve Block”) |
The literature search strategy is outlined in the Figure. The initial title search yielded a subset of possible articles that were then further included or excluded on the basis of the contents of the article’s abstract, wherein articles were again selected on the basis of the aforementioned inclusion and exclusion criteria. Articles selected in both the title and abstract phases underwent full-text review, during which the full text of each qualifying article was reviewed. In addition, the reference sections from articles undergoing full-text review were scanned to identify any additional studies that had not been identified in the original literature search. Appropriate studies for final inclusion were then selected at this stage. The title, abstract, and full-text selection process were performed by 2 of the study authors (Dr. Steinhaus and Dr. Lynch), with any discrepancies being discussed and resolved by mutual agreement.

Continue to: For all 6 included studies...
For all 6 included studies,16-18,27-29 data were collected regarding the study specifics, patients included, and outcomes measured in the study. The journal of publication, type of study, level of evidence, and type of PNB, as well as the presence of a comparator group were noted (Table 2). Patient information included the number of patients at baseline and follow-up, mean age, gender, weight, height, body mass index, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) status, and the specific procedures performed. In addition, data were collected on outcomes, including postoperative pain, as well as secondary outcomes and additional findings reported by the studies (Table 3). Where possible, weighted averages were calculated across all studies to obtain aggregate data.
RESULTS
STUDY INCLUSION
Six studies, all published between 2012 and 2014, were included in this systematic review (Table 2). Three studies involved lumbar plexus block, 2 studies involved femoral nerve block, and 1 study evaluated fascia iliaca block. Two studies used a control group of patients who received only general anesthesia (compared with the treatment group who received both general anesthesia and PNB); another study compared intravenous morphine with PNB; and 1 study compared CSE alone with PNB in addition to epidural.
DEMOGRAPHIC DATA
Demographic data from the included studies are presented in Table 2. In total, 710 and 549 patients were evaluated at baseline and final follow-up, respectively, which represents a follow-up rate of 77%. The frequency-weighted mean age of patients receiving PNB was 37.0 years compared with 37.7 years in the comparison groups, and the studies reported a total of 281 (40.5%) male and 412 (59.5%) female patients. The procedures performed were heterogeneously reported; therefore, totals were not tabulated, although the reported procedures included osteochondroplasty, labral débridement, labral and/or capsular repair, gluteus minimus repair, and synovectomy.
POSTOPERATIVE PAIN
Four studies reported on postoperative pain, and these data are presented in Table 3. In a retrospective study of patients receiving femoral nerve block in addition to general anesthesia, Dold and colleagues16 noted postoperative pain at 0, 15, 30, 45, and 60 minutes following arrival in the PACU, and discovered a statistically significantly lower level of pain at 60 minutes compared with inpatients receiving general anesthesia alone. YaDeau and colleagues18 found a significantly lower level of pain at rest in the PACU for those receiving CSE and lumbar plexus blockade compared with those receiving CSE alone. This significant difference did not persist at 24 hours or 6 months after the procedure, nor did it exist for pain with movement at any time point. Similarly, Schroeder and colleagues17 examined patients receiving general anesthesia and lumbar plexus block and found a significant reduction in pain immediately postoperatively in the PACU, though these effects disappeared the day following the procedure. Krych and colleagues27 also reported on postoperative pain in patients undergoing fascia iliaca blockade, although they did not include a comparator group. Outcome comparison between patients who received PNB and controls in the PACU and 1 day following the procedure are presented in Table 4.
ANALGESIC USE
Four studies reported on analgesic use after PNB, and these data are presented in Table 3. Dold and colleagues16 noted analgesic use intraoperatively, in the PACU, and in the surgical day care unit (SDCU). These authors found a significant reduction in morphine equivalent dose given in the operating room and in the PACU in the group receiving PNB, with a nonsignificant trend toward lower use of oxycodone in the SDCU. Schroeder and colleagues17 similarly reported significant reductions in morphine equivalent dose intraoperatively and in Phase I recovery for patients receiving PNB, and these differences disappeared in Phase II recovery as well as intraoperatively if the block dose was considered. In addition, these authors found a significant reduction in the use of fentanyl and hydromorphone in the operating room in the PNB group, as well as a significant reduction in the proportion of patients receiving ketorolac in the operating room or PACU. Finally, YaDeau and colleagues18 reported total analgesic usage in the PACU among PNB patients compared with those receiving CSE alone and showed a strong trend toward reduced use in the PNB group, although this difference was not significant (P = .051). PACU analgesic use is presented in Table 4.
Continue to: Postoperative nausea...
POSTOPERATIVE NAUSEA/VOMITING AND ANTIEMETIC USE
Five studies presented data on nausea, vomiting, or antiemetic use following PNB and are shown in Table 3. YaDeau and colleagues18 reported nausea among 34% of patients in the PNB group, compared with 20% in the control group, vomiting in 2% and 7%, respectively, and antiemetic use in 12% of both groups. Dold and colleagues16 identified a similar trend, with 41.1% of patients in the PNB group and 32.5% of patients in the control group experiencing postoperative nausea or vomiting, while Krych and colleagues27 noted only 10% of PNB patients with mild nausea and none requiring antiemetic use. In their study of patients receiving PNB, Schroeder and colleagues17 found a significant reduction in antiemetic use among PNB patients compared with those receiving general anesthesia alone. Similarly, Ward and colleagues29 noted a significant difference in postoperative nausea, with 10% of patients in the PNB group experiencing postoperative nausea compared with 75% of those in the comparator group who received intravenous morphine. The mean percentage of patients experiencing postoperative nausea and/or vomiting is shown in Table 4.
DISCHARGE TIME
Four studies presented data on discharge time from the PACU and are summarized in Table 3. Three of these studies included a comparator group. Both Dold and colleagues16 and YaDeau and colleagues18 reported an increase in the time to discharge for patients receiving PNB, although these differences were not significant. The study by Ward and colleagues,29 on the other hand, noted a significant reduction in the time to discharge for the PNB group. In addition to these studies, Krych and colleagues27 examined the time from skin closure to discharge for patients receiving PNB, noting a mean 199 minutes for the patients in their study. Mean times to discharge for the PNB and control groups are presented in Table 4.
INPATIENT ADMISSION
Four studies presented data on the proportion of study participants who were admitted as inpatients, and these data are shown in Table 3. Dold and colleagues16 reported no inpatient admissions in their PNB group compared with 5.0% for the control group (both cases of pain control), while YaDeau and colleagues18 found that 3 admissions occurred, with 2 in the control group (1 for oxygen desaturation and the other for intractable pain and nausea) and 1 from the PNB group (epidural spread and urinary retention). Two additional studies reported data on PNB groups alone. Krych and colleagues27 observed no overnight admissions in their study, while Nye and colleagues28 reported 1 readmission for bilateral leg numbness and weakness due to epidural spread, which resolved following discontinuation of the block. The mean proportion of inpatient admissions is presented in Table 4.
SATISFACTION
A total of 3 studies examined patient satisfaction, and these data are presented in Table 3. In their study, Ward and colleagues29 reported a significantly greater rate of satisfaction at 1 day postoperatively among the patients in the PNB group (90%) than among patients who received intravenous morphine (25%) (P < .0001). Similarly, YaDeau and colleagues18 noted greater satisfaction among the PNB group than among the control group, with PNB patients rating their satisfaction at a mean of 8.6 and control patients at a mean of 7.9 on a 10-point scale (0-10) 24 hours postoperatively, although this difference was not significant. Finally, Krych and colleagues27 found that 67% of patients were “very satisfied” and 33% were “satisfied”, based on a Likert scale.
COMPLICATIONS
Four studies presented data on complications, and these findings are summarized in Table 3. In their work, Nye and colleagues28 reported most extensively on complications associated with PNB. Overall, the authors found a rate of significant complications of 3.8%. In terms of specific complications, they noted local anesthetic systemic toxicity (0.9%), epidural spread (0.5%), sensory or motor deficits (9.4%), falls (0.5%), and catheter issues. In their study of patients receiving PNB and CSE, YaDeau and colleagues18 identified 1 patient in the PNB group with epidural spread and urinary retention, while they noted 1 case of oxygen desaturation and another case of intractable pain and nausea in the group receiving CSE alone, all 3 of which required inpatient admission. They found no permanent adverse events attributable to the PNB. In another study, Dold and colleagues16 observed no complications in patients receiving PNB compared with those in 2 admissions in the control group for inadequate pain control. Similarly, Krych and colleagues27 identified no complications in patients who received PNB in their study.
DISCUSSION
Hip arthroscopy has experienced a substantial gain in popularity in recent years, emerging as a beneficial technique for both the diagnosis and treatment of diverse hip pathologies in patients spanning a variety of demographics. Nevertheless, postoperative pain control, as well as medication side effects and unwanted patient admissions, present major challenges to the treating surgeon. As an adjuvant measure, peripheral nerve block represents one option to improve postoperative pain management, while at the same time addressing the adverse effects of considerable opioid use, which is commonly seen in these patients. Early experience with this method in hip arthroscopy was reported in a case series by Lee and colleagues.12 In an attempt to reduce postoperative pain, as well as limit the adverse effects and delay in discharge associated with considerable opioid use in the PACU, the authors used preoperative paravertebral blocks of L1 and L2 in 2 patients requiring hip arthroscopy with encouraging results. Since then, a number of studies have attempted the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy.16-18,27-29 However, we were unable to identify any prior reviews reporting on peripheral nerve blockade in hip arthroscopy, and thus this study is unique in providing a greater understanding of the outcomes associated with PNB use.
In general, we found that PNB was associated with improved outcomes. Based on the studies included in this review, there was a statistically significantly lower level of pain in the PACU for femoral nerve block (compared with general anesthesia alone)16 and lumbar plexus blockade (compared with general anesthesia17 and CSE18 alone). Nevertheless, these effects are likely short-lived, with differences disappearing the day following the procedure. In terms of analgesic use, 2 studies report significant reductions in analgesic use intraoperatively and in the PACU/Phase I recovery,16,17 with a third reporting a strong trend toward reduced analgesic use in the PACU (P = .051).18 Finally, we report fewer admissions for the PNB group, as well as high rates of satisfaction and few complications across these studies.
Continue to: Unlike these measures...
Unlike these measures, postoperative nausea, vomiting, and antiemetic use, as well as time to discharge, showed more mixed results. With regard to nausea/vomiting, 2 studies16,18 reported nonsignificantly increased rates in the PNB group, whereas others reported significant reductions in nausea/vomiting29 and in the proportion of patients receiving antiemetics.17 Similarly, mixed results were seen in terms of patient discharge time from the PACU. Two studies16,18 reported a nonsignificant increase in time to discharge for the PNB group, while another29 noted a significant reduction for the PNB group compared with those receiving intravenous morphine. These mixed results were surprising, as we expected reductions in opioid use to result in fewer instances of nausea/vomiting and a quicker time to discharge. The reasons underlying these findings are not clear, although it has been suggested that current discharge guidelines and clinical pathways limit the ability to take advantage of the accelerated timeline offered by regional anesthesia.16,30 As experience with PNB grows, our guidelines and pathways are likely to adapt to capitalize on these advantages, and future studies may show more reliable improvements in these measures.
While rare, the risk of bleeding requiring blood transfusion following hip arthroscopy is one of the most common complications of this procedure. Though the studies included in this review did not report on the need for transfusion, a recent study by Cvetanovich and colleagues10 used a national database and found that, of patients undergoing hip arthroscopy (n = 1338), 0.4% (n = 5) had bleeding requiring a transfusion, with 0.3% (n = 4) requiring return to the operating room, similar to an earlier study by Clarke and colleagues,31 who noted bleeding from the portal site in 0.4% of hip arthroscopy patients. In terms of risk factors, Cvetanovich and colleagues10 found that ASA class, older age, and prior cardiac surgery were significantly associated with minor and overall complications, whereas both regional anesthesia/monitored anesthesia care and alcohol consumption of >2 drinks a day were significantly associated with minor complications, including bleeding requiring transfusions. They noted, however, that these risk factors accounted for only 5% of the variance in complication rates, indicating that other unidentified variables better explained the variance in complication rates. These authors concluded that complications associated with hip arthroscopy are so rare that we may not be able to predict which risk factors or anesthesia types are more likely to cause them. Further characterization of bleeding following hip arthroscopy and its associated risk factors is a valuable area for future research.
LIMITATIONS
Our study contains a number of limitations. This review included studies whose level of evidence varied from I to IV; therefore, our study is limited by any bias or heterogeneity introduced in patient recruitment, selection, variability of technique, data collection, and analysis used in these studies. This heterogeneity is most apparent in the block types and comparator groups. Furthermore, several different outcome measures were reported across the 6 studies used in this review, which decreased the relevance of any one of these individual outcomes. Finally, given the limited data that currently exist for the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy, we are unable to note meaningful differences between various types of PNBs, such as differences in postoperative pain or other measures such as quadriceps weakness, which can accompany femoral nerve block.12 While it is important to read our work with these limitations in mind, this systematic review is, to our knowledge, the only comprehensive review to date of studies reporting on PNB in hip arthroscopy, providing clinicians and patients with a greater understanding of the associated outcomes across these studies.
CONCLUSION
This systematic review shows improved outcomes and few complications with PNB use in hip arthroscopy, with reductions in postoperative pain, analgesic use, and the rate of inpatient admissions. Although opioid use was reduced in these studies, we found similar rates of postoperative nausea/vomiting as well as similar time to discharge from the PACU, which may reflect our continued reliance on outdated discharge guidelines and clinical pathways. Current attempts to provide peripheral nerve blockade are quite varied, with studies targeting femoral nerve, fascia iliaca, L1/L2 paravertebral, and lumbar plexus blockade. Future research efforts with a large prospective trial investigating these techniques should focus on which of these PNBs presents the optimal risk-benefit profile for hip arthroscopy patients and thus appropriately address the clinical questions at hand.
This paper will be judged for the Resident Writer’s Award.
ABSTRACT
Pain control following hip arthroscopy presents a significant clinical challenge, with postoperative pain requiring considerable opioid use. Peripheral nerve blocks (PNBs) have emerged as one option to improve pain and limit the consequences of opioid use. The purpose of this study is to provide a comprehensive review of outcomes associated with PNB in hip arthroscopy. We hypothesize that the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy leads to improved outcomes and is associated with few complications. A systematic review of PubMed, Medline, Scopus, and Embase databases was conducted through January 2015 for English-language articles reporting outcome data, with 2 reviewers independently reviewing studies for inclusion. When available, similar outcomes were combined to generate frequency-weighted means. Six studies met the inclusion criteria for this review, reporting on 710 patients undergoing hip arthroscopy. The mean ages were 37.0 and 37.7 years for the PNB and comparator groups, respectively, with a reported total of 281 (40.5%) male and 412 (59.5%) female patients. Postoperative post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) pain was consistently reduced in the PNB group, with the use of a lower morphine equivalent dose and lower rates of inpatient admission, compared with that in the control groups. Postoperative nausea and/or vomiting as well as PACU discharge time showed mixed results. High satisfaction and few complications were reported. In conclusion, PNB is associated with reductions in postoperative pain, analgesic use, and the rate of inpatient admissions, though similar rates of nausea/vomiting and time to discharge were reported. Current PNB techniques are varied, and future research efforts should focus on examining which of these methods provides the optimal risk-benefit profile in hip arthroscopy.
Continue to: Hip arthroscopy has emerged...
Hip arthroscopy has emerged as a useful procedure in the diagnosis and treatment of hip pathology,1-8 experiencing a substantial rise in popularity in recent years, with the number of procedures growing by a factor of 18 from 1999 to 20099 and 25 from 2006 to 2013.10 Though hip arthroscopy is beneficial in many cases, marked postoperative pain has presented a substantial challenge, with patients requiring considerable doses of opiate-based medications in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU).11,12 Increased narcotic use carries increased side effects, including postoperative nausea and vomiting,13 and poorly managed pain leads to increased unplanned admissions.14 Furthermore, patients with chronic hip pain and long-term opioid use may experience heightened and prolonged pain following the procedure, owing to medication tolerance and reduced opioid efficacy in this setting.15
Several pain control strategies have been employed in patients undergoing hip arthroscopy. General anesthesia16,17 and combined spinal epidural (CSE)18 are commonly used. However, such techniques rely heavily on opioids for postoperative pain control,11 and epidural anesthesia commonly requires adjunctive treatments (eg, neuromuscular blockade) to ensure muscle relaxation for joint distraction.19 One technique that has been employed recently is peripheral nerve block (PNB), which has been associated with a significant decrease in postoperative opioid use and nausea and vomiting.13,20 This method has proven successful in other fields of arthroscopy, including shoulder arthroscopy, in which it resulted in faster recovery, reduced opioid consumption,21 and demonstrated cost-effectiveness22 compared with general anesthesia and knee arthroscopy.23-26 As it is a relatively new field, little is known about the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy.
The goal of this systematic review was to comprehensively review the studies reporting on PNB in hip arthroscopy. We specifically focused on outcomes, including postoperative pain; analgesic use; nausea, vomiting, and antiemetic use; discharge time; inpatient admission; and patient satisfaction, as well as the complications associated with the use of PNB. Our knowledge of outcomes associated with PNB in hip arthroscopy is based on a few individual studies that have reported on small groups of patients using a variety of outcome measures and other findings. Furthermore, each of these studies commonly reflects the experience of an individual surgeon at a single institution and, when taken alone, may not be an accurate representation of the more general outcomes associated with PNB. A comprehensive review of such studies will provide surgeons, anesthesiologists, and patients with a better understanding of the anticipated outcomes of using PNB in hip arthroscopy. We hypothesize that the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy leads to improved outcomes and is associated with few complications.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A systematic review of outcomes associated with PNB in hip arthroscopy was performed using the available English-language literature in accordance with the guidelines laid out by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses statement and included studies retrieved from the PubMed, Medline, Scopus, and Embase computerized literature databases. Searches were executed comprising all years from database inception through January 2015. Articles were retrieved by an electronic search of medical subject headings and keyword terms and their respective combinations (Table 1). The inclusion criteria for studies in this systematic review were studies that (1) were written in the English language and (2) reported explicit outcome data. The exclusion criteria were (1) review articles, meta-analyses, case reports, abstracts/conference papers, comments/letters, or technique articles without reported patient data and (2) basic research, biomechanics, or animal/cadaveric studies without reported patient data.
Table 1. Search Terms Entered to Identify English-Language Studies Through January 2015
Database | Search terms |
PubMed, Scopus | Keyword: (hip AND arthroscopy) AND (pain control OR pain management OR pain regimen OR nerve block OR spinal anesthesia OR regional anesthesia OR general anesthesia) |
Medline | MeSH (includes both MeSH terms and keywords): (Hip) AND (Arthroscopy) AND (“Pain Management” OR “Anesthesia, General” OR “Anesthesia” OR “Anesthesia, Inhalation”, OR “Balanced Anesthesia” OR “Anesthesia, Local” OR “Anesthesia, Spinal” OR “Anesthesia, Conduction” OR “Nerve Block”) |
Embase | MeSH (includes both MeSH terms and keywords): (Hip) AND (Arthroscopy) AND (“Pain Management” OR “General Anesthesia” OR “Anesthesia” OR “Inhalation Anesthesia”, OR “Balanced Anesthesia” OR “Local Anesthesia” OR “Spinal Anesthesia” OR “Regional Anesthesia” OR “Nerve Block”) |
The literature search strategy is outlined in the Figure. The initial title search yielded a subset of possible articles that were then further included or excluded on the basis of the contents of the article’s abstract, wherein articles were again selected on the basis of the aforementioned inclusion and exclusion criteria. Articles selected in both the title and abstract phases underwent full-text review, during which the full text of each qualifying article was reviewed. In addition, the reference sections from articles undergoing full-text review were scanned to identify any additional studies that had not been identified in the original literature search. Appropriate studies for final inclusion were then selected at this stage. The title, abstract, and full-text selection process were performed by 2 of the study authors (Dr. Steinhaus and Dr. Lynch), with any discrepancies being discussed and resolved by mutual agreement.

Continue to: For all 6 included studies...
For all 6 included studies,16-18,27-29 data were collected regarding the study specifics, patients included, and outcomes measured in the study. The journal of publication, type of study, level of evidence, and type of PNB, as well as the presence of a comparator group were noted (Table 2). Patient information included the number of patients at baseline and follow-up, mean age, gender, weight, height, body mass index, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) status, and the specific procedures performed. In addition, data were collected on outcomes, including postoperative pain, as well as secondary outcomes and additional findings reported by the studies (Table 3). Where possible, weighted averages were calculated across all studies to obtain aggregate data.
RESULTS
STUDY INCLUSION
Six studies, all published between 2012 and 2014, were included in this systematic review (Table 2). Three studies involved lumbar plexus block, 2 studies involved femoral nerve block, and 1 study evaluated fascia iliaca block. Two studies used a control group of patients who received only general anesthesia (compared with the treatment group who received both general anesthesia and PNB); another study compared intravenous morphine with PNB; and 1 study compared CSE alone with PNB in addition to epidural.
DEMOGRAPHIC DATA
Demographic data from the included studies are presented in Table 2. In total, 710 and 549 patients were evaluated at baseline and final follow-up, respectively, which represents a follow-up rate of 77%. The frequency-weighted mean age of patients receiving PNB was 37.0 years compared with 37.7 years in the comparison groups, and the studies reported a total of 281 (40.5%) male and 412 (59.5%) female patients. The procedures performed were heterogeneously reported; therefore, totals were not tabulated, although the reported procedures included osteochondroplasty, labral débridement, labral and/or capsular repair, gluteus minimus repair, and synovectomy.
POSTOPERATIVE PAIN
Four studies reported on postoperative pain, and these data are presented in Table 3. In a retrospective study of patients receiving femoral nerve block in addition to general anesthesia, Dold and colleagues16 noted postoperative pain at 0, 15, 30, 45, and 60 minutes following arrival in the PACU, and discovered a statistically significantly lower level of pain at 60 minutes compared with inpatients receiving general anesthesia alone. YaDeau and colleagues18 found a significantly lower level of pain at rest in the PACU for those receiving CSE and lumbar plexus blockade compared with those receiving CSE alone. This significant difference did not persist at 24 hours or 6 months after the procedure, nor did it exist for pain with movement at any time point. Similarly, Schroeder and colleagues17 examined patients receiving general anesthesia and lumbar plexus block and found a significant reduction in pain immediately postoperatively in the PACU, though these effects disappeared the day following the procedure. Krych and colleagues27 also reported on postoperative pain in patients undergoing fascia iliaca blockade, although they did not include a comparator group. Outcome comparison between patients who received PNB and controls in the PACU and 1 day following the procedure are presented in Table 4.
ANALGESIC USE
Four studies reported on analgesic use after PNB, and these data are presented in Table 3. Dold and colleagues16 noted analgesic use intraoperatively, in the PACU, and in the surgical day care unit (SDCU). These authors found a significant reduction in morphine equivalent dose given in the operating room and in the PACU in the group receiving PNB, with a nonsignificant trend toward lower use of oxycodone in the SDCU. Schroeder and colleagues17 similarly reported significant reductions in morphine equivalent dose intraoperatively and in Phase I recovery for patients receiving PNB, and these differences disappeared in Phase II recovery as well as intraoperatively if the block dose was considered. In addition, these authors found a significant reduction in the use of fentanyl and hydromorphone in the operating room in the PNB group, as well as a significant reduction in the proportion of patients receiving ketorolac in the operating room or PACU. Finally, YaDeau and colleagues18 reported total analgesic usage in the PACU among PNB patients compared with those receiving CSE alone and showed a strong trend toward reduced use in the PNB group, although this difference was not significant (P = .051). PACU analgesic use is presented in Table 4.
Continue to: Postoperative nausea...
POSTOPERATIVE NAUSEA/VOMITING AND ANTIEMETIC USE
Five studies presented data on nausea, vomiting, or antiemetic use following PNB and are shown in Table 3. YaDeau and colleagues18 reported nausea among 34% of patients in the PNB group, compared with 20% in the control group, vomiting in 2% and 7%, respectively, and antiemetic use in 12% of both groups. Dold and colleagues16 identified a similar trend, with 41.1% of patients in the PNB group and 32.5% of patients in the control group experiencing postoperative nausea or vomiting, while Krych and colleagues27 noted only 10% of PNB patients with mild nausea and none requiring antiemetic use. In their study of patients receiving PNB, Schroeder and colleagues17 found a significant reduction in antiemetic use among PNB patients compared with those receiving general anesthesia alone. Similarly, Ward and colleagues29 noted a significant difference in postoperative nausea, with 10% of patients in the PNB group experiencing postoperative nausea compared with 75% of those in the comparator group who received intravenous morphine. The mean percentage of patients experiencing postoperative nausea and/or vomiting is shown in Table 4.
DISCHARGE TIME
Four studies presented data on discharge time from the PACU and are summarized in Table 3. Three of these studies included a comparator group. Both Dold and colleagues16 and YaDeau and colleagues18 reported an increase in the time to discharge for patients receiving PNB, although these differences were not significant. The study by Ward and colleagues,29 on the other hand, noted a significant reduction in the time to discharge for the PNB group. In addition to these studies, Krych and colleagues27 examined the time from skin closure to discharge for patients receiving PNB, noting a mean 199 minutes for the patients in their study. Mean times to discharge for the PNB and control groups are presented in Table 4.
INPATIENT ADMISSION
Four studies presented data on the proportion of study participants who were admitted as inpatients, and these data are shown in Table 3. Dold and colleagues16 reported no inpatient admissions in their PNB group compared with 5.0% for the control group (both cases of pain control), while YaDeau and colleagues18 found that 3 admissions occurred, with 2 in the control group (1 for oxygen desaturation and the other for intractable pain and nausea) and 1 from the PNB group (epidural spread and urinary retention). Two additional studies reported data on PNB groups alone. Krych and colleagues27 observed no overnight admissions in their study, while Nye and colleagues28 reported 1 readmission for bilateral leg numbness and weakness due to epidural spread, which resolved following discontinuation of the block. The mean proportion of inpatient admissions is presented in Table 4.
SATISFACTION
A total of 3 studies examined patient satisfaction, and these data are presented in Table 3. In their study, Ward and colleagues29 reported a significantly greater rate of satisfaction at 1 day postoperatively among the patients in the PNB group (90%) than among patients who received intravenous morphine (25%) (P < .0001). Similarly, YaDeau and colleagues18 noted greater satisfaction among the PNB group than among the control group, with PNB patients rating their satisfaction at a mean of 8.6 and control patients at a mean of 7.9 on a 10-point scale (0-10) 24 hours postoperatively, although this difference was not significant. Finally, Krych and colleagues27 found that 67% of patients were “very satisfied” and 33% were “satisfied”, based on a Likert scale.
COMPLICATIONS
Four studies presented data on complications, and these findings are summarized in Table 3. In their work, Nye and colleagues28 reported most extensively on complications associated with PNB. Overall, the authors found a rate of significant complications of 3.8%. In terms of specific complications, they noted local anesthetic systemic toxicity (0.9%), epidural spread (0.5%), sensory or motor deficits (9.4%), falls (0.5%), and catheter issues. In their study of patients receiving PNB and CSE, YaDeau and colleagues18 identified 1 patient in the PNB group with epidural spread and urinary retention, while they noted 1 case of oxygen desaturation and another case of intractable pain and nausea in the group receiving CSE alone, all 3 of which required inpatient admission. They found no permanent adverse events attributable to the PNB. In another study, Dold and colleagues16 observed no complications in patients receiving PNB compared with those in 2 admissions in the control group for inadequate pain control. Similarly, Krych and colleagues27 identified no complications in patients who received PNB in their study.
DISCUSSION
Hip arthroscopy has experienced a substantial gain in popularity in recent years, emerging as a beneficial technique for both the diagnosis and treatment of diverse hip pathologies in patients spanning a variety of demographics. Nevertheless, postoperative pain control, as well as medication side effects and unwanted patient admissions, present major challenges to the treating surgeon. As an adjuvant measure, peripheral nerve block represents one option to improve postoperative pain management, while at the same time addressing the adverse effects of considerable opioid use, which is commonly seen in these patients. Early experience with this method in hip arthroscopy was reported in a case series by Lee and colleagues.12 In an attempt to reduce postoperative pain, as well as limit the adverse effects and delay in discharge associated with considerable opioid use in the PACU, the authors used preoperative paravertebral blocks of L1 and L2 in 2 patients requiring hip arthroscopy with encouraging results. Since then, a number of studies have attempted the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy.16-18,27-29 However, we were unable to identify any prior reviews reporting on peripheral nerve blockade in hip arthroscopy, and thus this study is unique in providing a greater understanding of the outcomes associated with PNB use.
In general, we found that PNB was associated with improved outcomes. Based on the studies included in this review, there was a statistically significantly lower level of pain in the PACU for femoral nerve block (compared with general anesthesia alone)16 and lumbar plexus blockade (compared with general anesthesia17 and CSE18 alone). Nevertheless, these effects are likely short-lived, with differences disappearing the day following the procedure. In terms of analgesic use, 2 studies report significant reductions in analgesic use intraoperatively and in the PACU/Phase I recovery,16,17 with a third reporting a strong trend toward reduced analgesic use in the PACU (P = .051).18 Finally, we report fewer admissions for the PNB group, as well as high rates of satisfaction and few complications across these studies.
Continue to: Unlike these measures...
Unlike these measures, postoperative nausea, vomiting, and antiemetic use, as well as time to discharge, showed more mixed results. With regard to nausea/vomiting, 2 studies16,18 reported nonsignificantly increased rates in the PNB group, whereas others reported significant reductions in nausea/vomiting29 and in the proportion of patients receiving antiemetics.17 Similarly, mixed results were seen in terms of patient discharge time from the PACU. Two studies16,18 reported a nonsignificant increase in time to discharge for the PNB group, while another29 noted a significant reduction for the PNB group compared with those receiving intravenous morphine. These mixed results were surprising, as we expected reductions in opioid use to result in fewer instances of nausea/vomiting and a quicker time to discharge. The reasons underlying these findings are not clear, although it has been suggested that current discharge guidelines and clinical pathways limit the ability to take advantage of the accelerated timeline offered by regional anesthesia.16,30 As experience with PNB grows, our guidelines and pathways are likely to adapt to capitalize on these advantages, and future studies may show more reliable improvements in these measures.
While rare, the risk of bleeding requiring blood transfusion following hip arthroscopy is one of the most common complications of this procedure. Though the studies included in this review did not report on the need for transfusion, a recent study by Cvetanovich and colleagues10 used a national database and found that, of patients undergoing hip arthroscopy (n = 1338), 0.4% (n = 5) had bleeding requiring a transfusion, with 0.3% (n = 4) requiring return to the operating room, similar to an earlier study by Clarke and colleagues,31 who noted bleeding from the portal site in 0.4% of hip arthroscopy patients. In terms of risk factors, Cvetanovich and colleagues10 found that ASA class, older age, and prior cardiac surgery were significantly associated with minor and overall complications, whereas both regional anesthesia/monitored anesthesia care and alcohol consumption of >2 drinks a day were significantly associated with minor complications, including bleeding requiring transfusions. They noted, however, that these risk factors accounted for only 5% of the variance in complication rates, indicating that other unidentified variables better explained the variance in complication rates. These authors concluded that complications associated with hip arthroscopy are so rare that we may not be able to predict which risk factors or anesthesia types are more likely to cause them. Further characterization of bleeding following hip arthroscopy and its associated risk factors is a valuable area for future research.
LIMITATIONS
Our study contains a number of limitations. This review included studies whose level of evidence varied from I to IV; therefore, our study is limited by any bias or heterogeneity introduced in patient recruitment, selection, variability of technique, data collection, and analysis used in these studies. This heterogeneity is most apparent in the block types and comparator groups. Furthermore, several different outcome measures were reported across the 6 studies used in this review, which decreased the relevance of any one of these individual outcomes. Finally, given the limited data that currently exist for the use of PNB in hip arthroscopy, we are unable to note meaningful differences between various types of PNBs, such as differences in postoperative pain or other measures such as quadriceps weakness, which can accompany femoral nerve block.12 While it is important to read our work with these limitations in mind, this systematic review is, to our knowledge, the only comprehensive review to date of studies reporting on PNB in hip arthroscopy, providing clinicians and patients with a greater understanding of the associated outcomes across these studies.
CONCLUSION
This systematic review shows improved outcomes and few complications with PNB use in hip arthroscopy, with reductions in postoperative pain, analgesic use, and the rate of inpatient admissions. Although opioid use was reduced in these studies, we found similar rates of postoperative nausea/vomiting as well as similar time to discharge from the PACU, which may reflect our continued reliance on outdated discharge guidelines and clinical pathways. Current attempts to provide peripheral nerve blockade are quite varied, with studies targeting femoral nerve, fascia iliaca, L1/L2 paravertebral, and lumbar plexus blockade. Future research efforts with a large prospective trial investigating these techniques should focus on which of these PNBs presents the optimal risk-benefit profile for hip arthroscopy patients and thus appropriately address the clinical questions at hand.
This paper will be judged for the Resident Writer’s Award.
- Baber YF, Robinson AH, Villar RN. Is diagnostic arthroscopy of the hip worthwhile? A prospective review of 328 adults investigated for hip pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81:600-603.
- Byrd JW, Jones KS. Arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement: minimum 2-year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2011;27:1379-1388.
- Larson CM, Giveans MR. Arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement: early outcomes measures. Arthroscopy. 2008;24:540-546.
- O'Leary JA, Berend K, Vail TP. The relationship between diagnosis and outcome in arthroscopy of the hip. Arthroscopy. 2001;17:181-188.
- Philippon M, Schenker M, Briggs K, Kuppersmith D. Femoroacetabular impingement in 45 professional athletes: associated pathologies and return to sport following arthroscopic decompression. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007;15:908-914.
- Potter BK, Freedman BA, Andersen RC, Bojescul JA, Kuklo TR, Murphy KP. Correlation of Short Form-36 and disability status with outcomes of arthroscopic acetabular labral debridement. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33:864-870.
- Robertson WJ, Kadrmas WR, Kelly BT. Arthroscopic management of labral tears in the hip: a systematic review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;455:88-92.
- Yusaf MA, Hame SL. Arthroscopy of the hip. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2008;7:269-274.
- Colvin AC, Harrast J, Harner C. Trends in hip arthroscopy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94:e23.
- Cvetanovich GL, Chalmers PN, Levy DM, et al. Hip arthroscopy surgical volume trends and 30-day postoperative complications. Arthroscopy. 2016 Apr 8. [Epub before print].
- Baker JF, Byrne DP, Hunter K, Mulhall KJ. Post-operative opiate requirements after hip arthroscopy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19:1399-1402.
- Lee EM, Murphy KP, Ben-David B. Postoperative analgesia for hip arthroscopy: combined L1 and L2 paravertebral blocks. J Clin Anesth. 2008;20:462-465.
- Ganesh A, Rose JB, Wells L, et al. Continuous peripheral nerve blockade for inpatient and outpatient postoperative analgesia in children. Anesth Analg. 2007;105:1234-1242.
- Williams BA, Kentor ML, Vogt MT, et al. Femoral-sciatic nerve blocks for complex outpatient knee surgery are associated with less postoperative pain before same-day discharge: a review of 1,200 consecutive cases from the period 1996-1999. Anesthesiology. 2003;98:1206-1213.
- Zywiel MG, Stroh DA, Lee SY, Bonutti PM, Mont MA. Chronic opioid use prior to total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93:1988-1993.
- Dold AP, Murnaghan L, Xing J, Abdallah FW, Brull R, Whelan DB. Preoperative femoral nerve block in hip arthroscopic surgery: a retrospective review of 108 consecutive cases. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42:144-149.
- Schroeder KM, Donnelly MJ, Anderson BM, Ford MP, Keene JS. The analgesic impact of preoperative lumbar plexus blocks for hip arthroscopy. A retrospective review. Hip Int. 2013;23:93-98.
- YaDeau JT, Tedore T, Goytizolo EA, et al. Lumbar plexus blockade reduces pain after hip arthroscopy: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Anesth Analg. 2012;115:968-972.
- Smart LR, Oetgen M, Noonan B, Medvecky M. Beginning hip arthroscopy: indications, positioning, portals, basic techniques, and complications. Arthroscopy. 2007;23:1348-1353.
- Stevens M, Harrison G, McGrail M. A modified fascia iliaca compartment block has significant morphine-sparing effect after total hip arthroplasty. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2007;35:949-952.
- Lehmann LJ, Loosen G, Weiss C, Schmittner MD. Interscalene plexus block versus general anaesthesia for shoulder surgery: a randomized controlled study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25:255-261.
- Gonano C, Kettner SC, Ernstbrunner M, Schebesta K, Chiari A, Marhofer P. Comparison of economical aspects of interscalene brachial plexus blockade and general anaesthesia for arthroscopic shoulder surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2009;103:428-433.
- Hadzic A, Karaca PE, Hobeika P, et al. Peripheral nerve blocks result in superior recovery profile compared with general anesthesia in outpatient knee arthroscopy. Anesth Analg. 2005;100:976-981.
- Hsu LP, Oh S, Nuber GW, et al. Nerve block of the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve in knee arthroscopy: a prospective, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95:1465-1472.
- Montes FR, Zarate E, Grueso R, et al. Comparison of spinal anesthesia with combined sciatic-femoral nerve block for outpatient knee arthroscopy. J Clin Anesth. 2008;20:415-420.
- Wulf H, Lowe J, Gnutzmann KH, Steinfeldt T. Femoral nerve block with ropivacaine or bupivacaine in day case anterior crucial ligament reconstruction. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2010;54:414-420.
- Krych AJ, Baran S, Kuzma SA, Smith HM, Johnson RL, Levy BA. Utility of multimodal analgesia with fascia iliaca blockade for acute pain management following hip arthroscopy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22:843-847.
- Nye ZB, Horn JL, Crittenden W, Abrahams MS, Aziz MF. Ambulatory continuous posterior lumbar plexus blocks following hip arthroscopy: a review of 213 cases. J Clin Anesth. 2013;25:268-274.
- Ward JP, Albert DB, Altman R, Goldstein RY, Cuff G, Youm T. Are femoral nerve blocks effective for early postoperative pain management after hip arthroscopy? Arthroscopy. 2012;28:1064-1069.
- Liu SS, Strodtbeck WM, Richman JM, Wu CL. A comparison of regional versus general anesthesia for ambulatory anesthesia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesth Analg. 2005;101:1634-1642.
- Clarke MT, Arora A, Villar RN. Hip arthroscopy: complications in 1054 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;406:84-88.
- Baber YF, Robinson AH, Villar RN. Is diagnostic arthroscopy of the hip worthwhile? A prospective review of 328 adults investigated for hip pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81:600-603.
- Byrd JW, Jones KS. Arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement: minimum 2-year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2011;27:1379-1388.
- Larson CM, Giveans MR. Arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement: early outcomes measures. Arthroscopy. 2008;24:540-546.
- O'Leary JA, Berend K, Vail TP. The relationship between diagnosis and outcome in arthroscopy of the hip. Arthroscopy. 2001;17:181-188.
- Philippon M, Schenker M, Briggs K, Kuppersmith D. Femoroacetabular impingement in 45 professional athletes: associated pathologies and return to sport following arthroscopic decompression. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007;15:908-914.
- Potter BK, Freedman BA, Andersen RC, Bojescul JA, Kuklo TR, Murphy KP. Correlation of Short Form-36 and disability status with outcomes of arthroscopic acetabular labral debridement. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33:864-870.
- Robertson WJ, Kadrmas WR, Kelly BT. Arthroscopic management of labral tears in the hip: a systematic review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;455:88-92.
- Yusaf MA, Hame SL. Arthroscopy of the hip. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2008;7:269-274.
- Colvin AC, Harrast J, Harner C. Trends in hip arthroscopy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94:e23.
- Cvetanovich GL, Chalmers PN, Levy DM, et al. Hip arthroscopy surgical volume trends and 30-day postoperative complications. Arthroscopy. 2016 Apr 8. [Epub before print].
- Baker JF, Byrne DP, Hunter K, Mulhall KJ. Post-operative opiate requirements after hip arthroscopy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19:1399-1402.
- Lee EM, Murphy KP, Ben-David B. Postoperative analgesia for hip arthroscopy: combined L1 and L2 paravertebral blocks. J Clin Anesth. 2008;20:462-465.
- Ganesh A, Rose JB, Wells L, et al. Continuous peripheral nerve blockade for inpatient and outpatient postoperative analgesia in children. Anesth Analg. 2007;105:1234-1242.
- Williams BA, Kentor ML, Vogt MT, et al. Femoral-sciatic nerve blocks for complex outpatient knee surgery are associated with less postoperative pain before same-day discharge: a review of 1,200 consecutive cases from the period 1996-1999. Anesthesiology. 2003;98:1206-1213.
- Zywiel MG, Stroh DA, Lee SY, Bonutti PM, Mont MA. Chronic opioid use prior to total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93:1988-1993.
- Dold AP, Murnaghan L, Xing J, Abdallah FW, Brull R, Whelan DB. Preoperative femoral nerve block in hip arthroscopic surgery: a retrospective review of 108 consecutive cases. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42:144-149.
- Schroeder KM, Donnelly MJ, Anderson BM, Ford MP, Keene JS. The analgesic impact of preoperative lumbar plexus blocks for hip arthroscopy. A retrospective review. Hip Int. 2013;23:93-98.
- YaDeau JT, Tedore T, Goytizolo EA, et al. Lumbar plexus blockade reduces pain after hip arthroscopy: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Anesth Analg. 2012;115:968-972.
- Smart LR, Oetgen M, Noonan B, Medvecky M. Beginning hip arthroscopy: indications, positioning, portals, basic techniques, and complications. Arthroscopy. 2007;23:1348-1353.
- Stevens M, Harrison G, McGrail M. A modified fascia iliaca compartment block has significant morphine-sparing effect after total hip arthroplasty. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2007;35:949-952.
- Lehmann LJ, Loosen G, Weiss C, Schmittner MD. Interscalene plexus block versus general anaesthesia for shoulder surgery: a randomized controlled study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25:255-261.
- Gonano C, Kettner SC, Ernstbrunner M, Schebesta K, Chiari A, Marhofer P. Comparison of economical aspects of interscalene brachial plexus blockade and general anaesthesia for arthroscopic shoulder surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2009;103:428-433.
- Hadzic A, Karaca PE, Hobeika P, et al. Peripheral nerve blocks result in superior recovery profile compared with general anesthesia in outpatient knee arthroscopy. Anesth Analg. 2005;100:976-981.
- Hsu LP, Oh S, Nuber GW, et al. Nerve block of the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve in knee arthroscopy: a prospective, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95:1465-1472.
- Montes FR, Zarate E, Grueso R, et al. Comparison of spinal anesthesia with combined sciatic-femoral nerve block for outpatient knee arthroscopy. J Clin Anesth. 2008;20:415-420.
- Wulf H, Lowe J, Gnutzmann KH, Steinfeldt T. Femoral nerve block with ropivacaine or bupivacaine in day case anterior crucial ligament reconstruction. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2010;54:414-420.
- Krych AJ, Baran S, Kuzma SA, Smith HM, Johnson RL, Levy BA. Utility of multimodal analgesia with fascia iliaca blockade for acute pain management following hip arthroscopy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22:843-847.
- Nye ZB, Horn JL, Crittenden W, Abrahams MS, Aziz MF. Ambulatory continuous posterior lumbar plexus blocks following hip arthroscopy: a review of 213 cases. J Clin Anesth. 2013;25:268-274.
- Ward JP, Albert DB, Altman R, Goldstein RY, Cuff G, Youm T. Are femoral nerve blocks effective for early postoperative pain management after hip arthroscopy? Arthroscopy. 2012;28:1064-1069.
- Liu SS, Strodtbeck WM, Richman JM, Wu CL. A comparison of regional versus general anesthesia for ambulatory anesthesia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesth Analg. 2005;101:1634-1642.
- Clarke MT, Arora A, Villar RN. Hip arthroscopy: complications in 1054 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;406:84-88.
TAKE-HOME POINTS
- Postoperative PACU pain was consistently reduced in the PNB group.
- Patients with PNBs had lower postoperative pain medication requirements and lower rates of inpatient admission compared with controls.
- Similar rates of nausea/vomiting and time to discharge were reported for PNB patients and controls.
- PNBs are associated with high rates of satisfaction and few complications.
- Future research should focus on comparing across PNB techniques.
Proximal Humerus Fracture 3-D Modeling
ABSTRACT
The objective of this study is to determine the reproducibility and feasibility of using 3-dimensional (3-D) computer simulation of proximal humerus fracture computed tomography (CT) scans for fracture reduction. We hypothesized that anatomic reconstruction with 3-D models would be anatomically accurate and reproducible.
Preoperative CT scans of 28 patients with 3- and 4-part (AO classification 11-B1, 11-B2, 11-C1, 11-C2) proximal humerus fractures who were treated by hemiarthroplasty were converted into 3-D computer models. The displaced fractured fragments were anatomically reduced with computer simulation by 2 fellowship-trained shoulder surgeons, and measurements were made of the reconstructed proximal humerus.
The measurements of the reconstructed models had very good to excellent interobserver and intraobserver reliability. The reconstructions of these humerus fractures showed interclass correlation coefficients ranging from 0.71 to 0.93 between 1 observer and from 0.82 to 0.98 between 2 different observers. The fracture reduction was judged against normal proximal humerus geometry to determine reduction accuracy.
The 3-D modeling techniques used to reconstruct 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures were reliable and accurate. This technique of modeling and reconstructing proximal humerus fractures could be used to enhance the preoperative planning of open reduction and internal fixation or hemiarthroplasty for 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures.
The treatment of proximal humerus fractures is influenced by multiple factors, including patient age, associated injuries, bone quality, and fracture pattern. Three- and 4-part fractures are among the more severe of these fractures, which may result in vascular compromise to the humeral head, leading to avascular necrosis. Surgical goals for the management of these fractures are to optimize functional outcomes by re-creating a stable construct with a functional rotator cuff by open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF), hemiarthroplasty with tuberosity ORIF, or reverse shoulder replacement. Achieving a good outcome following hemiarthroplasty is dependent on many factors, including anatomic tuberosity healing and component positioning.1,2,3 Repairing the greater tuberosity in a near-anatomic position has been shown to greatly affect the results of hemiarthroplasty for fracture.3,4
Continue to: Three-dimensional (3-D) modeling...
Three-dimensional (3-D) modeling is increasingly being used in preoperative planning of shoulder arthroplasty and determining proper proximal humeral fracture treatment. 5 However, no studies have examined the reconstruction of a fractured proximal humerus into native anatomy using computer simulation. The purpose of this study is to determine the accuracy and reliability of anatomically reconstructing the preinjury proximal humerus using 3-D computer models created from postinjury computed tomography (CT) scans. The results of this study could lead to useful techniques employing CT–based models for patient-specific preoperative planning of proximal humeral fracture ORIF and during tuberosity reduction and fixation during hemiarthroplasty for fracture. We hypothesize that it is feasible to reconstruct the original anatomy of the proximal humerus by using 3-D computer modeling of proximal humerus fractures with high reliability based on interobserver and intraobserver review.
METHODS
After Institutional Review Board approval was obtained, we reviewed the medical records of consecutive patients with a diagnosis of proximal humeral fracture and the treatment codes for hemiarthroplasty from 2000 to 2013. Inclusion criteria included 3- and 4-part fractures (AO classifications 11-B1, 11-B2, 11-C1, 11-C2). CT scans with insufficient quality to differentiate bone from soft tissue (inadequate signal-to-noise ratio) were excluded from the study. A total of 28 patients with adequate CT scans met the criteria for inclusion in this study.
The CT scan protocol included 0.5-mm axial cuts with inclusion of the proximal humerus in the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine format. These CT scans were converted into patient-specific 3-D computer models of the shoulder using Mimics software (Materialise Inc.). The use of this software to produce anatomically accurate models has previously been verified in a shoulder model.6,7 The tuberosity fragments were then individually separated from each other using the voxel-selecting capabilities of 3-D software and manipulated with translation and rotation for anatomic reduction (Figures 1A-1D, Figure 2).
The de-identified anatomically reconstructed shoulder models were then uploaded into Materialise’s Magics rapid prototyping software, and a user-defined humeral Cartesian coordinate system was defined with anatomic landmarks as reference points to standardize the position of each model (Figure 3).8,9
A series of measurements were made on these models to assess the validity and reliability of the reassembly. The bicipital groove at the anatomic neck was used to measure humeral head version as described by Kummer and colleagues.10 The head-shaft angle, humeral head-greater tuberosity distance, humeral head-bicipital groove angle, and posterior and medial humeral head offset were measured directly on the reconstructed humerus.
Continue to: Two fellowship-trained shoulder...
Two fellowship-trained shoulder surgeons independently reassembled these fracture fragments via computer simulation. Interobserver reliability testing was conducted on these reconstructions by measuring the geometry between the 2 different surgeons’ reconstructions. Intraobserver reliability testing was conducted by 1 surgeon repeating the reconstructions with 4-week intervals between trials and measuring the geometry between the 2 different trials. The average dimensions of the reconstructed proximal humerus fractures were compared with the geometry of normal humeri reported in previously conducted anatomic studies.11,12,13
STATISTICS
The measured dimensions of the 28 reassembled proximal humeri models were averaged across all trials between the 2 fellowship-trained surgeons and compared with the range of normal dimensions of a healthy proximal humerus using the 2 one-sided tests (TOST) method for equivalence between 2 means given a range. The interobserver and intraobserver reliabilities were quantified using the interclass correlation coefficient. An excellent correlation was defined as a correlation coefficient >0.81; very good was defined as 0.61 to 0.80; and good was defined as 0.41 to 0.60.
RESULTS
Of the patients studied, 9 (32.1%) were male, and the average age at the time of CT scanning was 72 years. Of the 28 patients with fracture, 18 (64.2%) had 3-part fractures (AO classifications 11-B1, 11-B2), and 10 (35.8%) had 4-part fractures (AO classifications 11-C1, 11-C2). When examining the location of the intertubercular fracture line, we found that 13 (46.4%) fractures went through the bicipital groove. Of the remaining fracture lines, 9 (32.1%) extended into the greater tuberosity and 6 (21.4%) extended into the lesser tuberosity.
All users were able to reconstruct all 28 fractures using this technique. The average measured dimensions fell within the range of dimensions of a normal healthy proximal humerus specified in the literature to within a 95% confidence interval using the TOST for equivalence, in which we compared measured values with ranges reported in the literature (Table).11,12,13
Table. Dimensions of Proximal Humerus Geometry
| Normal Parameters | Average Dimensions From Trials | Dimensions From Literature |
| Head shaft angle | 43.5° ± 1° | 42.5° ± 12.5° |
| Head to greater tuberosity distance | 4.9 mm ± 0.4 mm | 8 mm ± 3.2 mm |
Head to bicipital groove angle (anatomic neck) | 26.4° ± 2° | 27.3° ± 14° |
| Posterior humeral head offset | 1.6 mm ± 0.3 mm | 4 mm ± 6 mm |
| Medial humeral head offset | 4.5 mm ± 0.3 mm | 9 mm ± 5 mm |
The reconstructions of these humerus fractures showed intraclass correlation coefficients ranging from 0.71 to 0.93 in 1 observer and interclass correlation coefficients from 0.82 to 0.98 between 2 different observers (Table).
DISCUSSION
This study demonstrates that it is feasible to reliably and accurately reconstruct the original anatomy of the proximal humerus by using 3-D computer modeling of proximal humerus fractures. Poor outcomes after hemiarthroplasty for proximal humerus fractures are mostly related to tuberosity malpositioning, resorption, or failure of fixation and resultant dysfunction of the rotator cuff.14,15,16 These studies highlight the importance of accurate tuberosity reduction during surgical care of these fractures.
Continue to: The 3-D computer model...
The 3-D computer model reconstruction of 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures were reliable and valid. The interclass correlation coefficients showed very good to excellent interobserver and intraobserver reliability for all measurements conducted. The averaged dimensions from all trials fell within the appropriate range of dimensions for a normal healthy humerus reported in the literature, as verified by the TOST method.11,12,13 The 3-D modeling capabilities demonstrated in this study allowed a greater understanding of the fracture patterns present in 3- and 4-part (AO classifications 11-B1, 11-B2, 11-C1, 11-C2) humerus fractures.
Overreduction of greater tuberosity to create cortical overlap with the lateral shaft may be used to promote bony union. As a result of this distalization, there may be extra strains placed on the rotator cuff, making the patient more prone to rotator cuff tear, as well as improperly balancing the dynamic stabilizers of the shoulder. Poor clinical outcomes in hemiarthroplasty for proximal humerus fractures have been correlated with a greater tuberosity placed distal relative to the humeral head by 1 cm in a study2 and by 2 cm in another.3
This study has several limitations. The first is the assumption that our injured patients had preinjury proximal humerus geometry within the range of normal dimensions of a healthy humerus. Unfortunately, because we were unable to obtain CT scans of the contralateral shoulder, we had to use standard proximal humerus geometry as the control. Another limitation, inherent in the technique, is that only cortical and dense trabecular bone was modeled, so that comminuted or osteoporotic bone was not well modeled. This study did not correlate the findings from these models with clinical outcomes. A prospective study is needed to evaluate the impact of this 3-D modeling on fracture reductions and clinical outcomes.
This study demonstrates that patient-specific modeling of proximal humerus fracture 3-D CT scans may help surgeons reliably and accurately reconstruct fractures. This technique may have utility in the preoperative planning of tuberosity fracture reduction and hemiarthroplasty. It gives surgeons the ability to visualize fracture fragments, and the process of reconstructing the fragments may help surgeons understand the required maneuvers for reduction at the time of surgery. This technique also provides dimensions of the patient’s native humerus, thus potentially improving the anatomic accuracy of the reduction or hemiarthroplasty reconstruction. With the new trend toward patient-specific instrumentation, this study also provides a means of planning the size of the humeral prostheses as well as the version relative to the biceps groove and intertubercular fracture line.
CONCLUSION
This study demonstrates the feasibility of using 3-D computer modeling of complex proximal humerus fractures in anatomic reconstruction. These techniques of computer-simulated 3-D models are valid and reliable. We believe that this technique of modeling and reconstructing proximal humerus fractures could be used to enhance the preoperative planning of hemiarthroplasty for 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures by providing improved understanding of the patient’s native humeral geometry and tuberosity reduction.
1. Boileau P, Krishnan SG, Tinsi L, Walch G, Coste JS, Mole D. Tuberosity malposition and migration: reasons for poor outcomes after hemiarthroplasty for displaced fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002;11(5):401-412. doi:10.1067/mse.2002.124527.
2. Mighell MA, Kolm GP, Collinge CA, Frankle MA. Outcomes of hemiarthroplasty for fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(6):569-577. doi:10.1016/S1058274603002131.
3. Greiner SH, Kaab MJ, Kroning I, Scheibel M, Perka C. Reconstruction of humeral length and centering of the prosthetic head in hemiarthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(5):709-714. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2008.03.004.
4. Smith AM, Mardones RM, Sperling JW, Cofield RH. Early complications of operatively treated proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(1):14-24. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2006.05.008.
5. Scalise JJ, Codsi MJ, Bryan J, Iannotti JP. The three-dimensional glenoid vault model can estimate normal glenoid version in osteoarthritis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(3):487-491. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2007.09.006.
6. Bryce CD, Pennypacker JL, Kulkarni N, et al. Validation of three-dimensional models of in situ scapulae. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(5):825-832. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2008.01.141.
7. Yongpravat C, Kim HM, Gardner TR, Bigliani LU, Levine WN, Ahmad CS. Glenoid implant orientation and cement failure in total shoulder arthroplasty: a finite element analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(7):940-947. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2012.09.007.
8. Boileau P, Walch G. The three-dimensional geometry of the proximal humerus. Implications for surgical technique and prosthetic design. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79(5):857-865. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.79B5.0790857.
9. Wu G, van der Helm FC, Veeger HE, et al. ISB recommendation on definitions of joint coordinate systems of various joints for the reporting of human joint motion--Part II: shoulder, elbow, wrist and hand. J Biomech. 2005;38(5):981-992.
10. Kummer FJ, Perkins R, Zuckerman JD. The use of the bicipital groove for alignment of the humeral stem in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7(2):144-146. doi:10.1016/S1058-2746(98)90225-7.
11. Iannotti JP, Gabriel JP, Schneck SL, Evans BG, Misra S. The normal glenohumeral relationships. An anatomical study of one hundred and forty shoulders. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74(4):491-500.
12. Pearl ML, Volk AG. Coronal plane geometry of the proximal humerus relevant to prosthetic arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1996;5(4):320-326. doi:10.1016/S1058-2746(96)80060-7.
13. Pearl ML. Proximal humeral anatomy in shoulder arthroplasty: Implications for prosthetic design and surgical technique. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14(1 Suppl S):99S-104S. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2004.09.025.
14. Prakash U, McGurty DW, Dent JA. Hemiarthroplasty for severe fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002;11(5):428-430. doi:10.1067/mse.2002.126615.
15. Robinson CM, Page RS, Hill RM, Sanders DL, Court-Brown CM, Wakefield AE. Primary hemiarthroplasty for treatment of proximal humeral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(7):1215-1223.
16. Zyto K, Wallace WA, Frostick SP, Preston BJ. Outcome after hemiarthroplasty for three- and four-part fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7(2):85-89. doi:10.1016/S1058-2746(98)90215-4.
ABSTRACT
The objective of this study is to determine the reproducibility and feasibility of using 3-dimensional (3-D) computer simulation of proximal humerus fracture computed tomography (CT) scans for fracture reduction. We hypothesized that anatomic reconstruction with 3-D models would be anatomically accurate and reproducible.
Preoperative CT scans of 28 patients with 3- and 4-part (AO classification 11-B1, 11-B2, 11-C1, 11-C2) proximal humerus fractures who were treated by hemiarthroplasty were converted into 3-D computer models. The displaced fractured fragments were anatomically reduced with computer simulation by 2 fellowship-trained shoulder surgeons, and measurements were made of the reconstructed proximal humerus.
The measurements of the reconstructed models had very good to excellent interobserver and intraobserver reliability. The reconstructions of these humerus fractures showed interclass correlation coefficients ranging from 0.71 to 0.93 between 1 observer and from 0.82 to 0.98 between 2 different observers. The fracture reduction was judged against normal proximal humerus geometry to determine reduction accuracy.
The 3-D modeling techniques used to reconstruct 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures were reliable and accurate. This technique of modeling and reconstructing proximal humerus fractures could be used to enhance the preoperative planning of open reduction and internal fixation or hemiarthroplasty for 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures.
The treatment of proximal humerus fractures is influenced by multiple factors, including patient age, associated injuries, bone quality, and fracture pattern. Three- and 4-part fractures are among the more severe of these fractures, which may result in vascular compromise to the humeral head, leading to avascular necrosis. Surgical goals for the management of these fractures are to optimize functional outcomes by re-creating a stable construct with a functional rotator cuff by open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF), hemiarthroplasty with tuberosity ORIF, or reverse shoulder replacement. Achieving a good outcome following hemiarthroplasty is dependent on many factors, including anatomic tuberosity healing and component positioning.1,2,3 Repairing the greater tuberosity in a near-anatomic position has been shown to greatly affect the results of hemiarthroplasty for fracture.3,4
Continue to: Three-dimensional (3-D) modeling...
Three-dimensional (3-D) modeling is increasingly being used in preoperative planning of shoulder arthroplasty and determining proper proximal humeral fracture treatment. 5 However, no studies have examined the reconstruction of a fractured proximal humerus into native anatomy using computer simulation. The purpose of this study is to determine the accuracy and reliability of anatomically reconstructing the preinjury proximal humerus using 3-D computer models created from postinjury computed tomography (CT) scans. The results of this study could lead to useful techniques employing CT–based models for patient-specific preoperative planning of proximal humeral fracture ORIF and during tuberosity reduction and fixation during hemiarthroplasty for fracture. We hypothesize that it is feasible to reconstruct the original anatomy of the proximal humerus by using 3-D computer modeling of proximal humerus fractures with high reliability based on interobserver and intraobserver review.
METHODS
After Institutional Review Board approval was obtained, we reviewed the medical records of consecutive patients with a diagnosis of proximal humeral fracture and the treatment codes for hemiarthroplasty from 2000 to 2013. Inclusion criteria included 3- and 4-part fractures (AO classifications 11-B1, 11-B2, 11-C1, 11-C2). CT scans with insufficient quality to differentiate bone from soft tissue (inadequate signal-to-noise ratio) were excluded from the study. A total of 28 patients with adequate CT scans met the criteria for inclusion in this study.
The CT scan protocol included 0.5-mm axial cuts with inclusion of the proximal humerus in the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine format. These CT scans were converted into patient-specific 3-D computer models of the shoulder using Mimics software (Materialise Inc.). The use of this software to produce anatomically accurate models has previously been verified in a shoulder model.6,7 The tuberosity fragments were then individually separated from each other using the voxel-selecting capabilities of 3-D software and manipulated with translation and rotation for anatomic reduction (Figures 1A-1D, Figure 2).
The de-identified anatomically reconstructed shoulder models were then uploaded into Materialise’s Magics rapid prototyping software, and a user-defined humeral Cartesian coordinate system was defined with anatomic landmarks as reference points to standardize the position of each model (Figure 3).8,9
A series of measurements were made on these models to assess the validity and reliability of the reassembly. The bicipital groove at the anatomic neck was used to measure humeral head version as described by Kummer and colleagues.10 The head-shaft angle, humeral head-greater tuberosity distance, humeral head-bicipital groove angle, and posterior and medial humeral head offset were measured directly on the reconstructed humerus.
Continue to: Two fellowship-trained shoulder...
Two fellowship-trained shoulder surgeons independently reassembled these fracture fragments via computer simulation. Interobserver reliability testing was conducted on these reconstructions by measuring the geometry between the 2 different surgeons’ reconstructions. Intraobserver reliability testing was conducted by 1 surgeon repeating the reconstructions with 4-week intervals between trials and measuring the geometry between the 2 different trials. The average dimensions of the reconstructed proximal humerus fractures were compared with the geometry of normal humeri reported in previously conducted anatomic studies.11,12,13
STATISTICS
The measured dimensions of the 28 reassembled proximal humeri models were averaged across all trials between the 2 fellowship-trained surgeons and compared with the range of normal dimensions of a healthy proximal humerus using the 2 one-sided tests (TOST) method for equivalence between 2 means given a range. The interobserver and intraobserver reliabilities were quantified using the interclass correlation coefficient. An excellent correlation was defined as a correlation coefficient >0.81; very good was defined as 0.61 to 0.80; and good was defined as 0.41 to 0.60.
RESULTS
Of the patients studied, 9 (32.1%) were male, and the average age at the time of CT scanning was 72 years. Of the 28 patients with fracture, 18 (64.2%) had 3-part fractures (AO classifications 11-B1, 11-B2), and 10 (35.8%) had 4-part fractures (AO classifications 11-C1, 11-C2). When examining the location of the intertubercular fracture line, we found that 13 (46.4%) fractures went through the bicipital groove. Of the remaining fracture lines, 9 (32.1%) extended into the greater tuberosity and 6 (21.4%) extended into the lesser tuberosity.
All users were able to reconstruct all 28 fractures using this technique. The average measured dimensions fell within the range of dimensions of a normal healthy proximal humerus specified in the literature to within a 95% confidence interval using the TOST for equivalence, in which we compared measured values with ranges reported in the literature (Table).11,12,13
Table. Dimensions of Proximal Humerus Geometry
| Normal Parameters | Average Dimensions From Trials | Dimensions From Literature |
| Head shaft angle | 43.5° ± 1° | 42.5° ± 12.5° |
| Head to greater tuberosity distance | 4.9 mm ± 0.4 mm | 8 mm ± 3.2 mm |
Head to bicipital groove angle (anatomic neck) | 26.4° ± 2° | 27.3° ± 14° |
| Posterior humeral head offset | 1.6 mm ± 0.3 mm | 4 mm ± 6 mm |
| Medial humeral head offset | 4.5 mm ± 0.3 mm | 9 mm ± 5 mm |
The reconstructions of these humerus fractures showed intraclass correlation coefficients ranging from 0.71 to 0.93 in 1 observer and interclass correlation coefficients from 0.82 to 0.98 between 2 different observers (Table).
DISCUSSION
This study demonstrates that it is feasible to reliably and accurately reconstruct the original anatomy of the proximal humerus by using 3-D computer modeling of proximal humerus fractures. Poor outcomes after hemiarthroplasty for proximal humerus fractures are mostly related to tuberosity malpositioning, resorption, or failure of fixation and resultant dysfunction of the rotator cuff.14,15,16 These studies highlight the importance of accurate tuberosity reduction during surgical care of these fractures.
Continue to: The 3-D computer model...
The 3-D computer model reconstruction of 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures were reliable and valid. The interclass correlation coefficients showed very good to excellent interobserver and intraobserver reliability for all measurements conducted. The averaged dimensions from all trials fell within the appropriate range of dimensions for a normal healthy humerus reported in the literature, as verified by the TOST method.11,12,13 The 3-D modeling capabilities demonstrated in this study allowed a greater understanding of the fracture patterns present in 3- and 4-part (AO classifications 11-B1, 11-B2, 11-C1, 11-C2) humerus fractures.
Overreduction of greater tuberosity to create cortical overlap with the lateral shaft may be used to promote bony union. As a result of this distalization, there may be extra strains placed on the rotator cuff, making the patient more prone to rotator cuff tear, as well as improperly balancing the dynamic stabilizers of the shoulder. Poor clinical outcomes in hemiarthroplasty for proximal humerus fractures have been correlated with a greater tuberosity placed distal relative to the humeral head by 1 cm in a study2 and by 2 cm in another.3
This study has several limitations. The first is the assumption that our injured patients had preinjury proximal humerus geometry within the range of normal dimensions of a healthy humerus. Unfortunately, because we were unable to obtain CT scans of the contralateral shoulder, we had to use standard proximal humerus geometry as the control. Another limitation, inherent in the technique, is that only cortical and dense trabecular bone was modeled, so that comminuted or osteoporotic bone was not well modeled. This study did not correlate the findings from these models with clinical outcomes. A prospective study is needed to evaluate the impact of this 3-D modeling on fracture reductions and clinical outcomes.
This study demonstrates that patient-specific modeling of proximal humerus fracture 3-D CT scans may help surgeons reliably and accurately reconstruct fractures. This technique may have utility in the preoperative planning of tuberosity fracture reduction and hemiarthroplasty. It gives surgeons the ability to visualize fracture fragments, and the process of reconstructing the fragments may help surgeons understand the required maneuvers for reduction at the time of surgery. This technique also provides dimensions of the patient’s native humerus, thus potentially improving the anatomic accuracy of the reduction or hemiarthroplasty reconstruction. With the new trend toward patient-specific instrumentation, this study also provides a means of planning the size of the humeral prostheses as well as the version relative to the biceps groove and intertubercular fracture line.
CONCLUSION
This study demonstrates the feasibility of using 3-D computer modeling of complex proximal humerus fractures in anatomic reconstruction. These techniques of computer-simulated 3-D models are valid and reliable. We believe that this technique of modeling and reconstructing proximal humerus fractures could be used to enhance the preoperative planning of hemiarthroplasty for 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures by providing improved understanding of the patient’s native humeral geometry and tuberosity reduction.
ABSTRACT
The objective of this study is to determine the reproducibility and feasibility of using 3-dimensional (3-D) computer simulation of proximal humerus fracture computed tomography (CT) scans for fracture reduction. We hypothesized that anatomic reconstruction with 3-D models would be anatomically accurate and reproducible.
Preoperative CT scans of 28 patients with 3- and 4-part (AO classification 11-B1, 11-B2, 11-C1, 11-C2) proximal humerus fractures who were treated by hemiarthroplasty were converted into 3-D computer models. The displaced fractured fragments were anatomically reduced with computer simulation by 2 fellowship-trained shoulder surgeons, and measurements were made of the reconstructed proximal humerus.
The measurements of the reconstructed models had very good to excellent interobserver and intraobserver reliability. The reconstructions of these humerus fractures showed interclass correlation coefficients ranging from 0.71 to 0.93 between 1 observer and from 0.82 to 0.98 between 2 different observers. The fracture reduction was judged against normal proximal humerus geometry to determine reduction accuracy.
The 3-D modeling techniques used to reconstruct 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures were reliable and accurate. This technique of modeling and reconstructing proximal humerus fractures could be used to enhance the preoperative planning of open reduction and internal fixation or hemiarthroplasty for 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures.
The treatment of proximal humerus fractures is influenced by multiple factors, including patient age, associated injuries, bone quality, and fracture pattern. Three- and 4-part fractures are among the more severe of these fractures, which may result in vascular compromise to the humeral head, leading to avascular necrosis. Surgical goals for the management of these fractures are to optimize functional outcomes by re-creating a stable construct with a functional rotator cuff by open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF), hemiarthroplasty with tuberosity ORIF, or reverse shoulder replacement. Achieving a good outcome following hemiarthroplasty is dependent on many factors, including anatomic tuberosity healing and component positioning.1,2,3 Repairing the greater tuberosity in a near-anatomic position has been shown to greatly affect the results of hemiarthroplasty for fracture.3,4
Continue to: Three-dimensional (3-D) modeling...
Three-dimensional (3-D) modeling is increasingly being used in preoperative planning of shoulder arthroplasty and determining proper proximal humeral fracture treatment. 5 However, no studies have examined the reconstruction of a fractured proximal humerus into native anatomy using computer simulation. The purpose of this study is to determine the accuracy and reliability of anatomically reconstructing the preinjury proximal humerus using 3-D computer models created from postinjury computed tomography (CT) scans. The results of this study could lead to useful techniques employing CT–based models for patient-specific preoperative planning of proximal humeral fracture ORIF and during tuberosity reduction and fixation during hemiarthroplasty for fracture. We hypothesize that it is feasible to reconstruct the original anatomy of the proximal humerus by using 3-D computer modeling of proximal humerus fractures with high reliability based on interobserver and intraobserver review.
METHODS
After Institutional Review Board approval was obtained, we reviewed the medical records of consecutive patients with a diagnosis of proximal humeral fracture and the treatment codes for hemiarthroplasty from 2000 to 2013. Inclusion criteria included 3- and 4-part fractures (AO classifications 11-B1, 11-B2, 11-C1, 11-C2). CT scans with insufficient quality to differentiate bone from soft tissue (inadequate signal-to-noise ratio) were excluded from the study. A total of 28 patients with adequate CT scans met the criteria for inclusion in this study.
The CT scan protocol included 0.5-mm axial cuts with inclusion of the proximal humerus in the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine format. These CT scans were converted into patient-specific 3-D computer models of the shoulder using Mimics software (Materialise Inc.). The use of this software to produce anatomically accurate models has previously been verified in a shoulder model.6,7 The tuberosity fragments were then individually separated from each other using the voxel-selecting capabilities of 3-D software and manipulated with translation and rotation for anatomic reduction (Figures 1A-1D, Figure 2).
The de-identified anatomically reconstructed shoulder models were then uploaded into Materialise’s Magics rapid prototyping software, and a user-defined humeral Cartesian coordinate system was defined with anatomic landmarks as reference points to standardize the position of each model (Figure 3).8,9
A series of measurements were made on these models to assess the validity and reliability of the reassembly. The bicipital groove at the anatomic neck was used to measure humeral head version as described by Kummer and colleagues.10 The head-shaft angle, humeral head-greater tuberosity distance, humeral head-bicipital groove angle, and posterior and medial humeral head offset were measured directly on the reconstructed humerus.
Continue to: Two fellowship-trained shoulder...
Two fellowship-trained shoulder surgeons independently reassembled these fracture fragments via computer simulation. Interobserver reliability testing was conducted on these reconstructions by measuring the geometry between the 2 different surgeons’ reconstructions. Intraobserver reliability testing was conducted by 1 surgeon repeating the reconstructions with 4-week intervals between trials and measuring the geometry between the 2 different trials. The average dimensions of the reconstructed proximal humerus fractures were compared with the geometry of normal humeri reported in previously conducted anatomic studies.11,12,13
STATISTICS
The measured dimensions of the 28 reassembled proximal humeri models were averaged across all trials between the 2 fellowship-trained surgeons and compared with the range of normal dimensions of a healthy proximal humerus using the 2 one-sided tests (TOST) method for equivalence between 2 means given a range. The interobserver and intraobserver reliabilities were quantified using the interclass correlation coefficient. An excellent correlation was defined as a correlation coefficient >0.81; very good was defined as 0.61 to 0.80; and good was defined as 0.41 to 0.60.
RESULTS
Of the patients studied, 9 (32.1%) were male, and the average age at the time of CT scanning was 72 years. Of the 28 patients with fracture, 18 (64.2%) had 3-part fractures (AO classifications 11-B1, 11-B2), and 10 (35.8%) had 4-part fractures (AO classifications 11-C1, 11-C2). When examining the location of the intertubercular fracture line, we found that 13 (46.4%) fractures went through the bicipital groove. Of the remaining fracture lines, 9 (32.1%) extended into the greater tuberosity and 6 (21.4%) extended into the lesser tuberosity.
All users were able to reconstruct all 28 fractures using this technique. The average measured dimensions fell within the range of dimensions of a normal healthy proximal humerus specified in the literature to within a 95% confidence interval using the TOST for equivalence, in which we compared measured values with ranges reported in the literature (Table).11,12,13
Table. Dimensions of Proximal Humerus Geometry
| Normal Parameters | Average Dimensions From Trials | Dimensions From Literature |
| Head shaft angle | 43.5° ± 1° | 42.5° ± 12.5° |
| Head to greater tuberosity distance | 4.9 mm ± 0.4 mm | 8 mm ± 3.2 mm |
Head to bicipital groove angle (anatomic neck) | 26.4° ± 2° | 27.3° ± 14° |
| Posterior humeral head offset | 1.6 mm ± 0.3 mm | 4 mm ± 6 mm |
| Medial humeral head offset | 4.5 mm ± 0.3 mm | 9 mm ± 5 mm |
The reconstructions of these humerus fractures showed intraclass correlation coefficients ranging from 0.71 to 0.93 in 1 observer and interclass correlation coefficients from 0.82 to 0.98 between 2 different observers (Table).
DISCUSSION
This study demonstrates that it is feasible to reliably and accurately reconstruct the original anatomy of the proximal humerus by using 3-D computer modeling of proximal humerus fractures. Poor outcomes after hemiarthroplasty for proximal humerus fractures are mostly related to tuberosity malpositioning, resorption, or failure of fixation and resultant dysfunction of the rotator cuff.14,15,16 These studies highlight the importance of accurate tuberosity reduction during surgical care of these fractures.
Continue to: The 3-D computer model...
The 3-D computer model reconstruction of 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures were reliable and valid. The interclass correlation coefficients showed very good to excellent interobserver and intraobserver reliability for all measurements conducted. The averaged dimensions from all trials fell within the appropriate range of dimensions for a normal healthy humerus reported in the literature, as verified by the TOST method.11,12,13 The 3-D modeling capabilities demonstrated in this study allowed a greater understanding of the fracture patterns present in 3- and 4-part (AO classifications 11-B1, 11-B2, 11-C1, 11-C2) humerus fractures.
Overreduction of greater tuberosity to create cortical overlap with the lateral shaft may be used to promote bony union. As a result of this distalization, there may be extra strains placed on the rotator cuff, making the patient more prone to rotator cuff tear, as well as improperly balancing the dynamic stabilizers of the shoulder. Poor clinical outcomes in hemiarthroplasty for proximal humerus fractures have been correlated with a greater tuberosity placed distal relative to the humeral head by 1 cm in a study2 and by 2 cm in another.3
This study has several limitations. The first is the assumption that our injured patients had preinjury proximal humerus geometry within the range of normal dimensions of a healthy humerus. Unfortunately, because we were unable to obtain CT scans of the contralateral shoulder, we had to use standard proximal humerus geometry as the control. Another limitation, inherent in the technique, is that only cortical and dense trabecular bone was modeled, so that comminuted or osteoporotic bone was not well modeled. This study did not correlate the findings from these models with clinical outcomes. A prospective study is needed to evaluate the impact of this 3-D modeling on fracture reductions and clinical outcomes.
This study demonstrates that patient-specific modeling of proximal humerus fracture 3-D CT scans may help surgeons reliably and accurately reconstruct fractures. This technique may have utility in the preoperative planning of tuberosity fracture reduction and hemiarthroplasty. It gives surgeons the ability to visualize fracture fragments, and the process of reconstructing the fragments may help surgeons understand the required maneuvers for reduction at the time of surgery. This technique also provides dimensions of the patient’s native humerus, thus potentially improving the anatomic accuracy of the reduction or hemiarthroplasty reconstruction. With the new trend toward patient-specific instrumentation, this study also provides a means of planning the size of the humeral prostheses as well as the version relative to the biceps groove and intertubercular fracture line.
CONCLUSION
This study demonstrates the feasibility of using 3-D computer modeling of complex proximal humerus fractures in anatomic reconstruction. These techniques of computer-simulated 3-D models are valid and reliable. We believe that this technique of modeling and reconstructing proximal humerus fractures could be used to enhance the preoperative planning of hemiarthroplasty for 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures by providing improved understanding of the patient’s native humeral geometry and tuberosity reduction.
1. Boileau P, Krishnan SG, Tinsi L, Walch G, Coste JS, Mole D. Tuberosity malposition and migration: reasons for poor outcomes after hemiarthroplasty for displaced fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002;11(5):401-412. doi:10.1067/mse.2002.124527.
2. Mighell MA, Kolm GP, Collinge CA, Frankle MA. Outcomes of hemiarthroplasty for fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(6):569-577. doi:10.1016/S1058274603002131.
3. Greiner SH, Kaab MJ, Kroning I, Scheibel M, Perka C. Reconstruction of humeral length and centering of the prosthetic head in hemiarthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(5):709-714. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2008.03.004.
4. Smith AM, Mardones RM, Sperling JW, Cofield RH. Early complications of operatively treated proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(1):14-24. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2006.05.008.
5. Scalise JJ, Codsi MJ, Bryan J, Iannotti JP. The three-dimensional glenoid vault model can estimate normal glenoid version in osteoarthritis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(3):487-491. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2007.09.006.
6. Bryce CD, Pennypacker JL, Kulkarni N, et al. Validation of three-dimensional models of in situ scapulae. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(5):825-832. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2008.01.141.
7. Yongpravat C, Kim HM, Gardner TR, Bigliani LU, Levine WN, Ahmad CS. Glenoid implant orientation and cement failure in total shoulder arthroplasty: a finite element analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(7):940-947. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2012.09.007.
8. Boileau P, Walch G. The three-dimensional geometry of the proximal humerus. Implications for surgical technique and prosthetic design. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79(5):857-865. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.79B5.0790857.
9. Wu G, van der Helm FC, Veeger HE, et al. ISB recommendation on definitions of joint coordinate systems of various joints for the reporting of human joint motion--Part II: shoulder, elbow, wrist and hand. J Biomech. 2005;38(5):981-992.
10. Kummer FJ, Perkins R, Zuckerman JD. The use of the bicipital groove for alignment of the humeral stem in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7(2):144-146. doi:10.1016/S1058-2746(98)90225-7.
11. Iannotti JP, Gabriel JP, Schneck SL, Evans BG, Misra S. The normal glenohumeral relationships. An anatomical study of one hundred and forty shoulders. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74(4):491-500.
12. Pearl ML, Volk AG. Coronal plane geometry of the proximal humerus relevant to prosthetic arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1996;5(4):320-326. doi:10.1016/S1058-2746(96)80060-7.
13. Pearl ML. Proximal humeral anatomy in shoulder arthroplasty: Implications for prosthetic design and surgical technique. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14(1 Suppl S):99S-104S. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2004.09.025.
14. Prakash U, McGurty DW, Dent JA. Hemiarthroplasty for severe fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002;11(5):428-430. doi:10.1067/mse.2002.126615.
15. Robinson CM, Page RS, Hill RM, Sanders DL, Court-Brown CM, Wakefield AE. Primary hemiarthroplasty for treatment of proximal humeral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(7):1215-1223.
16. Zyto K, Wallace WA, Frostick SP, Preston BJ. Outcome after hemiarthroplasty for three- and four-part fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7(2):85-89. doi:10.1016/S1058-2746(98)90215-4.
1. Boileau P, Krishnan SG, Tinsi L, Walch G, Coste JS, Mole D. Tuberosity malposition and migration: reasons for poor outcomes after hemiarthroplasty for displaced fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002;11(5):401-412. doi:10.1067/mse.2002.124527.
2. Mighell MA, Kolm GP, Collinge CA, Frankle MA. Outcomes of hemiarthroplasty for fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(6):569-577. doi:10.1016/S1058274603002131.
3. Greiner SH, Kaab MJ, Kroning I, Scheibel M, Perka C. Reconstruction of humeral length and centering of the prosthetic head in hemiarthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(5):709-714. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2008.03.004.
4. Smith AM, Mardones RM, Sperling JW, Cofield RH. Early complications of operatively treated proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(1):14-24. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2006.05.008.
5. Scalise JJ, Codsi MJ, Bryan J, Iannotti JP. The three-dimensional glenoid vault model can estimate normal glenoid version in osteoarthritis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(3):487-491. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2007.09.006.
6. Bryce CD, Pennypacker JL, Kulkarni N, et al. Validation of three-dimensional models of in situ scapulae. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(5):825-832. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2008.01.141.
7. Yongpravat C, Kim HM, Gardner TR, Bigliani LU, Levine WN, Ahmad CS. Glenoid implant orientation and cement failure in total shoulder arthroplasty: a finite element analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(7):940-947. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2012.09.007.
8. Boileau P, Walch G. The three-dimensional geometry of the proximal humerus. Implications for surgical technique and prosthetic design. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79(5):857-865. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.79B5.0790857.
9. Wu G, van der Helm FC, Veeger HE, et al. ISB recommendation on definitions of joint coordinate systems of various joints for the reporting of human joint motion--Part II: shoulder, elbow, wrist and hand. J Biomech. 2005;38(5):981-992.
10. Kummer FJ, Perkins R, Zuckerman JD. The use of the bicipital groove for alignment of the humeral stem in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7(2):144-146. doi:10.1016/S1058-2746(98)90225-7.
11. Iannotti JP, Gabriel JP, Schneck SL, Evans BG, Misra S. The normal glenohumeral relationships. An anatomical study of one hundred and forty shoulders. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74(4):491-500.
12. Pearl ML, Volk AG. Coronal plane geometry of the proximal humerus relevant to prosthetic arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1996;5(4):320-326. doi:10.1016/S1058-2746(96)80060-7.
13. Pearl ML. Proximal humeral anatomy in shoulder arthroplasty: Implications for prosthetic design and surgical technique. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14(1 Suppl S):99S-104S. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2004.09.025.
14. Prakash U, McGurty DW, Dent JA. Hemiarthroplasty for severe fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002;11(5):428-430. doi:10.1067/mse.2002.126615.
15. Robinson CM, Page RS, Hill RM, Sanders DL, Court-Brown CM, Wakefield AE. Primary hemiarthroplasty for treatment of proximal humeral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(7):1215-1223.
16. Zyto K, Wallace WA, Frostick SP, Preston BJ. Outcome after hemiarthroplasty for three- and four-part fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7(2):85-89. doi:10.1016/S1058-2746(98)90215-4.
TAKE-HOME POINTS
- Proximal humerus fractures may be better understood with 3-D CT imaging.
- 3-D computer modeling of complex proximal humerus fractures allows an understanding of tuebroisty reduction durring ORIF or hemiarthroplasty.
- 3-D modeling enhances preoperative planning for hemiarthroplasty implant size and position relative to the repaired tuberosity fragments.
- 3-D modeling of fracture reduction can help surgeons understand the patient’s native humeral geometry and anatomy.
- Preoperative evaluation of fracture characteristics and fragment reduction help surgeons better understand surgical solutions.
Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Total Shoulder Arthroplasty With a Hybrid Dual-Radii Glenoid Component
Take-Home Points
- The authors have developed a total shoulder glenoid prosthesis that conforms with the humeral head in its center and is nonconforming on its peripheral edge.
- All clinical survey and range of motion parameters demonstrated statistically significant improvements at final follow-up.
- Only 3 shoulders (1.7%) required revision surgery.
- Eighty-six (63%) of 136 shoulders demonstrated no radiographic evidence of glenoid loosening.
- This is the first and largest study that evaluates the clinical and radiographic outcomes of this hybrid shoulder prosthesis.
Fixation of the glenoid component is the limiting factor in modern total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA). Glenoid loosening, the most common long-term complication, necessitates revision in up to 12% of patients.1-4 By contrast, humeral component loosening is relatively uncommon, affecting as few as 0.34% of patients.5 Multiple long-term studies have found consistently high rates (45%-93%) of radiolucencies around the glenoid component.3,6,7 Although their clinical significance has been debated, radiolucencies around the glenoid component raise concern about progressive loss of fixation.
Since TSA was introduced in the 1970s, complications with the glenoid component have been addressed with 2 different designs: conforming (congruent) and nonconforming. In a congruent articulation, the radii of curvature of the glenoid and humeral head components are identical, whereas they differ in a nonconforming model. Joint conformity is inversely related to glenohumeral translation.8 Neer’s original TSA was made congruent in order to limit translation and maximize the contact area. However, this design results in edge loading and a so-called rocking-horse phenomenon, which may lead to glenoid loosening.9-13 Surgeons therefore have increasingly turned to nonconforming implants. In the nonconforming design, the radius of curvature of the humeral head is smaller than that of the glenoid. Although this design may reduce edge loading,14 it allows more translation and reduces the relative contact area of the glenohumeral joint. As a result, more contact stress is transmitted to the glenoid component, leading to polyethylene deformation and wear.15,16
Dual radii of curvature are designed to augment joint stability without increasing component wear. Biomechanical data have indicated that edge loading is not increased by having a central conforming region added to a nonconforming model.17 The clinical value of this prosthesis, however, has not been determined. Therefore, we conducted a study to describe the intermediate-term clinical and radiographic outcomes of TSAs that use a novel hybrid glenoid component.
Materials and Methods
This study was approved (protocol AAAD3473) by the Institutional Review Board of Columbia University and was conducted in compliance with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) regulations.
Patient Selection
At Columbia University Medical Center, Dr. Bigliani performed 196 TSAs with a hybrid glenoid component (Bigliani-Flatow; Zimmer Biomet) in 169 patients between September 1998 and November 2007. All patients had received a diagnosis of primary glenohumeral arthritis as defined by Neer.18 Patients with previous surgery such as rotator cuff repair or subacromial decompression were included in our review, and patients with a nonprimary form of arthritis, such as rheumatoid, posttraumatic, or post-capsulorrhaphy arthritis, were excluded.
Operative Technique
For all surgeries, Dr. Bigliani performed a subscapularis tenotomy with regional anesthesia and a standard deltopectoral approach. A partial anterior capsulectomy was performed to increase the glenoid’s visibility. The inferior labrum was removed with a needle-tip bovie while the axillary nerve was being protected with a metal finger or narrow Darrach retractor. After reaming and trialing, the final glenoid component was cemented into place. Cement was placed only in the peg or keel holes and pressurized twice before final implantation. Of the 196 glenoid components, 168 (86%) were pegged and 28 (14%) keeled; in addition,190 of these components were all-polyethylene, whereas 6 had trabecular-metal backing. All glenoid components incorporated the hybrid design of dual radii of curvature. After the glenoid was cemented, the final humeral component was placed in 30° of retroversion. Whenever posterior wear was found, retroversion was reduced by 5° to 10°. The humeral prosthesis was cemented in cases (104/196, 53%) of poor bone quality or a large canal.
After surgery, the patient’s sling was fitted with an abduction pillow and a swathe, to be worn the first 24 hours, and the arm was passively ranged. Patients typically were discharged on postoperative day 2. Then, for 2 weeks, they followed an assisted passive range of motion (ROM) protocol, with limited external rotation, for promotion of subscapularis healing.
Clinical Outcomes
Dr. Bigliani assessed preoperative ROM in all planes. During initial evaluation, patients completed a questionnaire that consisted of the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey19,20 (SF-36) and the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons21 (ASES) and Simple Shoulder Test22 (SST) surveys. Postoperative clinical data were collected from office follow-up visits, survey questionnaires, or both. Postoperative office data included ROM, subscapularis integrity testing (belly-press or lift-off), and any complications. Patients with <1 year of office follow-up were excluded. In addition, the same survey questionnaire that was used before surgery was mailed to all patients after surgery; then, for anyone who did not respond by mail, we attempted contact by telephone. Neer criteria were based on patients’ subjective assessment of each arm on a 3-point Likert scale (1 = very satisfied, 2 = satisfied, 3 = dissatisfied). Patients were also asked about any specific complications or revision operations since their index procedure.
Physical examination and office follow-up data were obtained for 129 patients (148/196 shoulders, 76% follow-up) at a mean of 3.7 years (range 1.0-10.2 years) after surgery. Surveys were completed by 117 patients (139/196 shoulders, 71% follow-up) at a mean of 5.1 years (range, 1.6-11.2 years) after surgery. Only 15 patients had neither 1 year of office follow-up nor a completed questionnaire. The remaining 154 patients (178/196 shoulders, 91% follow-up) had clinical follow-up with office, mail, or telephone questionnaire at a mean of 4.8 years (range, 1.0-11.2 years) after surgery. This cohort of patients was used to determine rates of surgical revisions, subscapularis tears, dislocations, and other complications.
Radiographic Outcomes
Patients were included in the radiographic analysis if they had a shoulder radiograph at least 1 year after surgery. One hundred nineteen patients (136/196 shoulders, 69% follow-up) had radiographic follow-up at a mean of 3.7 years (range, 1.0-9.4 years) after surgery.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with Stata Version 10.0. Paired t tests were used to compare preoperative and postoperative numerical data, including ROM and survey scores. We calculated 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and set statistical significance at P < .05. For qualitative measures, the Fisher exact test was used. Survivorship analysis was performed according to the Kaplan-Meier method, with right-censored data for no event or missing data.25
Results
Clinical Analysis of Demographics
In demographics, the clinical and radiographic patient subgroups were similar to each other and to the overall study population (Table 2). Of 196 patients overall, 16 (8%) had a concomitant rotator cuff repair, and 27 (14%) underwent staged bilateral shoulder arthroplasties.
Clinical Analysis of ROM and Survey Scores
Operative shoulder ROM in forward elevation, external rotation at side, external rotation in abduction, and internal rotation all showed statistically significant (P < .001) improvement from before surgery to after surgery. Over 3.7 years, mean (SD) forward elevation improved from 107.3° (34.8°) to 159.0° (29.4°), external rotation at side improved from 20.4° (16.7°) to 49.4° (11.3°), and external rotation in abduction improved from 53.7° (24.3°) to 84.7° (9.1°). Internal rotation improved from a mean (SD) vertebral level of S1 (6.0 levels) to T9 (3.7 levels).
All validated survey scores also showed statistically significant (P < .001) improvement from before surgery to after surgery. Over 5.1 years, mean (SD) SF-36 scores improved from 64.9 (13.4) to 73.6 (17.1), ASES scores improved from 41.1 (22.5) to 82.7 (17.7), SST scores improved from 3.9 (2.8) to 9.7 (2.2), and visual analog scale pain scores improved from 5.6 (3.2) to 1.4 (2.1). Of 139 patients with follow-up, 130 (93.5%) were either satisfied or very satisfied with their TSA, and only 119 (86%) were either satisfied or very satisfied with the nonoperative shoulder.
Clinical Analysis of Postoperative Complications
Of the 178 shoulders evaluated for complications, 3 (1.7%) underwent revision surgery. Mean time to revision was 2.3 years (range, 1.5-3.9 years). Two revisions involved the glenoid component, and the third involved the humerus. In one of the glenoid cases, a 77-year-old woman fell and sustained a fracture at the base of the trabecular metal glenoid pegs; her component was revised to an all-polyethylene component, and she had no further complications. In the other glenoid case, a 73-year-old man’s all-polyethylene component loosened after 2 years and was revised to a trabecular metal implant, which loosened as well and was later converted to a hemiarthroplasty. In the humeral case, a 33-year-old man had his 4-year-old index TSA revised to a cemented stem and had no further complications.
Table 4 compares the clinical and radiographic outcomes of patients who required subscapularis repair, capsular shift, or implant revision with the outcomes of all other study patients, and Figure 3 shows Kaplan-Meier survivorship.
Postoperative Radiographic Analysis
Glenoid Component. At a mean of 3.7 years (minimum, 1 year) after surgery, 86 (63%) of 136 radiographically evaluated shoulders showed no glenoid lucencies; the other 50 (37%) showed ≥1 lucency. Of the 136 shoulders, 33 (24%) had a Lazarus score of 1, 15 (11%) had a score of 2, and only 2 (2%) had a score of 3. None of the shoulders had a score of 4 or 5.
Humeral Component. Of the 136 shoulders, 91 (67%) showed no lucencies in any of the 8 humeral stem zones; the other 45 (33%) showed 1 to 3 lucencies. Thirty (22%) of the 136 shoulders had 1 stem lucency zone, 8 (6%) had 2, and 3 (2%) had 3. None of the shoulders had >3 periprosthetic zones with lucent lines.
Discussion
In this article, we describe a hybrid glenoid TSA component with dual radii of curvature. Its central portion is congruent with the humeral head, and its peripheral portion is noncongruent and larger. The most significant finding of our study is the low rate (1.1%) of glenoid component revision 4.8 years after surgery. This rate is the lowest that has been reported in a study of ≥100 patients. Overall implant survival appeared as an almost flat Kaplan-Meir curve. We attribute this low revision rate to improved biomechanics with the hybrid glenoid design.
Symptomatic glenoid component loosening is the most common TSA complication.1,26-28 In a review of 73 Neer TSAs, Cofield7 found glenoid radiolucencies in 71% of patients 3.8 years after surgery. Radiographic evidence of loosening, defined as component migration, or tilt, or a circumferential lucency 1.5 mm thick, was present in another 11% of patients, and 4.1% developed symptomatic loosening that required glenoid revision. In a study with 12.2-year follow-up, Torchia and colleagues3 found rates of 84% for glenoid radiolucencies, 44% for radiographic loosening, and 5.6% for symptomatic loosening that required revision. In a systematic review of studies with follow-up of ≥10 years, Bohsali and colleagues27 found similar lucency and radiographic loosening rates and a 7% glenoid revision rate. These data suggest glenoid radiolucencies may progress to component loosening.
Degree of joint congruence is a key factor in glenoid loosening. Neer’s congruent design increases the contact area with concentric loading and reduces glenohumeral translation, which leads to reduced polyethylene wear and improved joint stability. In extreme arm positions, however, humeral head subluxation results in edge loading and a glenoid rocking-horse effect.9-13,17,29-31 Conversely, nonconforming implants allow increased glenohumeral translation without edge loading,14 though they also reduce the relative glenohumeral contact area and thus transmit more contact stress to the glenoid.16,17 A hybrid glenoid component with central conforming and peripheral nonconforming zones may reduce the rocking-horse effect while maximizing ROM and joint stability. Wang and colleagues32 studied the biomechanical properties of this glenoid design and found that the addition of a central conforming region did not increase edge loading.
Additional results from our study support the efficacy of a hybrid glenoid component. Patients’ clinical outcomes improved significantly. At 5.1 years after surgery, 93.5% of patients were satisfied or very satisfied with their procedure and reported less satisfaction (86%) with the nonoperative shoulder. Also significant was the reduced number of radiolucencies. At 3.7 years after surgery, the overall percentage of shoulders with ≥1 glenoid radiolucency was 37%, considerably lower than the 82% reported by Cofield7 and the rates in more recent studies.3,16,33-36 Of the 178 shoulders in our study, 10 (5.6%) had subscapularis tears, and 6 (3.4%) of 178 had these tears surgically repaired. This 3.4% compares favorably with the 5.9% (of 119 patients) found by Miller and colleagues37 28 months after surgery. Of our 178 shoulders, 27 (15.2%) had clinically significant postoperative complications; 18 (10.1%) of the 178 had these complications surgically treated, and 9 (5.1%) had them managed nonoperatively. Bohsali and colleagues27 systematically reviewed 33 TSA studies and found a slightly higher complication rate (16.3%) 5.3 years after surgery. Furthermore, in our study, the 11 patients who underwent revision, capsular shift, or subscapularis repair had final outcomes comparable to those of the rest of our study population.
Our study had several potential weaknesses. First, its minimum clinical and radiographic follow-up was 1 year, whereas most long-term TSA series set a minimum of 2 years. We used 1 year because this was the first clinical study of the hybrid glenoid component design, and we wanted to maximize its sample size by reporting on intermediate-length outcomes. Even so, 93% (166/178) of our clinical patients and 83% (113/136) of our radiographic patients have had ≥2 years of follow-up, and we continue to follow all study patients for long-term outcomes. Another weakness of the study was its lack of a uniform group of patients with all the office, survey, complications, and radiographic data. Our retrospective study design made it difficult to obtain such a group without significantly reducing the sample size, so we divided patients into 4 data groups. A third potential weakness was the study’s variable method for collecting complications data. Rates of complications in the 178 shoulders were calculated from either office evaluation or patient self-report by mail or telephone. This data collection method is subject to recall bias, but mail and telephone contact was needed so the study would capture the large number of patients who had traveled to our institution for their surgery or had since moved away. Fourth, belly-press and lift-off tests were used in part to assess subscapularis function, but recent literature suggests post-TSA subscapularis assessment can be unreliable.38 These tests may be positive in up to two-thirds of patients after 2 years.39 Fifth, the generalizability of our findings to diagnoses such as rheumatoid and posttraumatic arthritis is limited. We had to restrict the study to patients with primary glenohumeral arthritis in order to minimize confounders.
This study’s main strength is its description of the clinical and radiographic outcomes of using a single prosthetic system in operations performed by a single surgeon in a large number of patients. This was the first and largest study evaluating the clinical and radiographic outcomes of this hybrid glenoid implant. Excluding patients with nonprimary arthritis allowed us to minimize potential confounding factors that affect patient outcomes. In conclusion, our study results showed the favorable clinical and radiographic outcomes of TSAs that have a hybrid glenoid component with dual radii of curvature. At a mean of 3.7 years after surgery, 63% of patients had no glenoid lucencies, and, at a mean of 4.8 years, only 1.7% of patients required revision. We continue to follow these patients to obtain long-term results of this innovative prosthesis.
1. Rodosky MW, Bigliani LU. Indications for glenoid resurfacing in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1996;5(3):231-248.
2. Boyd AD Jr, Thomas WH, Scott RD, Sledge CB, Thornhill TS. Total shoulder arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty. Indications for glenoid resurfacing. J Arthroplasty. 1990;5(4):329-336.
3. Torchia ME, Cofield RH, Settergren CR. Total shoulder arthroplasty with the Neer prosthesis: long-term results. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1997;6(6):495-505.
4. Iannotti JP, Norris TR. Influence of preoperative factors on outcome of shoulder arthroplasty for glenohumeral osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85(2):251-258.
5. Cofield RH. Degenerative and arthritic problems of the glenohumeral joint. In: Rockwood CA, Matsen FA, eds. The Shoulder. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 1990:740-745.
6. Neer CS 2nd, Watson KC, Stanton FJ. Recent experience in total shoulder replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64(3):319-337.
7. Cofield RH. Total shoulder arthroplasty with the Neer prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(6):899-906.
8. Karduna AR, Williams GR, Williams JL, Iannotti JP. Kinematics of the glenohumeral joint: influences of muscle forces, ligamentous constraints, and articular geometry. J Orthop Res. 1996;14(6):986-993.
9. Karduna AR, Williams GR, Iannotti JP, Williams JL. Total shoulder arthroplasty biomechanics: a study of the forces and strains at the glenoid component. J Biomech Eng. 1998;120(1):92-99.
10. Karduna AR, Williams GR, Williams JL, Iannotti JP. Glenohumeral joint translations before and after total shoulder arthroplasty. A study in cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(8):1166-1174.
11. Matsen FA 3rd, Clinton J, Lynch J, Bertelsen A, Richardson ML. Glenoid component failure in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(4):885-896.
12. Franklin JL, Barrett WP, Jackins SE, Matsen FA 3rd. Glenoid loosening in total shoulder arthroplasty. Association with rotator cuff deficiency. J Arthroplasty. 1988;3(1):39-46.
13. Barrett WP, Franklin JL, Jackins SE, Wyss CR, Matsen FA 3rd. Total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(6):865-872.
14. Harryman DT, Sidles JA, Harris SL, Lippitt SB, Matsen FA 3rd. The effect of articular conformity and the size of the humeral head component on laxity and motion after glenohumeral arthroplasty. A study in cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77(4):555-563.
15. Flatow EL. Prosthetic design considerations in total shoulder arthroplasty. Semin Arthroplasty. 1995;6(4):233-244.
16. Klimkiewicz JJ, Iannotti JP, Rubash HE, Shanbhag AS. Aseptic loosening of the humeral component in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7(4):422-426.
17. Wang VM, Krishnan R, Ugwonali OF, Flatow EL, Bigliani LU, Ateshian GA. Biomechanical evaluation of a novel glenoid design in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14(1 suppl S):129S-140S.
18. Neer CS 2nd. Replacement arthroplasty for glenohumeral osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56(1):1-13.
19. Boorman RS, Kopjar B, Fehringer E, Churchill RS, Smith K, Matsen FA 3rd. The effect of total shoulder arthroplasty on self-assessed health status is comparable to that of total hip arthroplasty and coronary artery bypass grafting. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(2):158-163.
20. Patel AA, Donegan D, Albert T. The 36-Item Short Form. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2007;15(2):126-134.
21. Richards RR, An KN, Bigliani LU, et al. A standardized method for the assessment of shoulder function. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1994;3(6):347-352.
22. Wright RW, Baumgarten KM. Shoulder outcomes measures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(7):436-444.
23. Lazarus MD, Jensen KL, Southworth C, Matsen FA 3rd. The radiographic evaluation of keeled and pegged glenoid component insertion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(7):1174-1182.
24. Sperling JW, Cofield RH, O’Driscoll SW, Torchia ME, Rowland CM. Radiographic assessment of ingrowth total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2000;9(6):507-513.
25. Dinse GE, Lagakos SW. Nonparametric estimation of lifetime and disease onset distributions from incomplete observations. Biometrics. 1982;38(4):921-932.
26. Baumgarten KM, Lashgari CJ, Yamaguchi K. Glenoid resurfacing in shoulder arthroplasty: indications and contraindications. Instr Course Lect. 2004;53:3-11.
27. Bohsali KI, Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr. Complications of total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(10):2279-2292.
28. Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr. Complications of total shoulder-replacement arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(4):603-616.
29. Poppen NK, Walker PS. Normal and abnormal motion of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976;58(2):195-201.
30. Cotton RE, Rideout DF. Tears of the humeral rotator cuff; a radiological and pathological necropsy survey. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1964;46:314-328.
31. Bigliani LU, Kelkar R, Flatow EL, Pollock RG, Mow VC. Glenohumeral stability. Biomechanical properties of passive and active stabilizers. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(330):13-30.
32. Wang VM, Sugalski MT, Levine WN, Pawluk RJ, Mow VC, Bigliani LU. Comparison of glenohumeral mechanics following a capsular shift and anterior tightening. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(6):1312-1322.
33. Young A, Walch G, Boileau P, et al. A multicentre study of the long-term results of using a flat-back polyethylene glenoid component in shoulder replacement for primary osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(2):210-216.
34. Khan A, Bunker TD, Kitson JB. Clinical and radiological follow-up of the Aequalis third-generation cemented total shoulder replacement: a minimum ten-year study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91(12):1594-1600.
35. Walch G, Edwards TB, Boulahia A, Boileau P, Mole D, Adeleine P. The influence of glenohumeral prosthetic mismatch on glenoid radiolucent lines: results of a multicenter study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(12):2186-2191.
36. Bartelt R, Sperling JW, Schleck CD, Cofield RH. Shoulder arthroplasty in patients aged fifty-five years or younger with osteoarthritis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(1):123-130.
37. Miller BS, Joseph TA, Noonan TJ, Horan MP, Hawkins RJ. Rupture of the subscapularis tendon after shoulder arthroplasty: diagnosis, treatment, and outcome. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14(5):492-496.
38. Armstrong A, Lashgari C, Teefey S, Menendez J, Yamaguchi K, Galatz LM. Ultrasound evaluation and clinical correlation of subscapularis repair after total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15(5):541-548.
39. Miller SL, Hazrati Y, Klepps S, Chiang A, Flatow EL. Loss of subscapularis function after total shoulder replacement: a seldom recognized problem. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(1):29-34.
Take-Home Points
- The authors have developed a total shoulder glenoid prosthesis that conforms with the humeral head in its center and is nonconforming on its peripheral edge.
- All clinical survey and range of motion parameters demonstrated statistically significant improvements at final follow-up.
- Only 3 shoulders (1.7%) required revision surgery.
- Eighty-six (63%) of 136 shoulders demonstrated no radiographic evidence of glenoid loosening.
- This is the first and largest study that evaluates the clinical and radiographic outcomes of this hybrid shoulder prosthesis.
Fixation of the glenoid component is the limiting factor in modern total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA). Glenoid loosening, the most common long-term complication, necessitates revision in up to 12% of patients.1-4 By contrast, humeral component loosening is relatively uncommon, affecting as few as 0.34% of patients.5 Multiple long-term studies have found consistently high rates (45%-93%) of radiolucencies around the glenoid component.3,6,7 Although their clinical significance has been debated, radiolucencies around the glenoid component raise concern about progressive loss of fixation.
Since TSA was introduced in the 1970s, complications with the glenoid component have been addressed with 2 different designs: conforming (congruent) and nonconforming. In a congruent articulation, the radii of curvature of the glenoid and humeral head components are identical, whereas they differ in a nonconforming model. Joint conformity is inversely related to glenohumeral translation.8 Neer’s original TSA was made congruent in order to limit translation and maximize the contact area. However, this design results in edge loading and a so-called rocking-horse phenomenon, which may lead to glenoid loosening.9-13 Surgeons therefore have increasingly turned to nonconforming implants. In the nonconforming design, the radius of curvature of the humeral head is smaller than that of the glenoid. Although this design may reduce edge loading,14 it allows more translation and reduces the relative contact area of the glenohumeral joint. As a result, more contact stress is transmitted to the glenoid component, leading to polyethylene deformation and wear.15,16
Dual radii of curvature are designed to augment joint stability without increasing component wear. Biomechanical data have indicated that edge loading is not increased by having a central conforming region added to a nonconforming model.17 The clinical value of this prosthesis, however, has not been determined. Therefore, we conducted a study to describe the intermediate-term clinical and radiographic outcomes of TSAs that use a novel hybrid glenoid component.
Materials and Methods
This study was approved (protocol AAAD3473) by the Institutional Review Board of Columbia University and was conducted in compliance with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) regulations.
Patient Selection
At Columbia University Medical Center, Dr. Bigliani performed 196 TSAs with a hybrid glenoid component (Bigliani-Flatow; Zimmer Biomet) in 169 patients between September 1998 and November 2007. All patients had received a diagnosis of primary glenohumeral arthritis as defined by Neer.18 Patients with previous surgery such as rotator cuff repair or subacromial decompression were included in our review, and patients with a nonprimary form of arthritis, such as rheumatoid, posttraumatic, or post-capsulorrhaphy arthritis, were excluded.
Operative Technique
For all surgeries, Dr. Bigliani performed a subscapularis tenotomy with regional anesthesia and a standard deltopectoral approach. A partial anterior capsulectomy was performed to increase the glenoid’s visibility. The inferior labrum was removed with a needle-tip bovie while the axillary nerve was being protected with a metal finger or narrow Darrach retractor. After reaming and trialing, the final glenoid component was cemented into place. Cement was placed only in the peg or keel holes and pressurized twice before final implantation. Of the 196 glenoid components, 168 (86%) were pegged and 28 (14%) keeled; in addition,190 of these components were all-polyethylene, whereas 6 had trabecular-metal backing. All glenoid components incorporated the hybrid design of dual radii of curvature. After the glenoid was cemented, the final humeral component was placed in 30° of retroversion. Whenever posterior wear was found, retroversion was reduced by 5° to 10°. The humeral prosthesis was cemented in cases (104/196, 53%) of poor bone quality or a large canal.
After surgery, the patient’s sling was fitted with an abduction pillow and a swathe, to be worn the first 24 hours, and the arm was passively ranged. Patients typically were discharged on postoperative day 2. Then, for 2 weeks, they followed an assisted passive range of motion (ROM) protocol, with limited external rotation, for promotion of subscapularis healing.
Clinical Outcomes
Dr. Bigliani assessed preoperative ROM in all planes. During initial evaluation, patients completed a questionnaire that consisted of the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey19,20 (SF-36) and the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons21 (ASES) and Simple Shoulder Test22 (SST) surveys. Postoperative clinical data were collected from office follow-up visits, survey questionnaires, or both. Postoperative office data included ROM, subscapularis integrity testing (belly-press or lift-off), and any complications. Patients with <1 year of office follow-up were excluded. In addition, the same survey questionnaire that was used before surgery was mailed to all patients after surgery; then, for anyone who did not respond by mail, we attempted contact by telephone. Neer criteria were based on patients’ subjective assessment of each arm on a 3-point Likert scale (1 = very satisfied, 2 = satisfied, 3 = dissatisfied). Patients were also asked about any specific complications or revision operations since their index procedure.
Physical examination and office follow-up data were obtained for 129 patients (148/196 shoulders, 76% follow-up) at a mean of 3.7 years (range 1.0-10.2 years) after surgery. Surveys were completed by 117 patients (139/196 shoulders, 71% follow-up) at a mean of 5.1 years (range, 1.6-11.2 years) after surgery. Only 15 patients had neither 1 year of office follow-up nor a completed questionnaire. The remaining 154 patients (178/196 shoulders, 91% follow-up) had clinical follow-up with office, mail, or telephone questionnaire at a mean of 4.8 years (range, 1.0-11.2 years) after surgery. This cohort of patients was used to determine rates of surgical revisions, subscapularis tears, dislocations, and other complications.
Radiographic Outcomes
Patients were included in the radiographic analysis if they had a shoulder radiograph at least 1 year after surgery. One hundred nineteen patients (136/196 shoulders, 69% follow-up) had radiographic follow-up at a mean of 3.7 years (range, 1.0-9.4 years) after surgery.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with Stata Version 10.0. Paired t tests were used to compare preoperative and postoperative numerical data, including ROM and survey scores. We calculated 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and set statistical significance at P < .05. For qualitative measures, the Fisher exact test was used. Survivorship analysis was performed according to the Kaplan-Meier method, with right-censored data for no event or missing data.25
Results
Clinical Analysis of Demographics
In demographics, the clinical and radiographic patient subgroups were similar to each other and to the overall study population (Table 2). Of 196 patients overall, 16 (8%) had a concomitant rotator cuff repair, and 27 (14%) underwent staged bilateral shoulder arthroplasties.
Clinical Analysis of ROM and Survey Scores
Operative shoulder ROM in forward elevation, external rotation at side, external rotation in abduction, and internal rotation all showed statistically significant (P < .001) improvement from before surgery to after surgery. Over 3.7 years, mean (SD) forward elevation improved from 107.3° (34.8°) to 159.0° (29.4°), external rotation at side improved from 20.4° (16.7°) to 49.4° (11.3°), and external rotation in abduction improved from 53.7° (24.3°) to 84.7° (9.1°). Internal rotation improved from a mean (SD) vertebral level of S1 (6.0 levels) to T9 (3.7 levels).
All validated survey scores also showed statistically significant (P < .001) improvement from before surgery to after surgery. Over 5.1 years, mean (SD) SF-36 scores improved from 64.9 (13.4) to 73.6 (17.1), ASES scores improved from 41.1 (22.5) to 82.7 (17.7), SST scores improved from 3.9 (2.8) to 9.7 (2.2), and visual analog scale pain scores improved from 5.6 (3.2) to 1.4 (2.1). Of 139 patients with follow-up, 130 (93.5%) were either satisfied or very satisfied with their TSA, and only 119 (86%) were either satisfied or very satisfied with the nonoperative shoulder.
Clinical Analysis of Postoperative Complications
Of the 178 shoulders evaluated for complications, 3 (1.7%) underwent revision surgery. Mean time to revision was 2.3 years (range, 1.5-3.9 years). Two revisions involved the glenoid component, and the third involved the humerus. In one of the glenoid cases, a 77-year-old woman fell and sustained a fracture at the base of the trabecular metal glenoid pegs; her component was revised to an all-polyethylene component, and she had no further complications. In the other glenoid case, a 73-year-old man’s all-polyethylene component loosened after 2 years and was revised to a trabecular metal implant, which loosened as well and was later converted to a hemiarthroplasty. In the humeral case, a 33-year-old man had his 4-year-old index TSA revised to a cemented stem and had no further complications.
Table 4 compares the clinical and radiographic outcomes of patients who required subscapularis repair, capsular shift, or implant revision with the outcomes of all other study patients, and Figure 3 shows Kaplan-Meier survivorship.
Postoperative Radiographic Analysis
Glenoid Component. At a mean of 3.7 years (minimum, 1 year) after surgery, 86 (63%) of 136 radiographically evaluated shoulders showed no glenoid lucencies; the other 50 (37%) showed ≥1 lucency. Of the 136 shoulders, 33 (24%) had a Lazarus score of 1, 15 (11%) had a score of 2, and only 2 (2%) had a score of 3. None of the shoulders had a score of 4 or 5.
Humeral Component. Of the 136 shoulders, 91 (67%) showed no lucencies in any of the 8 humeral stem zones; the other 45 (33%) showed 1 to 3 lucencies. Thirty (22%) of the 136 shoulders had 1 stem lucency zone, 8 (6%) had 2, and 3 (2%) had 3. None of the shoulders had >3 periprosthetic zones with lucent lines.
Discussion
In this article, we describe a hybrid glenoid TSA component with dual radii of curvature. Its central portion is congruent with the humeral head, and its peripheral portion is noncongruent and larger. The most significant finding of our study is the low rate (1.1%) of glenoid component revision 4.8 years after surgery. This rate is the lowest that has been reported in a study of ≥100 patients. Overall implant survival appeared as an almost flat Kaplan-Meir curve. We attribute this low revision rate to improved biomechanics with the hybrid glenoid design.
Symptomatic glenoid component loosening is the most common TSA complication.1,26-28 In a review of 73 Neer TSAs, Cofield7 found glenoid radiolucencies in 71% of patients 3.8 years after surgery. Radiographic evidence of loosening, defined as component migration, or tilt, or a circumferential lucency 1.5 mm thick, was present in another 11% of patients, and 4.1% developed symptomatic loosening that required glenoid revision. In a study with 12.2-year follow-up, Torchia and colleagues3 found rates of 84% for glenoid radiolucencies, 44% for radiographic loosening, and 5.6% for symptomatic loosening that required revision. In a systematic review of studies with follow-up of ≥10 years, Bohsali and colleagues27 found similar lucency and radiographic loosening rates and a 7% glenoid revision rate. These data suggest glenoid radiolucencies may progress to component loosening.
Degree of joint congruence is a key factor in glenoid loosening. Neer’s congruent design increases the contact area with concentric loading and reduces glenohumeral translation, which leads to reduced polyethylene wear and improved joint stability. In extreme arm positions, however, humeral head subluxation results in edge loading and a glenoid rocking-horse effect.9-13,17,29-31 Conversely, nonconforming implants allow increased glenohumeral translation without edge loading,14 though they also reduce the relative glenohumeral contact area and thus transmit more contact stress to the glenoid.16,17 A hybrid glenoid component with central conforming and peripheral nonconforming zones may reduce the rocking-horse effect while maximizing ROM and joint stability. Wang and colleagues32 studied the biomechanical properties of this glenoid design and found that the addition of a central conforming region did not increase edge loading.
Additional results from our study support the efficacy of a hybrid glenoid component. Patients’ clinical outcomes improved significantly. At 5.1 years after surgery, 93.5% of patients were satisfied or very satisfied with their procedure and reported less satisfaction (86%) with the nonoperative shoulder. Also significant was the reduced number of radiolucencies. At 3.7 years after surgery, the overall percentage of shoulders with ≥1 glenoid radiolucency was 37%, considerably lower than the 82% reported by Cofield7 and the rates in more recent studies.3,16,33-36 Of the 178 shoulders in our study, 10 (5.6%) had subscapularis tears, and 6 (3.4%) of 178 had these tears surgically repaired. This 3.4% compares favorably with the 5.9% (of 119 patients) found by Miller and colleagues37 28 months after surgery. Of our 178 shoulders, 27 (15.2%) had clinically significant postoperative complications; 18 (10.1%) of the 178 had these complications surgically treated, and 9 (5.1%) had them managed nonoperatively. Bohsali and colleagues27 systematically reviewed 33 TSA studies and found a slightly higher complication rate (16.3%) 5.3 years after surgery. Furthermore, in our study, the 11 patients who underwent revision, capsular shift, or subscapularis repair had final outcomes comparable to those of the rest of our study population.
Our study had several potential weaknesses. First, its minimum clinical and radiographic follow-up was 1 year, whereas most long-term TSA series set a minimum of 2 years. We used 1 year because this was the first clinical study of the hybrid glenoid component design, and we wanted to maximize its sample size by reporting on intermediate-length outcomes. Even so, 93% (166/178) of our clinical patients and 83% (113/136) of our radiographic patients have had ≥2 years of follow-up, and we continue to follow all study patients for long-term outcomes. Another weakness of the study was its lack of a uniform group of patients with all the office, survey, complications, and radiographic data. Our retrospective study design made it difficult to obtain such a group without significantly reducing the sample size, so we divided patients into 4 data groups. A third potential weakness was the study’s variable method for collecting complications data. Rates of complications in the 178 shoulders were calculated from either office evaluation or patient self-report by mail or telephone. This data collection method is subject to recall bias, but mail and telephone contact was needed so the study would capture the large number of patients who had traveled to our institution for their surgery or had since moved away. Fourth, belly-press and lift-off tests were used in part to assess subscapularis function, but recent literature suggests post-TSA subscapularis assessment can be unreliable.38 These tests may be positive in up to two-thirds of patients after 2 years.39 Fifth, the generalizability of our findings to diagnoses such as rheumatoid and posttraumatic arthritis is limited. We had to restrict the study to patients with primary glenohumeral arthritis in order to minimize confounders.
This study’s main strength is its description of the clinical and radiographic outcomes of using a single prosthetic system in operations performed by a single surgeon in a large number of patients. This was the first and largest study evaluating the clinical and radiographic outcomes of this hybrid glenoid implant. Excluding patients with nonprimary arthritis allowed us to minimize potential confounding factors that affect patient outcomes. In conclusion, our study results showed the favorable clinical and radiographic outcomes of TSAs that have a hybrid glenoid component with dual radii of curvature. At a mean of 3.7 years after surgery, 63% of patients had no glenoid lucencies, and, at a mean of 4.8 years, only 1.7% of patients required revision. We continue to follow these patients to obtain long-term results of this innovative prosthesis.
Take-Home Points
- The authors have developed a total shoulder glenoid prosthesis that conforms with the humeral head in its center and is nonconforming on its peripheral edge.
- All clinical survey and range of motion parameters demonstrated statistically significant improvements at final follow-up.
- Only 3 shoulders (1.7%) required revision surgery.
- Eighty-six (63%) of 136 shoulders demonstrated no radiographic evidence of glenoid loosening.
- This is the first and largest study that evaluates the clinical and radiographic outcomes of this hybrid shoulder prosthesis.
Fixation of the glenoid component is the limiting factor in modern total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA). Glenoid loosening, the most common long-term complication, necessitates revision in up to 12% of patients.1-4 By contrast, humeral component loosening is relatively uncommon, affecting as few as 0.34% of patients.5 Multiple long-term studies have found consistently high rates (45%-93%) of radiolucencies around the glenoid component.3,6,7 Although their clinical significance has been debated, radiolucencies around the glenoid component raise concern about progressive loss of fixation.
Since TSA was introduced in the 1970s, complications with the glenoid component have been addressed with 2 different designs: conforming (congruent) and nonconforming. In a congruent articulation, the radii of curvature of the glenoid and humeral head components are identical, whereas they differ in a nonconforming model. Joint conformity is inversely related to glenohumeral translation.8 Neer’s original TSA was made congruent in order to limit translation and maximize the contact area. However, this design results in edge loading and a so-called rocking-horse phenomenon, which may lead to glenoid loosening.9-13 Surgeons therefore have increasingly turned to nonconforming implants. In the nonconforming design, the radius of curvature of the humeral head is smaller than that of the glenoid. Although this design may reduce edge loading,14 it allows more translation and reduces the relative contact area of the glenohumeral joint. As a result, more contact stress is transmitted to the glenoid component, leading to polyethylene deformation and wear.15,16
Dual radii of curvature are designed to augment joint stability without increasing component wear. Biomechanical data have indicated that edge loading is not increased by having a central conforming region added to a nonconforming model.17 The clinical value of this prosthesis, however, has not been determined. Therefore, we conducted a study to describe the intermediate-term clinical and radiographic outcomes of TSAs that use a novel hybrid glenoid component.
Materials and Methods
This study was approved (protocol AAAD3473) by the Institutional Review Board of Columbia University and was conducted in compliance with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) regulations.
Patient Selection
At Columbia University Medical Center, Dr. Bigliani performed 196 TSAs with a hybrid glenoid component (Bigliani-Flatow; Zimmer Biomet) in 169 patients between September 1998 and November 2007. All patients had received a diagnosis of primary glenohumeral arthritis as defined by Neer.18 Patients with previous surgery such as rotator cuff repair or subacromial decompression were included in our review, and patients with a nonprimary form of arthritis, such as rheumatoid, posttraumatic, or post-capsulorrhaphy arthritis, were excluded.
Operative Technique
For all surgeries, Dr. Bigliani performed a subscapularis tenotomy with regional anesthesia and a standard deltopectoral approach. A partial anterior capsulectomy was performed to increase the glenoid’s visibility. The inferior labrum was removed with a needle-tip bovie while the axillary nerve was being protected with a metal finger or narrow Darrach retractor. After reaming and trialing, the final glenoid component was cemented into place. Cement was placed only in the peg or keel holes and pressurized twice before final implantation. Of the 196 glenoid components, 168 (86%) were pegged and 28 (14%) keeled; in addition,190 of these components were all-polyethylene, whereas 6 had trabecular-metal backing. All glenoid components incorporated the hybrid design of dual radii of curvature. After the glenoid was cemented, the final humeral component was placed in 30° of retroversion. Whenever posterior wear was found, retroversion was reduced by 5° to 10°. The humeral prosthesis was cemented in cases (104/196, 53%) of poor bone quality or a large canal.
After surgery, the patient’s sling was fitted with an abduction pillow and a swathe, to be worn the first 24 hours, and the arm was passively ranged. Patients typically were discharged on postoperative day 2. Then, for 2 weeks, they followed an assisted passive range of motion (ROM) protocol, with limited external rotation, for promotion of subscapularis healing.
Clinical Outcomes
Dr. Bigliani assessed preoperative ROM in all planes. During initial evaluation, patients completed a questionnaire that consisted of the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey19,20 (SF-36) and the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons21 (ASES) and Simple Shoulder Test22 (SST) surveys. Postoperative clinical data were collected from office follow-up visits, survey questionnaires, or both. Postoperative office data included ROM, subscapularis integrity testing (belly-press or lift-off), and any complications. Patients with <1 year of office follow-up were excluded. In addition, the same survey questionnaire that was used before surgery was mailed to all patients after surgery; then, for anyone who did not respond by mail, we attempted contact by telephone. Neer criteria were based on patients’ subjective assessment of each arm on a 3-point Likert scale (1 = very satisfied, 2 = satisfied, 3 = dissatisfied). Patients were also asked about any specific complications or revision operations since their index procedure.
Physical examination and office follow-up data were obtained for 129 patients (148/196 shoulders, 76% follow-up) at a mean of 3.7 years (range 1.0-10.2 years) after surgery. Surveys were completed by 117 patients (139/196 shoulders, 71% follow-up) at a mean of 5.1 years (range, 1.6-11.2 years) after surgery. Only 15 patients had neither 1 year of office follow-up nor a completed questionnaire. The remaining 154 patients (178/196 shoulders, 91% follow-up) had clinical follow-up with office, mail, or telephone questionnaire at a mean of 4.8 years (range, 1.0-11.2 years) after surgery. This cohort of patients was used to determine rates of surgical revisions, subscapularis tears, dislocations, and other complications.
Radiographic Outcomes
Patients were included in the radiographic analysis if they had a shoulder radiograph at least 1 year after surgery. One hundred nineteen patients (136/196 shoulders, 69% follow-up) had radiographic follow-up at a mean of 3.7 years (range, 1.0-9.4 years) after surgery.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with Stata Version 10.0. Paired t tests were used to compare preoperative and postoperative numerical data, including ROM and survey scores. We calculated 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and set statistical significance at P < .05. For qualitative measures, the Fisher exact test was used. Survivorship analysis was performed according to the Kaplan-Meier method, with right-censored data for no event or missing data.25
Results
Clinical Analysis of Demographics
In demographics, the clinical and radiographic patient subgroups were similar to each other and to the overall study population (Table 2). Of 196 patients overall, 16 (8%) had a concomitant rotator cuff repair, and 27 (14%) underwent staged bilateral shoulder arthroplasties.
Clinical Analysis of ROM and Survey Scores
Operative shoulder ROM in forward elevation, external rotation at side, external rotation in abduction, and internal rotation all showed statistically significant (P < .001) improvement from before surgery to after surgery. Over 3.7 years, mean (SD) forward elevation improved from 107.3° (34.8°) to 159.0° (29.4°), external rotation at side improved from 20.4° (16.7°) to 49.4° (11.3°), and external rotation in abduction improved from 53.7° (24.3°) to 84.7° (9.1°). Internal rotation improved from a mean (SD) vertebral level of S1 (6.0 levels) to T9 (3.7 levels).
All validated survey scores also showed statistically significant (P < .001) improvement from before surgery to after surgery. Over 5.1 years, mean (SD) SF-36 scores improved from 64.9 (13.4) to 73.6 (17.1), ASES scores improved from 41.1 (22.5) to 82.7 (17.7), SST scores improved from 3.9 (2.8) to 9.7 (2.2), and visual analog scale pain scores improved from 5.6 (3.2) to 1.4 (2.1). Of 139 patients with follow-up, 130 (93.5%) were either satisfied or very satisfied with their TSA, and only 119 (86%) were either satisfied or very satisfied with the nonoperative shoulder.
Clinical Analysis of Postoperative Complications
Of the 178 shoulders evaluated for complications, 3 (1.7%) underwent revision surgery. Mean time to revision was 2.3 years (range, 1.5-3.9 years). Two revisions involved the glenoid component, and the third involved the humerus. In one of the glenoid cases, a 77-year-old woman fell and sustained a fracture at the base of the trabecular metal glenoid pegs; her component was revised to an all-polyethylene component, and she had no further complications. In the other glenoid case, a 73-year-old man’s all-polyethylene component loosened after 2 years and was revised to a trabecular metal implant, which loosened as well and was later converted to a hemiarthroplasty. In the humeral case, a 33-year-old man had his 4-year-old index TSA revised to a cemented stem and had no further complications.
Table 4 compares the clinical and radiographic outcomes of patients who required subscapularis repair, capsular shift, or implant revision with the outcomes of all other study patients, and Figure 3 shows Kaplan-Meier survivorship.
Postoperative Radiographic Analysis
Glenoid Component. At a mean of 3.7 years (minimum, 1 year) after surgery, 86 (63%) of 136 radiographically evaluated shoulders showed no glenoid lucencies; the other 50 (37%) showed ≥1 lucency. Of the 136 shoulders, 33 (24%) had a Lazarus score of 1, 15 (11%) had a score of 2, and only 2 (2%) had a score of 3. None of the shoulders had a score of 4 or 5.
Humeral Component. Of the 136 shoulders, 91 (67%) showed no lucencies in any of the 8 humeral stem zones; the other 45 (33%) showed 1 to 3 lucencies. Thirty (22%) of the 136 shoulders had 1 stem lucency zone, 8 (6%) had 2, and 3 (2%) had 3. None of the shoulders had >3 periprosthetic zones with lucent lines.
Discussion
In this article, we describe a hybrid glenoid TSA component with dual radii of curvature. Its central portion is congruent with the humeral head, and its peripheral portion is noncongruent and larger. The most significant finding of our study is the low rate (1.1%) of glenoid component revision 4.8 years after surgery. This rate is the lowest that has been reported in a study of ≥100 patients. Overall implant survival appeared as an almost flat Kaplan-Meir curve. We attribute this low revision rate to improved biomechanics with the hybrid glenoid design.
Symptomatic glenoid component loosening is the most common TSA complication.1,26-28 In a review of 73 Neer TSAs, Cofield7 found glenoid radiolucencies in 71% of patients 3.8 years after surgery. Radiographic evidence of loosening, defined as component migration, or tilt, or a circumferential lucency 1.5 mm thick, was present in another 11% of patients, and 4.1% developed symptomatic loosening that required glenoid revision. In a study with 12.2-year follow-up, Torchia and colleagues3 found rates of 84% for glenoid radiolucencies, 44% for radiographic loosening, and 5.6% for symptomatic loosening that required revision. In a systematic review of studies with follow-up of ≥10 years, Bohsali and colleagues27 found similar lucency and radiographic loosening rates and a 7% glenoid revision rate. These data suggest glenoid radiolucencies may progress to component loosening.
Degree of joint congruence is a key factor in glenoid loosening. Neer’s congruent design increases the contact area with concentric loading and reduces glenohumeral translation, which leads to reduced polyethylene wear and improved joint stability. In extreme arm positions, however, humeral head subluxation results in edge loading and a glenoid rocking-horse effect.9-13,17,29-31 Conversely, nonconforming implants allow increased glenohumeral translation without edge loading,14 though they also reduce the relative glenohumeral contact area and thus transmit more contact stress to the glenoid.16,17 A hybrid glenoid component with central conforming and peripheral nonconforming zones may reduce the rocking-horse effect while maximizing ROM and joint stability. Wang and colleagues32 studied the biomechanical properties of this glenoid design and found that the addition of a central conforming region did not increase edge loading.
Additional results from our study support the efficacy of a hybrid glenoid component. Patients’ clinical outcomes improved significantly. At 5.1 years after surgery, 93.5% of patients were satisfied or very satisfied with their procedure and reported less satisfaction (86%) with the nonoperative shoulder. Also significant was the reduced number of radiolucencies. At 3.7 years after surgery, the overall percentage of shoulders with ≥1 glenoid radiolucency was 37%, considerably lower than the 82% reported by Cofield7 and the rates in more recent studies.3,16,33-36 Of the 178 shoulders in our study, 10 (5.6%) had subscapularis tears, and 6 (3.4%) of 178 had these tears surgically repaired. This 3.4% compares favorably with the 5.9% (of 119 patients) found by Miller and colleagues37 28 months after surgery. Of our 178 shoulders, 27 (15.2%) had clinically significant postoperative complications; 18 (10.1%) of the 178 had these complications surgically treated, and 9 (5.1%) had them managed nonoperatively. Bohsali and colleagues27 systematically reviewed 33 TSA studies and found a slightly higher complication rate (16.3%) 5.3 years after surgery. Furthermore, in our study, the 11 patients who underwent revision, capsular shift, or subscapularis repair had final outcomes comparable to those of the rest of our study population.
Our study had several potential weaknesses. First, its minimum clinical and radiographic follow-up was 1 year, whereas most long-term TSA series set a minimum of 2 years. We used 1 year because this was the first clinical study of the hybrid glenoid component design, and we wanted to maximize its sample size by reporting on intermediate-length outcomes. Even so, 93% (166/178) of our clinical patients and 83% (113/136) of our radiographic patients have had ≥2 years of follow-up, and we continue to follow all study patients for long-term outcomes. Another weakness of the study was its lack of a uniform group of patients with all the office, survey, complications, and radiographic data. Our retrospective study design made it difficult to obtain such a group without significantly reducing the sample size, so we divided patients into 4 data groups. A third potential weakness was the study’s variable method for collecting complications data. Rates of complications in the 178 shoulders were calculated from either office evaluation or patient self-report by mail or telephone. This data collection method is subject to recall bias, but mail and telephone contact was needed so the study would capture the large number of patients who had traveled to our institution for their surgery or had since moved away. Fourth, belly-press and lift-off tests were used in part to assess subscapularis function, but recent literature suggests post-TSA subscapularis assessment can be unreliable.38 These tests may be positive in up to two-thirds of patients after 2 years.39 Fifth, the generalizability of our findings to diagnoses such as rheumatoid and posttraumatic arthritis is limited. We had to restrict the study to patients with primary glenohumeral arthritis in order to minimize confounders.
This study’s main strength is its description of the clinical and radiographic outcomes of using a single prosthetic system in operations performed by a single surgeon in a large number of patients. This was the first and largest study evaluating the clinical and radiographic outcomes of this hybrid glenoid implant. Excluding patients with nonprimary arthritis allowed us to minimize potential confounding factors that affect patient outcomes. In conclusion, our study results showed the favorable clinical and radiographic outcomes of TSAs that have a hybrid glenoid component with dual radii of curvature. At a mean of 3.7 years after surgery, 63% of patients had no glenoid lucencies, and, at a mean of 4.8 years, only 1.7% of patients required revision. We continue to follow these patients to obtain long-term results of this innovative prosthesis.
1. Rodosky MW, Bigliani LU. Indications for glenoid resurfacing in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1996;5(3):231-248.
2. Boyd AD Jr, Thomas WH, Scott RD, Sledge CB, Thornhill TS. Total shoulder arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty. Indications for glenoid resurfacing. J Arthroplasty. 1990;5(4):329-336.
3. Torchia ME, Cofield RH, Settergren CR. Total shoulder arthroplasty with the Neer prosthesis: long-term results. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1997;6(6):495-505.
4. Iannotti JP, Norris TR. Influence of preoperative factors on outcome of shoulder arthroplasty for glenohumeral osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85(2):251-258.
5. Cofield RH. Degenerative and arthritic problems of the glenohumeral joint. In: Rockwood CA, Matsen FA, eds. The Shoulder. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 1990:740-745.
6. Neer CS 2nd, Watson KC, Stanton FJ. Recent experience in total shoulder replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64(3):319-337.
7. Cofield RH. Total shoulder arthroplasty with the Neer prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(6):899-906.
8. Karduna AR, Williams GR, Williams JL, Iannotti JP. Kinematics of the glenohumeral joint: influences of muscle forces, ligamentous constraints, and articular geometry. J Orthop Res. 1996;14(6):986-993.
9. Karduna AR, Williams GR, Iannotti JP, Williams JL. Total shoulder arthroplasty biomechanics: a study of the forces and strains at the glenoid component. J Biomech Eng. 1998;120(1):92-99.
10. Karduna AR, Williams GR, Williams JL, Iannotti JP. Glenohumeral joint translations before and after total shoulder arthroplasty. A study in cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(8):1166-1174.
11. Matsen FA 3rd, Clinton J, Lynch J, Bertelsen A, Richardson ML. Glenoid component failure in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(4):885-896.
12. Franklin JL, Barrett WP, Jackins SE, Matsen FA 3rd. Glenoid loosening in total shoulder arthroplasty. Association with rotator cuff deficiency. J Arthroplasty. 1988;3(1):39-46.
13. Barrett WP, Franklin JL, Jackins SE, Wyss CR, Matsen FA 3rd. Total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(6):865-872.
14. Harryman DT, Sidles JA, Harris SL, Lippitt SB, Matsen FA 3rd. The effect of articular conformity and the size of the humeral head component on laxity and motion after glenohumeral arthroplasty. A study in cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77(4):555-563.
15. Flatow EL. Prosthetic design considerations in total shoulder arthroplasty. Semin Arthroplasty. 1995;6(4):233-244.
16. Klimkiewicz JJ, Iannotti JP, Rubash HE, Shanbhag AS. Aseptic loosening of the humeral component in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7(4):422-426.
17. Wang VM, Krishnan R, Ugwonali OF, Flatow EL, Bigliani LU, Ateshian GA. Biomechanical evaluation of a novel glenoid design in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14(1 suppl S):129S-140S.
18. Neer CS 2nd. Replacement arthroplasty for glenohumeral osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56(1):1-13.
19. Boorman RS, Kopjar B, Fehringer E, Churchill RS, Smith K, Matsen FA 3rd. The effect of total shoulder arthroplasty on self-assessed health status is comparable to that of total hip arthroplasty and coronary artery bypass grafting. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(2):158-163.
20. Patel AA, Donegan D, Albert T. The 36-Item Short Form. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2007;15(2):126-134.
21. Richards RR, An KN, Bigliani LU, et al. A standardized method for the assessment of shoulder function. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1994;3(6):347-352.
22. Wright RW, Baumgarten KM. Shoulder outcomes measures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(7):436-444.
23. Lazarus MD, Jensen KL, Southworth C, Matsen FA 3rd. The radiographic evaluation of keeled and pegged glenoid component insertion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(7):1174-1182.
24. Sperling JW, Cofield RH, O’Driscoll SW, Torchia ME, Rowland CM. Radiographic assessment of ingrowth total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2000;9(6):507-513.
25. Dinse GE, Lagakos SW. Nonparametric estimation of lifetime and disease onset distributions from incomplete observations. Biometrics. 1982;38(4):921-932.
26. Baumgarten KM, Lashgari CJ, Yamaguchi K. Glenoid resurfacing in shoulder arthroplasty: indications and contraindications. Instr Course Lect. 2004;53:3-11.
27. Bohsali KI, Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr. Complications of total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(10):2279-2292.
28. Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr. Complications of total shoulder-replacement arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(4):603-616.
29. Poppen NK, Walker PS. Normal and abnormal motion of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976;58(2):195-201.
30. Cotton RE, Rideout DF. Tears of the humeral rotator cuff; a radiological and pathological necropsy survey. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1964;46:314-328.
31. Bigliani LU, Kelkar R, Flatow EL, Pollock RG, Mow VC. Glenohumeral stability. Biomechanical properties of passive and active stabilizers. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(330):13-30.
32. Wang VM, Sugalski MT, Levine WN, Pawluk RJ, Mow VC, Bigliani LU. Comparison of glenohumeral mechanics following a capsular shift and anterior tightening. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(6):1312-1322.
33. Young A, Walch G, Boileau P, et al. A multicentre study of the long-term results of using a flat-back polyethylene glenoid component in shoulder replacement for primary osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(2):210-216.
34. Khan A, Bunker TD, Kitson JB. Clinical and radiological follow-up of the Aequalis third-generation cemented total shoulder replacement: a minimum ten-year study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91(12):1594-1600.
35. Walch G, Edwards TB, Boulahia A, Boileau P, Mole D, Adeleine P. The influence of glenohumeral prosthetic mismatch on glenoid radiolucent lines: results of a multicenter study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(12):2186-2191.
36. Bartelt R, Sperling JW, Schleck CD, Cofield RH. Shoulder arthroplasty in patients aged fifty-five years or younger with osteoarthritis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(1):123-130.
37. Miller BS, Joseph TA, Noonan TJ, Horan MP, Hawkins RJ. Rupture of the subscapularis tendon after shoulder arthroplasty: diagnosis, treatment, and outcome. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14(5):492-496.
38. Armstrong A, Lashgari C, Teefey S, Menendez J, Yamaguchi K, Galatz LM. Ultrasound evaluation and clinical correlation of subscapularis repair after total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15(5):541-548.
39. Miller SL, Hazrati Y, Klepps S, Chiang A, Flatow EL. Loss of subscapularis function after total shoulder replacement: a seldom recognized problem. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(1):29-34.
1. Rodosky MW, Bigliani LU. Indications for glenoid resurfacing in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1996;5(3):231-248.
2. Boyd AD Jr, Thomas WH, Scott RD, Sledge CB, Thornhill TS. Total shoulder arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty. Indications for glenoid resurfacing. J Arthroplasty. 1990;5(4):329-336.
3. Torchia ME, Cofield RH, Settergren CR. Total shoulder arthroplasty with the Neer prosthesis: long-term results. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1997;6(6):495-505.
4. Iannotti JP, Norris TR. Influence of preoperative factors on outcome of shoulder arthroplasty for glenohumeral osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85(2):251-258.
5. Cofield RH. Degenerative and arthritic problems of the glenohumeral joint. In: Rockwood CA, Matsen FA, eds. The Shoulder. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 1990:740-745.
6. Neer CS 2nd, Watson KC, Stanton FJ. Recent experience in total shoulder replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64(3):319-337.
7. Cofield RH. Total shoulder arthroplasty with the Neer prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(6):899-906.
8. Karduna AR, Williams GR, Williams JL, Iannotti JP. Kinematics of the glenohumeral joint: influences of muscle forces, ligamentous constraints, and articular geometry. J Orthop Res. 1996;14(6):986-993.
9. Karduna AR, Williams GR, Iannotti JP, Williams JL. Total shoulder arthroplasty biomechanics: a study of the forces and strains at the glenoid component. J Biomech Eng. 1998;120(1):92-99.
10. Karduna AR, Williams GR, Williams JL, Iannotti JP. Glenohumeral joint translations before and after total shoulder arthroplasty. A study in cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(8):1166-1174.
11. Matsen FA 3rd, Clinton J, Lynch J, Bertelsen A, Richardson ML. Glenoid component failure in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(4):885-896.
12. Franklin JL, Barrett WP, Jackins SE, Matsen FA 3rd. Glenoid loosening in total shoulder arthroplasty. Association with rotator cuff deficiency. J Arthroplasty. 1988;3(1):39-46.
13. Barrett WP, Franklin JL, Jackins SE, Wyss CR, Matsen FA 3rd. Total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(6):865-872.
14. Harryman DT, Sidles JA, Harris SL, Lippitt SB, Matsen FA 3rd. The effect of articular conformity and the size of the humeral head component on laxity and motion after glenohumeral arthroplasty. A study in cadavera. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77(4):555-563.
15. Flatow EL. Prosthetic design considerations in total shoulder arthroplasty. Semin Arthroplasty. 1995;6(4):233-244.
16. Klimkiewicz JJ, Iannotti JP, Rubash HE, Shanbhag AS. Aseptic loosening of the humeral component in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7(4):422-426.
17. Wang VM, Krishnan R, Ugwonali OF, Flatow EL, Bigliani LU, Ateshian GA. Biomechanical evaluation of a novel glenoid design in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14(1 suppl S):129S-140S.
18. Neer CS 2nd. Replacement arthroplasty for glenohumeral osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56(1):1-13.
19. Boorman RS, Kopjar B, Fehringer E, Churchill RS, Smith K, Matsen FA 3rd. The effect of total shoulder arthroplasty on self-assessed health status is comparable to that of total hip arthroplasty and coronary artery bypass grafting. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(2):158-163.
20. Patel AA, Donegan D, Albert T. The 36-Item Short Form. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2007;15(2):126-134.
21. Richards RR, An KN, Bigliani LU, et al. A standardized method for the assessment of shoulder function. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1994;3(6):347-352.
22. Wright RW, Baumgarten KM. Shoulder outcomes measures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(7):436-444.
23. Lazarus MD, Jensen KL, Southworth C, Matsen FA 3rd. The radiographic evaluation of keeled and pegged glenoid component insertion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(7):1174-1182.
24. Sperling JW, Cofield RH, O’Driscoll SW, Torchia ME, Rowland CM. Radiographic assessment of ingrowth total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2000;9(6):507-513.
25. Dinse GE, Lagakos SW. Nonparametric estimation of lifetime and disease onset distributions from incomplete observations. Biometrics. 1982;38(4):921-932.
26. Baumgarten KM, Lashgari CJ, Yamaguchi K. Glenoid resurfacing in shoulder arthroplasty: indications and contraindications. Instr Course Lect. 2004;53:3-11.
27. Bohsali KI, Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr. Complications of total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(10):2279-2292.
28. Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr. Complications of total shoulder-replacement arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(4):603-616.
29. Poppen NK, Walker PS. Normal and abnormal motion of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976;58(2):195-201.
30. Cotton RE, Rideout DF. Tears of the humeral rotator cuff; a radiological and pathological necropsy survey. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1964;46:314-328.
31. Bigliani LU, Kelkar R, Flatow EL, Pollock RG, Mow VC. Glenohumeral stability. Biomechanical properties of passive and active stabilizers. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(330):13-30.
32. Wang VM, Sugalski MT, Levine WN, Pawluk RJ, Mow VC, Bigliani LU. Comparison of glenohumeral mechanics following a capsular shift and anterior tightening. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(6):1312-1322.
33. Young A, Walch G, Boileau P, et al. A multicentre study of the long-term results of using a flat-back polyethylene glenoid component in shoulder replacement for primary osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(2):210-216.
34. Khan A, Bunker TD, Kitson JB. Clinical and radiological follow-up of the Aequalis third-generation cemented total shoulder replacement: a minimum ten-year study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91(12):1594-1600.
35. Walch G, Edwards TB, Boulahia A, Boileau P, Mole D, Adeleine P. The influence of glenohumeral prosthetic mismatch on glenoid radiolucent lines: results of a multicenter study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(12):2186-2191.
36. Bartelt R, Sperling JW, Schleck CD, Cofield RH. Shoulder arthroplasty in patients aged fifty-five years or younger with osteoarthritis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(1):123-130.
37. Miller BS, Joseph TA, Noonan TJ, Horan MP, Hawkins RJ. Rupture of the subscapularis tendon after shoulder arthroplasty: diagnosis, treatment, and outcome. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14(5):492-496.
38. Armstrong A, Lashgari C, Teefey S, Menendez J, Yamaguchi K, Galatz LM. Ultrasound evaluation and clinical correlation of subscapularis repair after total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15(5):541-548.
39. Miller SL, Hazrati Y, Klepps S, Chiang A, Flatow EL. Loss of subscapularis function after total shoulder replacement: a seldom recognized problem. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(1):29-34.
Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Indomethacin on Biomechanics of Rotator Cuff Repair
Take-Home Points
- The optimal centrifugation protocol for production of rat PRP is 1300 rpm for 5 minutes.
- PRP administration in RCR improves tendon biomechanics in a rat model.
- Administration of NSAIDs following RCR has no significant effect on tendon biomechanical properties.
- NSAIDs may be co-administered with PRP without reducing efficacy of PRP.
- The role of PRP and NSAIDs in human RCR remains unclear.
Rotator cuff tears are a common source of shoulder pain and disability among older adults and athletes. Full-thickness tears alone occur in up to 30% of adults older than 60 years.1 Surgical repair is plagued by an unpredictable rate of recurrence (range, 11%-94%).1-10 As a result of improved suture materials, knotting patterns, and anchor designs, hardware issues are no longer the primary cause of rotator cuff repair (RCR) failures; now the principal mode of failure is biologic.2 Animal model studies have found that, after injury and subsequent healing, the tendon–bone interface remains abnormal.11 Rotator cuff research therefore has focused largely on biological enhancement of tendon-to-bone healing.
One means of biological augmentation is autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP), which has supraphysiologic concentrations of platelets and their secreted growth factors. Although there is no consensus on the long-term efficacy of PRP, some studies suggest PRP accelerates healing over short and intermediate terms, which may contribute to a more rapid decrease in pain and more rapid return to normal activities.12-18 Similarly, systemic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have long been used to treat musculoskeletal injuries, including rotator cuff pathology. However, NSAIDs inhibit cyclooxygenase activity, and clinical and experimental data have shown that cyclooxygenase 2 function is crucial in normal tendon-to-bone healing.19-21
Comprehensive studies have been conducted on the efficacy of both PRP and NSAIDs, but the interaction of concurrently used PRP and NSAIDs has not been determined. As many physicians use both modalities in the treatment of soft-tissue injuries, it is important to study the potential interactions when coadministered. Prior studies in small animal models suggest NSAIDs may impair tendon-to-bone healing in RCR, but there is no evidence regarding the effect of NSAIDs on the efficacy of PRP treatment.21
We conducted a study to determine the interaction of PRP and NSAIDs when used as adjuncts to RCR in a rat model. We hypothesized that PRP would increase the strength of RCR and that NSAIDs would interfere with the effects of PRP. A preliminary study objective was to determine an appropriate centrifugation protocol for producing PRP from rat blood, for use in this study and in future rat-based studies of PRP.
Materials and Methods
Part A: Pretesting Determination of PRP Centrifugation Protocol
Fourteen adult male Fischer rats were used in part A of this study, which was conducted to determine an appropriate PRP centrifugation protocol. Traditional PRP centrifugation protocols are established for human blood, but rat red blood cells (RBCs) and human RBCs differ in size.22 In our preliminary study, we wanted to determine the adjusted centrifuge speed and duration for producing clinically optimal PRP from rats. Clinically optimal PRP has reduced levels of RBCs, which decrease platelet affinity. Although the role of leukocytes in PRP preparations is debated, reducing the number of white blood cells (WBCs) decreases the number of matrix metalloproteinases and reactive oxygen species that may lead to inflammation. We used the platelet index (ratio of platelets to WBCs) and the RBC count to quantify the quality of our PRP sample.
Each rat in part A was anesthetized while supine. We used the Autologous Conditioned Plasma (ACP) system (Arthrex), which requires only 1 centrifugation cycle to create PRP. About 9 mL or 10 mL of blood was obtained by cardiac aspiration using an ACP Double Syringe (Arthrex). After blood retrieval, a thoracotomy was performed to confirm each rat’s death.
Part B: Determining the Effects of PRP and NSAIDs on RCR in a Rat Model
Operative Cohort. Of the 34 Fischer rats used in part B of this study, 6 were used as blood donors for PRP production, and the other 28 underwent bilateral rotator cuff surgeries. We used donor rats to maximize the amount of PRP retrieval, allocating about 1 donor rat per 5 operative rats. Fischer rats are an inbred strain, so the PRP from a donor Fischer rat simulates autologous blood in other Fischer rats. Use of allogenic blood is consistent with prior rat PRP studies.23,24
Operative Technique. Each bilateral surgery was performed by a single board-certified shoulder surgeon, and the anesthetic and surgical protocols were followed as approved by the home institution’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Before surgery, blood was harvested for PRP production from donor rats, as described earlier, and centrifuged for 5 minutes × 1300 rpm. After anesthetic induction and skin incision, the deltoid muscle was cut to expose the acromion and underlying rotator cuff. The distal supraspinatus tendon was sharply detached from the greater tuberosity. A bone-tunnel RCR was performed by drilling a transverse tunnel across the greater tuberosity and affixing the tendon to its footprint with a 5-0 polypropylene suture (Prolene; Ethicon). Each rat was then randomly assigned to receive 50 µL of donor PRP injected in 1 operative shoulder and saline in the contralateral shoulder. Injections were made in the supraspinatus tendon at its attachment to the humerus. Deltoid and skin were closed with 4-0 polyglactin (Vicryl) suture (Ethicon) and staples, respectively.
Tendon Preparation. Immediately post mortem, each shoulder was grossly dissected to isolate the supraspinatus muscle attached to the humerus. Shoulders were then frozen in 0.15-M saline solution until specified biomechanical testing dates.
On day of dimensional/biomechanical testing, each specimen was thawed at room temperature and finely dissected under a microscope (Stemi 200-C; Car Zeiss). After dissection, the humeral shaft was embedded in polymethylmethacrylate within a test tube. The free end of the supraspinatus tendon was glued within a “tab” of waterproofed emery cloth, leaving about 2 mm of tendon between the tab and the greater tuberosity.
Biomechanical Analysis. A 5848 MicroTester (Instron) was used for biomechanical testing. Each tabbed tendon, held by a pneumatic clamp attached to the MicroTester, was tested in a preconditioning phase and then a ramp-to-failure phase. A constant drip of 0.15-M saline was run through the apparatus to simulate physiologic hydration of tissue. After the embedded specimen was secure within the loading apparatus, an initial tensile preload of 0.2 N was applied. After preloading, the tendon was run through a preconditioning phase to account for viscoelastic relaxation. Immediately after preconditioning, each tendon was subjected to failure testing at a ramp rate of 0.1 mm/s. Force data were collected as a function of displacement, allowing for the calculation of 4 biomechanical parameters: failure force, tendon stiffness and normalized stiffness, energy to failure, and total energy. Tendon stiffness is the slope of a curve-fit line of the initial peak; failure force is the force of the highest peak; energy to failure is the area under the curve (AUC) to the highest peak; and total energy is the AUC from the start of failure ramping to the point at which the tendon is torn off completely. Two-way ANOVA was used to assess the differences between treatment groups and diet groups for all parameters. Statistical significance was set at P < .05.
A power analysis was performed to determine ability to detect differences between cohorts. For power of 80% and P = .05, a difference of 16% of the mean could be detected for failure force, 30% for energy to failure, 14% for total energy to failure, and 24% for stiffness. In addition, a difference of 4% of the mean could be detected for tendon length, 6% for width, and 10% for thickness.
Results
Across all collective treatment-diet groups and biomechanical parameters, there was only 1 statistically significant difference. Mean (SD) energy to failure was significantly higher (P = .03) in shoulders treated with PRP, 11.7 (7.3) N-mm, than in those treated without PRP, 8.7 (4.6) N-mm (Figure 4). There were no statistically significant differences between shoulders treated with indomethacin and those treated without indomethacin (Table 3), and no statistically significant relationships between treatment and drug for any other biomechanical parameter (Figures 5-7).
Discussion
Our preliminary objective in this study was to determine the optimal centrifugation protocol for producing rat-based PRP. Optimal PRP requires a dense concentration of platelets as well as reduced levels of RBCs and WBCs.25 We used the platelet index to quantify the quality of our PRP samples, and we obtained the highest platelet index for the protocol of 5 minutes × 1300 rpm. This finding may be useful in later rat studies involving PRP.
The primary objective of this study was to assess the effect of the interaction of PRP and NSAIDs on RCR. PRP has been found to augment RCR,12,26,27 but indomethacin may impair healing.21,25 We hypothesized that shoulders treated with PRP would have more biomechanical strength than control shoulders and that indomethacin would decrease biomechanical strength.
Our data showed increased energy to failure of the rotator cuff with PRP injections (P = .03). All other biomechanical parameters showed no significant differences with PRP treatment, though there were statistically insignificant trends of increased total energy, failure force, and stiffness in the PRP cohorts. There were no statistically significant differences between the indomethacin and no-indomethacin groups, and indomethacin had no effect on the efficacy of PRP treatment. It should be noted that the measurements of total energy, energy to failure, and failure force best reflect the strength of the tendon–bone interface. Other biomechanical measures, such as stiffness and normalized stiffness, are physical properties of the tendon itself and apply less to enthesis strength, which was the primary focus of this study.
Beck and colleagues23 studied the effect of allogeneic PRP on RCR in a rat model. They tested biomechanical and histologic outcomes 7, 14, and 21 days after surgery. There was no significant difference in failure load between the 2 groups at any time point. Compared with failure strain in the control group, failure strain in the PRP group was decreased at 7 days, normalized at 14 days, and increased at 21 days. The authors hypothesized that increased tendon failure strain at 21 days may have reduced forces being transmitted to the suture fixation site, which may be clinically significant and warrants further investigation. In a similar study, by Dolkart and colleagues,28 intraoperative PRP administration enhanced the maximal load-to-failure and stiffness of rats’ repaired rotator cuffs. On histologic examination, tendons treated with PRP (vs control tendons) had more organized collagen. Although these studies have limitations similar to our study, these results further support improved tendon-to-bone healing with PRP.
In clinical application, Barber and colleagues26 found that, compared with controls, suturing PRP fibrin matrix into the rotator cuff during repair decreased the incidence of magnetic resonance imaging–detected retears. However, in 2 prospective, randomized trials, Castricini and colleagues29 and Weber and colleagues30 found that use of PRP in RCR did not improve outcomes. All 3 studies differ from ours in that they used fibrin matrix. However, Ersen and colleagues31 found no difference in the effects of PRP on rotator cuff healing between injection and fibrin matrix; PRP improved biomechanical properties of repaired rotator cuff independent of administration method. In a meta-analysis of PRP supplementation in RCR, Warth and colleagues32 found a statistically significant improvement in retear rates for tears >3 cm repaired with a double-row technique, but otherwise no overall improvement in retear rates or outcome scores with PRP. The authors acknowledged that the significant heterogeneity of the studies in their meta-analysis may have affected the quality of their data.
Although our study provides some insight into the effectiveness of PRP in tendon repair, the lack of standardization in PRP preparation and time points tested makes comparisons with similar studies difficult.33 Recent reports have emphasized that not all PRP separation systems yield similar products.33 Platelet concentrations, and therefore platelet-derived growth factor concentrations, differ between systems and may yield different clinical outcomes. Our decision to use leukocyte-reduced PRP is supported by a meta-analysis by Riboh and colleagues,34 who reviewed the literature on the effect of leukocyte concentration on the efficacy of PRP products. They found that, in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis, use of leukocyte-poor PRP resulted in improved functional outcomes scores in comparison with placebo, but this improvement did not occur with leukocyte-rich PRP. However, there is still no consensus on optimal preparation, dosing, and route of administration of PRP, and preparations described in the literature vary.
This study also assessed the interaction of PRP and NSAIDs. Although there were no statistically significant differences between treatment and diet, shoulders treated with indomethacin alone showed a trend toward weaker biomechanical parameters in comparison with shoulders treated with saline alone, with PRP alone, or with both PRP and indomethacin. A larger sample would be needed to establish statistical significance. These trends are not surprising, as Cohen and colleagues21 found that NSAIDs, specifically indomethacin and celecoxib, significantly inhibited rotator cuff tendon-to-bone healing. The authors also found that a 2-week course of indomethacin was sufficient to significantly inhibit tendon-to-bone healing. In fact, although the drugs were discontinued after 14 days, biomechanical properties were negatively affected up to 8 weeks after repair. Our results differ from theirs even though the 2 studies used similar doses and administration protocols.
One strength of this study was that all surgeries were performed by a single board-certified surgeon using a standardized technique. In addition, a control group was established, and personnel and techniques for all fine dissections and biomechanical tests were consistent throughout. Blinded randomization and diet normalization, as well as adequate power for detecting significant effects, strengthened the study as well.
The study had several limitations. First, whereas most human rotator cuff tears are chronic, we used a model of acute injury and repair. As acute tears that are immediately repaired are more likely to heal, detection of differences between cohorts is less likely. However, using an acute model is still the most reliable strategy for inducing a controlled injury with reproducible severity. Second, we analyzed data at only 1 time point, which may not provide an accurate representation of long-term effects. Third, systemic administration of indomethacin did not allow for intra-rat shoulder comparisons of the different drug groups. Fourth, although it is possible that the dosage of NSAID was insufficient to produce significant differences in biomechanics, our dosage was consistent with that used in a study that found a significant effect on tendon healing.21
Conclusion
Our study found that the strength of the supraspinatus tendon enthesis as defined by energy to failure was increased with intratendinous PRP injection. Indomethacin showed no statistical effect, but there was a trend toward reduced strength after repair. However, the extent to which coadministration of indomethacin affects PRP remains unclear, and these data cannot necessarily be extrapolated to the typical human rotator cuff tear caused by chronic repetitive stress.
1. Kinsella KG, Velkoff VA. An Aging World: 2001. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office; 2001. https://www.census.gov/prod/2001pubs/p95-01-1.pdf. Published November 2001. Accessed September 24, 2017.
2. Gamradt SC, Rodeo SA, Warren RF. Platelet rich plasma in rotator cuff repair. Tech Orthop. 2007;22(1):26-33.
3. Galatz LM, Ball CM, Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Yamaguchi K. The outcome and repair integrity of completely arthroscopically repaired large and massive rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(2):219-224.
4. Harryman DT, Mack LA, Wang KY. Repairs of the rotator cuff. Correlation of functional results with integrity of the cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73(7):982-989.
5. Bishop J, Klepps S, Lo IK, Bird J, Gladstone JN, Flatow EL. Cuff integrity after arthroscopic versus open rotator cuff repair: a prospective study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15(3):290-299.
6. Boileau P, Brassart N, Watkinson DJ, Carles M. Arthroscopic repair of full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus: does the tendon really heal? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(6):1229-1240.
7. Gerber C, Fuchs B, Hodler J. The results of repair of massive tears of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(4):505-515.
8. Lafosse L, Brozska R, Toussaint B, Gobezie R. The outcome and structural integrity of arthroscopic rotator cuff repair with use of the double-row suture anchor technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(7):1533-1541.
9. Levy O, Venkateswaran B, Even T, Ravenscroft M, Copeland S. Mid-term clinical and sonographic outcome of arthroscopic repair of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(10):1341-1347.
10. Zumstein MA, Jost B, Hempel J, Hodler J, Gerber C. The clinical and structural long-term results of open repair of massive tears of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(11):2423-2431.
11. Gerber C, Schneeberger AG, Perren SM, Nyffeler RW. Experimental rotator cuff repair. A preliminary study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81(9):1281-1290.
12. Randelli P, Arrigoni P, Ragone V, Aliprandi A, Cabitza P. Platelet rich plasma in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a prospective RCT study, 2-year follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(4):518-528.
13. Akeda K, An HS, Okuma M, et al. Platelet-rich plasma stimulates porcine articular chondrocyte proliferation and matrix biosynthesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;14(12):1272-1280.
14. de Mos M, van der Windt AE, Jahr H, et al. Can platelet-rich plasma enhance tendon repair? A cell culture study. Am J Sports Med. 2008;36(6):1171-1178.
15. Harmon KG. Muscle injuries and PRP: what does the science say? Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(9):616-617.
16. Kasten P, Vogel J, Geiger F, Niemeyer P, Luginbühl R, Szalay K. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on healing in critical-size long-bone defects. Biomaterials. 2008;29(29):3983-3992.
17. Mei-Dan O, Mann G, Maffulli N. Platelet-rich plasma: any substance into it? Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(9):618-619.
18. Murray MM, Spindler KP, Ballard P, Welch TP, Zurakowski D, Nanney LB. Enhanced histologic repair in a central wound in the anterior cruciate ligament with a collagen-platelet-rich plasma scaffold. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(8):1007-1017.
19. Virchenko O, Skoglund B, Aspenberg P. Parecoxib impairs early tendon repair but improves later remodeling. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(7):1743-1747.
20. Aspenberg P. Differential inhibition of fracture healing by non-selective and cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(3):684.
21. Cohen DB, Kawamura S, Ehteshami JR, Rodeo SA. Indomethacin and celecoxib impair rotator cuff tendon-to-bone healing. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(3):362-369.
22. Balazs T, Grice HC, Airth JM. On counting the blood cells of the rat with an electronic counter. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1960;24(9):273-275.
23. Beck J, Evans D, Tonino PM, Yong S, Callaci JJ. The biomechanical and histologic effects of platelet-rich plasma on rat rotator cuff repairs. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(9):2037-2044.
24. Aspenberg P, Virchenko O. Platelet concentrate injection improves Achilles tendon repair in rats. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004;75(1):93-99.
25. Chechik O, Dolkart O, Mozes G, Rak O, Alhajajra F, Maman E. Timing matters: NSAIDs interfere with the late proliferation stage of a repaired rotator cuff tendon healing in rats. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(4):515-520.
26. Barber FA, Hrnack SA, Snyder SJ, Hapa O. Rotator cuff repair healing influenced by platelet-rich plasma construct augmentation. Arthroscopy. 2011;27(8):1029-1035.
27. Randelli PS, Arrigoni P, Cabitza P, Volpi P, Maffulli N. Autologous platelet rich plasma for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. A pilot study. Disabil Rehabil. 2008;30(20-22):1584-1589.
28. Dolkart O, Chechik O, Zarfati Y, Brosh T, Alhajajra F, Maman E. A single dose of platelet-rich plasma improves the organization and strength of a surgically repaired rotator cuff tendon in rats. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(9):1271-1277.
29. Castricini R, Longo UG, De Benedetto M, et al. Platelet-rich plasma augmentation for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(2):258-265.
30. Weber SC, Kauffman JI, Parise C, Weber SJ, Katz SD. Platelet-rich fibrin matrix in the management of arthroscopic repair of the rotator cuff: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded study. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(2):263-270.
31. Ersen A, Demirhan M, Atalar AC, Kapicioğlu M, Baysal G. Platelet-rich plasma for enhancing surgical rotator cuff repair: evaluation and comparison of two application methods in a rat model. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(3):405-411.
32. Warth RJ, Dornan GJ, James EW, Horan MP, Millett PJ. Clinical and structural outcomes after arthroscopic repair of full-thickness rotator cuff tears with and without platelet-rich product supplementation: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(2):306-320.
33. Bergeson AG, Tashjian RZ, Greis PE, Crim J, Stoddard GJ, Burks RT. Effects of platelet-rich fibrin matrix on repair integrity of at-risk rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(2):286-293.
34. Riboh JC, Saltzman BM, Yanke AB, Fortier L, Cole BJ. Effect of leukocyte concentration on the efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(3):792-800.
Take-Home Points
- The optimal centrifugation protocol for production of rat PRP is 1300 rpm for 5 minutes.
- PRP administration in RCR improves tendon biomechanics in a rat model.
- Administration of NSAIDs following RCR has no significant effect on tendon biomechanical properties.
- NSAIDs may be co-administered with PRP without reducing efficacy of PRP.
- The role of PRP and NSAIDs in human RCR remains unclear.
Rotator cuff tears are a common source of shoulder pain and disability among older adults and athletes. Full-thickness tears alone occur in up to 30% of adults older than 60 years.1 Surgical repair is plagued by an unpredictable rate of recurrence (range, 11%-94%).1-10 As a result of improved suture materials, knotting patterns, and anchor designs, hardware issues are no longer the primary cause of rotator cuff repair (RCR) failures; now the principal mode of failure is biologic.2 Animal model studies have found that, after injury and subsequent healing, the tendon–bone interface remains abnormal.11 Rotator cuff research therefore has focused largely on biological enhancement of tendon-to-bone healing.
One means of biological augmentation is autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP), which has supraphysiologic concentrations of platelets and their secreted growth factors. Although there is no consensus on the long-term efficacy of PRP, some studies suggest PRP accelerates healing over short and intermediate terms, which may contribute to a more rapid decrease in pain and more rapid return to normal activities.12-18 Similarly, systemic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have long been used to treat musculoskeletal injuries, including rotator cuff pathology. However, NSAIDs inhibit cyclooxygenase activity, and clinical and experimental data have shown that cyclooxygenase 2 function is crucial in normal tendon-to-bone healing.19-21
Comprehensive studies have been conducted on the efficacy of both PRP and NSAIDs, but the interaction of concurrently used PRP and NSAIDs has not been determined. As many physicians use both modalities in the treatment of soft-tissue injuries, it is important to study the potential interactions when coadministered. Prior studies in small animal models suggest NSAIDs may impair tendon-to-bone healing in RCR, but there is no evidence regarding the effect of NSAIDs on the efficacy of PRP treatment.21
We conducted a study to determine the interaction of PRP and NSAIDs when used as adjuncts to RCR in a rat model. We hypothesized that PRP would increase the strength of RCR and that NSAIDs would interfere with the effects of PRP. A preliminary study objective was to determine an appropriate centrifugation protocol for producing PRP from rat blood, for use in this study and in future rat-based studies of PRP.
Materials and Methods
Part A: Pretesting Determination of PRP Centrifugation Protocol
Fourteen adult male Fischer rats were used in part A of this study, which was conducted to determine an appropriate PRP centrifugation protocol. Traditional PRP centrifugation protocols are established for human blood, but rat red blood cells (RBCs) and human RBCs differ in size.22 In our preliminary study, we wanted to determine the adjusted centrifuge speed and duration for producing clinically optimal PRP from rats. Clinically optimal PRP has reduced levels of RBCs, which decrease platelet affinity. Although the role of leukocytes in PRP preparations is debated, reducing the number of white blood cells (WBCs) decreases the number of matrix metalloproteinases and reactive oxygen species that may lead to inflammation. We used the platelet index (ratio of platelets to WBCs) and the RBC count to quantify the quality of our PRP sample.
Each rat in part A was anesthetized while supine. We used the Autologous Conditioned Plasma (ACP) system (Arthrex), which requires only 1 centrifugation cycle to create PRP. About 9 mL or 10 mL of blood was obtained by cardiac aspiration using an ACP Double Syringe (Arthrex). After blood retrieval, a thoracotomy was performed to confirm each rat’s death.
Part B: Determining the Effects of PRP and NSAIDs on RCR in a Rat Model
Operative Cohort. Of the 34 Fischer rats used in part B of this study, 6 were used as blood donors for PRP production, and the other 28 underwent bilateral rotator cuff surgeries. We used donor rats to maximize the amount of PRP retrieval, allocating about 1 donor rat per 5 operative rats. Fischer rats are an inbred strain, so the PRP from a donor Fischer rat simulates autologous blood in other Fischer rats. Use of allogenic blood is consistent with prior rat PRP studies.23,24
Operative Technique. Each bilateral surgery was performed by a single board-certified shoulder surgeon, and the anesthetic and surgical protocols were followed as approved by the home institution’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Before surgery, blood was harvested for PRP production from donor rats, as described earlier, and centrifuged for 5 minutes × 1300 rpm. After anesthetic induction and skin incision, the deltoid muscle was cut to expose the acromion and underlying rotator cuff. The distal supraspinatus tendon was sharply detached from the greater tuberosity. A bone-tunnel RCR was performed by drilling a transverse tunnel across the greater tuberosity and affixing the tendon to its footprint with a 5-0 polypropylene suture (Prolene; Ethicon). Each rat was then randomly assigned to receive 50 µL of donor PRP injected in 1 operative shoulder and saline in the contralateral shoulder. Injections were made in the supraspinatus tendon at its attachment to the humerus. Deltoid and skin were closed with 4-0 polyglactin (Vicryl) suture (Ethicon) and staples, respectively.
Tendon Preparation. Immediately post mortem, each shoulder was grossly dissected to isolate the supraspinatus muscle attached to the humerus. Shoulders were then frozen in 0.15-M saline solution until specified biomechanical testing dates.
On day of dimensional/biomechanical testing, each specimen was thawed at room temperature and finely dissected under a microscope (Stemi 200-C; Car Zeiss). After dissection, the humeral shaft was embedded in polymethylmethacrylate within a test tube. The free end of the supraspinatus tendon was glued within a “tab” of waterproofed emery cloth, leaving about 2 mm of tendon between the tab and the greater tuberosity.
Biomechanical Analysis. A 5848 MicroTester (Instron) was used for biomechanical testing. Each tabbed tendon, held by a pneumatic clamp attached to the MicroTester, was tested in a preconditioning phase and then a ramp-to-failure phase. A constant drip of 0.15-M saline was run through the apparatus to simulate physiologic hydration of tissue. After the embedded specimen was secure within the loading apparatus, an initial tensile preload of 0.2 N was applied. After preloading, the tendon was run through a preconditioning phase to account for viscoelastic relaxation. Immediately after preconditioning, each tendon was subjected to failure testing at a ramp rate of 0.1 mm/s. Force data were collected as a function of displacement, allowing for the calculation of 4 biomechanical parameters: failure force, tendon stiffness and normalized stiffness, energy to failure, and total energy. Tendon stiffness is the slope of a curve-fit line of the initial peak; failure force is the force of the highest peak; energy to failure is the area under the curve (AUC) to the highest peak; and total energy is the AUC from the start of failure ramping to the point at which the tendon is torn off completely. Two-way ANOVA was used to assess the differences between treatment groups and diet groups for all parameters. Statistical significance was set at P < .05.
A power analysis was performed to determine ability to detect differences between cohorts. For power of 80% and P = .05, a difference of 16% of the mean could be detected for failure force, 30% for energy to failure, 14% for total energy to failure, and 24% for stiffness. In addition, a difference of 4% of the mean could be detected for tendon length, 6% for width, and 10% for thickness.
Results
Across all collective treatment-diet groups and biomechanical parameters, there was only 1 statistically significant difference. Mean (SD) energy to failure was significantly higher (P = .03) in shoulders treated with PRP, 11.7 (7.3) N-mm, than in those treated without PRP, 8.7 (4.6) N-mm (Figure 4). There were no statistically significant differences between shoulders treated with indomethacin and those treated without indomethacin (Table 3), and no statistically significant relationships between treatment and drug for any other biomechanical parameter (Figures 5-7).
Discussion
Our preliminary objective in this study was to determine the optimal centrifugation protocol for producing rat-based PRP. Optimal PRP requires a dense concentration of platelets as well as reduced levels of RBCs and WBCs.25 We used the platelet index to quantify the quality of our PRP samples, and we obtained the highest platelet index for the protocol of 5 minutes × 1300 rpm. This finding may be useful in later rat studies involving PRP.
The primary objective of this study was to assess the effect of the interaction of PRP and NSAIDs on RCR. PRP has been found to augment RCR,12,26,27 but indomethacin may impair healing.21,25 We hypothesized that shoulders treated with PRP would have more biomechanical strength than control shoulders and that indomethacin would decrease biomechanical strength.
Our data showed increased energy to failure of the rotator cuff with PRP injections (P = .03). All other biomechanical parameters showed no significant differences with PRP treatment, though there were statistically insignificant trends of increased total energy, failure force, and stiffness in the PRP cohorts. There were no statistically significant differences between the indomethacin and no-indomethacin groups, and indomethacin had no effect on the efficacy of PRP treatment. It should be noted that the measurements of total energy, energy to failure, and failure force best reflect the strength of the tendon–bone interface. Other biomechanical measures, such as stiffness and normalized stiffness, are physical properties of the tendon itself and apply less to enthesis strength, which was the primary focus of this study.
Beck and colleagues23 studied the effect of allogeneic PRP on RCR in a rat model. They tested biomechanical and histologic outcomes 7, 14, and 21 days after surgery. There was no significant difference in failure load between the 2 groups at any time point. Compared with failure strain in the control group, failure strain in the PRP group was decreased at 7 days, normalized at 14 days, and increased at 21 days. The authors hypothesized that increased tendon failure strain at 21 days may have reduced forces being transmitted to the suture fixation site, which may be clinically significant and warrants further investigation. In a similar study, by Dolkart and colleagues,28 intraoperative PRP administration enhanced the maximal load-to-failure and stiffness of rats’ repaired rotator cuffs. On histologic examination, tendons treated with PRP (vs control tendons) had more organized collagen. Although these studies have limitations similar to our study, these results further support improved tendon-to-bone healing with PRP.
In clinical application, Barber and colleagues26 found that, compared with controls, suturing PRP fibrin matrix into the rotator cuff during repair decreased the incidence of magnetic resonance imaging–detected retears. However, in 2 prospective, randomized trials, Castricini and colleagues29 and Weber and colleagues30 found that use of PRP in RCR did not improve outcomes. All 3 studies differ from ours in that they used fibrin matrix. However, Ersen and colleagues31 found no difference in the effects of PRP on rotator cuff healing between injection and fibrin matrix; PRP improved biomechanical properties of repaired rotator cuff independent of administration method. In a meta-analysis of PRP supplementation in RCR, Warth and colleagues32 found a statistically significant improvement in retear rates for tears >3 cm repaired with a double-row technique, but otherwise no overall improvement in retear rates or outcome scores with PRP. The authors acknowledged that the significant heterogeneity of the studies in their meta-analysis may have affected the quality of their data.
Although our study provides some insight into the effectiveness of PRP in tendon repair, the lack of standardization in PRP preparation and time points tested makes comparisons with similar studies difficult.33 Recent reports have emphasized that not all PRP separation systems yield similar products.33 Platelet concentrations, and therefore platelet-derived growth factor concentrations, differ between systems and may yield different clinical outcomes. Our decision to use leukocyte-reduced PRP is supported by a meta-analysis by Riboh and colleagues,34 who reviewed the literature on the effect of leukocyte concentration on the efficacy of PRP products. They found that, in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis, use of leukocyte-poor PRP resulted in improved functional outcomes scores in comparison with placebo, but this improvement did not occur with leukocyte-rich PRP. However, there is still no consensus on optimal preparation, dosing, and route of administration of PRP, and preparations described in the literature vary.
This study also assessed the interaction of PRP and NSAIDs. Although there were no statistically significant differences between treatment and diet, shoulders treated with indomethacin alone showed a trend toward weaker biomechanical parameters in comparison with shoulders treated with saline alone, with PRP alone, or with both PRP and indomethacin. A larger sample would be needed to establish statistical significance. These trends are not surprising, as Cohen and colleagues21 found that NSAIDs, specifically indomethacin and celecoxib, significantly inhibited rotator cuff tendon-to-bone healing. The authors also found that a 2-week course of indomethacin was sufficient to significantly inhibit tendon-to-bone healing. In fact, although the drugs were discontinued after 14 days, biomechanical properties were negatively affected up to 8 weeks after repair. Our results differ from theirs even though the 2 studies used similar doses and administration protocols.
One strength of this study was that all surgeries were performed by a single board-certified surgeon using a standardized technique. In addition, a control group was established, and personnel and techniques for all fine dissections and biomechanical tests were consistent throughout. Blinded randomization and diet normalization, as well as adequate power for detecting significant effects, strengthened the study as well.
The study had several limitations. First, whereas most human rotator cuff tears are chronic, we used a model of acute injury and repair. As acute tears that are immediately repaired are more likely to heal, detection of differences between cohorts is less likely. However, using an acute model is still the most reliable strategy for inducing a controlled injury with reproducible severity. Second, we analyzed data at only 1 time point, which may not provide an accurate representation of long-term effects. Third, systemic administration of indomethacin did not allow for intra-rat shoulder comparisons of the different drug groups. Fourth, although it is possible that the dosage of NSAID was insufficient to produce significant differences in biomechanics, our dosage was consistent with that used in a study that found a significant effect on tendon healing.21
Conclusion
Our study found that the strength of the supraspinatus tendon enthesis as defined by energy to failure was increased with intratendinous PRP injection. Indomethacin showed no statistical effect, but there was a trend toward reduced strength after repair. However, the extent to which coadministration of indomethacin affects PRP remains unclear, and these data cannot necessarily be extrapolated to the typical human rotator cuff tear caused by chronic repetitive stress.
Take-Home Points
- The optimal centrifugation protocol for production of rat PRP is 1300 rpm for 5 minutes.
- PRP administration in RCR improves tendon biomechanics in a rat model.
- Administration of NSAIDs following RCR has no significant effect on tendon biomechanical properties.
- NSAIDs may be co-administered with PRP without reducing efficacy of PRP.
- The role of PRP and NSAIDs in human RCR remains unclear.
Rotator cuff tears are a common source of shoulder pain and disability among older adults and athletes. Full-thickness tears alone occur in up to 30% of adults older than 60 years.1 Surgical repair is plagued by an unpredictable rate of recurrence (range, 11%-94%).1-10 As a result of improved suture materials, knotting patterns, and anchor designs, hardware issues are no longer the primary cause of rotator cuff repair (RCR) failures; now the principal mode of failure is biologic.2 Animal model studies have found that, after injury and subsequent healing, the tendon–bone interface remains abnormal.11 Rotator cuff research therefore has focused largely on biological enhancement of tendon-to-bone healing.
One means of biological augmentation is autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP), which has supraphysiologic concentrations of platelets and their secreted growth factors. Although there is no consensus on the long-term efficacy of PRP, some studies suggest PRP accelerates healing over short and intermediate terms, which may contribute to a more rapid decrease in pain and more rapid return to normal activities.12-18 Similarly, systemic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have long been used to treat musculoskeletal injuries, including rotator cuff pathology. However, NSAIDs inhibit cyclooxygenase activity, and clinical and experimental data have shown that cyclooxygenase 2 function is crucial in normal tendon-to-bone healing.19-21
Comprehensive studies have been conducted on the efficacy of both PRP and NSAIDs, but the interaction of concurrently used PRP and NSAIDs has not been determined. As many physicians use both modalities in the treatment of soft-tissue injuries, it is important to study the potential interactions when coadministered. Prior studies in small animal models suggest NSAIDs may impair tendon-to-bone healing in RCR, but there is no evidence regarding the effect of NSAIDs on the efficacy of PRP treatment.21
We conducted a study to determine the interaction of PRP and NSAIDs when used as adjuncts to RCR in a rat model. We hypothesized that PRP would increase the strength of RCR and that NSAIDs would interfere with the effects of PRP. A preliminary study objective was to determine an appropriate centrifugation protocol for producing PRP from rat blood, for use in this study and in future rat-based studies of PRP.
Materials and Methods
Part A: Pretesting Determination of PRP Centrifugation Protocol
Fourteen adult male Fischer rats were used in part A of this study, which was conducted to determine an appropriate PRP centrifugation protocol. Traditional PRP centrifugation protocols are established for human blood, but rat red blood cells (RBCs) and human RBCs differ in size.22 In our preliminary study, we wanted to determine the adjusted centrifuge speed and duration for producing clinically optimal PRP from rats. Clinically optimal PRP has reduced levels of RBCs, which decrease platelet affinity. Although the role of leukocytes in PRP preparations is debated, reducing the number of white blood cells (WBCs) decreases the number of matrix metalloproteinases and reactive oxygen species that may lead to inflammation. We used the platelet index (ratio of platelets to WBCs) and the RBC count to quantify the quality of our PRP sample.
Each rat in part A was anesthetized while supine. We used the Autologous Conditioned Plasma (ACP) system (Arthrex), which requires only 1 centrifugation cycle to create PRP. About 9 mL or 10 mL of blood was obtained by cardiac aspiration using an ACP Double Syringe (Arthrex). After blood retrieval, a thoracotomy was performed to confirm each rat’s death.
Part B: Determining the Effects of PRP and NSAIDs on RCR in a Rat Model
Operative Cohort. Of the 34 Fischer rats used in part B of this study, 6 were used as blood donors for PRP production, and the other 28 underwent bilateral rotator cuff surgeries. We used donor rats to maximize the amount of PRP retrieval, allocating about 1 donor rat per 5 operative rats. Fischer rats are an inbred strain, so the PRP from a donor Fischer rat simulates autologous blood in other Fischer rats. Use of allogenic blood is consistent with prior rat PRP studies.23,24
Operative Technique. Each bilateral surgery was performed by a single board-certified shoulder surgeon, and the anesthetic and surgical protocols were followed as approved by the home institution’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Before surgery, blood was harvested for PRP production from donor rats, as described earlier, and centrifuged for 5 minutes × 1300 rpm. After anesthetic induction and skin incision, the deltoid muscle was cut to expose the acromion and underlying rotator cuff. The distal supraspinatus tendon was sharply detached from the greater tuberosity. A bone-tunnel RCR was performed by drilling a transverse tunnel across the greater tuberosity and affixing the tendon to its footprint with a 5-0 polypropylene suture (Prolene; Ethicon). Each rat was then randomly assigned to receive 50 µL of donor PRP injected in 1 operative shoulder and saline in the contralateral shoulder. Injections were made in the supraspinatus tendon at its attachment to the humerus. Deltoid and skin were closed with 4-0 polyglactin (Vicryl) suture (Ethicon) and staples, respectively.
Tendon Preparation. Immediately post mortem, each shoulder was grossly dissected to isolate the supraspinatus muscle attached to the humerus. Shoulders were then frozen in 0.15-M saline solution until specified biomechanical testing dates.
On day of dimensional/biomechanical testing, each specimen was thawed at room temperature and finely dissected under a microscope (Stemi 200-C; Car Zeiss). After dissection, the humeral shaft was embedded in polymethylmethacrylate within a test tube. The free end of the supraspinatus tendon was glued within a “tab” of waterproofed emery cloth, leaving about 2 mm of tendon between the tab and the greater tuberosity.
Biomechanical Analysis. A 5848 MicroTester (Instron) was used for biomechanical testing. Each tabbed tendon, held by a pneumatic clamp attached to the MicroTester, was tested in a preconditioning phase and then a ramp-to-failure phase. A constant drip of 0.15-M saline was run through the apparatus to simulate physiologic hydration of tissue. After the embedded specimen was secure within the loading apparatus, an initial tensile preload of 0.2 N was applied. After preloading, the tendon was run through a preconditioning phase to account for viscoelastic relaxation. Immediately after preconditioning, each tendon was subjected to failure testing at a ramp rate of 0.1 mm/s. Force data were collected as a function of displacement, allowing for the calculation of 4 biomechanical parameters: failure force, tendon stiffness and normalized stiffness, energy to failure, and total energy. Tendon stiffness is the slope of a curve-fit line of the initial peak; failure force is the force of the highest peak; energy to failure is the area under the curve (AUC) to the highest peak; and total energy is the AUC from the start of failure ramping to the point at which the tendon is torn off completely. Two-way ANOVA was used to assess the differences between treatment groups and diet groups for all parameters. Statistical significance was set at P < .05.
A power analysis was performed to determine ability to detect differences between cohorts. For power of 80% and P = .05, a difference of 16% of the mean could be detected for failure force, 30% for energy to failure, 14% for total energy to failure, and 24% for stiffness. In addition, a difference of 4% of the mean could be detected for tendon length, 6% for width, and 10% for thickness.
Results
Across all collective treatment-diet groups and biomechanical parameters, there was only 1 statistically significant difference. Mean (SD) energy to failure was significantly higher (P = .03) in shoulders treated with PRP, 11.7 (7.3) N-mm, than in those treated without PRP, 8.7 (4.6) N-mm (Figure 4). There were no statistically significant differences between shoulders treated with indomethacin and those treated without indomethacin (Table 3), and no statistically significant relationships between treatment and drug for any other biomechanical parameter (Figures 5-7).
Discussion
Our preliminary objective in this study was to determine the optimal centrifugation protocol for producing rat-based PRP. Optimal PRP requires a dense concentration of platelets as well as reduced levels of RBCs and WBCs.25 We used the platelet index to quantify the quality of our PRP samples, and we obtained the highest platelet index for the protocol of 5 minutes × 1300 rpm. This finding may be useful in later rat studies involving PRP.
The primary objective of this study was to assess the effect of the interaction of PRP and NSAIDs on RCR. PRP has been found to augment RCR,12,26,27 but indomethacin may impair healing.21,25 We hypothesized that shoulders treated with PRP would have more biomechanical strength than control shoulders and that indomethacin would decrease biomechanical strength.
Our data showed increased energy to failure of the rotator cuff with PRP injections (P = .03). All other biomechanical parameters showed no significant differences with PRP treatment, though there were statistically insignificant trends of increased total energy, failure force, and stiffness in the PRP cohorts. There were no statistically significant differences between the indomethacin and no-indomethacin groups, and indomethacin had no effect on the efficacy of PRP treatment. It should be noted that the measurements of total energy, energy to failure, and failure force best reflect the strength of the tendon–bone interface. Other biomechanical measures, such as stiffness and normalized stiffness, are physical properties of the tendon itself and apply less to enthesis strength, which was the primary focus of this study.
Beck and colleagues23 studied the effect of allogeneic PRP on RCR in a rat model. They tested biomechanical and histologic outcomes 7, 14, and 21 days after surgery. There was no significant difference in failure load between the 2 groups at any time point. Compared with failure strain in the control group, failure strain in the PRP group was decreased at 7 days, normalized at 14 days, and increased at 21 days. The authors hypothesized that increased tendon failure strain at 21 days may have reduced forces being transmitted to the suture fixation site, which may be clinically significant and warrants further investigation. In a similar study, by Dolkart and colleagues,28 intraoperative PRP administration enhanced the maximal load-to-failure and stiffness of rats’ repaired rotator cuffs. On histologic examination, tendons treated with PRP (vs control tendons) had more organized collagen. Although these studies have limitations similar to our study, these results further support improved tendon-to-bone healing with PRP.
In clinical application, Barber and colleagues26 found that, compared with controls, suturing PRP fibrin matrix into the rotator cuff during repair decreased the incidence of magnetic resonance imaging–detected retears. However, in 2 prospective, randomized trials, Castricini and colleagues29 and Weber and colleagues30 found that use of PRP in RCR did not improve outcomes. All 3 studies differ from ours in that they used fibrin matrix. However, Ersen and colleagues31 found no difference in the effects of PRP on rotator cuff healing between injection and fibrin matrix; PRP improved biomechanical properties of repaired rotator cuff independent of administration method. In a meta-analysis of PRP supplementation in RCR, Warth and colleagues32 found a statistically significant improvement in retear rates for tears >3 cm repaired with a double-row technique, but otherwise no overall improvement in retear rates or outcome scores with PRP. The authors acknowledged that the significant heterogeneity of the studies in their meta-analysis may have affected the quality of their data.
Although our study provides some insight into the effectiveness of PRP in tendon repair, the lack of standardization in PRP preparation and time points tested makes comparisons with similar studies difficult.33 Recent reports have emphasized that not all PRP separation systems yield similar products.33 Platelet concentrations, and therefore platelet-derived growth factor concentrations, differ between systems and may yield different clinical outcomes. Our decision to use leukocyte-reduced PRP is supported by a meta-analysis by Riboh and colleagues,34 who reviewed the literature on the effect of leukocyte concentration on the efficacy of PRP products. They found that, in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis, use of leukocyte-poor PRP resulted in improved functional outcomes scores in comparison with placebo, but this improvement did not occur with leukocyte-rich PRP. However, there is still no consensus on optimal preparation, dosing, and route of administration of PRP, and preparations described in the literature vary.
This study also assessed the interaction of PRP and NSAIDs. Although there were no statistically significant differences between treatment and diet, shoulders treated with indomethacin alone showed a trend toward weaker biomechanical parameters in comparison with shoulders treated with saline alone, with PRP alone, or with both PRP and indomethacin. A larger sample would be needed to establish statistical significance. These trends are not surprising, as Cohen and colleagues21 found that NSAIDs, specifically indomethacin and celecoxib, significantly inhibited rotator cuff tendon-to-bone healing. The authors also found that a 2-week course of indomethacin was sufficient to significantly inhibit tendon-to-bone healing. In fact, although the drugs were discontinued after 14 days, biomechanical properties were negatively affected up to 8 weeks after repair. Our results differ from theirs even though the 2 studies used similar doses and administration protocols.
One strength of this study was that all surgeries were performed by a single board-certified surgeon using a standardized technique. In addition, a control group was established, and personnel and techniques for all fine dissections and biomechanical tests were consistent throughout. Blinded randomization and diet normalization, as well as adequate power for detecting significant effects, strengthened the study as well.
The study had several limitations. First, whereas most human rotator cuff tears are chronic, we used a model of acute injury and repair. As acute tears that are immediately repaired are more likely to heal, detection of differences between cohorts is less likely. However, using an acute model is still the most reliable strategy for inducing a controlled injury with reproducible severity. Second, we analyzed data at only 1 time point, which may not provide an accurate representation of long-term effects. Third, systemic administration of indomethacin did not allow for intra-rat shoulder comparisons of the different drug groups. Fourth, although it is possible that the dosage of NSAID was insufficient to produce significant differences in biomechanics, our dosage was consistent with that used in a study that found a significant effect on tendon healing.21
Conclusion
Our study found that the strength of the supraspinatus tendon enthesis as defined by energy to failure was increased with intratendinous PRP injection. Indomethacin showed no statistical effect, but there was a trend toward reduced strength after repair. However, the extent to which coadministration of indomethacin affects PRP remains unclear, and these data cannot necessarily be extrapolated to the typical human rotator cuff tear caused by chronic repetitive stress.
1. Kinsella KG, Velkoff VA. An Aging World: 2001. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office; 2001. https://www.census.gov/prod/2001pubs/p95-01-1.pdf. Published November 2001. Accessed September 24, 2017.
2. Gamradt SC, Rodeo SA, Warren RF. Platelet rich plasma in rotator cuff repair. Tech Orthop. 2007;22(1):26-33.
3. Galatz LM, Ball CM, Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Yamaguchi K. The outcome and repair integrity of completely arthroscopically repaired large and massive rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(2):219-224.
4. Harryman DT, Mack LA, Wang KY. Repairs of the rotator cuff. Correlation of functional results with integrity of the cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73(7):982-989.
5. Bishop J, Klepps S, Lo IK, Bird J, Gladstone JN, Flatow EL. Cuff integrity after arthroscopic versus open rotator cuff repair: a prospective study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15(3):290-299.
6. Boileau P, Brassart N, Watkinson DJ, Carles M. Arthroscopic repair of full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus: does the tendon really heal? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(6):1229-1240.
7. Gerber C, Fuchs B, Hodler J. The results of repair of massive tears of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(4):505-515.
8. Lafosse L, Brozska R, Toussaint B, Gobezie R. The outcome and structural integrity of arthroscopic rotator cuff repair with use of the double-row suture anchor technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(7):1533-1541.
9. Levy O, Venkateswaran B, Even T, Ravenscroft M, Copeland S. Mid-term clinical and sonographic outcome of arthroscopic repair of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(10):1341-1347.
10. Zumstein MA, Jost B, Hempel J, Hodler J, Gerber C. The clinical and structural long-term results of open repair of massive tears of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(11):2423-2431.
11. Gerber C, Schneeberger AG, Perren SM, Nyffeler RW. Experimental rotator cuff repair. A preliminary study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81(9):1281-1290.
12. Randelli P, Arrigoni P, Ragone V, Aliprandi A, Cabitza P. Platelet rich plasma in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a prospective RCT study, 2-year follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(4):518-528.
13. Akeda K, An HS, Okuma M, et al. Platelet-rich plasma stimulates porcine articular chondrocyte proliferation and matrix biosynthesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;14(12):1272-1280.
14. de Mos M, van der Windt AE, Jahr H, et al. Can platelet-rich plasma enhance tendon repair? A cell culture study. Am J Sports Med. 2008;36(6):1171-1178.
15. Harmon KG. Muscle injuries and PRP: what does the science say? Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(9):616-617.
16. Kasten P, Vogel J, Geiger F, Niemeyer P, Luginbühl R, Szalay K. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on healing in critical-size long-bone defects. Biomaterials. 2008;29(29):3983-3992.
17. Mei-Dan O, Mann G, Maffulli N. Platelet-rich plasma: any substance into it? Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(9):618-619.
18. Murray MM, Spindler KP, Ballard P, Welch TP, Zurakowski D, Nanney LB. Enhanced histologic repair in a central wound in the anterior cruciate ligament with a collagen-platelet-rich plasma scaffold. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(8):1007-1017.
19. Virchenko O, Skoglund B, Aspenberg P. Parecoxib impairs early tendon repair but improves later remodeling. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(7):1743-1747.
20. Aspenberg P. Differential inhibition of fracture healing by non-selective and cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(3):684.
21. Cohen DB, Kawamura S, Ehteshami JR, Rodeo SA. Indomethacin and celecoxib impair rotator cuff tendon-to-bone healing. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(3):362-369.
22. Balazs T, Grice HC, Airth JM. On counting the blood cells of the rat with an electronic counter. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1960;24(9):273-275.
23. Beck J, Evans D, Tonino PM, Yong S, Callaci JJ. The biomechanical and histologic effects of platelet-rich plasma on rat rotator cuff repairs. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(9):2037-2044.
24. Aspenberg P, Virchenko O. Platelet concentrate injection improves Achilles tendon repair in rats. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004;75(1):93-99.
25. Chechik O, Dolkart O, Mozes G, Rak O, Alhajajra F, Maman E. Timing matters: NSAIDs interfere with the late proliferation stage of a repaired rotator cuff tendon healing in rats. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(4):515-520.
26. Barber FA, Hrnack SA, Snyder SJ, Hapa O. Rotator cuff repair healing influenced by platelet-rich plasma construct augmentation. Arthroscopy. 2011;27(8):1029-1035.
27. Randelli PS, Arrigoni P, Cabitza P, Volpi P, Maffulli N. Autologous platelet rich plasma for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. A pilot study. Disabil Rehabil. 2008;30(20-22):1584-1589.
28. Dolkart O, Chechik O, Zarfati Y, Brosh T, Alhajajra F, Maman E. A single dose of platelet-rich plasma improves the organization and strength of a surgically repaired rotator cuff tendon in rats. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(9):1271-1277.
29. Castricini R, Longo UG, De Benedetto M, et al. Platelet-rich plasma augmentation for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(2):258-265.
30. Weber SC, Kauffman JI, Parise C, Weber SJ, Katz SD. Platelet-rich fibrin matrix in the management of arthroscopic repair of the rotator cuff: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded study. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(2):263-270.
31. Ersen A, Demirhan M, Atalar AC, Kapicioğlu M, Baysal G. Platelet-rich plasma for enhancing surgical rotator cuff repair: evaluation and comparison of two application methods in a rat model. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(3):405-411.
32. Warth RJ, Dornan GJ, James EW, Horan MP, Millett PJ. Clinical and structural outcomes after arthroscopic repair of full-thickness rotator cuff tears with and without platelet-rich product supplementation: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(2):306-320.
33. Bergeson AG, Tashjian RZ, Greis PE, Crim J, Stoddard GJ, Burks RT. Effects of platelet-rich fibrin matrix on repair integrity of at-risk rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(2):286-293.
34. Riboh JC, Saltzman BM, Yanke AB, Fortier L, Cole BJ. Effect of leukocyte concentration on the efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(3):792-800.
1. Kinsella KG, Velkoff VA. An Aging World: 2001. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office; 2001. https://www.census.gov/prod/2001pubs/p95-01-1.pdf. Published November 2001. Accessed September 24, 2017.
2. Gamradt SC, Rodeo SA, Warren RF. Platelet rich plasma in rotator cuff repair. Tech Orthop. 2007;22(1):26-33.
3. Galatz LM, Ball CM, Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Yamaguchi K. The outcome and repair integrity of completely arthroscopically repaired large and massive rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(2):219-224.
4. Harryman DT, Mack LA, Wang KY. Repairs of the rotator cuff. Correlation of functional results with integrity of the cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73(7):982-989.
5. Bishop J, Klepps S, Lo IK, Bird J, Gladstone JN, Flatow EL. Cuff integrity after arthroscopic versus open rotator cuff repair: a prospective study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15(3):290-299.
6. Boileau P, Brassart N, Watkinson DJ, Carles M. Arthroscopic repair of full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus: does the tendon really heal? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(6):1229-1240.
7. Gerber C, Fuchs B, Hodler J. The results of repair of massive tears of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(4):505-515.
8. Lafosse L, Brozska R, Toussaint B, Gobezie R. The outcome and structural integrity of arthroscopic rotator cuff repair with use of the double-row suture anchor technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(7):1533-1541.
9. Levy O, Venkateswaran B, Even T, Ravenscroft M, Copeland S. Mid-term clinical and sonographic outcome of arthroscopic repair of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(10):1341-1347.
10. Zumstein MA, Jost B, Hempel J, Hodler J, Gerber C. The clinical and structural long-term results of open repair of massive tears of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(11):2423-2431.
11. Gerber C, Schneeberger AG, Perren SM, Nyffeler RW. Experimental rotator cuff repair. A preliminary study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81(9):1281-1290.
12. Randelli P, Arrigoni P, Ragone V, Aliprandi A, Cabitza P. Platelet rich plasma in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a prospective RCT study, 2-year follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(4):518-528.
13. Akeda K, An HS, Okuma M, et al. Platelet-rich plasma stimulates porcine articular chondrocyte proliferation and matrix biosynthesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;14(12):1272-1280.
14. de Mos M, van der Windt AE, Jahr H, et al. Can platelet-rich plasma enhance tendon repair? A cell culture study. Am J Sports Med. 2008;36(6):1171-1178.
15. Harmon KG. Muscle injuries and PRP: what does the science say? Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(9):616-617.
16. Kasten P, Vogel J, Geiger F, Niemeyer P, Luginbühl R, Szalay K. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on healing in critical-size long-bone defects. Biomaterials. 2008;29(29):3983-3992.
17. Mei-Dan O, Mann G, Maffulli N. Platelet-rich plasma: any substance into it? Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(9):618-619.
18. Murray MM, Spindler KP, Ballard P, Welch TP, Zurakowski D, Nanney LB. Enhanced histologic repair in a central wound in the anterior cruciate ligament with a collagen-platelet-rich plasma scaffold. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(8):1007-1017.
19. Virchenko O, Skoglund B, Aspenberg P. Parecoxib impairs early tendon repair but improves later remodeling. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(7):1743-1747.
20. Aspenberg P. Differential inhibition of fracture healing by non-selective and cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(3):684.
21. Cohen DB, Kawamura S, Ehteshami JR, Rodeo SA. Indomethacin and celecoxib impair rotator cuff tendon-to-bone healing. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(3):362-369.
22. Balazs T, Grice HC, Airth JM. On counting the blood cells of the rat with an electronic counter. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1960;24(9):273-275.
23. Beck J, Evans D, Tonino PM, Yong S, Callaci JJ. The biomechanical and histologic effects of platelet-rich plasma on rat rotator cuff repairs. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(9):2037-2044.
24. Aspenberg P, Virchenko O. Platelet concentrate injection improves Achilles tendon repair in rats. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004;75(1):93-99.
25. Chechik O, Dolkart O, Mozes G, Rak O, Alhajajra F, Maman E. Timing matters: NSAIDs interfere with the late proliferation stage of a repaired rotator cuff tendon healing in rats. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(4):515-520.
26. Barber FA, Hrnack SA, Snyder SJ, Hapa O. Rotator cuff repair healing influenced by platelet-rich plasma construct augmentation. Arthroscopy. 2011;27(8):1029-1035.
27. Randelli PS, Arrigoni P, Cabitza P, Volpi P, Maffulli N. Autologous platelet rich plasma for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. A pilot study. Disabil Rehabil. 2008;30(20-22):1584-1589.
28. Dolkart O, Chechik O, Zarfati Y, Brosh T, Alhajajra F, Maman E. A single dose of platelet-rich plasma improves the organization and strength of a surgically repaired rotator cuff tendon in rats. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(9):1271-1277.
29. Castricini R, Longo UG, De Benedetto M, et al. Platelet-rich plasma augmentation for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(2):258-265.
30. Weber SC, Kauffman JI, Parise C, Weber SJ, Katz SD. Platelet-rich fibrin matrix in the management of arthroscopic repair of the rotator cuff: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded study. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(2):263-270.
31. Ersen A, Demirhan M, Atalar AC, Kapicioğlu M, Baysal G. Platelet-rich plasma for enhancing surgical rotator cuff repair: evaluation and comparison of two application methods in a rat model. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(3):405-411.
32. Warth RJ, Dornan GJ, James EW, Horan MP, Millett PJ. Clinical and structural outcomes after arthroscopic repair of full-thickness rotator cuff tears with and without platelet-rich product supplementation: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(2):306-320.
33. Bergeson AG, Tashjian RZ, Greis PE, Crim J, Stoddard GJ, Burks RT. Effects of platelet-rich fibrin matrix on repair integrity of at-risk rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(2):286-293.
34. Riboh JC, Saltzman BM, Yanke AB, Fortier L, Cole BJ. Effect of leukocyte concentration on the efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(3):792-800.
Reliability of 3-Dimensional Glenoid Component Templating and Correlation to Intraoperative Component Selection
Take-Home Points
- Guidelines regarding glenoid component size selection for primary TSA are lacking.
- Intraoperative in situ glenoid sizing may not be ideal.
- 3-D digital models may be utilized for preoperative templating of glenoid component size in primary TSA.
- 3-D templating that allows for superior-inferior, anterior-posterior, and rotational translation can lead to consistent and reproducible templating of glenoid component size.
- 3-D templating may reduce the risks of implant overhang, peg penetration, and decreased stability ratio.
In 1974, Neer1 introduced the shoulder prosthesis. In 1982, Neer and colleagues2 found significant improvement in shoulder pain and function in patients with glenohumeral osteoarthritis treated with the Neer prosthesis. Since then, use of total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) has increased. Between 1993 and 2007, TSA use increased 319% in the United States.3 Long-term outcomes studies have found implant survivorship ranging from 87% to 93% at 10 to 15 years.4
Although TSA is a successful procedure, glenoid component failure is the most common complication.5-10 Outcomes of revision surgery for glenoid instability are inferior to those of primary TSA.11 Recent research findings highlight the effect of glenoid size on TSA complications.12 A larger glenoid component increases the stability ratio (peak subluxation force divided by compression load).12 However, insufficient glenoid bone stock, small glenoid diameter, and inability to fit a properly sized reamer owing to soft-tissue constraints may lead surgeons to choose a smaller glenoid component in order to avoid peg penetration, overhang, and soft-tissue damage, respectively. Therefore, preoperative templating of glenoid size is a potential strategy for minimizing complications.
Templating is performed for proximal humeral components, but glenoid sizing typically is deferred to intraoperative in situ sizing with implant-specific targeting guides. This glenoid sizing practice arose out of a lack of standard digital glenoid templates and difficulty in selecting glenoid size based on plain radiographs and/or 2-dimensional (2-D) computed tomography (CT) scans. However, targeting devices are sporadically used during surgery, and intraoperative glenoid vault dimension estimates derived from visualization and palpation are often inaccurate. Often, rather than directly assess glenoid morphology, surgeons infer glenoid size from the size and sex of patients.13
Three-dimensional (3-D) CT can be used to accurately assess glenoid version, bone loss, and implant fit.14-19 We conducted a study to determine if 3-D digital imaging can be consistently and reproducibly used for preoperative templating of glenoid component size and to determine if glenoid sizes derived from templating correlate with the sizes of subsequently implanted glenoids.
Materials and Methods
This retrospective study was conducted at the Center for Shoulder, Elbow, and Sports Medicine at Columbia University Medical Center in New York City and was approved by our Institutional Review Board. Included in the study were all patients who underwent primary TSA for primary glenohumeral osteoarthritis over a 12-month period. Patients were required to have preoperative CT performed according to our study protocol. The CT protocol consisted of 0.5-mm axial cuts of the entire scapula and 3-D reconstruction of the scapula, glenoid, glenohumeral articulation, and proximal humerus. Patients were excluded from the study for primary TSA for a secondary cause of glenohumeral osteoarthritis, inflammatory arthritis, connective tissue disease, prior contralateral TSA, and prior ipsilateral scapula, glenoid, and proximal humerus surgery. Ultimately, 24 patients were included in the study.
CT data were formatted for preoperative templating. The CT images of each patient’s scapula were uploaded into Materialise Interactive Medical Image Control System (Mimics) software. Mimics allows 3-D image rendering and editing from various imaging modalities and formats. The software was used to create the 3-D scapula models for templating. Prior studies have validated the anatomical precision of 3-D models created with Mimics.20
Mimics was also used to digitize in 3-D the glenoid components from the Bigliani-Flatow Shoulder System (Zimmer Biomet). Glenoid components of 3 different sizes (40 mm, 46 mm, 52 mm) were used. (The Bigliani glenoid component was digitized, as this implant system was used for primary TSA in all 24 patients.) Each glenoid component was traced in 3-D with a Gage 2000 coordinate-measuring machine (Brown & Sharpe) and was processed with custom software. The custom software, cited in previous work by our group,17 created the same coordinate system for each scapula based on anatomical reference points. These digitized 3-D images of glenoid components were uploaded with the digitized 3-D scapulae derived from patients’ CT scans to the Magics software. Magics allows for manipulation and interaction of multiple 3-D models by creating electronic stereolithography files that provide 3-D surface geometry.
Three fellowship-trained shoulder surgeons and 4 shoulder fellows templated the most appropriately sized glenoid component for each of the 24 patients. At the time of templating, the surgeon was blinded to the size of the glenoid implant used in the surgery. In Magics, each scapula was positioned in 3-D similar to how it would appear with the patient in the beach-chair position during surgery. In both study arms, surgeons selected the largest component that maximized the area of contact while avoiding peg penetration of the glenoid vault or component overhang. In addition, surgeons were instructed to correct glenoid version to as near neutral as possible with component positioning but were not permitted to remove glenoid bone stock to correct deformity. All surgeons based placement of the glenoid component on the patient’s actual bone stock and not on osteophytes, which are readily appreciable on 3-D CT.
In study arm 1, the 3-D view of the glenoid was restricted to the initial view in the beach-chair position. The surgeon then manipulated the 3-D glenoid component template across a single 2-D plane, either the superior-inferior plane or the anterior-posterior plane, over the surface of the 3-D glenoid (Figure 1).
In study arm 2, surgeons were permitted to rotate the 3-D glenoid template and scapula in any manner (Figure 2).
Interobserver agreement was determined by comparing prosthetic glenoid component size selection among all study surgeons, and intraobserver agreement was determined by comparing glenoid size selection during 2 sessions separated by at least 3 weeks.
After each trial, the order of patients’ scapula images was randomly rearranged to reduce recall bias. Kappa (κ) coefficients were calculated for interobserver and intraobserver agreement. Kappas ranged from −1.0 (least agreement) to +1.0 (complete agreement). A κ of 0 indicated an observer selection was equivalent to random chance. The level of agreement was categorized according to κ using a system described by Landis and Koch21 (Table 1).
Results
The group of 24 patients consisted of 15 men and 9 women. Mean age was 70.3 years (range, 56-88 years). Primary TSA was performed in 14 right shoulders and 10 left shoulders. Of the 24 patients, 20 (83%) had a 46-mm glenoid component implanted, 3 male patients had a 52-mm glenoid component implanted, and 1 female patient had a 40-mm glenoid component implanted.
Study Arm 1: Glenoid Templating Based on 2 df
In study arm 1, overall intraobserver agreement was substantial, as defined in the statistical literature.21 Among all surgeons who participated, intraobserver agreeement was 0.76 (substantial), 0.60 (substantial), and 0.58 (moderate) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.67, substantial agreement). Trial 1 interobserver agreement was 0.56 (moderate) (P < .001), 0.25 (fair) (P < .001), and 0.21 (fair) (P < .001) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.36, fair agreement) (P < .001), and trial 2 interobserver agreement was 0.58 (moderate) (P < .001), 0.18 (poor) (P = .003), and 0.24 (fair) (P <.001) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.32, fair agreement) (P < .001). In study arm 1, therefore, trials 1 and 2 both showed fair interobserver agreement.
Study Arm 2: Glenoid Templating Based on 6 df
In study arm 2, a mean correlation of 0.42 (moderate agreement) was found between glenoid component size in 3-D templating and the glenoid component size ultimately selected during surgery (Table 3).
In study arm 2, overall intraobserver agreement was moderate. Among all surgeons who participated, intraobserver agreement was 0.80 (excellent), 0.43 (moderate), and 0.47 (moderate) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.58, moderate agreement). Trial 1 interobserver agreement was 0.75 (substantial) (P < .001), 0.39 (fair) (P < .001), and 0.50 (moderate) (P < .001) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.54, moderate agreement) (P < .001), and trial 2 interobserver agreement was 0.66 (substantial) (P < .001), 0.28 (fair) (P = .003), and 0.40 (moderate) (P < .001) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.43, moderate agreement) (P < .001).
Discussion
Our results showed that 3-D glenoid templating had reproducible intraobserver and interobserver agreement. Overall intraobserver agreement was substantial (κ = 0.67) for study arm 1 and moderate (κ = 0.58) for study arm 2. Interobserver agreement was fair for trials 1 and 2 (κ = 0.36 and 0.32) in arm 1 and moderate for trials 1 and 2 (κ = 0.54 and 0.43) in arm 2.
Intraobserver and interobserver agreement values, particularly in study arm 2, which incorporated rotation (6 df), are consistent with values in commonly used classification systems, such as the Neer system for proximal humerus fractures, the Frykman system for distal radius fractures, and the King system for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.22-30 Sidor and colleagues27 found overall interobserver agreement of 0.50 and overall intraobserver agreement of 0.66 for the Neer system, and Illarramendi and colleagues24 found overall interobserver agreement of 0.43 and overall intraobserver agreement of 0.61 for the Frykman system.
In study arm 2, overall interobserver and intraobserver agreement was moderate. A higher level of surgeon agreement is unlikely given the lack of well-defined parameters for determining glenoid component size. Therefore, glenoid size selection is largely a matter of surgeon preference. More research is needed to establish concrete guidelines for glenoid component size selection. Once guidelines are adopted, interobserver agreement in templating may increase.
In both study arms, the component that surgeons selected during templating tended to be smaller than the component they selected during surgery. In study arm 1, 32% of patients had a smaller component selected based on computer modeling, and 7% had a larger component selected. In study arm 2, the difference was narrower: 27% of patients had a smaller component selected during templating, and 16% had a larger component selected. A statistically significant difference (P < .001) in templated and implanted component sizes was found between men and women: Templated glenoid components were smaller than implanted components in 53% of women and larger than implanted components in 33% of men. Differences between templated and implanted components may be attributable to visualization differences. During templating, the entire glenoid can be visualized and the slightest peg penetration or component overhang detected; in contrast, during surgery, anatomical constraints preclude such a comprehensive assessment.
Differences in agreement between templated and implanted glenoid components suggest that the size of implanted components may not be ideal. In this study, the distribution of the templated glenoid sizes was much wider than that of the implanted glenoid sizes. During templating, each glenoid component can be definitively visualized and assessed for possible peg penetration and overhang. Visualization allows surgeons to base glenoid size selection solely on glenoid morphology, as opposed to factors such as patient sex and height. In addition, interobserver and intraobserver agreement values for the 40-mm glenoid component were considerably higher than those for components of other sizes, indicating that the 40-mm component was consistently and reproducibly selected for the same patients. Hence, templating may particularly help prevent peg penetration and component overhang for patients with a smaller diameter glenoid.
More research on 3-D templating is warranted given the results of this study and other studies.12,17,31 Scalise and colleagues31 found that, in TSA planning, surgeons’ use of 2-D (vs 3-D) imaging led them to overestimate glenoid component sizes (P = .006). In our study, the glenoid size selected during 3-D templating was, in many cases, smaller than the size selected during surgery. In order to avoid peg penetration and glenoid overhang, anecdotal guidelines commonly used in glenoid size selection, likely was the driving force in selecting smaller glenoid components during templating. Although anterior, superior, and inferior glenoid overhang typically can be assessed during surgery, posterior overhang is more difficult to evaluate. Three-dimensional modeling allows surgeons to determine optimal glenoid component size and position. In addition, intraoperative evaluation of glenoid component peg penetration is challenging, and peg penetration becomes evident only after it has occurred. During templating, however, surgeons were able to easily assess for peg penetration, and smaller glenoid components were selected.
A limitation of this study is that intraoperative glenoid version correction or peg containment was not quantified. More research is needed on the relationship between glenoid size selection and component overhang and peg penetration. Another limitation was use of only 1 TSA system (with 3 glenoid sizes, all with inline pegs); reliability of 3-D templating was not evaluated across different component designs. Last, given the absence of guidelines for glenoid component size selection, there was surgeon bias in preoperative templating and in intraoperative selection of glenoid size. Surgeons had differing opinions on the importance of maximizing the contact area of the component and correcting glenoid deformity and version.
Our study results showed that preoperative 3-D templating that allows for superior-inferior, anterior-posterior, and rotational translation was consistent and reproducible in determining glenoid component size, and use of this templating may reduce the risks of implant overhang, peg penetration, and decreased stability ratio. These results highlight the possibility that glenoid component sizes selected during surgery may not be ideal. More research is needed to determine if intraoperative glenoid size selection leads to adequate version correction and peg containment. The present study supports use of 3-D templating in primary TSA planning.
1. Neer CS 2nd. Replacement arthroplasty for glenohumeral osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56(1):1-13.
2. Neer CS 2nd, Watson KC, Stanton FJ. Recent experience in total shoulder replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64(3):319-337.
3. Day JS, Lau E, Ong KL, Williams GR, Ramsey ML, Kurtz SM. Prevalence and projections of total shoulder and elbow arthroplasty in the United States to 2015. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(8):1115-1120.
4. Torchia ME, Cofield RH, Settergren CR. Total shoulder arthroplasty with the Neer prosthesis: long-term results. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1997;6(6):495-505.
5. Barrett WP, Franklin JL, Jackins SE, Wyss CR, Matsen FA 3rd. Total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(6):865-872.
6. Bohsali KI, Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr. Complications of total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(10):2279-2292.
7. Matsen FA 3rd, Bicknell RT, Lippitt SB. Shoulder arthroplasty: the socket perspective. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(5 suppl):S241-S247.
8. Matsen FA 3rd, Clinton J, Lynch J, Bertelsen A, Richardson ML. Glenoid component failure in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(4):885-896.
9. Pearl ML, Romeo AA, Wirth MA, Yamaguchi K, Nicholson GP, Creighton RA. Decision making in contemporary shoulder arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2005;54:69-85.
10. Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr. Complications of total shoulder-replacement arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(4):603-616.
11. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Sperling JW, Rowland CM, Cofield RH. Instability after shoulder arthroplasty: results of surgical treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85(4):622-631.
12. Tammachote N, Sperling JW, Berglund LJ, Steinmann SP, Cofield RH, An KN. The effect of glenoid component size on the stability of total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(3 suppl):S102-S106.
13. Iannotti JP, Greeson C, Downing D, Sabesan V, Bryan JA. Effect of glenoid deformity on glenoid component placement in primary shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(1):48-55.
14. Briem D, Ruecker AH, Neumann J, et al. 3D fluoroscopic navigated reaming of the glenoid for total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA). Comput Aided Surg. 2011;16(2):93-99.
15. Budge MD, Lewis GS, Schaefer E, Coquia S, Flemming DJ, Armstrong AD. Comparison of standard two-dimensional and three-dimensional corrected glenoid version measurements. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(4):577-583.
16. Chuang TY, Adams CR, Burkhart SS. Use of preoperative three-dimensional computed tomography to quantify glenoid bone loss in shoulder instability. Arthroscopy. 2008;24(4):376-382.
17. Nowak DD, Bahu MJ, Gardner TR, et al. Simulation of surgical glenoid resurfacing using three-dimensional computed tomography of the arthritic glenohumeral joint: the amount of glenoid retroversion that can be corrected. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18(5):680-688.
18. Scalise JJ, Bryan J, Polster J, Brems JJ, Iannotti JP. Quantitative analysis of glenoid bone loss in osteoarthritis using three-dimensional computed tomography scans. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(2):328-335.
19. Scalise JJ, Codsi MJ, Bryan J, Iannotti JP. The three-dimensional glenoid vault model can estimate normal glenoid version in osteoarthritis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(3):487-491.
20. Bryce CD, Pennypacker JL, Kulkarni N, et al. Validation of three-dimensional models of in situ scapulae. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(5):825-832.
21. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1):159-174.
22. Cummings RJ, Loveless EA, Campbell J, Samelson S, Mazur JM. Interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility of the system of King et al. for the classification of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(8):1107-1111.
23. Humphrey CA, Dirschl DR, Ellis TJ. Interobserver reliability of a CT-based fracture classification system. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19(9):616-622.
24. Illarramendi A, González Della Valle A, Segal E, De Carli P, Maignon G, Gallucci G. Evaluation of simplified Frykman and AO classifications of fractures of the distal radius. Assessment of interobserver and intraobserver agreement. Int Orthop. 1998;22(2):111-115.
25. Lenke LG, Betz RR, Bridwell KH, et al. Intraobserver and interobserver reliability of the classification of thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(8):1097-1106.
26. Ploegmakers JJ, Mader K, Pennig D, Verheyen CC. Four distal radial fracture classification systems tested amongst a large panel of Dutch trauma surgeons. Injury. 2007;38(11):1268-1272.
27. Sidor ML, Zuckerman JD, Lyon T, Koval K, Cuomo F, Schoenberg N. The Neer classification system for proximal humeral fractures. An assessment of interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(12):1745-1750.
28. Siebenrock KA, Gerber C. The reproducibility of classification of fractures of the proximal end of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(12):1751-1755.
29. Thomsen NO, Overgaard S, Olsen LH, Hansen H, Nielsen ST. Observer variation in the radiographic classification of ankle fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73(4):676-678.
30. Ward WT, Vogt M, Grudziak JS, Tümer Y, Cook PC, Fitch RD. Severin classification system for evaluation of the results of operative treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. A study of intraobserver and interobserver reliability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(5):656-663.
31. Scalise JJ, Codsi MJ, Bryan J, Brems JJ, Iannotti JP. The influence of three-dimensional computed tomography images of the shoulder in preoperative planning for total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(11):2438-2445.
Take-Home Points
- Guidelines regarding glenoid component size selection for primary TSA are lacking.
- Intraoperative in situ glenoid sizing may not be ideal.
- 3-D digital models may be utilized for preoperative templating of glenoid component size in primary TSA.
- 3-D templating that allows for superior-inferior, anterior-posterior, and rotational translation can lead to consistent and reproducible templating of glenoid component size.
- 3-D templating may reduce the risks of implant overhang, peg penetration, and decreased stability ratio.
In 1974, Neer1 introduced the shoulder prosthesis. In 1982, Neer and colleagues2 found significant improvement in shoulder pain and function in patients with glenohumeral osteoarthritis treated with the Neer prosthesis. Since then, use of total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) has increased. Between 1993 and 2007, TSA use increased 319% in the United States.3 Long-term outcomes studies have found implant survivorship ranging from 87% to 93% at 10 to 15 years.4
Although TSA is a successful procedure, glenoid component failure is the most common complication.5-10 Outcomes of revision surgery for glenoid instability are inferior to those of primary TSA.11 Recent research findings highlight the effect of glenoid size on TSA complications.12 A larger glenoid component increases the stability ratio (peak subluxation force divided by compression load).12 However, insufficient glenoid bone stock, small glenoid diameter, and inability to fit a properly sized reamer owing to soft-tissue constraints may lead surgeons to choose a smaller glenoid component in order to avoid peg penetration, overhang, and soft-tissue damage, respectively. Therefore, preoperative templating of glenoid size is a potential strategy for minimizing complications.
Templating is performed for proximal humeral components, but glenoid sizing typically is deferred to intraoperative in situ sizing with implant-specific targeting guides. This glenoid sizing practice arose out of a lack of standard digital glenoid templates and difficulty in selecting glenoid size based on plain radiographs and/or 2-dimensional (2-D) computed tomography (CT) scans. However, targeting devices are sporadically used during surgery, and intraoperative glenoid vault dimension estimates derived from visualization and palpation are often inaccurate. Often, rather than directly assess glenoid morphology, surgeons infer glenoid size from the size and sex of patients.13
Three-dimensional (3-D) CT can be used to accurately assess glenoid version, bone loss, and implant fit.14-19 We conducted a study to determine if 3-D digital imaging can be consistently and reproducibly used for preoperative templating of glenoid component size and to determine if glenoid sizes derived from templating correlate with the sizes of subsequently implanted glenoids.
Materials and Methods
This retrospective study was conducted at the Center for Shoulder, Elbow, and Sports Medicine at Columbia University Medical Center in New York City and was approved by our Institutional Review Board. Included in the study were all patients who underwent primary TSA for primary glenohumeral osteoarthritis over a 12-month period. Patients were required to have preoperative CT performed according to our study protocol. The CT protocol consisted of 0.5-mm axial cuts of the entire scapula and 3-D reconstruction of the scapula, glenoid, glenohumeral articulation, and proximal humerus. Patients were excluded from the study for primary TSA for a secondary cause of glenohumeral osteoarthritis, inflammatory arthritis, connective tissue disease, prior contralateral TSA, and prior ipsilateral scapula, glenoid, and proximal humerus surgery. Ultimately, 24 patients were included in the study.
CT data were formatted for preoperative templating. The CT images of each patient’s scapula were uploaded into Materialise Interactive Medical Image Control System (Mimics) software. Mimics allows 3-D image rendering and editing from various imaging modalities and formats. The software was used to create the 3-D scapula models for templating. Prior studies have validated the anatomical precision of 3-D models created with Mimics.20
Mimics was also used to digitize in 3-D the glenoid components from the Bigliani-Flatow Shoulder System (Zimmer Biomet). Glenoid components of 3 different sizes (40 mm, 46 mm, 52 mm) were used. (The Bigliani glenoid component was digitized, as this implant system was used for primary TSA in all 24 patients.) Each glenoid component was traced in 3-D with a Gage 2000 coordinate-measuring machine (Brown & Sharpe) and was processed with custom software. The custom software, cited in previous work by our group,17 created the same coordinate system for each scapula based on anatomical reference points. These digitized 3-D images of glenoid components were uploaded with the digitized 3-D scapulae derived from patients’ CT scans to the Magics software. Magics allows for manipulation and interaction of multiple 3-D models by creating electronic stereolithography files that provide 3-D surface geometry.
Three fellowship-trained shoulder surgeons and 4 shoulder fellows templated the most appropriately sized glenoid component for each of the 24 patients. At the time of templating, the surgeon was blinded to the size of the glenoid implant used in the surgery. In Magics, each scapula was positioned in 3-D similar to how it would appear with the patient in the beach-chair position during surgery. In both study arms, surgeons selected the largest component that maximized the area of contact while avoiding peg penetration of the glenoid vault or component overhang. In addition, surgeons were instructed to correct glenoid version to as near neutral as possible with component positioning but were not permitted to remove glenoid bone stock to correct deformity. All surgeons based placement of the glenoid component on the patient’s actual bone stock and not on osteophytes, which are readily appreciable on 3-D CT.
In study arm 1, the 3-D view of the glenoid was restricted to the initial view in the beach-chair position. The surgeon then manipulated the 3-D glenoid component template across a single 2-D plane, either the superior-inferior plane or the anterior-posterior plane, over the surface of the 3-D glenoid (Figure 1).
In study arm 2, surgeons were permitted to rotate the 3-D glenoid template and scapula in any manner (Figure 2).
Interobserver agreement was determined by comparing prosthetic glenoid component size selection among all study surgeons, and intraobserver agreement was determined by comparing glenoid size selection during 2 sessions separated by at least 3 weeks.
After each trial, the order of patients’ scapula images was randomly rearranged to reduce recall bias. Kappa (κ) coefficients were calculated for interobserver and intraobserver agreement. Kappas ranged from −1.0 (least agreement) to +1.0 (complete agreement). A κ of 0 indicated an observer selection was equivalent to random chance. The level of agreement was categorized according to κ using a system described by Landis and Koch21 (Table 1).
Results
The group of 24 patients consisted of 15 men and 9 women. Mean age was 70.3 years (range, 56-88 years). Primary TSA was performed in 14 right shoulders and 10 left shoulders. Of the 24 patients, 20 (83%) had a 46-mm glenoid component implanted, 3 male patients had a 52-mm glenoid component implanted, and 1 female patient had a 40-mm glenoid component implanted.
Study Arm 1: Glenoid Templating Based on 2 df
In study arm 1, overall intraobserver agreement was substantial, as defined in the statistical literature.21 Among all surgeons who participated, intraobserver agreeement was 0.76 (substantial), 0.60 (substantial), and 0.58 (moderate) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.67, substantial agreement). Trial 1 interobserver agreement was 0.56 (moderate) (P < .001), 0.25 (fair) (P < .001), and 0.21 (fair) (P < .001) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.36, fair agreement) (P < .001), and trial 2 interobserver agreement was 0.58 (moderate) (P < .001), 0.18 (poor) (P = .003), and 0.24 (fair) (P <.001) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.32, fair agreement) (P < .001). In study arm 1, therefore, trials 1 and 2 both showed fair interobserver agreement.
Study Arm 2: Glenoid Templating Based on 6 df
In study arm 2, a mean correlation of 0.42 (moderate agreement) was found between glenoid component size in 3-D templating and the glenoid component size ultimately selected during surgery (Table 3).
In study arm 2, overall intraobserver agreement was moderate. Among all surgeons who participated, intraobserver agreement was 0.80 (excellent), 0.43 (moderate), and 0.47 (moderate) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.58, moderate agreement). Trial 1 interobserver agreement was 0.75 (substantial) (P < .001), 0.39 (fair) (P < .001), and 0.50 (moderate) (P < .001) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.54, moderate agreement) (P < .001), and trial 2 interobserver agreement was 0.66 (substantial) (P < .001), 0.28 (fair) (P = .003), and 0.40 (moderate) (P < .001) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.43, moderate agreement) (P < .001).
Discussion
Our results showed that 3-D glenoid templating had reproducible intraobserver and interobserver agreement. Overall intraobserver agreement was substantial (κ = 0.67) for study arm 1 and moderate (κ = 0.58) for study arm 2. Interobserver agreement was fair for trials 1 and 2 (κ = 0.36 and 0.32) in arm 1 and moderate for trials 1 and 2 (κ = 0.54 and 0.43) in arm 2.
Intraobserver and interobserver agreement values, particularly in study arm 2, which incorporated rotation (6 df), are consistent with values in commonly used classification systems, such as the Neer system for proximal humerus fractures, the Frykman system for distal radius fractures, and the King system for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.22-30 Sidor and colleagues27 found overall interobserver agreement of 0.50 and overall intraobserver agreement of 0.66 for the Neer system, and Illarramendi and colleagues24 found overall interobserver agreement of 0.43 and overall intraobserver agreement of 0.61 for the Frykman system.
In study arm 2, overall interobserver and intraobserver agreement was moderate. A higher level of surgeon agreement is unlikely given the lack of well-defined parameters for determining glenoid component size. Therefore, glenoid size selection is largely a matter of surgeon preference. More research is needed to establish concrete guidelines for glenoid component size selection. Once guidelines are adopted, interobserver agreement in templating may increase.
In both study arms, the component that surgeons selected during templating tended to be smaller than the component they selected during surgery. In study arm 1, 32% of patients had a smaller component selected based on computer modeling, and 7% had a larger component selected. In study arm 2, the difference was narrower: 27% of patients had a smaller component selected during templating, and 16% had a larger component selected. A statistically significant difference (P < .001) in templated and implanted component sizes was found between men and women: Templated glenoid components were smaller than implanted components in 53% of women and larger than implanted components in 33% of men. Differences between templated and implanted components may be attributable to visualization differences. During templating, the entire glenoid can be visualized and the slightest peg penetration or component overhang detected; in contrast, during surgery, anatomical constraints preclude such a comprehensive assessment.
Differences in agreement between templated and implanted glenoid components suggest that the size of implanted components may not be ideal. In this study, the distribution of the templated glenoid sizes was much wider than that of the implanted glenoid sizes. During templating, each glenoid component can be definitively visualized and assessed for possible peg penetration and overhang. Visualization allows surgeons to base glenoid size selection solely on glenoid morphology, as opposed to factors such as patient sex and height. In addition, interobserver and intraobserver agreement values for the 40-mm glenoid component were considerably higher than those for components of other sizes, indicating that the 40-mm component was consistently and reproducibly selected for the same patients. Hence, templating may particularly help prevent peg penetration and component overhang for patients with a smaller diameter glenoid.
More research on 3-D templating is warranted given the results of this study and other studies.12,17,31 Scalise and colleagues31 found that, in TSA planning, surgeons’ use of 2-D (vs 3-D) imaging led them to overestimate glenoid component sizes (P = .006). In our study, the glenoid size selected during 3-D templating was, in many cases, smaller than the size selected during surgery. In order to avoid peg penetration and glenoid overhang, anecdotal guidelines commonly used in glenoid size selection, likely was the driving force in selecting smaller glenoid components during templating. Although anterior, superior, and inferior glenoid overhang typically can be assessed during surgery, posterior overhang is more difficult to evaluate. Three-dimensional modeling allows surgeons to determine optimal glenoid component size and position. In addition, intraoperative evaluation of glenoid component peg penetration is challenging, and peg penetration becomes evident only after it has occurred. During templating, however, surgeons were able to easily assess for peg penetration, and smaller glenoid components were selected.
A limitation of this study is that intraoperative glenoid version correction or peg containment was not quantified. More research is needed on the relationship between glenoid size selection and component overhang and peg penetration. Another limitation was use of only 1 TSA system (with 3 glenoid sizes, all with inline pegs); reliability of 3-D templating was not evaluated across different component designs. Last, given the absence of guidelines for glenoid component size selection, there was surgeon bias in preoperative templating and in intraoperative selection of glenoid size. Surgeons had differing opinions on the importance of maximizing the contact area of the component and correcting glenoid deformity and version.
Our study results showed that preoperative 3-D templating that allows for superior-inferior, anterior-posterior, and rotational translation was consistent and reproducible in determining glenoid component size, and use of this templating may reduce the risks of implant overhang, peg penetration, and decreased stability ratio. These results highlight the possibility that glenoid component sizes selected during surgery may not be ideal. More research is needed to determine if intraoperative glenoid size selection leads to adequate version correction and peg containment. The present study supports use of 3-D templating in primary TSA planning.
Take-Home Points
- Guidelines regarding glenoid component size selection for primary TSA are lacking.
- Intraoperative in situ glenoid sizing may not be ideal.
- 3-D digital models may be utilized for preoperative templating of glenoid component size in primary TSA.
- 3-D templating that allows for superior-inferior, anterior-posterior, and rotational translation can lead to consistent and reproducible templating of glenoid component size.
- 3-D templating may reduce the risks of implant overhang, peg penetration, and decreased stability ratio.
In 1974, Neer1 introduced the shoulder prosthesis. In 1982, Neer and colleagues2 found significant improvement in shoulder pain and function in patients with glenohumeral osteoarthritis treated with the Neer prosthesis. Since then, use of total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) has increased. Between 1993 and 2007, TSA use increased 319% in the United States.3 Long-term outcomes studies have found implant survivorship ranging from 87% to 93% at 10 to 15 years.4
Although TSA is a successful procedure, glenoid component failure is the most common complication.5-10 Outcomes of revision surgery for glenoid instability are inferior to those of primary TSA.11 Recent research findings highlight the effect of glenoid size on TSA complications.12 A larger glenoid component increases the stability ratio (peak subluxation force divided by compression load).12 However, insufficient glenoid bone stock, small glenoid diameter, and inability to fit a properly sized reamer owing to soft-tissue constraints may lead surgeons to choose a smaller glenoid component in order to avoid peg penetration, overhang, and soft-tissue damage, respectively. Therefore, preoperative templating of glenoid size is a potential strategy for minimizing complications.
Templating is performed for proximal humeral components, but glenoid sizing typically is deferred to intraoperative in situ sizing with implant-specific targeting guides. This glenoid sizing practice arose out of a lack of standard digital glenoid templates and difficulty in selecting glenoid size based on plain radiographs and/or 2-dimensional (2-D) computed tomography (CT) scans. However, targeting devices are sporadically used during surgery, and intraoperative glenoid vault dimension estimates derived from visualization and palpation are often inaccurate. Often, rather than directly assess glenoid morphology, surgeons infer glenoid size from the size and sex of patients.13
Three-dimensional (3-D) CT can be used to accurately assess glenoid version, bone loss, and implant fit.14-19 We conducted a study to determine if 3-D digital imaging can be consistently and reproducibly used for preoperative templating of glenoid component size and to determine if glenoid sizes derived from templating correlate with the sizes of subsequently implanted glenoids.
Materials and Methods
This retrospective study was conducted at the Center for Shoulder, Elbow, and Sports Medicine at Columbia University Medical Center in New York City and was approved by our Institutional Review Board. Included in the study were all patients who underwent primary TSA for primary glenohumeral osteoarthritis over a 12-month period. Patients were required to have preoperative CT performed according to our study protocol. The CT protocol consisted of 0.5-mm axial cuts of the entire scapula and 3-D reconstruction of the scapula, glenoid, glenohumeral articulation, and proximal humerus. Patients were excluded from the study for primary TSA for a secondary cause of glenohumeral osteoarthritis, inflammatory arthritis, connective tissue disease, prior contralateral TSA, and prior ipsilateral scapula, glenoid, and proximal humerus surgery. Ultimately, 24 patients were included in the study.
CT data were formatted for preoperative templating. The CT images of each patient’s scapula were uploaded into Materialise Interactive Medical Image Control System (Mimics) software. Mimics allows 3-D image rendering and editing from various imaging modalities and formats. The software was used to create the 3-D scapula models for templating. Prior studies have validated the anatomical precision of 3-D models created with Mimics.20
Mimics was also used to digitize in 3-D the glenoid components from the Bigliani-Flatow Shoulder System (Zimmer Biomet). Glenoid components of 3 different sizes (40 mm, 46 mm, 52 mm) were used. (The Bigliani glenoid component was digitized, as this implant system was used for primary TSA in all 24 patients.) Each glenoid component was traced in 3-D with a Gage 2000 coordinate-measuring machine (Brown & Sharpe) and was processed with custom software. The custom software, cited in previous work by our group,17 created the same coordinate system for each scapula based on anatomical reference points. These digitized 3-D images of glenoid components were uploaded with the digitized 3-D scapulae derived from patients’ CT scans to the Magics software. Magics allows for manipulation and interaction of multiple 3-D models by creating electronic stereolithography files that provide 3-D surface geometry.
Three fellowship-trained shoulder surgeons and 4 shoulder fellows templated the most appropriately sized glenoid component for each of the 24 patients. At the time of templating, the surgeon was blinded to the size of the glenoid implant used in the surgery. In Magics, each scapula was positioned in 3-D similar to how it would appear with the patient in the beach-chair position during surgery. In both study arms, surgeons selected the largest component that maximized the area of contact while avoiding peg penetration of the glenoid vault or component overhang. In addition, surgeons were instructed to correct glenoid version to as near neutral as possible with component positioning but were not permitted to remove glenoid bone stock to correct deformity. All surgeons based placement of the glenoid component on the patient’s actual bone stock and not on osteophytes, which are readily appreciable on 3-D CT.
In study arm 1, the 3-D view of the glenoid was restricted to the initial view in the beach-chair position. The surgeon then manipulated the 3-D glenoid component template across a single 2-D plane, either the superior-inferior plane or the anterior-posterior plane, over the surface of the 3-D glenoid (Figure 1).
In study arm 2, surgeons were permitted to rotate the 3-D glenoid template and scapula in any manner (Figure 2).
Interobserver agreement was determined by comparing prosthetic glenoid component size selection among all study surgeons, and intraobserver agreement was determined by comparing glenoid size selection during 2 sessions separated by at least 3 weeks.
After each trial, the order of patients’ scapula images was randomly rearranged to reduce recall bias. Kappa (κ) coefficients were calculated for interobserver and intraobserver agreement. Kappas ranged from −1.0 (least agreement) to +1.0 (complete agreement). A κ of 0 indicated an observer selection was equivalent to random chance. The level of agreement was categorized according to κ using a system described by Landis and Koch21 (Table 1).
Results
The group of 24 patients consisted of 15 men and 9 women. Mean age was 70.3 years (range, 56-88 years). Primary TSA was performed in 14 right shoulders and 10 left shoulders. Of the 24 patients, 20 (83%) had a 46-mm glenoid component implanted, 3 male patients had a 52-mm glenoid component implanted, and 1 female patient had a 40-mm glenoid component implanted.
Study Arm 1: Glenoid Templating Based on 2 df
In study arm 1, overall intraobserver agreement was substantial, as defined in the statistical literature.21 Among all surgeons who participated, intraobserver agreeement was 0.76 (substantial), 0.60 (substantial), and 0.58 (moderate) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.67, substantial agreement). Trial 1 interobserver agreement was 0.56 (moderate) (P < .001), 0.25 (fair) (P < .001), and 0.21 (fair) (P < .001) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.36, fair agreement) (P < .001), and trial 2 interobserver agreement was 0.58 (moderate) (P < .001), 0.18 (poor) (P = .003), and 0.24 (fair) (P <.001) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.32, fair agreement) (P < .001). In study arm 1, therefore, trials 1 and 2 both showed fair interobserver agreement.
Study Arm 2: Glenoid Templating Based on 6 df
In study arm 2, a mean correlation of 0.42 (moderate agreement) was found between glenoid component size in 3-D templating and the glenoid component size ultimately selected during surgery (Table 3).
In study arm 2, overall intraobserver agreement was moderate. Among all surgeons who participated, intraobserver agreement was 0.80 (excellent), 0.43 (moderate), and 0.47 (moderate) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.58, moderate agreement). Trial 1 interobserver agreement was 0.75 (substantial) (P < .001), 0.39 (fair) (P < .001), and 0.50 (moderate) (P < .001) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.54, moderate agreement) (P < .001), and trial 2 interobserver agreement was 0.66 (substantial) (P < .001), 0.28 (fair) (P = .003), and 0.40 (moderate) (P < .001) for the 40-mm, 46-mm, and 52-mm glenoid components, respectively (overall κ = 0.43, moderate agreement) (P < .001).
Discussion
Our results showed that 3-D glenoid templating had reproducible intraobserver and interobserver agreement. Overall intraobserver agreement was substantial (κ = 0.67) for study arm 1 and moderate (κ = 0.58) for study arm 2. Interobserver agreement was fair for trials 1 and 2 (κ = 0.36 and 0.32) in arm 1 and moderate for trials 1 and 2 (κ = 0.54 and 0.43) in arm 2.
Intraobserver and interobserver agreement values, particularly in study arm 2, which incorporated rotation (6 df), are consistent with values in commonly used classification systems, such as the Neer system for proximal humerus fractures, the Frykman system for distal radius fractures, and the King system for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.22-30 Sidor and colleagues27 found overall interobserver agreement of 0.50 and overall intraobserver agreement of 0.66 for the Neer system, and Illarramendi and colleagues24 found overall interobserver agreement of 0.43 and overall intraobserver agreement of 0.61 for the Frykman system.
In study arm 2, overall interobserver and intraobserver agreement was moderate. A higher level of surgeon agreement is unlikely given the lack of well-defined parameters for determining glenoid component size. Therefore, glenoid size selection is largely a matter of surgeon preference. More research is needed to establish concrete guidelines for glenoid component size selection. Once guidelines are adopted, interobserver agreement in templating may increase.
In both study arms, the component that surgeons selected during templating tended to be smaller than the component they selected during surgery. In study arm 1, 32% of patients had a smaller component selected based on computer modeling, and 7% had a larger component selected. In study arm 2, the difference was narrower: 27% of patients had a smaller component selected during templating, and 16% had a larger component selected. A statistically significant difference (P < .001) in templated and implanted component sizes was found between men and women: Templated glenoid components were smaller than implanted components in 53% of women and larger than implanted components in 33% of men. Differences between templated and implanted components may be attributable to visualization differences. During templating, the entire glenoid can be visualized and the slightest peg penetration or component overhang detected; in contrast, during surgery, anatomical constraints preclude such a comprehensive assessment.
Differences in agreement between templated and implanted glenoid components suggest that the size of implanted components may not be ideal. In this study, the distribution of the templated glenoid sizes was much wider than that of the implanted glenoid sizes. During templating, each glenoid component can be definitively visualized and assessed for possible peg penetration and overhang. Visualization allows surgeons to base glenoid size selection solely on glenoid morphology, as opposed to factors such as patient sex and height. In addition, interobserver and intraobserver agreement values for the 40-mm glenoid component were considerably higher than those for components of other sizes, indicating that the 40-mm component was consistently and reproducibly selected for the same patients. Hence, templating may particularly help prevent peg penetration and component overhang for patients with a smaller diameter glenoid.
More research on 3-D templating is warranted given the results of this study and other studies.12,17,31 Scalise and colleagues31 found that, in TSA planning, surgeons’ use of 2-D (vs 3-D) imaging led them to overestimate glenoid component sizes (P = .006). In our study, the glenoid size selected during 3-D templating was, in many cases, smaller than the size selected during surgery. In order to avoid peg penetration and glenoid overhang, anecdotal guidelines commonly used in glenoid size selection, likely was the driving force in selecting smaller glenoid components during templating. Although anterior, superior, and inferior glenoid overhang typically can be assessed during surgery, posterior overhang is more difficult to evaluate. Three-dimensional modeling allows surgeons to determine optimal glenoid component size and position. In addition, intraoperative evaluation of glenoid component peg penetration is challenging, and peg penetration becomes evident only after it has occurred. During templating, however, surgeons were able to easily assess for peg penetration, and smaller glenoid components were selected.
A limitation of this study is that intraoperative glenoid version correction or peg containment was not quantified. More research is needed on the relationship between glenoid size selection and component overhang and peg penetration. Another limitation was use of only 1 TSA system (with 3 glenoid sizes, all with inline pegs); reliability of 3-D templating was not evaluated across different component designs. Last, given the absence of guidelines for glenoid component size selection, there was surgeon bias in preoperative templating and in intraoperative selection of glenoid size. Surgeons had differing opinions on the importance of maximizing the contact area of the component and correcting glenoid deformity and version.
Our study results showed that preoperative 3-D templating that allows for superior-inferior, anterior-posterior, and rotational translation was consistent and reproducible in determining glenoid component size, and use of this templating may reduce the risks of implant overhang, peg penetration, and decreased stability ratio. These results highlight the possibility that glenoid component sizes selected during surgery may not be ideal. More research is needed to determine if intraoperative glenoid size selection leads to adequate version correction and peg containment. The present study supports use of 3-D templating in primary TSA planning.
1. Neer CS 2nd. Replacement arthroplasty for glenohumeral osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56(1):1-13.
2. Neer CS 2nd, Watson KC, Stanton FJ. Recent experience in total shoulder replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64(3):319-337.
3. Day JS, Lau E, Ong KL, Williams GR, Ramsey ML, Kurtz SM. Prevalence and projections of total shoulder and elbow arthroplasty in the United States to 2015. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(8):1115-1120.
4. Torchia ME, Cofield RH, Settergren CR. Total shoulder arthroplasty with the Neer prosthesis: long-term results. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1997;6(6):495-505.
5. Barrett WP, Franklin JL, Jackins SE, Wyss CR, Matsen FA 3rd. Total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(6):865-872.
6. Bohsali KI, Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr. Complications of total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(10):2279-2292.
7. Matsen FA 3rd, Bicknell RT, Lippitt SB. Shoulder arthroplasty: the socket perspective. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(5 suppl):S241-S247.
8. Matsen FA 3rd, Clinton J, Lynch J, Bertelsen A, Richardson ML. Glenoid component failure in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(4):885-896.
9. Pearl ML, Romeo AA, Wirth MA, Yamaguchi K, Nicholson GP, Creighton RA. Decision making in contemporary shoulder arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2005;54:69-85.
10. Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr. Complications of total shoulder-replacement arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(4):603-616.
11. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Sperling JW, Rowland CM, Cofield RH. Instability after shoulder arthroplasty: results of surgical treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85(4):622-631.
12. Tammachote N, Sperling JW, Berglund LJ, Steinmann SP, Cofield RH, An KN. The effect of glenoid component size on the stability of total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(3 suppl):S102-S106.
13. Iannotti JP, Greeson C, Downing D, Sabesan V, Bryan JA. Effect of glenoid deformity on glenoid component placement in primary shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(1):48-55.
14. Briem D, Ruecker AH, Neumann J, et al. 3D fluoroscopic navigated reaming of the glenoid for total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA). Comput Aided Surg. 2011;16(2):93-99.
15. Budge MD, Lewis GS, Schaefer E, Coquia S, Flemming DJ, Armstrong AD. Comparison of standard two-dimensional and three-dimensional corrected glenoid version measurements. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(4):577-583.
16. Chuang TY, Adams CR, Burkhart SS. Use of preoperative three-dimensional computed tomography to quantify glenoid bone loss in shoulder instability. Arthroscopy. 2008;24(4):376-382.
17. Nowak DD, Bahu MJ, Gardner TR, et al. Simulation of surgical glenoid resurfacing using three-dimensional computed tomography of the arthritic glenohumeral joint: the amount of glenoid retroversion that can be corrected. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18(5):680-688.
18. Scalise JJ, Bryan J, Polster J, Brems JJ, Iannotti JP. Quantitative analysis of glenoid bone loss in osteoarthritis using three-dimensional computed tomography scans. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(2):328-335.
19. Scalise JJ, Codsi MJ, Bryan J, Iannotti JP. The three-dimensional glenoid vault model can estimate normal glenoid version in osteoarthritis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(3):487-491.
20. Bryce CD, Pennypacker JL, Kulkarni N, et al. Validation of three-dimensional models of in situ scapulae. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(5):825-832.
21. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1):159-174.
22. Cummings RJ, Loveless EA, Campbell J, Samelson S, Mazur JM. Interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility of the system of King et al. for the classification of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(8):1107-1111.
23. Humphrey CA, Dirschl DR, Ellis TJ. Interobserver reliability of a CT-based fracture classification system. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19(9):616-622.
24. Illarramendi A, González Della Valle A, Segal E, De Carli P, Maignon G, Gallucci G. Evaluation of simplified Frykman and AO classifications of fractures of the distal radius. Assessment of interobserver and intraobserver agreement. Int Orthop. 1998;22(2):111-115.
25. Lenke LG, Betz RR, Bridwell KH, et al. Intraobserver and interobserver reliability of the classification of thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(8):1097-1106.
26. Ploegmakers JJ, Mader K, Pennig D, Verheyen CC. Four distal radial fracture classification systems tested amongst a large panel of Dutch trauma surgeons. Injury. 2007;38(11):1268-1272.
27. Sidor ML, Zuckerman JD, Lyon T, Koval K, Cuomo F, Schoenberg N. The Neer classification system for proximal humeral fractures. An assessment of interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(12):1745-1750.
28. Siebenrock KA, Gerber C. The reproducibility of classification of fractures of the proximal end of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(12):1751-1755.
29. Thomsen NO, Overgaard S, Olsen LH, Hansen H, Nielsen ST. Observer variation in the radiographic classification of ankle fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73(4):676-678.
30. Ward WT, Vogt M, Grudziak JS, Tümer Y, Cook PC, Fitch RD. Severin classification system for evaluation of the results of operative treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. A study of intraobserver and interobserver reliability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(5):656-663.
31. Scalise JJ, Codsi MJ, Bryan J, Brems JJ, Iannotti JP. The influence of three-dimensional computed tomography images of the shoulder in preoperative planning for total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(11):2438-2445.
1. Neer CS 2nd. Replacement arthroplasty for glenohumeral osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56(1):1-13.
2. Neer CS 2nd, Watson KC, Stanton FJ. Recent experience in total shoulder replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64(3):319-337.
3. Day JS, Lau E, Ong KL, Williams GR, Ramsey ML, Kurtz SM. Prevalence and projections of total shoulder and elbow arthroplasty in the United States to 2015. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(8):1115-1120.
4. Torchia ME, Cofield RH, Settergren CR. Total shoulder arthroplasty with the Neer prosthesis: long-term results. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1997;6(6):495-505.
5. Barrett WP, Franklin JL, Jackins SE, Wyss CR, Matsen FA 3rd. Total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(6):865-872.
6. Bohsali KI, Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr. Complications of total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(10):2279-2292.
7. Matsen FA 3rd, Bicknell RT, Lippitt SB. Shoulder arthroplasty: the socket perspective. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(5 suppl):S241-S247.
8. Matsen FA 3rd, Clinton J, Lynch J, Bertelsen A, Richardson ML. Glenoid component failure in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(4):885-896.
9. Pearl ML, Romeo AA, Wirth MA, Yamaguchi K, Nicholson GP, Creighton RA. Decision making in contemporary shoulder arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2005;54:69-85.
10. Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr. Complications of total shoulder-replacement arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(4):603-616.
11. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Sperling JW, Rowland CM, Cofield RH. Instability after shoulder arthroplasty: results of surgical treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85(4):622-631.
12. Tammachote N, Sperling JW, Berglund LJ, Steinmann SP, Cofield RH, An KN. The effect of glenoid component size on the stability of total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(3 suppl):S102-S106.
13. Iannotti JP, Greeson C, Downing D, Sabesan V, Bryan JA. Effect of glenoid deformity on glenoid component placement in primary shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(1):48-55.
14. Briem D, Ruecker AH, Neumann J, et al. 3D fluoroscopic navigated reaming of the glenoid for total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA). Comput Aided Surg. 2011;16(2):93-99.
15. Budge MD, Lewis GS, Schaefer E, Coquia S, Flemming DJ, Armstrong AD. Comparison of standard two-dimensional and three-dimensional corrected glenoid version measurements. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(4):577-583.
16. Chuang TY, Adams CR, Burkhart SS. Use of preoperative three-dimensional computed tomography to quantify glenoid bone loss in shoulder instability. Arthroscopy. 2008;24(4):376-382.
17. Nowak DD, Bahu MJ, Gardner TR, et al. Simulation of surgical glenoid resurfacing using three-dimensional computed tomography of the arthritic glenohumeral joint: the amount of glenoid retroversion that can be corrected. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18(5):680-688.
18. Scalise JJ, Bryan J, Polster J, Brems JJ, Iannotti JP. Quantitative analysis of glenoid bone loss in osteoarthritis using three-dimensional computed tomography scans. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(2):328-335.
19. Scalise JJ, Codsi MJ, Bryan J, Iannotti JP. The three-dimensional glenoid vault model can estimate normal glenoid version in osteoarthritis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(3):487-491.
20. Bryce CD, Pennypacker JL, Kulkarni N, et al. Validation of three-dimensional models of in situ scapulae. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(5):825-832.
21. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1):159-174.
22. Cummings RJ, Loveless EA, Campbell J, Samelson S, Mazur JM. Interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility of the system of King et al. for the classification of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(8):1107-1111.
23. Humphrey CA, Dirschl DR, Ellis TJ. Interobserver reliability of a CT-based fracture classification system. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19(9):616-622.
24. Illarramendi A, González Della Valle A, Segal E, De Carli P, Maignon G, Gallucci G. Evaluation of simplified Frykman and AO classifications of fractures of the distal radius. Assessment of interobserver and intraobserver agreement. Int Orthop. 1998;22(2):111-115.
25. Lenke LG, Betz RR, Bridwell KH, et al. Intraobserver and interobserver reliability of the classification of thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(8):1097-1106.
26. Ploegmakers JJ, Mader K, Pennig D, Verheyen CC. Four distal radial fracture classification systems tested amongst a large panel of Dutch trauma surgeons. Injury. 2007;38(11):1268-1272.
27. Sidor ML, Zuckerman JD, Lyon T, Koval K, Cuomo F, Schoenberg N. The Neer classification system for proximal humeral fractures. An assessment of interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(12):1745-1750.
28. Siebenrock KA, Gerber C. The reproducibility of classification of fractures of the proximal end of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(12):1751-1755.
29. Thomsen NO, Overgaard S, Olsen LH, Hansen H, Nielsen ST. Observer variation in the radiographic classification of ankle fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73(4):676-678.
30. Ward WT, Vogt M, Grudziak JS, Tümer Y, Cook PC, Fitch RD. Severin classification system for evaluation of the results of operative treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. A study of intraobserver and interobserver reliability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(5):656-663.
31. Scalise JJ, Codsi MJ, Bryan J, Brems JJ, Iannotti JP. The influence of three-dimensional computed tomography images of the shoulder in preoperative planning for total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(11):2438-2445.
Head, Neck, and Shoulder Injuries in Ice Hockey: Current Concepts
Take-Home Points
- Hockey is a high-speed collision sport with one of the highest injury rates among all sports.
- Use of a helmet with visors or full-face shields significantly reduces the risk for eye injury.
- Broken portions of teeth should be found and placed in a protective medium such as saline, saliva, or milk for transport.
- A player with unresolved concussion symptoms should not be allowed to return to the ice.
- Shoulder dominance, which determines stick grip, is an important consideration in the treatment of shoulder instability in an ice hockey player.
On a surface of ice in Windsor, Nova Scotia in the middle of the 19th century, the modern game of ice hockey evolved.1 A blend of hurley, a Gaelic sport, and lacrosse, from the native Mi’kmaq culture, the sport of ice hockey gained rapidly in popularity throughout Canada and is now the country’s national sport. Hockey quickly spread to the United States and then Europe. It is presently played in 77 countries across the world.2
Hockey players can reach speeds of up to 48 km (~30 miles) per hour on razor-sharp skates on an ice surface surrounded by rigid plastic composite boards topped with plexiglass.3 They use sticks made of wood, aluminum, or a composite material to advance a 6-ounce vulcanized rubber puck on the opposing goal, and this puck sometimes reaches speeds over 160 km (~100 miles) per hour. Older, male players are allowed to make physical contact with their opposing counterparts to separate them from the puck (body-checking). Not surprisingly, the potential risk for injury in hockey is high. At the 2010 Winter Olympics, men’s ice hockey players had the highest rate of injury of any other competitors there—more than 30% were affected.4
Hockey is played and enjoyed by athletes ranging widely in age. Youth hockey leagues accept players as young as 5 years. Hockey can become a lifelong recreational activity. In North America, old timers’ leagues have many players up to age 70 years.6 According to International Ice Hockey Federation data for 2016, more than 543,000 and 639,500 people play hockey in the United States and Canada, respectively.2 Most of the rules, protective equipment, skates, ice surfaces, and goal sizes are the same in men’s and women’s hockey.7 The major difference is in body-checking—this practice is not allowed at any age in women’s ice hockey.
In this article, we review the evaluation and management of common head, neck, and shoulder hockey injuries for physicians who provide medical support and coverage for youth, amateur, and senior hockey teams.
Evaluation and Management of Common Hockey Injuries
Eye Injuries
Although eye injuries are less common than musculoskeletal injuries and concussions in hockey, they are a serious risk for recreational and competitive players alike. Furthermore, recovery may be difficult, and eye injuries can have serious lifelong consequences.8 In hockey, the most commonly reported eye injuries are periorbital contusions and lacerations, hyphema, corneal and conjunctival abrasions, orbital fractures, and ruptured globes (Table 2).9,10
As a contact sport, hockey often involves high-impact, blunt-force trauma. The trauma in hockey results from collisions with other players, the boards, hockey sticks, and pucks. It is therefore not surprising that the most common ocular injuries in this sport are periorbital contusions. Although most contusions cause only mild swelling and ecchymosis of the soft tissues around the eye, there is potential for serious consequences. In a Scandinavia study, Leivo and colleagues10 found that 9% of patients who sustained a periocular contusion also had a clinically significant secondary diagnosis, such as retinal tear or hemorrhage, eyelid laceration, vitreous hemorrhage, or retinal detachment. Although the study was hospital-based, and therefore biased toward more severe cases, its findings highlight the potential severity of eye injuries in hockey. Furthermore, the study found that the majority of players who sustained blunt trauma to the eye itself required lifelong follow-up because of increased risk for glaucoma. This is particularly true for hyphema, as this finding indicates significant damage to intraocular tissues.10Players can also sustain fractures of the orbital bones, including orbital blowout fractures. Typical signs and symptoms of blowout fractures include diplopia, proptosis or enophthalmos, infraorbital hypoesthesia, painful and decreased extraocular movement (particularly upgaze), and palpable crepitance caused by sinus air entering the lower eyelid.11 If orbital fracture is suspected, as it should be in any case in which the injured player experiences pain with eye movement or diplopia, the player should be referred to the ED for computed tomography (CT) and ophthalmologic evaluation.12 Continued participation seriously risks making the injury much worse, particularly should another impact occur. In addition, given the impact needed to cause orbital fractures, consideration must be given to the potential for a coexisting concussion injury.
Severe direct trauma to the eye—from a puck, a stick, or a fist—can result in a ruptured globe, a particularly serious injury that requires immediate surgical attention. Signs and symptoms of a ruptured globe are rarely subtle, but associated eyelid swelling or laceration may obscure the injury, delaying proper diagnosis and treatment. More obvious signs include severely reduced vision, hemorrhagic chemosis (swelling) of the conjunctiva, and an irregular or peaked pupil. If a rupture or any significant intraocular injury is suspected, it is crucial to avoid applying any pressure to the globe, as this can significantly worsen the damage to the intraocular tissues. Use of a helmet with protective shields and cages attached markedly reduces the risk for such injuries.13All eye injuries require prompt assessment, which allows for appropriate management and prevention of secondary damage.14 Initial evaluation of a patient with ocular trauma should begin with external examination for lacerations, swelling, or orbital rim step-off deformity. The physician should also check visual acuity in order to assess for significant vision impairment (counting fingers or reading a sign in the arena; confrontation visual fields). This should be done before attending to any periocular injuries, with the uninjured side serving as a control. Next, the physician should assess the extraocular eye movements as well as the size, shape, and reactivity of the pupils. Particular attention should be paid to detecting any deficit in extraocular movement or irregularity in pupil size, shape, or reactivity, as such findings are highly suggestive of serious injury to the globe.13 Hyphema (blood in anterior chamber of eye anterior to pupil) should be suspected if vision is reduced and the pupil cannot be clearly visualized. However, a bright red clot is not always apparent at time of injury or if the amount of blood is small. An irregular pupil, or a pupil that does not constrict well to light, is also a red flag for serious contusion injury to the eye, and requires ophthalmologic evaluation. It is important to keep in mind that blunt trauma severe enough to produce hyphema or an irregular and poorly reactive pupil is often associated with retinal damage as well, including retinal edema or detachment.
Minor injuries (eg, small foreign bodies, minor periocular contusions and lacerations) can often be managed rink-side. Foreign bodies not embedded in the cornea, but lodged under the upper eyelid, can sometimes be removed by everting the eyelid and sweeping with a moistened cotton swab or using diffuse, sterile saline irrigation.11 Corneal abrasions generally cause severe pain, photophobia, and tearing and are easily diagnosed with use of topical fluorescein and a blue light. A topical anesthetic can be extremely helpful in this setting, as it allows for proper pain-free evaluation, but should never be used in an ongoing manner for pain relief. Small lacerations of the brow can be sutured with 5-0 or 6-0 nylon or closed with 2-Octyl cyanoacrylate tissue adhesive (Dermabond). Eyelid lacerations, unless very small, are best managed by an ophthalmologist; care must be taken to rule out injury to the deeper orbital tissues and eye. If serious injury is suspected, or the eye cannot be appropriately evaluated, it should be stabilized and protected with a protective shield or plastic cup, and the player should be transferred to an ED for appropriate ophthalmologic evaluation.13Most eye injuries are accidental, caused by sticks or deflected pucks, but 18% are acquired in fights.8 Use of visors or full-face cages effectively minimizes the rate of eye injuries.8,13,15,16 In a cohort study of 282 elite amateur ice hockey players, the risk of eye injury was 4.7 times higher in players without face protection than in players who used half-face shields; there were no eye injuries in players who used full-face protection.13 For visors to prevent eye injury, they must be positioned to cover the eyes and the lower edge of the nose in all projections.10
Dental Injuries
The incidence and type of facial and dental injuries depend directly on the type of face protection used.11,17,18 In a study of face, head, and neck injuries in elite amateur ice hockey players, Stuart and colleagues13 found game-related injury rates of 158.9 per 1000 player-hours in players without face protection, 73.5 in players who used half-face shields, and 23.2 in players who used full-face shields. Players who wore full-face shields had facial, head, and neck injury rates of only 23.2 per 1000 player-game hours.13 Other studies clearly support the important role face shields play in lowering injury risk in hockey. Face and head injuries account for 20% to 40% of all hockey-related injuries,3,16,19 and dental injuries up to 11.5%.20 In a study from Finland, Lahti and colleagues19 found that over a 2-year period, 479 hockey players sustained injuries, including 650 separate dental injuries. The most commonly diagnosed dental injury was an uncomplicated crown fracture, and the most common cause was a hit with a hockey stick, which accounted for 52.7% and 40.3% of dental injuries in games and practices, respectively.19
In the management of dental fractures, the broken portions of teeth should be found and placed in a transportation-protective medium, such as saline, saliva, or milk,16 which can improve functional and esthetic replacement outcomes.21,22 Loose pieces of teeth should not be left in the player’s mouth. The residual tooth should be stabilized and exposure to air and occlusion limited. Dental fractures can affect the enamel, the enamel and dentin structures (uncomplicated fracture), or enamel, dentin, and pulp (complicated).23 Fractures involving only the enamel do not require urgent dental evaluation. Dentin or pulp involvement may cause temperature and air sensitivity.23 If a tooth is air-sensitive, the player should be referred to a specialist immediately.11
Direct trauma can cause instability without displacement (subluxation) or complete displacement of the tooth from its alveolar socket (avulsion).23 An avulsed tooth should be handled by the crown to avoid further damage to the root and periodontal ligament.16,24 The tooth should be rinsed gently with saline and reimplanted in its socket, ideally within 5 to 10 minutes,23with the athlete biting down gently on gauze to hold the tooth in place. A 1-mL supraperiosteal infiltration of 1% or 2% lidocaine hydrochloride (1:100,000 epinephrine) can be given into the apex of the tooth being anesthetized (Figure 1).
Concussions
A concussion is a “complex pathophysiological process affecting the brain, induced by traumatic biomechanical forces.”25 Concussion is largely a functional disturbance instead of a structural injury, owing to the rotational and/or shearing forces involved. Many studies have identified concussion as the most common type of injury in all of youth hockey.26 Concussions account for up to 19% of all injuries in men’s collegiate hockey.3
Concussion can be challenging to diagnose on the ice. The most important factor in concussion management is symptom reporting by the athlete.27 Despite significant efforts in education and awareness, student athletes, especially hockey players, withhold reporting a possible concussion.28 Reasons for underreporting include fear of letting down other players and coaches, thinking the injury is not severe enough to warrant evaluation, and fear of losing standing with the current team or future teams.28
As postinjury concussion assessments are ideal when comparisons can be made with preseason (baseline) scores, preseason testing is becoming standard in professional, college, junior, and high school hockey. This testing involves the Sport Concussion Assessment Tool, 3rd edition (SCAT3), and the King-Devick (K-D) test.30,31 Some youth leagues have baseline testing as well, though the frequency of baseline testing in their players is controversial,32 as the adolescent mind’s processing speed and memory increase exponentially.33 For these younger athletes, it may be necessary to perform baseline testing more frequently than annually.32 A physician can use baseline test results to help diagnose a concussion at the rink and then track the athlete’s recovery and help with return-to-play decisions.29 Vision involves almost half of the brain’s circuits,34 including areas vulnerable to head impact. A neuro-ophthalmologic test can assess for irregularities in accommodation, convergence, ocular muscle balance, pursuit, and saccades.29 The K-D test is a visual performance examination that allows easy and objective assessment of eye movements. Use of both the K-D test and the SCAT3 at the rink may increase the number of concussions detected.29,35 We recommend that physicians use both tests to assess for concussion at the hockey rink.
Initial treatment involves a period of physical rest and relative cognitive rest. Acute worsening of symptoms warrants urgent imaging to rule out a subdural or subarachnoid bleed. Once a player is symptom-free, a graded return-to-play protocol should be followed (Table 4).
On the prevention side, great efforts have been made to improve hockey helmets. (Some manufacturers claim to have made concussion-proof helmets, but there is no evidence supporting this claim.6) Numerous investigators have reported a lower overall injury rate in players who wear a helmet and a full-face shield.6,13 In addition, rule changes aimed at decreasing head contact have been implemented to decrease the incidence of sport-related concussions.36 Moreover, education on proper helmet use and wear should be emphasized. A study of the effects of hockey helmet fit on cervical motion found that 7 (39%) of 18 players wore a game or competition helmet so loosely that it could be removed without unbuttoning its chinstrap.37 Improperly worn helmets cannot prevent injury as well as properly worn helmets can.
Cervical Spine Injuries
Whereas American football is associated with a higher annual number of nonfatal catastrophic neck injuries, hockey has a 3 to 6 times higher incidence of cervical spine injuries and spinal cord damage.38,39 A Canadian Ice Hockey Spinal Injuries Registry review of the period 2006 to 2011 identified 44 cervical spine injuries, 7.3 per year on average.40 Severe injury, defined as complete motor and sensory loss, complete motor loss and incomplete sensory, or complete motor loss, occurred in 4 (9.1%) of the 44 injured players. In hockey, a major mechanism of cervical spine injury is an axial load to the slightly flexed spine.39 Of 355 hockey-related cervical spine injuries in a Canada study, 95 (35.5%) were caused by a check from behind.40,41 The Canadian neurosurgeons’ work led to rule changes prohibiting checks from behind, and this prohibition has reduced the incidence of cervical spine injuries in ice hockey.38,40
Team physicians should be comfortable managing serious neck and spine injuries on the ice. Initial evaluation should follow the standard ABCs (airway, breathing, circulation). The physician places a hand on each side of the head to stabilize the neck until the initial examination is complete. The goal is to minimize cervical spine motion until transportation to the hospital for advanced imaging and definitive treatment.37 The decision to remove or leave on the helmet is now controversial. Hockey helmets differ from football helmets in that their chinstraps do not afford significant cervical stabilization, and the helmets have less padding and cover less of the head; in addition, a shockingly high percentage of hockey players do not wear properly fitting helmets.37 In one study, 3-dimensional motion analysis of a hockey player during the logroll technique showed less transverse and sagittal cervical plane motion with the helmet removed than with the helmet (properly fitting or not) in place; the authors recommended removing the helmet to limit extraneous cervical spine motion during the technique.37 However, 2 other studies found that helmet removal can result in significantly increased cervical spine motion of the immobilized hockey player.42,43Recommendation 4 of the recently released interassociation consensus statement of the National Athletic Trainers’ Association reads, “Protective athletic equipment should be removed before transport to an emergency facility for an athlete-patient with suspected cervical spine instability.”44 This represents a shift from leaving the helmet and shoulder pads in place. For ice hockey players with suspected cervical spine injury, more research is needed on cervical motion during the entire sequence—partial logrolls, spine-boarding, placement of cervical collar before or after logroll, and different immobilization techniques for transport.37
The athlete must be carefully transferred to a spine board with either logroll or lift-and-slide. Although an extrication cervical collar can be placed before the spine board is placed, the effectiveness of this collar in executing the spine-board transfer is not proven.45 When the player is on the spine board, the head can be secured with pads and straps en route to the hospital.
Return-to-Play Criteria for Cervical Spine Injuries There is no clear consensus on return-to-play guidelines for cervical spine injuries in athletes.46
Shoulder Injuries
For hockey players, the upper extremity traditionally has been considered a well-protected area.48 However, shoulder pads are considerably more flexible in hockey than in football and other collision sports. In addition, hockey gloves allow a fair amount of motion for stick handling, and the wrist may be in maximal flexion or extension when a hit against the boards or the ice occurs. Open-ice checking, board collisions, and hockey stick use have been postulated as reasons for the high incidence of upper extremity injuries in hockey. Researchers in Finland found that upper extremity injuries accounted for up to 31% of all hockey injuries.49 More than 50% of these injuries resulted from checking or board collisions. Furthermore, study findings highlighted a low rate of injury in younger players and indicated the rate increases with age.49,50
In hockey players, the acromioclavicular (AC) joint is the most commonly injured shoulder structure.51 The mechanism of injury can be a board collision or an open-ice hit, but most often is a direct blow to the shoulder. The collision disrupts the AC joint and can sprain or tear the coracoclavicular ligaments. The Rockwood classification is used to categorize AC joint injuries (Figure 2).
Initial management involves icing the AC joint and placing a sling for comfort. Type I and type II injuries can be managed with progressive range-of-motion (ROM) exercises, strengthening, cryotherapy, and a period of rest. Treatment of type III injuries remains controversial,52 but in hockey players these injuries are almost always treated nonoperatively. Return to play requires full motion, normal strength, and minimal discomfort. Players return a few days to 2 weeks after a grade I injury; recovery from grade II injuries may take 2 to 3 weeks, and recovery from grade III injuries, 6 to 12 weeks. Surgical treatment is usually required in type IV and type V injuries, but we have had experience treating these injuries nonoperatively in high-level players. AC joint reinjury in hockey players is common, and surgical treatment should be approached cautiously, as delayed fracture after return to sport has been reported.53 Special precautions should be taken in collision athletes who undergo AC joint reconstruction. In the anatomical reconstruction described by Carofino and Mazzocca,54 2 holes are drilled in the clavicle; these holes are a potential source of fracture when the collision athlete returns to sport (Figure 3).
Clavicle fracture is another common hockey injury.55 Studies have shown clavicle fractures proportionally occur most often in people 15 to 19 years old.49 The injury presents with pain and deformity over the clavicle; in more severe fractures, skin tenting is identified. Initial management of suspected clavicle fracture includes cryotherapy, sling, and radiographs. Radiographs should include an AP view and then a 45° cephalad view, which eliminates overshadowing from the ribs. Most clavicle fractures are successfully managed nonoperatively, though there is evidence that significantly displaced or comminuted fractures have better union rates and shoulder function when treated with open reduction and internal fixation.56 After a clavicle fracture, return to skating and noncontact practice usually takes 8 weeks, with return to full contact occurring around 12 weeks.
Sternoclavicular injuries are relatively uncommon, but potentially serious. Special attention should also be given to adolescent athletes with sternoclavicular pain. Although sternoclavicular dislocations have been reported in hockey players, instead these likely are fractures involving the medial clavicle physis.57
The shoulder is the most commonly dislocated major joint, and the incidence of shoulder dislocation in elite hockey players is 8% to 21%.50,58 Anterior shoulder instability occurs from a fall with the shoulder in an abducted, externally rotated and extended position or from a direct anteriorly placed impact to the posterior shoulder. We recommend taking players off the ice for evaluation. Depending on physician comfort, the shoulder can be reduced in the training room, and the athlete sent for radiographs after reduction. If resources or support for closed reduction is not available at the rink, the athlete should be sent to the ED. Initial radiographic evaluation of a player with shoulder injury begins with plain radiographs, including a true AP (Grashey) view with the humerus in neutral, internal, and external rotation and an axillary view. The axillary radiograph is crucial in determining anterior or posterior dislocation. If the patient cannot tolerate the pain associated with having an axillary radiograph taken, a Velpeau radiograph can be used. This radiograph is taken with the patient’s arm in a sling and with the patient leaning back 30° while the x-ray beam is directed superior to inferior.
CT is performed for a suspected osseous injury. CT is more accurate than plain radiographs in showing glenoid and humeral fractures in the acute setting as well as the amount of bone loss in the case of chronic instability. Magnetic resonance arthrography is the imaging modality of choice for the diagnoses of capsulolabral injury.
After shoulder reduction, treatment with a sling, cryotherapy, and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug is initiated. In a Minnesota study of nonoperative management of shoulder instability, 9 of 10 hockey players were able to return to play the same season, and 6 of the 10 required surgery at the end of the season.59
Compared with noncontact athletes, hockey players and other collision athletes are at increased risk for recurrence.60-62 For collision athletes who want to continue playing their sport after recurrent instability, surgery is recommended. A shoulder instability study in Toronto found that more than 54% of 24 professional hockey players had associated Hill-Sachs lesions, but only 3 shoulders (12.5%) had glenoid defects.50 Arthroscopic and open techniques both demonstrate good results, and identification of bone loss can help determine which surgery to recommend.63 Hockey players can usually return to sport 6 months after shoulder stabilization.
Another important consideration in managing shoulder instability in hockey players is shoulder dominance, which determines stick grip. A left-handed player places the right hand on top of the stick for support, but most of the motion associated with shooting the puck—including abduction and external rotation—occurs with the left shoulder. Thus, a left-handed player with a history of previous left-side shoulder dislocation may dislocate with each shot, but a right-handed player with left shoulder instability may have considerably less trouble on the ice.58Shoulder and rotator cuff contusions (RCCs) occur in hockey and other collision sports.49,64 RCCs almost always result from a direct blow to the shoulder, and present with shoulder function loss, weakness, and pain.
Summary
Hockey is a high-speed collision sport with one of the highest injury rates among all sports. Physicians caring for youth, amateur, and senior hockey teams see a range of acute head, neck, and shoulder injuries. Although treatment of eye injuries, dental injuries, and concussions is not always considered orthopedic care, an orthopedic surgeon who is covering hockey needs to be comfortable managing these injuries acutely. Quality rink-side care minimizes the impact of the injury, maximizes the functional result, and expedites the safe return of the injured player back to the ice.
Am J Orthop. 2017;46(3):123-134. Copyright Frontline Medical Communications Inc. 2017. All rights reserved.
1. Vaughan G. The Puck Starts Here: The Origin of Canada’s Great Winter Game, Ice Hockey. Fredericton, Canada: Goose Lane Editions; 1996.
2. IIHF member national associations. International Ice Hockey Federation website. http://www.iihf.com/iihf-home/the-iihf/members. Accessed April 6, 2017.
3. Flik K, Lyman S, Marx RG. American collegiate men’s ice hockey: an analysis of injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(2):183-187.
4. Engebretsen L, Steffen K, Alonso JM, et al. Sports injuries and illnesses during the Winter Olympic Games 2010. Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(11):772-780.
5. Deits J, Yard EE, Collins CL, Fields SK, Comstock RD. Patients with ice hockey injuries presenting to US emergency departments, 1990-2006. J Athl Train. 2010;45(5):467-474.
6. Brooks A, Loud KJ, Brenner JS, et al. Reducing injury risk from body checking in boys’ youth ice hockey. Pediatrics. 2014;133(6):1151-1157.
7. Agel J, Harvey EJ. A 7-year review of men’s and women’s ice hockey injuries in the NCAA. Can J Surg. 2010;53(5):319-323.
8. Micieli JA, Zurakowski D, Ahmed, II. Impact of visors on eye and orbital injuries in the National Hockey League. Can J Ophthalmol. 2014;49(3):243-248.
9. Pashby TJ. Ocular injuries in hockey. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1988;28(3):228-231.
10. Leivo T, Haavisto AK, Sahraravand A. Sports-related eye injuries: the current picture. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015;93(3):224-231.
11. Cohn RM, Alaia MJ, Strauss EJ, Feldman AF. Rink-side management of ice hockey related injuries to the face, neck, and chest. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2013;71(4):253-256.
12. Reehal P. Facial injury in sport. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010;9(1):27-34.
13. Stuart MJ, Smith AM, Malo-Ortiguera SA, Fischer TL, Larson DR. A comparison of facial protection and the incidence of head, neck, and facial injuries in Junior A hockey players. A function of individual playing time. Am J Sports Med. 2002;30(1):39-44.
14. MacEwen CJ, McLatchie GR. Eye injuries in sport. Scott Med J. 2010;55(2):22-24.
15. Stevens ST, Lassonde M, de Beaumont L, Keenan JP. The effect of visors on head and facial injury in National Hockey League players. J Sci Med Sport. 2006;9(3):238-242.
16. Moslener MD, Wadsworth LT. Ice hockey: a team physician’s perspective. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010;9(3):134-138.
17. LaPrade RF, Burnett QM, Zarzour R, Moss R. The effect of the mandatory use of face masks on facial lacerations and head and neck injuries in ice hockey. A prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(6):773-775.
18. Benson BW, Mohtadi NG, Rose MS, Meeuwisse WH. Head and neck injuries among ice hockey players wearing full face shields vs half face shields. JAMA. 1999;282(24):2328-2332.
19. Lahti H, Sane J, Ylipaavalniemi P. Dental injuries in ice hockey games and training. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002;34(3):400-402.
20. Sane J, Ylipaavalniemi P, Leppanen H. Maxillofacial and dental ice hockey injuries. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1988;20(2):202-207.
21. Emerich K, Kaczmarek J. First aid for dental trauma caused by sports activities: state of knowledge, treatment and prevention. Sports Med. 2010;40(5):361-366.
22. Rosenberg H, Rosenberg H, Hickey M. Emergency management of a traumatic tooth avulsion. Ann Emerg Med. 2011;57(4):375-377.
23. Young EJ, Macias CR, Stephens L. Common dental injury management in athletes. Sports Health. 2015;7(3):250-255.
24. Andersson L, Andreasen JO, Day P, et al. International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth. Dent Traumatol. 2012;28(2):88-96.
25. McCrory P, Meeuwisse W, Johnston K, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport 3rd International Conference on Concussion in Sport held in Zurich, November 2008. Clin J Sport Med. 2009;19(3):185-200.
26. Schneider KJ, Meeuwisse WH, Kang J, Schneider GM, Emery CA. Preseason reports of neck pain, dizziness, and headache as risk factors for concussion in male youth ice hockey players. Clin J Sport Med. 2013;23(4):267-272.
27. McCrory P, Meeuwisse WH, Aubry M, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport: the 4th International Conference on Concussion in Sport held in Zurich, November 2012. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):250-258.
28. Delaney JS, Lamfookon C, Bloom GA, Al-Kashmiri A, Correa JA. Why university athletes choose not to reveal their concussion symptoms during a practice or game. Clin J Sport Med. 2015;25(2):113-125.
29. Ventura RE, Balcer LJ, Galetta SL. The concussion toolbox: the role of vision in the assessment of concussion. Semin Neurol. 2015;35(5):599-606.
30. Vartiainen MV, Holm A, Peltonen K, Luoto TM, Iverson GL, Hokkanen L. King-Devick test normative reference values for professional male ice hockey players. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25(3):e327-e330.
31. Galetta MS, Galetta KM, McCrossin J, et al. Saccades and memory: baseline associations of the King-Devick and SCAT2 SAC tests in professional ice hockey players. J Neurol Sci. 2013;328(1-2):28-31.
32. Vernau BT, Grady MF, Goodman A, et al. Oculomotor and neurocognitive assessment of youth ice hockey players: baseline associations and observations after concussion. Dev Neuropsychol. 2015;40(1):7-11.
33. Fry AF, Hale S. Relationships among processing speed, working memory, and fluid intelligence in children. Biol Psychol. 2000;54(1-3):1-34.
34. Felleman DJ, Van Essen DC. Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 1991;1(1):1-47.
35. Guskiewicz KM, Register-Mihalik J, McCrory P, et al. Evidence-based approach to revising the SCAT2: introducing the SCAT3. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):289-293.
36. Smith AM, Stuart MJ, Dodick DW, et al. Ice Hockey Summit II: zero tolerance for head hits and fighting. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2015;14(2):135-144.
37. Mihalik JP, Beard JR, Petschauer MA, Prentice WE, Guskiewicz KM. Effect of ice hockey helmet fit on cervical spine motion during an emergency log roll procedure. Clin J Sport Med. 2008;18(5):394-398.
38. Banerjee R, Palumbo MA, Fadale PD. Catastrophic cervical spine injuries in the collision sport athlete, part 1: epidemiology, functional anatomy, and diagnosis. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(4):1077-1087.
39. Reynen PD, Clancy WG Jr. Cervical spine injury, hockey helmets, and face masks. Am J Sports Med. 1994;22(2):167-170.
40. Tator CH, Provvidenza C, Cassidy JD. Update and overview of spinal injuries in Canadian ice hockey, 1943 to 2011: the continuing need for injury prevention and education. Clin J Sport Med. 2016;26(3):232-238.
41. Tator CH, Edmonds VE, Lapczak L, Tator IB. Spinal injuries in ice hockey players, 1966-1987. Can J Surg. 1991;34(1):63-69.
42. Laprade RF, Schnetzler KA, Broxterman RJ, Wentorf F, Gilbert TJ. Cervical spine alignment in the immobilized ice hockey player. A computed tomographic analysis of the effects of helmet removal. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28(6):800-803.
43. Metz CM, Kuhn JE, Greenfield ML. Cervical spine alignment in immobilized hockey players: radiographic analysis with and without helmets and shoulder pads. Clin J Sport Med. 1998;8(2):92-95.
44. National Athletic Trainers’ Association. Appropriate prehospital management of the spine-injured athlete: updated from 1998 document. http://www.nata.org/sites/default/files/Executive-Summary-Spine-Injury-updated.pdf. Updated August 5, 2015. Accessed April 6, 2017.
45. Del Rossi G, Heffernan TP, Horodyski M, Rechtine GR. The effectiveness of extrication collars tested during the execution of spine-board transfer techniques. Spine J. 2004;4(6):619-623.
46. Morganti C, Sweeney CA, Albanese SA, Burak C, Hosea T, Connolly PJ. Return to play after cervical spine injury. Spine. 2001;26(10):1131-1136.
47. Huang P, Anissipour A, McGee W, Lemak L. Return-to-play recommendations after cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine injuries: a comprehensive review. Sports Health. 2016;8(1):19-25.
48. Shindle MK, Marx RG, Kelly BT, Bisson L, Burke CJ 3rd. Hockey injuries: a pediatric sport update. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010;22(1):54-60.
49. Molsa J, Kujala U, Myllynen P, Torstila I, Airaksinen O. Injuries to the upper extremity in ice hockey: analysis of a series of 760 injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31(5):751-757.
50. Dwyer T, Petrera M, Bleakney R, Theodoropoulos JS. Shoulder instability in ice hockey players: incidence, mechanism, and MRI findings. Clin Sports Med. 2013;32(4):803-813.
51. LaPrade RF, Wijdicks CA, Griffith CJ. Division I intercollegiate ice hockey team coverage. Br J Sports Med. 2009;43(13):1000-1005.
52. Willimon SC, Gaskill TR, Millett PJ. Acromioclavicular joint injuries: anatomy, diagnosis, and treatment. Phys Sportsmed. 2011;39(1):116-122.
53. Martetschlager F, Horan MP, Warth RJ, Millett PJ. Complications after anatomic fixation and reconstruction of the coracoclavicular ligaments. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(12):2896-2903.
54. Carofino BC, Mazzocca AD. The anatomic coracoclavicular ligament reconstruction: surgical technique and indications. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(2 suppl):37-46.
55. Laprade RF, Surowiec RK, Sochanska AN, et al. Epidemiology, identification, treatment and return to play of musculoskeletal-based ice hockey injuries. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(1):4-10.
56. Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(1):1-10.
57. Lee JT, Nasreddine AY, Black EM, Bae DS, Kocher MS. Posterior sternoclavicular joint injuries in skeletally immature patients. J Pediatr Orthop. 2014;34(4):369-375.
58. Hovelius L. Shoulder dislocation in Swedish ice hockey players. Am J Sports Med. 1978;6(6):373-377.
59. Buss DD, Lynch GP, Meyer CP, Huber SM, Freehill MQ. Nonoperative management for in-season athletes with anterior shoulder instability. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(6):1430-1433.
60. Mazzocca AD, Brown FM Jr, Carreira DS, Hayden J, Romeo AA. Arthroscopic anterior shoulder stabilization of collision and contact athletes. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(1):52-60.
61. Harris JD, Romeo AA. Arthroscopic management of the contact athlete with instability. Clin Sports Med. 2013;32(4):709-730.
62. Cho NS, Hwang JC, Rhee YG. Arthroscopic stabilization in anterior shoulder instability: collision athletes versus noncollision athletes. Arthroscopy. 2006;22(9):947-953.
63. Griffin JW, Brockmeier SF. Shoulder instability with concomitant bone loss in the athlete. Orthop Clin North Am. 2015;46(1):89-103.
64. Cohen SB, Towers JD, Bradley JP. Rotator cuff contusions of the shoulder in professional football players: epidemiology and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(3):442-447.
65. Lorentzon R, Wedrèn H, Pietilä T. Incidence, nature, and causes of ice hockey injuries. A three-year prospective study of a Swedish elite ice hockey team. Am J Sports Med. 1988;16(4):392-396.
66. Stuart MJ, Smith A. Injuries in Junior A ice hockey. A three-year prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(4):458-461.
67. Voaklander DC, Saunders LD, Quinney HA, Macnab RB. Epidemiology of recreational and old-timer ice hockey injuries. Clin J Sport Med. 1996;6(1):15-21.
68. Mölsä J, Airaksinen O, Näsman O, Torstila I. Ice hockey injuries in Finland. A prospective epidemiologic study. Am J Sports Med. 1997;25(4):495-499.
69. Ferrara MS, Schurr KT. Intercollegiate ice hockey injuries: a casual analysis. Clin J Sport Med. 1999;9(1):30-33.
70. Pinto M, Kuhn JE, Greenfield ML, Hawkins RJ. Prospective analysis of ice hockey injuries at the Junior A level over the course of one season. Clin J Sport Med. 1999;9(2):70-74.
71. Emery CA, Meeuwisse WH. Injury rates, risk factors, and mechanisms of injury in minor hockey. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(12):1960-1969.
72. Kuzuhara K, Shimamoto H, Mase Y. Ice hockey injuries in a Japanese elite team: a 3-year prospective study. J Athl Train. 2009;44(2):208-214.
73. Rishiraj N, Lloyd-Smith R, Lorenz T, Niven B, Michel M. University men’s ice hockey: rates and risk of injuries over 6-years. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2009;49(2):159-166.
74. Tuominen M, Stuart MJ, Aubry M, Kannus P, Parkkari J. Injuries in men’s international ice hockey: a 7-year study of the International Ice Hockey Federation Adult World Championship Tournaments and Olympic Winter Games. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(1):30-36.
75. Heckman JD, Bucholz RW. In: Rockwood CA, Green DP, Heckman JD, Bucholz RW, eds. Rockwood and Green’s Fractures in Adults, Volume 1. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001.
Take-Home Points
- Hockey is a high-speed collision sport with one of the highest injury rates among all sports.
- Use of a helmet with visors or full-face shields significantly reduces the risk for eye injury.
- Broken portions of teeth should be found and placed in a protective medium such as saline, saliva, or milk for transport.
- A player with unresolved concussion symptoms should not be allowed to return to the ice.
- Shoulder dominance, which determines stick grip, is an important consideration in the treatment of shoulder instability in an ice hockey player.
On a surface of ice in Windsor, Nova Scotia in the middle of the 19th century, the modern game of ice hockey evolved.1 A blend of hurley, a Gaelic sport, and lacrosse, from the native Mi’kmaq culture, the sport of ice hockey gained rapidly in popularity throughout Canada and is now the country’s national sport. Hockey quickly spread to the United States and then Europe. It is presently played in 77 countries across the world.2
Hockey players can reach speeds of up to 48 km (~30 miles) per hour on razor-sharp skates on an ice surface surrounded by rigid plastic composite boards topped with plexiglass.3 They use sticks made of wood, aluminum, or a composite material to advance a 6-ounce vulcanized rubber puck on the opposing goal, and this puck sometimes reaches speeds over 160 km (~100 miles) per hour. Older, male players are allowed to make physical contact with their opposing counterparts to separate them from the puck (body-checking). Not surprisingly, the potential risk for injury in hockey is high. At the 2010 Winter Olympics, men’s ice hockey players had the highest rate of injury of any other competitors there—more than 30% were affected.4
Hockey is played and enjoyed by athletes ranging widely in age. Youth hockey leagues accept players as young as 5 years. Hockey can become a lifelong recreational activity. In North America, old timers’ leagues have many players up to age 70 years.6 According to International Ice Hockey Federation data for 2016, more than 543,000 and 639,500 people play hockey in the United States and Canada, respectively.2 Most of the rules, protective equipment, skates, ice surfaces, and goal sizes are the same in men’s and women’s hockey.7 The major difference is in body-checking—this practice is not allowed at any age in women’s ice hockey.
In this article, we review the evaluation and management of common head, neck, and shoulder hockey injuries for physicians who provide medical support and coverage for youth, amateur, and senior hockey teams.
Evaluation and Management of Common Hockey Injuries
Eye Injuries
Although eye injuries are less common than musculoskeletal injuries and concussions in hockey, they are a serious risk for recreational and competitive players alike. Furthermore, recovery may be difficult, and eye injuries can have serious lifelong consequences.8 In hockey, the most commonly reported eye injuries are periorbital contusions and lacerations, hyphema, corneal and conjunctival abrasions, orbital fractures, and ruptured globes (Table 2).9,10
As a contact sport, hockey often involves high-impact, blunt-force trauma. The trauma in hockey results from collisions with other players, the boards, hockey sticks, and pucks. It is therefore not surprising that the most common ocular injuries in this sport are periorbital contusions. Although most contusions cause only mild swelling and ecchymosis of the soft tissues around the eye, there is potential for serious consequences. In a Scandinavia study, Leivo and colleagues10 found that 9% of patients who sustained a periocular contusion also had a clinically significant secondary diagnosis, such as retinal tear or hemorrhage, eyelid laceration, vitreous hemorrhage, or retinal detachment. Although the study was hospital-based, and therefore biased toward more severe cases, its findings highlight the potential severity of eye injuries in hockey. Furthermore, the study found that the majority of players who sustained blunt trauma to the eye itself required lifelong follow-up because of increased risk for glaucoma. This is particularly true for hyphema, as this finding indicates significant damage to intraocular tissues.10Players can also sustain fractures of the orbital bones, including orbital blowout fractures. Typical signs and symptoms of blowout fractures include diplopia, proptosis or enophthalmos, infraorbital hypoesthesia, painful and decreased extraocular movement (particularly upgaze), and palpable crepitance caused by sinus air entering the lower eyelid.11 If orbital fracture is suspected, as it should be in any case in which the injured player experiences pain with eye movement or diplopia, the player should be referred to the ED for computed tomography (CT) and ophthalmologic evaluation.12 Continued participation seriously risks making the injury much worse, particularly should another impact occur. In addition, given the impact needed to cause orbital fractures, consideration must be given to the potential for a coexisting concussion injury.
Severe direct trauma to the eye—from a puck, a stick, or a fist—can result in a ruptured globe, a particularly serious injury that requires immediate surgical attention. Signs and symptoms of a ruptured globe are rarely subtle, but associated eyelid swelling or laceration may obscure the injury, delaying proper diagnosis and treatment. More obvious signs include severely reduced vision, hemorrhagic chemosis (swelling) of the conjunctiva, and an irregular or peaked pupil. If a rupture or any significant intraocular injury is suspected, it is crucial to avoid applying any pressure to the globe, as this can significantly worsen the damage to the intraocular tissues. Use of a helmet with protective shields and cages attached markedly reduces the risk for such injuries.13All eye injuries require prompt assessment, which allows for appropriate management and prevention of secondary damage.14 Initial evaluation of a patient with ocular trauma should begin with external examination for lacerations, swelling, or orbital rim step-off deformity. The physician should also check visual acuity in order to assess for significant vision impairment (counting fingers or reading a sign in the arena; confrontation visual fields). This should be done before attending to any periocular injuries, with the uninjured side serving as a control. Next, the physician should assess the extraocular eye movements as well as the size, shape, and reactivity of the pupils. Particular attention should be paid to detecting any deficit in extraocular movement or irregularity in pupil size, shape, or reactivity, as such findings are highly suggestive of serious injury to the globe.13 Hyphema (blood in anterior chamber of eye anterior to pupil) should be suspected if vision is reduced and the pupil cannot be clearly visualized. However, a bright red clot is not always apparent at time of injury or if the amount of blood is small. An irregular pupil, or a pupil that does not constrict well to light, is also a red flag for serious contusion injury to the eye, and requires ophthalmologic evaluation. It is important to keep in mind that blunt trauma severe enough to produce hyphema or an irregular and poorly reactive pupil is often associated with retinal damage as well, including retinal edema or detachment.
Minor injuries (eg, small foreign bodies, minor periocular contusions and lacerations) can often be managed rink-side. Foreign bodies not embedded in the cornea, but lodged under the upper eyelid, can sometimes be removed by everting the eyelid and sweeping with a moistened cotton swab or using diffuse, sterile saline irrigation.11 Corneal abrasions generally cause severe pain, photophobia, and tearing and are easily diagnosed with use of topical fluorescein and a blue light. A topical anesthetic can be extremely helpful in this setting, as it allows for proper pain-free evaluation, but should never be used in an ongoing manner for pain relief. Small lacerations of the brow can be sutured with 5-0 or 6-0 nylon or closed with 2-Octyl cyanoacrylate tissue adhesive (Dermabond). Eyelid lacerations, unless very small, are best managed by an ophthalmologist; care must be taken to rule out injury to the deeper orbital tissues and eye. If serious injury is suspected, or the eye cannot be appropriately evaluated, it should be stabilized and protected with a protective shield or plastic cup, and the player should be transferred to an ED for appropriate ophthalmologic evaluation.13Most eye injuries are accidental, caused by sticks or deflected pucks, but 18% are acquired in fights.8 Use of visors or full-face cages effectively minimizes the rate of eye injuries.8,13,15,16 In a cohort study of 282 elite amateur ice hockey players, the risk of eye injury was 4.7 times higher in players without face protection than in players who used half-face shields; there were no eye injuries in players who used full-face protection.13 For visors to prevent eye injury, they must be positioned to cover the eyes and the lower edge of the nose in all projections.10
Dental Injuries
The incidence and type of facial and dental injuries depend directly on the type of face protection used.11,17,18 In a study of face, head, and neck injuries in elite amateur ice hockey players, Stuart and colleagues13 found game-related injury rates of 158.9 per 1000 player-hours in players without face protection, 73.5 in players who used half-face shields, and 23.2 in players who used full-face shields. Players who wore full-face shields had facial, head, and neck injury rates of only 23.2 per 1000 player-game hours.13 Other studies clearly support the important role face shields play in lowering injury risk in hockey. Face and head injuries account for 20% to 40% of all hockey-related injuries,3,16,19 and dental injuries up to 11.5%.20 In a study from Finland, Lahti and colleagues19 found that over a 2-year period, 479 hockey players sustained injuries, including 650 separate dental injuries. The most commonly diagnosed dental injury was an uncomplicated crown fracture, and the most common cause was a hit with a hockey stick, which accounted for 52.7% and 40.3% of dental injuries in games and practices, respectively.19
In the management of dental fractures, the broken portions of teeth should be found and placed in a transportation-protective medium, such as saline, saliva, or milk,16 which can improve functional and esthetic replacement outcomes.21,22 Loose pieces of teeth should not be left in the player’s mouth. The residual tooth should be stabilized and exposure to air and occlusion limited. Dental fractures can affect the enamel, the enamel and dentin structures (uncomplicated fracture), or enamel, dentin, and pulp (complicated).23 Fractures involving only the enamel do not require urgent dental evaluation. Dentin or pulp involvement may cause temperature and air sensitivity.23 If a tooth is air-sensitive, the player should be referred to a specialist immediately.11
Direct trauma can cause instability without displacement (subluxation) or complete displacement of the tooth from its alveolar socket (avulsion).23 An avulsed tooth should be handled by the crown to avoid further damage to the root and periodontal ligament.16,24 The tooth should be rinsed gently with saline and reimplanted in its socket, ideally within 5 to 10 minutes,23with the athlete biting down gently on gauze to hold the tooth in place. A 1-mL supraperiosteal infiltration of 1% or 2% lidocaine hydrochloride (1:100,000 epinephrine) can be given into the apex of the tooth being anesthetized (Figure 1).
Concussions
A concussion is a “complex pathophysiological process affecting the brain, induced by traumatic biomechanical forces.”25 Concussion is largely a functional disturbance instead of a structural injury, owing to the rotational and/or shearing forces involved. Many studies have identified concussion as the most common type of injury in all of youth hockey.26 Concussions account for up to 19% of all injuries in men’s collegiate hockey.3
Concussion can be challenging to diagnose on the ice. The most important factor in concussion management is symptom reporting by the athlete.27 Despite significant efforts in education and awareness, student athletes, especially hockey players, withhold reporting a possible concussion.28 Reasons for underreporting include fear of letting down other players and coaches, thinking the injury is not severe enough to warrant evaluation, and fear of losing standing with the current team or future teams.28
As postinjury concussion assessments are ideal when comparisons can be made with preseason (baseline) scores, preseason testing is becoming standard in professional, college, junior, and high school hockey. This testing involves the Sport Concussion Assessment Tool, 3rd edition (SCAT3), and the King-Devick (K-D) test.30,31 Some youth leagues have baseline testing as well, though the frequency of baseline testing in their players is controversial,32 as the adolescent mind’s processing speed and memory increase exponentially.33 For these younger athletes, it may be necessary to perform baseline testing more frequently than annually.32 A physician can use baseline test results to help diagnose a concussion at the rink and then track the athlete’s recovery and help with return-to-play decisions.29 Vision involves almost half of the brain’s circuits,34 including areas vulnerable to head impact. A neuro-ophthalmologic test can assess for irregularities in accommodation, convergence, ocular muscle balance, pursuit, and saccades.29 The K-D test is a visual performance examination that allows easy and objective assessment of eye movements. Use of both the K-D test and the SCAT3 at the rink may increase the number of concussions detected.29,35 We recommend that physicians use both tests to assess for concussion at the hockey rink.
Initial treatment involves a period of physical rest and relative cognitive rest. Acute worsening of symptoms warrants urgent imaging to rule out a subdural or subarachnoid bleed. Once a player is symptom-free, a graded return-to-play protocol should be followed (Table 4).
On the prevention side, great efforts have been made to improve hockey helmets. (Some manufacturers claim to have made concussion-proof helmets, but there is no evidence supporting this claim.6) Numerous investigators have reported a lower overall injury rate in players who wear a helmet and a full-face shield.6,13 In addition, rule changes aimed at decreasing head contact have been implemented to decrease the incidence of sport-related concussions.36 Moreover, education on proper helmet use and wear should be emphasized. A study of the effects of hockey helmet fit on cervical motion found that 7 (39%) of 18 players wore a game or competition helmet so loosely that it could be removed without unbuttoning its chinstrap.37 Improperly worn helmets cannot prevent injury as well as properly worn helmets can.
Cervical Spine Injuries
Whereas American football is associated with a higher annual number of nonfatal catastrophic neck injuries, hockey has a 3 to 6 times higher incidence of cervical spine injuries and spinal cord damage.38,39 A Canadian Ice Hockey Spinal Injuries Registry review of the period 2006 to 2011 identified 44 cervical spine injuries, 7.3 per year on average.40 Severe injury, defined as complete motor and sensory loss, complete motor loss and incomplete sensory, or complete motor loss, occurred in 4 (9.1%) of the 44 injured players. In hockey, a major mechanism of cervical spine injury is an axial load to the slightly flexed spine.39 Of 355 hockey-related cervical spine injuries in a Canada study, 95 (35.5%) were caused by a check from behind.40,41 The Canadian neurosurgeons’ work led to rule changes prohibiting checks from behind, and this prohibition has reduced the incidence of cervical spine injuries in ice hockey.38,40
Team physicians should be comfortable managing serious neck and spine injuries on the ice. Initial evaluation should follow the standard ABCs (airway, breathing, circulation). The physician places a hand on each side of the head to stabilize the neck until the initial examination is complete. The goal is to minimize cervical spine motion until transportation to the hospital for advanced imaging and definitive treatment.37 The decision to remove or leave on the helmet is now controversial. Hockey helmets differ from football helmets in that their chinstraps do not afford significant cervical stabilization, and the helmets have less padding and cover less of the head; in addition, a shockingly high percentage of hockey players do not wear properly fitting helmets.37 In one study, 3-dimensional motion analysis of a hockey player during the logroll technique showed less transverse and sagittal cervical plane motion with the helmet removed than with the helmet (properly fitting or not) in place; the authors recommended removing the helmet to limit extraneous cervical spine motion during the technique.37 However, 2 other studies found that helmet removal can result in significantly increased cervical spine motion of the immobilized hockey player.42,43Recommendation 4 of the recently released interassociation consensus statement of the National Athletic Trainers’ Association reads, “Protective athletic equipment should be removed before transport to an emergency facility for an athlete-patient with suspected cervical spine instability.”44 This represents a shift from leaving the helmet and shoulder pads in place. For ice hockey players with suspected cervical spine injury, more research is needed on cervical motion during the entire sequence—partial logrolls, spine-boarding, placement of cervical collar before or after logroll, and different immobilization techniques for transport.37
The athlete must be carefully transferred to a spine board with either logroll or lift-and-slide. Although an extrication cervical collar can be placed before the spine board is placed, the effectiveness of this collar in executing the spine-board transfer is not proven.45 When the player is on the spine board, the head can be secured with pads and straps en route to the hospital.
Return-to-Play Criteria for Cervical Spine Injuries There is no clear consensus on return-to-play guidelines for cervical spine injuries in athletes.46
Shoulder Injuries
For hockey players, the upper extremity traditionally has been considered a well-protected area.48 However, shoulder pads are considerably more flexible in hockey than in football and other collision sports. In addition, hockey gloves allow a fair amount of motion for stick handling, and the wrist may be in maximal flexion or extension when a hit against the boards or the ice occurs. Open-ice checking, board collisions, and hockey stick use have been postulated as reasons for the high incidence of upper extremity injuries in hockey. Researchers in Finland found that upper extremity injuries accounted for up to 31% of all hockey injuries.49 More than 50% of these injuries resulted from checking or board collisions. Furthermore, study findings highlighted a low rate of injury in younger players and indicated the rate increases with age.49,50
In hockey players, the acromioclavicular (AC) joint is the most commonly injured shoulder structure.51 The mechanism of injury can be a board collision or an open-ice hit, but most often is a direct blow to the shoulder. The collision disrupts the AC joint and can sprain or tear the coracoclavicular ligaments. The Rockwood classification is used to categorize AC joint injuries (Figure 2).
Initial management involves icing the AC joint and placing a sling for comfort. Type I and type II injuries can be managed with progressive range-of-motion (ROM) exercises, strengthening, cryotherapy, and a period of rest. Treatment of type III injuries remains controversial,52 but in hockey players these injuries are almost always treated nonoperatively. Return to play requires full motion, normal strength, and minimal discomfort. Players return a few days to 2 weeks after a grade I injury; recovery from grade II injuries may take 2 to 3 weeks, and recovery from grade III injuries, 6 to 12 weeks. Surgical treatment is usually required in type IV and type V injuries, but we have had experience treating these injuries nonoperatively in high-level players. AC joint reinjury in hockey players is common, and surgical treatment should be approached cautiously, as delayed fracture after return to sport has been reported.53 Special precautions should be taken in collision athletes who undergo AC joint reconstruction. In the anatomical reconstruction described by Carofino and Mazzocca,54 2 holes are drilled in the clavicle; these holes are a potential source of fracture when the collision athlete returns to sport (Figure 3).
Clavicle fracture is another common hockey injury.55 Studies have shown clavicle fractures proportionally occur most often in people 15 to 19 years old.49 The injury presents with pain and deformity over the clavicle; in more severe fractures, skin tenting is identified. Initial management of suspected clavicle fracture includes cryotherapy, sling, and radiographs. Radiographs should include an AP view and then a 45° cephalad view, which eliminates overshadowing from the ribs. Most clavicle fractures are successfully managed nonoperatively, though there is evidence that significantly displaced or comminuted fractures have better union rates and shoulder function when treated with open reduction and internal fixation.56 After a clavicle fracture, return to skating and noncontact practice usually takes 8 weeks, with return to full contact occurring around 12 weeks.
Sternoclavicular injuries are relatively uncommon, but potentially serious. Special attention should also be given to adolescent athletes with sternoclavicular pain. Although sternoclavicular dislocations have been reported in hockey players, instead these likely are fractures involving the medial clavicle physis.57
The shoulder is the most commonly dislocated major joint, and the incidence of shoulder dislocation in elite hockey players is 8% to 21%.50,58 Anterior shoulder instability occurs from a fall with the shoulder in an abducted, externally rotated and extended position or from a direct anteriorly placed impact to the posterior shoulder. We recommend taking players off the ice for evaluation. Depending on physician comfort, the shoulder can be reduced in the training room, and the athlete sent for radiographs after reduction. If resources or support for closed reduction is not available at the rink, the athlete should be sent to the ED. Initial radiographic evaluation of a player with shoulder injury begins with plain radiographs, including a true AP (Grashey) view with the humerus in neutral, internal, and external rotation and an axillary view. The axillary radiograph is crucial in determining anterior or posterior dislocation. If the patient cannot tolerate the pain associated with having an axillary radiograph taken, a Velpeau radiograph can be used. This radiograph is taken with the patient’s arm in a sling and with the patient leaning back 30° while the x-ray beam is directed superior to inferior.
CT is performed for a suspected osseous injury. CT is more accurate than plain radiographs in showing glenoid and humeral fractures in the acute setting as well as the amount of bone loss in the case of chronic instability. Magnetic resonance arthrography is the imaging modality of choice for the diagnoses of capsulolabral injury.
After shoulder reduction, treatment with a sling, cryotherapy, and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug is initiated. In a Minnesota study of nonoperative management of shoulder instability, 9 of 10 hockey players were able to return to play the same season, and 6 of the 10 required surgery at the end of the season.59
Compared with noncontact athletes, hockey players and other collision athletes are at increased risk for recurrence.60-62 For collision athletes who want to continue playing their sport after recurrent instability, surgery is recommended. A shoulder instability study in Toronto found that more than 54% of 24 professional hockey players had associated Hill-Sachs lesions, but only 3 shoulders (12.5%) had glenoid defects.50 Arthroscopic and open techniques both demonstrate good results, and identification of bone loss can help determine which surgery to recommend.63 Hockey players can usually return to sport 6 months after shoulder stabilization.
Another important consideration in managing shoulder instability in hockey players is shoulder dominance, which determines stick grip. A left-handed player places the right hand on top of the stick for support, but most of the motion associated with shooting the puck—including abduction and external rotation—occurs with the left shoulder. Thus, a left-handed player with a history of previous left-side shoulder dislocation may dislocate with each shot, but a right-handed player with left shoulder instability may have considerably less trouble on the ice.58Shoulder and rotator cuff contusions (RCCs) occur in hockey and other collision sports.49,64 RCCs almost always result from a direct blow to the shoulder, and present with shoulder function loss, weakness, and pain.
Summary
Hockey is a high-speed collision sport with one of the highest injury rates among all sports. Physicians caring for youth, amateur, and senior hockey teams see a range of acute head, neck, and shoulder injuries. Although treatment of eye injuries, dental injuries, and concussions is not always considered orthopedic care, an orthopedic surgeon who is covering hockey needs to be comfortable managing these injuries acutely. Quality rink-side care minimizes the impact of the injury, maximizes the functional result, and expedites the safe return of the injured player back to the ice.
Am J Orthop. 2017;46(3):123-134. Copyright Frontline Medical Communications Inc. 2017. All rights reserved.
Take-Home Points
- Hockey is a high-speed collision sport with one of the highest injury rates among all sports.
- Use of a helmet with visors or full-face shields significantly reduces the risk for eye injury.
- Broken portions of teeth should be found and placed in a protective medium such as saline, saliva, or milk for transport.
- A player with unresolved concussion symptoms should not be allowed to return to the ice.
- Shoulder dominance, which determines stick grip, is an important consideration in the treatment of shoulder instability in an ice hockey player.
On a surface of ice in Windsor, Nova Scotia in the middle of the 19th century, the modern game of ice hockey evolved.1 A blend of hurley, a Gaelic sport, and lacrosse, from the native Mi’kmaq culture, the sport of ice hockey gained rapidly in popularity throughout Canada and is now the country’s national sport. Hockey quickly spread to the United States and then Europe. It is presently played in 77 countries across the world.2
Hockey players can reach speeds of up to 48 km (~30 miles) per hour on razor-sharp skates on an ice surface surrounded by rigid plastic composite boards topped with plexiglass.3 They use sticks made of wood, aluminum, or a composite material to advance a 6-ounce vulcanized rubber puck on the opposing goal, and this puck sometimes reaches speeds over 160 km (~100 miles) per hour. Older, male players are allowed to make physical contact with their opposing counterparts to separate them from the puck (body-checking). Not surprisingly, the potential risk for injury in hockey is high. At the 2010 Winter Olympics, men’s ice hockey players had the highest rate of injury of any other competitors there—more than 30% were affected.4
Hockey is played and enjoyed by athletes ranging widely in age. Youth hockey leagues accept players as young as 5 years. Hockey can become a lifelong recreational activity. In North America, old timers’ leagues have many players up to age 70 years.6 According to International Ice Hockey Federation data for 2016, more than 543,000 and 639,500 people play hockey in the United States and Canada, respectively.2 Most of the rules, protective equipment, skates, ice surfaces, and goal sizes are the same in men’s and women’s hockey.7 The major difference is in body-checking—this practice is not allowed at any age in women’s ice hockey.
In this article, we review the evaluation and management of common head, neck, and shoulder hockey injuries for physicians who provide medical support and coverage for youth, amateur, and senior hockey teams.
Evaluation and Management of Common Hockey Injuries
Eye Injuries
Although eye injuries are less common than musculoskeletal injuries and concussions in hockey, they are a serious risk for recreational and competitive players alike. Furthermore, recovery may be difficult, and eye injuries can have serious lifelong consequences.8 In hockey, the most commonly reported eye injuries are periorbital contusions and lacerations, hyphema, corneal and conjunctival abrasions, orbital fractures, and ruptured globes (Table 2).9,10
As a contact sport, hockey often involves high-impact, blunt-force trauma. The trauma in hockey results from collisions with other players, the boards, hockey sticks, and pucks. It is therefore not surprising that the most common ocular injuries in this sport are periorbital contusions. Although most contusions cause only mild swelling and ecchymosis of the soft tissues around the eye, there is potential for serious consequences. In a Scandinavia study, Leivo and colleagues10 found that 9% of patients who sustained a periocular contusion also had a clinically significant secondary diagnosis, such as retinal tear or hemorrhage, eyelid laceration, vitreous hemorrhage, or retinal detachment. Although the study was hospital-based, and therefore biased toward more severe cases, its findings highlight the potential severity of eye injuries in hockey. Furthermore, the study found that the majority of players who sustained blunt trauma to the eye itself required lifelong follow-up because of increased risk for glaucoma. This is particularly true for hyphema, as this finding indicates significant damage to intraocular tissues.10Players can also sustain fractures of the orbital bones, including orbital blowout fractures. Typical signs and symptoms of blowout fractures include diplopia, proptosis or enophthalmos, infraorbital hypoesthesia, painful and decreased extraocular movement (particularly upgaze), and palpable crepitance caused by sinus air entering the lower eyelid.11 If orbital fracture is suspected, as it should be in any case in which the injured player experiences pain with eye movement or diplopia, the player should be referred to the ED for computed tomography (CT) and ophthalmologic evaluation.12 Continued participation seriously risks making the injury much worse, particularly should another impact occur. In addition, given the impact needed to cause orbital fractures, consideration must be given to the potential for a coexisting concussion injury.
Severe direct trauma to the eye—from a puck, a stick, or a fist—can result in a ruptured globe, a particularly serious injury that requires immediate surgical attention. Signs and symptoms of a ruptured globe are rarely subtle, but associated eyelid swelling or laceration may obscure the injury, delaying proper diagnosis and treatment. More obvious signs include severely reduced vision, hemorrhagic chemosis (swelling) of the conjunctiva, and an irregular or peaked pupil. If a rupture or any significant intraocular injury is suspected, it is crucial to avoid applying any pressure to the globe, as this can significantly worsen the damage to the intraocular tissues. Use of a helmet with protective shields and cages attached markedly reduces the risk for such injuries.13All eye injuries require prompt assessment, which allows for appropriate management and prevention of secondary damage.14 Initial evaluation of a patient with ocular trauma should begin with external examination for lacerations, swelling, or orbital rim step-off deformity. The physician should also check visual acuity in order to assess for significant vision impairment (counting fingers or reading a sign in the arena; confrontation visual fields). This should be done before attending to any periocular injuries, with the uninjured side serving as a control. Next, the physician should assess the extraocular eye movements as well as the size, shape, and reactivity of the pupils. Particular attention should be paid to detecting any deficit in extraocular movement or irregularity in pupil size, shape, or reactivity, as such findings are highly suggestive of serious injury to the globe.13 Hyphema (blood in anterior chamber of eye anterior to pupil) should be suspected if vision is reduced and the pupil cannot be clearly visualized. However, a bright red clot is not always apparent at time of injury or if the amount of blood is small. An irregular pupil, or a pupil that does not constrict well to light, is also a red flag for serious contusion injury to the eye, and requires ophthalmologic evaluation. It is important to keep in mind that blunt trauma severe enough to produce hyphema or an irregular and poorly reactive pupil is often associated with retinal damage as well, including retinal edema or detachment.
Minor injuries (eg, small foreign bodies, minor periocular contusions and lacerations) can often be managed rink-side. Foreign bodies not embedded in the cornea, but lodged under the upper eyelid, can sometimes be removed by everting the eyelid and sweeping with a moistened cotton swab or using diffuse, sterile saline irrigation.11 Corneal abrasions generally cause severe pain, photophobia, and tearing and are easily diagnosed with use of topical fluorescein and a blue light. A topical anesthetic can be extremely helpful in this setting, as it allows for proper pain-free evaluation, but should never be used in an ongoing manner for pain relief. Small lacerations of the brow can be sutured with 5-0 or 6-0 nylon or closed with 2-Octyl cyanoacrylate tissue adhesive (Dermabond). Eyelid lacerations, unless very small, are best managed by an ophthalmologist; care must be taken to rule out injury to the deeper orbital tissues and eye. If serious injury is suspected, or the eye cannot be appropriately evaluated, it should be stabilized and protected with a protective shield or plastic cup, and the player should be transferred to an ED for appropriate ophthalmologic evaluation.13Most eye injuries are accidental, caused by sticks or deflected pucks, but 18% are acquired in fights.8 Use of visors or full-face cages effectively minimizes the rate of eye injuries.8,13,15,16 In a cohort study of 282 elite amateur ice hockey players, the risk of eye injury was 4.7 times higher in players without face protection than in players who used half-face shields; there were no eye injuries in players who used full-face protection.13 For visors to prevent eye injury, they must be positioned to cover the eyes and the lower edge of the nose in all projections.10
Dental Injuries
The incidence and type of facial and dental injuries depend directly on the type of face protection used.11,17,18 In a study of face, head, and neck injuries in elite amateur ice hockey players, Stuart and colleagues13 found game-related injury rates of 158.9 per 1000 player-hours in players without face protection, 73.5 in players who used half-face shields, and 23.2 in players who used full-face shields. Players who wore full-face shields had facial, head, and neck injury rates of only 23.2 per 1000 player-game hours.13 Other studies clearly support the important role face shields play in lowering injury risk in hockey. Face and head injuries account for 20% to 40% of all hockey-related injuries,3,16,19 and dental injuries up to 11.5%.20 In a study from Finland, Lahti and colleagues19 found that over a 2-year period, 479 hockey players sustained injuries, including 650 separate dental injuries. The most commonly diagnosed dental injury was an uncomplicated crown fracture, and the most common cause was a hit with a hockey stick, which accounted for 52.7% and 40.3% of dental injuries in games and practices, respectively.19
In the management of dental fractures, the broken portions of teeth should be found and placed in a transportation-protective medium, such as saline, saliva, or milk,16 which can improve functional and esthetic replacement outcomes.21,22 Loose pieces of teeth should not be left in the player’s mouth. The residual tooth should be stabilized and exposure to air and occlusion limited. Dental fractures can affect the enamel, the enamel and dentin structures (uncomplicated fracture), or enamel, dentin, and pulp (complicated).23 Fractures involving only the enamel do not require urgent dental evaluation. Dentin or pulp involvement may cause temperature and air sensitivity.23 If a tooth is air-sensitive, the player should be referred to a specialist immediately.11
Direct trauma can cause instability without displacement (subluxation) or complete displacement of the tooth from its alveolar socket (avulsion).23 An avulsed tooth should be handled by the crown to avoid further damage to the root and periodontal ligament.16,24 The tooth should be rinsed gently with saline and reimplanted in its socket, ideally within 5 to 10 minutes,23with the athlete biting down gently on gauze to hold the tooth in place. A 1-mL supraperiosteal infiltration of 1% or 2% lidocaine hydrochloride (1:100,000 epinephrine) can be given into the apex of the tooth being anesthetized (Figure 1).
Concussions
A concussion is a “complex pathophysiological process affecting the brain, induced by traumatic biomechanical forces.”25 Concussion is largely a functional disturbance instead of a structural injury, owing to the rotational and/or shearing forces involved. Many studies have identified concussion as the most common type of injury in all of youth hockey.26 Concussions account for up to 19% of all injuries in men’s collegiate hockey.3
Concussion can be challenging to diagnose on the ice. The most important factor in concussion management is symptom reporting by the athlete.27 Despite significant efforts in education and awareness, student athletes, especially hockey players, withhold reporting a possible concussion.28 Reasons for underreporting include fear of letting down other players and coaches, thinking the injury is not severe enough to warrant evaluation, and fear of losing standing with the current team or future teams.28
As postinjury concussion assessments are ideal when comparisons can be made with preseason (baseline) scores, preseason testing is becoming standard in professional, college, junior, and high school hockey. This testing involves the Sport Concussion Assessment Tool, 3rd edition (SCAT3), and the King-Devick (K-D) test.30,31 Some youth leagues have baseline testing as well, though the frequency of baseline testing in their players is controversial,32 as the adolescent mind’s processing speed and memory increase exponentially.33 For these younger athletes, it may be necessary to perform baseline testing more frequently than annually.32 A physician can use baseline test results to help diagnose a concussion at the rink and then track the athlete’s recovery and help with return-to-play decisions.29 Vision involves almost half of the brain’s circuits,34 including areas vulnerable to head impact. A neuro-ophthalmologic test can assess for irregularities in accommodation, convergence, ocular muscle balance, pursuit, and saccades.29 The K-D test is a visual performance examination that allows easy and objective assessment of eye movements. Use of both the K-D test and the SCAT3 at the rink may increase the number of concussions detected.29,35 We recommend that physicians use both tests to assess for concussion at the hockey rink.
Initial treatment involves a period of physical rest and relative cognitive rest. Acute worsening of symptoms warrants urgent imaging to rule out a subdural or subarachnoid bleed. Once a player is symptom-free, a graded return-to-play protocol should be followed (Table 4).
On the prevention side, great efforts have been made to improve hockey helmets. (Some manufacturers claim to have made concussion-proof helmets, but there is no evidence supporting this claim.6) Numerous investigators have reported a lower overall injury rate in players who wear a helmet and a full-face shield.6,13 In addition, rule changes aimed at decreasing head contact have been implemented to decrease the incidence of sport-related concussions.36 Moreover, education on proper helmet use and wear should be emphasized. A study of the effects of hockey helmet fit on cervical motion found that 7 (39%) of 18 players wore a game or competition helmet so loosely that it could be removed without unbuttoning its chinstrap.37 Improperly worn helmets cannot prevent injury as well as properly worn helmets can.
Cervical Spine Injuries
Whereas American football is associated with a higher annual number of nonfatal catastrophic neck injuries, hockey has a 3 to 6 times higher incidence of cervical spine injuries and spinal cord damage.38,39 A Canadian Ice Hockey Spinal Injuries Registry review of the period 2006 to 2011 identified 44 cervical spine injuries, 7.3 per year on average.40 Severe injury, defined as complete motor and sensory loss, complete motor loss and incomplete sensory, or complete motor loss, occurred in 4 (9.1%) of the 44 injured players. In hockey, a major mechanism of cervical spine injury is an axial load to the slightly flexed spine.39 Of 355 hockey-related cervical spine injuries in a Canada study, 95 (35.5%) were caused by a check from behind.40,41 The Canadian neurosurgeons’ work led to rule changes prohibiting checks from behind, and this prohibition has reduced the incidence of cervical spine injuries in ice hockey.38,40
Team physicians should be comfortable managing serious neck and spine injuries on the ice. Initial evaluation should follow the standard ABCs (airway, breathing, circulation). The physician places a hand on each side of the head to stabilize the neck until the initial examination is complete. The goal is to minimize cervical spine motion until transportation to the hospital for advanced imaging and definitive treatment.37 The decision to remove or leave on the helmet is now controversial. Hockey helmets differ from football helmets in that their chinstraps do not afford significant cervical stabilization, and the helmets have less padding and cover less of the head; in addition, a shockingly high percentage of hockey players do not wear properly fitting helmets.37 In one study, 3-dimensional motion analysis of a hockey player during the logroll technique showed less transverse and sagittal cervical plane motion with the helmet removed than with the helmet (properly fitting or not) in place; the authors recommended removing the helmet to limit extraneous cervical spine motion during the technique.37 However, 2 other studies found that helmet removal can result in significantly increased cervical spine motion of the immobilized hockey player.42,43Recommendation 4 of the recently released interassociation consensus statement of the National Athletic Trainers’ Association reads, “Protective athletic equipment should be removed before transport to an emergency facility for an athlete-patient with suspected cervical spine instability.”44 This represents a shift from leaving the helmet and shoulder pads in place. For ice hockey players with suspected cervical spine injury, more research is needed on cervical motion during the entire sequence—partial logrolls, spine-boarding, placement of cervical collar before or after logroll, and different immobilization techniques for transport.37
The athlete must be carefully transferred to a spine board with either logroll or lift-and-slide. Although an extrication cervical collar can be placed before the spine board is placed, the effectiveness of this collar in executing the spine-board transfer is not proven.45 When the player is on the spine board, the head can be secured with pads and straps en route to the hospital.
Return-to-Play Criteria for Cervical Spine Injuries There is no clear consensus on return-to-play guidelines for cervical spine injuries in athletes.46
Shoulder Injuries
For hockey players, the upper extremity traditionally has been considered a well-protected area.48 However, shoulder pads are considerably more flexible in hockey than in football and other collision sports. In addition, hockey gloves allow a fair amount of motion for stick handling, and the wrist may be in maximal flexion or extension when a hit against the boards or the ice occurs. Open-ice checking, board collisions, and hockey stick use have been postulated as reasons for the high incidence of upper extremity injuries in hockey. Researchers in Finland found that upper extremity injuries accounted for up to 31% of all hockey injuries.49 More than 50% of these injuries resulted from checking or board collisions. Furthermore, study findings highlighted a low rate of injury in younger players and indicated the rate increases with age.49,50
In hockey players, the acromioclavicular (AC) joint is the most commonly injured shoulder structure.51 The mechanism of injury can be a board collision or an open-ice hit, but most often is a direct blow to the shoulder. The collision disrupts the AC joint and can sprain or tear the coracoclavicular ligaments. The Rockwood classification is used to categorize AC joint injuries (Figure 2).
Initial management involves icing the AC joint and placing a sling for comfort. Type I and type II injuries can be managed with progressive range-of-motion (ROM) exercises, strengthening, cryotherapy, and a period of rest. Treatment of type III injuries remains controversial,52 but in hockey players these injuries are almost always treated nonoperatively. Return to play requires full motion, normal strength, and minimal discomfort. Players return a few days to 2 weeks after a grade I injury; recovery from grade II injuries may take 2 to 3 weeks, and recovery from grade III injuries, 6 to 12 weeks. Surgical treatment is usually required in type IV and type V injuries, but we have had experience treating these injuries nonoperatively in high-level players. AC joint reinjury in hockey players is common, and surgical treatment should be approached cautiously, as delayed fracture after return to sport has been reported.53 Special precautions should be taken in collision athletes who undergo AC joint reconstruction. In the anatomical reconstruction described by Carofino and Mazzocca,54 2 holes are drilled in the clavicle; these holes are a potential source of fracture when the collision athlete returns to sport (Figure 3).
Clavicle fracture is another common hockey injury.55 Studies have shown clavicle fractures proportionally occur most often in people 15 to 19 years old.49 The injury presents with pain and deformity over the clavicle; in more severe fractures, skin tenting is identified. Initial management of suspected clavicle fracture includes cryotherapy, sling, and radiographs. Radiographs should include an AP view and then a 45° cephalad view, which eliminates overshadowing from the ribs. Most clavicle fractures are successfully managed nonoperatively, though there is evidence that significantly displaced or comminuted fractures have better union rates and shoulder function when treated with open reduction and internal fixation.56 After a clavicle fracture, return to skating and noncontact practice usually takes 8 weeks, with return to full contact occurring around 12 weeks.
Sternoclavicular injuries are relatively uncommon, but potentially serious. Special attention should also be given to adolescent athletes with sternoclavicular pain. Although sternoclavicular dislocations have been reported in hockey players, instead these likely are fractures involving the medial clavicle physis.57
The shoulder is the most commonly dislocated major joint, and the incidence of shoulder dislocation in elite hockey players is 8% to 21%.50,58 Anterior shoulder instability occurs from a fall with the shoulder in an abducted, externally rotated and extended position or from a direct anteriorly placed impact to the posterior shoulder. We recommend taking players off the ice for evaluation. Depending on physician comfort, the shoulder can be reduced in the training room, and the athlete sent for radiographs after reduction. If resources or support for closed reduction is not available at the rink, the athlete should be sent to the ED. Initial radiographic evaluation of a player with shoulder injury begins with plain radiographs, including a true AP (Grashey) view with the humerus in neutral, internal, and external rotation and an axillary view. The axillary radiograph is crucial in determining anterior or posterior dislocation. If the patient cannot tolerate the pain associated with having an axillary radiograph taken, a Velpeau radiograph can be used. This radiograph is taken with the patient’s arm in a sling and with the patient leaning back 30° while the x-ray beam is directed superior to inferior.
CT is performed for a suspected osseous injury. CT is more accurate than plain radiographs in showing glenoid and humeral fractures in the acute setting as well as the amount of bone loss in the case of chronic instability. Magnetic resonance arthrography is the imaging modality of choice for the diagnoses of capsulolabral injury.
After shoulder reduction, treatment with a sling, cryotherapy, and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug is initiated. In a Minnesota study of nonoperative management of shoulder instability, 9 of 10 hockey players were able to return to play the same season, and 6 of the 10 required surgery at the end of the season.59
Compared with noncontact athletes, hockey players and other collision athletes are at increased risk for recurrence.60-62 For collision athletes who want to continue playing their sport after recurrent instability, surgery is recommended. A shoulder instability study in Toronto found that more than 54% of 24 professional hockey players had associated Hill-Sachs lesions, but only 3 shoulders (12.5%) had glenoid defects.50 Arthroscopic and open techniques both demonstrate good results, and identification of bone loss can help determine which surgery to recommend.63 Hockey players can usually return to sport 6 months after shoulder stabilization.
Another important consideration in managing shoulder instability in hockey players is shoulder dominance, which determines stick grip. A left-handed player places the right hand on top of the stick for support, but most of the motion associated with shooting the puck—including abduction and external rotation—occurs with the left shoulder. Thus, a left-handed player with a history of previous left-side shoulder dislocation may dislocate with each shot, but a right-handed player with left shoulder instability may have considerably less trouble on the ice.58Shoulder and rotator cuff contusions (RCCs) occur in hockey and other collision sports.49,64 RCCs almost always result from a direct blow to the shoulder, and present with shoulder function loss, weakness, and pain.
Summary
Hockey is a high-speed collision sport with one of the highest injury rates among all sports. Physicians caring for youth, amateur, and senior hockey teams see a range of acute head, neck, and shoulder injuries. Although treatment of eye injuries, dental injuries, and concussions is not always considered orthopedic care, an orthopedic surgeon who is covering hockey needs to be comfortable managing these injuries acutely. Quality rink-side care minimizes the impact of the injury, maximizes the functional result, and expedites the safe return of the injured player back to the ice.
Am J Orthop. 2017;46(3):123-134. Copyright Frontline Medical Communications Inc. 2017. All rights reserved.
1. Vaughan G. The Puck Starts Here: The Origin of Canada’s Great Winter Game, Ice Hockey. Fredericton, Canada: Goose Lane Editions; 1996.
2. IIHF member national associations. International Ice Hockey Federation website. http://www.iihf.com/iihf-home/the-iihf/members. Accessed April 6, 2017.
3. Flik K, Lyman S, Marx RG. American collegiate men’s ice hockey: an analysis of injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(2):183-187.
4. Engebretsen L, Steffen K, Alonso JM, et al. Sports injuries and illnesses during the Winter Olympic Games 2010. Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(11):772-780.
5. Deits J, Yard EE, Collins CL, Fields SK, Comstock RD. Patients with ice hockey injuries presenting to US emergency departments, 1990-2006. J Athl Train. 2010;45(5):467-474.
6. Brooks A, Loud KJ, Brenner JS, et al. Reducing injury risk from body checking in boys’ youth ice hockey. Pediatrics. 2014;133(6):1151-1157.
7. Agel J, Harvey EJ. A 7-year review of men’s and women’s ice hockey injuries in the NCAA. Can J Surg. 2010;53(5):319-323.
8. Micieli JA, Zurakowski D, Ahmed, II. Impact of visors on eye and orbital injuries in the National Hockey League. Can J Ophthalmol. 2014;49(3):243-248.
9. Pashby TJ. Ocular injuries in hockey. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1988;28(3):228-231.
10. Leivo T, Haavisto AK, Sahraravand A. Sports-related eye injuries: the current picture. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015;93(3):224-231.
11. Cohn RM, Alaia MJ, Strauss EJ, Feldman AF. Rink-side management of ice hockey related injuries to the face, neck, and chest. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2013;71(4):253-256.
12. Reehal P. Facial injury in sport. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010;9(1):27-34.
13. Stuart MJ, Smith AM, Malo-Ortiguera SA, Fischer TL, Larson DR. A comparison of facial protection and the incidence of head, neck, and facial injuries in Junior A hockey players. A function of individual playing time. Am J Sports Med. 2002;30(1):39-44.
14. MacEwen CJ, McLatchie GR. Eye injuries in sport. Scott Med J. 2010;55(2):22-24.
15. Stevens ST, Lassonde M, de Beaumont L, Keenan JP. The effect of visors on head and facial injury in National Hockey League players. J Sci Med Sport. 2006;9(3):238-242.
16. Moslener MD, Wadsworth LT. Ice hockey: a team physician’s perspective. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010;9(3):134-138.
17. LaPrade RF, Burnett QM, Zarzour R, Moss R. The effect of the mandatory use of face masks on facial lacerations and head and neck injuries in ice hockey. A prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(6):773-775.
18. Benson BW, Mohtadi NG, Rose MS, Meeuwisse WH. Head and neck injuries among ice hockey players wearing full face shields vs half face shields. JAMA. 1999;282(24):2328-2332.
19. Lahti H, Sane J, Ylipaavalniemi P. Dental injuries in ice hockey games and training. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002;34(3):400-402.
20. Sane J, Ylipaavalniemi P, Leppanen H. Maxillofacial and dental ice hockey injuries. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1988;20(2):202-207.
21. Emerich K, Kaczmarek J. First aid for dental trauma caused by sports activities: state of knowledge, treatment and prevention. Sports Med. 2010;40(5):361-366.
22. Rosenberg H, Rosenberg H, Hickey M. Emergency management of a traumatic tooth avulsion. Ann Emerg Med. 2011;57(4):375-377.
23. Young EJ, Macias CR, Stephens L. Common dental injury management in athletes. Sports Health. 2015;7(3):250-255.
24. Andersson L, Andreasen JO, Day P, et al. International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth. Dent Traumatol. 2012;28(2):88-96.
25. McCrory P, Meeuwisse W, Johnston K, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport 3rd International Conference on Concussion in Sport held in Zurich, November 2008. Clin J Sport Med. 2009;19(3):185-200.
26. Schneider KJ, Meeuwisse WH, Kang J, Schneider GM, Emery CA. Preseason reports of neck pain, dizziness, and headache as risk factors for concussion in male youth ice hockey players. Clin J Sport Med. 2013;23(4):267-272.
27. McCrory P, Meeuwisse WH, Aubry M, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport: the 4th International Conference on Concussion in Sport held in Zurich, November 2012. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):250-258.
28. Delaney JS, Lamfookon C, Bloom GA, Al-Kashmiri A, Correa JA. Why university athletes choose not to reveal their concussion symptoms during a practice or game. Clin J Sport Med. 2015;25(2):113-125.
29. Ventura RE, Balcer LJ, Galetta SL. The concussion toolbox: the role of vision in the assessment of concussion. Semin Neurol. 2015;35(5):599-606.
30. Vartiainen MV, Holm A, Peltonen K, Luoto TM, Iverson GL, Hokkanen L. King-Devick test normative reference values for professional male ice hockey players. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25(3):e327-e330.
31. Galetta MS, Galetta KM, McCrossin J, et al. Saccades and memory: baseline associations of the King-Devick and SCAT2 SAC tests in professional ice hockey players. J Neurol Sci. 2013;328(1-2):28-31.
32. Vernau BT, Grady MF, Goodman A, et al. Oculomotor and neurocognitive assessment of youth ice hockey players: baseline associations and observations after concussion. Dev Neuropsychol. 2015;40(1):7-11.
33. Fry AF, Hale S. Relationships among processing speed, working memory, and fluid intelligence in children. Biol Psychol. 2000;54(1-3):1-34.
34. Felleman DJ, Van Essen DC. Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 1991;1(1):1-47.
35. Guskiewicz KM, Register-Mihalik J, McCrory P, et al. Evidence-based approach to revising the SCAT2: introducing the SCAT3. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):289-293.
36. Smith AM, Stuart MJ, Dodick DW, et al. Ice Hockey Summit II: zero tolerance for head hits and fighting. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2015;14(2):135-144.
37. Mihalik JP, Beard JR, Petschauer MA, Prentice WE, Guskiewicz KM. Effect of ice hockey helmet fit on cervical spine motion during an emergency log roll procedure. Clin J Sport Med. 2008;18(5):394-398.
38. Banerjee R, Palumbo MA, Fadale PD. Catastrophic cervical spine injuries in the collision sport athlete, part 1: epidemiology, functional anatomy, and diagnosis. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(4):1077-1087.
39. Reynen PD, Clancy WG Jr. Cervical spine injury, hockey helmets, and face masks. Am J Sports Med. 1994;22(2):167-170.
40. Tator CH, Provvidenza C, Cassidy JD. Update and overview of spinal injuries in Canadian ice hockey, 1943 to 2011: the continuing need for injury prevention and education. Clin J Sport Med. 2016;26(3):232-238.
41. Tator CH, Edmonds VE, Lapczak L, Tator IB. Spinal injuries in ice hockey players, 1966-1987. Can J Surg. 1991;34(1):63-69.
42. Laprade RF, Schnetzler KA, Broxterman RJ, Wentorf F, Gilbert TJ. Cervical spine alignment in the immobilized ice hockey player. A computed tomographic analysis of the effects of helmet removal. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28(6):800-803.
43. Metz CM, Kuhn JE, Greenfield ML. Cervical spine alignment in immobilized hockey players: radiographic analysis with and without helmets and shoulder pads. Clin J Sport Med. 1998;8(2):92-95.
44. National Athletic Trainers’ Association. Appropriate prehospital management of the spine-injured athlete: updated from 1998 document. http://www.nata.org/sites/default/files/Executive-Summary-Spine-Injury-updated.pdf. Updated August 5, 2015. Accessed April 6, 2017.
45. Del Rossi G, Heffernan TP, Horodyski M, Rechtine GR. The effectiveness of extrication collars tested during the execution of spine-board transfer techniques. Spine J. 2004;4(6):619-623.
46. Morganti C, Sweeney CA, Albanese SA, Burak C, Hosea T, Connolly PJ. Return to play after cervical spine injury. Spine. 2001;26(10):1131-1136.
47. Huang P, Anissipour A, McGee W, Lemak L. Return-to-play recommendations after cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine injuries: a comprehensive review. Sports Health. 2016;8(1):19-25.
48. Shindle MK, Marx RG, Kelly BT, Bisson L, Burke CJ 3rd. Hockey injuries: a pediatric sport update. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010;22(1):54-60.
49. Molsa J, Kujala U, Myllynen P, Torstila I, Airaksinen O. Injuries to the upper extremity in ice hockey: analysis of a series of 760 injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31(5):751-757.
50. Dwyer T, Petrera M, Bleakney R, Theodoropoulos JS. Shoulder instability in ice hockey players: incidence, mechanism, and MRI findings. Clin Sports Med. 2013;32(4):803-813.
51. LaPrade RF, Wijdicks CA, Griffith CJ. Division I intercollegiate ice hockey team coverage. Br J Sports Med. 2009;43(13):1000-1005.
52. Willimon SC, Gaskill TR, Millett PJ. Acromioclavicular joint injuries: anatomy, diagnosis, and treatment. Phys Sportsmed. 2011;39(1):116-122.
53. Martetschlager F, Horan MP, Warth RJ, Millett PJ. Complications after anatomic fixation and reconstruction of the coracoclavicular ligaments. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(12):2896-2903.
54. Carofino BC, Mazzocca AD. The anatomic coracoclavicular ligament reconstruction: surgical technique and indications. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(2 suppl):37-46.
55. Laprade RF, Surowiec RK, Sochanska AN, et al. Epidemiology, identification, treatment and return to play of musculoskeletal-based ice hockey injuries. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(1):4-10.
56. Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(1):1-10.
57. Lee JT, Nasreddine AY, Black EM, Bae DS, Kocher MS. Posterior sternoclavicular joint injuries in skeletally immature patients. J Pediatr Orthop. 2014;34(4):369-375.
58. Hovelius L. Shoulder dislocation in Swedish ice hockey players. Am J Sports Med. 1978;6(6):373-377.
59. Buss DD, Lynch GP, Meyer CP, Huber SM, Freehill MQ. Nonoperative management for in-season athletes with anterior shoulder instability. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(6):1430-1433.
60. Mazzocca AD, Brown FM Jr, Carreira DS, Hayden J, Romeo AA. Arthroscopic anterior shoulder stabilization of collision and contact athletes. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(1):52-60.
61. Harris JD, Romeo AA. Arthroscopic management of the contact athlete with instability. Clin Sports Med. 2013;32(4):709-730.
62. Cho NS, Hwang JC, Rhee YG. Arthroscopic stabilization in anterior shoulder instability: collision athletes versus noncollision athletes. Arthroscopy. 2006;22(9):947-953.
63. Griffin JW, Brockmeier SF. Shoulder instability with concomitant bone loss in the athlete. Orthop Clin North Am. 2015;46(1):89-103.
64. Cohen SB, Towers JD, Bradley JP. Rotator cuff contusions of the shoulder in professional football players: epidemiology and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(3):442-447.
65. Lorentzon R, Wedrèn H, Pietilä T. Incidence, nature, and causes of ice hockey injuries. A three-year prospective study of a Swedish elite ice hockey team. Am J Sports Med. 1988;16(4):392-396.
66. Stuart MJ, Smith A. Injuries in Junior A ice hockey. A three-year prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(4):458-461.
67. Voaklander DC, Saunders LD, Quinney HA, Macnab RB. Epidemiology of recreational and old-timer ice hockey injuries. Clin J Sport Med. 1996;6(1):15-21.
68. Mölsä J, Airaksinen O, Näsman O, Torstila I. Ice hockey injuries in Finland. A prospective epidemiologic study. Am J Sports Med. 1997;25(4):495-499.
69. Ferrara MS, Schurr KT. Intercollegiate ice hockey injuries: a casual analysis. Clin J Sport Med. 1999;9(1):30-33.
70. Pinto M, Kuhn JE, Greenfield ML, Hawkins RJ. Prospective analysis of ice hockey injuries at the Junior A level over the course of one season. Clin J Sport Med. 1999;9(2):70-74.
71. Emery CA, Meeuwisse WH. Injury rates, risk factors, and mechanisms of injury in minor hockey. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(12):1960-1969.
72. Kuzuhara K, Shimamoto H, Mase Y. Ice hockey injuries in a Japanese elite team: a 3-year prospective study. J Athl Train. 2009;44(2):208-214.
73. Rishiraj N, Lloyd-Smith R, Lorenz T, Niven B, Michel M. University men’s ice hockey: rates and risk of injuries over 6-years. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2009;49(2):159-166.
74. Tuominen M, Stuart MJ, Aubry M, Kannus P, Parkkari J. Injuries in men’s international ice hockey: a 7-year study of the International Ice Hockey Federation Adult World Championship Tournaments and Olympic Winter Games. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(1):30-36.
75. Heckman JD, Bucholz RW. In: Rockwood CA, Green DP, Heckman JD, Bucholz RW, eds. Rockwood and Green’s Fractures in Adults, Volume 1. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001.
1. Vaughan G. The Puck Starts Here: The Origin of Canada’s Great Winter Game, Ice Hockey. Fredericton, Canada: Goose Lane Editions; 1996.
2. IIHF member national associations. International Ice Hockey Federation website. http://www.iihf.com/iihf-home/the-iihf/members. Accessed April 6, 2017.
3. Flik K, Lyman S, Marx RG. American collegiate men’s ice hockey: an analysis of injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(2):183-187.
4. Engebretsen L, Steffen K, Alonso JM, et al. Sports injuries and illnesses during the Winter Olympic Games 2010. Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(11):772-780.
5. Deits J, Yard EE, Collins CL, Fields SK, Comstock RD. Patients with ice hockey injuries presenting to US emergency departments, 1990-2006. J Athl Train. 2010;45(5):467-474.
6. Brooks A, Loud KJ, Brenner JS, et al. Reducing injury risk from body checking in boys’ youth ice hockey. Pediatrics. 2014;133(6):1151-1157.
7. Agel J, Harvey EJ. A 7-year review of men’s and women’s ice hockey injuries in the NCAA. Can J Surg. 2010;53(5):319-323.
8. Micieli JA, Zurakowski D, Ahmed, II. Impact of visors on eye and orbital injuries in the National Hockey League. Can J Ophthalmol. 2014;49(3):243-248.
9. Pashby TJ. Ocular injuries in hockey. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1988;28(3):228-231.
10. Leivo T, Haavisto AK, Sahraravand A. Sports-related eye injuries: the current picture. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015;93(3):224-231.
11. Cohn RM, Alaia MJ, Strauss EJ, Feldman AF. Rink-side management of ice hockey related injuries to the face, neck, and chest. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2013;71(4):253-256.
12. Reehal P. Facial injury in sport. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010;9(1):27-34.
13. Stuart MJ, Smith AM, Malo-Ortiguera SA, Fischer TL, Larson DR. A comparison of facial protection and the incidence of head, neck, and facial injuries in Junior A hockey players. A function of individual playing time. Am J Sports Med. 2002;30(1):39-44.
14. MacEwen CJ, McLatchie GR. Eye injuries in sport. Scott Med J. 2010;55(2):22-24.
15. Stevens ST, Lassonde M, de Beaumont L, Keenan JP. The effect of visors on head and facial injury in National Hockey League players. J Sci Med Sport. 2006;9(3):238-242.
16. Moslener MD, Wadsworth LT. Ice hockey: a team physician’s perspective. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010;9(3):134-138.
17. LaPrade RF, Burnett QM, Zarzour R, Moss R. The effect of the mandatory use of face masks on facial lacerations and head and neck injuries in ice hockey. A prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(6):773-775.
18. Benson BW, Mohtadi NG, Rose MS, Meeuwisse WH. Head and neck injuries among ice hockey players wearing full face shields vs half face shields. JAMA. 1999;282(24):2328-2332.
19. Lahti H, Sane J, Ylipaavalniemi P. Dental injuries in ice hockey games and training. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002;34(3):400-402.
20. Sane J, Ylipaavalniemi P, Leppanen H. Maxillofacial and dental ice hockey injuries. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1988;20(2):202-207.
21. Emerich K, Kaczmarek J. First aid for dental trauma caused by sports activities: state of knowledge, treatment and prevention. Sports Med. 2010;40(5):361-366.
22. Rosenberg H, Rosenberg H, Hickey M. Emergency management of a traumatic tooth avulsion. Ann Emerg Med. 2011;57(4):375-377.
23. Young EJ, Macias CR, Stephens L. Common dental injury management in athletes. Sports Health. 2015;7(3):250-255.
24. Andersson L, Andreasen JO, Day P, et al. International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth. Dent Traumatol. 2012;28(2):88-96.
25. McCrory P, Meeuwisse W, Johnston K, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport 3rd International Conference on Concussion in Sport held in Zurich, November 2008. Clin J Sport Med. 2009;19(3):185-200.
26. Schneider KJ, Meeuwisse WH, Kang J, Schneider GM, Emery CA. Preseason reports of neck pain, dizziness, and headache as risk factors for concussion in male youth ice hockey players. Clin J Sport Med. 2013;23(4):267-272.
27. McCrory P, Meeuwisse WH, Aubry M, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport: the 4th International Conference on Concussion in Sport held in Zurich, November 2012. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):250-258.
28. Delaney JS, Lamfookon C, Bloom GA, Al-Kashmiri A, Correa JA. Why university athletes choose not to reveal their concussion symptoms during a practice or game. Clin J Sport Med. 2015;25(2):113-125.
29. Ventura RE, Balcer LJ, Galetta SL. The concussion toolbox: the role of vision in the assessment of concussion. Semin Neurol. 2015;35(5):599-606.
30. Vartiainen MV, Holm A, Peltonen K, Luoto TM, Iverson GL, Hokkanen L. King-Devick test normative reference values for professional male ice hockey players. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25(3):e327-e330.
31. Galetta MS, Galetta KM, McCrossin J, et al. Saccades and memory: baseline associations of the King-Devick and SCAT2 SAC tests in professional ice hockey players. J Neurol Sci. 2013;328(1-2):28-31.
32. Vernau BT, Grady MF, Goodman A, et al. Oculomotor and neurocognitive assessment of youth ice hockey players: baseline associations and observations after concussion. Dev Neuropsychol. 2015;40(1):7-11.
33. Fry AF, Hale S. Relationships among processing speed, working memory, and fluid intelligence in children. Biol Psychol. 2000;54(1-3):1-34.
34. Felleman DJ, Van Essen DC. Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 1991;1(1):1-47.
35. Guskiewicz KM, Register-Mihalik J, McCrory P, et al. Evidence-based approach to revising the SCAT2: introducing the SCAT3. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(5):289-293.
36. Smith AM, Stuart MJ, Dodick DW, et al. Ice Hockey Summit II: zero tolerance for head hits and fighting. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2015;14(2):135-144.
37. Mihalik JP, Beard JR, Petschauer MA, Prentice WE, Guskiewicz KM. Effect of ice hockey helmet fit on cervical spine motion during an emergency log roll procedure. Clin J Sport Med. 2008;18(5):394-398.
38. Banerjee R, Palumbo MA, Fadale PD. Catastrophic cervical spine injuries in the collision sport athlete, part 1: epidemiology, functional anatomy, and diagnosis. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(4):1077-1087.
39. Reynen PD, Clancy WG Jr. Cervical spine injury, hockey helmets, and face masks. Am J Sports Med. 1994;22(2):167-170.
40. Tator CH, Provvidenza C, Cassidy JD. Update and overview of spinal injuries in Canadian ice hockey, 1943 to 2011: the continuing need for injury prevention and education. Clin J Sport Med. 2016;26(3):232-238.
41. Tator CH, Edmonds VE, Lapczak L, Tator IB. Spinal injuries in ice hockey players, 1966-1987. Can J Surg. 1991;34(1):63-69.
42. Laprade RF, Schnetzler KA, Broxterman RJ, Wentorf F, Gilbert TJ. Cervical spine alignment in the immobilized ice hockey player. A computed tomographic analysis of the effects of helmet removal. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28(6):800-803.
43. Metz CM, Kuhn JE, Greenfield ML. Cervical spine alignment in immobilized hockey players: radiographic analysis with and without helmets and shoulder pads. Clin J Sport Med. 1998;8(2):92-95.
44. National Athletic Trainers’ Association. Appropriate prehospital management of the spine-injured athlete: updated from 1998 document. http://www.nata.org/sites/default/files/Executive-Summary-Spine-Injury-updated.pdf. Updated August 5, 2015. Accessed April 6, 2017.
45. Del Rossi G, Heffernan TP, Horodyski M, Rechtine GR. The effectiveness of extrication collars tested during the execution of spine-board transfer techniques. Spine J. 2004;4(6):619-623.
46. Morganti C, Sweeney CA, Albanese SA, Burak C, Hosea T, Connolly PJ. Return to play after cervical spine injury. Spine. 2001;26(10):1131-1136.
47. Huang P, Anissipour A, McGee W, Lemak L. Return-to-play recommendations after cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine injuries: a comprehensive review. Sports Health. 2016;8(1):19-25.
48. Shindle MK, Marx RG, Kelly BT, Bisson L, Burke CJ 3rd. Hockey injuries: a pediatric sport update. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010;22(1):54-60.
49. Molsa J, Kujala U, Myllynen P, Torstila I, Airaksinen O. Injuries to the upper extremity in ice hockey: analysis of a series of 760 injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31(5):751-757.
50. Dwyer T, Petrera M, Bleakney R, Theodoropoulos JS. Shoulder instability in ice hockey players: incidence, mechanism, and MRI findings. Clin Sports Med. 2013;32(4):803-813.
51. LaPrade RF, Wijdicks CA, Griffith CJ. Division I intercollegiate ice hockey team coverage. Br J Sports Med. 2009;43(13):1000-1005.
52. Willimon SC, Gaskill TR, Millett PJ. Acromioclavicular joint injuries: anatomy, diagnosis, and treatment. Phys Sportsmed. 2011;39(1):116-122.
53. Martetschlager F, Horan MP, Warth RJ, Millett PJ. Complications after anatomic fixation and reconstruction of the coracoclavicular ligaments. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(12):2896-2903.
54. Carofino BC, Mazzocca AD. The anatomic coracoclavicular ligament reconstruction: surgical technique and indications. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(2 suppl):37-46.
55. Laprade RF, Surowiec RK, Sochanska AN, et al. Epidemiology, identification, treatment and return to play of musculoskeletal-based ice hockey injuries. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(1):4-10.
56. Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(1):1-10.
57. Lee JT, Nasreddine AY, Black EM, Bae DS, Kocher MS. Posterior sternoclavicular joint injuries in skeletally immature patients. J Pediatr Orthop. 2014;34(4):369-375.
58. Hovelius L. Shoulder dislocation in Swedish ice hockey players. Am J Sports Med. 1978;6(6):373-377.
59. Buss DD, Lynch GP, Meyer CP, Huber SM, Freehill MQ. Nonoperative management for in-season athletes with anterior shoulder instability. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(6):1430-1433.
60. Mazzocca AD, Brown FM Jr, Carreira DS, Hayden J, Romeo AA. Arthroscopic anterior shoulder stabilization of collision and contact athletes. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(1):52-60.
61. Harris JD, Romeo AA. Arthroscopic management of the contact athlete with instability. Clin Sports Med. 2013;32(4):709-730.
62. Cho NS, Hwang JC, Rhee YG. Arthroscopic stabilization in anterior shoulder instability: collision athletes versus noncollision athletes. Arthroscopy. 2006;22(9):947-953.
63. Griffin JW, Brockmeier SF. Shoulder instability with concomitant bone loss in the athlete. Orthop Clin North Am. 2015;46(1):89-103.
64. Cohen SB, Towers JD, Bradley JP. Rotator cuff contusions of the shoulder in professional football players: epidemiology and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(3):442-447.
65. Lorentzon R, Wedrèn H, Pietilä T. Incidence, nature, and causes of ice hockey injuries. A three-year prospective study of a Swedish elite ice hockey team. Am J Sports Med. 1988;16(4):392-396.
66. Stuart MJ, Smith A. Injuries in Junior A ice hockey. A three-year prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(4):458-461.
67. Voaklander DC, Saunders LD, Quinney HA, Macnab RB. Epidemiology of recreational and old-timer ice hockey injuries. Clin J Sport Med. 1996;6(1):15-21.
68. Mölsä J, Airaksinen O, Näsman O, Torstila I. Ice hockey injuries in Finland. A prospective epidemiologic study. Am J Sports Med. 1997;25(4):495-499.
69. Ferrara MS, Schurr KT. Intercollegiate ice hockey injuries: a casual analysis. Clin J Sport Med. 1999;9(1):30-33.
70. Pinto M, Kuhn JE, Greenfield ML, Hawkins RJ. Prospective analysis of ice hockey injuries at the Junior A level over the course of one season. Clin J Sport Med. 1999;9(2):70-74.
71. Emery CA, Meeuwisse WH. Injury rates, risk factors, and mechanisms of injury in minor hockey. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(12):1960-1969.
72. Kuzuhara K, Shimamoto H, Mase Y. Ice hockey injuries in a Japanese elite team: a 3-year prospective study. J Athl Train. 2009;44(2):208-214.
73. Rishiraj N, Lloyd-Smith R, Lorenz T, Niven B, Michel M. University men’s ice hockey: rates and risk of injuries over 6-years. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2009;49(2):159-166.
74. Tuominen M, Stuart MJ, Aubry M, Kannus P, Parkkari J. Injuries in men’s international ice hockey: a 7-year study of the International Ice Hockey Federation Adult World Championship Tournaments and Olympic Winter Games. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(1):30-36.
75. Heckman JD, Bucholz RW. In: Rockwood CA, Green DP, Heckman JD, Bucholz RW, eds. Rockwood and Green’s Fractures in Adults, Volume 1. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001.