User login
Men who have sex with men (MSM) were younger at HIV diagnosis in 2016 than in 2008, but those living with the disease were older, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.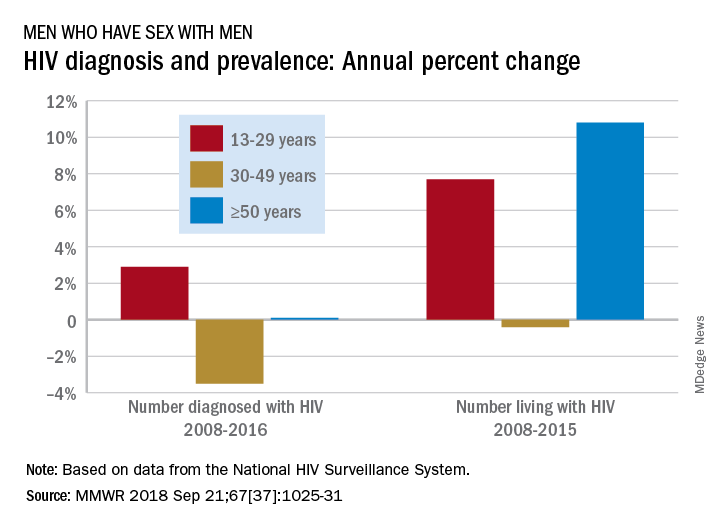
Among MSM aged 13-29 years, the number diagnosed with HIV increased by 2.9% per year from 2008 to 2016 but dropped 3.5% per year for those aged 30-49 and rose just 0.1% annually among those aged 50 and older. Over the period from 2008 to 2015, the number of MSM aged 50 and older who were living with HIV increased by 10.8% per year, compared with an annual percent change of 7.7% for those aged 13-29 and –0.4% for those aged 30-49, Andrew Mitsch, MPH, and his associates at the CDC’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention reported in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The size of the population of MSM living with HIV went from 384,000 in 2008 to 523,000 in 2016, with 13- to 29-year-olds going from 10.7% of the population to 13.3%, 30- to 49-year-olds dropping from 61% to 44%, and the 50-and-older group increasing from 28.3% to 42.7%, they said.
“The increase in annual diagnosis of HIV infections among younger MSM might reflect increased HIV testing, in addition to ongoing transmission,” they suggested, and increased prevalence among older men is probably the “result of increased survival associated with widespread use of antiretroviral therapy, surviving middle age, and advancing to the older group.”
The investigators also noted the persistence of racial/ethnic disparities over the course of the study. Among the three largest groups, whites had the smallest increase in new diagnoses for 13- to 29-year-olds and the largest decrease for 30- to 49-year-olds, and they were second to blacks in the less-than-or-equal-to-50-years-of-age group, according to data from the National HIV Surveillance System.
“Promotion of care and treatment by public health agencies and private sector partners to achieve viral suppression among MSM with diagnosed HIV infection will improve health outcomes and reduce transmission to others, particularly if prevention efforts are tailored to specific age groups,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE: Mitsch A et al. MMWR 2018 Sep 21;67(37):1025-31.
Men who have sex with men (MSM) were younger at HIV diagnosis in 2016 than in 2008, but those living with the disease were older, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Among MSM aged 13-29 years, the number diagnosed with HIV increased by 2.9% per year from 2008 to 2016 but dropped 3.5% per year for those aged 30-49 and rose just 0.1% annually among those aged 50 and older. Over the period from 2008 to 2015, the number of MSM aged 50 and older who were living with HIV increased by 10.8% per year, compared with an annual percent change of 7.7% for those aged 13-29 and –0.4% for those aged 30-49, Andrew Mitsch, MPH, and his associates at the CDC’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention reported in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The size of the population of MSM living with HIV went from 384,000 in 2008 to 523,000 in 2016, with 13- to 29-year-olds going from 10.7% of the population to 13.3%, 30- to 49-year-olds dropping from 61% to 44%, and the 50-and-older group increasing from 28.3% to 42.7%, they said.
“The increase in annual diagnosis of HIV infections among younger MSM might reflect increased HIV testing, in addition to ongoing transmission,” they suggested, and increased prevalence among older men is probably the “result of increased survival associated with widespread use of antiretroviral therapy, surviving middle age, and advancing to the older group.”
The investigators also noted the persistence of racial/ethnic disparities over the course of the study. Among the three largest groups, whites had the smallest increase in new diagnoses for 13- to 29-year-olds and the largest decrease for 30- to 49-year-olds, and they were second to blacks in the less-than-or-equal-to-50-years-of-age group, according to data from the National HIV Surveillance System.
“Promotion of care and treatment by public health agencies and private sector partners to achieve viral suppression among MSM with diagnosed HIV infection will improve health outcomes and reduce transmission to others, particularly if prevention efforts are tailored to specific age groups,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE: Mitsch A et al. MMWR 2018 Sep 21;67(37):1025-31.
Men who have sex with men (MSM) were younger at HIV diagnosis in 2016 than in 2008, but those living with the disease were older, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Among MSM aged 13-29 years, the number diagnosed with HIV increased by 2.9% per year from 2008 to 2016 but dropped 3.5% per year for those aged 30-49 and rose just 0.1% annually among those aged 50 and older. Over the period from 2008 to 2015, the number of MSM aged 50 and older who were living with HIV increased by 10.8% per year, compared with an annual percent change of 7.7% for those aged 13-29 and –0.4% for those aged 30-49, Andrew Mitsch, MPH, and his associates at the CDC’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention reported in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The size of the population of MSM living with HIV went from 384,000 in 2008 to 523,000 in 2016, with 13- to 29-year-olds going from 10.7% of the population to 13.3%, 30- to 49-year-olds dropping from 61% to 44%, and the 50-and-older group increasing from 28.3% to 42.7%, they said.
“The increase in annual diagnosis of HIV infections among younger MSM might reflect increased HIV testing, in addition to ongoing transmission,” they suggested, and increased prevalence among older men is probably the “result of increased survival associated with widespread use of antiretroviral therapy, surviving middle age, and advancing to the older group.”
The investigators also noted the persistence of racial/ethnic disparities over the course of the study. Among the three largest groups, whites had the smallest increase in new diagnoses for 13- to 29-year-olds and the largest decrease for 30- to 49-year-olds, and they were second to blacks in the less-than-or-equal-to-50-years-of-age group, according to data from the National HIV Surveillance System.
“Promotion of care and treatment by public health agencies and private sector partners to achieve viral suppression among MSM with diagnosed HIV infection will improve health outcomes and reduce transmission to others, particularly if prevention efforts are tailored to specific age groups,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE: Mitsch A et al. MMWR 2018 Sep 21;67(37):1025-31.
FROM MMWR