User login
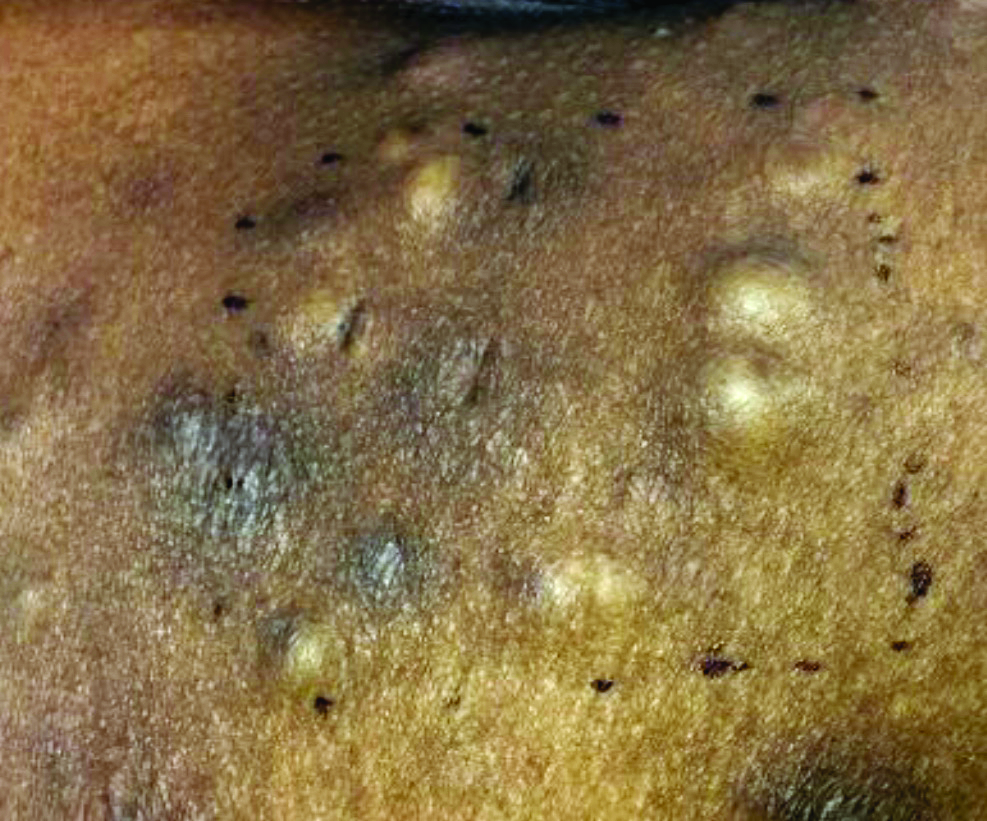
Different types of steatocystoma multiplex have been described: localized, generalized, facial, acral, and suppurative (in which the lesions resemble hidradenitis suppurativa).
This condition is autosomal dominant and is linked to defects in KRT17 gene, which instructs the production of keratin 17. However, some cases of steatocystoma multiplex occur sporadically with no mutation in the KRT17 gene; in them, the cause is unknown. Steatocystoma multiplex may be associated with eruptive vellus hair cysts and pachyonychia congenita (nail and teeth abnormalities and palmoplantar keratoderma). Lesions often appear during adolescence, when an individual hits puberty. Hormones likely influence the development of the cysts from the pilosebaceous unit. If there is a single steatocystoma, it is called steatocystoma simplex.
Steatocystomas do not resolve on their own. The small, benign cysts are located fairly superficial in the dermis. If punctured, they drain a yellow, oily liquid sebum. Lesions may become inflamed and may heal with scarring, as in acne. They may be treated by incision and drainage or excision to remove the cyst wall. Electrosurgery and cryotherapy may be used. Oral antibiotics may improve inflamed lesions. There are reports in the literature in which isotretinoin has helped; however, it is not curative. In some cases, the lesions can reoccur and may even be worse.
Case and photo submitted by: Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD; Aventura, Fla.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Different types of steatocystoma multiplex have been described: localized, generalized, facial, acral, and suppurative (in which the lesions resemble hidradenitis suppurativa).
This condition is autosomal dominant and is linked to defects in KRT17 gene, which instructs the production of keratin 17. However, some cases of steatocystoma multiplex occur sporadically with no mutation in the KRT17 gene; in them, the cause is unknown. Steatocystoma multiplex may be associated with eruptive vellus hair cysts and pachyonychia congenita (nail and teeth abnormalities and palmoplantar keratoderma). Lesions often appear during adolescence, when an individual hits puberty. Hormones likely influence the development of the cysts from the pilosebaceous unit. If there is a single steatocystoma, it is called steatocystoma simplex.
Steatocystomas do not resolve on their own. The small, benign cysts are located fairly superficial in the dermis. If punctured, they drain a yellow, oily liquid sebum. Lesions may become inflamed and may heal with scarring, as in acne. They may be treated by incision and drainage or excision to remove the cyst wall. Electrosurgery and cryotherapy may be used. Oral antibiotics may improve inflamed lesions. There are reports in the literature in which isotretinoin has helped; however, it is not curative. In some cases, the lesions can reoccur and may even be worse.
Case and photo submitted by: Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD; Aventura, Fla.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
Different types of steatocystoma multiplex have been described: localized, generalized, facial, acral, and suppurative (in which the lesions resemble hidradenitis suppurativa).
This condition is autosomal dominant and is linked to defects in KRT17 gene, which instructs the production of keratin 17. However, some cases of steatocystoma multiplex occur sporadically with no mutation in the KRT17 gene; in them, the cause is unknown. Steatocystoma multiplex may be associated with eruptive vellus hair cysts and pachyonychia congenita (nail and teeth abnormalities and palmoplantar keratoderma). Lesions often appear during adolescence, when an individual hits puberty. Hormones likely influence the development of the cysts from the pilosebaceous unit. If there is a single steatocystoma, it is called steatocystoma simplex.
Steatocystomas do not resolve on their own. The small, benign cysts are located fairly superficial in the dermis. If punctured, they drain a yellow, oily liquid sebum. Lesions may become inflamed and may heal with scarring, as in acne. They may be treated by incision and drainage or excision to remove the cyst wall. Electrosurgery and cryotherapy may be used. Oral antibiotics may improve inflamed lesions. There are reports in the literature in which isotretinoin has helped; however, it is not curative. In some cases, the lesions can reoccur and may even be worse.
Case and photo submitted by: Donna Bilu Martin, MD; Premier Dermatology, MD; Aventura, Fla.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.