User login
The Diagnosis: Netherton Syndrome
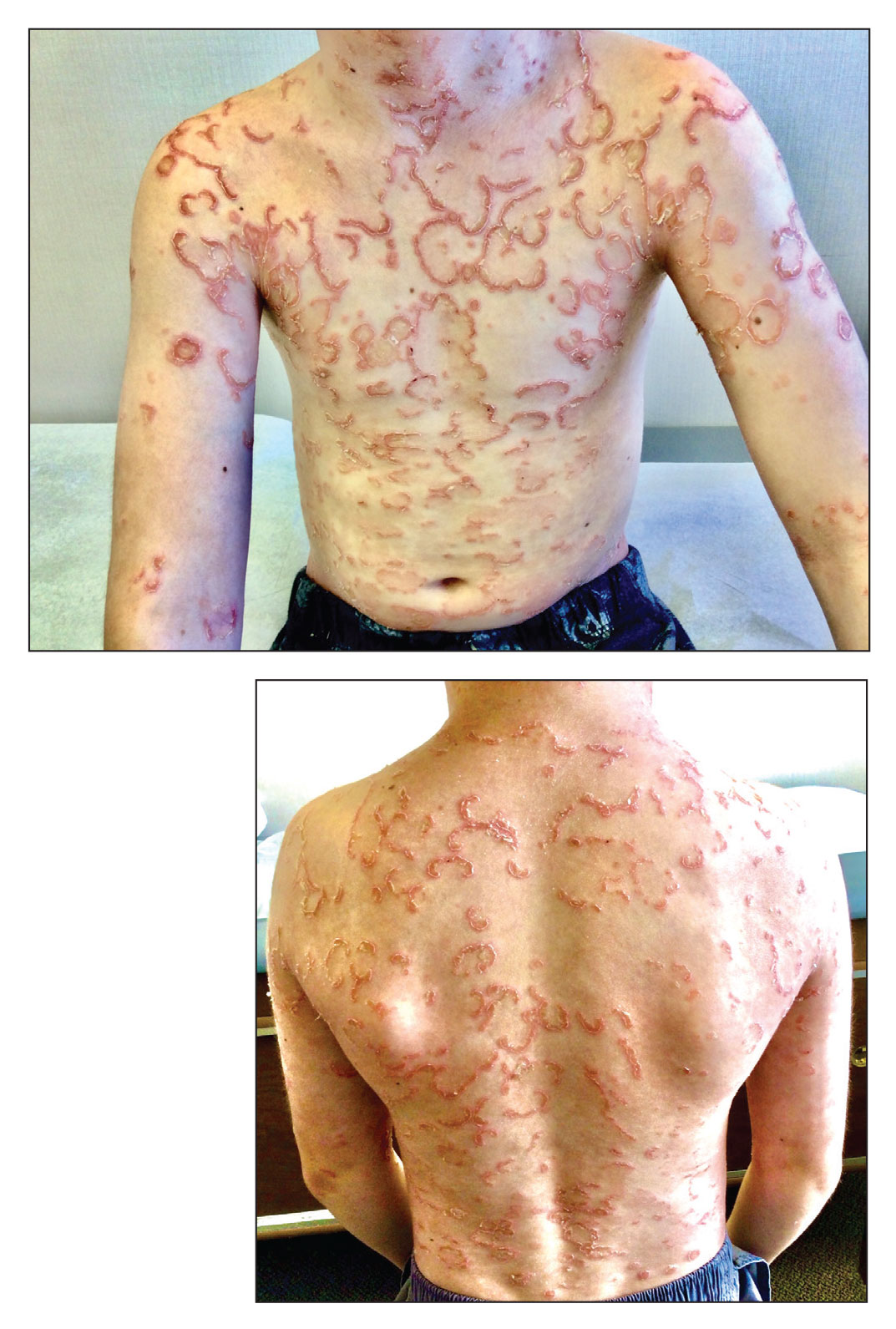
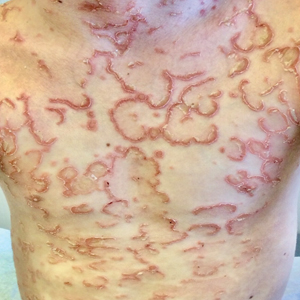
A punch biopsy from the right lower back supported the clinical diagnosis of ichthyosis linearis circumflexa. The patient underwent genetic testing and was found to have a heterozygous mutation in the serine protease inhibitor Kazal type 5 gene, SPINK5, that was consistent with a diagnosis of Netherton syndrome.
Netherton syndrome is an autosomal-recessive genodermatosis characterized by a triad of congenital ichthyosis, hair shaft abnormalities, and atopic diatheses.1,2 It affects approximately 1 in 200,000 live births2,3; however, it is considered by many to be underdiagnosed due to the variability in the clinical appearance. Therefore, the incidence of Netherton syndrome may actually be closer 1 in 50,000 live births.1 The manifestations of the disease are caused by a germline mutation in the SPINK5 gene, which encodes the serine protease inhibitor LEKTI.1,2 Dysfunctional LEKTI results in increased proteolytic activity of the lipid-processing enzymes in the stratum corneum, resulting in a disruption in the lipid bilayer.1 Dysfunctional LEKTI also results in a loss of the antiinflammatory and antimicrobial function of the stratum corneum. Clinical features of Netherton syndrome usually present at birth or shortly thereafter.1 Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma, or the continuous peeling of the skin, is a common presentation seen at birth and in the neonatal period.2 As the patient ages, the dermatologic manifestations evolve into serpiginous and circinate, erythematous plaques with a characteristic peripheral, double-edged scaling.1,2 This distinctive finding is termed ichthyosis linearis circumflexa and is pathognomonic for the syndrome.2 Lesions often affect the trunk and extremities and demonstrate an undulating course.1 Because eczematous and lichenified plaques in flexural areas as well as pruritus are common clinical features, this disease often is misdiagnosed as atopic dermatitis,1,3 as was the case in our patient.
Patients with Netherton syndrome can present with various hair abnormalities. Trichorrhexis invaginata, known as bamboo hair, is the intussusception of the hair shaft and is characteristic of the disease.3 It develops from a reduced number of disulfide bonds, which results in cortical softening.1 Trichorrhexis invaginata may not be present at birth and often improves with age.1,3 Other hair shaft abnormalities such as pili torti, trichorrhexis nodosa, and helical hair also may be observed in Netherton syndrome.1 Extracutaneous manifestations also are typical. There is immune dysregulation of memory B cells and natural killer cells, which manifests as frequent respiratory and skin infections as well as sepsis.1,2 Patients also may have increased levels of serum IgE and eosinophilia resulting in atopy and allergic reactions to various triggers such as foods.1 The neonatal period also may be complicated by dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, inability to regulate body temperature, and failure to thrive.1,3
When there is an extensive disruption of the skin barrier during the neonatal period, there may be severe electrolyte imbalances and thermoregulatory challenges necessitating treatment in the neonatal intensive care unit. Cutaneous disease can be treated with topical therapies with variable success.1 Topical therapies for symptom management include emollients, corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, calcipotriene, and retinoids; however, utmost caution must be employed with these therapies due to the increased risk for systemic absorption resulting from the disturbance of the skin barrier. When therapy with topical tacrolimus is implemented, monitoring of serum drug levels is required.1 Pruritus may be treated symptomatically with oral antihistamines. Intravenous immunoglobulin has been shown to decrease the frequency of infections and improve skin inflammation. Systemic retinoids have unpredictable effects and result in improvement of disease in some patients but exacerbation in others. Phototherapy with narrowband UVB, psoralen plus UVA, UVA1, and balneophototherapy also are effective treatments for cutaneous disease.1 Dupilumab has been shown to decrease pruritus, improve hair abnormalities, and improve skin disease, thereby demonstrating its effectiveness in treating the atopy and ichthyosis in Netherton syndrome.4
The differential diagnosis includes other figurate erythemas including erythema marginatum and erythrokeratodermia variabilis. Erythema marginatum is a cutaneous manifestation of acute rheumatic fever and is characterized by migratory polycyclic erythematous plaques without overlying scale, usually on the trunk and proximal extremities.5 Erythrokeratodermia variabilis is caused by heterozygous mutations in gap junction protein beta 3, GJB3, and gap junction protein beta 4, GJB4, and is characterized by transient geographic and erythematous patches and stable scaly plaques; however, double-edged scaling is not a feature.1 Acrodermatitis enteropathica is an autosomal-recessive disorder caused by mutations in the zinc transporter SLC39A4. Cutaneous manifestations occur after weaning from breast milk and are characterized by erythematous plaques with erosions, vesicles, and scaling, which characteristically occur in the perioral and perianal locations.6 Neonatal lupus is a form of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Typical skin lesions are erythematous annular plaques with overlying scaling, which may be present at birth and have a predilection for the face and other sun-exposed areas. Lesions generally resolve after clearance of the pathogenic maternal antibodies.7
- Richard G, Ringpfeil F. Ichthyoses, erythrokeratodermas, and related disorders. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:888-923.
- Garza JI, Herz-Ruelas ME, Guerrero-González GA, et al. Netherton syndrome: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(suppl 1):AB129.
- Heymann W. Appending the appendages: new perspectives on Netherton syndrome and green nail syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:735-736.
- Murase C, Takeichi T, Taki T, et al. Successful dupilumab treatment for ichthyotic and atopic features of Netherton syndrome. J Dermatol Sci. 2021;102:126-129.
- España A. Figurate erythemas. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:320-331.
- Noguera-Morel L, McLeish Schaefer S, Hivnor C. Nutritional diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:793-809.
- Lee L, Werth V. Lupus erythematosus. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:662-680.
The Diagnosis: Netherton Syndrome
A punch biopsy from the right lower back supported the clinical diagnosis of ichthyosis linearis circumflexa. The patient underwent genetic testing and was found to have a heterozygous mutation in the serine protease inhibitor Kazal type 5 gene, SPINK5, that was consistent with a diagnosis of Netherton syndrome.
Netherton syndrome is an autosomal-recessive genodermatosis characterized by a triad of congenital ichthyosis, hair shaft abnormalities, and atopic diatheses.1,2 It affects approximately 1 in 200,000 live births2,3; however, it is considered by many to be underdiagnosed due to the variability in the clinical appearance. Therefore, the incidence of Netherton syndrome may actually be closer 1 in 50,000 live births.1 The manifestations of the disease are caused by a germline mutation in the SPINK5 gene, which encodes the serine protease inhibitor LEKTI.1,2 Dysfunctional LEKTI results in increased proteolytic activity of the lipid-processing enzymes in the stratum corneum, resulting in a disruption in the lipid bilayer.1 Dysfunctional LEKTI also results in a loss of the antiinflammatory and antimicrobial function of the stratum corneum. Clinical features of Netherton syndrome usually present at birth or shortly thereafter.1 Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma, or the continuous peeling of the skin, is a common presentation seen at birth and in the neonatal period.2 As the patient ages, the dermatologic manifestations evolve into serpiginous and circinate, erythematous plaques with a characteristic peripheral, double-edged scaling.1,2 This distinctive finding is termed ichthyosis linearis circumflexa and is pathognomonic for the syndrome.2 Lesions often affect the trunk and extremities and demonstrate an undulating course.1 Because eczematous and lichenified plaques in flexural areas as well as pruritus are common clinical features, this disease often is misdiagnosed as atopic dermatitis,1,3 as was the case in our patient.
Patients with Netherton syndrome can present with various hair abnormalities. Trichorrhexis invaginata, known as bamboo hair, is the intussusception of the hair shaft and is characteristic of the disease.3 It develops from a reduced number of disulfide bonds, which results in cortical softening.1 Trichorrhexis invaginata may not be present at birth and often improves with age.1,3 Other hair shaft abnormalities such as pili torti, trichorrhexis nodosa, and helical hair also may be observed in Netherton syndrome.1 Extracutaneous manifestations also are typical. There is immune dysregulation of memory B cells and natural killer cells, which manifests as frequent respiratory and skin infections as well as sepsis.1,2 Patients also may have increased levels of serum IgE and eosinophilia resulting in atopy and allergic reactions to various triggers such as foods.1 The neonatal period also may be complicated by dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, inability to regulate body temperature, and failure to thrive.1,3
When there is an extensive disruption of the skin barrier during the neonatal period, there may be severe electrolyte imbalances and thermoregulatory challenges necessitating treatment in the neonatal intensive care unit. Cutaneous disease can be treated with topical therapies with variable success.1 Topical therapies for symptom management include emollients, corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, calcipotriene, and retinoids; however, utmost caution must be employed with these therapies due to the increased risk for systemic absorption resulting from the disturbance of the skin barrier. When therapy with topical tacrolimus is implemented, monitoring of serum drug levels is required.1 Pruritus may be treated symptomatically with oral antihistamines. Intravenous immunoglobulin has been shown to decrease the frequency of infections and improve skin inflammation. Systemic retinoids have unpredictable effects and result in improvement of disease in some patients but exacerbation in others. Phototherapy with narrowband UVB, psoralen plus UVA, UVA1, and balneophototherapy also are effective treatments for cutaneous disease.1 Dupilumab has been shown to decrease pruritus, improve hair abnormalities, and improve skin disease, thereby demonstrating its effectiveness in treating the atopy and ichthyosis in Netherton syndrome.4
The differential diagnosis includes other figurate erythemas including erythema marginatum and erythrokeratodermia variabilis. Erythema marginatum is a cutaneous manifestation of acute rheumatic fever and is characterized by migratory polycyclic erythematous plaques without overlying scale, usually on the trunk and proximal extremities.5 Erythrokeratodermia variabilis is caused by heterozygous mutations in gap junction protein beta 3, GJB3, and gap junction protein beta 4, GJB4, and is characterized by transient geographic and erythematous patches and stable scaly plaques; however, double-edged scaling is not a feature.1 Acrodermatitis enteropathica is an autosomal-recessive disorder caused by mutations in the zinc transporter SLC39A4. Cutaneous manifestations occur after weaning from breast milk and are characterized by erythematous plaques with erosions, vesicles, and scaling, which characteristically occur in the perioral and perianal locations.6 Neonatal lupus is a form of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Typical skin lesions are erythematous annular plaques with overlying scaling, which may be present at birth and have a predilection for the face and other sun-exposed areas. Lesions generally resolve after clearance of the pathogenic maternal antibodies.7
The Diagnosis: Netherton Syndrome
A punch biopsy from the right lower back supported the clinical diagnosis of ichthyosis linearis circumflexa. The patient underwent genetic testing and was found to have a heterozygous mutation in the serine protease inhibitor Kazal type 5 gene, SPINK5, that was consistent with a diagnosis of Netherton syndrome.
Netherton syndrome is an autosomal-recessive genodermatosis characterized by a triad of congenital ichthyosis, hair shaft abnormalities, and atopic diatheses.1,2 It affects approximately 1 in 200,000 live births2,3; however, it is considered by many to be underdiagnosed due to the variability in the clinical appearance. Therefore, the incidence of Netherton syndrome may actually be closer 1 in 50,000 live births.1 The manifestations of the disease are caused by a germline mutation in the SPINK5 gene, which encodes the serine protease inhibitor LEKTI.1,2 Dysfunctional LEKTI results in increased proteolytic activity of the lipid-processing enzymes in the stratum corneum, resulting in a disruption in the lipid bilayer.1 Dysfunctional LEKTI also results in a loss of the antiinflammatory and antimicrobial function of the stratum corneum. Clinical features of Netherton syndrome usually present at birth or shortly thereafter.1 Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma, or the continuous peeling of the skin, is a common presentation seen at birth and in the neonatal period.2 As the patient ages, the dermatologic manifestations evolve into serpiginous and circinate, erythematous plaques with a characteristic peripheral, double-edged scaling.1,2 This distinctive finding is termed ichthyosis linearis circumflexa and is pathognomonic for the syndrome.2 Lesions often affect the trunk and extremities and demonstrate an undulating course.1 Because eczematous and lichenified plaques in flexural areas as well as pruritus are common clinical features, this disease often is misdiagnosed as atopic dermatitis,1,3 as was the case in our patient.
Patients with Netherton syndrome can present with various hair abnormalities. Trichorrhexis invaginata, known as bamboo hair, is the intussusception of the hair shaft and is characteristic of the disease.3 It develops from a reduced number of disulfide bonds, which results in cortical softening.1 Trichorrhexis invaginata may not be present at birth and often improves with age.1,3 Other hair shaft abnormalities such as pili torti, trichorrhexis nodosa, and helical hair also may be observed in Netherton syndrome.1 Extracutaneous manifestations also are typical. There is immune dysregulation of memory B cells and natural killer cells, which manifests as frequent respiratory and skin infections as well as sepsis.1,2 Patients also may have increased levels of serum IgE and eosinophilia resulting in atopy and allergic reactions to various triggers such as foods.1 The neonatal period also may be complicated by dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, inability to regulate body temperature, and failure to thrive.1,3
When there is an extensive disruption of the skin barrier during the neonatal period, there may be severe electrolyte imbalances and thermoregulatory challenges necessitating treatment in the neonatal intensive care unit. Cutaneous disease can be treated with topical therapies with variable success.1 Topical therapies for symptom management include emollients, corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, calcipotriene, and retinoids; however, utmost caution must be employed with these therapies due to the increased risk for systemic absorption resulting from the disturbance of the skin barrier. When therapy with topical tacrolimus is implemented, monitoring of serum drug levels is required.1 Pruritus may be treated symptomatically with oral antihistamines. Intravenous immunoglobulin has been shown to decrease the frequency of infections and improve skin inflammation. Systemic retinoids have unpredictable effects and result in improvement of disease in some patients but exacerbation in others. Phototherapy with narrowband UVB, psoralen plus UVA, UVA1, and balneophototherapy also are effective treatments for cutaneous disease.1 Dupilumab has been shown to decrease pruritus, improve hair abnormalities, and improve skin disease, thereby demonstrating its effectiveness in treating the atopy and ichthyosis in Netherton syndrome.4
The differential diagnosis includes other figurate erythemas including erythema marginatum and erythrokeratodermia variabilis. Erythema marginatum is a cutaneous manifestation of acute rheumatic fever and is characterized by migratory polycyclic erythematous plaques without overlying scale, usually on the trunk and proximal extremities.5 Erythrokeratodermia variabilis is caused by heterozygous mutations in gap junction protein beta 3, GJB3, and gap junction protein beta 4, GJB4, and is characterized by transient geographic and erythematous patches and stable scaly plaques; however, double-edged scaling is not a feature.1 Acrodermatitis enteropathica is an autosomal-recessive disorder caused by mutations in the zinc transporter SLC39A4. Cutaneous manifestations occur after weaning from breast milk and are characterized by erythematous plaques with erosions, vesicles, and scaling, which characteristically occur in the perioral and perianal locations.6 Neonatal lupus is a form of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Typical skin lesions are erythematous annular plaques with overlying scaling, which may be present at birth and have a predilection for the face and other sun-exposed areas. Lesions generally resolve after clearance of the pathogenic maternal antibodies.7
- Richard G, Ringpfeil F. Ichthyoses, erythrokeratodermas, and related disorders. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:888-923.
- Garza JI, Herz-Ruelas ME, Guerrero-González GA, et al. Netherton syndrome: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(suppl 1):AB129.
- Heymann W. Appending the appendages: new perspectives on Netherton syndrome and green nail syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:735-736.
- Murase C, Takeichi T, Taki T, et al. Successful dupilumab treatment for ichthyotic and atopic features of Netherton syndrome. J Dermatol Sci. 2021;102:126-129.
- España A. Figurate erythemas. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:320-331.
- Noguera-Morel L, McLeish Schaefer S, Hivnor C. Nutritional diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:793-809.
- Lee L, Werth V. Lupus erythematosus. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:662-680.
- Richard G, Ringpfeil F. Ichthyoses, erythrokeratodermas, and related disorders. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:888-923.
- Garza JI, Herz-Ruelas ME, Guerrero-González GA, et al. Netherton syndrome: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(suppl 1):AB129.
- Heymann W. Appending the appendages: new perspectives on Netherton syndrome and green nail syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:735-736.
- Murase C, Takeichi T, Taki T, et al. Successful dupilumab treatment for ichthyotic and atopic features of Netherton syndrome. J Dermatol Sci. 2021;102:126-129.
- España A. Figurate erythemas. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:320-331.
- Noguera-Morel L, McLeish Schaefer S, Hivnor C. Nutritional diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:793-809.
- Lee L, Werth V. Lupus erythematosus. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:662-680.
A 9-year-old boy presented to the dermatology clinic with a scaly eruption distributed throughout the body that had been present since birth. He had been diagnosed with atopic dermatitis by multiple dermatologists prior to the current presentation and had been treated with various topical steroids with minimal improvement. He had no family history of similar eruptions and no personal history of asthma or allergies. Physical examination revealed erythematous, serpiginous, polycyclic plaques with peripheral, double-edged scaling. Decreased hair density of the lateral eyebrows also was observed.