User login
Elderly adults with hypertension who are newly prescribed a calcium-channel blocker (CCB), compared to other antihypertensive agents, are at least twice as likely to be given a loop diuretic over the following months, a large cohort study suggests.
The likelihood remained elevated for as long as a year after the start of a CCB and was more pronounced when comparing CCBs to any other kind of medication.
“Our findings suggest that many older adults who begin taking a CCB may subsequently experience a prescribing cascade” when loop diuretics are prescribed for peripheral edema, a known CCB adverse effect, that is misinterpreted as a new medical condition, Rachel D. Savage, PhD, Women’s College Hospital, Toronto, Canada, told theheart.org/Medscape Cardiology.
Edema caused by CCBs is caused by fluid redistribution, not overload, and “treating euvolemic individuals with a diuretic places them at increased risk of overdiuresis, leading to falls, urinary incontinence, acute kidney injury, electrolyte imbalances, and a cascade of other downstream consequences to which older adults are especially vulnerable,” explain Savage and coauthors of the analysis published online February 24 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
However, 1.4% of the cohort had been prescribed a loop diuretic, and 4.5% had been given any diuretic within 90 days after the start of CCBs. The corresponding rates were 0.7% and 3.4%, respectively, for patients who had started on ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) rather than a CCB.
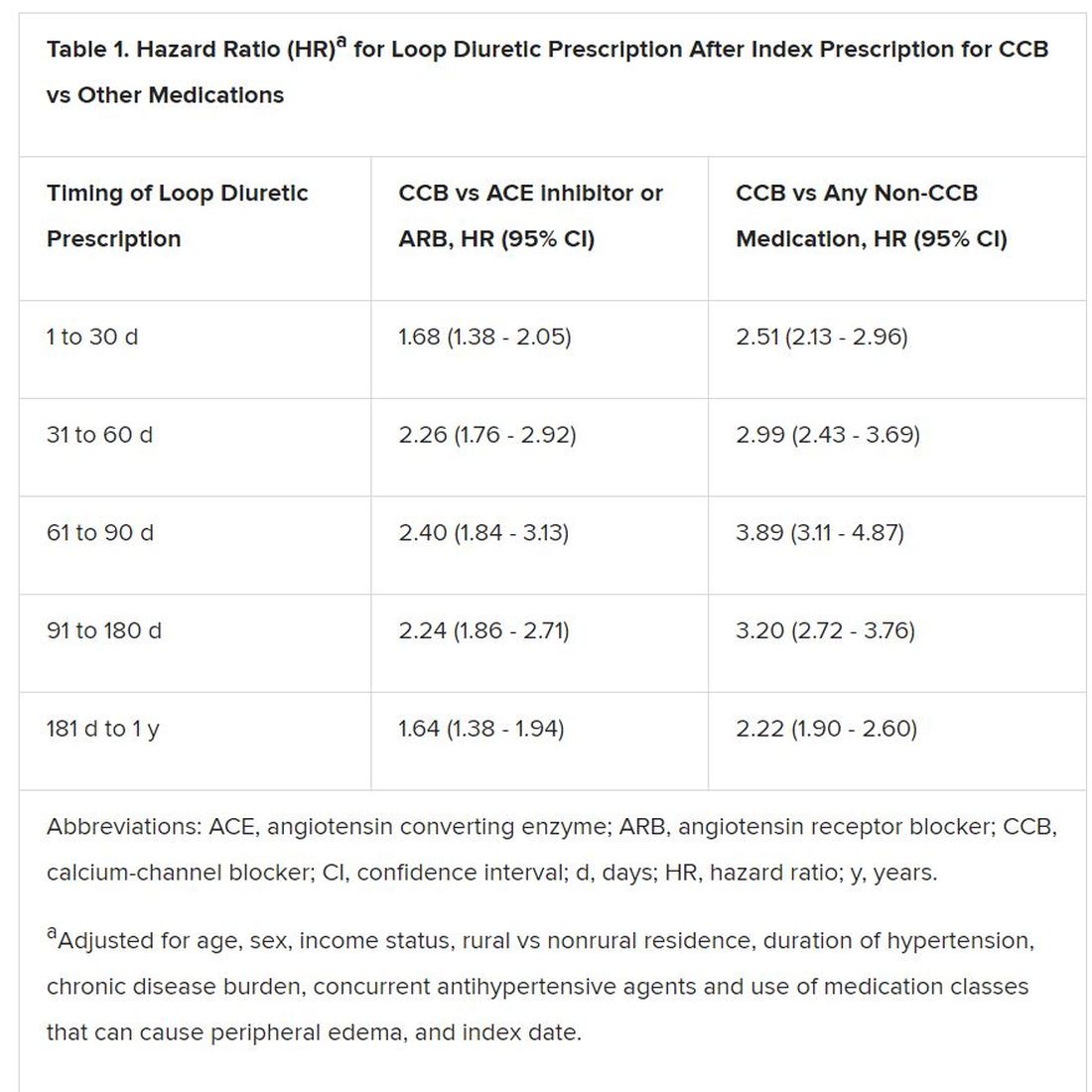
Also, Savage observed, “the likelihood of being prescribed a loop diuretic following initiation of a CCB changed over time and was greatest 61 to 90 days postinitiation.” At that point, it was increased 2.4 times compared with initiation of an ACE inhibitor or an ARB in an adjusted analysis and increased almost 4 times compared with starting on any non-CCB agent.
Importantly, the actual prevalence of peripheral edema among those started on CCBs, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, or any non-CCB medication was not available in the data sets.
However, “the main message for clinicians is to consider medication side effects as a potential cause for new symptoms when patients present. We also encourage patients to ask prescribers about whether new symptoms could be caused by a medication,” senior author Lisa M. McCarthy, PharmD, told theheart.org/Medscape Cardiology.
“If a patient experiences peripheral edema while taking a CCB, we would encourage clinicians to consider whether the calcium-channel blocker is still necessary, whether it could be discontinued or the dose reduced, or whether the patient can be switched to another therapy,” she said.
Based on the current analysis, if the rate of CCB-induced peripheral edema is assumed to be 10%, which is consistent with the literature, then “potentially 7% to 14% of people who develop edema while taking a calcium channel blocker may then receive a loop diuretic,” an accompanying editorial notes.
“Patients with polypharmacy are at heightened risk of being exposed to [a] series of prescribing cascades if their current use of medications is not carefully discussed before the decision to add a new antihypertensive,” observe Timothy S. Anderson, MD, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, and Michael A. Steinman, MD, San Francisco Veterans Affairs Medical Center and University of California, San Francisco.
“The initial prescribing cascade can set off many other negative consequences, including adverse drug events, potentially avoidable diagnostic testing, and hospitalizations,” the editorialists caution.
“Identifying prescribing cascades and their consequences is an important step to stem the tide of polypharmacy and inform deprescribing efforts.”
The analysis was based on administrative data from almost 340,000 adults in the community aged 66 years or older with hypertension and new drug prescriptions over 5 years ending in September 2016, the report notes. Their mean age was 74.5 years and 56.5% were women.
The data set included 41,086 patients who were newly prescribed a CCB; 66,494 who were newly prescribed an ACE inhibitor or ARB; and 231,439 newly prescribed any medication other than a CCB. The prescribed CCB was amlodipine in 79.6% of patients.
Although loop diuretics could possibly have been prescribed sometimes as a second-tier antihypertensive in the absence of peripheral edema, “we made efforts, through the design of our study, to limit this where possible,” Savage said in an interview.
For example, the focus was on loop diuretics, which aren’t generally recommended for blood-pressure lowering. Also, patients with heart failure and those with a recent history of diuretic or other antihypertensive medication use had been excluded, she said.
“As such, our cohort comprised individuals with new-onset or milder hypertension for whom diuretics would unlikely to be prescribed as part of guideline-based hypertension management.”
Although amlodipine was the most commonly prescribed CCB, the potential for a prescribing cascade seemed to be a class effect and to apply at a range of dosages.
That was unexpected, McCarthy observed, because “peripheral edema occurs more commonly in people taking dihydropyridine CCBs, like amlodipine, compared to non–dihydropyridine CCBs, such as verapamil and diltiazem.”
Savage, McCarthy, their coauthors, and the editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Elderly adults with hypertension who are newly prescribed a calcium-channel blocker (CCB), compared to other antihypertensive agents, are at least twice as likely to be given a loop diuretic over the following months, a large cohort study suggests.
The likelihood remained elevated for as long as a year after the start of a CCB and was more pronounced when comparing CCBs to any other kind of medication.
“Our findings suggest that many older adults who begin taking a CCB may subsequently experience a prescribing cascade” when loop diuretics are prescribed for peripheral edema, a known CCB adverse effect, that is misinterpreted as a new medical condition, Rachel D. Savage, PhD, Women’s College Hospital, Toronto, Canada, told theheart.org/Medscape Cardiology.
Edema caused by CCBs is caused by fluid redistribution, not overload, and “treating euvolemic individuals with a diuretic places them at increased risk of overdiuresis, leading to falls, urinary incontinence, acute kidney injury, electrolyte imbalances, and a cascade of other downstream consequences to which older adults are especially vulnerable,” explain Savage and coauthors of the analysis published online February 24 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
However, 1.4% of the cohort had been prescribed a loop diuretic, and 4.5% had been given any diuretic within 90 days after the start of CCBs. The corresponding rates were 0.7% and 3.4%, respectively, for patients who had started on ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) rather than a CCB.
Also, Savage observed, “the likelihood of being prescribed a loop diuretic following initiation of a CCB changed over time and was greatest 61 to 90 days postinitiation.” At that point, it was increased 2.4 times compared with initiation of an ACE inhibitor or an ARB in an adjusted analysis and increased almost 4 times compared with starting on any non-CCB agent.
Importantly, the actual prevalence of peripheral edema among those started on CCBs, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, or any non-CCB medication was not available in the data sets.
However, “the main message for clinicians is to consider medication side effects as a potential cause for new symptoms when patients present. We also encourage patients to ask prescribers about whether new symptoms could be caused by a medication,” senior author Lisa M. McCarthy, PharmD, told theheart.org/Medscape Cardiology.
“If a patient experiences peripheral edema while taking a CCB, we would encourage clinicians to consider whether the calcium-channel blocker is still necessary, whether it could be discontinued or the dose reduced, or whether the patient can be switched to another therapy,” she said.
Based on the current analysis, if the rate of CCB-induced peripheral edema is assumed to be 10%, which is consistent with the literature, then “potentially 7% to 14% of people who develop edema while taking a calcium channel blocker may then receive a loop diuretic,” an accompanying editorial notes.
“Patients with polypharmacy are at heightened risk of being exposed to [a] series of prescribing cascades if their current use of medications is not carefully discussed before the decision to add a new antihypertensive,” observe Timothy S. Anderson, MD, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, and Michael A. Steinman, MD, San Francisco Veterans Affairs Medical Center and University of California, San Francisco.
“The initial prescribing cascade can set off many other negative consequences, including adverse drug events, potentially avoidable diagnostic testing, and hospitalizations,” the editorialists caution.
“Identifying prescribing cascades and their consequences is an important step to stem the tide of polypharmacy and inform deprescribing efforts.”
The analysis was based on administrative data from almost 340,000 adults in the community aged 66 years or older with hypertension and new drug prescriptions over 5 years ending in September 2016, the report notes. Their mean age was 74.5 years and 56.5% were women.
The data set included 41,086 patients who were newly prescribed a CCB; 66,494 who were newly prescribed an ACE inhibitor or ARB; and 231,439 newly prescribed any medication other than a CCB. The prescribed CCB was amlodipine in 79.6% of patients.
Although loop diuretics could possibly have been prescribed sometimes as a second-tier antihypertensive in the absence of peripheral edema, “we made efforts, through the design of our study, to limit this where possible,” Savage said in an interview.
For example, the focus was on loop diuretics, which aren’t generally recommended for blood-pressure lowering. Also, patients with heart failure and those with a recent history of diuretic or other antihypertensive medication use had been excluded, she said.
“As such, our cohort comprised individuals with new-onset or milder hypertension for whom diuretics would unlikely to be prescribed as part of guideline-based hypertension management.”
Although amlodipine was the most commonly prescribed CCB, the potential for a prescribing cascade seemed to be a class effect and to apply at a range of dosages.
That was unexpected, McCarthy observed, because “peripheral edema occurs more commonly in people taking dihydropyridine CCBs, like amlodipine, compared to non–dihydropyridine CCBs, such as verapamil and diltiazem.”
Savage, McCarthy, their coauthors, and the editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Elderly adults with hypertension who are newly prescribed a calcium-channel blocker (CCB), compared to other antihypertensive agents, are at least twice as likely to be given a loop diuretic over the following months, a large cohort study suggests.
The likelihood remained elevated for as long as a year after the start of a CCB and was more pronounced when comparing CCBs to any other kind of medication.
“Our findings suggest that many older adults who begin taking a CCB may subsequently experience a prescribing cascade” when loop diuretics are prescribed for peripheral edema, a known CCB adverse effect, that is misinterpreted as a new medical condition, Rachel D. Savage, PhD, Women’s College Hospital, Toronto, Canada, told theheart.org/Medscape Cardiology.
Edema caused by CCBs is caused by fluid redistribution, not overload, and “treating euvolemic individuals with a diuretic places them at increased risk of overdiuresis, leading to falls, urinary incontinence, acute kidney injury, electrolyte imbalances, and a cascade of other downstream consequences to which older adults are especially vulnerable,” explain Savage and coauthors of the analysis published online February 24 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
However, 1.4% of the cohort had been prescribed a loop diuretic, and 4.5% had been given any diuretic within 90 days after the start of CCBs. The corresponding rates were 0.7% and 3.4%, respectively, for patients who had started on ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) rather than a CCB.
Also, Savage observed, “the likelihood of being prescribed a loop diuretic following initiation of a CCB changed over time and was greatest 61 to 90 days postinitiation.” At that point, it was increased 2.4 times compared with initiation of an ACE inhibitor or an ARB in an adjusted analysis and increased almost 4 times compared with starting on any non-CCB agent.
Importantly, the actual prevalence of peripheral edema among those started on CCBs, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, or any non-CCB medication was not available in the data sets.
However, “the main message for clinicians is to consider medication side effects as a potential cause for new symptoms when patients present. We also encourage patients to ask prescribers about whether new symptoms could be caused by a medication,” senior author Lisa M. McCarthy, PharmD, told theheart.org/Medscape Cardiology.
“If a patient experiences peripheral edema while taking a CCB, we would encourage clinicians to consider whether the calcium-channel blocker is still necessary, whether it could be discontinued or the dose reduced, or whether the patient can be switched to another therapy,” she said.
Based on the current analysis, if the rate of CCB-induced peripheral edema is assumed to be 10%, which is consistent with the literature, then “potentially 7% to 14% of people who develop edema while taking a calcium channel blocker may then receive a loop diuretic,” an accompanying editorial notes.
“Patients with polypharmacy are at heightened risk of being exposed to [a] series of prescribing cascades if their current use of medications is not carefully discussed before the decision to add a new antihypertensive,” observe Timothy S. Anderson, MD, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, and Michael A. Steinman, MD, San Francisco Veterans Affairs Medical Center and University of California, San Francisco.
“The initial prescribing cascade can set off many other negative consequences, including adverse drug events, potentially avoidable diagnostic testing, and hospitalizations,” the editorialists caution.
“Identifying prescribing cascades and their consequences is an important step to stem the tide of polypharmacy and inform deprescribing efforts.”
The analysis was based on administrative data from almost 340,000 adults in the community aged 66 years or older with hypertension and new drug prescriptions over 5 years ending in September 2016, the report notes. Their mean age was 74.5 years and 56.5% were women.
The data set included 41,086 patients who were newly prescribed a CCB; 66,494 who were newly prescribed an ACE inhibitor or ARB; and 231,439 newly prescribed any medication other than a CCB. The prescribed CCB was amlodipine in 79.6% of patients.
Although loop diuretics could possibly have been prescribed sometimes as a second-tier antihypertensive in the absence of peripheral edema, “we made efforts, through the design of our study, to limit this where possible,” Savage said in an interview.
For example, the focus was on loop diuretics, which aren’t generally recommended for blood-pressure lowering. Also, patients with heart failure and those with a recent history of diuretic or other antihypertensive medication use had been excluded, she said.
“As such, our cohort comprised individuals with new-onset or milder hypertension for whom diuretics would unlikely to be prescribed as part of guideline-based hypertension management.”
Although amlodipine was the most commonly prescribed CCB, the potential for a prescribing cascade seemed to be a class effect and to apply at a range of dosages.
That was unexpected, McCarthy observed, because “peripheral edema occurs more commonly in people taking dihydropyridine CCBs, like amlodipine, compared to non–dihydropyridine CCBs, such as verapamil and diltiazem.”
Savage, McCarthy, their coauthors, and the editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.