User login
To the Editor:
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common skin condition with an increasing prevalence, affecting up to 20% of children and 3% of adults.1,2 More than 80% of patients with AD have elevated IgE levels.3,4 IgE modulates the inflammatory response in AD in several ways including “a biphasic immediate/late phase reaction, allergen presentation by IgE-bearing Langerhans cells, allergen-induced activation of IgE-bearing macrophages, and IgE autoreactivity to human proteins.”5 Historically, most therapies have focused on mitigating the allergic symptoms caused by degranulated effector cells, such as antihistamines. However, a new class of biologically engineered medications (eg, anti-IgE [omalizumab]) aim to prevent the initiation of the allergic response.6 Variable success has been reported using omalizumab in the treatment of AD, though the majority of studies have shown improvement, especially when used in combination with conventional therapies.4,5,7-22 Omalizumab dosage is determined by body weight and pretreatment serum total IgE levels and is administered via subcutaneous injections every 2 to 4 weeks.6,7,23-26 However, the dosing tables are based on asthma therapy, in which serum IgE levels may be much lower than chronic AD,7,24 and the appropriate dosage in AD patients with markedly elevated IgE is unclear. We report an interesting case of a 57-year-old man with erythroderma from long-standing severe chronic AD that was unresponsive to conventional therapy as well as an associated serum IgE level of 17,183 IU/mL who dramatically improved when omalizumab was added to his treatment regimen.
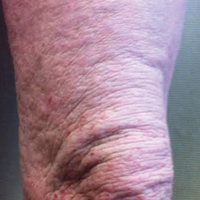
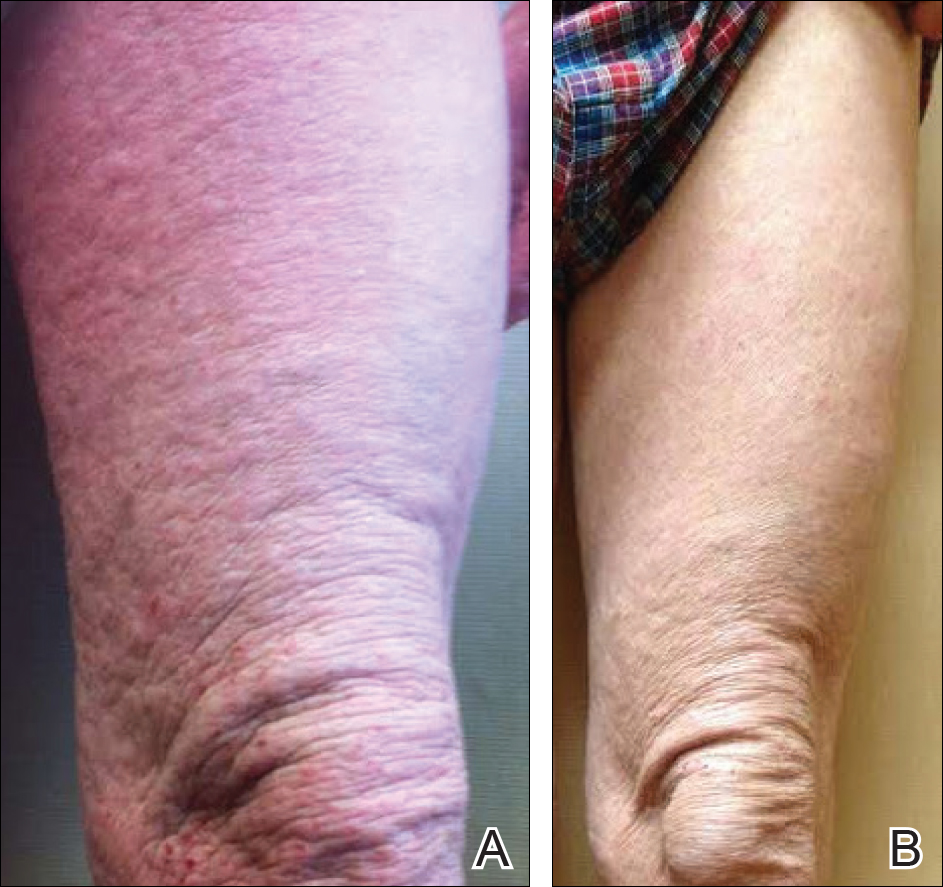
A 57-year-old man presented with essentially 100% body surface area involvement of AD with erythroderma and pruritus. Severe AD developed at infancy and cleared at 5 years of age; childhood onset of asthma was responsive to theophylline and oral inhalers. He developed recurrent AD and asthma at 38 years of age, which was progressive and developed into severe recalcitrant erythroderma by 50 years of age. His AD was unresponsive to multiple therapies, including topical steroids, antibiotics, tacrolimus, bleach baths, antihistamines, methotrexate (15 mg weekly for 1 year, then 12.5 mg weekly for 6 months), UVB phototherapy, and psoralen plus UVA photochemotherapy. He had minimal improvement with cyclosporine (200 mg daily for 4 weeks) and mycophenolate mofetil (3 g daily), and required systemic steroids for relief. The skin was violaceous and lichenified (Figure, A). Laboratory studies were normal, except for a serum IgE level of 17,183 IU/mL (reference range, <150 IU/mL) and peripheral blood eosinophilia up to 29.8% (reference range, 1%–5%) of the differential. Skin biopsies showed AD progressing to lichen simplex chronicus. Omalizumab was added to the therapeutic regimen at a dose of 375 mg every 2 weeks, with noticeable improvement after 3 months. The patient had approximately 80% to 90% clearing with resolution of erythroderma and pruritus, and only limited residual lichenification (Figure, B). The mycophenolate was tapered slowly, and the patient experienced a mild flare at 1 g daily. He is presently on 1 g of mycophenolate daily and omalizumab (375 mg every 2 weeks) and remains remarkably improved. His IgE level decreased to 11,983 IU/mL.
Omalizumab is a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that specifically binds to the FcεRI domain of serum IgE. It blocks binding to high-affinity receptors on effector cells, primarily mast cells, basophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells; it also decreases free IgE serum levels and downregulates the IgE receptor.4,6-10,23-25,27,28 Currently, omalizumab is US Food and Drug Administration approved for moderate to severe persistent asthma in patients 6 years or older with a positive aeroallergen skin test and IgE levels up to 700 IU/mL.6,7,23-25,27,28
However, scattered case reports and small case series have described variable success in the treatment of severe AD that is unresponsive to conventional therapy in patients with markedly elevated serum IgE levels.4,5,7-22 The majority of patients (approximately 80% of published cases yielded by a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms omalizumab and atopic dermatitis) showed improvement when measured by clinical severity scores and quality of life improvement, especially when used in conjunction with conventional therapy. Possible reasons for reported treatment failure include insufficient dosage, lack of established treatment guidelines for markedly elevated serum IgE levels, severity of disease, or variable response with failure to lower IgE level below a required threshold.7,9,23,24,27
Krathen and Hsu9 reported treatment failure with omalizumab for AD in 3 patients with serum IgE levels ranging from 5440 and 24,400 IU/mL, and one review indicated omalizumab may work best in patients with only moderately elevated serum IgE levels.21 However, Toledo et al18 reported efficacy of low-dose omalizumab for pretreatment IgE levels up to 30,000 IU/mL in 6 of 11 reported cases. The pretreatment serum IgE level is not predictive of response, and lowering the serum IgE level without normalization can be efficacious,12,23 as in the current case. Serum IgE levels are not used for monitoring therapeutic response or calculating future dosing, given potential increases in serum IgE levels during and after therapy (for up to 12 months) secondary to the formation of anti-IgE:IgE complexes.6,28 Omalizumab appears most effective when used in combination with conventional therapies. Hopefully ongoing studies will further elucidate the role of omalizumab in recalcitrant AD with elevated serum IgE levels.
- Schultz-Larsen F, Diepgen T, Svennson A. The occurrence of atopic dermatitis in north Europe: an international questionnaire study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:760-764.
- Laughter D, Istvan JA, Tofte SJ, et al. The presence of atopic dermatitis in Oregon schoolchildren. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:649-655.
- Jones HE, Inouye JC, McGerity JL, et al. Atopic disease and serum immunoglobulin-E. Br J Dermatol. 1975;92:17-25.
- Abramovits W. A clinician’s paradigm in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53(1, suppl 1):570-577.
- Leung D, Soter N. Cellular and immunologic mechanisms in atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44(suppl):S1-S12.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Briefing document on safety. Omalizumab (Xolair) (recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody to IgE) for treatment of allergic asthma. http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/03/briefing/3952B1_02_FDA-Xolair-Safety.pdf. Published April 18, 2003. Accessed June 23, 2014.
- Lane JE, Cheyney JM, Lane TN, et al. Treatment of recalcitrant atopic dermatitis with omalizumab. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:68-72.
- Caruso C, Gaeta F, Valluzzi RL, et al. Omalizumab efficacy in a girl with atopic eczema. Allergy. 2010;65:278-279.
- Krathen RA, Hsu S. Failure of omalizumab for the treatment of severe atopic dermatitis. J Am Dermatol. 2005;53:338-340.
- Fernández-Antón Martínez MC, Leis-Dosil V, Alfageme-Roldán F, et al. Omalizumab for the treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2012;103:624-628.
- Pelaia G, Gallelli L, Romeo P, et al. Omalizumab decreases exacerbation frequency, oral intake of corticosteroids and peripheral blood eosinophils in atopic patients with uncontrolled asthma. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011;49:713-721.
- Belloni B, Ziai M, Lim A, et al. Low-dose anti-IgE therapy in patients with atopic eczema with high serum IgE levels. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120:1223-1225.
- Park SY, Choi MR, Na JI, et al. Recalcitrant atopic dermatitis treated with omalizumab. Ann Dermatol. 2010;22:349-352.
- Velling P, Skowasch D, Pabst S. Improvement of quality of life in patients with concomitant allergic asthma and atopic dermatitis: one year follow-up of omalizumab therapy. Eur J Med Res. 2011;15:407-410.
- Amrol D. Anti-immunoglobulin E in the treatment of refractory atopic dermatitis. South Med J. 2010;103:554-558.
- Heil PM, Maurer D, Klein B, et al. Omalizumab therapy in atopic dermatitis: depletion of IgE does not improve the clinical course-a randomized, placebo-controlled and double blind study. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:990-998.
- Ramírez del Pozo ME, Contreras Contreras E, López Tiro J, et al. Omalizumab (anti-IgE antibody) in the treatment of severe atopic dermatitis. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2011;21:416-417.
- Toledo F, Silvestre JF, Muñoz C. Combined therapy with low-dose omalizumab and intravenous immunoglobulin for severe atopic dermatitis: report of four cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1325-1327.
- Sheinkopf LE, Rafi AW, Katz RM. Efficacy of omalizumab in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: a pilot study. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008;29:530-537.
- Incorvia C, Pravettoni C, Mauro M, et al. Effectiveness of omalizumab in a patient with severe asthma and atopic dermatitis. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2008:69:78-80.
- Schmitt J, Schäkel K. Omalizumab as a therapeutic option in atopic eczema. Current evidence and potential benefit [in German]. Hautarzt. 2007;58:130-132.
- Thaiwat S, Sangasapaviliya A. Omalizumab treatment in severe atopic dermatitis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2011;29:357-360.
- Kopp MV. Omalizumab: anti-IgE therapy in allergy. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011;11:101-106.
- Vichyanond P. Omalizumab in allergic diseases, a recent review. Asian Pc J Allergy Immunol. 2011;29:209-219.
- Scheinfeld N. Omalizumab. A recombinant humanized monoclonal IgE-blocking antibody. Dermatol Online J. 2005;11:2.
- Lowe PJ, Georgiou P, Canvin J. Revision of omalizumab dosing table for dosing every 4 instead of 2 weeks for specific ranges of bodyweight and baseline IgE [published online ahead of print December 8, 2014]. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015;71:68-77.
- Vigo PG, Girgis KR, Pfuetze BL, et al. Efficacy of anti-IgE therapy in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:168-170.
- Hanifin J, Chan S. Biochemical and immunologic mechanisms in atopic dermatitis: new targets for emerging therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:72-77.
To the Editor:
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common skin condition with an increasing prevalence, affecting up to 20% of children and 3% of adults.1,2 More than 80% of patients with AD have elevated IgE levels.3,4 IgE modulates the inflammatory response in AD in several ways including “a biphasic immediate/late phase reaction, allergen presentation by IgE-bearing Langerhans cells, allergen-induced activation of IgE-bearing macrophages, and IgE autoreactivity to human proteins.”5 Historically, most therapies have focused on mitigating the allergic symptoms caused by degranulated effector cells, such as antihistamines. However, a new class of biologically engineered medications (eg, anti-IgE [omalizumab]) aim to prevent the initiation of the allergic response.6 Variable success has been reported using omalizumab in the treatment of AD, though the majority of studies have shown improvement, especially when used in combination with conventional therapies.4,5,7-22 Omalizumab dosage is determined by body weight and pretreatment serum total IgE levels and is administered via subcutaneous injections every 2 to 4 weeks.6,7,23-26 However, the dosing tables are based on asthma therapy, in which serum IgE levels may be much lower than chronic AD,7,24 and the appropriate dosage in AD patients with markedly elevated IgE is unclear. We report an interesting case of a 57-year-old man with erythroderma from long-standing severe chronic AD that was unresponsive to conventional therapy as well as an associated serum IgE level of 17,183 IU/mL who dramatically improved when omalizumab was added to his treatment regimen.
A 57-year-old man presented with essentially 100% body surface area involvement of AD with erythroderma and pruritus. Severe AD developed at infancy and cleared at 5 years of age; childhood onset of asthma was responsive to theophylline and oral inhalers. He developed recurrent AD and asthma at 38 years of age, which was progressive and developed into severe recalcitrant erythroderma by 50 years of age. His AD was unresponsive to multiple therapies, including topical steroids, antibiotics, tacrolimus, bleach baths, antihistamines, methotrexate (15 mg weekly for 1 year, then 12.5 mg weekly for 6 months), UVB phototherapy, and psoralen plus UVA photochemotherapy. He had minimal improvement with cyclosporine (200 mg daily for 4 weeks) and mycophenolate mofetil (3 g daily), and required systemic steroids for relief. The skin was violaceous and lichenified (Figure, A). Laboratory studies were normal, except for a serum IgE level of 17,183 IU/mL (reference range, <150 IU/mL) and peripheral blood eosinophilia up to 29.8% (reference range, 1%–5%) of the differential. Skin biopsies showed AD progressing to lichen simplex chronicus. Omalizumab was added to the therapeutic regimen at a dose of 375 mg every 2 weeks, with noticeable improvement after 3 months. The patient had approximately 80% to 90% clearing with resolution of erythroderma and pruritus, and only limited residual lichenification (Figure, B). The mycophenolate was tapered slowly, and the patient experienced a mild flare at 1 g daily. He is presently on 1 g of mycophenolate daily and omalizumab (375 mg every 2 weeks) and remains remarkably improved. His IgE level decreased to 11,983 IU/mL.

Omalizumab is a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that specifically binds to the FcεRI domain of serum IgE. It blocks binding to high-affinity receptors on effector cells, primarily mast cells, basophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells; it also decreases free IgE serum levels and downregulates the IgE receptor.4,6-10,23-25,27,28 Currently, omalizumab is US Food and Drug Administration approved for moderate to severe persistent asthma in patients 6 years or older with a positive aeroallergen skin test and IgE levels up to 700 IU/mL.6,7,23-25,27,28
However, scattered case reports and small case series have described variable success in the treatment of severe AD that is unresponsive to conventional therapy in patients with markedly elevated serum IgE levels.4,5,7-22 The majority of patients (approximately 80% of published cases yielded by a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms omalizumab and atopic dermatitis) showed improvement when measured by clinical severity scores and quality of life improvement, especially when used in conjunction with conventional therapy. Possible reasons for reported treatment failure include insufficient dosage, lack of established treatment guidelines for markedly elevated serum IgE levels, severity of disease, or variable response with failure to lower IgE level below a required threshold.7,9,23,24,27
Krathen and Hsu9 reported treatment failure with omalizumab for AD in 3 patients with serum IgE levels ranging from 5440 and 24,400 IU/mL, and one review indicated omalizumab may work best in patients with only moderately elevated serum IgE levels.21 However, Toledo et al18 reported efficacy of low-dose omalizumab for pretreatment IgE levels up to 30,000 IU/mL in 6 of 11 reported cases. The pretreatment serum IgE level is not predictive of response, and lowering the serum IgE level without normalization can be efficacious,12,23 as in the current case. Serum IgE levels are not used for monitoring therapeutic response or calculating future dosing, given potential increases in serum IgE levels during and after therapy (for up to 12 months) secondary to the formation of anti-IgE:IgE complexes.6,28 Omalizumab appears most effective when used in combination with conventional therapies. Hopefully ongoing studies will further elucidate the role of omalizumab in recalcitrant AD with elevated serum IgE levels.
To the Editor:
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common skin condition with an increasing prevalence, affecting up to 20% of children and 3% of adults.1,2 More than 80% of patients with AD have elevated IgE levels.3,4 IgE modulates the inflammatory response in AD in several ways including “a biphasic immediate/late phase reaction, allergen presentation by IgE-bearing Langerhans cells, allergen-induced activation of IgE-bearing macrophages, and IgE autoreactivity to human proteins.”5 Historically, most therapies have focused on mitigating the allergic symptoms caused by degranulated effector cells, such as antihistamines. However, a new class of biologically engineered medications (eg, anti-IgE [omalizumab]) aim to prevent the initiation of the allergic response.6 Variable success has been reported using omalizumab in the treatment of AD, though the majority of studies have shown improvement, especially when used in combination with conventional therapies.4,5,7-22 Omalizumab dosage is determined by body weight and pretreatment serum total IgE levels and is administered via subcutaneous injections every 2 to 4 weeks.6,7,23-26 However, the dosing tables are based on asthma therapy, in which serum IgE levels may be much lower than chronic AD,7,24 and the appropriate dosage in AD patients with markedly elevated IgE is unclear. We report an interesting case of a 57-year-old man with erythroderma from long-standing severe chronic AD that was unresponsive to conventional therapy as well as an associated serum IgE level of 17,183 IU/mL who dramatically improved when omalizumab was added to his treatment regimen.
A 57-year-old man presented with essentially 100% body surface area involvement of AD with erythroderma and pruritus. Severe AD developed at infancy and cleared at 5 years of age; childhood onset of asthma was responsive to theophylline and oral inhalers. He developed recurrent AD and asthma at 38 years of age, which was progressive and developed into severe recalcitrant erythroderma by 50 years of age. His AD was unresponsive to multiple therapies, including topical steroids, antibiotics, tacrolimus, bleach baths, antihistamines, methotrexate (15 mg weekly for 1 year, then 12.5 mg weekly for 6 months), UVB phototherapy, and psoralen plus UVA photochemotherapy. He had minimal improvement with cyclosporine (200 mg daily for 4 weeks) and mycophenolate mofetil (3 g daily), and required systemic steroids for relief. The skin was violaceous and lichenified (Figure, A). Laboratory studies were normal, except for a serum IgE level of 17,183 IU/mL (reference range, <150 IU/mL) and peripheral blood eosinophilia up to 29.8% (reference range, 1%–5%) of the differential. Skin biopsies showed AD progressing to lichen simplex chronicus. Omalizumab was added to the therapeutic regimen at a dose of 375 mg every 2 weeks, with noticeable improvement after 3 months. The patient had approximately 80% to 90% clearing with resolution of erythroderma and pruritus, and only limited residual lichenification (Figure, B). The mycophenolate was tapered slowly, and the patient experienced a mild flare at 1 g daily. He is presently on 1 g of mycophenolate daily and omalizumab (375 mg every 2 weeks) and remains remarkably improved. His IgE level decreased to 11,983 IU/mL.

Omalizumab is a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that specifically binds to the FcεRI domain of serum IgE. It blocks binding to high-affinity receptors on effector cells, primarily mast cells, basophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells; it also decreases free IgE serum levels and downregulates the IgE receptor.4,6-10,23-25,27,28 Currently, omalizumab is US Food and Drug Administration approved for moderate to severe persistent asthma in patients 6 years or older with a positive aeroallergen skin test and IgE levels up to 700 IU/mL.6,7,23-25,27,28
However, scattered case reports and small case series have described variable success in the treatment of severe AD that is unresponsive to conventional therapy in patients with markedly elevated serum IgE levels.4,5,7-22 The majority of patients (approximately 80% of published cases yielded by a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms omalizumab and atopic dermatitis) showed improvement when measured by clinical severity scores and quality of life improvement, especially when used in conjunction with conventional therapy. Possible reasons for reported treatment failure include insufficient dosage, lack of established treatment guidelines for markedly elevated serum IgE levels, severity of disease, or variable response with failure to lower IgE level below a required threshold.7,9,23,24,27
Krathen and Hsu9 reported treatment failure with omalizumab for AD in 3 patients with serum IgE levels ranging from 5440 and 24,400 IU/mL, and one review indicated omalizumab may work best in patients with only moderately elevated serum IgE levels.21 However, Toledo et al18 reported efficacy of low-dose omalizumab for pretreatment IgE levels up to 30,000 IU/mL in 6 of 11 reported cases. The pretreatment serum IgE level is not predictive of response, and lowering the serum IgE level without normalization can be efficacious,12,23 as in the current case. Serum IgE levels are not used for monitoring therapeutic response or calculating future dosing, given potential increases in serum IgE levels during and after therapy (for up to 12 months) secondary to the formation of anti-IgE:IgE complexes.6,28 Omalizumab appears most effective when used in combination with conventional therapies. Hopefully ongoing studies will further elucidate the role of omalizumab in recalcitrant AD with elevated serum IgE levels.
- Schultz-Larsen F, Diepgen T, Svennson A. The occurrence of atopic dermatitis in north Europe: an international questionnaire study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:760-764.
- Laughter D, Istvan JA, Tofte SJ, et al. The presence of atopic dermatitis in Oregon schoolchildren. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:649-655.
- Jones HE, Inouye JC, McGerity JL, et al. Atopic disease and serum immunoglobulin-E. Br J Dermatol. 1975;92:17-25.
- Abramovits W. A clinician’s paradigm in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53(1, suppl 1):570-577.
- Leung D, Soter N. Cellular and immunologic mechanisms in atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44(suppl):S1-S12.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Briefing document on safety. Omalizumab (Xolair) (recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody to IgE) for treatment of allergic asthma. http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/03/briefing/3952B1_02_FDA-Xolair-Safety.pdf. Published April 18, 2003. Accessed June 23, 2014.
- Lane JE, Cheyney JM, Lane TN, et al. Treatment of recalcitrant atopic dermatitis with omalizumab. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:68-72.
- Caruso C, Gaeta F, Valluzzi RL, et al. Omalizumab efficacy in a girl with atopic eczema. Allergy. 2010;65:278-279.
- Krathen RA, Hsu S. Failure of omalizumab for the treatment of severe atopic dermatitis. J Am Dermatol. 2005;53:338-340.
- Fernández-Antón Martínez MC, Leis-Dosil V, Alfageme-Roldán F, et al. Omalizumab for the treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2012;103:624-628.
- Pelaia G, Gallelli L, Romeo P, et al. Omalizumab decreases exacerbation frequency, oral intake of corticosteroids and peripheral blood eosinophils in atopic patients with uncontrolled asthma. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011;49:713-721.
- Belloni B, Ziai M, Lim A, et al. Low-dose anti-IgE therapy in patients with atopic eczema with high serum IgE levels. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120:1223-1225.
- Park SY, Choi MR, Na JI, et al. Recalcitrant atopic dermatitis treated with omalizumab. Ann Dermatol. 2010;22:349-352.
- Velling P, Skowasch D, Pabst S. Improvement of quality of life in patients with concomitant allergic asthma and atopic dermatitis: one year follow-up of omalizumab therapy. Eur J Med Res. 2011;15:407-410.
- Amrol D. Anti-immunoglobulin E in the treatment of refractory atopic dermatitis. South Med J. 2010;103:554-558.
- Heil PM, Maurer D, Klein B, et al. Omalizumab therapy in atopic dermatitis: depletion of IgE does not improve the clinical course-a randomized, placebo-controlled and double blind study. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:990-998.
- Ramírez del Pozo ME, Contreras Contreras E, López Tiro J, et al. Omalizumab (anti-IgE antibody) in the treatment of severe atopic dermatitis. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2011;21:416-417.
- Toledo F, Silvestre JF, Muñoz C. Combined therapy with low-dose omalizumab and intravenous immunoglobulin for severe atopic dermatitis: report of four cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1325-1327.
- Sheinkopf LE, Rafi AW, Katz RM. Efficacy of omalizumab in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: a pilot study. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008;29:530-537.
- Incorvia C, Pravettoni C, Mauro M, et al. Effectiveness of omalizumab in a patient with severe asthma and atopic dermatitis. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2008:69:78-80.
- Schmitt J, Schäkel K. Omalizumab as a therapeutic option in atopic eczema. Current evidence and potential benefit [in German]. Hautarzt. 2007;58:130-132.
- Thaiwat S, Sangasapaviliya A. Omalizumab treatment in severe atopic dermatitis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2011;29:357-360.
- Kopp MV. Omalizumab: anti-IgE therapy in allergy. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011;11:101-106.
- Vichyanond P. Omalizumab in allergic diseases, a recent review. Asian Pc J Allergy Immunol. 2011;29:209-219.
- Scheinfeld N. Omalizumab. A recombinant humanized monoclonal IgE-blocking antibody. Dermatol Online J. 2005;11:2.
- Lowe PJ, Georgiou P, Canvin J. Revision of omalizumab dosing table for dosing every 4 instead of 2 weeks for specific ranges of bodyweight and baseline IgE [published online ahead of print December 8, 2014]. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015;71:68-77.
- Vigo PG, Girgis KR, Pfuetze BL, et al. Efficacy of anti-IgE therapy in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:168-170.
- Hanifin J, Chan S. Biochemical and immunologic mechanisms in atopic dermatitis: new targets for emerging therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:72-77.
- Schultz-Larsen F, Diepgen T, Svennson A. The occurrence of atopic dermatitis in north Europe: an international questionnaire study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:760-764.
- Laughter D, Istvan JA, Tofte SJ, et al. The presence of atopic dermatitis in Oregon schoolchildren. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:649-655.
- Jones HE, Inouye JC, McGerity JL, et al. Atopic disease and serum immunoglobulin-E. Br J Dermatol. 1975;92:17-25.
- Abramovits W. A clinician’s paradigm in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53(1, suppl 1):570-577.
- Leung D, Soter N. Cellular and immunologic mechanisms in atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44(suppl):S1-S12.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Briefing document on safety. Omalizumab (Xolair) (recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody to IgE) for treatment of allergic asthma. http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/03/briefing/3952B1_02_FDA-Xolair-Safety.pdf. Published April 18, 2003. Accessed June 23, 2014.
- Lane JE, Cheyney JM, Lane TN, et al. Treatment of recalcitrant atopic dermatitis with omalizumab. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:68-72.
- Caruso C, Gaeta F, Valluzzi RL, et al. Omalizumab efficacy in a girl with atopic eczema. Allergy. 2010;65:278-279.
- Krathen RA, Hsu S. Failure of omalizumab for the treatment of severe atopic dermatitis. J Am Dermatol. 2005;53:338-340.
- Fernández-Antón Martínez MC, Leis-Dosil V, Alfageme-Roldán F, et al. Omalizumab for the treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2012;103:624-628.
- Pelaia G, Gallelli L, Romeo P, et al. Omalizumab decreases exacerbation frequency, oral intake of corticosteroids and peripheral blood eosinophils in atopic patients with uncontrolled asthma. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011;49:713-721.
- Belloni B, Ziai M, Lim A, et al. Low-dose anti-IgE therapy in patients with atopic eczema with high serum IgE levels. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120:1223-1225.
- Park SY, Choi MR, Na JI, et al. Recalcitrant atopic dermatitis treated with omalizumab. Ann Dermatol. 2010;22:349-352.
- Velling P, Skowasch D, Pabst S. Improvement of quality of life in patients with concomitant allergic asthma and atopic dermatitis: one year follow-up of omalizumab therapy. Eur J Med Res. 2011;15:407-410.
- Amrol D. Anti-immunoglobulin E in the treatment of refractory atopic dermatitis. South Med J. 2010;103:554-558.
- Heil PM, Maurer D, Klein B, et al. Omalizumab therapy in atopic dermatitis: depletion of IgE does not improve the clinical course-a randomized, placebo-controlled and double blind study. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010;8:990-998.
- Ramírez del Pozo ME, Contreras Contreras E, López Tiro J, et al. Omalizumab (anti-IgE antibody) in the treatment of severe atopic dermatitis. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2011;21:416-417.
- Toledo F, Silvestre JF, Muñoz C. Combined therapy with low-dose omalizumab and intravenous immunoglobulin for severe atopic dermatitis: report of four cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1325-1327.
- Sheinkopf LE, Rafi AW, Katz RM. Efficacy of omalizumab in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: a pilot study. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008;29:530-537.
- Incorvia C, Pravettoni C, Mauro M, et al. Effectiveness of omalizumab in a patient with severe asthma and atopic dermatitis. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2008:69:78-80.
- Schmitt J, Schäkel K. Omalizumab as a therapeutic option in atopic eczema. Current evidence and potential benefit [in German]. Hautarzt. 2007;58:130-132.
- Thaiwat S, Sangasapaviliya A. Omalizumab treatment in severe atopic dermatitis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2011;29:357-360.
- Kopp MV. Omalizumab: anti-IgE therapy in allergy. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011;11:101-106.
- Vichyanond P. Omalizumab in allergic diseases, a recent review. Asian Pc J Allergy Immunol. 2011;29:209-219.
- Scheinfeld N. Omalizumab. A recombinant humanized monoclonal IgE-blocking antibody. Dermatol Online J. 2005;11:2.
- Lowe PJ, Georgiou P, Canvin J. Revision of omalizumab dosing table for dosing every 4 instead of 2 weeks for specific ranges of bodyweight and baseline IgE [published online ahead of print December 8, 2014]. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015;71:68-77.
- Vigo PG, Girgis KR, Pfuetze BL, et al. Efficacy of anti-IgE therapy in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:168-170.
- Hanifin J, Chan S. Biochemical and immunologic mechanisms in atopic dermatitis: new targets for emerging therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:72-77.
Practice Points
- Omalizumab can be effective in treating patients with severe recalcitrant atopic dermatitis with markedly elevated serum IgE.
- Omalizumab appears most effective when used in combination with conventional therapies.