User login
Veterans who interact with the criminal justice system (ie, justice-involved veterans) have heightened rates of mental health and psychosocial needs, including posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), substance use disorder, depression, suicidal ideation and attempt, and homelessness.1,2 Alongside these criminogenic risk factors, recidivism is common among justice-involved veterans: About 70% of incarcerated veterans disclosed at least one prior incarceration.3
To address the complex interplay of psychosocial factors, mental health concerns, and justice involvement among veterans, veterans treatment courts (VTCs) emerged as an alternative to incarceration.4 VTC participation often consists of integrated treatment and rehabilitative services (eg, vocational training, health care), ongoing monitoring for substance use, graduated responses to address treatment adherence, and ongoing communication with the judge and legal counsel.4
A primary aim of these courts is to address psychosocial needs believed to underlie criminal behavior, thus reducing risk of recidivism and promoting successful recovery and community integration for eligible veterans. To do so, VTCs collaborate with community-based and/or US Department of Veterans Affairs services, such as the Veterans Justice Outreach program (VJO). VJO specialists identify and refer justice-involved veterans to Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and community care and serve as a liaison between VTC staff and VHA health care professionals (HCPs).5
VTC outcome studies highlight the importance of not only diverting veterans to problem-solving courts, but also ensuring their optimal participation. Successful graduates of VTC programs demonstrate significant improvements in mental health symptoms, life satisfaction, and social support, as well as lower rates of law enforcement interactions.6,7 However, less is known about supporting those veterans who have difficulty engaging in VTCs and either discontinue participation or require lengthier periods of participation to meet court graduation requirements.8 One possibility to improve engagement among these veterans is to enhance court practices to best meet their needs.
In addition to delivering treatment, VHA mental health professionals may serve a critical interdisciplinary role by lending expertise to support VTC practices. For example, equipping court professionals with clinical knowledge and skills related to motivation may strengthen the staff’s interactions with participants, enabling them to address barriers as they arise and to facilitate veterans’ treatment adherence. Additionally, responsiveness to the impact of trauma exposure, which is common among this population, may prove important as related symptoms can affect veterans’ engagement, receptivity, and behavior in court settings. Indeed, prior examinations of justice-involved veterans have found trauma exposure rates ranging from 60% to 90% and PTSD rates ranging from 27% to 40%.1,2 Notably, involvement with the justice system (eg, incarceration) may itself further increase risk of trauma exposure (eg, experiencing a physical or sexual assault in prison) or exacerbate existing PTSD.9 Nonetheless, whereas many drug courts and domestic violence courts have been established, problem-solving courts with a specialized focus on trauma exposure remain rare, suggesting a potential gap in court training.
VHA HCPs have the potential to facilitate justice-involved veterans’ successful court and treatment participation by coordinating with VJO specialists to provide training and consultation to the courts. Supporting efforts to effectively and responsively address criminogenic risk (eg, mental health) in VTC settings may in turn reduce the likelihood of recidivism.10 Given the elevated rates of trauma exposure among justice-involved veterans and the relative lack of trauma-focused VTCs, we developed a trauma-informed training for VTC professionals that centered on related clinical presentations of justice-involved veterans and frequently occurring challenges in the context of court participation.
Program Development
This educational program aimed to (1) provide psychoeducation on trauma exposure, PTSD, and existing evidence-based treatments; (2) present clinical considerations for justice-involved veterans related to trauma exposure and/or PTSD; and (3) introduce skills to facilitate effective communication and trauma-informed care practices among professionals working with veterans in a treatment court.
Prior to piloting the program, we conducted a needs assessment with VTC professionals and identified relevant theoretical constructs and brief interventions for inclusion in the training. Additionally, given the dearth of prior research on mental health education for VTCs, the team consulted with the developers of PTSD 101, a VHA workshop for veterans’ families that promotes psychoeducation, support, and effective communication.11 Doing so informed approaches to delivering education to nonclinical audiences that interact with veterans with histories of trauma exposure. As this was a program development project, it was determined to be exempt from institutional review board review.
Needs Assessment
In the initial stages of development, local VJO specialists identified regional VTCs and facilitated introductions to these courts. Two of the 3 Rocky Mountain region VTCs that were contacted expressed interest in receiving trauma-informed training. Based on preliminary interest, the facilitators conducted a needs assessment with VJO and VTC staff from these 2 courts to capture requests for specific content and past experiences with other mental health trainings.
Guided by the focus group model, the needs assessments took place during three 1-hour meetings with VJO specialists and a 1-hour meeting with VJO specialists, VTC professionals, and community-based clinical partners.12 Additionally, attending a VTC graduation and court session allowed for observations of court practices and interactions with veterans. A total of 13 professionals (judges, court coordinators, case managers, peer mentors, VJO specialists, and clinicians who specialize in substance use disorder and intimate partner violence) participated in the needs assessments.
The most critical need identified by court professionals was a focus on how to apply knowledge about trauma and PTSD to interactions with justice-involved veterans. This was reportedly absent from prior training sessions the courts had received. Both Rocky Mountain region VTCs expressed a strong interest in and openness to adapting practices based on research and practice recommendations. Additional requests that emerged included a refresher on psychoeducation related to trauma and how to address the personal impact of working with this population (eg, compassion fatigue).
Training Components
Based on the needs identified by VTC professionals and informed by consultation with the developers of PTSD 101,
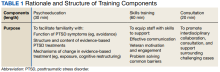
Psychoeducation. The initial portion of the training consisted of psychoeducation to increase VTC staff familiarity with the distinctions between trauma exposure and a formal diagnosis of PTSD, mechanisms underlying PTSD, and evidence-based treatment. To deepen conceptual understanding of trauma and PTSD beyond an overview of criteria set forth in The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), psychoeducation centered on the drivers of avoidance (eg, short-term benefit vs long-term consequences), behaviors that often facilitate avoidance (eg, substance use), functions underlying these behaviors (eg, distress reduction), and structure and mechanisms of change in evidence-based treatments for PTSD, including cognitive processing therapy and prolonged exposure.13,14
Fostering court familiarity with cognitive processing therapy and prolonged exposure may bolster veteran engagement in treatment through regular reinforcement of skills and concepts introduced in therapy. This may prove particularly salient given the limited engagement with mental health treatment and elevated dropout rates from PTSD treatment among the general veteran population.15,16
Exercises and metaphors were used to illustrate concepts in multiple ways. For example, training attendees engaged in a “stop, drop, and roll” thought exercise in which they were asked to brainstorm behavioral reactions to catching on fire. This exercise illustrated the tendency for individuals to revert to common yet unhelpful attempts at problem solving (eg, running due to panic, which would exacerbate the fire), particularly in crisis and without prior education regarding adaptive ways to respond. Attendee-generated examples, such as running, were used to demonstrate the importance of practicing and reinforcing skill development prior to a crisis, to ensure proficiency and optimal response. Additionally, in prompting consideration of one’s response tendencies, this exercise may engender empathy and understanding for veterans.
Skills training. Efforts to promote veteran engagement in court, facilitate motivation and readiness for change, and address barriers that arise (eg, distress associated with court appearances) may support successful and timely graduation. As such, skills training constituted the largest component of the training and drew from observations of court practices and the VTCs’ identified challenges. Consistent with the project’s aims and reported needs of the court, skills that target common presentations following trauma exposure (eg, avoidance, hypervigilance) were prioritized for this pilot training. Strategies included brief interventions from dialectical behavior therapy, acceptance and commitment therapy, and motivational interviewing to strengthen the support provided by staff to veterans and address their needs (Table 2).
Training attendees also participated in exercises to reiterate skills. For example, attendees completed an ambivalence matrix using an audience-identified common behavior that is difficult to change (eg, heavy alcohol use as a coping mechanism for distress).
Attendees engaged in an exercise that involved identifying unhelpful thoughts and behaviors, targets for validation, and veteran strengths from a hypothetical case vignette. This vignette involved a VTC participant who initially engaged effectively but began to demonstrate difficulty appropriately engaging in court and mental health treatment as well as challenging interactions with VTC staff (eg, raised voice during court sessions, not respecting communication boundaries).
Pilot Test
Based on scheduling parameters communicated by court coordinators, the pilot training was designed as a presentation during times reserved for court staffing meetings. To accommodate court preferences due to the COVID-19 pandemic, one 90-minute training was conducted virtually in March 2022, and the other training was conducted in person in April 2022 for 2 hours. The trainings were facilitated by 2 VHA clinical psychologists and included the judge, court coordinator, VJO specialist, peer mentors, case managers, probation/parole officers, and community-based HCPs who partner with the court (eg, social workers, psychologists). About 12 to 15 professionals attended each training session.
Feedback
Feedback was solicited from attendees via an anonymous online survey. Seven participants completed the survey; the response rate of about 20% was consistent with those observed for other surveys of court professionals.20 Many attendees also provided feedback directly to the facilitators. Feedback highlighted that the skills-based components not only were perceived as most helpful but also notably distinguished this training. “What set this training apart from other training events was the practical applications,” one attendee noted. “It was not just information or education, both instructors did an incredible job of explaining exactly how we could apply the knowledge they were sharing. They did this in such a way that it was easy to understand and apply.”
Specific skills were consistently identified as helpful, including managing intense emotions, addressing ambivalence, and approaching sanctions and rewards. Additionally, employing a less formal approach to the training, with relatable overviews of concepts and immediate responsiveness to requests for expansion on a topic, was perceived as a unique benefit: Another attendee appreciated that “It was beneficial to sit around a table with a less formal presentation and be able to ask questions.” This approach seemed particularly well suited for the program’s cross-disciplinary audience. Attendees reported that they valued the relatively limited focus on DSM-5 criteria. Attendees emphasized that education specific to veterans on evidence-based PTSD treatments, psychoeducation, and avoidance was very helpful. Respondents also recommended that the training be lengthened to a daylong workshop to accommodate greater opportunity to practice skills and consultation.
The consultation portion of the training provided insight into additional areas of importance to incorporate into future iterations. Identified needs included appropriate and realistic boundary setting (eg, addressing disruptions in the courtroom), suggestions for improving and expanding homework assigned by the court, and ways to address concerns about PTSD treatment shared by veterans in court (eg, attributing substance use relapses to the intensiveness of trauma-focused treatment vs lack of familiarity with alternate coping skills). Additionally, the VTC professionals’ desire to support mental health professionals’ work with veterans was clearly evident, highlighting the bidirectional value of interdisciplinary collaboration between VHA mental health professionals and VTC professionals.
Discussion
A trauma-informed training was developed and delivered to 2 VTCs in the Rocky Mountain region with the goal of providing relevant psychoeducation and introducing skills to bolster court practices that address veteran needs. Psychoeducational components of the training that were particularly well received and prompted significant participant engagement included discussions and examples of avoidance, levels of validation, language to facilitate motivation and address barriers, mechanisms underlying treatment, and potential functions underlying limited veteran treatment engagement. Distress tolerance, approaches to sanctions and rewards, and use of ambivalence matrices to guide motivation were identified as particularly helpful skills.
The pilot phase of this trauma-informed training provided valuable insights into developing mental health trainings for VTCs. Specifically, VTCs may benefit from the expertise of VHA HCPs and are particularly interested in learning brief skills to improve their practices. The usefulness of such trainings may be bolstered by efforts to form relationships with the court to identify their perceived needs and employing an iterative process that is responsive to feedback both during and after the training. Last, each stage of this project was strengthened by collaboration with VJO specialists, highlighting the importance of future collaboration between VJO and VHA mental health clinics to further support justice-involved veterans. For example, VJO specialists were instrumental in identifying training needs related to veterans’ clinical presentations in court, facilitating introductions to local VTCs, and helping to address barriers to piloting, like scheduling.
Modifications and Future Directions
The insights gained through the process of training design, delivery, and feedback inform future development of this training. Based on the feedback received, subsequent versions of the training may be expanded into a half- or full-day workshop to allow for adequate time for skills training and feedback, as well as consultation. Doing so will enable facilitators to further foster attendees’ familiarity with and confidence in their ability to use these skills. Furthermore, the consultation portion of this training revealed areas that may benefit from greater attention, including how to address challenging interactions in court (eg, addressing gender dynamics between court professionals and participants) and better support veterans who are having difficulty engaging in mental health treatment (eg, courts’ observation of high rates of dropout around the third or fourth session of evidence-based treatment for PTSD). Last, all attendees who responded to the survey expressed interest in a brief resource guide based on the training, emphasizing the need for ready access to key skills and concepts to support the use of strategies learned.
An additional future aim of this project is to conduct a more thorough evaluation of the needs and outcomes related to this trauma-informed training for VTC professionals. With the rapid growth of VTCs nationwide, relatively little examination of court processes and practices has occurred, and there is a lack of research on the development or effectiveness of mental health trainings provided to VTCs.21 Therefore, we intend to conduct larger scale qualitative interviews with court personnel and VJO specialists to obtain a clearer understanding of the needs related to skills-based training and gaps in psychoeducation. These comprehensive needs assessments may also capture common comorbidities that were not incorporated into the pilot training (eg, substance use disorders) but may be important training targets for court professionals. This information will be used to inform subsequent expansion and adaptation of the training into a longer workshop. Program evaluation will be conducted via survey-based feedback on perceived usefulness of the workshop and self-report of confidence in and use of strategies to improve court practices. Furthermore, efforts to obtain veteran outcome data, such as treatment engagement and successful participation in VTC, may be pursued.
Limitations
This training development and pilot project provided valuable foundational information regarding a largely unexamined component of treatment courts—the benefit of skills-based trainings to facilitate court practices related to justice-involved veterans. However, it is worth noting that survey responses were limited; thus, the feedback received may not reflect all attendees’ perceptions. Additionally, because both training sessions were conducted solely with 2 courts in the Rocky Mountain area, feedback may be limited to the needs of this geographic region.
Conclusions
A trauma-informed training was developed for VTCs to facilitate relevant understanding of justice-involved veterans’ needs and presentations in court, introduce skills to address challenges that arise (eg, motivation, emotional dysregulation), and provide interdisciplinary support to court professionals. This training was an important step toward fostering strong collaborations between VHA HCPs and community-based veterans courts, and feedback received during development and following implementation highlighted the perceived need for a skills-based approach to such trainings. Further program development and evaluation can strengthen this training and provide a foundation for dissemination to a broader scope of VTCs, with the goal of reducing recidivism risk among justice-involved veterans by promoting effective engagement in problem-solving court.
1. Blodgett JC, Avoundjian T, Finlay AK, et al. Prevalence of mental health disorders among justice-involved veterans. Epidemiol Rev. 2015;37(1):163-176. doi:10.1093/epirev/mxu003
2. Saxon AJ, Davis TM, Sloan KL, McKnight KM, McFall ME, Kivlahan DR. Trauma, symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, and associated problems among incarcerated veterans. Psychiatr Serv. 2001;52(7):959-964. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.52.7.959
3. Bronson J, Carson AC, Noonan M. Veterans in prison and jail, 2011-12. December 2015. Accessed January 11, 2023. https://bjs.ojp.gov/content/pub/pdf/vpj1112.pdf
4. Cartwright T. “To care for him who shall have borne the battle”: the recent development of veterans treatment courts in America. Stanford Law Rev. 2011;22(1):295-316.
5. Finlay AK, Smelson D, Sawh L, et al. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Justice Outreach Program: connecting justice-involved veterans with mental health and substance use disorder Treatment. Crim Justice Policy Rev. 2016;27(2):10.1177/0887403414562601. doi:10.1177/0887403414562601
6. Knudsen KJ, Wingenfeld S. A specialized treatment court for veterans with trauma exposure: implications for the field. Community Ment Health J. 2016;52(2):127-135. doi:10.1007/s10597-015-9845-9
7. Montgomery LM, Olson JN. Veterans treatment court impact on veteran mental health and life satisfaction. J Psychol Behav Sci. 2018;6(1):1-4. doi:10.15640/jpbs.v6n1a1
8. Tsai J, Finlay A, Flatley B, Kasprow WJ, Clark S. A national study of veterans treatment court participants: who benefits and who recidivates. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2018;45(2):236-244. doi:10.1007/s10488-017-0816-z
9. Wolff NL, Shi J. Trauma and incarcerated persons. In: Scott CL, ed. Handbook of Correctional Mental Health. American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.; 2010:277-320.
10. Bonta J, Andrews DA. Risk-need-responsivity model for offender assessment and rehabilitation. Rehabilitation. 2007;6:1-22. https://www.publicsafety.gc.ca/cnt/rsrcs/pblctns/rsk-nd-rspnsvty/index-en.aspx
11. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Mental Health and Suicide Prevention, Family Services Section; Caska-Wallace CM, Campbell SB, Glynn SM. PTSD 101 for family and friends: a support and education workshop. 2020.
12. Tipping J. Focus groups: a method of needs assessment. J Contin Educ Health Prof. 1998;18(3):150-154. doi:10.1002/chp.1340180304
13. Resick PA, Monson CM, Chard KM. Cognitive Processing Therapy for PTSD: A Comprehensive Manual. The Guilford Press; 2017.
14. Foa EB, Hembree EA, Rothbaum BO. Prolonged Exposure Therapy for PTSD: Emotional Processing of Traumatic Experiences: Therapist Guide. Oxford University Press; 2007. doi:10.1093/med:psych/9780195308501.001.0001
15. Seal KH, Maguen S, Cohen B, et al. VA mental health services utilization in Iraq and Afghanistan veterans in the first year of receiving new mental health diagnoses. J Trauma Stress. 2010;23(1):5-16. doi:10.1002/jts.20493
16. Edwards-Stewart A, Smolenski DJ, Bush NE, et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder treatment dropout among military and veteran populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Trauma Stress. 2021;34(4):808-818. doi:10.1002/jts.22653
17. Linehan MM. Dialectical Behavior Therapy Skills Training Manual. 2nd ed. Guildford Press; 2015.
18. Hayes SC, Strosahl KD, Wilson KG. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy: The Process and Practice of Mindful Change. 2nd ed. Guildford Press; 2016.
19. Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational Interviewing: Preparing People for Change. 2nd ed. The Guildford Press; 2002.
20. National Center for State Courts. A survey of members of major national court organizations. October 2010. Accessed January 11, 2023. https://www.ncsc.org/__data/assets/pdf_file/0015/16350/survey-summary-10-26.pdf
21. Baldwin JM, Brooke EJ. Pausing in the wake of rapid adoption: a call to critically examine the veterans treatment court concept. J Offender Rehabil. 2019;58(1):1-29. doi:10.1080/10509674.2018.1549181
Veterans who interact with the criminal justice system (ie, justice-involved veterans) have heightened rates of mental health and psychosocial needs, including posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), substance use disorder, depression, suicidal ideation and attempt, and homelessness.1,2 Alongside these criminogenic risk factors, recidivism is common among justice-involved veterans: About 70% of incarcerated veterans disclosed at least one prior incarceration.3
To address the complex interplay of psychosocial factors, mental health concerns, and justice involvement among veterans, veterans treatment courts (VTCs) emerged as an alternative to incarceration.4 VTC participation often consists of integrated treatment and rehabilitative services (eg, vocational training, health care), ongoing monitoring for substance use, graduated responses to address treatment adherence, and ongoing communication with the judge and legal counsel.4
A primary aim of these courts is to address psychosocial needs believed to underlie criminal behavior, thus reducing risk of recidivism and promoting successful recovery and community integration for eligible veterans. To do so, VTCs collaborate with community-based and/or US Department of Veterans Affairs services, such as the Veterans Justice Outreach program (VJO). VJO specialists identify and refer justice-involved veterans to Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and community care and serve as a liaison between VTC staff and VHA health care professionals (HCPs).5
VTC outcome studies highlight the importance of not only diverting veterans to problem-solving courts, but also ensuring their optimal participation. Successful graduates of VTC programs demonstrate significant improvements in mental health symptoms, life satisfaction, and social support, as well as lower rates of law enforcement interactions.6,7 However, less is known about supporting those veterans who have difficulty engaging in VTCs and either discontinue participation or require lengthier periods of participation to meet court graduation requirements.8 One possibility to improve engagement among these veterans is to enhance court practices to best meet their needs.
In addition to delivering treatment, VHA mental health professionals may serve a critical interdisciplinary role by lending expertise to support VTC practices. For example, equipping court professionals with clinical knowledge and skills related to motivation may strengthen the staff’s interactions with participants, enabling them to address barriers as they arise and to facilitate veterans’ treatment adherence. Additionally, responsiveness to the impact of trauma exposure, which is common among this population, may prove important as related symptoms can affect veterans’ engagement, receptivity, and behavior in court settings. Indeed, prior examinations of justice-involved veterans have found trauma exposure rates ranging from 60% to 90% and PTSD rates ranging from 27% to 40%.1,2 Notably, involvement with the justice system (eg, incarceration) may itself further increase risk of trauma exposure (eg, experiencing a physical or sexual assault in prison) or exacerbate existing PTSD.9 Nonetheless, whereas many drug courts and domestic violence courts have been established, problem-solving courts with a specialized focus on trauma exposure remain rare, suggesting a potential gap in court training.
VHA HCPs have the potential to facilitate justice-involved veterans’ successful court and treatment participation by coordinating with VJO specialists to provide training and consultation to the courts. Supporting efforts to effectively and responsively address criminogenic risk (eg, mental health) in VTC settings may in turn reduce the likelihood of recidivism.10 Given the elevated rates of trauma exposure among justice-involved veterans and the relative lack of trauma-focused VTCs, we developed a trauma-informed training for VTC professionals that centered on related clinical presentations of justice-involved veterans and frequently occurring challenges in the context of court participation.
Program Development
This educational program aimed to (1) provide psychoeducation on trauma exposure, PTSD, and existing evidence-based treatments; (2) present clinical considerations for justice-involved veterans related to trauma exposure and/or PTSD; and (3) introduce skills to facilitate effective communication and trauma-informed care practices among professionals working with veterans in a treatment court.
Prior to piloting the program, we conducted a needs assessment with VTC professionals and identified relevant theoretical constructs and brief interventions for inclusion in the training. Additionally, given the dearth of prior research on mental health education for VTCs, the team consulted with the developers of PTSD 101, a VHA workshop for veterans’ families that promotes psychoeducation, support, and effective communication.11 Doing so informed approaches to delivering education to nonclinical audiences that interact with veterans with histories of trauma exposure. As this was a program development project, it was determined to be exempt from institutional review board review.
Needs Assessment
In the initial stages of development, local VJO specialists identified regional VTCs and facilitated introductions to these courts. Two of the 3 Rocky Mountain region VTCs that were contacted expressed interest in receiving trauma-informed training. Based on preliminary interest, the facilitators conducted a needs assessment with VJO and VTC staff from these 2 courts to capture requests for specific content and past experiences with other mental health trainings.
Guided by the focus group model, the needs assessments took place during three 1-hour meetings with VJO specialists and a 1-hour meeting with VJO specialists, VTC professionals, and community-based clinical partners.12 Additionally, attending a VTC graduation and court session allowed for observations of court practices and interactions with veterans. A total of 13 professionals (judges, court coordinators, case managers, peer mentors, VJO specialists, and clinicians who specialize in substance use disorder and intimate partner violence) participated in the needs assessments.
The most critical need identified by court professionals was a focus on how to apply knowledge about trauma and PTSD to interactions with justice-involved veterans. This was reportedly absent from prior training sessions the courts had received. Both Rocky Mountain region VTCs expressed a strong interest in and openness to adapting practices based on research and practice recommendations. Additional requests that emerged included a refresher on psychoeducation related to trauma and how to address the personal impact of working with this population (eg, compassion fatigue).
Training Components
Based on the needs identified by VTC professionals and informed by consultation with the developers of PTSD 101,
Psychoeducation. The initial portion of the training consisted of psychoeducation to increase VTC staff familiarity with the distinctions between trauma exposure and a formal diagnosis of PTSD, mechanisms underlying PTSD, and evidence-based treatment. To deepen conceptual understanding of trauma and PTSD beyond an overview of criteria set forth in The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), psychoeducation centered on the drivers of avoidance (eg, short-term benefit vs long-term consequences), behaviors that often facilitate avoidance (eg, substance use), functions underlying these behaviors (eg, distress reduction), and structure and mechanisms of change in evidence-based treatments for PTSD, including cognitive processing therapy and prolonged exposure.13,14
Fostering court familiarity with cognitive processing therapy and prolonged exposure may bolster veteran engagement in treatment through regular reinforcement of skills and concepts introduced in therapy. This may prove particularly salient given the limited engagement with mental health treatment and elevated dropout rates from PTSD treatment among the general veteran population.15,16
Exercises and metaphors were used to illustrate concepts in multiple ways. For example, training attendees engaged in a “stop, drop, and roll” thought exercise in which they were asked to brainstorm behavioral reactions to catching on fire. This exercise illustrated the tendency for individuals to revert to common yet unhelpful attempts at problem solving (eg, running due to panic, which would exacerbate the fire), particularly in crisis and without prior education regarding adaptive ways to respond. Attendee-generated examples, such as running, were used to demonstrate the importance of practicing and reinforcing skill development prior to a crisis, to ensure proficiency and optimal response. Additionally, in prompting consideration of one’s response tendencies, this exercise may engender empathy and understanding for veterans.
Skills training. Efforts to promote veteran engagement in court, facilitate motivation and readiness for change, and address barriers that arise (eg, distress associated with court appearances) may support successful and timely graduation. As such, skills training constituted the largest component of the training and drew from observations of court practices and the VTCs’ identified challenges. Consistent with the project’s aims and reported needs of the court, skills that target common presentations following trauma exposure (eg, avoidance, hypervigilance) were prioritized for this pilot training. Strategies included brief interventions from dialectical behavior therapy, acceptance and commitment therapy, and motivational interviewing to strengthen the support provided by staff to veterans and address their needs (Table 2).
Training attendees also participated in exercises to reiterate skills. For example, attendees completed an ambivalence matrix using an audience-identified common behavior that is difficult to change (eg, heavy alcohol use as a coping mechanism for distress).
Attendees engaged in an exercise that involved identifying unhelpful thoughts and behaviors, targets for validation, and veteran strengths from a hypothetical case vignette. This vignette involved a VTC participant who initially engaged effectively but began to demonstrate difficulty appropriately engaging in court and mental health treatment as well as challenging interactions with VTC staff (eg, raised voice during court sessions, not respecting communication boundaries).
Pilot Test
Based on scheduling parameters communicated by court coordinators, the pilot training was designed as a presentation during times reserved for court staffing meetings. To accommodate court preferences due to the COVID-19 pandemic, one 90-minute training was conducted virtually in March 2022, and the other training was conducted in person in April 2022 for 2 hours. The trainings were facilitated by 2 VHA clinical psychologists and included the judge, court coordinator, VJO specialist, peer mentors, case managers, probation/parole officers, and community-based HCPs who partner with the court (eg, social workers, psychologists). About 12 to 15 professionals attended each training session.
Feedback
Feedback was solicited from attendees via an anonymous online survey. Seven participants completed the survey; the response rate of about 20% was consistent with those observed for other surveys of court professionals.20 Many attendees also provided feedback directly to the facilitators. Feedback highlighted that the skills-based components not only were perceived as most helpful but also notably distinguished this training. “What set this training apart from other training events was the practical applications,” one attendee noted. “It was not just information or education, both instructors did an incredible job of explaining exactly how we could apply the knowledge they were sharing. They did this in such a way that it was easy to understand and apply.”
Specific skills were consistently identified as helpful, including managing intense emotions, addressing ambivalence, and approaching sanctions and rewards. Additionally, employing a less formal approach to the training, with relatable overviews of concepts and immediate responsiveness to requests for expansion on a topic, was perceived as a unique benefit: Another attendee appreciated that “It was beneficial to sit around a table with a less formal presentation and be able to ask questions.” This approach seemed particularly well suited for the program’s cross-disciplinary audience. Attendees reported that they valued the relatively limited focus on DSM-5 criteria. Attendees emphasized that education specific to veterans on evidence-based PTSD treatments, psychoeducation, and avoidance was very helpful. Respondents also recommended that the training be lengthened to a daylong workshop to accommodate greater opportunity to practice skills and consultation.
The consultation portion of the training provided insight into additional areas of importance to incorporate into future iterations. Identified needs included appropriate and realistic boundary setting (eg, addressing disruptions in the courtroom), suggestions for improving and expanding homework assigned by the court, and ways to address concerns about PTSD treatment shared by veterans in court (eg, attributing substance use relapses to the intensiveness of trauma-focused treatment vs lack of familiarity with alternate coping skills). Additionally, the VTC professionals’ desire to support mental health professionals’ work with veterans was clearly evident, highlighting the bidirectional value of interdisciplinary collaboration between VHA mental health professionals and VTC professionals.
Discussion
A trauma-informed training was developed and delivered to 2 VTCs in the Rocky Mountain region with the goal of providing relevant psychoeducation and introducing skills to bolster court practices that address veteran needs. Psychoeducational components of the training that were particularly well received and prompted significant participant engagement included discussions and examples of avoidance, levels of validation, language to facilitate motivation and address barriers, mechanisms underlying treatment, and potential functions underlying limited veteran treatment engagement. Distress tolerance, approaches to sanctions and rewards, and use of ambivalence matrices to guide motivation were identified as particularly helpful skills.
The pilot phase of this trauma-informed training provided valuable insights into developing mental health trainings for VTCs. Specifically, VTCs may benefit from the expertise of VHA HCPs and are particularly interested in learning brief skills to improve their practices. The usefulness of such trainings may be bolstered by efforts to form relationships with the court to identify their perceived needs and employing an iterative process that is responsive to feedback both during and after the training. Last, each stage of this project was strengthened by collaboration with VJO specialists, highlighting the importance of future collaboration between VJO and VHA mental health clinics to further support justice-involved veterans. For example, VJO specialists were instrumental in identifying training needs related to veterans’ clinical presentations in court, facilitating introductions to local VTCs, and helping to address barriers to piloting, like scheduling.
Modifications and Future Directions
The insights gained through the process of training design, delivery, and feedback inform future development of this training. Based on the feedback received, subsequent versions of the training may be expanded into a half- or full-day workshop to allow for adequate time for skills training and feedback, as well as consultation. Doing so will enable facilitators to further foster attendees’ familiarity with and confidence in their ability to use these skills. Furthermore, the consultation portion of this training revealed areas that may benefit from greater attention, including how to address challenging interactions in court (eg, addressing gender dynamics between court professionals and participants) and better support veterans who are having difficulty engaging in mental health treatment (eg, courts’ observation of high rates of dropout around the third or fourth session of evidence-based treatment for PTSD). Last, all attendees who responded to the survey expressed interest in a brief resource guide based on the training, emphasizing the need for ready access to key skills and concepts to support the use of strategies learned.
An additional future aim of this project is to conduct a more thorough evaluation of the needs and outcomes related to this trauma-informed training for VTC professionals. With the rapid growth of VTCs nationwide, relatively little examination of court processes and practices has occurred, and there is a lack of research on the development or effectiveness of mental health trainings provided to VTCs.21 Therefore, we intend to conduct larger scale qualitative interviews with court personnel and VJO specialists to obtain a clearer understanding of the needs related to skills-based training and gaps in psychoeducation. These comprehensive needs assessments may also capture common comorbidities that were not incorporated into the pilot training (eg, substance use disorders) but may be important training targets for court professionals. This information will be used to inform subsequent expansion and adaptation of the training into a longer workshop. Program evaluation will be conducted via survey-based feedback on perceived usefulness of the workshop and self-report of confidence in and use of strategies to improve court practices. Furthermore, efforts to obtain veteran outcome data, such as treatment engagement and successful participation in VTC, may be pursued.
Limitations
This training development and pilot project provided valuable foundational information regarding a largely unexamined component of treatment courts—the benefit of skills-based trainings to facilitate court practices related to justice-involved veterans. However, it is worth noting that survey responses were limited; thus, the feedback received may not reflect all attendees’ perceptions. Additionally, because both training sessions were conducted solely with 2 courts in the Rocky Mountain area, feedback may be limited to the needs of this geographic region.
Conclusions
A trauma-informed training was developed for VTCs to facilitate relevant understanding of justice-involved veterans’ needs and presentations in court, introduce skills to address challenges that arise (eg, motivation, emotional dysregulation), and provide interdisciplinary support to court professionals. This training was an important step toward fostering strong collaborations between VHA HCPs and community-based veterans courts, and feedback received during development and following implementation highlighted the perceived need for a skills-based approach to such trainings. Further program development and evaluation can strengthen this training and provide a foundation for dissemination to a broader scope of VTCs, with the goal of reducing recidivism risk among justice-involved veterans by promoting effective engagement in problem-solving court.
Veterans who interact with the criminal justice system (ie, justice-involved veterans) have heightened rates of mental health and psychosocial needs, including posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), substance use disorder, depression, suicidal ideation and attempt, and homelessness.1,2 Alongside these criminogenic risk factors, recidivism is common among justice-involved veterans: About 70% of incarcerated veterans disclosed at least one prior incarceration.3
To address the complex interplay of psychosocial factors, mental health concerns, and justice involvement among veterans, veterans treatment courts (VTCs) emerged as an alternative to incarceration.4 VTC participation often consists of integrated treatment and rehabilitative services (eg, vocational training, health care), ongoing monitoring for substance use, graduated responses to address treatment adherence, and ongoing communication with the judge and legal counsel.4
A primary aim of these courts is to address psychosocial needs believed to underlie criminal behavior, thus reducing risk of recidivism and promoting successful recovery and community integration for eligible veterans. To do so, VTCs collaborate with community-based and/or US Department of Veterans Affairs services, such as the Veterans Justice Outreach program (VJO). VJO specialists identify and refer justice-involved veterans to Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and community care and serve as a liaison between VTC staff and VHA health care professionals (HCPs).5
VTC outcome studies highlight the importance of not only diverting veterans to problem-solving courts, but also ensuring their optimal participation. Successful graduates of VTC programs demonstrate significant improvements in mental health symptoms, life satisfaction, and social support, as well as lower rates of law enforcement interactions.6,7 However, less is known about supporting those veterans who have difficulty engaging in VTCs and either discontinue participation or require lengthier periods of participation to meet court graduation requirements.8 One possibility to improve engagement among these veterans is to enhance court practices to best meet their needs.
In addition to delivering treatment, VHA mental health professionals may serve a critical interdisciplinary role by lending expertise to support VTC practices. For example, equipping court professionals with clinical knowledge and skills related to motivation may strengthen the staff’s interactions with participants, enabling them to address barriers as they arise and to facilitate veterans’ treatment adherence. Additionally, responsiveness to the impact of trauma exposure, which is common among this population, may prove important as related symptoms can affect veterans’ engagement, receptivity, and behavior in court settings. Indeed, prior examinations of justice-involved veterans have found trauma exposure rates ranging from 60% to 90% and PTSD rates ranging from 27% to 40%.1,2 Notably, involvement with the justice system (eg, incarceration) may itself further increase risk of trauma exposure (eg, experiencing a physical or sexual assault in prison) or exacerbate existing PTSD.9 Nonetheless, whereas many drug courts and domestic violence courts have been established, problem-solving courts with a specialized focus on trauma exposure remain rare, suggesting a potential gap in court training.
VHA HCPs have the potential to facilitate justice-involved veterans’ successful court and treatment participation by coordinating with VJO specialists to provide training and consultation to the courts. Supporting efforts to effectively and responsively address criminogenic risk (eg, mental health) in VTC settings may in turn reduce the likelihood of recidivism.10 Given the elevated rates of trauma exposure among justice-involved veterans and the relative lack of trauma-focused VTCs, we developed a trauma-informed training for VTC professionals that centered on related clinical presentations of justice-involved veterans and frequently occurring challenges in the context of court participation.
Program Development
This educational program aimed to (1) provide psychoeducation on trauma exposure, PTSD, and existing evidence-based treatments; (2) present clinical considerations for justice-involved veterans related to trauma exposure and/or PTSD; and (3) introduce skills to facilitate effective communication and trauma-informed care practices among professionals working with veterans in a treatment court.
Prior to piloting the program, we conducted a needs assessment with VTC professionals and identified relevant theoretical constructs and brief interventions for inclusion in the training. Additionally, given the dearth of prior research on mental health education for VTCs, the team consulted with the developers of PTSD 101, a VHA workshop for veterans’ families that promotes psychoeducation, support, and effective communication.11 Doing so informed approaches to delivering education to nonclinical audiences that interact with veterans with histories of trauma exposure. As this was a program development project, it was determined to be exempt from institutional review board review.
Needs Assessment
In the initial stages of development, local VJO specialists identified regional VTCs and facilitated introductions to these courts. Two of the 3 Rocky Mountain region VTCs that were contacted expressed interest in receiving trauma-informed training. Based on preliminary interest, the facilitators conducted a needs assessment with VJO and VTC staff from these 2 courts to capture requests for specific content and past experiences with other mental health trainings.
Guided by the focus group model, the needs assessments took place during three 1-hour meetings with VJO specialists and a 1-hour meeting with VJO specialists, VTC professionals, and community-based clinical partners.12 Additionally, attending a VTC graduation and court session allowed for observations of court practices and interactions with veterans. A total of 13 professionals (judges, court coordinators, case managers, peer mentors, VJO specialists, and clinicians who specialize in substance use disorder and intimate partner violence) participated in the needs assessments.
The most critical need identified by court professionals was a focus on how to apply knowledge about trauma and PTSD to interactions with justice-involved veterans. This was reportedly absent from prior training sessions the courts had received. Both Rocky Mountain region VTCs expressed a strong interest in and openness to adapting practices based on research and practice recommendations. Additional requests that emerged included a refresher on psychoeducation related to trauma and how to address the personal impact of working with this population (eg, compassion fatigue).
Training Components
Based on the needs identified by VTC professionals and informed by consultation with the developers of PTSD 101,
Psychoeducation. The initial portion of the training consisted of psychoeducation to increase VTC staff familiarity with the distinctions between trauma exposure and a formal diagnosis of PTSD, mechanisms underlying PTSD, and evidence-based treatment. To deepen conceptual understanding of trauma and PTSD beyond an overview of criteria set forth in The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), psychoeducation centered on the drivers of avoidance (eg, short-term benefit vs long-term consequences), behaviors that often facilitate avoidance (eg, substance use), functions underlying these behaviors (eg, distress reduction), and structure and mechanisms of change in evidence-based treatments for PTSD, including cognitive processing therapy and prolonged exposure.13,14
Fostering court familiarity with cognitive processing therapy and prolonged exposure may bolster veteran engagement in treatment through regular reinforcement of skills and concepts introduced in therapy. This may prove particularly salient given the limited engagement with mental health treatment and elevated dropout rates from PTSD treatment among the general veteran population.15,16
Exercises and metaphors were used to illustrate concepts in multiple ways. For example, training attendees engaged in a “stop, drop, and roll” thought exercise in which they were asked to brainstorm behavioral reactions to catching on fire. This exercise illustrated the tendency for individuals to revert to common yet unhelpful attempts at problem solving (eg, running due to panic, which would exacerbate the fire), particularly in crisis and without prior education regarding adaptive ways to respond. Attendee-generated examples, such as running, were used to demonstrate the importance of practicing and reinforcing skill development prior to a crisis, to ensure proficiency and optimal response. Additionally, in prompting consideration of one’s response tendencies, this exercise may engender empathy and understanding for veterans.
Skills training. Efforts to promote veteran engagement in court, facilitate motivation and readiness for change, and address barriers that arise (eg, distress associated with court appearances) may support successful and timely graduation. As such, skills training constituted the largest component of the training and drew from observations of court practices and the VTCs’ identified challenges. Consistent with the project’s aims and reported needs of the court, skills that target common presentations following trauma exposure (eg, avoidance, hypervigilance) were prioritized for this pilot training. Strategies included brief interventions from dialectical behavior therapy, acceptance and commitment therapy, and motivational interviewing to strengthen the support provided by staff to veterans and address their needs (Table 2).
Training attendees also participated in exercises to reiterate skills. For example, attendees completed an ambivalence matrix using an audience-identified common behavior that is difficult to change (eg, heavy alcohol use as a coping mechanism for distress).
Attendees engaged in an exercise that involved identifying unhelpful thoughts and behaviors, targets for validation, and veteran strengths from a hypothetical case vignette. This vignette involved a VTC participant who initially engaged effectively but began to demonstrate difficulty appropriately engaging in court and mental health treatment as well as challenging interactions with VTC staff (eg, raised voice during court sessions, not respecting communication boundaries).
Pilot Test
Based on scheduling parameters communicated by court coordinators, the pilot training was designed as a presentation during times reserved for court staffing meetings. To accommodate court preferences due to the COVID-19 pandemic, one 90-minute training was conducted virtually in March 2022, and the other training was conducted in person in April 2022 for 2 hours. The trainings were facilitated by 2 VHA clinical psychologists and included the judge, court coordinator, VJO specialist, peer mentors, case managers, probation/parole officers, and community-based HCPs who partner with the court (eg, social workers, psychologists). About 12 to 15 professionals attended each training session.
Feedback
Feedback was solicited from attendees via an anonymous online survey. Seven participants completed the survey; the response rate of about 20% was consistent with those observed for other surveys of court professionals.20 Many attendees also provided feedback directly to the facilitators. Feedback highlighted that the skills-based components not only were perceived as most helpful but also notably distinguished this training. “What set this training apart from other training events was the practical applications,” one attendee noted. “It was not just information or education, both instructors did an incredible job of explaining exactly how we could apply the knowledge they were sharing. They did this in such a way that it was easy to understand and apply.”
Specific skills were consistently identified as helpful, including managing intense emotions, addressing ambivalence, and approaching sanctions and rewards. Additionally, employing a less formal approach to the training, with relatable overviews of concepts and immediate responsiveness to requests for expansion on a topic, was perceived as a unique benefit: Another attendee appreciated that “It was beneficial to sit around a table with a less formal presentation and be able to ask questions.” This approach seemed particularly well suited for the program’s cross-disciplinary audience. Attendees reported that they valued the relatively limited focus on DSM-5 criteria. Attendees emphasized that education specific to veterans on evidence-based PTSD treatments, psychoeducation, and avoidance was very helpful. Respondents also recommended that the training be lengthened to a daylong workshop to accommodate greater opportunity to practice skills and consultation.
The consultation portion of the training provided insight into additional areas of importance to incorporate into future iterations. Identified needs included appropriate and realistic boundary setting (eg, addressing disruptions in the courtroom), suggestions for improving and expanding homework assigned by the court, and ways to address concerns about PTSD treatment shared by veterans in court (eg, attributing substance use relapses to the intensiveness of trauma-focused treatment vs lack of familiarity with alternate coping skills). Additionally, the VTC professionals’ desire to support mental health professionals’ work with veterans was clearly evident, highlighting the bidirectional value of interdisciplinary collaboration between VHA mental health professionals and VTC professionals.
Discussion
A trauma-informed training was developed and delivered to 2 VTCs in the Rocky Mountain region with the goal of providing relevant psychoeducation and introducing skills to bolster court practices that address veteran needs. Psychoeducational components of the training that were particularly well received and prompted significant participant engagement included discussions and examples of avoidance, levels of validation, language to facilitate motivation and address barriers, mechanisms underlying treatment, and potential functions underlying limited veteran treatment engagement. Distress tolerance, approaches to sanctions and rewards, and use of ambivalence matrices to guide motivation were identified as particularly helpful skills.
The pilot phase of this trauma-informed training provided valuable insights into developing mental health trainings for VTCs. Specifically, VTCs may benefit from the expertise of VHA HCPs and are particularly interested in learning brief skills to improve their practices. The usefulness of such trainings may be bolstered by efforts to form relationships with the court to identify their perceived needs and employing an iterative process that is responsive to feedback both during and after the training. Last, each stage of this project was strengthened by collaboration with VJO specialists, highlighting the importance of future collaboration between VJO and VHA mental health clinics to further support justice-involved veterans. For example, VJO specialists were instrumental in identifying training needs related to veterans’ clinical presentations in court, facilitating introductions to local VTCs, and helping to address barriers to piloting, like scheduling.
Modifications and Future Directions
The insights gained through the process of training design, delivery, and feedback inform future development of this training. Based on the feedback received, subsequent versions of the training may be expanded into a half- or full-day workshop to allow for adequate time for skills training and feedback, as well as consultation. Doing so will enable facilitators to further foster attendees’ familiarity with and confidence in their ability to use these skills. Furthermore, the consultation portion of this training revealed areas that may benefit from greater attention, including how to address challenging interactions in court (eg, addressing gender dynamics between court professionals and participants) and better support veterans who are having difficulty engaging in mental health treatment (eg, courts’ observation of high rates of dropout around the third or fourth session of evidence-based treatment for PTSD). Last, all attendees who responded to the survey expressed interest in a brief resource guide based on the training, emphasizing the need for ready access to key skills and concepts to support the use of strategies learned.
An additional future aim of this project is to conduct a more thorough evaluation of the needs and outcomes related to this trauma-informed training for VTC professionals. With the rapid growth of VTCs nationwide, relatively little examination of court processes and practices has occurred, and there is a lack of research on the development or effectiveness of mental health trainings provided to VTCs.21 Therefore, we intend to conduct larger scale qualitative interviews with court personnel and VJO specialists to obtain a clearer understanding of the needs related to skills-based training and gaps in psychoeducation. These comprehensive needs assessments may also capture common comorbidities that were not incorporated into the pilot training (eg, substance use disorders) but may be important training targets for court professionals. This information will be used to inform subsequent expansion and adaptation of the training into a longer workshop. Program evaluation will be conducted via survey-based feedback on perceived usefulness of the workshop and self-report of confidence in and use of strategies to improve court practices. Furthermore, efforts to obtain veteran outcome data, such as treatment engagement and successful participation in VTC, may be pursued.
Limitations
This training development and pilot project provided valuable foundational information regarding a largely unexamined component of treatment courts—the benefit of skills-based trainings to facilitate court practices related to justice-involved veterans. However, it is worth noting that survey responses were limited; thus, the feedback received may not reflect all attendees’ perceptions. Additionally, because both training sessions were conducted solely with 2 courts in the Rocky Mountain area, feedback may be limited to the needs of this geographic region.
Conclusions
A trauma-informed training was developed for VTCs to facilitate relevant understanding of justice-involved veterans’ needs and presentations in court, introduce skills to address challenges that arise (eg, motivation, emotional dysregulation), and provide interdisciplinary support to court professionals. This training was an important step toward fostering strong collaborations between VHA HCPs and community-based veterans courts, and feedback received during development and following implementation highlighted the perceived need for a skills-based approach to such trainings. Further program development and evaluation can strengthen this training and provide a foundation for dissemination to a broader scope of VTCs, with the goal of reducing recidivism risk among justice-involved veterans by promoting effective engagement in problem-solving court.
1. Blodgett JC, Avoundjian T, Finlay AK, et al. Prevalence of mental health disorders among justice-involved veterans. Epidemiol Rev. 2015;37(1):163-176. doi:10.1093/epirev/mxu003
2. Saxon AJ, Davis TM, Sloan KL, McKnight KM, McFall ME, Kivlahan DR. Trauma, symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, and associated problems among incarcerated veterans. Psychiatr Serv. 2001;52(7):959-964. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.52.7.959
3. Bronson J, Carson AC, Noonan M. Veterans in prison and jail, 2011-12. December 2015. Accessed January 11, 2023. https://bjs.ojp.gov/content/pub/pdf/vpj1112.pdf
4. Cartwright T. “To care for him who shall have borne the battle”: the recent development of veterans treatment courts in America. Stanford Law Rev. 2011;22(1):295-316.
5. Finlay AK, Smelson D, Sawh L, et al. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Justice Outreach Program: connecting justice-involved veterans with mental health and substance use disorder Treatment. Crim Justice Policy Rev. 2016;27(2):10.1177/0887403414562601. doi:10.1177/0887403414562601
6. Knudsen KJ, Wingenfeld S. A specialized treatment court for veterans with trauma exposure: implications for the field. Community Ment Health J. 2016;52(2):127-135. doi:10.1007/s10597-015-9845-9
7. Montgomery LM, Olson JN. Veterans treatment court impact on veteran mental health and life satisfaction. J Psychol Behav Sci. 2018;6(1):1-4. doi:10.15640/jpbs.v6n1a1
8. Tsai J, Finlay A, Flatley B, Kasprow WJ, Clark S. A national study of veterans treatment court participants: who benefits and who recidivates. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2018;45(2):236-244. doi:10.1007/s10488-017-0816-z
9. Wolff NL, Shi J. Trauma and incarcerated persons. In: Scott CL, ed. Handbook of Correctional Mental Health. American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.; 2010:277-320.
10. Bonta J, Andrews DA. Risk-need-responsivity model for offender assessment and rehabilitation. Rehabilitation. 2007;6:1-22. https://www.publicsafety.gc.ca/cnt/rsrcs/pblctns/rsk-nd-rspnsvty/index-en.aspx
11. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Mental Health and Suicide Prevention, Family Services Section; Caska-Wallace CM, Campbell SB, Glynn SM. PTSD 101 for family and friends: a support and education workshop. 2020.
12. Tipping J. Focus groups: a method of needs assessment. J Contin Educ Health Prof. 1998;18(3):150-154. doi:10.1002/chp.1340180304
13. Resick PA, Monson CM, Chard KM. Cognitive Processing Therapy for PTSD: A Comprehensive Manual. The Guilford Press; 2017.
14. Foa EB, Hembree EA, Rothbaum BO. Prolonged Exposure Therapy for PTSD: Emotional Processing of Traumatic Experiences: Therapist Guide. Oxford University Press; 2007. doi:10.1093/med:psych/9780195308501.001.0001
15. Seal KH, Maguen S, Cohen B, et al. VA mental health services utilization in Iraq and Afghanistan veterans in the first year of receiving new mental health diagnoses. J Trauma Stress. 2010;23(1):5-16. doi:10.1002/jts.20493
16. Edwards-Stewart A, Smolenski DJ, Bush NE, et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder treatment dropout among military and veteran populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Trauma Stress. 2021;34(4):808-818. doi:10.1002/jts.22653
17. Linehan MM. Dialectical Behavior Therapy Skills Training Manual. 2nd ed. Guildford Press; 2015.
18. Hayes SC, Strosahl KD, Wilson KG. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy: The Process and Practice of Mindful Change. 2nd ed. Guildford Press; 2016.
19. Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational Interviewing: Preparing People for Change. 2nd ed. The Guildford Press; 2002.
20. National Center for State Courts. A survey of members of major national court organizations. October 2010. Accessed January 11, 2023. https://www.ncsc.org/__data/assets/pdf_file/0015/16350/survey-summary-10-26.pdf
21. Baldwin JM, Brooke EJ. Pausing in the wake of rapid adoption: a call to critically examine the veterans treatment court concept. J Offender Rehabil. 2019;58(1):1-29. doi:10.1080/10509674.2018.1549181
1. Blodgett JC, Avoundjian T, Finlay AK, et al. Prevalence of mental health disorders among justice-involved veterans. Epidemiol Rev. 2015;37(1):163-176. doi:10.1093/epirev/mxu003
2. Saxon AJ, Davis TM, Sloan KL, McKnight KM, McFall ME, Kivlahan DR. Trauma, symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, and associated problems among incarcerated veterans. Psychiatr Serv. 2001;52(7):959-964. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.52.7.959
3. Bronson J, Carson AC, Noonan M. Veterans in prison and jail, 2011-12. December 2015. Accessed January 11, 2023. https://bjs.ojp.gov/content/pub/pdf/vpj1112.pdf
4. Cartwright T. “To care for him who shall have borne the battle”: the recent development of veterans treatment courts in America. Stanford Law Rev. 2011;22(1):295-316.
5. Finlay AK, Smelson D, Sawh L, et al. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Veterans Justice Outreach Program: connecting justice-involved veterans with mental health and substance use disorder Treatment. Crim Justice Policy Rev. 2016;27(2):10.1177/0887403414562601. doi:10.1177/0887403414562601
6. Knudsen KJ, Wingenfeld S. A specialized treatment court for veterans with trauma exposure: implications for the field. Community Ment Health J. 2016;52(2):127-135. doi:10.1007/s10597-015-9845-9
7. Montgomery LM, Olson JN. Veterans treatment court impact on veteran mental health and life satisfaction. J Psychol Behav Sci. 2018;6(1):1-4. doi:10.15640/jpbs.v6n1a1
8. Tsai J, Finlay A, Flatley B, Kasprow WJ, Clark S. A national study of veterans treatment court participants: who benefits and who recidivates. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2018;45(2):236-244. doi:10.1007/s10488-017-0816-z
9. Wolff NL, Shi J. Trauma and incarcerated persons. In: Scott CL, ed. Handbook of Correctional Mental Health. American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.; 2010:277-320.
10. Bonta J, Andrews DA. Risk-need-responsivity model for offender assessment and rehabilitation. Rehabilitation. 2007;6:1-22. https://www.publicsafety.gc.ca/cnt/rsrcs/pblctns/rsk-nd-rspnsvty/index-en.aspx
11. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Mental Health and Suicide Prevention, Family Services Section; Caska-Wallace CM, Campbell SB, Glynn SM. PTSD 101 for family and friends: a support and education workshop. 2020.
12. Tipping J. Focus groups: a method of needs assessment. J Contin Educ Health Prof. 1998;18(3):150-154. doi:10.1002/chp.1340180304
13. Resick PA, Monson CM, Chard KM. Cognitive Processing Therapy for PTSD: A Comprehensive Manual. The Guilford Press; 2017.
14. Foa EB, Hembree EA, Rothbaum BO. Prolonged Exposure Therapy for PTSD: Emotional Processing of Traumatic Experiences: Therapist Guide. Oxford University Press; 2007. doi:10.1093/med:psych/9780195308501.001.0001
15. Seal KH, Maguen S, Cohen B, et al. VA mental health services utilization in Iraq and Afghanistan veterans in the first year of receiving new mental health diagnoses. J Trauma Stress. 2010;23(1):5-16. doi:10.1002/jts.20493
16. Edwards-Stewart A, Smolenski DJ, Bush NE, et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder treatment dropout among military and veteran populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Trauma Stress. 2021;34(4):808-818. doi:10.1002/jts.22653
17. Linehan MM. Dialectical Behavior Therapy Skills Training Manual. 2nd ed. Guildford Press; 2015.
18. Hayes SC, Strosahl KD, Wilson KG. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy: The Process and Practice of Mindful Change. 2nd ed. Guildford Press; 2016.
19. Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational Interviewing: Preparing People for Change. 2nd ed. The Guildford Press; 2002.
20. National Center for State Courts. A survey of members of major national court organizations. October 2010. Accessed January 11, 2023. https://www.ncsc.org/__data/assets/pdf_file/0015/16350/survey-summary-10-26.pdf
21. Baldwin JM, Brooke EJ. Pausing in the wake of rapid adoption: a call to critically examine the veterans treatment court concept. J Offender Rehabil. 2019;58(1):1-29. doi:10.1080/10509674.2018.1549181