User login
Health care spending in the United States remained relatively flat from 2019 to 2021 and only increased 2.7% in 2021, reaching $4.3 billion or $12,914 per person. Physician services account for 15% of health care spending (Figure). Relative value units (RVUs) signify the time it took a physician to complete a task multiplied by a conversion factor (CF). When RVUs initially were created in 1992 by what is now the Centers for Medicare &Medicaid Services (CMS), the CF was $32.00. Thirty-one years later, the CF is $33.89 in 2023; however, it would be $66.00 if the CF had increased with inflation.1 If the proposed 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule (MPFS) is adopted, the payment formula would decrease by 3.4% ($32.75) relative to the 2023 fee schedule ($33.89), which would be a 9% decrease relative to 2019 ($36.04).2,3 This reduction is due to the budget neutrality adjustment required by changes in RVUs, implementation of the evaluation and management (E/M) add-on code G2211, and proposed increases in primary are services.2,3 Since 2001, Medicare physician payment has declined by 26%.4 Adjustments to the CF typically are made based on 3 factors: (1) the Medicare Economic Index (MEI); (2) an expenditure target performance adjustment; and (3) miscellaneous adjustments, including those for budget neutrality required by law. Despite continued substantial increases in practice expenses, physicians’ reimbursement has remained flat while other service providers, such as those in skilled nursing facilities and hospitals, have received favorable payment increases compared to practice cost inflation and the Consumer Price Index.4
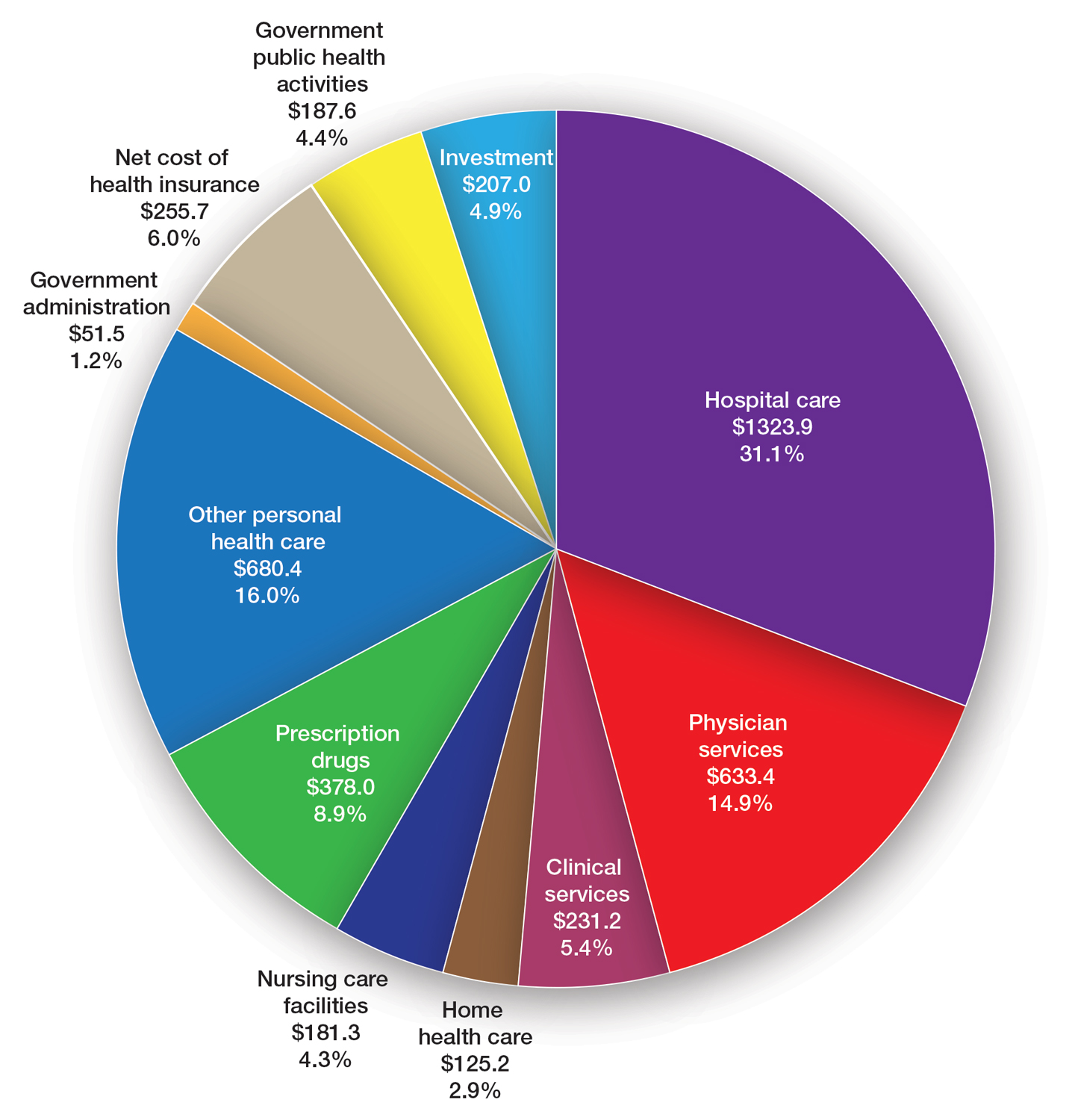
The CMS will not incorporate 2017 MEI cost weights for the RVUs in the MPFS rate setting for 2024 because all key measures of practice expenses in the MEI accelerated in 2022. Instead, the CMS is updating data on practice expense per hour to calculate payment for physician services with a survey for physician practices that launched on July 31, 2023.5 The American Medical Association contracted with Mathematica, an independent research company, to conduct a physician practice information survey that will be used to determine indirect practice expenses. Physicians should be on the lookout for emails regarding completion of these surveys and the appropriate financial expert in their practice should be contacted so the responses are accurate, as these data are key to future updates in the Medicare pay formula used to reimburse physicians.
Impact of Medicare Cuts
The recent congressional debt limit deal set spending caps for the next 2 fiscal years. Dermatology is facing an overall payment reduction of 1.87% (range, 1%–4%).2,3 The impact will depend on the services offered in an individual practice; for example, payment for a punch biopsy (Current Procedural Terminology [CPT] code 11104) would decrease by 3.9%. Payment for benign destruction (CPT code 17110) would decrease by 2.8%, and payment for even simple E/M of an established patient (CPT code 99213) would decrease by 1.6%. Overall, there would be a reduction of 2.75% for dermatopathology services, with a decrease of 2% for CPT code 88305 global and decreases for the technical component of 1% and professional component of 3%.2,3
Medicare cuts have reached a critical level, and physicians cannot continue to absorb the costs to own and operate their practices.4 This has led to health market consolidation, which in turn limits competition and patient access while driving up health care costs and driving down the quality of care. Small independent rural practices as well as those caring for historically marginalized patients will be disproportionately affected.
Proposed Addition of E/M Code G2211
In the calendar year (CY) 2021 final rule, the CMS tried to adopt a new add-on code—G2211—patients with a serious or complex condition that typically require referral and coordination of multispecialty care. Per the CMS, the primary policy goal of G2211 is to increase payments to primary care physicians and to reimburse them more appropriately for the care provided to patients with a serious or complex condition.2,3 It can be reported in conjunction with all office and outpatient E/M visits to better account for additional resources associated with primary care, or similarly ongoing medical care related to a patient’s single, serious condition, or complex condition.3 Typically, G2211 would not be used by dermatologists, as this add-on code requires visit complexity inherent to E/M associated with medical care services that serve as the continuing focal point for all needed health care services and/or with medical care services that are part of ongoing care related to a patient’s single serious condition or a complex condition.2,3
Initially, the CMS assumed that G2211 would be reported with 90% of all office and outpatient E/M visit claims, which would account for a considerable portion of total MPFS schedule spending; however, the House of Medicine disagreed and believed it would be 75%.2,3 Given the extremely high utilization estimate, G2211 would have had a substantial effect on budget neutrality, accounting for an estimated increase of $3.3 billion and a corresponding 3.0% cut to the CY 2021 MPFS. Because of the potential payment reductions to physicians and a successful advocacy effort by organized medicine, including the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA), Congress delayed implementation of G2211 until CY 2024. Modifier -25 cannot be reported with G2211. The CMS revised its utilization assumptions from 90% of all E/M services to an initial utilization of 38% and then 54% when fully adopted. The proposed 2024 payment for G2211 is an additional $16.05.2,3
Advancing Health Equity With Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System G Codes
The CMS is proposing coding and payment for several new services to help underserved populations, including addressing unmet health-related social needs that can potentially interfere with the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions, which includes paying for certain caregiver training services as well as payment for community health integration services.2,3 These are the first MPFS services designed to include care involving community health workers, who link underserved communities with critical health care and social services in the community. Additionally, the rule also proposes coding and payment for evaluating the risks related to social factors that affect a patient’s health, such as access to affordable quality health care, that can take place during an annual wellness visit or in combination with an E/M visit.2,3 As dermatologists, we should be familiar with this set of G codes, as we will likely use them in practice for patients with transportation needs.
Advocacy Efforts on Medicare Payment Reform
Medicare physician payment reform needs to happen at a national level. Advocacy efforts by the AADA and other groups have been underway to mitigate the proposed 2024 cuts. The Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act (HR 2474) is a bill that was introduced by a bipartisan coalition of physicians to provide an inflation-based increase in Medicare payments in 2024 and beyond.6
Other Legislative Updates Affecting Dermatology
Modifier -25—Cigna’s policy requiring dermatologists to submit documentation to use modifier -25 when billing with E/M CPT codes 99212 through 99215 has been delayed indefinitely.7 If a payer denies a dermatologist payment, contact the AADA Patient Access and Payer Relations committee (privatepayer@aad.org) for assistance.
Telehealth and Digital Pathology—Recent legislation authorized extension of many of the Medicare telehealth and digital pathology flexibilities that were put in place during the COVID-19 public health emergency through December 31, 2024.8,9 Seventeen newly approved CPT telemedicine codes for new and established patient audio-visual and audio-only visits recently were surveyed.2,3 The data from the survey will be used as a key element in assigning a specific RVU to the CMS and will be included in the MPFS.
Thirty additional new digital pathology add-on CPT category III codes for 2024 were added to the ones from 2023.2,3 These codes can be used to report additional clinical staff work and service requirements associated with digitizing glass microscope slides for primary diagnosis. They cannot be used for archival or educational purposes, clinical conferences, training, or validating artificial intelligence algorithms. Category III codes used for emerging technologies have no assigned RVUs or reimbursement.2,3
The Cures Act—The Cures Act aims to ensure that patients have timely access to their health information.10 It requires all physicians to make their office notes, laboratory results, and other diagnostic reports available to patients as soon as the office receives them. The rules went into effect on April 5, 2021, with a limited definition of electronic health information; on October 6, 2022, the Cures Act rule expanded to include all electronic health information. The AADA has urged the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology to collaborate with stakeholder organizations to re-evaluate federal policies concerning the immediate release of electronic health information and information blocking, particularly in cases with life-altering diagnoses.10 They stressed the importance of prioritizing the well-being and emotional stability of patients and enhancing care by providing patients adequate time and support to process, comprehend, and discuss findings with their physician.
Proposed 2024 Medicare Quality Payment Program Requirements
The CMS proposed to increase the performance threshold in the quality payment program from 75 to 82 points for the 2024 Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) performance period, impacting the 2026 payment year.2,3,11 As a result of this increase, there could be more MIPS-eligible clinicians receiving penalties, which could be a reduction of up to 9%. The AADA will firmly oppose any increase in the threshold and strongly urge CMS to maintain the 75-point threshold. The performance category weights for the 2024 performance year will remain unchanged from the 2023 performance year.2,3,11
2024 Proposed Quality MIPS Measures Set—The CMS proposed to remove the topped-out MIPS measure 138 (coordination of care for melanoma).2,3,11 Additionally, it proposed to remove MIPS measure 402 (tobacco use and help with quitting among adolescents) as a quality measure from MIPS because the agency believes it is duplicative of measure 226 (preventive care and screening: tobacco use: screening and cessation intervention).2,3,11
MIPS Value Pathways—The CMS consolidated 2 previously established MIPS value pathways (MVPs): the Promoting Wellness MVP and the Optimizing Chronic Disease Management MVP.2,3,11 Proposed new MVPs for 2024 include Focusing on Women’s Health; Quality Care for the Treatment of Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorders; Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Disorders Including Hepatitis C and HIV; Quality Care in Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders; and Rehabilitative Support for Musculoskeletal Care. Dermatology is not impacted; however, the CMS plans to sunset traditional MIPS and replace it with MVPs—the future of MIPS.2,3,11 The AADA maintains that traditional MIPS should continue to be an option because MVPs have a limited number of measures for dermatologists.
Update on Reporting Suture Removal
There are 2 new CPT add-on codes—15853 and 15854—for the removal of sutures or staples not requiring anesthesia to be listed separately in addition to an appropriate E/M service. These add-on codes went into effect on January 1, 2023.12 These codes were created with the intent to capture and ensure remuneration for practice expenses that are not included in a stand-alone E/M encounter that occur after a 0-day procedure (eg, services reported with CPT codes 11102–11107 and 11300–11313) for wound check and suture removal where appropriate. These new add-on codes do not have physician work RVUs assigned to them because they are only for practice expenses (eg, clinical staff time, disposable supplies, use of equipment); CPT code 15853 is reported for the removal of sutures or staples, and CPT code 15854 is reported when both sutures and staples are removed. These codes can only be reported if an E/M service also is reported for the patient encounter.12
Final Thoughts
The AADA is working with the House of Medicine and the medical specialty community to develop specific proposals to reform the Medicare payment system.4 The proposed 2024 MPFS was released on July 13, 2023, and final regulations are expected in the late fall of 2023. The AADA will continue to engage with the CMS, but it is important for physicians to learn about and support advocacy priorities and efforts as well as join forces to protect their practices. As health care professionals, we have unique insights into the challenges and needs of our patients and the health care system. Advocacy can take various forms, such as supporting or opposing specific legislations, participating in grassroots campaigns, engaging with policymakers, and/or joining professional organizations that advocate for health care–related issues. Get involved, stay informed, and stay engaged through dermatology medical societies; together we can make a difference.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. NHE fact sheet. Updated September 6, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/NationalHealthExpendData/NHE-Fact-Sheet
- Medicare and Medicaid Programs; CY 2024 payment policies under the physician fee schedule and other changes to part B payment and coverage policies; Medicare shared savings program requirements; Medicare advantage; Medicare and Medicaid provider and supplier enrollment policies; and basic health program. Fed Regist. 2023;88:52262-53197. To be codified at 42 CFR §405, §410, §411, §414, §415, §418, §422, §423, §424, §425, §455, §489, §491, §495, §498, and §600. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2023/08/07/2023-14624/medicare-and-medicaid-programs-cy-2024-payment-policies-under-the-physician-fee-schedule-and-other
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar year (CY) 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule proposed rule. Published July 13, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/calendar-year-cy-2024-medicare-physician-fee-schedule-proposed-rule
- American Medical Association. Payment reform. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/health-care-advocacypayment-reform
- American Medical Association. Physician answers on this survey will shape future Medicare pay. Published July 31, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/medicare-medicaid/physician-answers-survey-will-shape-future -medicare-pay
- Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act, HR 2474, 118 Congress (2023-2024). https://www.congress.gov/bill/118th-congress/house-bill/2474
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. Academy advocacy priorities. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.aad.org/member/advocacy/priorities
- College of American Pathologists. Remote sign-out of cases with digital pathology FAQs. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cap.org/covid-19/remote-sign-out-faqs
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Telehealth. Updated September 6, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/medicare/coverage/telehealth
- The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology. ONC’s Cures Act final rule. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.healthit.gov/topic/oncs-cures-act-final-rule
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar Year (CY) 2024 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (PFS) Notice of Proposed Rule Making Quality Payment Program Policy Overview: Proposals and Requests for Information. Accessed September 12, 2023. https://email.aadresources.org/e3t/Ctc/I6+113/cVKqx04/VVWzj43dDbctW8c23GW1ZLnJHW1xTZ7Q50Y DYN89Qzy5nCVhV3Zsc37CgFV9W5Ck4-D42qs9BW38PtXn4LSlNLW1QKpPL4xT8BMW6Mcwww3FdwCHN3vfGTMXbtF-W2-Zzfy5WHDg6W88tx1F1KgsgxW7zDzT46C2sFXW800vQJ3lLsS_W5D6f1d30-f3cN1njgZ_dX7xkW447ldH2-kgc5VCs7Xg1GY6dsN87pLVJqJG5XW8VWwD-7VxVkJN777f5fJL7jBW8RxkQM1lcSDjVV746T3C-stpN52V_S5xj7q6W3_vldf3p1Yk2Vbd4ZD3cPrHqW5Pwv9m567fkzW1vfDm51H-T7rW1jVrxl8gstXyW5RVTn8863CVFW8g6LgK2YdhpkW34HC4z3_pGYgW8V_qWH3g-tTlW4S3RD-1dKry7W4_rW8d1ssZ1fVwXQjQ9krVMW8Y0bTt8Nr5CNW6vbG0h3wyx59W8WCrNW50p5n6W1r-VBC2rKh93N4W2RyYr7vvm3kxG1
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Chapter III surgery: integumentary system CPT codes 10000-19999 for Medicare national correct coding initiative policy manual. Updated January 1, 2023. Accessed September 26, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/medicare-ncci-policy-manual-2023-chapter-3.pdf
Health care spending in the United States remained relatively flat from 2019 to 2021 and only increased 2.7% in 2021, reaching $4.3 billion or $12,914 per person. Physician services account for 15% of health care spending (Figure). Relative value units (RVUs) signify the time it took a physician to complete a task multiplied by a conversion factor (CF). When RVUs initially were created in 1992 by what is now the Centers for Medicare &Medicaid Services (CMS), the CF was $32.00. Thirty-one years later, the CF is $33.89 in 2023; however, it would be $66.00 if the CF had increased with inflation.1 If the proposed 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule (MPFS) is adopted, the payment formula would decrease by 3.4% ($32.75) relative to the 2023 fee schedule ($33.89), which would be a 9% decrease relative to 2019 ($36.04).2,3 This reduction is due to the budget neutrality adjustment required by changes in RVUs, implementation of the evaluation and management (E/M) add-on code G2211, and proposed increases in primary are services.2,3 Since 2001, Medicare physician payment has declined by 26%.4 Adjustments to the CF typically are made based on 3 factors: (1) the Medicare Economic Index (MEI); (2) an expenditure target performance adjustment; and (3) miscellaneous adjustments, including those for budget neutrality required by law. Despite continued substantial increases in practice expenses, physicians’ reimbursement has remained flat while other service providers, such as those in skilled nursing facilities and hospitals, have received favorable payment increases compared to practice cost inflation and the Consumer Price Index.4

The CMS will not incorporate 2017 MEI cost weights for the RVUs in the MPFS rate setting for 2024 because all key measures of practice expenses in the MEI accelerated in 2022. Instead, the CMS is updating data on practice expense per hour to calculate payment for physician services with a survey for physician practices that launched on July 31, 2023.5 The American Medical Association contracted with Mathematica, an independent research company, to conduct a physician practice information survey that will be used to determine indirect practice expenses. Physicians should be on the lookout for emails regarding completion of these surveys and the appropriate financial expert in their practice should be contacted so the responses are accurate, as these data are key to future updates in the Medicare pay formula used to reimburse physicians.
Impact of Medicare Cuts
The recent congressional debt limit deal set spending caps for the next 2 fiscal years. Dermatology is facing an overall payment reduction of 1.87% (range, 1%–4%).2,3 The impact will depend on the services offered in an individual practice; for example, payment for a punch biopsy (Current Procedural Terminology [CPT] code 11104) would decrease by 3.9%. Payment for benign destruction (CPT code 17110) would decrease by 2.8%, and payment for even simple E/M of an established patient (CPT code 99213) would decrease by 1.6%. Overall, there would be a reduction of 2.75% for dermatopathology services, with a decrease of 2% for CPT code 88305 global and decreases for the technical component of 1% and professional component of 3%.2,3
Medicare cuts have reached a critical level, and physicians cannot continue to absorb the costs to own and operate their practices.4 This has led to health market consolidation, which in turn limits competition and patient access while driving up health care costs and driving down the quality of care. Small independent rural practices as well as those caring for historically marginalized patients will be disproportionately affected.
Proposed Addition of E/M Code G2211
In the calendar year (CY) 2021 final rule, the CMS tried to adopt a new add-on code—G2211—patients with a serious or complex condition that typically require referral and coordination of multispecialty care. Per the CMS, the primary policy goal of G2211 is to increase payments to primary care physicians and to reimburse them more appropriately for the care provided to patients with a serious or complex condition.2,3 It can be reported in conjunction with all office and outpatient E/M visits to better account for additional resources associated with primary care, or similarly ongoing medical care related to a patient’s single, serious condition, or complex condition.3 Typically, G2211 would not be used by dermatologists, as this add-on code requires visit complexity inherent to E/M associated with medical care services that serve as the continuing focal point for all needed health care services and/or with medical care services that are part of ongoing care related to a patient’s single serious condition or a complex condition.2,3
Initially, the CMS assumed that G2211 would be reported with 90% of all office and outpatient E/M visit claims, which would account for a considerable portion of total MPFS schedule spending; however, the House of Medicine disagreed and believed it would be 75%.2,3 Given the extremely high utilization estimate, G2211 would have had a substantial effect on budget neutrality, accounting for an estimated increase of $3.3 billion and a corresponding 3.0% cut to the CY 2021 MPFS. Because of the potential payment reductions to physicians and a successful advocacy effort by organized medicine, including the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA), Congress delayed implementation of G2211 until CY 2024. Modifier -25 cannot be reported with G2211. The CMS revised its utilization assumptions from 90% of all E/M services to an initial utilization of 38% and then 54% when fully adopted. The proposed 2024 payment for G2211 is an additional $16.05.2,3
Advancing Health Equity With Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System G Codes
The CMS is proposing coding and payment for several new services to help underserved populations, including addressing unmet health-related social needs that can potentially interfere with the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions, which includes paying for certain caregiver training services as well as payment for community health integration services.2,3 These are the first MPFS services designed to include care involving community health workers, who link underserved communities with critical health care and social services in the community. Additionally, the rule also proposes coding and payment for evaluating the risks related to social factors that affect a patient’s health, such as access to affordable quality health care, that can take place during an annual wellness visit or in combination with an E/M visit.2,3 As dermatologists, we should be familiar with this set of G codes, as we will likely use them in practice for patients with transportation needs.
Advocacy Efforts on Medicare Payment Reform
Medicare physician payment reform needs to happen at a national level. Advocacy efforts by the AADA and other groups have been underway to mitigate the proposed 2024 cuts. The Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act (HR 2474) is a bill that was introduced by a bipartisan coalition of physicians to provide an inflation-based increase in Medicare payments in 2024 and beyond.6
Other Legislative Updates Affecting Dermatology
Modifier -25—Cigna’s policy requiring dermatologists to submit documentation to use modifier -25 when billing with E/M CPT codes 99212 through 99215 has been delayed indefinitely.7 If a payer denies a dermatologist payment, contact the AADA Patient Access and Payer Relations committee (privatepayer@aad.org) for assistance.
Telehealth and Digital Pathology—Recent legislation authorized extension of many of the Medicare telehealth and digital pathology flexibilities that were put in place during the COVID-19 public health emergency through December 31, 2024.8,9 Seventeen newly approved CPT telemedicine codes for new and established patient audio-visual and audio-only visits recently were surveyed.2,3 The data from the survey will be used as a key element in assigning a specific RVU to the CMS and will be included in the MPFS.
Thirty additional new digital pathology add-on CPT category III codes for 2024 were added to the ones from 2023.2,3 These codes can be used to report additional clinical staff work and service requirements associated with digitizing glass microscope slides for primary diagnosis. They cannot be used for archival or educational purposes, clinical conferences, training, or validating artificial intelligence algorithms. Category III codes used for emerging technologies have no assigned RVUs or reimbursement.2,3
The Cures Act—The Cures Act aims to ensure that patients have timely access to their health information.10 It requires all physicians to make their office notes, laboratory results, and other diagnostic reports available to patients as soon as the office receives them. The rules went into effect on April 5, 2021, with a limited definition of electronic health information; on October 6, 2022, the Cures Act rule expanded to include all electronic health information. The AADA has urged the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology to collaborate with stakeholder organizations to re-evaluate federal policies concerning the immediate release of electronic health information and information blocking, particularly in cases with life-altering diagnoses.10 They stressed the importance of prioritizing the well-being and emotional stability of patients and enhancing care by providing patients adequate time and support to process, comprehend, and discuss findings with their physician.
Proposed 2024 Medicare Quality Payment Program Requirements
The CMS proposed to increase the performance threshold in the quality payment program from 75 to 82 points for the 2024 Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) performance period, impacting the 2026 payment year.2,3,11 As a result of this increase, there could be more MIPS-eligible clinicians receiving penalties, which could be a reduction of up to 9%. The AADA will firmly oppose any increase in the threshold and strongly urge CMS to maintain the 75-point threshold. The performance category weights for the 2024 performance year will remain unchanged from the 2023 performance year.2,3,11
2024 Proposed Quality MIPS Measures Set—The CMS proposed to remove the topped-out MIPS measure 138 (coordination of care for melanoma).2,3,11 Additionally, it proposed to remove MIPS measure 402 (tobacco use and help with quitting among adolescents) as a quality measure from MIPS because the agency believes it is duplicative of measure 226 (preventive care and screening: tobacco use: screening and cessation intervention).2,3,11
MIPS Value Pathways—The CMS consolidated 2 previously established MIPS value pathways (MVPs): the Promoting Wellness MVP and the Optimizing Chronic Disease Management MVP.2,3,11 Proposed new MVPs for 2024 include Focusing on Women’s Health; Quality Care for the Treatment of Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorders; Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Disorders Including Hepatitis C and HIV; Quality Care in Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders; and Rehabilitative Support for Musculoskeletal Care. Dermatology is not impacted; however, the CMS plans to sunset traditional MIPS and replace it with MVPs—the future of MIPS.2,3,11 The AADA maintains that traditional MIPS should continue to be an option because MVPs have a limited number of measures for dermatologists.
Update on Reporting Suture Removal
There are 2 new CPT add-on codes—15853 and 15854—for the removal of sutures or staples not requiring anesthesia to be listed separately in addition to an appropriate E/M service. These add-on codes went into effect on January 1, 2023.12 These codes were created with the intent to capture and ensure remuneration for practice expenses that are not included in a stand-alone E/M encounter that occur after a 0-day procedure (eg, services reported with CPT codes 11102–11107 and 11300–11313) for wound check and suture removal where appropriate. These new add-on codes do not have physician work RVUs assigned to them because they are only for practice expenses (eg, clinical staff time, disposable supplies, use of equipment); CPT code 15853 is reported for the removal of sutures or staples, and CPT code 15854 is reported when both sutures and staples are removed. These codes can only be reported if an E/M service also is reported for the patient encounter.12
Final Thoughts
The AADA is working with the House of Medicine and the medical specialty community to develop specific proposals to reform the Medicare payment system.4 The proposed 2024 MPFS was released on July 13, 2023, and final regulations are expected in the late fall of 2023. The AADA will continue to engage with the CMS, but it is important for physicians to learn about and support advocacy priorities and efforts as well as join forces to protect their practices. As health care professionals, we have unique insights into the challenges and needs of our patients and the health care system. Advocacy can take various forms, such as supporting or opposing specific legislations, participating in grassroots campaigns, engaging with policymakers, and/or joining professional organizations that advocate for health care–related issues. Get involved, stay informed, and stay engaged through dermatology medical societies; together we can make a difference.
Health care spending in the United States remained relatively flat from 2019 to 2021 and only increased 2.7% in 2021, reaching $4.3 billion or $12,914 per person. Physician services account for 15% of health care spending (Figure). Relative value units (RVUs) signify the time it took a physician to complete a task multiplied by a conversion factor (CF). When RVUs initially were created in 1992 by what is now the Centers for Medicare &Medicaid Services (CMS), the CF was $32.00. Thirty-one years later, the CF is $33.89 in 2023; however, it would be $66.00 if the CF had increased with inflation.1 If the proposed 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule (MPFS) is adopted, the payment formula would decrease by 3.4% ($32.75) relative to the 2023 fee schedule ($33.89), which would be a 9% decrease relative to 2019 ($36.04).2,3 This reduction is due to the budget neutrality adjustment required by changes in RVUs, implementation of the evaluation and management (E/M) add-on code G2211, and proposed increases in primary are services.2,3 Since 2001, Medicare physician payment has declined by 26%.4 Adjustments to the CF typically are made based on 3 factors: (1) the Medicare Economic Index (MEI); (2) an expenditure target performance adjustment; and (3) miscellaneous adjustments, including those for budget neutrality required by law. Despite continued substantial increases in practice expenses, physicians’ reimbursement has remained flat while other service providers, such as those in skilled nursing facilities and hospitals, have received favorable payment increases compared to practice cost inflation and the Consumer Price Index.4

The CMS will not incorporate 2017 MEI cost weights for the RVUs in the MPFS rate setting for 2024 because all key measures of practice expenses in the MEI accelerated in 2022. Instead, the CMS is updating data on practice expense per hour to calculate payment for physician services with a survey for physician practices that launched on July 31, 2023.5 The American Medical Association contracted with Mathematica, an independent research company, to conduct a physician practice information survey that will be used to determine indirect practice expenses. Physicians should be on the lookout for emails regarding completion of these surveys and the appropriate financial expert in their practice should be contacted so the responses are accurate, as these data are key to future updates in the Medicare pay formula used to reimburse physicians.
Impact of Medicare Cuts
The recent congressional debt limit deal set spending caps for the next 2 fiscal years. Dermatology is facing an overall payment reduction of 1.87% (range, 1%–4%).2,3 The impact will depend on the services offered in an individual practice; for example, payment for a punch biopsy (Current Procedural Terminology [CPT] code 11104) would decrease by 3.9%. Payment for benign destruction (CPT code 17110) would decrease by 2.8%, and payment for even simple E/M of an established patient (CPT code 99213) would decrease by 1.6%. Overall, there would be a reduction of 2.75% for dermatopathology services, with a decrease of 2% for CPT code 88305 global and decreases for the technical component of 1% and professional component of 3%.2,3
Medicare cuts have reached a critical level, and physicians cannot continue to absorb the costs to own and operate their practices.4 This has led to health market consolidation, which in turn limits competition and patient access while driving up health care costs and driving down the quality of care. Small independent rural practices as well as those caring for historically marginalized patients will be disproportionately affected.
Proposed Addition of E/M Code G2211
In the calendar year (CY) 2021 final rule, the CMS tried to adopt a new add-on code—G2211—patients with a serious or complex condition that typically require referral and coordination of multispecialty care. Per the CMS, the primary policy goal of G2211 is to increase payments to primary care physicians and to reimburse them more appropriately for the care provided to patients with a serious or complex condition.2,3 It can be reported in conjunction with all office and outpatient E/M visits to better account for additional resources associated with primary care, or similarly ongoing medical care related to a patient’s single, serious condition, or complex condition.3 Typically, G2211 would not be used by dermatologists, as this add-on code requires visit complexity inherent to E/M associated with medical care services that serve as the continuing focal point for all needed health care services and/or with medical care services that are part of ongoing care related to a patient’s single serious condition or a complex condition.2,3
Initially, the CMS assumed that G2211 would be reported with 90% of all office and outpatient E/M visit claims, which would account for a considerable portion of total MPFS schedule spending; however, the House of Medicine disagreed and believed it would be 75%.2,3 Given the extremely high utilization estimate, G2211 would have had a substantial effect on budget neutrality, accounting for an estimated increase of $3.3 billion and a corresponding 3.0% cut to the CY 2021 MPFS. Because of the potential payment reductions to physicians and a successful advocacy effort by organized medicine, including the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA), Congress delayed implementation of G2211 until CY 2024. Modifier -25 cannot be reported with G2211. The CMS revised its utilization assumptions from 90% of all E/M services to an initial utilization of 38% and then 54% when fully adopted. The proposed 2024 payment for G2211 is an additional $16.05.2,3
Advancing Health Equity With Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System G Codes
The CMS is proposing coding and payment for several new services to help underserved populations, including addressing unmet health-related social needs that can potentially interfere with the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions, which includes paying for certain caregiver training services as well as payment for community health integration services.2,3 These are the first MPFS services designed to include care involving community health workers, who link underserved communities with critical health care and social services in the community. Additionally, the rule also proposes coding and payment for evaluating the risks related to social factors that affect a patient’s health, such as access to affordable quality health care, that can take place during an annual wellness visit or in combination with an E/M visit.2,3 As dermatologists, we should be familiar with this set of G codes, as we will likely use them in practice for patients with transportation needs.
Advocacy Efforts on Medicare Payment Reform
Medicare physician payment reform needs to happen at a national level. Advocacy efforts by the AADA and other groups have been underway to mitigate the proposed 2024 cuts. The Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act (HR 2474) is a bill that was introduced by a bipartisan coalition of physicians to provide an inflation-based increase in Medicare payments in 2024 and beyond.6
Other Legislative Updates Affecting Dermatology
Modifier -25—Cigna’s policy requiring dermatologists to submit documentation to use modifier -25 when billing with E/M CPT codes 99212 through 99215 has been delayed indefinitely.7 If a payer denies a dermatologist payment, contact the AADA Patient Access and Payer Relations committee (privatepayer@aad.org) for assistance.
Telehealth and Digital Pathology—Recent legislation authorized extension of many of the Medicare telehealth and digital pathology flexibilities that were put in place during the COVID-19 public health emergency through December 31, 2024.8,9 Seventeen newly approved CPT telemedicine codes for new and established patient audio-visual and audio-only visits recently were surveyed.2,3 The data from the survey will be used as a key element in assigning a specific RVU to the CMS and will be included in the MPFS.
Thirty additional new digital pathology add-on CPT category III codes for 2024 were added to the ones from 2023.2,3 These codes can be used to report additional clinical staff work and service requirements associated with digitizing glass microscope slides for primary diagnosis. They cannot be used for archival or educational purposes, clinical conferences, training, or validating artificial intelligence algorithms. Category III codes used for emerging technologies have no assigned RVUs or reimbursement.2,3
The Cures Act—The Cures Act aims to ensure that patients have timely access to their health information.10 It requires all physicians to make their office notes, laboratory results, and other diagnostic reports available to patients as soon as the office receives them. The rules went into effect on April 5, 2021, with a limited definition of electronic health information; on October 6, 2022, the Cures Act rule expanded to include all electronic health information. The AADA has urged the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology to collaborate with stakeholder organizations to re-evaluate federal policies concerning the immediate release of electronic health information and information blocking, particularly in cases with life-altering diagnoses.10 They stressed the importance of prioritizing the well-being and emotional stability of patients and enhancing care by providing patients adequate time and support to process, comprehend, and discuss findings with their physician.
Proposed 2024 Medicare Quality Payment Program Requirements
The CMS proposed to increase the performance threshold in the quality payment program from 75 to 82 points for the 2024 Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) performance period, impacting the 2026 payment year.2,3,11 As a result of this increase, there could be more MIPS-eligible clinicians receiving penalties, which could be a reduction of up to 9%. The AADA will firmly oppose any increase in the threshold and strongly urge CMS to maintain the 75-point threshold. The performance category weights for the 2024 performance year will remain unchanged from the 2023 performance year.2,3,11
2024 Proposed Quality MIPS Measures Set—The CMS proposed to remove the topped-out MIPS measure 138 (coordination of care for melanoma).2,3,11 Additionally, it proposed to remove MIPS measure 402 (tobacco use and help with quitting among adolescents) as a quality measure from MIPS because the agency believes it is duplicative of measure 226 (preventive care and screening: tobacco use: screening and cessation intervention).2,3,11
MIPS Value Pathways—The CMS consolidated 2 previously established MIPS value pathways (MVPs): the Promoting Wellness MVP and the Optimizing Chronic Disease Management MVP.2,3,11 Proposed new MVPs for 2024 include Focusing on Women’s Health; Quality Care for the Treatment of Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorders; Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Disorders Including Hepatitis C and HIV; Quality Care in Mental Health and Substance Use Disorders; and Rehabilitative Support for Musculoskeletal Care. Dermatology is not impacted; however, the CMS plans to sunset traditional MIPS and replace it with MVPs—the future of MIPS.2,3,11 The AADA maintains that traditional MIPS should continue to be an option because MVPs have a limited number of measures for dermatologists.
Update on Reporting Suture Removal
There are 2 new CPT add-on codes—15853 and 15854—for the removal of sutures or staples not requiring anesthesia to be listed separately in addition to an appropriate E/M service. These add-on codes went into effect on January 1, 2023.12 These codes were created with the intent to capture and ensure remuneration for practice expenses that are not included in a stand-alone E/M encounter that occur after a 0-day procedure (eg, services reported with CPT codes 11102–11107 and 11300–11313) for wound check and suture removal where appropriate. These new add-on codes do not have physician work RVUs assigned to them because they are only for practice expenses (eg, clinical staff time, disposable supplies, use of equipment); CPT code 15853 is reported for the removal of sutures or staples, and CPT code 15854 is reported when both sutures and staples are removed. These codes can only be reported if an E/M service also is reported for the patient encounter.12
Final Thoughts
The AADA is working with the House of Medicine and the medical specialty community to develop specific proposals to reform the Medicare payment system.4 The proposed 2024 MPFS was released on July 13, 2023, and final regulations are expected in the late fall of 2023. The AADA will continue to engage with the CMS, but it is important for physicians to learn about and support advocacy priorities and efforts as well as join forces to protect their practices. As health care professionals, we have unique insights into the challenges and needs of our patients and the health care system. Advocacy can take various forms, such as supporting or opposing specific legislations, participating in grassroots campaigns, engaging with policymakers, and/or joining professional organizations that advocate for health care–related issues. Get involved, stay informed, and stay engaged through dermatology medical societies; together we can make a difference.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. NHE fact sheet. Updated September 6, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/NationalHealthExpendData/NHE-Fact-Sheet
- Medicare and Medicaid Programs; CY 2024 payment policies under the physician fee schedule and other changes to part B payment and coverage policies; Medicare shared savings program requirements; Medicare advantage; Medicare and Medicaid provider and supplier enrollment policies; and basic health program. Fed Regist. 2023;88:52262-53197. To be codified at 42 CFR §405, §410, §411, §414, §415, §418, §422, §423, §424, §425, §455, §489, §491, §495, §498, and §600. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2023/08/07/2023-14624/medicare-and-medicaid-programs-cy-2024-payment-policies-under-the-physician-fee-schedule-and-other
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar year (CY) 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule proposed rule. Published July 13, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/calendar-year-cy-2024-medicare-physician-fee-schedule-proposed-rule
- American Medical Association. Payment reform. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/health-care-advocacypayment-reform
- American Medical Association. Physician answers on this survey will shape future Medicare pay. Published July 31, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/medicare-medicaid/physician-answers-survey-will-shape-future -medicare-pay
- Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act, HR 2474, 118 Congress (2023-2024). https://www.congress.gov/bill/118th-congress/house-bill/2474
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. Academy advocacy priorities. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.aad.org/member/advocacy/priorities
- College of American Pathologists. Remote sign-out of cases with digital pathology FAQs. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cap.org/covid-19/remote-sign-out-faqs
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Telehealth. Updated September 6, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/medicare/coverage/telehealth
- The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology. ONC’s Cures Act final rule. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.healthit.gov/topic/oncs-cures-act-final-rule
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar Year (CY) 2024 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (PFS) Notice of Proposed Rule Making Quality Payment Program Policy Overview: Proposals and Requests for Information. Accessed September 12, 2023. https://email.aadresources.org/e3t/Ctc/I6+113/cVKqx04/VVWzj43dDbctW8c23GW1ZLnJHW1xTZ7Q50Y DYN89Qzy5nCVhV3Zsc37CgFV9W5Ck4-D42qs9BW38PtXn4LSlNLW1QKpPL4xT8BMW6Mcwww3FdwCHN3vfGTMXbtF-W2-Zzfy5WHDg6W88tx1F1KgsgxW7zDzT46C2sFXW800vQJ3lLsS_W5D6f1d30-f3cN1njgZ_dX7xkW447ldH2-kgc5VCs7Xg1GY6dsN87pLVJqJG5XW8VWwD-7VxVkJN777f5fJL7jBW8RxkQM1lcSDjVV746T3C-stpN52V_S5xj7q6W3_vldf3p1Yk2Vbd4ZD3cPrHqW5Pwv9m567fkzW1vfDm51H-T7rW1jVrxl8gstXyW5RVTn8863CVFW8g6LgK2YdhpkW34HC4z3_pGYgW8V_qWH3g-tTlW4S3RD-1dKry7W4_rW8d1ssZ1fVwXQjQ9krVMW8Y0bTt8Nr5CNW6vbG0h3wyx59W8WCrNW50p5n6W1r-VBC2rKh93N4W2RyYr7vvm3kxG1
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Chapter III surgery: integumentary system CPT codes 10000-19999 for Medicare national correct coding initiative policy manual. Updated January 1, 2023. Accessed September 26, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/medicare-ncci-policy-manual-2023-chapter-3.pdf
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. NHE fact sheet. Updated September 6, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/NationalHealthExpendData/NHE-Fact-Sheet
- Medicare and Medicaid Programs; CY 2024 payment policies under the physician fee schedule and other changes to part B payment and coverage policies; Medicare shared savings program requirements; Medicare advantage; Medicare and Medicaid provider and supplier enrollment policies; and basic health program. Fed Regist. 2023;88:52262-53197. To be codified at 42 CFR §405, §410, §411, §414, §415, §418, §422, §423, §424, §425, §455, §489, §491, §495, §498, and §600. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2023/08/07/2023-14624/medicare-and-medicaid-programs-cy-2024-payment-policies-under-the-physician-fee-schedule-and-other
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar year (CY) 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule proposed rule. Published July 13, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/calendar-year-cy-2024-medicare-physician-fee-schedule-proposed-rule
- American Medical Association. Payment reform. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/health-care-advocacypayment-reform
- American Medical Association. Physician answers on this survey will shape future Medicare pay. Published July 31, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/medicare-medicaid/physician-answers-survey-will-shape-future -medicare-pay
- Strengthening Medicare for Patients and Providers Act, HR 2474, 118 Congress (2023-2024). https://www.congress.gov/bill/118th-congress/house-bill/2474
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. Academy advocacy priorities. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.aad.org/member/advocacy/priorities
- College of American Pathologists. Remote sign-out of cases with digital pathology FAQs. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cap.org/covid-19/remote-sign-out-faqs
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Telehealth. Updated September 6, 2023. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/medicare/coverage/telehealth
- The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology. ONC’s Cures Act final rule. Accessed September 18, 2023. https://www.healthit.gov/topic/oncs-cures-act-final-rule
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar Year (CY) 2024 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (PFS) Notice of Proposed Rule Making Quality Payment Program Policy Overview: Proposals and Requests for Information. Accessed September 12, 2023. https://email.aadresources.org/e3t/Ctc/I6+113/cVKqx04/VVWzj43dDbctW8c23GW1ZLnJHW1xTZ7Q50Y DYN89Qzy5nCVhV3Zsc37CgFV9W5Ck4-D42qs9BW38PtXn4LSlNLW1QKpPL4xT8BMW6Mcwww3FdwCHN3vfGTMXbtF-W2-Zzfy5WHDg6W88tx1F1KgsgxW7zDzT46C2sFXW800vQJ3lLsS_W5D6f1d30-f3cN1njgZ_dX7xkW447ldH2-kgc5VCs7Xg1GY6dsN87pLVJqJG5XW8VWwD-7VxVkJN777f5fJL7jBW8RxkQM1lcSDjVV746T3C-stpN52V_S5xj7q6W3_vldf3p1Yk2Vbd4ZD3cPrHqW5Pwv9m567fkzW1vfDm51H-T7rW1jVrxl8gstXyW5RVTn8863CVFW8g6LgK2YdhpkW34HC4z3_pGYgW8V_qWH3g-tTlW4S3RD-1dKry7W4_rW8d1ssZ1fVwXQjQ9krVMW8Y0bTt8Nr5CNW6vbG0h3wyx59W8WCrNW50p5n6W1r-VBC2rKh93N4W2RyYr7vvm3kxG1
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Chapter III surgery: integumentary system CPT codes 10000-19999 for Medicare national correct coding initiative policy manual. Updated January 1, 2023. Accessed September 26, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/medicare-ncci-policy-manual-2023-chapter-3.pdf
PRACTICE POINTS
- The proposed 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule published by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services in July 2023 will negatively impact dermatology practices.
- The final regulations are expected in November 2023.