User login
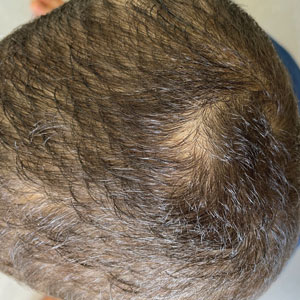
Tinea capitis (TC) most often is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. The peak incidence is between 3 and 7 years of age. Noninflammatory TC typically presents as fine scaling with single or multiple scaly patches of circular alopecia (grey patches); diffuse or patchy, fine, white, adherent scaling of the scalp resembling generalized dandruff with subtle hair loss; or single or multiple patches of well-demarcated areas of alopecia with fine scale studded with broken-off hairs at the scalp surface, resulting in a black dot appearance. Inflammatory variants of TC include kerion and favus.1 Herein, updates on diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of TC are provided, as well as a discussion of changes in the fungal microbiome associated with TC. Lastly, insights to some queries that practitioners may encounter when treating children with TC are provided.
Genetic Susceptibility
Molecular techniques have identified a number of macrophage regulator, leukocyte activation and migration, and cutaneous permeability genes associated with susceptibility to TC. These findings indicate that genetically determined deficiency in adaptive immune responses may affect the predisposition to dermatophyte infections.2
Clinical Varieties of Infection
Dermatophytes causing ringworm are capable of invading the hair shafts and can simultaneously invade smooth or glabrous skin (eg, T tonsurans, Trichophyton schoenleinii, Trichophyton violaceum). Some causative dermatophytes can even penetrate the nails (eg, Trichophyton soudanense). The clinical presentation is dependent on 3 main patterns of hair invasion3:
• Ectothrix: A mid-follicular pattern of invasion with hyphae growing down to the hair bulb that commonly is caused by Microsporum species. It clinically presents with scaling and inflammation with hair shafts breaking 2 to 3 mm above the scalp level.
• Endothrix: This pattern is nonfluorescent on Wood lamp examination, and hairs often break at the scalp level (black dot type). Trichophyton tonsurans, T soudanense, Trichophyton rubrum, and T violaceum are common causes.
• Favus: In this pattern, T schoenleinii is a common cause, and hairs grow to considerable lengths above the scalp with less damage than the other patterns. The hair shafts present with characteristic air spaces, and hyphae form clusters at the level of the epidermis.
Diagnosis
Optimal treatment of TC relies on proper identification of the causative agent. Fungal culture remains the gold standard of mycologic diagnosis regardless of its delayed results, which may take up to 4 weeks for proper identification of the fungal colonies and require ample expertise to interpret the morphologic features of the grown colonies.4
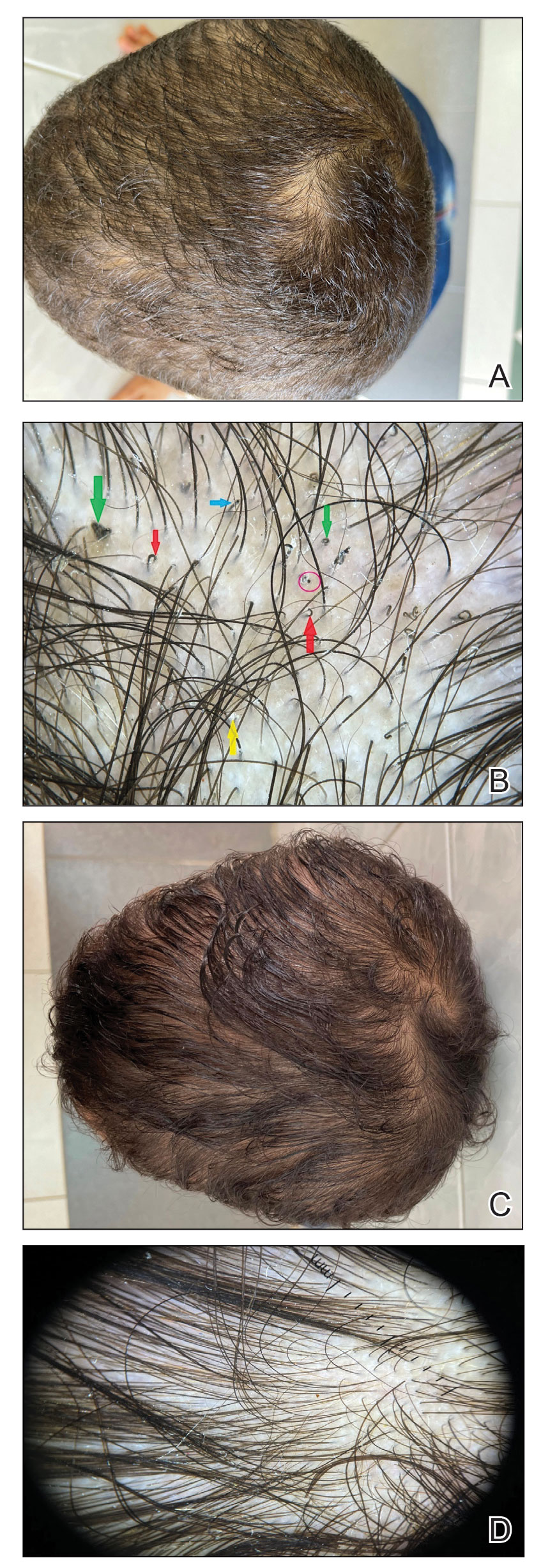
Other tests such as the potassium hydroxide preparation are nonspecific and do not identify the dermatophyte species. Although this method has been reported to have 5% to 15% false-negative results in routine practice depending on the skill of the observer and the quality of sampling, microscopic examination is essential, as it may allow the clinician to start treatment sooner pending culture results. The use of a Wood lamp is not suitable for definitive species identification, as this technique primarily is useful for observing fluorescence in ectothrix infection caused by Microsporum species, with the exception of T schoenleinii; otherwise, Trichophyton species, which cause endothrix infections, do not fluoresce.5Polymerase chain reaction is a sensitive technique that can help identify both the genus and species of common dermatophytes. Common target sequences include the ribosomal internal transcribed spacer and translation elongation factor 1α. The use of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry also has become popular for dermatophyte identification.6Trichoscopic diagnosis of TC, which is simple and noninvasive, is becoming increasingly popular. Features such as short, broken, black dot, comma, corkscrew, and/or zigzag hairs, as well as perifollicular scaling, are helpful for diagnosing TC (Figure). Moreover, trichoscopy can be useful for differentiating other common causes of hair loss, such as trichotillomania and alopecia areata. It had been reported that the trichoscopic features of TC can be seen as early as 2 weeks after starting treatment and therefore this can be a reliable period in which to follow-up with the patient to evaluate progress. The disappearance of black dots and comma hairs can be appreciated from 2 weeks onwards by trichoscopic evaluation.4
Treatment
The common recommendation for first-line treatment of TC is the use of systemic antifungals with the use of a topical agent as an adjuvant to prevent the spread of fungal spores. For almost 6 decades, griseofulvin had been the gold-standard fungistatic used for treating TC in patients older than 2 years until the 2007 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of terbinafine fungicidal oral granules for treatment of TC in patients older than 4 years.7
Meta-analyses have demonstrated comparable efficacy for a 4-week course of terbinafine compared to 6 weeks of griseofulvin for TC based on the infectious organism. Terbinafine demonstrated superiority in treating T tonsurans and a similar efficacy in treating T violaceum, while griseofulvin was superior in treating M canis and other Microsporum species.8,9
The off-label use of fluconazole and itraconazole to treat TC is gaining popularity, with limited trials showing increased evidence of their effectiveness. There is not much clinical evidence to support the use of other oral antifungals, including the newer azoles such as voriconazole or posaconazole.9
Newer limited evidence has shown the off-label use of photodynamic therapy to be a promising alternative to systemic antifungal therapy in treating TC, pending validation by larger sample trials.10In my practice, I have found that severe cases of TC demonstrating inflammation or possible widespread id reactions are better treated with oral steroids. Ketoconazole shampoo or selenium sulfide used 2 to 3 times weekly to prevent spread in the early phases of therapy is a good adjunct to systemic treatment. Cases with kerions should be assessed for the possibility of a coexisting bacterial infection under the crusts, and if confirmed, antibiotics should be started.9The commonly used systemic antifungals generally are safe with a low side-effect profile, but there is a risk for hepatotoxicity. The FDA recommends that baseline alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase levels should be obtained prior to beginning a terbinafine-based treatment regimen.11 The American Academy of Pediatrics has specifically stated that laboratory testing of serum hepatic enzymes is not a requirement if a griseofulvin-based regimen does not exceed 8 weeks; however, transaminase levels (alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase) should be considered in patients using terbinafine at baseline or if treatment is prolonged beyond 4 to 6 weeks.12 In agreement with the FDA guidelines, the Canadian Pediatric Society has suggested that liver enzymes should be periodically monitored in patients being treated with terbinafine beyond 4 to 6 weeks.13
Changes in the Fungal Microbiome
Research has shown that changes in the fungal microbiome were associated with an altered bacterial community in patients with TC. During fungal infection, the relative abundances of Cutibacterium and Corynebacterium increased, and the relative abundance of Streptococcus decreased. In addition, some uncommon bacterial genera such as Herbaspirillum and Methylorubrum were detected on the scalp in TC.14
Carrier State
Carrier state is determined for those siblings and contacts of cases with a clinically normal scalp that are positive on culture. Those individuals could represent a potential reservoir responsible for contamination (or recontamination) of the patient as well as treatment failure. Opinions remain divided as to whether to use oral antifungal therapy in these carriers or maintain therapy on antifungal shampoos containing ketoconazole or povidone-iodine. Due to the paucity of available data, my experience has shown that it is sufficient to use antifungal shampoos for such carriers. In zoophilic infections, it is important to identify and treat the animal source.6-9
Final Thoughts
Successful treatment of TC requires accurate identification of the pathogen, which commonly is achieved via fungal culture. Despite its practical value, the conventional identification of dermatophytes based on morphologic features can be highly challenging due to the low positive rate and delayed results. Trichoscopy is a quick, handy, and noninvasive tool that can better indicate the diagnosis and also is helpful for follow-up on treatment progress. Due to better understanding of the immunology and genetic susceptibility associated with TC spread, the current treatment pipeline holds more insight into better control of this condition. Increased surveillance, prompt diagnosis, and early onset of systemic treatment are the key to proper prevention of spread of TC.
- Leung AKC, Hon KL, Leong KF, et al. Tinea capitis: an updated review. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2020;14:58-68.
- Abdel-Rahman SM, Preuett BL. Genetic predictors of susceptibility to cutaneous fungal infections: a pilot genome wide association study to refine a candidate gene search. J Dermatol Sci. 2012;67:147-152.
- Hay RJ. Tinea capitis: current status. Mycopathologia. 2017;182:87-93.
- Wahbah HR, Atallah RB, Eldahshan RM, et al. A prospective clinical and trichoscopic study of tinea capitis in children during treatment [published online May 23, 2022]. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15582. doi:10.1111/dth.15582
- Salehi Z, Shams-Ghahfarokhi M, Razzaghi-Abyaneh M. Molecular epidemiology, genetic diversity, and antifungal susceptibility of major pathogenic dermatophytes isolated from human dermatophytosis. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:643509.
- Lamisil. Package insert. Novartis; 2011. Accessed October 17, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/020539s021lbl.pdf
- Gupta AK, Drummond-Main C. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing particular doses of griseofulvin and terbinafine for the treatment of tinea capitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:1-6.
- Tey HL, Tan AS, Chan YC. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing griseofulvin and terbinafine in the treatment of tinea capitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:663-670.
- Gupta AK, Friedlander SF, Simkovich AJ. Tinea capitis: an update. Pediatr Dermatol. 2022;39:167-172.
- Aspiroz C, Melcon B, Cerro PA, et al. Tinea capitis caused by Microsporum canis treated with methyl-aminolevulinate daylight photodynamic therapy and ketoconazole shampooing. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:567-568.
- Aleohin N, Bar J, Bar-Ilan E, et al. Laboratory monitoring during antifungal treatment of paediatric tinea capitis. Mycoses. 2021;64:157-161.
- Kimberlin DW, Brady MT, Jackson MA, et al, eds. Tinea capitis. In: Red Book 2018-2021: Report of the Committee of Infectious Diseases. American Academy of Pediatrics; 2018:798-801.
- Bortolussi R, Martin S, Audcent T, et al. Antifungal agents for common outpatient paediatric infections. Canadian Paediatric Society website. Published June 20, 2019. Accessed October 4, 2022. https://www.cps.ca/en/documents/position/antifungal-agents-common-infections
- Tao R, Zhu P, Zhou Y, et al. Altered skin fungal and bacterial community compositions in tinea capitis. Mycoses. 2022;65:834-840.
Tinea capitis (TC) most often is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. The peak incidence is between 3 and 7 years of age. Noninflammatory TC typically presents as fine scaling with single or multiple scaly patches of circular alopecia (grey patches); diffuse or patchy, fine, white, adherent scaling of the scalp resembling generalized dandruff with subtle hair loss; or single or multiple patches of well-demarcated areas of alopecia with fine scale studded with broken-off hairs at the scalp surface, resulting in a black dot appearance. Inflammatory variants of TC include kerion and favus.1 Herein, updates on diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of TC are provided, as well as a discussion of changes in the fungal microbiome associated with TC. Lastly, insights to some queries that practitioners may encounter when treating children with TC are provided.
Genetic Susceptibility
Molecular techniques have identified a number of macrophage regulator, leukocyte activation and migration, and cutaneous permeability genes associated with susceptibility to TC. These findings indicate that genetically determined deficiency in adaptive immune responses may affect the predisposition to dermatophyte infections.2
Clinical Varieties of Infection
Dermatophytes causing ringworm are capable of invading the hair shafts and can simultaneously invade smooth or glabrous skin (eg, T tonsurans, Trichophyton schoenleinii, Trichophyton violaceum). Some causative dermatophytes can even penetrate the nails (eg, Trichophyton soudanense). The clinical presentation is dependent on 3 main patterns of hair invasion3:
• Ectothrix: A mid-follicular pattern of invasion with hyphae growing down to the hair bulb that commonly is caused by Microsporum species. It clinically presents with scaling and inflammation with hair shafts breaking 2 to 3 mm above the scalp level.
• Endothrix: This pattern is nonfluorescent on Wood lamp examination, and hairs often break at the scalp level (black dot type). Trichophyton tonsurans, T soudanense, Trichophyton rubrum, and T violaceum are common causes.
• Favus: In this pattern, T schoenleinii is a common cause, and hairs grow to considerable lengths above the scalp with less damage than the other patterns. The hair shafts present with characteristic air spaces, and hyphae form clusters at the level of the epidermis.
Diagnosis
Optimal treatment of TC relies on proper identification of the causative agent. Fungal culture remains the gold standard of mycologic diagnosis regardless of its delayed results, which may take up to 4 weeks for proper identification of the fungal colonies and require ample expertise to interpret the morphologic features of the grown colonies.4
Other tests such as the potassium hydroxide preparation are nonspecific and do not identify the dermatophyte species. Although this method has been reported to have 5% to 15% false-negative results in routine practice depending on the skill of the observer and the quality of sampling, microscopic examination is essential, as it may allow the clinician to start treatment sooner pending culture results. The use of a Wood lamp is not suitable for definitive species identification, as this technique primarily is useful for observing fluorescence in ectothrix infection caused by Microsporum species, with the exception of T schoenleinii; otherwise, Trichophyton species, which cause endothrix infections, do not fluoresce.5Polymerase chain reaction is a sensitive technique that can help identify both the genus and species of common dermatophytes. Common target sequences include the ribosomal internal transcribed spacer and translation elongation factor 1α. The use of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry also has become popular for dermatophyte identification.6Trichoscopic diagnosis of TC, which is simple and noninvasive, is becoming increasingly popular. Features such as short, broken, black dot, comma, corkscrew, and/or zigzag hairs, as well as perifollicular scaling, are helpful for diagnosing TC (Figure). Moreover, trichoscopy can be useful for differentiating other common causes of hair loss, such as trichotillomania and alopecia areata. It had been reported that the trichoscopic features of TC can be seen as early as 2 weeks after starting treatment and therefore this can be a reliable period in which to follow-up with the patient to evaluate progress. The disappearance of black dots and comma hairs can be appreciated from 2 weeks onwards by trichoscopic evaluation.4

Treatment
The common recommendation for first-line treatment of TC is the use of systemic antifungals with the use of a topical agent as an adjuvant to prevent the spread of fungal spores. For almost 6 decades, griseofulvin had been the gold-standard fungistatic used for treating TC in patients older than 2 years until the 2007 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of terbinafine fungicidal oral granules for treatment of TC in patients older than 4 years.7
Meta-analyses have demonstrated comparable efficacy for a 4-week course of terbinafine compared to 6 weeks of griseofulvin for TC based on the infectious organism. Terbinafine demonstrated superiority in treating T tonsurans and a similar efficacy in treating T violaceum, while griseofulvin was superior in treating M canis and other Microsporum species.8,9
The off-label use of fluconazole and itraconazole to treat TC is gaining popularity, with limited trials showing increased evidence of their effectiveness. There is not much clinical evidence to support the use of other oral antifungals, including the newer azoles such as voriconazole or posaconazole.9
Newer limited evidence has shown the off-label use of photodynamic therapy to be a promising alternative to systemic antifungal therapy in treating TC, pending validation by larger sample trials.10In my practice, I have found that severe cases of TC demonstrating inflammation or possible widespread id reactions are better treated with oral steroids. Ketoconazole shampoo or selenium sulfide used 2 to 3 times weekly to prevent spread in the early phases of therapy is a good adjunct to systemic treatment. Cases with kerions should be assessed for the possibility of a coexisting bacterial infection under the crusts, and if confirmed, antibiotics should be started.9The commonly used systemic antifungals generally are safe with a low side-effect profile, but there is a risk for hepatotoxicity. The FDA recommends that baseline alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase levels should be obtained prior to beginning a terbinafine-based treatment regimen.11 The American Academy of Pediatrics has specifically stated that laboratory testing of serum hepatic enzymes is not a requirement if a griseofulvin-based regimen does not exceed 8 weeks; however, transaminase levels (alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase) should be considered in patients using terbinafine at baseline or if treatment is prolonged beyond 4 to 6 weeks.12 In agreement with the FDA guidelines, the Canadian Pediatric Society has suggested that liver enzymes should be periodically monitored in patients being treated with terbinafine beyond 4 to 6 weeks.13
Changes in the Fungal Microbiome
Research has shown that changes in the fungal microbiome were associated with an altered bacterial community in patients with TC. During fungal infection, the relative abundances of Cutibacterium and Corynebacterium increased, and the relative abundance of Streptococcus decreased. In addition, some uncommon bacterial genera such as Herbaspirillum and Methylorubrum were detected on the scalp in TC.14
Carrier State
Carrier state is determined for those siblings and contacts of cases with a clinically normal scalp that are positive on culture. Those individuals could represent a potential reservoir responsible for contamination (or recontamination) of the patient as well as treatment failure. Opinions remain divided as to whether to use oral antifungal therapy in these carriers or maintain therapy on antifungal shampoos containing ketoconazole or povidone-iodine. Due to the paucity of available data, my experience has shown that it is sufficient to use antifungal shampoos for such carriers. In zoophilic infections, it is important to identify and treat the animal source.6-9
Final Thoughts
Successful treatment of TC requires accurate identification of the pathogen, which commonly is achieved via fungal culture. Despite its practical value, the conventional identification of dermatophytes based on morphologic features can be highly challenging due to the low positive rate and delayed results. Trichoscopy is a quick, handy, and noninvasive tool that can better indicate the diagnosis and also is helpful for follow-up on treatment progress. Due to better understanding of the immunology and genetic susceptibility associated with TC spread, the current treatment pipeline holds more insight into better control of this condition. Increased surveillance, prompt diagnosis, and early onset of systemic treatment are the key to proper prevention of spread of TC.
Tinea capitis (TC) most often is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. The peak incidence is between 3 and 7 years of age. Noninflammatory TC typically presents as fine scaling with single or multiple scaly patches of circular alopecia (grey patches); diffuse or patchy, fine, white, adherent scaling of the scalp resembling generalized dandruff with subtle hair loss; or single or multiple patches of well-demarcated areas of alopecia with fine scale studded with broken-off hairs at the scalp surface, resulting in a black dot appearance. Inflammatory variants of TC include kerion and favus.1 Herein, updates on diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of TC are provided, as well as a discussion of changes in the fungal microbiome associated with TC. Lastly, insights to some queries that practitioners may encounter when treating children with TC are provided.
Genetic Susceptibility
Molecular techniques have identified a number of macrophage regulator, leukocyte activation and migration, and cutaneous permeability genes associated with susceptibility to TC. These findings indicate that genetically determined deficiency in adaptive immune responses may affect the predisposition to dermatophyte infections.2
Clinical Varieties of Infection
Dermatophytes causing ringworm are capable of invading the hair shafts and can simultaneously invade smooth or glabrous skin (eg, T tonsurans, Trichophyton schoenleinii, Trichophyton violaceum). Some causative dermatophytes can even penetrate the nails (eg, Trichophyton soudanense). The clinical presentation is dependent on 3 main patterns of hair invasion3:
• Ectothrix: A mid-follicular pattern of invasion with hyphae growing down to the hair bulb that commonly is caused by Microsporum species. It clinically presents with scaling and inflammation with hair shafts breaking 2 to 3 mm above the scalp level.
• Endothrix: This pattern is nonfluorescent on Wood lamp examination, and hairs often break at the scalp level (black dot type). Trichophyton tonsurans, T soudanense, Trichophyton rubrum, and T violaceum are common causes.
• Favus: In this pattern, T schoenleinii is a common cause, and hairs grow to considerable lengths above the scalp with less damage than the other patterns. The hair shafts present with characteristic air spaces, and hyphae form clusters at the level of the epidermis.
Diagnosis
Optimal treatment of TC relies on proper identification of the causative agent. Fungal culture remains the gold standard of mycologic diagnosis regardless of its delayed results, which may take up to 4 weeks for proper identification of the fungal colonies and require ample expertise to interpret the morphologic features of the grown colonies.4
Other tests such as the potassium hydroxide preparation are nonspecific and do not identify the dermatophyte species. Although this method has been reported to have 5% to 15% false-negative results in routine practice depending on the skill of the observer and the quality of sampling, microscopic examination is essential, as it may allow the clinician to start treatment sooner pending culture results. The use of a Wood lamp is not suitable for definitive species identification, as this technique primarily is useful for observing fluorescence in ectothrix infection caused by Microsporum species, with the exception of T schoenleinii; otherwise, Trichophyton species, which cause endothrix infections, do not fluoresce.5Polymerase chain reaction is a sensitive technique that can help identify both the genus and species of common dermatophytes. Common target sequences include the ribosomal internal transcribed spacer and translation elongation factor 1α. The use of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry also has become popular for dermatophyte identification.6Trichoscopic diagnosis of TC, which is simple and noninvasive, is becoming increasingly popular. Features such as short, broken, black dot, comma, corkscrew, and/or zigzag hairs, as well as perifollicular scaling, are helpful for diagnosing TC (Figure). Moreover, trichoscopy can be useful for differentiating other common causes of hair loss, such as trichotillomania and alopecia areata. It had been reported that the trichoscopic features of TC can be seen as early as 2 weeks after starting treatment and therefore this can be a reliable period in which to follow-up with the patient to evaluate progress. The disappearance of black dots and comma hairs can be appreciated from 2 weeks onwards by trichoscopic evaluation.4

Treatment
The common recommendation for first-line treatment of TC is the use of systemic antifungals with the use of a topical agent as an adjuvant to prevent the spread of fungal spores. For almost 6 decades, griseofulvin had been the gold-standard fungistatic used for treating TC in patients older than 2 years until the 2007 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of terbinafine fungicidal oral granules for treatment of TC in patients older than 4 years.7
Meta-analyses have demonstrated comparable efficacy for a 4-week course of terbinafine compared to 6 weeks of griseofulvin for TC based on the infectious organism. Terbinafine demonstrated superiority in treating T tonsurans and a similar efficacy in treating T violaceum, while griseofulvin was superior in treating M canis and other Microsporum species.8,9
The off-label use of fluconazole and itraconazole to treat TC is gaining popularity, with limited trials showing increased evidence of their effectiveness. There is not much clinical evidence to support the use of other oral antifungals, including the newer azoles such as voriconazole or posaconazole.9
Newer limited evidence has shown the off-label use of photodynamic therapy to be a promising alternative to systemic antifungal therapy in treating TC, pending validation by larger sample trials.10In my practice, I have found that severe cases of TC demonstrating inflammation or possible widespread id reactions are better treated with oral steroids. Ketoconazole shampoo or selenium sulfide used 2 to 3 times weekly to prevent spread in the early phases of therapy is a good adjunct to systemic treatment. Cases with kerions should be assessed for the possibility of a coexisting bacterial infection under the crusts, and if confirmed, antibiotics should be started.9The commonly used systemic antifungals generally are safe with a low side-effect profile, but there is a risk for hepatotoxicity. The FDA recommends that baseline alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase levels should be obtained prior to beginning a terbinafine-based treatment regimen.11 The American Academy of Pediatrics has specifically stated that laboratory testing of serum hepatic enzymes is not a requirement if a griseofulvin-based regimen does not exceed 8 weeks; however, transaminase levels (alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase) should be considered in patients using terbinafine at baseline or if treatment is prolonged beyond 4 to 6 weeks.12 In agreement with the FDA guidelines, the Canadian Pediatric Society has suggested that liver enzymes should be periodically monitored in patients being treated with terbinafine beyond 4 to 6 weeks.13
Changes in the Fungal Microbiome
Research has shown that changes in the fungal microbiome were associated with an altered bacterial community in patients with TC. During fungal infection, the relative abundances of Cutibacterium and Corynebacterium increased, and the relative abundance of Streptococcus decreased. In addition, some uncommon bacterial genera such as Herbaspirillum and Methylorubrum were detected on the scalp in TC.14
Carrier State
Carrier state is determined for those siblings and contacts of cases with a clinically normal scalp that are positive on culture. Those individuals could represent a potential reservoir responsible for contamination (or recontamination) of the patient as well as treatment failure. Opinions remain divided as to whether to use oral antifungal therapy in these carriers or maintain therapy on antifungal shampoos containing ketoconazole or povidone-iodine. Due to the paucity of available data, my experience has shown that it is sufficient to use antifungal shampoos for such carriers. In zoophilic infections, it is important to identify and treat the animal source.6-9
Final Thoughts
Successful treatment of TC requires accurate identification of the pathogen, which commonly is achieved via fungal culture. Despite its practical value, the conventional identification of dermatophytes based on morphologic features can be highly challenging due to the low positive rate and delayed results. Trichoscopy is a quick, handy, and noninvasive tool that can better indicate the diagnosis and also is helpful for follow-up on treatment progress. Due to better understanding of the immunology and genetic susceptibility associated with TC spread, the current treatment pipeline holds more insight into better control of this condition. Increased surveillance, prompt diagnosis, and early onset of systemic treatment are the key to proper prevention of spread of TC.
- Leung AKC, Hon KL, Leong KF, et al. Tinea capitis: an updated review. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2020;14:58-68.
- Abdel-Rahman SM, Preuett BL. Genetic predictors of susceptibility to cutaneous fungal infections: a pilot genome wide association study to refine a candidate gene search. J Dermatol Sci. 2012;67:147-152.
- Hay RJ. Tinea capitis: current status. Mycopathologia. 2017;182:87-93.
- Wahbah HR, Atallah RB, Eldahshan RM, et al. A prospective clinical and trichoscopic study of tinea capitis in children during treatment [published online May 23, 2022]. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15582. doi:10.1111/dth.15582
- Salehi Z, Shams-Ghahfarokhi M, Razzaghi-Abyaneh M. Molecular epidemiology, genetic diversity, and antifungal susceptibility of major pathogenic dermatophytes isolated from human dermatophytosis. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:643509.
- Lamisil. Package insert. Novartis; 2011. Accessed October 17, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/020539s021lbl.pdf
- Gupta AK, Drummond-Main C. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing particular doses of griseofulvin and terbinafine for the treatment of tinea capitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:1-6.
- Tey HL, Tan AS, Chan YC. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing griseofulvin and terbinafine in the treatment of tinea capitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:663-670.
- Gupta AK, Friedlander SF, Simkovich AJ. Tinea capitis: an update. Pediatr Dermatol. 2022;39:167-172.
- Aspiroz C, Melcon B, Cerro PA, et al. Tinea capitis caused by Microsporum canis treated with methyl-aminolevulinate daylight photodynamic therapy and ketoconazole shampooing. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:567-568.
- Aleohin N, Bar J, Bar-Ilan E, et al. Laboratory monitoring during antifungal treatment of paediatric tinea capitis. Mycoses. 2021;64:157-161.
- Kimberlin DW, Brady MT, Jackson MA, et al, eds. Tinea capitis. In: Red Book 2018-2021: Report of the Committee of Infectious Diseases. American Academy of Pediatrics; 2018:798-801.
- Bortolussi R, Martin S, Audcent T, et al. Antifungal agents for common outpatient paediatric infections. Canadian Paediatric Society website. Published June 20, 2019. Accessed October 4, 2022. https://www.cps.ca/en/documents/position/antifungal-agents-common-infections
- Tao R, Zhu P, Zhou Y, et al. Altered skin fungal and bacterial community compositions in tinea capitis. Mycoses. 2022;65:834-840.
- Leung AKC, Hon KL, Leong KF, et al. Tinea capitis: an updated review. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2020;14:58-68.
- Abdel-Rahman SM, Preuett BL. Genetic predictors of susceptibility to cutaneous fungal infections: a pilot genome wide association study to refine a candidate gene search. J Dermatol Sci. 2012;67:147-152.
- Hay RJ. Tinea capitis: current status. Mycopathologia. 2017;182:87-93.
- Wahbah HR, Atallah RB, Eldahshan RM, et al. A prospective clinical and trichoscopic study of tinea capitis in children during treatment [published online May 23, 2022]. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15582. doi:10.1111/dth.15582
- Salehi Z, Shams-Ghahfarokhi M, Razzaghi-Abyaneh M. Molecular epidemiology, genetic diversity, and antifungal susceptibility of major pathogenic dermatophytes isolated from human dermatophytosis. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:643509.
- Lamisil. Package insert. Novartis; 2011. Accessed October 17, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/020539s021lbl.pdf
- Gupta AK, Drummond-Main C. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing particular doses of griseofulvin and terbinafine for the treatment of tinea capitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:1-6.
- Tey HL, Tan AS, Chan YC. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials comparing griseofulvin and terbinafine in the treatment of tinea capitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:663-670.
- Gupta AK, Friedlander SF, Simkovich AJ. Tinea capitis: an update. Pediatr Dermatol. 2022;39:167-172.
- Aspiroz C, Melcon B, Cerro PA, et al. Tinea capitis caused by Microsporum canis treated with methyl-aminolevulinate daylight photodynamic therapy and ketoconazole shampooing. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:567-568.
- Aleohin N, Bar J, Bar-Ilan E, et al. Laboratory monitoring during antifungal treatment of paediatric tinea capitis. Mycoses. 2021;64:157-161.
- Kimberlin DW, Brady MT, Jackson MA, et al, eds. Tinea capitis. In: Red Book 2018-2021: Report of the Committee of Infectious Diseases. American Academy of Pediatrics; 2018:798-801.
- Bortolussi R, Martin S, Audcent T, et al. Antifungal agents for common outpatient paediatric infections. Canadian Paediatric Society website. Published June 20, 2019. Accessed October 4, 2022. https://www.cps.ca/en/documents/position/antifungal-agents-common-infections
- Tao R, Zhu P, Zhou Y, et al. Altered skin fungal and bacterial community compositions in tinea capitis. Mycoses. 2022;65:834-840.