User login
Q: On the basis of the skin findings, which test should be ordered to establish a diagnosis?
- Serum anti-nuclear antibody (ANA)
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin serum level
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)
- Serum amylase
A: The lesions of a lobular, neutrophilic panniculitis should raise the possibility of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Hence, measuring the alpha-1 antitrypsin serum level is the best answer.
Many other conditions can give rise to panniculitis, including pancreatitis, lupus, and sarcoidosis, each of which is suggested by the various other test choices above. However, although the ANA level might be elevated in lupus, the ANA is quite nonspecific. The serum ACE level is frequently ordered as a screening test for sarcoidosis, although it has very little utility in its diagnosis. Panniculitis due to pancreatitis with an elevated serum amylase level would be relatively unlikely in the absence of pancreatic symptoms (eg, abdominal pain).
Panniculitis may be the only clinical manifestation of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, which can also be accompanied (depending on the phenotype) by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cirrhosis. Since alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is underrecognized in general, suspecting it when patients present with panniculitis will likely enhance its detection. Similarly, national guidelines recommend testing for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency in patients with either symptomatic, fixed airflow obstruction or cirrhosis that is otherwise unexplained, as well as in patients with panniculitis.1
PANNICULITIS DUE TO ALPHA-1 ANTITRYPSIN DEFICIENCY

Likely due to proteolytic damage
Though incompletely understood, the panniculitis in alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is likely the result of unopposed proteolytic damage in the subcutaneous fat by membrane-bound serine proteases, akin to the pathogenesis of pulmonary emphysema in people with severe deficiency of alpha-1 antitrypsin. Supporting evidence for the inflammatory, proteolytic pathogenesis of panniculitis in alpha-1 anti-trypsin deficiency includes the presence of inflammatory exudates in the subcutaneous tissues, as well as the rapid improvement seen with the infusion of purified pooled human alpha-1 proteinase inhibitor.2–4
Red, painful nodules
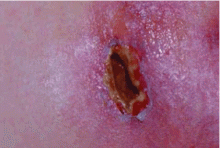
Panniculitis due to alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency classically presents as red, painful nodules that may break down and ooze an oily discharge.5–10 As in the patient presented here, common sites of occurrence are areas of trauma, eg, on the thighs and buttocks, abdomen, and upper extremities (Figure 1). Indeed, in a review of the 41 reported cases of panniculitis related to alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, Geraminejad et al11 reported that the erythe-matous plaques and nodules occurred on the thighs, hips, buttocks, or groin in 44% of cases in which the location was cited. Factors predisposing to panniculitis include trauma (cited in 35% of instances), cryosurgery, and, in the case of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, extravasation of intravenous clarithromycin (Biaxin).11–13
Clinical features that distinguish the panniculitis associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency from other types of panniculitis include ulceration and an oily discharge, both of which were present in the patient discussed here.
Neutrophils, necrosis, scarring, fibrosis
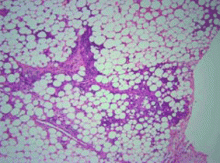
Several distinctive phases and features characterize the histology of panniculitis associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.5,7 Initially, neutrophils briskly infiltrate the reticular dermis, splaying the collagen bundles. In the subcutaneous fat, the neutrophilic infiltrate is in a lobular pattern, affecting individual adipocytes. Rarely, a septal pattern or a mixed lobular and septal pattern can be seen. This phase is followed by dissolution of the dermal collagen, with liquefactive necrosis of the subcutaneous fat (clinically appearing as ulceration and leading to oily drainage). In the late stage, there is scarring and fibrosis with little or no inflammation.
Various treatments tried
Various therapies for panniculitis associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency have been tried, including corticosteroids, doxycycline (Vibramycin), dapsone, plasma exchange, liver transplantation, and intravenous pooled human plasma alpha-1 proteinase inhibitor (so-called augmentation therapy). Because panniculitis associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is rare, neither controlled, blinded studies nor even large observational series have been reported. However, the limited reported experience with augmentation therapy suggests that it can confer rapid and dramatic improvement in panniculitis in patients with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
- American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: standards for the diagnosis and management of individuals with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003; 168:818–900.
- Smith KC, Pittelkow MR, Su WP. Panniculitis associated with severe alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Treatment and review of the literature. Arch Dermatol 1987; 123:1655–1661.
- Furey NL, Golden RS, Potts SR. Treatment of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, massive edema, and panniculitis with alpha-1 protease inhibitor [letter]. Ann Intern Med 1996; 125:699.
- O’Riordan K, Blei A, Rao MS, Abecassis M. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency-associated panniculitis: resolution with intravenous alpha-1 antitrypsin administration and liver transplantation. Transplantation 1997; 63:480–482.
- Stoller JK, Piliang M. Panniculitis in alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency: a review. Clin Pulm Med 2008; 15:113–117.
- Hendrick SJ, Silverman AK, Solomon AR, Headington JT. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency associated with panniculitis. J Am Acad Derm 1988; 18:684–692.
- Loche F, Tremeau-Martinage C, Laplanche G, Massip P, Bazex J. Panniculitis revealing qualitative alpha-1 antitrypsine deficiency (MS variant). Eur J Dermatol 1999; 9:565–567.
- McBean J, Sable A, Maude J, Robinson-Bostom L. Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency panniculitis. Cutis 2003; 71:205–209.
- Pittelkow MR, Smith KC, Su WP. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency and panniculitis. Perspectives on disease relationship and replacement therapy. Am J Med 1988; 84:80–86.
- Requena L, Sánchez Yus E. Panniculitis. Part II. Mostly lobular panniculitis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2001; 45:325–361.
- Geraminejad P, DeBloom JR, Walling HW, Sontheimer RD, VanBeek M. Alpha-1-antitrypsin associated panniculitis: the MS variant. J Am Acad Dermatol 2004; 51:645–655.
- Linares-Barrios M, Conejo-Mir IS, Artola Igarza JL, Navarrete M. Panniculitis due to alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency induced by cryosurgery [letter]. Br J Dermatol 1998; 138:552–553.
- Parr DG, Stewart DG, Hero I, Stockley RA. Panniculitis secondary to extravasation of clarithromycin in a patient with alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency (phenotype PiZ). Br J Dermatol 2003; 149:410–413.
Q: On the basis of the skin findings, which test should be ordered to establish a diagnosis?
- Serum anti-nuclear antibody (ANA)
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin serum level
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)
- Serum amylase
A: The lesions of a lobular, neutrophilic panniculitis should raise the possibility of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Hence, measuring the alpha-1 antitrypsin serum level is the best answer.
Many other conditions can give rise to panniculitis, including pancreatitis, lupus, and sarcoidosis, each of which is suggested by the various other test choices above. However, although the ANA level might be elevated in lupus, the ANA is quite nonspecific. The serum ACE level is frequently ordered as a screening test for sarcoidosis, although it has very little utility in its diagnosis. Panniculitis due to pancreatitis with an elevated serum amylase level would be relatively unlikely in the absence of pancreatic symptoms (eg, abdominal pain).
Panniculitis may be the only clinical manifestation of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, which can also be accompanied (depending on the phenotype) by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cirrhosis. Since alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is underrecognized in general, suspecting it when patients present with panniculitis will likely enhance its detection. Similarly, national guidelines recommend testing for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency in patients with either symptomatic, fixed airflow obstruction or cirrhosis that is otherwise unexplained, as well as in patients with panniculitis.1
PANNICULITIS DUE TO ALPHA-1 ANTITRYPSIN DEFICIENCY

Likely due to proteolytic damage
Though incompletely understood, the panniculitis in alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is likely the result of unopposed proteolytic damage in the subcutaneous fat by membrane-bound serine proteases, akin to the pathogenesis of pulmonary emphysema in people with severe deficiency of alpha-1 antitrypsin. Supporting evidence for the inflammatory, proteolytic pathogenesis of panniculitis in alpha-1 anti-trypsin deficiency includes the presence of inflammatory exudates in the subcutaneous tissues, as well as the rapid improvement seen with the infusion of purified pooled human alpha-1 proteinase inhibitor.2–4
Red, painful nodules
Panniculitis due to alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency classically presents as red, painful nodules that may break down and ooze an oily discharge.5–10 As in the patient presented here, common sites of occurrence are areas of trauma, eg, on the thighs and buttocks, abdomen, and upper extremities (Figure 1). Indeed, in a review of the 41 reported cases of panniculitis related to alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, Geraminejad et al11 reported that the erythe-matous plaques and nodules occurred on the thighs, hips, buttocks, or groin in 44% of cases in which the location was cited. Factors predisposing to panniculitis include trauma (cited in 35% of instances), cryosurgery, and, in the case of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, extravasation of intravenous clarithromycin (Biaxin).11–13
Clinical features that distinguish the panniculitis associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency from other types of panniculitis include ulceration and an oily discharge, both of which were present in the patient discussed here.
Neutrophils, necrosis, scarring, fibrosis
Several distinctive phases and features characterize the histology of panniculitis associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.5,7 Initially, neutrophils briskly infiltrate the reticular dermis, splaying the collagen bundles. In the subcutaneous fat, the neutrophilic infiltrate is in a lobular pattern, affecting individual adipocytes. Rarely, a septal pattern or a mixed lobular and septal pattern can be seen. This phase is followed by dissolution of the dermal collagen, with liquefactive necrosis of the subcutaneous fat (clinically appearing as ulceration and leading to oily drainage). In the late stage, there is scarring and fibrosis with little or no inflammation.
Various treatments tried
Various therapies for panniculitis associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency have been tried, including corticosteroids, doxycycline (Vibramycin), dapsone, plasma exchange, liver transplantation, and intravenous pooled human plasma alpha-1 proteinase inhibitor (so-called augmentation therapy). Because panniculitis associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is rare, neither controlled, blinded studies nor even large observational series have been reported. However, the limited reported experience with augmentation therapy suggests that it can confer rapid and dramatic improvement in panniculitis in patients with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
Q: On the basis of the skin findings, which test should be ordered to establish a diagnosis?
- Serum anti-nuclear antibody (ANA)
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin serum level
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)
- Serum amylase
A: The lesions of a lobular, neutrophilic panniculitis should raise the possibility of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Hence, measuring the alpha-1 antitrypsin serum level is the best answer.
Many other conditions can give rise to panniculitis, including pancreatitis, lupus, and sarcoidosis, each of which is suggested by the various other test choices above. However, although the ANA level might be elevated in lupus, the ANA is quite nonspecific. The serum ACE level is frequently ordered as a screening test for sarcoidosis, although it has very little utility in its diagnosis. Panniculitis due to pancreatitis with an elevated serum amylase level would be relatively unlikely in the absence of pancreatic symptoms (eg, abdominal pain).
Panniculitis may be the only clinical manifestation of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, which can also be accompanied (depending on the phenotype) by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cirrhosis. Since alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is underrecognized in general, suspecting it when patients present with panniculitis will likely enhance its detection. Similarly, national guidelines recommend testing for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency in patients with either symptomatic, fixed airflow obstruction or cirrhosis that is otherwise unexplained, as well as in patients with panniculitis.1
PANNICULITIS DUE TO ALPHA-1 ANTITRYPSIN DEFICIENCY

Likely due to proteolytic damage
Though incompletely understood, the panniculitis in alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is likely the result of unopposed proteolytic damage in the subcutaneous fat by membrane-bound serine proteases, akin to the pathogenesis of pulmonary emphysema in people with severe deficiency of alpha-1 antitrypsin. Supporting evidence for the inflammatory, proteolytic pathogenesis of panniculitis in alpha-1 anti-trypsin deficiency includes the presence of inflammatory exudates in the subcutaneous tissues, as well as the rapid improvement seen with the infusion of purified pooled human alpha-1 proteinase inhibitor.2–4
Red, painful nodules
Panniculitis due to alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency classically presents as red, painful nodules that may break down and ooze an oily discharge.5–10 As in the patient presented here, common sites of occurrence are areas of trauma, eg, on the thighs and buttocks, abdomen, and upper extremities (Figure 1). Indeed, in a review of the 41 reported cases of panniculitis related to alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, Geraminejad et al11 reported that the erythe-matous plaques and nodules occurred on the thighs, hips, buttocks, or groin in 44% of cases in which the location was cited. Factors predisposing to panniculitis include trauma (cited in 35% of instances), cryosurgery, and, in the case of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, extravasation of intravenous clarithromycin (Biaxin).11–13
Clinical features that distinguish the panniculitis associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency from other types of panniculitis include ulceration and an oily discharge, both of which were present in the patient discussed here.
Neutrophils, necrosis, scarring, fibrosis
Several distinctive phases and features characterize the histology of panniculitis associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.5,7 Initially, neutrophils briskly infiltrate the reticular dermis, splaying the collagen bundles. In the subcutaneous fat, the neutrophilic infiltrate is in a lobular pattern, affecting individual adipocytes. Rarely, a septal pattern or a mixed lobular and septal pattern can be seen. This phase is followed by dissolution of the dermal collagen, with liquefactive necrosis of the subcutaneous fat (clinically appearing as ulceration and leading to oily drainage). In the late stage, there is scarring and fibrosis with little or no inflammation.
Various treatments tried
Various therapies for panniculitis associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency have been tried, including corticosteroids, doxycycline (Vibramycin), dapsone, plasma exchange, liver transplantation, and intravenous pooled human plasma alpha-1 proteinase inhibitor (so-called augmentation therapy). Because panniculitis associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is rare, neither controlled, blinded studies nor even large observational series have been reported. However, the limited reported experience with augmentation therapy suggests that it can confer rapid and dramatic improvement in panniculitis in patients with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
- American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: standards for the diagnosis and management of individuals with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003; 168:818–900.
- Smith KC, Pittelkow MR, Su WP. Panniculitis associated with severe alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Treatment and review of the literature. Arch Dermatol 1987; 123:1655–1661.
- Furey NL, Golden RS, Potts SR. Treatment of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, massive edema, and panniculitis with alpha-1 protease inhibitor [letter]. Ann Intern Med 1996; 125:699.
- O’Riordan K, Blei A, Rao MS, Abecassis M. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency-associated panniculitis: resolution with intravenous alpha-1 antitrypsin administration and liver transplantation. Transplantation 1997; 63:480–482.
- Stoller JK, Piliang M. Panniculitis in alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency: a review. Clin Pulm Med 2008; 15:113–117.
- Hendrick SJ, Silverman AK, Solomon AR, Headington JT. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency associated with panniculitis. J Am Acad Derm 1988; 18:684–692.
- Loche F, Tremeau-Martinage C, Laplanche G, Massip P, Bazex J. Panniculitis revealing qualitative alpha-1 antitrypsine deficiency (MS variant). Eur J Dermatol 1999; 9:565–567.
- McBean J, Sable A, Maude J, Robinson-Bostom L. Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency panniculitis. Cutis 2003; 71:205–209.
- Pittelkow MR, Smith KC, Su WP. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency and panniculitis. Perspectives on disease relationship and replacement therapy. Am J Med 1988; 84:80–86.
- Requena L, Sánchez Yus E. Panniculitis. Part II. Mostly lobular panniculitis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2001; 45:325–361.
- Geraminejad P, DeBloom JR, Walling HW, Sontheimer RD, VanBeek M. Alpha-1-antitrypsin associated panniculitis: the MS variant. J Am Acad Dermatol 2004; 51:645–655.
- Linares-Barrios M, Conejo-Mir IS, Artola Igarza JL, Navarrete M. Panniculitis due to alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency induced by cryosurgery [letter]. Br J Dermatol 1998; 138:552–553.
- Parr DG, Stewart DG, Hero I, Stockley RA. Panniculitis secondary to extravasation of clarithromycin in a patient with alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency (phenotype PiZ). Br J Dermatol 2003; 149:410–413.
- American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: standards for the diagnosis and management of individuals with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003; 168:818–900.
- Smith KC, Pittelkow MR, Su WP. Panniculitis associated with severe alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Treatment and review of the literature. Arch Dermatol 1987; 123:1655–1661.
- Furey NL, Golden RS, Potts SR. Treatment of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, massive edema, and panniculitis with alpha-1 protease inhibitor [letter]. Ann Intern Med 1996; 125:699.
- O’Riordan K, Blei A, Rao MS, Abecassis M. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency-associated panniculitis: resolution with intravenous alpha-1 antitrypsin administration and liver transplantation. Transplantation 1997; 63:480–482.
- Stoller JK, Piliang M. Panniculitis in alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency: a review. Clin Pulm Med 2008; 15:113–117.
- Hendrick SJ, Silverman AK, Solomon AR, Headington JT. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency associated with panniculitis. J Am Acad Derm 1988; 18:684–692.
- Loche F, Tremeau-Martinage C, Laplanche G, Massip P, Bazex J. Panniculitis revealing qualitative alpha-1 antitrypsine deficiency (MS variant). Eur J Dermatol 1999; 9:565–567.
- McBean J, Sable A, Maude J, Robinson-Bostom L. Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency panniculitis. Cutis 2003; 71:205–209.
- Pittelkow MR, Smith KC, Su WP. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency and panniculitis. Perspectives on disease relationship and replacement therapy. Am J Med 1988; 84:80–86.
- Requena L, Sánchez Yus E. Panniculitis. Part II. Mostly lobular panniculitis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2001; 45:325–361.
- Geraminejad P, DeBloom JR, Walling HW, Sontheimer RD, VanBeek M. Alpha-1-antitrypsin associated panniculitis: the MS variant. J Am Acad Dermatol 2004; 51:645–655.
- Linares-Barrios M, Conejo-Mir IS, Artola Igarza JL, Navarrete M. Panniculitis due to alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency induced by cryosurgery [letter]. Br J Dermatol 1998; 138:552–553.
- Parr DG, Stewart DG, Hero I, Stockley RA. Panniculitis secondary to extravasation of clarithromycin in a patient with alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency (phenotype PiZ). Br J Dermatol 2003; 149:410–413.