User login
Primary cardiac tumors, either benign or malignant, are very rare. The combined incidence is 0.002% on pooled autopsy series.1 The benign tumors account for 63% of primary cardiac tumors and include myxoma, the most common, and followed by papillary fibroelastoma, fibroma, and hemangioma. The remaining 37% are malignant tumors, essentially predominated by sarcomas.1
Although myxoma is the most common tumor arising in the left atrium, we present a case that shows that sarcoma can also arise from the same chamber. In fact, sarcomas could mimic cardiac myxoma.2 The cardiac sarcomas can have similar clinical presentation and more importantly can share similar histopathological features. Sarcomas may have myxoid features.2 Cases diagnosed as cardiac myxomas should be diligently worked up to rule out the presence of sarcomas with myxoid features. In addition, foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals.3,4 In particular, 2 case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses in humans.5,6 We present here the case of a patient who was diagnosed with cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma 8 years after the placement of a Dacron graft.
Case presentation and summary
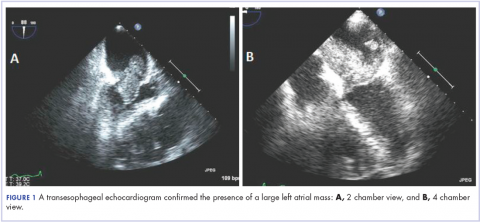
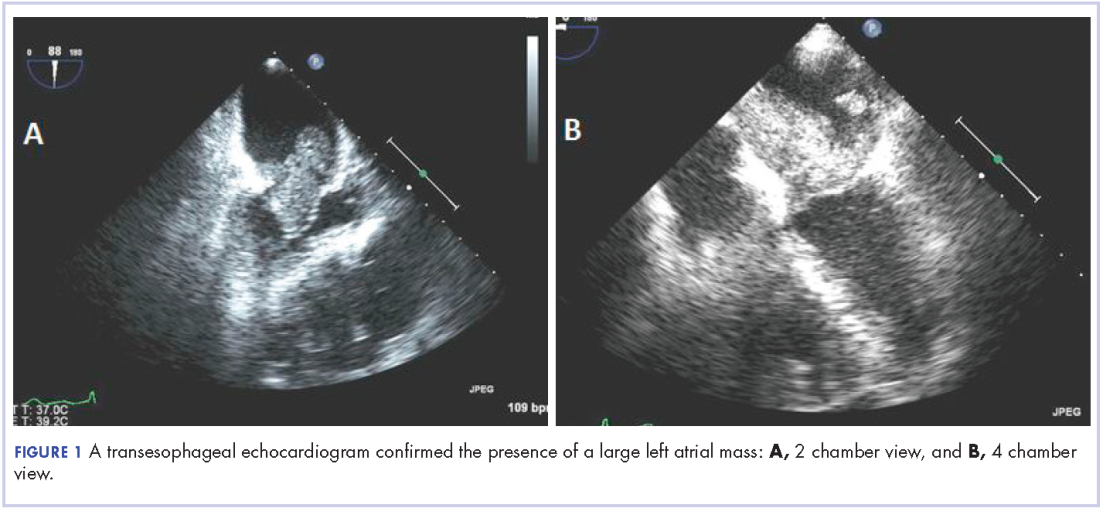
A 56-year-old woman with history of left atrial myxoma status after resection in 2005 and placement of a Dacron graft, morbid obesity, hypertension, and asthma presented to the emergency department with progressively worsening shortness of breath and blurry vision over period of 2 months. Acute coronary syndrome was ruled out by electrocardiogram and serial biomarkers. A computed-tomography angiogram was pursued because of her history of left atrial myxoma, and the results suggested the presence of a left atrial tumor. She underwent a transesophageal echocardiogram, which confirmed the presence of a large left atrial mass that likely was attached to the interatrial septum prolapsing across the mitral valve and was suggestive for recurrent left atrial myxoma (Figure 1). The results of a cardiac catheterization showed normal coronaries.
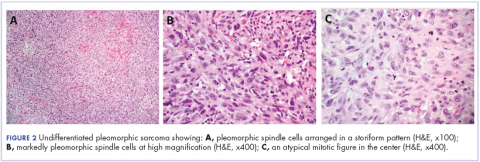
The patient subsequently underwent an excision of the left atrial tumor with profound internal and external myocardial cooling using antegrade blood cardioplegia under mildly hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass. Frozen sections showed high-grade malignancy in favor of sarcoma. The hematoxylin and eosin stained permanent sections showed sheets of malignant pleomorphic spindle cells focally arranged in a storiform pattern. There were areas of necrosis and abundant mitotic activity. By immunohistochemical (IHC) stains, the tumor cells were diffusely positive for vimentin, and negative for pan-cytokeratin antibody (AE1/AE3), S-100 protein, Melan-A antibody, HMB45, CD34, CD31, myogenin, and MYOD1. IHC stains for CK-OSCAR, desmin, and smooth muscle actin were focally positive, and a ki-67 stain showed a proliferation index of about 80%. The histologic and IHC findings were consistent with a final diagnosis of high-grade undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (Figure 2).
A positron emission tomography scan performed November 2013 did not show any other activity. The patient was scheduled for chemotherapy with adriamycin and ifosfamide with a plan for total of 6 cycles. Before her admission for the chemotherapy, the patient was admitted to the hospital for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response and had multiple complications requiring prolonged hospitalization and rehabilitation. Repeat imaging 2 months later showed diffuse metastatic disease. However, her performance status had declined and she was not eligible for chemotherapy. She was placed under hospice care.
Discussion
This case demonstrates development of a cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma, a rare tumor, after placement of a Dacron graft. Given that foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals,3,4 and a few case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses, 5-10 it seems that an exuberant host response around the foreign body might represent an important intermediate step in the development of the sarcoma.
There is no clearly defined pathogenesis that explains the link between a Dacron graft and sarcomas. In 1950s, Oppenheimer and colleagues described the formation of malignant tumors by various types of plastics, including Dacron, that were embedded in rats. 3,4 Most of the tumors were some form of sarcomas. It was inferred that physical properties of the plastics may have some role in tumor development. Plastics in sheet form or film that remained in situ for more than 6 months induced significant number of tumors compared with other forms such as sponges, films with holes, or powders.3,4 The 3-dimensional polymeric structure of the Dacron graft seems to play a role in induction of sarcoma as well. A pore diameter of less than 0.4 mm may increase tumorigenicity.11 The removal of the material before the 6-months mark does not lead to malignant tumors, which further supports the link between Dacron graft and formation of tumor. A pocket is formed around the foreign material after a certain period, as has been shown in histologic studies as the site of tumor origin.9,10
At the molecular level, the MDM-2/p53 pathway has been cited as possible mechanism for pathogenesis of intimal sarcoma.12,13 It has been suggested that endothelial dysplasia occurs as a precursor lesion in these sarcomas.14 The Dacron graft may cause a dysplastic effect on the endothelium leading to this precursor lesion and in certain cases transforming into sarcoma. Further definitive studies are required.
The primary treatment for cardiac sarcoma is surgical removal, although it is not always feasible. Findings in a Mayo clinic study showed that the median survival was 17 months for patients who underwent complete surgical excision, compared with 6 months for those who complete resection was not possible.15 In addition, a 10% survival rate at 1 year has been reported in primary cardiac sarcomas that are treated without any type of surgery.16
There is no clear-cut evidence supporting or refuting adjuvant chemotherapy for cardiac sarcoma. Some have inferred a potential benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy although definitive conclusions cannot be drawn. The median survival was 16.5 months in a case series of patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy, compared with 9 months and 11 months in 2 other case series.17,18,19 Multiple chemotherapy regimens have been used in the past for treatment. A retrospective s
Radiation showed some benefit in progression-free survival in a French retrospective study.21 Radiation therapies have been tried in other cases, as well in addition to chemotherapy. However, there is not enough data to support or refute it at this time.15,17,20 Several sporadic cases reported show benefit of cardiac transplantation.21,22
Conclusion
In consideration of the placement of the Dacron graft 8 years before the tumor occurrence, the anatomic proximity of the tumor to the Dacron graft, and the association between sarcoma with Dacron in medical literature, it seems logical to infer that this unusual malignancy in our patient is associated with the Dacron prosthesis.
1. Patil HR, Singh D, Hajdu M. Cardiac sarcoma presenting as heart failure and diagnosed as recurrent myxoma by echocardiogram. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010;11(4):E12.
2. Awamleh P, Alberca MT, Gamallo C, Enrech S, Sarraj A. Left atrium myxosarcoma: an exceptional cardiac malignant primary tumor. Clin Cardiol. 2007;30(6):306-308.
3. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Danishefsky I. Malignant tumors resulting from embedding plastics in rodents. Science. 1953;118:305-306.
4. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Willhite M, Danishefski, I. The latent period in carcinogenesis by plastics in rats and its relation to the presarcomatous stage. Cancer. 1958;11(1):204-213.
5. Almeida NJ, Hoang P, Biddle P, Arouni A, Esterbrooks D. Primary cardiac angiosarcoma: in a patient with a Dacron aortic prosthesis. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(1):61-65; discussion 65.
6. Stewart B, Manglik N, Zhao B, et al. Aortic intimal sarcoma: report of two cases with immunohistochemical analysis for pathogenesis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013;22(5):351-356.
7. Umscheid TW, Rouhani G, Morlang T, et al. Hemangiosarcoma after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Endovasc Ther. 2007;14(1):101-105.
8. Ben-Izhak O, Vlodavsky E, Ofer A, Engel A, Nitecky S, Hoffman A. Epithelioid angiosarcoma associated with a Dacron vascular graft. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23(11):1418-1422.
9. Fyfe BS, Quintana CS, Kaneko M, Griepp RB. Aortic sarcoma four years after Dacron graft insertion. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;58(6):1752-1754.
10. O’Connell TX, Fee HJ, Golding A. Sarcoma associated with Dacron prosthetic material: case report and review of the literature. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1976;72(1):94-96.
11. Karp RD, Johnson KH, Buoen LC, et al. Tumorogenesis by millipore filters in mice: histology and ultastructure of tissue reactions, as related to pore size. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973;51:1275-1285.
12. Bode-Lesniewska B, Zhao J, Speel EJ, et al. Gains of 12q13-14 and overexpression of mdm2 are frequent findings in intimal sarcomas of the pulmonary artery. Virchows Arch. 2001;438:57-65.
13. Zeitz C, Rossle M, Haas C, et al. MDM-2 oncoprotein overexpression, p53 gene mutation, and VEGF up-regulation in angiosarcomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;153:1425-1433.
14. Haber LM, Truong L. Immunohistochemical demonstration of the endothelialnature of aortic intimal sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Oct;12(10):798-802. PubMed PMID: 3138923.
15. Simpson L, Kumar SK, Okuno SH, et al. Malignant primary cardiac tumors: review of a single institution experience. Cancer. 2008;112(11):2440-2446.
16. Leja MJ, Shah DJ, Reardon MJ. Primary cardiac tumors. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(3):261-262.
17. Donsbeck AV, Ranchere D, Coindre JM, Le Gall F, Cordier JF, Loire R. Primary cardiac sarcomas: an immunohistochemical and grading study with long-term follow-up of 24 cases. Histopathology. 1999;34(4):295-304.
18. Putnam JB, Sweeney MS, Colon R, Lanza LA, Frazier OH, Cooley DC. Primary cardiac sarcomas. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990; 51; 906-910.
19. Murphy WR, Sweeney MS, Putnam JB et al. Surgical treatment of cardiac tumors: a 25-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990;49;612-618.
20. Llombart-Cussac A, Pivot X, Contesso G, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for primary cardiac sarcomas: the IGR experience. Br J Cancer. 1998;78(12):1624-1628.
21. Isambert N, Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, et al. Primary cardiac sarcomas: a retrospective study of the French Sarcoma Group. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(1):128-136.
22. Agaimy A, Rösch J, Weyand M, Strecker T. Primary and metastatic cardiac sarcomas: a 12-year experience at a German heart center. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(9):928-938.
Primary cardiac tumors, either benign or malignant, are very rare. The combined incidence is 0.002% on pooled autopsy series.1 The benign tumors account for 63% of primary cardiac tumors and include myxoma, the most common, and followed by papillary fibroelastoma, fibroma, and hemangioma. The remaining 37% are malignant tumors, essentially predominated by sarcomas.1
Although myxoma is the most common tumor arising in the left atrium, we present a case that shows that sarcoma can also arise from the same chamber. In fact, sarcomas could mimic cardiac myxoma.2 The cardiac sarcomas can have similar clinical presentation and more importantly can share similar histopathological features. Sarcomas may have myxoid features.2 Cases diagnosed as cardiac myxomas should be diligently worked up to rule out the presence of sarcomas with myxoid features. In addition, foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals.3,4 In particular, 2 case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses in humans.5,6 We present here the case of a patient who was diagnosed with cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma 8 years after the placement of a Dacron graft.
Case presentation and summary
A 56-year-old woman with history of left atrial myxoma status after resection in 2005 and placement of a Dacron graft, morbid obesity, hypertension, and asthma presented to the emergency department with progressively worsening shortness of breath and blurry vision over period of 2 months. Acute coronary syndrome was ruled out by electrocardiogram and serial biomarkers. A computed-tomography angiogram was pursued because of her history of left atrial myxoma, and the results suggested the presence of a left atrial tumor. She underwent a transesophageal echocardiogram, which confirmed the presence of a large left atrial mass that likely was attached to the interatrial septum prolapsing across the mitral valve and was suggestive for recurrent left atrial myxoma (Figure 1). The results of a cardiac catheterization showed normal coronaries.
The patient subsequently underwent an excision of the left atrial tumor with profound internal and external myocardial cooling using antegrade blood cardioplegia under mildly hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass. Frozen sections showed high-grade malignancy in favor of sarcoma. The hematoxylin and eosin stained permanent sections showed sheets of malignant pleomorphic spindle cells focally arranged in a storiform pattern. There were areas of necrosis and abundant mitotic activity. By immunohistochemical (IHC) stains, the tumor cells were diffusely positive for vimentin, and negative for pan-cytokeratin antibody (AE1/AE3), S-100 protein, Melan-A antibody, HMB45, CD34, CD31, myogenin, and MYOD1. IHC stains for CK-OSCAR, desmin, and smooth muscle actin were focally positive, and a ki-67 stain showed a proliferation index of about 80%. The histologic and IHC findings were consistent with a final diagnosis of high-grade undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (Figure 2).
A positron emission tomography scan performed November 2013 did not show any other activity. The patient was scheduled for chemotherapy with adriamycin and ifosfamide with a plan for total of 6 cycles. Before her admission for the chemotherapy, the patient was admitted to the hospital for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response and had multiple complications requiring prolonged hospitalization and rehabilitation. Repeat imaging 2 months later showed diffuse metastatic disease. However, her performance status had declined and she was not eligible for chemotherapy. She was placed under hospice care.
Discussion
This case demonstrates development of a cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma, a rare tumor, after placement of a Dacron graft. Given that foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals,3,4 and a few case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses, 5-10 it seems that an exuberant host response around the foreign body might represent an important intermediate step in the development of the sarcoma.
There is no clearly defined pathogenesis that explains the link between a Dacron graft and sarcomas. In 1950s, Oppenheimer and colleagues described the formation of malignant tumors by various types of plastics, including Dacron, that were embedded in rats. 3,4 Most of the tumors were some form of sarcomas. It was inferred that physical properties of the plastics may have some role in tumor development. Plastics in sheet form or film that remained in situ for more than 6 months induced significant number of tumors compared with other forms such as sponges, films with holes, or powders.3,4 The 3-dimensional polymeric structure of the Dacron graft seems to play a role in induction of sarcoma as well. A pore diameter of less than 0.4 mm may increase tumorigenicity.11 The removal of the material before the 6-months mark does not lead to malignant tumors, which further supports the link between Dacron graft and formation of tumor. A pocket is formed around the foreign material after a certain period, as has been shown in histologic studies as the site of tumor origin.9,10
At the molecular level, the MDM-2/p53 pathway has been cited as possible mechanism for pathogenesis of intimal sarcoma.12,13 It has been suggested that endothelial dysplasia occurs as a precursor lesion in these sarcomas.14 The Dacron graft may cause a dysplastic effect on the endothelium leading to this precursor lesion and in certain cases transforming into sarcoma. Further definitive studies are required.
The primary treatment for cardiac sarcoma is surgical removal, although it is not always feasible. Findings in a Mayo clinic study showed that the median survival was 17 months for patients who underwent complete surgical excision, compared with 6 months for those who complete resection was not possible.15 In addition, a 10% survival rate at 1 year has been reported in primary cardiac sarcomas that are treated without any type of surgery.16
There is no clear-cut evidence supporting or refuting adjuvant chemotherapy for cardiac sarcoma. Some have inferred a potential benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy although definitive conclusions cannot be drawn. The median survival was 16.5 months in a case series of patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy, compared with 9 months and 11 months in 2 other case series.17,18,19 Multiple chemotherapy regimens have been used in the past for treatment. A retrospective s
Radiation showed some benefit in progression-free survival in a French retrospective study.21 Radiation therapies have been tried in other cases, as well in addition to chemotherapy. However, there is not enough data to support or refute it at this time.15,17,20 Several sporadic cases reported show benefit of cardiac transplantation.21,22
Conclusion
In consideration of the placement of the Dacron graft 8 years before the tumor occurrence, the anatomic proximity of the tumor to the Dacron graft, and the association between sarcoma with Dacron in medical literature, it seems logical to infer that this unusual malignancy in our patient is associated with the Dacron prosthesis.
Primary cardiac tumors, either benign or malignant, are very rare. The combined incidence is 0.002% on pooled autopsy series.1 The benign tumors account for 63% of primary cardiac tumors and include myxoma, the most common, and followed by papillary fibroelastoma, fibroma, and hemangioma. The remaining 37% are malignant tumors, essentially predominated by sarcomas.1
Although myxoma is the most common tumor arising in the left atrium, we present a case that shows that sarcoma can also arise from the same chamber. In fact, sarcomas could mimic cardiac myxoma.2 The cardiac sarcomas can have similar clinical presentation and more importantly can share similar histopathological features. Sarcomas may have myxoid features.2 Cases diagnosed as cardiac myxomas should be diligently worked up to rule out the presence of sarcomas with myxoid features. In addition, foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals.3,4 In particular, 2 case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses in humans.5,6 We present here the case of a patient who was diagnosed with cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma 8 years after the placement of a Dacron graft.
Case presentation and summary
A 56-year-old woman with history of left atrial myxoma status after resection in 2005 and placement of a Dacron graft, morbid obesity, hypertension, and asthma presented to the emergency department with progressively worsening shortness of breath and blurry vision over period of 2 months. Acute coronary syndrome was ruled out by electrocardiogram and serial biomarkers. A computed-tomography angiogram was pursued because of her history of left atrial myxoma, and the results suggested the presence of a left atrial tumor. She underwent a transesophageal echocardiogram, which confirmed the presence of a large left atrial mass that likely was attached to the interatrial septum prolapsing across the mitral valve and was suggestive for recurrent left atrial myxoma (Figure 1). The results of a cardiac catheterization showed normal coronaries.
The patient subsequently underwent an excision of the left atrial tumor with profound internal and external myocardial cooling using antegrade blood cardioplegia under mildly hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass. Frozen sections showed high-grade malignancy in favor of sarcoma. The hematoxylin and eosin stained permanent sections showed sheets of malignant pleomorphic spindle cells focally arranged in a storiform pattern. There were areas of necrosis and abundant mitotic activity. By immunohistochemical (IHC) stains, the tumor cells were diffusely positive for vimentin, and negative for pan-cytokeratin antibody (AE1/AE3), S-100 protein, Melan-A antibody, HMB45, CD34, CD31, myogenin, and MYOD1. IHC stains for CK-OSCAR, desmin, and smooth muscle actin were focally positive, and a ki-67 stain showed a proliferation index of about 80%. The histologic and IHC findings were consistent with a final diagnosis of high-grade undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (Figure 2).
A positron emission tomography scan performed November 2013 did not show any other activity. The patient was scheduled for chemotherapy with adriamycin and ifosfamide with a plan for total of 6 cycles. Before her admission for the chemotherapy, the patient was admitted to the hospital for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response and had multiple complications requiring prolonged hospitalization and rehabilitation. Repeat imaging 2 months later showed diffuse metastatic disease. However, her performance status had declined and she was not eligible for chemotherapy. She was placed under hospice care.
Discussion
This case demonstrates development of a cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma, a rare tumor, after placement of a Dacron graft. Given that foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals,3,4 and a few case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses, 5-10 it seems that an exuberant host response around the foreign body might represent an important intermediate step in the development of the sarcoma.
There is no clearly defined pathogenesis that explains the link between a Dacron graft and sarcomas. In 1950s, Oppenheimer and colleagues described the formation of malignant tumors by various types of plastics, including Dacron, that were embedded in rats. 3,4 Most of the tumors were some form of sarcomas. It was inferred that physical properties of the plastics may have some role in tumor development. Plastics in sheet form or film that remained in situ for more than 6 months induced significant number of tumors compared with other forms such as sponges, films with holes, or powders.3,4 The 3-dimensional polymeric structure of the Dacron graft seems to play a role in induction of sarcoma as well. A pore diameter of less than 0.4 mm may increase tumorigenicity.11 The removal of the material before the 6-months mark does not lead to malignant tumors, which further supports the link between Dacron graft and formation of tumor. A pocket is formed around the foreign material after a certain period, as has been shown in histologic studies as the site of tumor origin.9,10
At the molecular level, the MDM-2/p53 pathway has been cited as possible mechanism for pathogenesis of intimal sarcoma.12,13 It has been suggested that endothelial dysplasia occurs as a precursor lesion in these sarcomas.14 The Dacron graft may cause a dysplastic effect on the endothelium leading to this precursor lesion and in certain cases transforming into sarcoma. Further definitive studies are required.
The primary treatment for cardiac sarcoma is surgical removal, although it is not always feasible. Findings in a Mayo clinic study showed that the median survival was 17 months for patients who underwent complete surgical excision, compared with 6 months for those who complete resection was not possible.15 In addition, a 10% survival rate at 1 year has been reported in primary cardiac sarcomas that are treated without any type of surgery.16
There is no clear-cut evidence supporting or refuting adjuvant chemotherapy for cardiac sarcoma. Some have inferred a potential benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy although definitive conclusions cannot be drawn. The median survival was 16.5 months in a case series of patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy, compared with 9 months and 11 months in 2 other case series.17,18,19 Multiple chemotherapy regimens have been used in the past for treatment. A retrospective s
Radiation showed some benefit in progression-free survival in a French retrospective study.21 Radiation therapies have been tried in other cases, as well in addition to chemotherapy. However, there is not enough data to support or refute it at this time.15,17,20 Several sporadic cases reported show benefit of cardiac transplantation.21,22
Conclusion
In consideration of the placement of the Dacron graft 8 years before the tumor occurrence, the anatomic proximity of the tumor to the Dacron graft, and the association between sarcoma with Dacron in medical literature, it seems logical to infer that this unusual malignancy in our patient is associated with the Dacron prosthesis.
1. Patil HR, Singh D, Hajdu M. Cardiac sarcoma presenting as heart failure and diagnosed as recurrent myxoma by echocardiogram. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010;11(4):E12.
2. Awamleh P, Alberca MT, Gamallo C, Enrech S, Sarraj A. Left atrium myxosarcoma: an exceptional cardiac malignant primary tumor. Clin Cardiol. 2007;30(6):306-308.
3. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Danishefsky I. Malignant tumors resulting from embedding plastics in rodents. Science. 1953;118:305-306.
4. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Willhite M, Danishefski, I. The latent period in carcinogenesis by plastics in rats and its relation to the presarcomatous stage. Cancer. 1958;11(1):204-213.
5. Almeida NJ, Hoang P, Biddle P, Arouni A, Esterbrooks D. Primary cardiac angiosarcoma: in a patient with a Dacron aortic prosthesis. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(1):61-65; discussion 65.
6. Stewart B, Manglik N, Zhao B, et al. Aortic intimal sarcoma: report of two cases with immunohistochemical analysis for pathogenesis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013;22(5):351-356.
7. Umscheid TW, Rouhani G, Morlang T, et al. Hemangiosarcoma after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Endovasc Ther. 2007;14(1):101-105.
8. Ben-Izhak O, Vlodavsky E, Ofer A, Engel A, Nitecky S, Hoffman A. Epithelioid angiosarcoma associated with a Dacron vascular graft. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23(11):1418-1422.
9. Fyfe BS, Quintana CS, Kaneko M, Griepp RB. Aortic sarcoma four years after Dacron graft insertion. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;58(6):1752-1754.
10. O’Connell TX, Fee HJ, Golding A. Sarcoma associated with Dacron prosthetic material: case report and review of the literature. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1976;72(1):94-96.
11. Karp RD, Johnson KH, Buoen LC, et al. Tumorogenesis by millipore filters in mice: histology and ultastructure of tissue reactions, as related to pore size. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973;51:1275-1285.
12. Bode-Lesniewska B, Zhao J, Speel EJ, et al. Gains of 12q13-14 and overexpression of mdm2 are frequent findings in intimal sarcomas of the pulmonary artery. Virchows Arch. 2001;438:57-65.
13. Zeitz C, Rossle M, Haas C, et al. MDM-2 oncoprotein overexpression, p53 gene mutation, and VEGF up-regulation in angiosarcomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;153:1425-1433.
14. Haber LM, Truong L. Immunohistochemical demonstration of the endothelialnature of aortic intimal sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Oct;12(10):798-802. PubMed PMID: 3138923.
15. Simpson L, Kumar SK, Okuno SH, et al. Malignant primary cardiac tumors: review of a single institution experience. Cancer. 2008;112(11):2440-2446.
16. Leja MJ, Shah DJ, Reardon MJ. Primary cardiac tumors. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(3):261-262.
17. Donsbeck AV, Ranchere D, Coindre JM, Le Gall F, Cordier JF, Loire R. Primary cardiac sarcomas: an immunohistochemical and grading study with long-term follow-up of 24 cases. Histopathology. 1999;34(4):295-304.
18. Putnam JB, Sweeney MS, Colon R, Lanza LA, Frazier OH, Cooley DC. Primary cardiac sarcomas. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990; 51; 906-910.
19. Murphy WR, Sweeney MS, Putnam JB et al. Surgical treatment of cardiac tumors: a 25-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990;49;612-618.
20. Llombart-Cussac A, Pivot X, Contesso G, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for primary cardiac sarcomas: the IGR experience. Br J Cancer. 1998;78(12):1624-1628.
21. Isambert N, Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, et al. Primary cardiac sarcomas: a retrospective study of the French Sarcoma Group. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(1):128-136.
22. Agaimy A, Rösch J, Weyand M, Strecker T. Primary and metastatic cardiac sarcomas: a 12-year experience at a German heart center. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(9):928-938.
1. Patil HR, Singh D, Hajdu M. Cardiac sarcoma presenting as heart failure and diagnosed as recurrent myxoma by echocardiogram. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010;11(4):E12.
2. Awamleh P, Alberca MT, Gamallo C, Enrech S, Sarraj A. Left atrium myxosarcoma: an exceptional cardiac malignant primary tumor. Clin Cardiol. 2007;30(6):306-308.
3. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Danishefsky I. Malignant tumors resulting from embedding plastics in rodents. Science. 1953;118:305-306.
4. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Willhite M, Danishefski, I. The latent period in carcinogenesis by plastics in rats and its relation to the presarcomatous stage. Cancer. 1958;11(1):204-213.
5. Almeida NJ, Hoang P, Biddle P, Arouni A, Esterbrooks D. Primary cardiac angiosarcoma: in a patient with a Dacron aortic prosthesis. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(1):61-65; discussion 65.
6. Stewart B, Manglik N, Zhao B, et al. Aortic intimal sarcoma: report of two cases with immunohistochemical analysis for pathogenesis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013;22(5):351-356.
7. Umscheid TW, Rouhani G, Morlang T, et al. Hemangiosarcoma after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Endovasc Ther. 2007;14(1):101-105.
8. Ben-Izhak O, Vlodavsky E, Ofer A, Engel A, Nitecky S, Hoffman A. Epithelioid angiosarcoma associated with a Dacron vascular graft. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23(11):1418-1422.
9. Fyfe BS, Quintana CS, Kaneko M, Griepp RB. Aortic sarcoma four years after Dacron graft insertion. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;58(6):1752-1754.
10. O’Connell TX, Fee HJ, Golding A. Sarcoma associated with Dacron prosthetic material: case report and review of the literature. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1976;72(1):94-96.
11. Karp RD, Johnson KH, Buoen LC, et al. Tumorogenesis by millipore filters in mice: histology and ultastructure of tissue reactions, as related to pore size. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973;51:1275-1285.
12. Bode-Lesniewska B, Zhao J, Speel EJ, et al. Gains of 12q13-14 and overexpression of mdm2 are frequent findings in intimal sarcomas of the pulmonary artery. Virchows Arch. 2001;438:57-65.
13. Zeitz C, Rossle M, Haas C, et al. MDM-2 oncoprotein overexpression, p53 gene mutation, and VEGF up-regulation in angiosarcomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;153:1425-1433.
14. Haber LM, Truong L. Immunohistochemical demonstration of the endothelialnature of aortic intimal sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Oct;12(10):798-802. PubMed PMID: 3138923.
15. Simpson L, Kumar SK, Okuno SH, et al. Malignant primary cardiac tumors: review of a single institution experience. Cancer. 2008;112(11):2440-2446.
16. Leja MJ, Shah DJ, Reardon MJ. Primary cardiac tumors. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(3):261-262.
17. Donsbeck AV, Ranchere D, Coindre JM, Le Gall F, Cordier JF, Loire R. Primary cardiac sarcomas: an immunohistochemical and grading study with long-term follow-up of 24 cases. Histopathology. 1999;34(4):295-304.
18. Putnam JB, Sweeney MS, Colon R, Lanza LA, Frazier OH, Cooley DC. Primary cardiac sarcomas. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990; 51; 906-910.
19. Murphy WR, Sweeney MS, Putnam JB et al. Surgical treatment of cardiac tumors: a 25-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990;49;612-618.
20. Llombart-Cussac A, Pivot X, Contesso G, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for primary cardiac sarcomas: the IGR experience. Br J Cancer. 1998;78(12):1624-1628.
21. Isambert N, Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, et al. Primary cardiac sarcomas: a retrospective study of the French Sarcoma Group. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(1):128-136.
22. Agaimy A, Rösch J, Weyand M, Strecker T. Primary and metastatic cardiac sarcomas: a 12-year experience at a German heart center. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(9):928-938.