User login
More weight loss linked with more benefit in STEP-HFpEF
AMSTERDAM – , including symptoms and physical limitations, exercise capacity, and inflammation, new analyses from the trial show.
At the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology where he presented these new findings, Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, also posited that weight loss produced by weekly subcutaneous injections of 2.4 mg semaglutide (Wegovy) for 52 weeks in the study does not fully explain the multiple mechanisms that may be involved in producing this intervention’s effects in the STEP-HFpEF trial.
His report earlier at the congress and in a simultaneously published report of the trial’s primary outcomes established a role for medically induced weight loss in managing patients with obesity-phenotype HFpEF in a total of 529 randomized individuals with HFpEF and obesity but without diabetes.
The new analyses showed that for one of the two primary endpoints – the change from baseline in patients’ assessment on the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire Clinical Summary Score (KCCQ), the placebo-adjusted average change was a 16.1-point improvement in the 51 people with a 5%-10% weight loss during the 1-year study, and a 21.6-point improvement in the 58 who had at least a 20% weight loss, a between-group average 5.5 point difference that represents a clinically meaningful incremental improvement in this validated metric of symptoms and functional limitations.
Similar weight-related differences in benefit also occurred for the secondary outcomes of changes from baseline in 6-minute walk distance and in levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), a measure of systemic inflammation.
In an adjusted regression model, every 10% drop from baseline body weight was significantly linked with a 6.4-point improvement in KCCQ score, a 14.4 meter improvement in 6-minute walk distance, and a 28% relative reduction from baseline in CRP, reported Dr. Kosiborod, a cardiologist and codirector of the Haverty Cardiometabolic Center of Excellence at Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, Mo.
These new, prespecified analyses also showed that people with obesity and HFpEF responded roughly the same to semaglutide treatment compared with placebo-treated controls regardless of their starting body mass index, including people with class 1 (30-34 kg/m2), class 2 (35-39 kg/m2), and class 3 (≥ 40 kg/m2) obesity.
Simultaneously with Dr. Kosiborod’s report at the congress, these findings appeared in a report posted online in Nature Medicine.
Not every benefit was fully mediated by weight loss
These analyses “do not tell us how much of the benefit was mediated by weight loss, but the data do say that the more weight a person lost, the more benefit they got,” Dr. Kosiborod explained in an interview. “That is not the same as saying that everything is mediated by weight. It doesn’t say that nothing beyond weight loss matters.”
He and his associates are planning a mediation analysis of data from STEP-HFpEF that will more directly address this issue.
“It’s likely that people who lost more weight with semaglutide also had greater benefits from other effects of semaglutide at the same time. Weight loss is a good surrogate marker” for the range of effects that a person receives from treatment with semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, Dr. Kosiborod said.
“GLP-1 receptor agonists may have direct effects on atherosclerosis, as well as other effects that are uncoupled from weight loss,” such as proven anti-inflammatory effects, he added.
Another exploratory effect from semaglutide treatment in the study and reported by Dr. Kosiborod was a significant reduction in serum levels of N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide, an association never previously seen with weight loss in people with heart failure.
“The outcomes we’ve already seen in STEP-HFpEF were largely symptomatic, which are extraordinarily important, but there may be a completely different relationship between weight and clinical events,” said John E. Deanfield, PhD, a professor of cardiology at University College Hospital, London, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Deanfield noted that important prognostic markers such as cholesterol levels and blood pressure reductions are usually not temporally related to weight loss. “The idea that [the benefits seen in STEP-HFpEF] are purely from weight loss is something we need to be careful about,” he said.
“My gut feeling is that at least 75% of the effect [in STEP-HFpEF} was due to weight loss,” said Naveed Sattar, PhD, professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, who was not associated with the research.
STEP-HFpEF was funded by Novo Nordisk, the company that markets semaglutide (Wegovy). Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant and adviser to, and has received honoraria from, Novo Nordisk. He has been a consultant to numerous other companies, received research grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Pfizer, honoraria from AstraZeneca, and is a stockholder in Artera Health and Saghmos Therapeutics. Dr. Deanfield has been a consultant to Novo Nordisk as well as to Aegerion, Amgen, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Takeda, and has received research funding from Aegerion, Colgate, MSD, Pfizer, and Roche. Dr. Sattar has been a consultant to Novo Nordisk as well as to Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche Diagnostics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM – , including symptoms and physical limitations, exercise capacity, and inflammation, new analyses from the trial show.
At the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology where he presented these new findings, Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, also posited that weight loss produced by weekly subcutaneous injections of 2.4 mg semaglutide (Wegovy) for 52 weeks in the study does not fully explain the multiple mechanisms that may be involved in producing this intervention’s effects in the STEP-HFpEF trial.
His report earlier at the congress and in a simultaneously published report of the trial’s primary outcomes established a role for medically induced weight loss in managing patients with obesity-phenotype HFpEF in a total of 529 randomized individuals with HFpEF and obesity but without diabetes.
The new analyses showed that for one of the two primary endpoints – the change from baseline in patients’ assessment on the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire Clinical Summary Score (KCCQ), the placebo-adjusted average change was a 16.1-point improvement in the 51 people with a 5%-10% weight loss during the 1-year study, and a 21.6-point improvement in the 58 who had at least a 20% weight loss, a between-group average 5.5 point difference that represents a clinically meaningful incremental improvement in this validated metric of symptoms and functional limitations.
Similar weight-related differences in benefit also occurred for the secondary outcomes of changes from baseline in 6-minute walk distance and in levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), a measure of systemic inflammation.
In an adjusted regression model, every 10% drop from baseline body weight was significantly linked with a 6.4-point improvement in KCCQ score, a 14.4 meter improvement in 6-minute walk distance, and a 28% relative reduction from baseline in CRP, reported Dr. Kosiborod, a cardiologist and codirector of the Haverty Cardiometabolic Center of Excellence at Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, Mo.
These new, prespecified analyses also showed that people with obesity and HFpEF responded roughly the same to semaglutide treatment compared with placebo-treated controls regardless of their starting body mass index, including people with class 1 (30-34 kg/m2), class 2 (35-39 kg/m2), and class 3 (≥ 40 kg/m2) obesity.
Simultaneously with Dr. Kosiborod’s report at the congress, these findings appeared in a report posted online in Nature Medicine.
Not every benefit was fully mediated by weight loss
These analyses “do not tell us how much of the benefit was mediated by weight loss, but the data do say that the more weight a person lost, the more benefit they got,” Dr. Kosiborod explained in an interview. “That is not the same as saying that everything is mediated by weight. It doesn’t say that nothing beyond weight loss matters.”
He and his associates are planning a mediation analysis of data from STEP-HFpEF that will more directly address this issue.
“It’s likely that people who lost more weight with semaglutide also had greater benefits from other effects of semaglutide at the same time. Weight loss is a good surrogate marker” for the range of effects that a person receives from treatment with semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, Dr. Kosiborod said.
“GLP-1 receptor agonists may have direct effects on atherosclerosis, as well as other effects that are uncoupled from weight loss,” such as proven anti-inflammatory effects, he added.
Another exploratory effect from semaglutide treatment in the study and reported by Dr. Kosiborod was a significant reduction in serum levels of N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide, an association never previously seen with weight loss in people with heart failure.
“The outcomes we’ve already seen in STEP-HFpEF were largely symptomatic, which are extraordinarily important, but there may be a completely different relationship between weight and clinical events,” said John E. Deanfield, PhD, a professor of cardiology at University College Hospital, London, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Deanfield noted that important prognostic markers such as cholesterol levels and blood pressure reductions are usually not temporally related to weight loss. “The idea that [the benefits seen in STEP-HFpEF] are purely from weight loss is something we need to be careful about,” he said.
“My gut feeling is that at least 75% of the effect [in STEP-HFpEF} was due to weight loss,” said Naveed Sattar, PhD, professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, who was not associated with the research.
STEP-HFpEF was funded by Novo Nordisk, the company that markets semaglutide (Wegovy). Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant and adviser to, and has received honoraria from, Novo Nordisk. He has been a consultant to numerous other companies, received research grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Pfizer, honoraria from AstraZeneca, and is a stockholder in Artera Health and Saghmos Therapeutics. Dr. Deanfield has been a consultant to Novo Nordisk as well as to Aegerion, Amgen, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Takeda, and has received research funding from Aegerion, Colgate, MSD, Pfizer, and Roche. Dr. Sattar has been a consultant to Novo Nordisk as well as to Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche Diagnostics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM – , including symptoms and physical limitations, exercise capacity, and inflammation, new analyses from the trial show.
At the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology where he presented these new findings, Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, also posited that weight loss produced by weekly subcutaneous injections of 2.4 mg semaglutide (Wegovy) for 52 weeks in the study does not fully explain the multiple mechanisms that may be involved in producing this intervention’s effects in the STEP-HFpEF trial.
His report earlier at the congress and in a simultaneously published report of the trial’s primary outcomes established a role for medically induced weight loss in managing patients with obesity-phenotype HFpEF in a total of 529 randomized individuals with HFpEF and obesity but without diabetes.
The new analyses showed that for one of the two primary endpoints – the change from baseline in patients’ assessment on the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire Clinical Summary Score (KCCQ), the placebo-adjusted average change was a 16.1-point improvement in the 51 people with a 5%-10% weight loss during the 1-year study, and a 21.6-point improvement in the 58 who had at least a 20% weight loss, a between-group average 5.5 point difference that represents a clinically meaningful incremental improvement in this validated metric of symptoms and functional limitations.
Similar weight-related differences in benefit also occurred for the secondary outcomes of changes from baseline in 6-minute walk distance and in levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), a measure of systemic inflammation.
In an adjusted regression model, every 10% drop from baseline body weight was significantly linked with a 6.4-point improvement in KCCQ score, a 14.4 meter improvement in 6-minute walk distance, and a 28% relative reduction from baseline in CRP, reported Dr. Kosiborod, a cardiologist and codirector of the Haverty Cardiometabolic Center of Excellence at Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, Mo.
These new, prespecified analyses also showed that people with obesity and HFpEF responded roughly the same to semaglutide treatment compared with placebo-treated controls regardless of their starting body mass index, including people with class 1 (30-34 kg/m2), class 2 (35-39 kg/m2), and class 3 (≥ 40 kg/m2) obesity.
Simultaneously with Dr. Kosiborod’s report at the congress, these findings appeared in a report posted online in Nature Medicine.
Not every benefit was fully mediated by weight loss
These analyses “do not tell us how much of the benefit was mediated by weight loss, but the data do say that the more weight a person lost, the more benefit they got,” Dr. Kosiborod explained in an interview. “That is not the same as saying that everything is mediated by weight. It doesn’t say that nothing beyond weight loss matters.”
He and his associates are planning a mediation analysis of data from STEP-HFpEF that will more directly address this issue.
“It’s likely that people who lost more weight with semaglutide also had greater benefits from other effects of semaglutide at the same time. Weight loss is a good surrogate marker” for the range of effects that a person receives from treatment with semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, Dr. Kosiborod said.
“GLP-1 receptor agonists may have direct effects on atherosclerosis, as well as other effects that are uncoupled from weight loss,” such as proven anti-inflammatory effects, he added.
Another exploratory effect from semaglutide treatment in the study and reported by Dr. Kosiborod was a significant reduction in serum levels of N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide, an association never previously seen with weight loss in people with heart failure.
“The outcomes we’ve already seen in STEP-HFpEF were largely symptomatic, which are extraordinarily important, but there may be a completely different relationship between weight and clinical events,” said John E. Deanfield, PhD, a professor of cardiology at University College Hospital, London, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Deanfield noted that important prognostic markers such as cholesterol levels and blood pressure reductions are usually not temporally related to weight loss. “The idea that [the benefits seen in STEP-HFpEF] are purely from weight loss is something we need to be careful about,” he said.
“My gut feeling is that at least 75% of the effect [in STEP-HFpEF} was due to weight loss,” said Naveed Sattar, PhD, professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, who was not associated with the research.
STEP-HFpEF was funded by Novo Nordisk, the company that markets semaglutide (Wegovy). Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant and adviser to, and has received honoraria from, Novo Nordisk. He has been a consultant to numerous other companies, received research grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Pfizer, honoraria from AstraZeneca, and is a stockholder in Artera Health and Saghmos Therapeutics. Dr. Deanfield has been a consultant to Novo Nordisk as well as to Aegerion, Amgen, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Takeda, and has received research funding from Aegerion, Colgate, MSD, Pfizer, and Roche. Dr. Sattar has been a consultant to Novo Nordisk as well as to Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche Diagnostics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT THE ESC CONGRESS 2023
IV iron shows only modest benefit in HF: HEART-FID
AMSTERDAM – , but the study failed to meet the specified more rigorous definition of significance (P = .01) on the primary hierarchical composite of death, hospitalizations for heart failure, or 6-minute walk distance.
The trial, which investigated intravenous ferric carboxymaltose treatment vs. placebo, also showed no statistical difference in the main secondary endpoint: time to cardiovascular death or first heart failure hospitalization.
It was hoped that HEART-FID, the largest study to date to look at intravenous iron supplementation in heart failure, would confirm benefits suggested in previous smaller studies, but its modest results seem to have, if anything, caused more uncertainly on whether supplementing iron is actually worthwhile.
The HEART-FID trial was presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
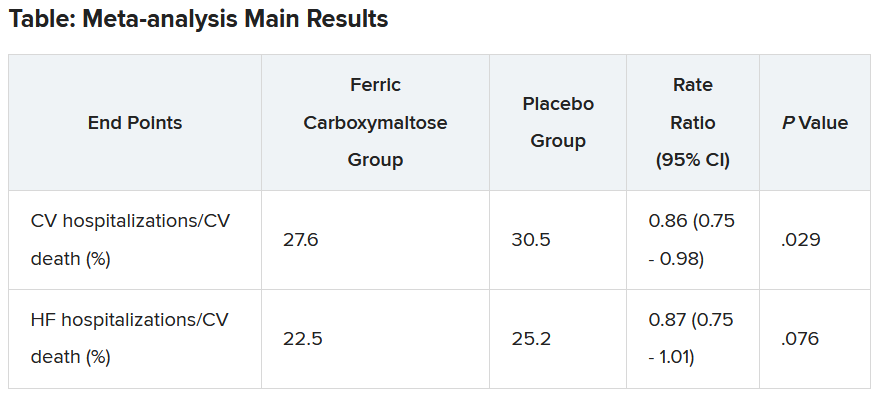
Another presentation at the ESC Congress reported a pooled meta-analysis of all the intravenous iron supplementation studies, including HEART-FID. This showed a significant reduction in one coprimary endpoint (cardiovascular hospitalization/CV death) but not in the other (heart failure hospitalization/CV death), which is the more traditional and well-recognized endpoint in heart failure trials.
The meta-analysis was also published online in the European Heart Journal.
HEART-FID lead investigator, Robert J. Mentz, MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C., said the totality of the evidence showed clinical benefits of intravenous iron supplementation with intravenous ferric carboxymaltose.
“I worry that people will focus on a P value rather than the actual clinical benefits seen across all the studies,” Dr. Mentz said in an interview. “Technically, this study was neutral in respect to the primary endpoint, but when we look at all the evidence with respect to ferric carboxymaltose, including this new pooled analysis, this does support clinical benefits.”
Comoderator of the ESC Hotline session at which the trial was presented, John McMurray, MD, University of Glasgow (Scotland), thought the trial had “muddied the waters a bit” on the issue of iron supplementation in heart failure.
“I would say we are in a less clear position on iron supplementation now than we were a few months ago. Those clinicians who have believed that checking iron levels and supplementing iron in those who are low is the right thing to do may now be wondering about that,” he told this news organization.
Dr. McMurray noted that initial impressions of the data from both HEART-FID and the meta-analysis suggested some benefit of intravenous iron on CV death/heart failure hospitalization in the first year, but on longer term follow-up, that benefit was less evident.
“We need to look further into why there is that discrepancy,” he said. “This could be a statistical phenomenon or could be something to do with the frequency of redosing over the longer term.”
He explained that several previous studies of intravenous iron supplementation in heart failure have reported apparent convincing benefits on quality of life and functional capacity, but there has been some uncertainty on this because of the difficulty in producing a placebo for intravenous iron.
“So, it would have been great to have some additional confirmation of these benefits and on harder endpoints,” he said, “but even in HEART-FID, there was only a small nonsignificant benefit in walking distance.”
HEART-FID
The HEART-FID trial randomly assigned 3,065 ambulatory patients with heart failure, a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or less, and iron deficiency to intravenous ferric carboxymaltose or placebo, given every 6 months as needed on the basis of iron indexes and hemoglobin levels, in addition to standard therapy for heart failure.
The primary outcome was a hierarchical composite of death within 12 months after randomization, hospitalizations for heart failure within 12 months after randomization, or change from baseline to 6 months in the 6-minute walk distance. The significance level was set at .01.
Results showed that death by month 12 occurred in 8.6% of the ferric carboxymaltose group and 10.3% of the placebo group; a total of 297 and 332 hospitalizations for heart failure, respectively, occurred by month 12; and the mean change from baseline to 6 months in the 6-minute walk distance was 8 meters in the ferric carboxymaltose group and 4 meters with placebo. The P value for the primary composite was .02.
The trial also used another method (unmatched win ratio) to analyze the hierarchical composite outcome in the ferric carboxymaltose group as compared with the placebo group that gave a result of 1.10 (99% confidence interval, 0.99-1.23).
During the follow-up period, CV death or hospitalization for heart failure (the main secondary outcome) occurred in 31.0% of the ferric carboxymaltose group and in 32.2% of the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.93; 96% CI, 0.81-1.06).
Repeated dosing of ferric carboxymaltose appeared to be safe, with an acceptable adverse-event profile in most patients. The number of patients with serious adverse events occurring during the treatment period was similar in the two groups (27.0% in the ferric carboxymaltose group and 26.2% in the placebo group).
‘It’s hard to argue that we are not disappointed’
Designated discussant of the HEART-FID study at the ESC HOTLINE session, Scott Solomon, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, described HEART-FID as “an extremely important and well-conducted trial.”
He noted that iron deficiency is extremely common in patients with heart failure, affecting at least about a third of patients, and is associated with reduced New York Heart Association class and reduced survival. Previous smaller studies have suggested benefit but have narrowly missed their primary endpoints. HEART-FID was a larger and sufficiently well-powered trial to test the hypothesis that iron supplementation can improve harder clinical endpoints.
Dr. Solomon said that the primary endpoint could be difficult to interpret, with a hierarchical composite, and a win ratio. “But I think it’s fair to say that the results are modest at best,” he added.
“When we look at the traditional cardiovascular death/heart failure hospitalization endpoint, one of the hard endpoints that we care about most in heart failure, it’s hard to argue that we are not disappointed,” he commented.
Referring to the P value of .01 threshold set for significance, which is based on new U.S. Food and Drug Administration regulatory standards, Dr. Solomon noted, “If they had used a standard P = .05 threshold, then they would be able to claim that this trial had met its primary endpoint. But, nevertheless, whatever threshold for significance we look at, the benefit was clearly modest.”
“As with all trials that show modest results, it will be useful to look at subgroups that are most likely to respond to the greatest extent to this therapy, and I look forward to learning more on this from further analyses,” Dr. Solomon concluded.
In an accompanying editorial in the New England Journal of Medicine, Pieter Martens, MD, and Wilfried Mullens, MD, PhD, Ziekenhuis Oost-Limburg, Genk, Belgium, and Hasselt (Belgium) University, point out that analyses from previous trials have suggested that intravenous iron did not have a treatment effect in patients with a transferrin saturation of more than 20%.
They note that, in the ferric carboxymaltose group in the HEART-FID trial, the mean transferrin saturation was 23.9% at baseline, higher than in previous studies.
Future analyses should assess the importance of the transferrin saturation value at baseline, which “could help redefine the definition of iron deficiency in patients with heart failure and, we hope, help clinicians determine which patients might benefit from intravenous iron supplementation,” they write.
Meta-analysis of trials
The meta-analysis of intravenous iron supplementation trials in heart failure was presented by Piotr Ponikowski, MD, Medical University Wroclaw (Poland).
The analysis pooled individual patient data from three double-blind, placebo-controlled trials – CONFIRM-HF 2, AFFIRM-AHF 3, and HEART-FID – giving a total of 4,475 patients, with 2,241 receiving ferric carboxymaltose and 2,234 receiving placebo.
The two prespecified composite primary endpoints were CV hospitalizations/CV death and heart failure hospitalizations/CV death.
These showed similar 13%-14% relative risk reductions with ferric carboxymaltose, but only the former was statistically significant.
Similar results were seen when a fourth trial – IRONMAN (an open-label trial) – was included. In this case, the heart failure hospitalization/CV death endpoint was also nonsignificantly reduced with ferric carboxymaltose (rate ratio, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.58-1.07).
Subgroup analysis suggested that patients with higher transferrin saturation levels appeared to have a lack of treatment effect, whereas those with lower transferrin saturation (< 15%) showed significant treatment benefits.
A higher 6-month cumulative dose of ferric carboxymaltose – likely the result of redosing – may be associated with a slightly greater treatment effect after 6 months, Dr. Ponikowski reported.
He concluded: “These data support the use of intravenous ferric carboxymaltose to treat iron deficiency among patients with heart failure with reduced/mildly reduced LVEF [left ventricular ejection fraction] to reduce the risk of future hospitalization.”
“Our findings support additional research to challenge the current definition of iron deficiency in heart failure as an indication for IV iron therapy and to identify eligibility criteria for optimal redosing strategy,” Dr. Ponikowski added.
Discussant of the meta-analysis presentation at the ESC Hotline session, Pardeep Jhund, MD, University of Glasgow, suggested that the endpoint of most interest would be heart failure hospitalization/CV death in the analysis that included the IRONMAN trial, “which unfortunately did not meet statistical significance.”
In answer to the question “Where does this leave clinicians when treating patients?”Dr. Jhund said, “After yet another meta-analysis, I think the role of IV iron in reducing morbidity and mortality outcomes in heart failure remains questionable.”
“While the absence of evidence is not evidence of absence, the wide confidence intervals of the treatment effect on heart failure hospitalization/CV death leaves a lot of room for doubt about the efficacy of IV iron for reducing HF hospitalizations,” he concluded.
The HEART-FID trial was funded by American Regent, a Daiichi Sankyo Group company. Dr. Mentz reports receiving research support from American Regent and honoraria from American Regent, Vifor, and Pharmacosmos. Dr. Ponikowski reports consultancy fees/honoraria from Vifor Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Servier, Novartis, Bayer, MSD, Pfizer, Moderna, Sanofi, and Radcliffe Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM – , but the study failed to meet the specified more rigorous definition of significance (P = .01) on the primary hierarchical composite of death, hospitalizations for heart failure, or 6-minute walk distance.
The trial, which investigated intravenous ferric carboxymaltose treatment vs. placebo, also showed no statistical difference in the main secondary endpoint: time to cardiovascular death or first heart failure hospitalization.
It was hoped that HEART-FID, the largest study to date to look at intravenous iron supplementation in heart failure, would confirm benefits suggested in previous smaller studies, but its modest results seem to have, if anything, caused more uncertainly on whether supplementing iron is actually worthwhile.
The HEART-FID trial was presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Another presentation at the ESC Congress reported a pooled meta-analysis of all the intravenous iron supplementation studies, including HEART-FID. This showed a significant reduction in one coprimary endpoint (cardiovascular hospitalization/CV death) but not in the other (heart failure hospitalization/CV death), which is the more traditional and well-recognized endpoint in heart failure trials.
The meta-analysis was also published online in the European Heart Journal.
HEART-FID lead investigator, Robert J. Mentz, MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C., said the totality of the evidence showed clinical benefits of intravenous iron supplementation with intravenous ferric carboxymaltose.
“I worry that people will focus on a P value rather than the actual clinical benefits seen across all the studies,” Dr. Mentz said in an interview. “Technically, this study was neutral in respect to the primary endpoint, but when we look at all the evidence with respect to ferric carboxymaltose, including this new pooled analysis, this does support clinical benefits.”
Comoderator of the ESC Hotline session at which the trial was presented, John McMurray, MD, University of Glasgow (Scotland), thought the trial had “muddied the waters a bit” on the issue of iron supplementation in heart failure.
“I would say we are in a less clear position on iron supplementation now than we were a few months ago. Those clinicians who have believed that checking iron levels and supplementing iron in those who are low is the right thing to do may now be wondering about that,” he told this news organization.
Dr. McMurray noted that initial impressions of the data from both HEART-FID and the meta-analysis suggested some benefit of intravenous iron on CV death/heart failure hospitalization in the first year, but on longer term follow-up, that benefit was less evident.
“We need to look further into why there is that discrepancy,” he said. “This could be a statistical phenomenon or could be something to do with the frequency of redosing over the longer term.”
He explained that several previous studies of intravenous iron supplementation in heart failure have reported apparent convincing benefits on quality of life and functional capacity, but there has been some uncertainty on this because of the difficulty in producing a placebo for intravenous iron.
“So, it would have been great to have some additional confirmation of these benefits and on harder endpoints,” he said, “but even in HEART-FID, there was only a small nonsignificant benefit in walking distance.”
HEART-FID
The HEART-FID trial randomly assigned 3,065 ambulatory patients with heart failure, a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or less, and iron deficiency to intravenous ferric carboxymaltose or placebo, given every 6 months as needed on the basis of iron indexes and hemoglobin levels, in addition to standard therapy for heart failure.
The primary outcome was a hierarchical composite of death within 12 months after randomization, hospitalizations for heart failure within 12 months after randomization, or change from baseline to 6 months in the 6-minute walk distance. The significance level was set at .01.
Results showed that death by month 12 occurred in 8.6% of the ferric carboxymaltose group and 10.3% of the placebo group; a total of 297 and 332 hospitalizations for heart failure, respectively, occurred by month 12; and the mean change from baseline to 6 months in the 6-minute walk distance was 8 meters in the ferric carboxymaltose group and 4 meters with placebo. The P value for the primary composite was .02.
The trial also used another method (unmatched win ratio) to analyze the hierarchical composite outcome in the ferric carboxymaltose group as compared with the placebo group that gave a result of 1.10 (99% confidence interval, 0.99-1.23).
During the follow-up period, CV death or hospitalization for heart failure (the main secondary outcome) occurred in 31.0% of the ferric carboxymaltose group and in 32.2% of the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.93; 96% CI, 0.81-1.06).
Repeated dosing of ferric carboxymaltose appeared to be safe, with an acceptable adverse-event profile in most patients. The number of patients with serious adverse events occurring during the treatment period was similar in the two groups (27.0% in the ferric carboxymaltose group and 26.2% in the placebo group).
‘It’s hard to argue that we are not disappointed’
Designated discussant of the HEART-FID study at the ESC HOTLINE session, Scott Solomon, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, described HEART-FID as “an extremely important and well-conducted trial.”
He noted that iron deficiency is extremely common in patients with heart failure, affecting at least about a third of patients, and is associated with reduced New York Heart Association class and reduced survival. Previous smaller studies have suggested benefit but have narrowly missed their primary endpoints. HEART-FID was a larger and sufficiently well-powered trial to test the hypothesis that iron supplementation can improve harder clinical endpoints.
Dr. Solomon said that the primary endpoint could be difficult to interpret, with a hierarchical composite, and a win ratio. “But I think it’s fair to say that the results are modest at best,” he added.
“When we look at the traditional cardiovascular death/heart failure hospitalization endpoint, one of the hard endpoints that we care about most in heart failure, it’s hard to argue that we are not disappointed,” he commented.
Referring to the P value of .01 threshold set for significance, which is based on new U.S. Food and Drug Administration regulatory standards, Dr. Solomon noted, “If they had used a standard P = .05 threshold, then they would be able to claim that this trial had met its primary endpoint. But, nevertheless, whatever threshold for significance we look at, the benefit was clearly modest.”
“As with all trials that show modest results, it will be useful to look at subgroups that are most likely to respond to the greatest extent to this therapy, and I look forward to learning more on this from further analyses,” Dr. Solomon concluded.
In an accompanying editorial in the New England Journal of Medicine, Pieter Martens, MD, and Wilfried Mullens, MD, PhD, Ziekenhuis Oost-Limburg, Genk, Belgium, and Hasselt (Belgium) University, point out that analyses from previous trials have suggested that intravenous iron did not have a treatment effect in patients with a transferrin saturation of more than 20%.
They note that, in the ferric carboxymaltose group in the HEART-FID trial, the mean transferrin saturation was 23.9% at baseline, higher than in previous studies.
Future analyses should assess the importance of the transferrin saturation value at baseline, which “could help redefine the definition of iron deficiency in patients with heart failure and, we hope, help clinicians determine which patients might benefit from intravenous iron supplementation,” they write.
Meta-analysis of trials
The meta-analysis of intravenous iron supplementation trials in heart failure was presented by Piotr Ponikowski, MD, Medical University Wroclaw (Poland).
The analysis pooled individual patient data from three double-blind, placebo-controlled trials – CONFIRM-HF 2, AFFIRM-AHF 3, and HEART-FID – giving a total of 4,475 patients, with 2,241 receiving ferric carboxymaltose and 2,234 receiving placebo.
The two prespecified composite primary endpoints were CV hospitalizations/CV death and heart failure hospitalizations/CV death.
These showed similar 13%-14% relative risk reductions with ferric carboxymaltose, but only the former was statistically significant.
Similar results were seen when a fourth trial – IRONMAN (an open-label trial) – was included. In this case, the heart failure hospitalization/CV death endpoint was also nonsignificantly reduced with ferric carboxymaltose (rate ratio, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.58-1.07).
Subgroup analysis suggested that patients with higher transferrin saturation levels appeared to have a lack of treatment effect, whereas those with lower transferrin saturation (< 15%) showed significant treatment benefits.
A higher 6-month cumulative dose of ferric carboxymaltose – likely the result of redosing – may be associated with a slightly greater treatment effect after 6 months, Dr. Ponikowski reported.
He concluded: “These data support the use of intravenous ferric carboxymaltose to treat iron deficiency among patients with heart failure with reduced/mildly reduced LVEF [left ventricular ejection fraction] to reduce the risk of future hospitalization.”
“Our findings support additional research to challenge the current definition of iron deficiency in heart failure as an indication for IV iron therapy and to identify eligibility criteria for optimal redosing strategy,” Dr. Ponikowski added.
Discussant of the meta-analysis presentation at the ESC Hotline session, Pardeep Jhund, MD, University of Glasgow, suggested that the endpoint of most interest would be heart failure hospitalization/CV death in the analysis that included the IRONMAN trial, “which unfortunately did not meet statistical significance.”
In answer to the question “Where does this leave clinicians when treating patients?”Dr. Jhund said, “After yet another meta-analysis, I think the role of IV iron in reducing morbidity and mortality outcomes in heart failure remains questionable.”
“While the absence of evidence is not evidence of absence, the wide confidence intervals of the treatment effect on heart failure hospitalization/CV death leaves a lot of room for doubt about the efficacy of IV iron for reducing HF hospitalizations,” he concluded.
The HEART-FID trial was funded by American Regent, a Daiichi Sankyo Group company. Dr. Mentz reports receiving research support from American Regent and honoraria from American Regent, Vifor, and Pharmacosmos. Dr. Ponikowski reports consultancy fees/honoraria from Vifor Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Servier, Novartis, Bayer, MSD, Pfizer, Moderna, Sanofi, and Radcliffe Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM – , but the study failed to meet the specified more rigorous definition of significance (P = .01) on the primary hierarchical composite of death, hospitalizations for heart failure, or 6-minute walk distance.
The trial, which investigated intravenous ferric carboxymaltose treatment vs. placebo, also showed no statistical difference in the main secondary endpoint: time to cardiovascular death or first heart failure hospitalization.
It was hoped that HEART-FID, the largest study to date to look at intravenous iron supplementation in heart failure, would confirm benefits suggested in previous smaller studies, but its modest results seem to have, if anything, caused more uncertainly on whether supplementing iron is actually worthwhile.
The HEART-FID trial was presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Another presentation at the ESC Congress reported a pooled meta-analysis of all the intravenous iron supplementation studies, including HEART-FID. This showed a significant reduction in one coprimary endpoint (cardiovascular hospitalization/CV death) but not in the other (heart failure hospitalization/CV death), which is the more traditional and well-recognized endpoint in heart failure trials.
The meta-analysis was also published online in the European Heart Journal.
HEART-FID lead investigator, Robert J. Mentz, MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C., said the totality of the evidence showed clinical benefits of intravenous iron supplementation with intravenous ferric carboxymaltose.
“I worry that people will focus on a P value rather than the actual clinical benefits seen across all the studies,” Dr. Mentz said in an interview. “Technically, this study was neutral in respect to the primary endpoint, but when we look at all the evidence with respect to ferric carboxymaltose, including this new pooled analysis, this does support clinical benefits.”
Comoderator of the ESC Hotline session at which the trial was presented, John McMurray, MD, University of Glasgow (Scotland), thought the trial had “muddied the waters a bit” on the issue of iron supplementation in heart failure.
“I would say we are in a less clear position on iron supplementation now than we were a few months ago. Those clinicians who have believed that checking iron levels and supplementing iron in those who are low is the right thing to do may now be wondering about that,” he told this news organization.
Dr. McMurray noted that initial impressions of the data from both HEART-FID and the meta-analysis suggested some benefit of intravenous iron on CV death/heart failure hospitalization in the first year, but on longer term follow-up, that benefit was less evident.
“We need to look further into why there is that discrepancy,” he said. “This could be a statistical phenomenon or could be something to do with the frequency of redosing over the longer term.”
He explained that several previous studies of intravenous iron supplementation in heart failure have reported apparent convincing benefits on quality of life and functional capacity, but there has been some uncertainty on this because of the difficulty in producing a placebo for intravenous iron.
“So, it would have been great to have some additional confirmation of these benefits and on harder endpoints,” he said, “but even in HEART-FID, there was only a small nonsignificant benefit in walking distance.”
HEART-FID
The HEART-FID trial randomly assigned 3,065 ambulatory patients with heart failure, a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or less, and iron deficiency to intravenous ferric carboxymaltose or placebo, given every 6 months as needed on the basis of iron indexes and hemoglobin levels, in addition to standard therapy for heart failure.
The primary outcome was a hierarchical composite of death within 12 months after randomization, hospitalizations for heart failure within 12 months after randomization, or change from baseline to 6 months in the 6-minute walk distance. The significance level was set at .01.
Results showed that death by month 12 occurred in 8.6% of the ferric carboxymaltose group and 10.3% of the placebo group; a total of 297 and 332 hospitalizations for heart failure, respectively, occurred by month 12; and the mean change from baseline to 6 months in the 6-minute walk distance was 8 meters in the ferric carboxymaltose group and 4 meters with placebo. The P value for the primary composite was .02.
The trial also used another method (unmatched win ratio) to analyze the hierarchical composite outcome in the ferric carboxymaltose group as compared with the placebo group that gave a result of 1.10 (99% confidence interval, 0.99-1.23).
During the follow-up period, CV death or hospitalization for heart failure (the main secondary outcome) occurred in 31.0% of the ferric carboxymaltose group and in 32.2% of the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.93; 96% CI, 0.81-1.06).
Repeated dosing of ferric carboxymaltose appeared to be safe, with an acceptable adverse-event profile in most patients. The number of patients with serious adverse events occurring during the treatment period was similar in the two groups (27.0% in the ferric carboxymaltose group and 26.2% in the placebo group).
‘It’s hard to argue that we are not disappointed’
Designated discussant of the HEART-FID study at the ESC HOTLINE session, Scott Solomon, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, described HEART-FID as “an extremely important and well-conducted trial.”
He noted that iron deficiency is extremely common in patients with heart failure, affecting at least about a third of patients, and is associated with reduced New York Heart Association class and reduced survival. Previous smaller studies have suggested benefit but have narrowly missed their primary endpoints. HEART-FID was a larger and sufficiently well-powered trial to test the hypothesis that iron supplementation can improve harder clinical endpoints.
Dr. Solomon said that the primary endpoint could be difficult to interpret, with a hierarchical composite, and a win ratio. “But I think it’s fair to say that the results are modest at best,” he added.
“When we look at the traditional cardiovascular death/heart failure hospitalization endpoint, one of the hard endpoints that we care about most in heart failure, it’s hard to argue that we are not disappointed,” he commented.
Referring to the P value of .01 threshold set for significance, which is based on new U.S. Food and Drug Administration regulatory standards, Dr. Solomon noted, “If they had used a standard P = .05 threshold, then they would be able to claim that this trial had met its primary endpoint. But, nevertheless, whatever threshold for significance we look at, the benefit was clearly modest.”
“As with all trials that show modest results, it will be useful to look at subgroups that are most likely to respond to the greatest extent to this therapy, and I look forward to learning more on this from further analyses,” Dr. Solomon concluded.
In an accompanying editorial in the New England Journal of Medicine, Pieter Martens, MD, and Wilfried Mullens, MD, PhD, Ziekenhuis Oost-Limburg, Genk, Belgium, and Hasselt (Belgium) University, point out that analyses from previous trials have suggested that intravenous iron did not have a treatment effect in patients with a transferrin saturation of more than 20%.
They note that, in the ferric carboxymaltose group in the HEART-FID trial, the mean transferrin saturation was 23.9% at baseline, higher than in previous studies.
Future analyses should assess the importance of the transferrin saturation value at baseline, which “could help redefine the definition of iron deficiency in patients with heart failure and, we hope, help clinicians determine which patients might benefit from intravenous iron supplementation,” they write.
Meta-analysis of trials
The meta-analysis of intravenous iron supplementation trials in heart failure was presented by Piotr Ponikowski, MD, Medical University Wroclaw (Poland).
The analysis pooled individual patient data from three double-blind, placebo-controlled trials – CONFIRM-HF 2, AFFIRM-AHF 3, and HEART-FID – giving a total of 4,475 patients, with 2,241 receiving ferric carboxymaltose and 2,234 receiving placebo.
The two prespecified composite primary endpoints were CV hospitalizations/CV death and heart failure hospitalizations/CV death.
These showed similar 13%-14% relative risk reductions with ferric carboxymaltose, but only the former was statistically significant.
Similar results were seen when a fourth trial – IRONMAN (an open-label trial) – was included. In this case, the heart failure hospitalization/CV death endpoint was also nonsignificantly reduced with ferric carboxymaltose (rate ratio, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.58-1.07).
Subgroup analysis suggested that patients with higher transferrin saturation levels appeared to have a lack of treatment effect, whereas those with lower transferrin saturation (< 15%) showed significant treatment benefits.
A higher 6-month cumulative dose of ferric carboxymaltose – likely the result of redosing – may be associated with a slightly greater treatment effect after 6 months, Dr. Ponikowski reported.
He concluded: “These data support the use of intravenous ferric carboxymaltose to treat iron deficiency among patients with heart failure with reduced/mildly reduced LVEF [left ventricular ejection fraction] to reduce the risk of future hospitalization.”
“Our findings support additional research to challenge the current definition of iron deficiency in heart failure as an indication for IV iron therapy and to identify eligibility criteria for optimal redosing strategy,” Dr. Ponikowski added.
Discussant of the meta-analysis presentation at the ESC Hotline session, Pardeep Jhund, MD, University of Glasgow, suggested that the endpoint of most interest would be heart failure hospitalization/CV death in the analysis that included the IRONMAN trial, “which unfortunately did not meet statistical significance.”
In answer to the question “Where does this leave clinicians when treating patients?”Dr. Jhund said, “After yet another meta-analysis, I think the role of IV iron in reducing morbidity and mortality outcomes in heart failure remains questionable.”
“While the absence of evidence is not evidence of absence, the wide confidence intervals of the treatment effect on heart failure hospitalization/CV death leaves a lot of room for doubt about the efficacy of IV iron for reducing HF hospitalizations,” he concluded.
The HEART-FID trial was funded by American Regent, a Daiichi Sankyo Group company. Dr. Mentz reports receiving research support from American Regent and honoraria from American Regent, Vifor, and Pharmacosmos. Dr. Ponikowski reports consultancy fees/honoraria from Vifor Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Servier, Novartis, Bayer, MSD, Pfizer, Moderna, Sanofi, and Radcliffe Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT THE ESC CONGRESS 2023
Traditional Chinese medicine improves outcomes in HFrEF
When added to guideline-directed therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), a traditional Chinese medicine called qiliqiangxin reduced the composite endpoint of cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization by more than 20%, results of a large placebo-controlled trial show.
reported Xinli Li, MD, PhD, First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, China.
Qiliqiangxin, a commonly used therapy in China for cardiovascular disease, is not a single chemical entity but a treatment composed of 11 plant-based substances that together are associated with diuretic effects, vasodilation, and “cardiotonic” activity, Dr. Li said. He also cited studies showing an upregulation effect on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-beta (PGC1-beta).
The results were presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
Hard endpoints pursued in rigorous design
There have been numerous studies of qiliqiangxin for cardiovascular diseases, including a double-blind study that associated this agent with a greater than 30% reduction in the surrogate endpoint of N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP).
In the newly completed multicenter trial, called QUEST, the goal was to determine whether this therapy could reduce hard endpoints relative to placebo in a rigorously conducted trial enrolling patients receiving an optimized triple-therapy heart failure regimen.
Few patients in the study received a sodium glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2 inhibitor), which was not a standard at the time the study was designed but is now part of the quadruple guideline-directed medical therapy in most European and North American guidelines.
In this trial, 3,119 patients were randomly assigned at 133 centers in China to take four capsules of qiliqiangxin or placebo three times per day. At a median follow-up of 18.3 months, outcomes were evaluable in nearly all 1,561 patients randomly assigned to the experimental therapy and 1,555 patients randomly assigned to placebo.
The key inclusion criteria were a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or less and a serum NT-proBNP level of at least 450 pg/mL. Patients in New York Heart Association class IV heart failure were excluded.
At enrollment, more than 80% of patients in both arms were receiving a renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, or angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor), more than 80% were receiving a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, and more than 85% were receiving a beta-blocker.
Death and hospitalization reduced 22%
By hazard ratio, the primary composite endpoint of CV death and heart failure hospitalization was reduced by 22% relative to placebo (HR, 0.78; P < .001). When evaluated separately, the relative reductions in these respective endpoints were 17% (HR, 0.83; P = .045) and 24% (HR, 0.76; P = .002).
The risk reduction was robust (HR, 0.76; P < .001) in patients with an ischemic cause but nonsignificant in those without (HR, 0.92; P = .575). A significant benefit was sustained in patients receiving an angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor (HR, 0.84; P = .041), as well as those who did not receive this class of drug (HR, 0.77; P = .012).
However, the benefit of qiliqiangxin among patients receiving all components of guideline-directed triple therapy (RAS inhibitor, beta-blocker, and mineralocorticoid antagonist) was only a trend (HR, 0.86; P = .079).
All-cause mortality, a secondary endpoint, was lower among patients randomly assigned to qiliqiangxin than to those assigned to placebo, but this difference fell just short of statistical significance (14.21% vs. 16.85%; P = .058).
Qiliqiangxin was well tolerated. The proportion of patients with a serious adverse event was numerically lower with qiliqiangxin than with placebo (17.43% vs. 19.74%), whereas discontinuations associated with an adverse event were numerically higher in the qiliqiangxin group (1.03% vs. 0.58%), albeit still very low in both study arms.
Overlap of drug benefits suspected
Given the safety of this drug and its highly significant reduction in a composite endpoint used in other major HFrEF trials, the ESC-invited discussant, Carolyn S.P. Lam, MBBS, PhD, National Heart Centre, Singapore, called the outcome “remarkable” and a validation for “the millions of people” who are already taking qiliqiangxin in China and other Asian countries.
Using the DAPA-HF trial as a point of reference, Dr. Lam noted that relative reduction in the composite endpoint of cardiovascular death for the SGLT-2 inhibitor dapagliflozin relative to placebo on top of triple guideline-directed medical therapy was lower (17% vs. 24%), but there were significant reductions in each of the components, as well as a nonsignificant signal of a mortality benefit.
However, Dr. Lam pointed out that there does seem to be more of an overlap for the benefits of qiliqiangxin than dapagliflozin relative to other components of triple therapy based on the lower rate of benefit when patients were optimized on triple therapy.
“The subgroup analysis [of this study] is very important,” Dr. Lam said. Qiliqiangxin may be best in patients who cannot take one or more of the components of triple therapy, she suggested, even though she called for further studies to test this theory. She also cautioned that the pill burden of four capsules taken three times per day might be onerous for some patients.
Of the many questions still to be answered, Dr. Lam noted that the low rate of enrollment for patients (< 10%) taking SGLT-2 inhibitors makes the contribution of qiliqiangxin unclear among those receiving the current standard of quadruple guideline-directed medical therapy.
She also suggested that it will be important to dissect the relative contribution of the different active ingredients of qiliqiangxin.
“This is not a purified compound that we are used to in Western medicine,” Dr. Lam said. While she praised the study as “scientifically rigorous” and indicated that the results support a clinical benefit from qiliqiangxin, she thinks an exploration of the mechanism or mechanisms of benefit is a next step in understanding where this therapy fits in HFrEF management.
Dr. Li reports financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Novartis, Roche, and Yiling. Dr. Lam reports financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical or device manufacturers, many of which produce therapies for heart failure, as well as with Medscape/WebMD Global LLC. The study was supported by the Chinese National Key Research and Development Project and Yiling Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When added to guideline-directed therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), a traditional Chinese medicine called qiliqiangxin reduced the composite endpoint of cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization by more than 20%, results of a large placebo-controlled trial show.
reported Xinli Li, MD, PhD, First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, China.
Qiliqiangxin, a commonly used therapy in China for cardiovascular disease, is not a single chemical entity but a treatment composed of 11 plant-based substances that together are associated with diuretic effects, vasodilation, and “cardiotonic” activity, Dr. Li said. He also cited studies showing an upregulation effect on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-beta (PGC1-beta).
The results were presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
Hard endpoints pursued in rigorous design
There have been numerous studies of qiliqiangxin for cardiovascular diseases, including a double-blind study that associated this agent with a greater than 30% reduction in the surrogate endpoint of N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP).
In the newly completed multicenter trial, called QUEST, the goal was to determine whether this therapy could reduce hard endpoints relative to placebo in a rigorously conducted trial enrolling patients receiving an optimized triple-therapy heart failure regimen.
Few patients in the study received a sodium glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2 inhibitor), which was not a standard at the time the study was designed but is now part of the quadruple guideline-directed medical therapy in most European and North American guidelines.
In this trial, 3,119 patients were randomly assigned at 133 centers in China to take four capsules of qiliqiangxin or placebo three times per day. At a median follow-up of 18.3 months, outcomes were evaluable in nearly all 1,561 patients randomly assigned to the experimental therapy and 1,555 patients randomly assigned to placebo.
The key inclusion criteria were a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or less and a serum NT-proBNP level of at least 450 pg/mL. Patients in New York Heart Association class IV heart failure were excluded.
At enrollment, more than 80% of patients in both arms were receiving a renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, or angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor), more than 80% were receiving a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, and more than 85% were receiving a beta-blocker.
Death and hospitalization reduced 22%
By hazard ratio, the primary composite endpoint of CV death and heart failure hospitalization was reduced by 22% relative to placebo (HR, 0.78; P < .001). When evaluated separately, the relative reductions in these respective endpoints were 17% (HR, 0.83; P = .045) and 24% (HR, 0.76; P = .002).
The risk reduction was robust (HR, 0.76; P < .001) in patients with an ischemic cause but nonsignificant in those without (HR, 0.92; P = .575). A significant benefit was sustained in patients receiving an angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor (HR, 0.84; P = .041), as well as those who did not receive this class of drug (HR, 0.77; P = .012).
However, the benefit of qiliqiangxin among patients receiving all components of guideline-directed triple therapy (RAS inhibitor, beta-blocker, and mineralocorticoid antagonist) was only a trend (HR, 0.86; P = .079).
All-cause mortality, a secondary endpoint, was lower among patients randomly assigned to qiliqiangxin than to those assigned to placebo, but this difference fell just short of statistical significance (14.21% vs. 16.85%; P = .058).
Qiliqiangxin was well tolerated. The proportion of patients with a serious adverse event was numerically lower with qiliqiangxin than with placebo (17.43% vs. 19.74%), whereas discontinuations associated with an adverse event were numerically higher in the qiliqiangxin group (1.03% vs. 0.58%), albeit still very low in both study arms.
Overlap of drug benefits suspected
Given the safety of this drug and its highly significant reduction in a composite endpoint used in other major HFrEF trials, the ESC-invited discussant, Carolyn S.P. Lam, MBBS, PhD, National Heart Centre, Singapore, called the outcome “remarkable” and a validation for “the millions of people” who are already taking qiliqiangxin in China and other Asian countries.
Using the DAPA-HF trial as a point of reference, Dr. Lam noted that relative reduction in the composite endpoint of cardiovascular death for the SGLT-2 inhibitor dapagliflozin relative to placebo on top of triple guideline-directed medical therapy was lower (17% vs. 24%), but there were significant reductions in each of the components, as well as a nonsignificant signal of a mortality benefit.
However, Dr. Lam pointed out that there does seem to be more of an overlap for the benefits of qiliqiangxin than dapagliflozin relative to other components of triple therapy based on the lower rate of benefit when patients were optimized on triple therapy.
“The subgroup analysis [of this study] is very important,” Dr. Lam said. Qiliqiangxin may be best in patients who cannot take one or more of the components of triple therapy, she suggested, even though she called for further studies to test this theory. She also cautioned that the pill burden of four capsules taken three times per day might be onerous for some patients.
Of the many questions still to be answered, Dr. Lam noted that the low rate of enrollment for patients (< 10%) taking SGLT-2 inhibitors makes the contribution of qiliqiangxin unclear among those receiving the current standard of quadruple guideline-directed medical therapy.
She also suggested that it will be important to dissect the relative contribution of the different active ingredients of qiliqiangxin.
“This is not a purified compound that we are used to in Western medicine,” Dr. Lam said. While she praised the study as “scientifically rigorous” and indicated that the results support a clinical benefit from qiliqiangxin, she thinks an exploration of the mechanism or mechanisms of benefit is a next step in understanding where this therapy fits in HFrEF management.
Dr. Li reports financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Novartis, Roche, and Yiling. Dr. Lam reports financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical or device manufacturers, many of which produce therapies for heart failure, as well as with Medscape/WebMD Global LLC. The study was supported by the Chinese National Key Research and Development Project and Yiling Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When added to guideline-directed therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), a traditional Chinese medicine called qiliqiangxin reduced the composite endpoint of cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization by more than 20%, results of a large placebo-controlled trial show.
reported Xinli Li, MD, PhD, First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, China.
Qiliqiangxin, a commonly used therapy in China for cardiovascular disease, is not a single chemical entity but a treatment composed of 11 plant-based substances that together are associated with diuretic effects, vasodilation, and “cardiotonic” activity, Dr. Li said. He also cited studies showing an upregulation effect on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-beta (PGC1-beta).
The results were presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
Hard endpoints pursued in rigorous design
There have been numerous studies of qiliqiangxin for cardiovascular diseases, including a double-blind study that associated this agent with a greater than 30% reduction in the surrogate endpoint of N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP).
In the newly completed multicenter trial, called QUEST, the goal was to determine whether this therapy could reduce hard endpoints relative to placebo in a rigorously conducted trial enrolling patients receiving an optimized triple-therapy heart failure regimen.
Few patients in the study received a sodium glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2 inhibitor), which was not a standard at the time the study was designed but is now part of the quadruple guideline-directed medical therapy in most European and North American guidelines.
In this trial, 3,119 patients were randomly assigned at 133 centers in China to take four capsules of qiliqiangxin or placebo three times per day. At a median follow-up of 18.3 months, outcomes were evaluable in nearly all 1,561 patients randomly assigned to the experimental therapy and 1,555 patients randomly assigned to placebo.
The key inclusion criteria were a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or less and a serum NT-proBNP level of at least 450 pg/mL. Patients in New York Heart Association class IV heart failure were excluded.
At enrollment, more than 80% of patients in both arms were receiving a renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, or angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor), more than 80% were receiving a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, and more than 85% were receiving a beta-blocker.
Death and hospitalization reduced 22%
By hazard ratio, the primary composite endpoint of CV death and heart failure hospitalization was reduced by 22% relative to placebo (HR, 0.78; P < .001). When evaluated separately, the relative reductions in these respective endpoints were 17% (HR, 0.83; P = .045) and 24% (HR, 0.76; P = .002).
The risk reduction was robust (HR, 0.76; P < .001) in patients with an ischemic cause but nonsignificant in those without (HR, 0.92; P = .575). A significant benefit was sustained in patients receiving an angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor (HR, 0.84; P = .041), as well as those who did not receive this class of drug (HR, 0.77; P = .012).
However, the benefit of qiliqiangxin among patients receiving all components of guideline-directed triple therapy (RAS inhibitor, beta-blocker, and mineralocorticoid antagonist) was only a trend (HR, 0.86; P = .079).
All-cause mortality, a secondary endpoint, was lower among patients randomly assigned to qiliqiangxin than to those assigned to placebo, but this difference fell just short of statistical significance (14.21% vs. 16.85%; P = .058).
Qiliqiangxin was well tolerated. The proportion of patients with a serious adverse event was numerically lower with qiliqiangxin than with placebo (17.43% vs. 19.74%), whereas discontinuations associated with an adverse event were numerically higher in the qiliqiangxin group (1.03% vs. 0.58%), albeit still very low in both study arms.
Overlap of drug benefits suspected
Given the safety of this drug and its highly significant reduction in a composite endpoint used in other major HFrEF trials, the ESC-invited discussant, Carolyn S.P. Lam, MBBS, PhD, National Heart Centre, Singapore, called the outcome “remarkable” and a validation for “the millions of people” who are already taking qiliqiangxin in China and other Asian countries.
Using the DAPA-HF trial as a point of reference, Dr. Lam noted that relative reduction in the composite endpoint of cardiovascular death for the SGLT-2 inhibitor dapagliflozin relative to placebo on top of triple guideline-directed medical therapy was lower (17% vs. 24%), but there were significant reductions in each of the components, as well as a nonsignificant signal of a mortality benefit.
However, Dr. Lam pointed out that there does seem to be more of an overlap for the benefits of qiliqiangxin than dapagliflozin relative to other components of triple therapy based on the lower rate of benefit when patients were optimized on triple therapy.
“The subgroup analysis [of this study] is very important,” Dr. Lam said. Qiliqiangxin may be best in patients who cannot take one or more of the components of triple therapy, she suggested, even though she called for further studies to test this theory. She also cautioned that the pill burden of four capsules taken three times per day might be onerous for some patients.
Of the many questions still to be answered, Dr. Lam noted that the low rate of enrollment for patients (< 10%) taking SGLT-2 inhibitors makes the contribution of qiliqiangxin unclear among those receiving the current standard of quadruple guideline-directed medical therapy.
She also suggested that it will be important to dissect the relative contribution of the different active ingredients of qiliqiangxin.
“This is not a purified compound that we are used to in Western medicine,” Dr. Lam said. While she praised the study as “scientifically rigorous” and indicated that the results support a clinical benefit from qiliqiangxin, she thinks an exploration of the mechanism or mechanisms of benefit is a next step in understanding where this therapy fits in HFrEF management.
Dr. Li reports financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Novartis, Roche, and Yiling. Dr. Lam reports financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical or device manufacturers, many of which produce therapies for heart failure, as well as with Medscape/WebMD Global LLC. The study was supported by the Chinese National Key Research and Development Project and Yiling Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESC CONGRESS 2023
Wegovy scores HFpEF benefits in people with obesity
AMSTERDAM – Adults with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) but without diabetes showed significant improvements in their heart failure-related symptoms and physical limitations, exercise function, and weight loss when treated with a weight-reducing dose of semaglutide for 52 weeks, compared with placebo, in the randomized STEP-HFpEF trial.
The results, which also showed the treatment’s safety in these patients, “indicate that treatment with semaglutide is a valuable therapeutic approach in the management of patients with HFpEF and obesity,” Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The findings establish semaglutide, a glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, as a second class of medication with proven efficacy and safety for people with HFpEF, joining two agents also proven beneficial for people with HFpEF, dapagliflozin (Farxiga) and empagliflozin (Jardiance), both from the class of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors.
When administered at the approved dose for weight loss of 2.4 mg, injected subcutaneously weekly for 52 weeks, semaglutide (Wegovy) produced an average 7.8-point incremental improvement in patients’ scores on the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ), a validated measure of symptoms and functional limitations, compared with controls who received placebo injections, as well as an average incremental weight loss from baseline, compared with placebo, of 10.7%. Both were significant effects, compared with placebo, and clinically meaningful benefits for the study’s two primary endpoints.
Simultaneously with Kosiborod’s report the results also appeared in a report posted online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
A ‘paradigm shift’ for medical weight loss in cardiology
The findings from this study with 529 randomized patients immediately propelled the weight loss formulation of semaglutide into the ranks of agents used to treat and prevent cardiovascular disease events. This evolution in the indications for semaglutide will be driven not only by the STEP-HFpEF results but also by findings from the SELECT trial, which tested the same semaglutide weight-loss dose in people with obesity, established cardiovascular disease, and had positive top-line results for prevention of major cardiovascular adverse events, according to a press release from Novo Nordisk on Aug. 8.
The STEP-HFpEF and SELECT results will trigger “a paradigm shift” for cardiologists, who will now need to consider prescribing a weight-loss medication to many of their patients, agents that until now were not part of the usual pharmacologic toolbox for cardiologists, said Dr. Kosiborod, a cardiologist and codirector of the Haverty Cardiometabolic Center of Excellence at Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, Mo. This shift will require education to bring the clinical cardiology community on board, he added in an interview.
Given that semaglutide administered at this dose already has a Food and Drug Administration–approved indication for weight loss in people with obesity or overweight plus at least one comorbidity, clinicians could immediately start using the treatment in people with obesity and HFpEF, said Dr. Kosiborod and other cardiologists.
Weekly semaglutide injections “could be considered a treatment option right now” for people with obesity and HFpEF, Dr. Kosiborod said during a press briefing.
Other experts agreed, especially because the STEP-HFpEF results confirmed that weight loss treatment with semaglutide was safe in this population.
‘A terrific win for patients’
The new findings are “a terrific win and game changer for patients with HFpEF,” commented Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, professor and cochief of cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved with the study.
“The magnitude of improvement in the patient-reported health status scores are large and impressive. These data support clinical use of this agent for individuals with HFpEF with a body mass index of 30 kg/m2, patients who already fall within existing indications,” Dr. Fonarow said in an interview.
“Given the improvements in clinical outcomes in the STEP-HFpEF and SELECT trials, cardiologists should be prescribing these medications to eligible patients without conditions,” he added. “The perception of [semaglutide] needs to shift and be viewed as a component of the comprehensive medical therapies provided to individuals with established cardiovascular disease or HFpEF who also have elevated body mass index to improve their clinical outcomes.”
Historically, cardiologists have had a concern that weight loss was potentially harmful in people with heart failure and that obesity was protective, a phenomenon known as the “obesity paradox,” but the STEP-HFpEF data help disprove that notion, commented Nancy K. Sweitzer, MD, PhD, a heart failure specialist and vice chair of clinical research in the department of medicine at Washington University in St. Louis, who also was not involved in the study.
No signal of an obesity paradox
“There’s been a concern in the heart failure community to use weight-loss strategies in people with heart failure because of this, but this evidence provides a lot of confidence that it’s safe to use this weight loss treatment. The results show that patients feel better and lose weight with no signal of harm,” Dr. Sweitzer said in an interview.
The “encouraging findings” for semaglutide in patients with HFpEF “potentially add a much needed extra option for these patients and provide another upstream treatment for patients with signs of this condition plus a high body mass index,” commented Yigal M. Pinto, MD, PhD, in an editorial that accompanied the published report.
“How these findings translate to hard end points remains to be established and will be important in determining the role of GLP-1 agonism,” wrote Dr. Pinto, a professor and heart failure specialist at Amsterdam University Medical Center.
But Dr. Kosiborod said that the improvement seen in the KCCQ score was itself an important benefit for patients. “Heart failure is defined clinically based on symptoms,” he noted, and results in prior studies documented that patients value improvements in symptoms and physical limitations even more than they value “hard endpoints” such as survival.
The new findings, which indicate that two different and expensive classes of medications are now standard of care for many people with HFpEF and obesity – the SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 receptor agonist semaglutide – also raise concerns over patient access and affordability, as many U.S. insurers have a history of requiring prior authorization, high copays, or coverage denials for these two medical classes.
But Dr. Sweitzer and Dr. Kosiborod both said that the insurance-coverage climate seems, in just the past couple of years or so, to have dramatically improved, although it’s still not ideal.
Prior authorization hoops have decreased
“We still have prior-authorization hoops to jump through, but I expect these will continue to decrease over time as evidence for clinical benefits [from weight loss] continues to accumulate,” said Dr. Sweitzer.
And “the SELECT data mean that cardiologists will need to become comfortable prescribing GLP-1 receptor agonists,” she added.
“It’s not okay for insurers to say we are not going to cover weight loss medications because it’s a cosmetic indication,” said Dr. Kosiborod. “Obesity appears to be very important in the pathogenesis and progression of heart failure, and if patients derive substantial benefit, they should have access to this treatment.”
The improvements in KCCQ score, as well as in several secondary and exploratory endpoints including a significant reduction in C-reactive protein (an indication of a potent anti-inflammatory effect), an average 20 m increase in 6-minute walk distance, a significant average drop in N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, and a drop in heart failure hospitalizations or urgent heart failure visits (although the trial was not powered to show differences in clinical events), “were the largest benefits in these outcomes we’ve seen,” compared with any other medical intervention in people with HFpEF, he noted.
“About 80% of U.S. patients with HFpEF have obesity or overweight,” Dr. Kosiborod noted. Using semaglutide on these patients “is an issue of access and insurance coverage. My hope is that these and other data will favorably change this.”
A related trial with a similar design, STEP-HFpEF DM, is still in progress and testing the same semaglutide treatment in adults with HFpEF, obesity, and type 2 diabetes, noted Dr. Kosiborod, who is also lead investigator for that study. He said those results will likely become available before the end of 2023.
The study was funded by Novo Nordisk, the company that markets semaglutide (Wegovy). Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant and adviser to and has received honoraria from Novo Nordisk. He has also been a consultant to numerous other companies, received research grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Pfizer, honoraria from AstraZeneca, and is a stockholder in Artera Health and Saghmos Therapeutics. Dr. Fonarow has been a consultant to Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, CHF Solutions, Cytokinetics, Edwards, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, Novartis, and Regeneron. Dr. Sweitzer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM – Adults with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) but without diabetes showed significant improvements in their heart failure-related symptoms and physical limitations, exercise function, and weight loss when treated with a weight-reducing dose of semaglutide for 52 weeks, compared with placebo, in the randomized STEP-HFpEF trial.
The results, which also showed the treatment’s safety in these patients, “indicate that treatment with semaglutide is a valuable therapeutic approach in the management of patients with HFpEF and obesity,” Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The findings establish semaglutide, a glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, as a second class of medication with proven efficacy and safety for people with HFpEF, joining two agents also proven beneficial for people with HFpEF, dapagliflozin (Farxiga) and empagliflozin (Jardiance), both from the class of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors.
When administered at the approved dose for weight loss of 2.4 mg, injected subcutaneously weekly for 52 weeks, semaglutide (Wegovy) produced an average 7.8-point incremental improvement in patients’ scores on the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ), a validated measure of symptoms and functional limitations, compared with controls who received placebo injections, as well as an average incremental weight loss from baseline, compared with placebo, of 10.7%. Both were significant effects, compared with placebo, and clinically meaningful benefits for the study’s two primary endpoints.
Simultaneously with Kosiborod’s report the results also appeared in a report posted online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
A ‘paradigm shift’ for medical weight loss in cardiology
The findings from this study with 529 randomized patients immediately propelled the weight loss formulation of semaglutide into the ranks of agents used to treat and prevent cardiovascular disease events. This evolution in the indications for semaglutide will be driven not only by the STEP-HFpEF results but also by findings from the SELECT trial, which tested the same semaglutide weight-loss dose in people with obesity, established cardiovascular disease, and had positive top-line results for prevention of major cardiovascular adverse events, according to a press release from Novo Nordisk on Aug. 8.
The STEP-HFpEF and SELECT results will trigger “a paradigm shift” for cardiologists, who will now need to consider prescribing a weight-loss medication to many of their patients, agents that until now were not part of the usual pharmacologic toolbox for cardiologists, said Dr. Kosiborod, a cardiologist and codirector of the Haverty Cardiometabolic Center of Excellence at Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, Mo. This shift will require education to bring the clinical cardiology community on board, he added in an interview.
Given that semaglutide administered at this dose already has a Food and Drug Administration–approved indication for weight loss in people with obesity or overweight plus at least one comorbidity, clinicians could immediately start using the treatment in people with obesity and HFpEF, said Dr. Kosiborod and other cardiologists.
Weekly semaglutide injections “could be considered a treatment option right now” for people with obesity and HFpEF, Dr. Kosiborod said during a press briefing.
Other experts agreed, especially because the STEP-HFpEF results confirmed that weight loss treatment with semaglutide was safe in this population.
‘A terrific win for patients’
The new findings are “a terrific win and game changer for patients with HFpEF,” commented Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, professor and cochief of cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved with the study.
“The magnitude of improvement in the patient-reported health status scores are large and impressive. These data support clinical use of this agent for individuals with HFpEF with a body mass index of 30 kg/m2, patients who already fall within existing indications,” Dr. Fonarow said in an interview.
“Given the improvements in clinical outcomes in the STEP-HFpEF and SELECT trials, cardiologists should be prescribing these medications to eligible patients without conditions,” he added. “The perception of [semaglutide] needs to shift and be viewed as a component of the comprehensive medical therapies provided to individuals with established cardiovascular disease or HFpEF who also have elevated body mass index to improve their clinical outcomes.”
Historically, cardiologists have had a concern that weight loss was potentially harmful in people with heart failure and that obesity was protective, a phenomenon known as the “obesity paradox,” but the STEP-HFpEF data help disprove that notion, commented Nancy K. Sweitzer, MD, PhD, a heart failure specialist and vice chair of clinical research in the department of medicine at Washington University in St. Louis, who also was not involved in the study.
No signal of an obesity paradox
“There’s been a concern in the heart failure community to use weight-loss strategies in people with heart failure because of this, but this evidence provides a lot of confidence that it’s safe to use this weight loss treatment. The results show that patients feel better and lose weight with no signal of harm,” Dr. Sweitzer said in an interview.
The “encouraging findings” for semaglutide in patients with HFpEF “potentially add a much needed extra option for these patients and provide another upstream treatment for patients with signs of this condition plus a high body mass index,” commented Yigal M. Pinto, MD, PhD, in an editorial that accompanied the published report.
“How these findings translate to hard end points remains to be established and will be important in determining the role of GLP-1 agonism,” wrote Dr. Pinto, a professor and heart failure specialist at Amsterdam University Medical Center.
But Dr. Kosiborod said that the improvement seen in the KCCQ score was itself an important benefit for patients. “Heart failure is defined clinically based on symptoms,” he noted, and results in prior studies documented that patients value improvements in symptoms and physical limitations even more than they value “hard endpoints” such as survival.
The new findings, which indicate that two different and expensive classes of medications are now standard of care for many people with HFpEF and obesity – the SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 receptor agonist semaglutide – also raise concerns over patient access and affordability, as many U.S. insurers have a history of requiring prior authorization, high copays, or coverage denials for these two medical classes.
But Dr. Sweitzer and Dr. Kosiborod both said that the insurance-coverage climate seems, in just the past couple of years or so, to have dramatically improved, although it’s still not ideal.
Prior authorization hoops have decreased
“We still have prior-authorization hoops to jump through, but I expect these will continue to decrease over time as evidence for clinical benefits [from weight loss] continues to accumulate,” said Dr. Sweitzer.
And “the SELECT data mean that cardiologists will need to become comfortable prescribing GLP-1 receptor agonists,” she added.
“It’s not okay for insurers to say we are not going to cover weight loss medications because it’s a cosmetic indication,” said Dr. Kosiborod. “Obesity appears to be very important in the pathogenesis and progression of heart failure, and if patients derive substantial benefit, they should have access to this treatment.”
The improvements in KCCQ score, as well as in several secondary and exploratory endpoints including a significant reduction in C-reactive protein (an indication of a potent anti-inflammatory effect), an average 20 m increase in 6-minute walk distance, a significant average drop in N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, and a drop in heart failure hospitalizations or urgent heart failure visits (although the trial was not powered to show differences in clinical events), “were the largest benefits in these outcomes we’ve seen,” compared with any other medical intervention in people with HFpEF, he noted.
“About 80% of U.S. patients with HFpEF have obesity or overweight,” Dr. Kosiborod noted. Using semaglutide on these patients “is an issue of access and insurance coverage. My hope is that these and other data will favorably change this.”
A related trial with a similar design, STEP-HFpEF DM, is still in progress and testing the same semaglutide treatment in adults with HFpEF, obesity, and type 2 diabetes, noted Dr. Kosiborod, who is also lead investigator for that study. He said those results will likely become available before the end of 2023.
The study was funded by Novo Nordisk, the company that markets semaglutide (Wegovy). Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant and adviser to and has received honoraria from Novo Nordisk. He has also been a consultant to numerous other companies, received research grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Pfizer, honoraria from AstraZeneca, and is a stockholder in Artera Health and Saghmos Therapeutics. Dr. Fonarow has been a consultant to Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, CHF Solutions, Cytokinetics, Edwards, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, Novartis, and Regeneron. Dr. Sweitzer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM – Adults with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) but without diabetes showed significant improvements in their heart failure-related symptoms and physical limitations, exercise function, and weight loss when treated with a weight-reducing dose of semaglutide for 52 weeks, compared with placebo, in the randomized STEP-HFpEF trial.
The results, which also showed the treatment’s safety in these patients, “indicate that treatment with semaglutide is a valuable therapeutic approach in the management of patients with HFpEF and obesity,” Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The findings establish semaglutide, a glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, as a second class of medication with proven efficacy and safety for people with HFpEF, joining two agents also proven beneficial for people with HFpEF, dapagliflozin (Farxiga) and empagliflozin (Jardiance), both from the class of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors.
When administered at the approved dose for weight loss of 2.4 mg, injected subcutaneously weekly for 52 weeks, semaglutide (Wegovy) produced an average 7.8-point incremental improvement in patients’ scores on the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ), a validated measure of symptoms and functional limitations, compared with controls who received placebo injections, as well as an average incremental weight loss from baseline, compared with placebo, of 10.7%. Both were significant effects, compared with placebo, and clinically meaningful benefits for the study’s two primary endpoints.
Simultaneously with Kosiborod’s report the results also appeared in a report posted online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
A ‘paradigm shift’ for medical weight loss in cardiology
The findings from this study with 529 randomized patients immediately propelled the weight loss formulation of semaglutide into the ranks of agents used to treat and prevent cardiovascular disease events. This evolution in the indications for semaglutide will be driven not only by the STEP-HFpEF results but also by findings from the SELECT trial, which tested the same semaglutide weight-loss dose in people with obesity, established cardiovascular disease, and had positive top-line results for prevention of major cardiovascular adverse events, according to a press release from Novo Nordisk on Aug. 8.
The STEP-HFpEF and SELECT results will trigger “a paradigm shift” for cardiologists, who will now need to consider prescribing a weight-loss medication to many of their patients, agents that until now were not part of the usual pharmacologic toolbox for cardiologists, said Dr. Kosiborod, a cardiologist and codirector of the Haverty Cardiometabolic Center of Excellence at Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, Mo. This shift will require education to bring the clinical cardiology community on board, he added in an interview.
Given that semaglutide administered at this dose already has a Food and Drug Administration–approved indication for weight loss in people with obesity or overweight plus at least one comorbidity, clinicians could immediately start using the treatment in people with obesity and HFpEF, said Dr. Kosiborod and other cardiologists.
Weekly semaglutide injections “could be considered a treatment option right now” for people with obesity and HFpEF, Dr. Kosiborod said during a press briefing.
Other experts agreed, especially because the STEP-HFpEF results confirmed that weight loss treatment with semaglutide was safe in this population.
‘A terrific win for patients’
The new findings are “a terrific win and game changer for patients with HFpEF,” commented Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, professor and cochief of cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved with the study.
“The magnitude of improvement in the patient-reported health status scores are large and impressive. These data support clinical use of this agent for individuals with HFpEF with a body mass index of 30 kg/m2, patients who already fall within existing indications,” Dr. Fonarow said in an interview.
“Given the improvements in clinical outcomes in the STEP-HFpEF and SELECT trials, cardiologists should be prescribing these medications to eligible patients without conditions,” he added. “The perception of [semaglutide] needs to shift and be viewed as a component of the comprehensive medical therapies provided to individuals with established cardiovascular disease or HFpEF who also have elevated body mass index to improve their clinical outcomes.”
Historically, cardiologists have had a concern that weight loss was potentially harmful in people with heart failure and that obesity was protective, a phenomenon known as the “obesity paradox,” but the STEP-HFpEF data help disprove that notion, commented Nancy K. Sweitzer, MD, PhD, a heart failure specialist and vice chair of clinical research in the department of medicine at Washington University in St. Louis, who also was not involved in the study.
No signal of an obesity paradox
“There’s been a concern in the heart failure community to use weight-loss strategies in people with heart failure because of this, but this evidence provides a lot of confidence that it’s safe to use this weight loss treatment. The results show that patients feel better and lose weight with no signal of harm,” Dr. Sweitzer said in an interview.
The “encouraging findings” for semaglutide in patients with HFpEF “potentially add a much needed extra option for these patients and provide another upstream treatment for patients with signs of this condition plus a high body mass index,” commented Yigal M. Pinto, MD, PhD, in an editorial that accompanied the published report.
“How these findings translate to hard end points remains to be established and will be important in determining the role of GLP-1 agonism,” wrote Dr. Pinto, a professor and heart failure specialist at Amsterdam University Medical Center.
But Dr. Kosiborod said that the improvement seen in the KCCQ score was itself an important benefit for patients. “Heart failure is defined clinically based on symptoms,” he noted, and results in prior studies documented that patients value improvements in symptoms and physical limitations even more than they value “hard endpoints” such as survival.
The new findings, which indicate that two different and expensive classes of medications are now standard of care for many people with HFpEF and obesity – the SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 receptor agonist semaglutide – also raise concerns over patient access and affordability, as many U.S. insurers have a history of requiring prior authorization, high copays, or coverage denials for these two medical classes.
But Dr. Sweitzer and Dr. Kosiborod both said that the insurance-coverage climate seems, in just the past couple of years or so, to have dramatically improved, although it’s still not ideal.
Prior authorization hoops have decreased
“We still have prior-authorization hoops to jump through, but I expect these will continue to decrease over time as evidence for clinical benefits [from weight loss] continues to accumulate,” said Dr. Sweitzer.
And “the SELECT data mean that cardiologists will need to become comfortable prescribing GLP-1 receptor agonists,” she added.
“It’s not okay for insurers to say we are not going to cover weight loss medications because it’s a cosmetic indication,” said Dr. Kosiborod. “Obesity appears to be very important in the pathogenesis and progression of heart failure, and if patients derive substantial benefit, they should have access to this treatment.”
The improvements in KCCQ score, as well as in several secondary and exploratory endpoints including a significant reduction in C-reactive protein (an indication of a potent anti-inflammatory effect), an average 20 m increase in 6-minute walk distance, a significant average drop in N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, and a drop in heart failure hospitalizations or urgent heart failure visits (although the trial was not powered to show differences in clinical events), “were the largest benefits in these outcomes we’ve seen,” compared with any other medical intervention in people with HFpEF, he noted.
“About 80% of U.S. patients with HFpEF have obesity or overweight,” Dr. Kosiborod noted. Using semaglutide on these patients “is an issue of access and insurance coverage. My hope is that these and other data will favorably change this.”
A related trial with a similar design, STEP-HFpEF DM, is still in progress and testing the same semaglutide treatment in adults with HFpEF, obesity, and type 2 diabetes, noted Dr. Kosiborod, who is also lead investigator for that study. He said those results will likely become available before the end of 2023.
The study was funded by Novo Nordisk, the company that markets semaglutide (Wegovy). Dr. Kosiborod has been a consultant and adviser to and has received honoraria from Novo Nordisk. He has also been a consultant to numerous other companies, received research grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Pfizer, honoraria from AstraZeneca, and is a stockholder in Artera Health and Saghmos Therapeutics. Dr. Fonarow has been a consultant to Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, CHF Solutions, Cytokinetics, Edwards, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, Novartis, and Regeneron. Dr. Sweitzer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT THE ESC CONGRESS 2023
How should muscle mass be measured in heart failure?
, research suggests.
In a single-center, retrospective study that included more than 800 patients, high MUAC (hazard ratio for combined events, 0.590) and high AMC (HR for combined events, 0.529) were associated with significantly better prognoses than low MUAC and low AMC.
The findings were “surprising,” Kentaro Kamiya, PT, PhD, and Shota Uchida, PT, PhD, of Kitasato University School of Allied Health Sciences in Kanagawa, Japan, said in an interview.
“These findings challenge the current recommendations found in sarcopenia guidelines,” they noted. The European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People and the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia recommend SMI, as measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), and CC as methods for screening skeletal muscle mass.
The study was published online in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology.
Arm measures prognostic
Sarcopenia, which is marked by a loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength, is associated with risks of adverse outcomes. Patients with heart failure have a high rate of sarcopenia, but assessing skeletal muscle mass in these patients is difficult because of the fluid retention they often have.
The investigators examined the association between skeletal muscle mass metrics, measured using bioelectrical impedance analysis, and anthropometric measures and prognosis in patients with heart failure.
SMI was calculated using the BIA by dividing appendicular skeletal muscle mass by height squared. MUAC and CC were measured to the nearest 1 mm using a plastic tape measure. AMC was calculated as follows: MUAC (cm) − (0.314 x triceps skinfold [TSF]). The TSF was measured to the nearest 2 mm with a skinfold caliper. The measuring spot for TSF was the same measuring spot for MUAC. MUAC, CC, and TSF were measured by trained physiotherapists or nurses.
The investigators identified 1,930 consecutive patients with heart failure who underwent cardiac rehabilitation during their hospitalization. They excluded from their analysis 1,013 patients who did not undergo a skeletal mass metrics evaluation and 48 who could not be followed up.
The analysis included 869 patients (median age, 73 years; 62% men). Patients were separated into three groups on the basis of the sex-specific tertiles of skeletal muscle mass. The study endpoint was all-cause death or readmission due to heart failure, and the median follow-up period was 1.24 years.
After the investigators adjusted the data for age, sex, New York Heart Association functional class III or IV, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), ischemic etiology, prior heart failure, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, log-transformed B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), the high MUAC and high AMC groups were associated with significantly better prognoses than their respective low groups. By contrast, high SMI and high CC were not associated with better prognoses.
Subgroup analyses showed no interactions between MUAC and age, sex, LVEF, BNP, eGFR, prior heart failure, beta-blocker use, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blocker use. However, diuretic agents significantly interacted with AMC (P = .03).
“These results support the use of MUAC and AMC to determine the risk stratification of sarcopenia and a poor prognosis in patients with heart failure and suggest that they may be useful in developing treatment strategies in patients with heart failure,” wrote the authors.
“When caring for patients with heart failure, it seems that the often overlooked and simple measure of arm circumference might carry significant prognostic value,” said Dr. Kamiya and Dr. Uchida. “So, as you cuff the arm for routine blood pressure measurement, it might be worthwhile to also pay attention to arm girth.”
Although the findings provide valuable insights, they should be approached with caution, Dr. Kamiya and Dr. Uchida added. “Before considering them practice-changing, further research is needed to validate these results in diverse patient cohorts.”
Prospective study needed
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Jonathan H. Whiteson, MD, vice chair of clinical operations and medical director of cardiac and pulmonary rehabilitation at NYU Langone Health’s Rusk Rehabilitation in New York, expressed concerns about the study methodology.
Methodologic weaknesses include the retrospective, observational nature of the study and the fact that incomplete data collection led to the exclusion of more than half of the potential participants, he said. In addition, “anthropometric measurements are prone to inter-rater error. It is not clear if the same or different researchers conducted these measurements.
“Furthermore, hospitalized patients may not be clinically stable when discharged,” said Dr. Whiteson. “It is recommended that biometrics for muscle mass and fluid retention be done when patients are at an optimized clinical state: that is, stabilized outpatients.”
For now, Dr. Whiteson concluded, the findings should be considered “interesting and suggestive of further study.” What’s needed is “a prospective study including all patients admitted with heart failure, but measurements done when the patient is stabilized as an outpatient.”
The study was partially supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI. Dr. Kamiya, Dr. Uchida, and Dr. Whiteson reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, research suggests.
In a single-center, retrospective study that included more than 800 patients, high MUAC (hazard ratio for combined events, 0.590) and high AMC (HR for combined events, 0.529) were associated with significantly better prognoses than low MUAC and low AMC.
The findings were “surprising,” Kentaro Kamiya, PT, PhD, and Shota Uchida, PT, PhD, of Kitasato University School of Allied Health Sciences in Kanagawa, Japan, said in an interview.
“These findings challenge the current recommendations found in sarcopenia guidelines,” they noted. The European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People and the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia recommend SMI, as measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), and CC as methods for screening skeletal muscle mass.
The study was published online in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology.
Arm measures prognostic
Sarcopenia, which is marked by a loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength, is associated with risks of adverse outcomes. Patients with heart failure have a high rate of sarcopenia, but assessing skeletal muscle mass in these patients is difficult because of the fluid retention they often have.
The investigators examined the association between skeletal muscle mass metrics, measured using bioelectrical impedance analysis, and anthropometric measures and prognosis in patients with heart failure.
SMI was calculated using the BIA by dividing appendicular skeletal muscle mass by height squared. MUAC and CC were measured to the nearest 1 mm using a plastic tape measure. AMC was calculated as follows: MUAC (cm) − (0.314 x triceps skinfold [TSF]). The TSF was measured to the nearest 2 mm with a skinfold caliper. The measuring spot for TSF was the same measuring spot for MUAC. MUAC, CC, and TSF were measured by trained physiotherapists or nurses.
The investigators identified 1,930 consecutive patients with heart failure who underwent cardiac rehabilitation during their hospitalization. They excluded from their analysis 1,013 patients who did not undergo a skeletal mass metrics evaluation and 48 who could not be followed up.
The analysis included 869 patients (median age, 73 years; 62% men). Patients were separated into three groups on the basis of the sex-specific tertiles of skeletal muscle mass. The study endpoint was all-cause death or readmission due to heart failure, and the median follow-up period was 1.24 years.
After the investigators adjusted the data for age, sex, New York Heart Association functional class III or IV, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), ischemic etiology, prior heart failure, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, log-transformed B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), the high MUAC and high AMC groups were associated with significantly better prognoses than their respective low groups. By contrast, high SMI and high CC were not associated with better prognoses.
Subgroup analyses showed no interactions between MUAC and age, sex, LVEF, BNP, eGFR, prior heart failure, beta-blocker use, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blocker use. However, diuretic agents significantly interacted with AMC (P = .03).
“These results support the use of MUAC and AMC to determine the risk stratification of sarcopenia and a poor prognosis in patients with heart failure and suggest that they may be useful in developing treatment strategies in patients with heart failure,” wrote the authors.
“When caring for patients with heart failure, it seems that the often overlooked and simple measure of arm circumference might carry significant prognostic value,” said Dr. Kamiya and Dr. Uchida. “So, as you cuff the arm for routine blood pressure measurement, it might be worthwhile to also pay attention to arm girth.”
Although the findings provide valuable insights, they should be approached with caution, Dr. Kamiya and Dr. Uchida added. “Before considering them practice-changing, further research is needed to validate these results in diverse patient cohorts.”
Prospective study needed
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Jonathan H. Whiteson, MD, vice chair of clinical operations and medical director of cardiac and pulmonary rehabilitation at NYU Langone Health’s Rusk Rehabilitation in New York, expressed concerns about the study methodology.
Methodologic weaknesses include the retrospective, observational nature of the study and the fact that incomplete data collection led to the exclusion of more than half of the potential participants, he said. In addition, “anthropometric measurements are prone to inter-rater error. It is not clear if the same or different researchers conducted these measurements.
“Furthermore, hospitalized patients may not be clinically stable when discharged,” said Dr. Whiteson. “It is recommended that biometrics for muscle mass and fluid retention be done when patients are at an optimized clinical state: that is, stabilized outpatients.”
For now, Dr. Whiteson concluded, the findings should be considered “interesting and suggestive of further study.” What’s needed is “a prospective study including all patients admitted with heart failure, but measurements done when the patient is stabilized as an outpatient.”
The study was partially supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI. Dr. Kamiya, Dr. Uchida, and Dr. Whiteson reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, research suggests.
In a single-center, retrospective study that included more than 800 patients, high MUAC (hazard ratio for combined events, 0.590) and high AMC (HR for combined events, 0.529) were associated with significantly better prognoses than low MUAC and low AMC.
The findings were “surprising,” Kentaro Kamiya, PT, PhD, and Shota Uchida, PT, PhD, of Kitasato University School of Allied Health Sciences in Kanagawa, Japan, said in an interview.
“These findings challenge the current recommendations found in sarcopenia guidelines,” they noted. The European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People and the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia recommend SMI, as measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), and CC as methods for screening skeletal muscle mass.
The study was published online in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology.
Arm measures prognostic
Sarcopenia, which is marked by a loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength, is associated with risks of adverse outcomes. Patients with heart failure have a high rate of sarcopenia, but assessing skeletal muscle mass in these patients is difficult because of the fluid retention they often have.
The investigators examined the association between skeletal muscle mass metrics, measured using bioelectrical impedance analysis, and anthropometric measures and prognosis in patients with heart failure.
SMI was calculated using the BIA by dividing appendicular skeletal muscle mass by height squared. MUAC and CC were measured to the nearest 1 mm using a plastic tape measure. AMC was calculated as follows: MUAC (cm) − (0.314 x triceps skinfold [TSF]). The TSF was measured to the nearest 2 mm with a skinfold caliper. The measuring spot for TSF was the same measuring spot for MUAC. MUAC, CC, and TSF were measured by trained physiotherapists or nurses.
The investigators identified 1,930 consecutive patients with heart failure who underwent cardiac rehabilitation during their hospitalization. They excluded from their analysis 1,013 patients who did not undergo a skeletal mass metrics evaluation and 48 who could not be followed up.
The analysis included 869 patients (median age, 73 years; 62% men). Patients were separated into three groups on the basis of the sex-specific tertiles of skeletal muscle mass. The study endpoint was all-cause death or readmission due to heart failure, and the median follow-up period was 1.24 years.
After the investigators adjusted the data for age, sex, New York Heart Association functional class III or IV, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), ischemic etiology, prior heart failure, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, log-transformed B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), the high MUAC and high AMC groups were associated with significantly better prognoses than their respective low groups. By contrast, high SMI and high CC were not associated with better prognoses.
Subgroup analyses showed no interactions between MUAC and age, sex, LVEF, BNP, eGFR, prior heart failure, beta-blocker use, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blocker use. However, diuretic agents significantly interacted with AMC (P = .03).
“These results support the use of MUAC and AMC to determine the risk stratification of sarcopenia and a poor prognosis in patients with heart failure and suggest that they may be useful in developing treatment strategies in patients with heart failure,” wrote the authors.
“When caring for patients with heart failure, it seems that the often overlooked and simple measure of arm circumference might carry significant prognostic value,” said Dr. Kamiya and Dr. Uchida. “So, as you cuff the arm for routine blood pressure measurement, it might be worthwhile to also pay attention to arm girth.”
Although the findings provide valuable insights, they should be approached with caution, Dr. Kamiya and Dr. Uchida added. “Before considering them practice-changing, further research is needed to validate these results in diverse patient cohorts.”
Prospective study needed
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Jonathan H. Whiteson, MD, vice chair of clinical operations and medical director of cardiac and pulmonary rehabilitation at NYU Langone Health’s Rusk Rehabilitation in New York, expressed concerns about the study methodology.
Methodologic weaknesses include the retrospective, observational nature of the study and the fact that incomplete data collection led to the exclusion of more than half of the potential participants, he said. In addition, “anthropometric measurements are prone to inter-rater error. It is not clear if the same or different researchers conducted these measurements.
“Furthermore, hospitalized patients may not be clinically stable when discharged,” said Dr. Whiteson. “It is recommended that biometrics for muscle mass and fluid retention be done when patients are at an optimized clinical state: that is, stabilized outpatients.”
For now, Dr. Whiteson concluded, the findings should be considered “interesting and suggestive of further study.” What’s needed is “a prospective study including all patients admitted with heart failure, but measurements done when the patient is stabilized as an outpatient.”
The study was partially supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI. Dr. Kamiya, Dr. Uchida, and Dr. Whiteson reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE CANADIAN JOURNAL OF CARDIOLOGY
Another FDA class I recall of Cardiosave Hybrid/Rescue IABPs
due to electrical failures in the power management board or solenoid board (power source path).
“Using an affected pump may cause serious adverse health events, including unstable blood pressure, injury (e.g., inadequate blood supply or a vital organ injury), and death,” the Food and Drug Administration said in the recall notice.
The FDA has identified this as a class I recall, the most serious type of recall due to the risk for serious injury or death. To date, Datascope/Maquet/Getinge received 26 complaints, but no reports of injuries or death.
The devices are indicated for acute coronary syndrome, cardiac and noncardiac surgery, and complications of heart failure in adults.
The recall includes a total of 4,586 Cardiosave Hybrid or Rescue IABP units distributed from March 2, 2012, to May 19, 2023. Product model numbers for the recalled Cardiosave Hybrid and Cardiosave Rescue are available online.
On June 5, Datascope/Maquet/Getinge sent an “important medical device advisory” to all affected customers. The letter advises customers to be sure there is an alternative IABP available to continue therapy and provide alternative hemodynamic support if there is no other means to continue counterpulsation therapy.
Customers with questions about this recall should contact their company representative or call technical support at 1-888-943-8872, Monday through Friday, between 8:00 a.m. and 6:00 p.m. ET.
Last March, Datascope/Getinge recalled 2,300 Cardiosave Hybrid or Rescue IABPs because the coiled cable connecting the display and base on some units may fail, causing an unexpected shutdown without warnings or alarms to alert the user.
The Cardiosave IABPs have also been previously flagged by the FDA for subpar battery performance and fluid leaks.
Any adverse events or suspected adverse events related to the recalled Cardiosave Hybrid/Rescue IABPs should be reported to the FDA through MedWatch, its adverse event reporting program.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
due to electrical failures in the power management board or solenoid board (power source path).
“Using an affected pump may cause serious adverse health events, including unstable blood pressure, injury (e.g., inadequate blood supply or a vital organ injury), and death,” the Food and Drug Administration said in the recall notice.
The FDA has identified this as a class I recall, the most serious type of recall due to the risk for serious injury or death. To date, Datascope/Maquet/Getinge received 26 complaints, but no reports of injuries or death.
The devices are indicated for acute coronary syndrome, cardiac and noncardiac surgery, and complications of heart failure in adults.
The recall includes a total of 4,586 Cardiosave Hybrid or Rescue IABP units distributed from March 2, 2012, to May 19, 2023. Product model numbers for the recalled Cardiosave Hybrid and Cardiosave Rescue are available online.
On June 5, Datascope/Maquet/Getinge sent an “important medical device advisory” to all affected customers. The letter advises customers to be sure there is an alternative IABP available to continue therapy and provide alternative hemodynamic support if there is no other means to continue counterpulsation therapy.
Customers with questions about this recall should contact their company representative or call technical support at 1-888-943-8872, Monday through Friday, between 8:00 a.m. and 6:00 p.m. ET.
Last March, Datascope/Getinge recalled 2,300 Cardiosave Hybrid or Rescue IABPs because the coiled cable connecting the display and base on some units may fail, causing an unexpected shutdown without warnings or alarms to alert the user.
The Cardiosave IABPs have also been previously flagged by the FDA for subpar battery performance and fluid leaks.
Any adverse events or suspected adverse events related to the recalled Cardiosave Hybrid/Rescue IABPs should be reported to the FDA through MedWatch, its adverse event reporting program.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
due to electrical failures in the power management board or solenoid board (power source path).
“Using an affected pump may cause serious adverse health events, including unstable blood pressure, injury (e.g., inadequate blood supply or a vital organ injury), and death,” the Food and Drug Administration said in the recall notice.
The FDA has identified this as a class I recall, the most serious type of recall due to the risk for serious injury or death. To date, Datascope/Maquet/Getinge received 26 complaints, but no reports of injuries or death.
The devices are indicated for acute coronary syndrome, cardiac and noncardiac surgery, and complications of heart failure in adults.
The recall includes a total of 4,586 Cardiosave Hybrid or Rescue IABP units distributed from March 2, 2012, to May 19, 2023. Product model numbers for the recalled Cardiosave Hybrid and Cardiosave Rescue are available online.
On June 5, Datascope/Maquet/Getinge sent an “important medical device advisory” to all affected customers. The letter advises customers to be sure there is an alternative IABP available to continue therapy and provide alternative hemodynamic support if there is no other means to continue counterpulsation therapy.
Customers with questions about this recall should contact their company representative or call technical support at 1-888-943-8872, Monday through Friday, between 8:00 a.m. and 6:00 p.m. ET.
Last March, Datascope/Getinge recalled 2,300 Cardiosave Hybrid or Rescue IABPs because the coiled cable connecting the display and base on some units may fail, causing an unexpected shutdown without warnings or alarms to alert the user.
The Cardiosave IABPs have also been previously flagged by the FDA for subpar battery performance and fluid leaks.
Any adverse events or suspected adverse events related to the recalled Cardiosave Hybrid/Rescue IABPs should be reported to the FDA through MedWatch, its adverse event reporting program.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Higher step counts tied to fewer symptoms in HF
Daily step counts between 1,000 and 5,000 were significantly associated with symptoms and physical limitations, as reflected in Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) total symptom (TS) and physical limitation (PL) scores.
Participants whose step counts increased by 2,000 steps per day demonstrated a 5.2-point increase in their KCCQ-TS scores and a 5.33-point increase in their KCCQ-PL scores, with higher scores reflecting improvement.
However, declines in step counts were not associated with significant declines in KCCQ-PL scores.
The findings are not yet ready to be implemented into practice, first author Jessica R. Golbus, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. However, she said, they “suggest that clinicians should interpret improvements in step counts as indicative of improving health status, though they should not necessarily be as concerned with reductions in step count.
“I would certainly, however, still encourage clinicians to discuss decrementing physical activity levels with their patients, though an intervention may not necessarily be warranted,” she added.
The study was published online in JACC: Heart Failure.
Nonlinear relationship
The investigators analyzed data from the Canagliflozin: Impact on Health Status, Quality of Life and Functional Status in Heart Failure (CHIEF-HF) trial, a randomized, controlled trial that enrolled participants with heart failure who had a smartphone.
Participants were given a Fitbit Versa 2 and completed serial KCCQs via the smartphone app.
The researchers assessed the relationship between daily step count and KCCQ-TS and KCCQ-PL scores at baseline, as well as changes in the scores between 2 and 12 weeks.
The study included 425 patients. The mean age was 63.5 years, 44.5% were women, and 83.3% were White; 40.9% had reduced ejection fraction, 59.1% had preserved ejection fraction, and 27.5% had type 2 diabetes.
At 2 weeks, the mean KCCQ-TS score was 62.7, and the mean KCCQ-PL score was 55.7.
KCCQ-TS scores increased by 2.5 points on average, and KCCQ-PL scores by 4 points through 12 weeks.
When categorized by 25-point ranges, the step count increased with increasing scores for both KCCQ-TS and KCCQ-PL. Those with KCCQ-TS scores of 0-24 averaged 2,437.6 steps daily, and those with scores of 75-100 averaged 4,870.9 steps daily.
Similarly, participants with KCCQ-PL scores of 0-24 averaged 2301.5 steps daily, and those with scores of 75-100 averaged 5,351.9. The relationship remained significant after adjustment.
There were nonlinear relationships between activity and KCCQ scores: Daily step counts below 5,000 steps were associated with KCCQ scores, but there was little association with counts above 5,000 steps.
Compared with participants who walked 2,000 steps per day, those who walked 1,000 had KCCQ-TS scores that were 3.11 points lower; participants who walked 3,000 had KCCQ-TS scores that were 2.89 points higher.
Similarly, participants who walked 1,000 steps per day had KCCQ-PL scores that were 5.36 points lower than those who walked 2,000 steps, and those who walked 3,000 steps had KCCQ-PL scores that were 4.97 points higher.
After adjustment, change in daily step counts was significantly associated with a change in KCCQ-PL scores from baseline through 12 weeks; for example, participants whose step counts increased by 2,000 steps per day experienced a 5.33 increase in their KCCQ-PL scores relative to participants whose step counts did not change.
‘New kid on the block’
Frederick Ho, PhD, a lecturer in public health at the University of Glasgow (Scotland), who is a volunteer spokesperson for the American Heart Association, called the study “promising.”
“The study follow-up is relatively short, so it is not known whether the association is valid longer term,” he said in an interview. “It is also possible that patients with more severe symptoms became physically less active, and at the same time had worse outcomes.
“A study with longer follow-up among patients from a broader background would provide confidence on the generalizability of the findings,” said Dr. Ho, who led a recent study that showed accelerometer-measured physical activity was associated with a lower risk of heart failure. “It’d also be interesting to validate the findings using different types of wearable devices.”
Previous studies have shown that wrist-worn wearables might overestimate light-intensity activities, compared with hip-worn devices, he noted. “I’d imagine that the findings would be slightly different due to different types of devices, but the overall premise should remain.”
In a related editorial, Mitchell Psotka, MD, PhD, writes that Dr. Golbus and colleagues “have thankfully moved our understanding of actigraphy forward, although it is still the new kid on the block and will require substantial further testing and validation before widespread reliable clinical and research use.”
Terminology and reporting features need to be standardized, and preferred methods of implementation need to be established, including how to wear the devices, he suggests.
Further research is needed to validate that “accelerometers and their digitally processed movement ‘counts’ actually measure activity and that this measured activity has clinical relevance.”
The study did not receive commercial funding. Dr. Golbus, Dr. Ho, and Dr. Psotka report no relevant relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Daily step counts between 1,000 and 5,000 were significantly associated with symptoms and physical limitations, as reflected in Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) total symptom (TS) and physical limitation (PL) scores.
Participants whose step counts increased by 2,000 steps per day demonstrated a 5.2-point increase in their KCCQ-TS scores and a 5.33-point increase in their KCCQ-PL scores, with higher scores reflecting improvement.
However, declines in step counts were not associated with significant declines in KCCQ-PL scores.
The findings are not yet ready to be implemented into practice, first author Jessica R. Golbus, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. However, she said, they “suggest that clinicians should interpret improvements in step counts as indicative of improving health status, though they should not necessarily be as concerned with reductions in step count.
“I would certainly, however, still encourage clinicians to discuss decrementing physical activity levels with their patients, though an intervention may not necessarily be warranted,” she added.
The study was published online in JACC: Heart Failure.
Nonlinear relationship
The investigators analyzed data from the Canagliflozin: Impact on Health Status, Quality of Life and Functional Status in Heart Failure (CHIEF-HF) trial, a randomized, controlled trial that enrolled participants with heart failure who had a smartphone.
Participants were given a Fitbit Versa 2 and completed serial KCCQs via the smartphone app.
The researchers assessed the relationship between daily step count and KCCQ-TS and KCCQ-PL scores at baseline, as well as changes in the scores between 2 and 12 weeks.
The study included 425 patients. The mean age was 63.5 years, 44.5% were women, and 83.3% were White; 40.9% had reduced ejection fraction, 59.1% had preserved ejection fraction, and 27.5% had type 2 diabetes.
At 2 weeks, the mean KCCQ-TS score was 62.7, and the mean KCCQ-PL score was 55.7.
KCCQ-TS scores increased by 2.5 points on average, and KCCQ-PL scores by 4 points through 12 weeks.
When categorized by 25-point ranges, the step count increased with increasing scores for both KCCQ-TS and KCCQ-PL. Those with KCCQ-TS scores of 0-24 averaged 2,437.6 steps daily, and those with scores of 75-100 averaged 4,870.9 steps daily.
Similarly, participants with KCCQ-PL scores of 0-24 averaged 2301.5 steps daily, and those with scores of 75-100 averaged 5,351.9. The relationship remained significant after adjustment.
There were nonlinear relationships between activity and KCCQ scores: Daily step counts below 5,000 steps were associated with KCCQ scores, but there was little association with counts above 5,000 steps.
Compared with participants who walked 2,000 steps per day, those who walked 1,000 had KCCQ-TS scores that were 3.11 points lower; participants who walked 3,000 had KCCQ-TS scores that were 2.89 points higher.
Similarly, participants who walked 1,000 steps per day had KCCQ-PL scores that were 5.36 points lower than those who walked 2,000 steps, and those who walked 3,000 steps had KCCQ-PL scores that were 4.97 points higher.
After adjustment, change in daily step counts was significantly associated with a change in KCCQ-PL scores from baseline through 12 weeks; for example, participants whose step counts increased by 2,000 steps per day experienced a 5.33 increase in their KCCQ-PL scores relative to participants whose step counts did not change.
‘New kid on the block’
Frederick Ho, PhD, a lecturer in public health at the University of Glasgow (Scotland), who is a volunteer spokesperson for the American Heart Association, called the study “promising.”
“The study follow-up is relatively short, so it is not known whether the association is valid longer term,” he said in an interview. “It is also possible that patients with more severe symptoms became physically less active, and at the same time had worse outcomes.
“A study with longer follow-up among patients from a broader background would provide confidence on the generalizability of the findings,” said Dr. Ho, who led a recent study that showed accelerometer-measured physical activity was associated with a lower risk of heart failure. “It’d also be interesting to validate the findings using different types of wearable devices.”
Previous studies have shown that wrist-worn wearables might overestimate light-intensity activities, compared with hip-worn devices, he noted. “I’d imagine that the findings would be slightly different due to different types of devices, but the overall premise should remain.”
In a related editorial, Mitchell Psotka, MD, PhD, writes that Dr. Golbus and colleagues “have thankfully moved our understanding of actigraphy forward, although it is still the new kid on the block and will require substantial further testing and validation before widespread reliable clinical and research use.”
Terminology and reporting features need to be standardized, and preferred methods of implementation need to be established, including how to wear the devices, he suggests.
Further research is needed to validate that “accelerometers and their digitally processed movement ‘counts’ actually measure activity and that this measured activity has clinical relevance.”
The study did not receive commercial funding. Dr. Golbus, Dr. Ho, and Dr. Psotka report no relevant relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Daily step counts between 1,000 and 5,000 were significantly associated with symptoms and physical limitations, as reflected in Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) total symptom (TS) and physical limitation (PL) scores.
Participants whose step counts increased by 2,000 steps per day demonstrated a 5.2-point increase in their KCCQ-TS scores and a 5.33-point increase in their KCCQ-PL scores, with higher scores reflecting improvement.
However, declines in step counts were not associated with significant declines in KCCQ-PL scores.
The findings are not yet ready to be implemented into practice, first author Jessica R. Golbus, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. However, she said, they “suggest that clinicians should interpret improvements in step counts as indicative of improving health status, though they should not necessarily be as concerned with reductions in step count.
“I would certainly, however, still encourage clinicians to discuss decrementing physical activity levels with their patients, though an intervention may not necessarily be warranted,” she added.
The study was published online in JACC: Heart Failure.
Nonlinear relationship
The investigators analyzed data from the Canagliflozin: Impact on Health Status, Quality of Life and Functional Status in Heart Failure (CHIEF-HF) trial, a randomized, controlled trial that enrolled participants with heart failure who had a smartphone.
Participants were given a Fitbit Versa 2 and completed serial KCCQs via the smartphone app.
The researchers assessed the relationship between daily step count and KCCQ-TS and KCCQ-PL scores at baseline, as well as changes in the scores between 2 and 12 weeks.
The study included 425 patients. The mean age was 63.5 years, 44.5% were women, and 83.3% were White; 40.9% had reduced ejection fraction, 59.1% had preserved ejection fraction, and 27.5% had type 2 diabetes.
At 2 weeks, the mean KCCQ-TS score was 62.7, and the mean KCCQ-PL score was 55.7.
KCCQ-TS scores increased by 2.5 points on average, and KCCQ-PL scores by 4 points through 12 weeks.
When categorized by 25-point ranges, the step count increased with increasing scores for both KCCQ-TS and KCCQ-PL. Those with KCCQ-TS scores of 0-24 averaged 2,437.6 steps daily, and those with scores of 75-100 averaged 4,870.9 steps daily.
Similarly, participants with KCCQ-PL scores of 0-24 averaged 2301.5 steps daily, and those with scores of 75-100 averaged 5,351.9. The relationship remained significant after adjustment.
There were nonlinear relationships between activity and KCCQ scores: Daily step counts below 5,000 steps were associated with KCCQ scores, but there was little association with counts above 5,000 steps.
Compared with participants who walked 2,000 steps per day, those who walked 1,000 had KCCQ-TS scores that were 3.11 points lower; participants who walked 3,000 had KCCQ-TS scores that were 2.89 points higher.
Similarly, participants who walked 1,000 steps per day had KCCQ-PL scores that were 5.36 points lower than those who walked 2,000 steps, and those who walked 3,000 steps had KCCQ-PL scores that were 4.97 points higher.
After adjustment, change in daily step counts was significantly associated with a change in KCCQ-PL scores from baseline through 12 weeks; for example, participants whose step counts increased by 2,000 steps per day experienced a 5.33 increase in their KCCQ-PL scores relative to participants whose step counts did not change.
‘New kid on the block’
Frederick Ho, PhD, a lecturer in public health at the University of Glasgow (Scotland), who is a volunteer spokesperson for the American Heart Association, called the study “promising.”
“The study follow-up is relatively short, so it is not known whether the association is valid longer term,” he said in an interview. “It is also possible that patients with more severe symptoms became physically less active, and at the same time had worse outcomes.
“A study with longer follow-up among patients from a broader background would provide confidence on the generalizability of the findings,” said Dr. Ho, who led a recent study that showed accelerometer-measured physical activity was associated with a lower risk of heart failure. “It’d also be interesting to validate the findings using different types of wearable devices.”
Previous studies have shown that wrist-worn wearables might overestimate light-intensity activities, compared with hip-worn devices, he noted. “I’d imagine that the findings would be slightly different due to different types of devices, but the overall premise should remain.”
In a related editorial, Mitchell Psotka, MD, PhD, writes that Dr. Golbus and colleagues “have thankfully moved our understanding of actigraphy forward, although it is still the new kid on the block and will require substantial further testing and validation before widespread reliable clinical and research use.”
Terminology and reporting features need to be standardized, and preferred methods of implementation need to be established, including how to wear the devices, he suggests.
Further research is needed to validate that “accelerometers and their digitally processed movement ‘counts’ actually measure activity and that this measured activity has clinical relevance.”
The study did not receive commercial funding. Dr. Golbus, Dr. Ho, and Dr. Psotka report no relevant relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JACC: HEART FAILURE
Early or delayed AFib ablation after heart failure hospitalization?
TOPLINE:
Among patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) hospitalized for worsening heart failure (HF), catheter (cath) ablation within 90 days of admission, compared with other times, is associated with reduced risk for all-cause mortality and HF-related mortality.
METHODOLOGY:
Cath ablation has become technically safer for patients with both AFib and HF, but the best timing for the ablation procedure after HF hospitalization has been unclear.
The study included 2,786 patients with HF who underwent cath ablation for AFib at 128 centers in the nationwide Japanese Registry of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure, were hospitalized with worsening HF, and survived at least 90 days after discharge.
The population included 103 individuals who underwent cath ablation within 90 days after admission; the remaining 2,683 participants served as the control group.
The researchers also looked at all-cause mortality 90 days after admission for HF in analysis of 83 early-ablation cases vs. 83 propensity-matched controls.
TAKEAWAY:
The early–cath ablation group was younger, predominantly male, had less history of prior HF hospitalizations, and greater incidence of paroxysmal AF, compared with the control group.
All-cause mortality was significantly lower in the early–cath ablation group than in the control group (hazard ratio, 0.38; 95% confidence interval, 0.24-0.60; P < .001) over a median of 4.1 years.
Risk reductions were similarly significant for secondary endpoints, including cardiovascular (CV) mortality and HF mortality.
In the matched cohort analysis (83 in both groups) all-cause mortality was significantly reduced for those in the early–cath ablation group, compared with the matched controls (HR, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.25-0.88; P = .014), with similarly significant risk reductions for CV mortality and HF mortality.
IN PRACTICE:
the report states. Early catheter ablation, as early as during the hospitalization for HF, “might be a way to stabilize HF and solve the problems associated with long hospitalization periods and polypharmacy.”
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Kazuo Sakamoto, MD, PhD, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, and colleagues. It was published online July 19, 2023 in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
LIMITATIONS:
The early-ablation cohort was much smaller than the control group, and the analysis could not adjust for any variation in institutional characteristics, such as location and available equipment. Other unmeasured potential confounders include duration of AFib and patient lifestyle characteristics and success or failure of ablation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Johnson & Johnson, the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, and Ministry of Health and Labor. Dr. Sakamoto reports no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Among patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) hospitalized for worsening heart failure (HF), catheter (cath) ablation within 90 days of admission, compared with other times, is associated with reduced risk for all-cause mortality and HF-related mortality.
METHODOLOGY:
Cath ablation has become technically safer for patients with both AFib and HF, but the best timing for the ablation procedure after HF hospitalization has been unclear.
The study included 2,786 patients with HF who underwent cath ablation for AFib at 128 centers in the nationwide Japanese Registry of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure, were hospitalized with worsening HF, and survived at least 90 days after discharge.
The population included 103 individuals who underwent cath ablation within 90 days after admission; the remaining 2,683 participants served as the control group.
The researchers also looked at all-cause mortality 90 days after admission for HF in analysis of 83 early-ablation cases vs. 83 propensity-matched controls.
TAKEAWAY:
The early–cath ablation group was younger, predominantly male, had less history of prior HF hospitalizations, and greater incidence of paroxysmal AF, compared with the control group.
All-cause mortality was significantly lower in the early–cath ablation group than in the control group (hazard ratio, 0.38; 95% confidence interval, 0.24-0.60; P < .001) over a median of 4.1 years.
Risk reductions were similarly significant for secondary endpoints, including cardiovascular (CV) mortality and HF mortality.
In the matched cohort analysis (83 in both groups) all-cause mortality was significantly reduced for those in the early–cath ablation group, compared with the matched controls (HR, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.25-0.88; P = .014), with similarly significant risk reductions for CV mortality and HF mortality.
IN PRACTICE:
the report states. Early catheter ablation, as early as during the hospitalization for HF, “might be a way to stabilize HF and solve the problems associated with long hospitalization periods and polypharmacy.”
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Kazuo Sakamoto, MD, PhD, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, and colleagues. It was published online July 19, 2023 in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
LIMITATIONS:
The early-ablation cohort was much smaller than the control group, and the analysis could not adjust for any variation in institutional characteristics, such as location and available equipment. Other unmeasured potential confounders include duration of AFib and patient lifestyle characteristics and success or failure of ablation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Johnson & Johnson, the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, and Ministry of Health and Labor. Dr. Sakamoto reports no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Among patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) hospitalized for worsening heart failure (HF), catheter (cath) ablation within 90 days of admission, compared with other times, is associated with reduced risk for all-cause mortality and HF-related mortality.
METHODOLOGY:
Cath ablation has become technically safer for patients with both AFib and HF, but the best timing for the ablation procedure after HF hospitalization has been unclear.
The study included 2,786 patients with HF who underwent cath ablation for AFib at 128 centers in the nationwide Japanese Registry of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure, were hospitalized with worsening HF, and survived at least 90 days after discharge.
The population included 103 individuals who underwent cath ablation within 90 days after admission; the remaining 2,683 participants served as the control group.
The researchers also looked at all-cause mortality 90 days after admission for HF in analysis of 83 early-ablation cases vs. 83 propensity-matched controls.
TAKEAWAY:
The early–cath ablation group was younger, predominantly male, had less history of prior HF hospitalizations, and greater incidence of paroxysmal AF, compared with the control group.
All-cause mortality was significantly lower in the early–cath ablation group than in the control group (hazard ratio, 0.38; 95% confidence interval, 0.24-0.60; P < .001) over a median of 4.1 years.
Risk reductions were similarly significant for secondary endpoints, including cardiovascular (CV) mortality and HF mortality.
In the matched cohort analysis (83 in both groups) all-cause mortality was significantly reduced for those in the early–cath ablation group, compared with the matched controls (HR, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.25-0.88; P = .014), with similarly significant risk reductions for CV mortality and HF mortality.
IN PRACTICE:
the report states. Early catheter ablation, as early as during the hospitalization for HF, “might be a way to stabilize HF and solve the problems associated with long hospitalization periods and polypharmacy.”
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Kazuo Sakamoto, MD, PhD, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, and colleagues. It was published online July 19, 2023 in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
LIMITATIONS:
The early-ablation cohort was much smaller than the control group, and the analysis could not adjust for any variation in institutional characteristics, such as location and available equipment. Other unmeasured potential confounders include duration of AFib and patient lifestyle characteristics and success or failure of ablation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by Johnson & Johnson, the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, and Ministry of Health and Labor. Dr. Sakamoto reports no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JACC: CLINICAL ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
Global burden of brain disorders surpasses cardiovascular disease and cancer
– at huge cost to health care systems and society, an analysis of data from the most recent Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study shows.
“The burden of brain conditions will increase as populations continue to grow and age,” said study presenter Shayla Smith, MPH, an epidemiologist at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, the University of Washington, Seattle, in a press release.
“By 2050, more than 50 million people will be aged 65-79,” she explained, adding that the COVID-19 pandemic “has also influenced the prevalence of mental disorders globally, as people were forced to isolate and social networks broke down.”
Other factors related to brain disorders, she noted, include education level, obesity, and smoking.
“There’s still research to be done on what is the most effective way to maintain brain health, but some literature suggests a healthy brain can be achieved through a healthy lifestyle of managing conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes, limiting alcohol consumption and smoking, prioritizing sleep, eating healthy, and staying physically and mentally active,” said Ms. Smith.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology.
An ‘ambitious exercise’
Coinvestigator Xaviera Steele, also from the IHME, told press conference attendees that the institute was established at the University of Washington in 2007 with the aim of “standardizing the measurement of health outcomes around the world and for all health conditions.”
A central part of that is the GBD study, “which is a very ambitious exercise in descriptive epidemiology in an effort to systematically quantify health loss” due to disease, injury, and risk factors over time, stratified by country, region, age, and sex. In addition, researchers are mapping and projecting trends over the next century and are estimating disease expenditure by country, by type of expense, and by condition “to derive a health care access and quality score for each health system in the world,” Ms. Steele said.
They are also estimating exposure to risk factors, how those risk factors contribute to health burden, and associated health outcomes by race and ethnicity to reflect the “disparities that we know are very prevalent in countries such as the United States.” From that work, Ms. Steele said that brain health and related conditions “do emerge as one of the more pressing challenges of the 21st century.”
Increase in dementia, mental health conditions
The data, which were gathered from 200,000 sources by the IHME, indicate that the number of individuals aged 65 years or older will increase by 350% by 2100. Ms. Steele underlined that “policy action will be needed to help families, who will struggle to provide high-quality care for their loved ones with dementia at a reasonable cost.”
The IHME calculates that in Europe health care spending on Alzheimer’s disease will increase by 226% between 2015 and 2040.
Turning to other conditions, Ms. Steele showed that since 1990, the number of individuals living with anxiety in the European region has increased by 14%, while the number living with depressive disorders has gone up by 13%.
Worldwide, the figures are even starker. Depression is estimated to affect 300 million people across the globe, which represents a 71% increase since 1990. The number of strokes increased by 95% over the same period.
Nevertheless, the “impact of brain conditions such as stroke has decreased since the 1990s due to improved treatments available,” Ms. Smith noted in the press release.
To estimate the toll caused by brain conditions, including neurologic disorders, mental disorders, cerebrovascular disease, brain cancer, brain injuries, and select infectious conditions, the researchers calculated disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
This, Ms. Smith explained in her presentation, “captures the morbidity and mortality associated with brain conditions” and is adjusted for patient location, age, and sex.
The investigators found that, globally, brain conditions accounted for more than 15% of all health loss in 2021, at 406 DALYs – more than the 206 million DALYs that were associated with cancer, and the 402 million that were linked to cardiovascular disease.
This health loss is associated with a $1.22 trillion loss in income for people living with health disorders worldwide and accounts for $1.14 trillion in direct health care costs.
The burden of mental disorders, neurologic conditions, and stroke is expected to increase dramatically between now and 2050, said Ms. Smith, who noted that health loss linked to brain conditions is higher in younger patients. This will create “new challenges for health systems, employers, patients, and families,” she said in the press release.
“Our goal is to see an improved prevention and treatment landscape for other brain conditions and reverse the growing health loss that we are currently forecasting.”
Worrying increase in stroke
Jurgita Valaikiene, MD, PhD, center of neurology, clinic of neurology and neurosurgery, Vilnius (Lithuania) University Faculty of Medicine, who chaired the session, was taken aback by the findings, particularly by the worldwide increase in stroke cases.
“I work in stroke,” she said, and “we spend a lot of time on the diagnosis of stroke” and its prevention. “We try to be faster, to catch asymptomatic stenosis in the neck or head, and to apply the best medical treatment to avoid a stroke. But despite that, the numbers are increasing. I understand the population is getting older ... but still it’s a huge number.”
Dr. Valaikiene pointed out that stroke is not necessarily a condition of aging, insofar as increasing age “is not related directly to stenosis in the neck. “For example, we can have healthier vessels in older age and unhealthy vessels, with high-grade stenosis, in someone aged 30 or 40 years.”
“There are a lot of risk factors, such as smoking, physical activity, and so on. It depends on the individual,” she added.
The study was funded by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
– at huge cost to health care systems and society, an analysis of data from the most recent Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study shows.
“The burden of brain conditions will increase as populations continue to grow and age,” said study presenter Shayla Smith, MPH, an epidemiologist at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, the University of Washington, Seattle, in a press release.
“By 2050, more than 50 million people will be aged 65-79,” she explained, adding that the COVID-19 pandemic “has also influenced the prevalence of mental disorders globally, as people were forced to isolate and social networks broke down.”
Other factors related to brain disorders, she noted, include education level, obesity, and smoking.
“There’s still research to be done on what is the most effective way to maintain brain health, but some literature suggests a healthy brain can be achieved through a healthy lifestyle of managing conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes, limiting alcohol consumption and smoking, prioritizing sleep, eating healthy, and staying physically and mentally active,” said Ms. Smith.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology.
An ‘ambitious exercise’
Coinvestigator Xaviera Steele, also from the IHME, told press conference attendees that the institute was established at the University of Washington in 2007 with the aim of “standardizing the measurement of health outcomes around the world and for all health conditions.”
A central part of that is the GBD study, “which is a very ambitious exercise in descriptive epidemiology in an effort to systematically quantify health loss” due to disease, injury, and risk factors over time, stratified by country, region, age, and sex. In addition, researchers are mapping and projecting trends over the next century and are estimating disease expenditure by country, by type of expense, and by condition “to derive a health care access and quality score for each health system in the world,” Ms. Steele said.
They are also estimating exposure to risk factors, how those risk factors contribute to health burden, and associated health outcomes by race and ethnicity to reflect the “disparities that we know are very prevalent in countries such as the United States.” From that work, Ms. Steele said that brain health and related conditions “do emerge as one of the more pressing challenges of the 21st century.”
Increase in dementia, mental health conditions
The data, which were gathered from 200,000 sources by the IHME, indicate that the number of individuals aged 65 years or older will increase by 350% by 2100. Ms. Steele underlined that “policy action will be needed to help families, who will struggle to provide high-quality care for their loved ones with dementia at a reasonable cost.”
The IHME calculates that in Europe health care spending on Alzheimer’s disease will increase by 226% between 2015 and 2040.
Turning to other conditions, Ms. Steele showed that since 1990, the number of individuals living with anxiety in the European region has increased by 14%, while the number living with depressive disorders has gone up by 13%.
Worldwide, the figures are even starker. Depression is estimated to affect 300 million people across the globe, which represents a 71% increase since 1990. The number of strokes increased by 95% over the same period.
Nevertheless, the “impact of brain conditions such as stroke has decreased since the 1990s due to improved treatments available,” Ms. Smith noted in the press release.
To estimate the toll caused by brain conditions, including neurologic disorders, mental disorders, cerebrovascular disease, brain cancer, brain injuries, and select infectious conditions, the researchers calculated disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
This, Ms. Smith explained in her presentation, “captures the morbidity and mortality associated with brain conditions” and is adjusted for patient location, age, and sex.
The investigators found that, globally, brain conditions accounted for more than 15% of all health loss in 2021, at 406 DALYs – more than the 206 million DALYs that were associated with cancer, and the 402 million that were linked to cardiovascular disease.
This health loss is associated with a $1.22 trillion loss in income for people living with health disorders worldwide and accounts for $1.14 trillion in direct health care costs.
The burden of mental disorders, neurologic conditions, and stroke is expected to increase dramatically between now and 2050, said Ms. Smith, who noted that health loss linked to brain conditions is higher in younger patients. This will create “new challenges for health systems, employers, patients, and families,” she said in the press release.
“Our goal is to see an improved prevention and treatment landscape for other brain conditions and reverse the growing health loss that we are currently forecasting.”
Worrying increase in stroke
Jurgita Valaikiene, MD, PhD, center of neurology, clinic of neurology and neurosurgery, Vilnius (Lithuania) University Faculty of Medicine, who chaired the session, was taken aback by the findings, particularly by the worldwide increase in stroke cases.
“I work in stroke,” she said, and “we spend a lot of time on the diagnosis of stroke” and its prevention. “We try to be faster, to catch asymptomatic stenosis in the neck or head, and to apply the best medical treatment to avoid a stroke. But despite that, the numbers are increasing. I understand the population is getting older ... but still it’s a huge number.”
Dr. Valaikiene pointed out that stroke is not necessarily a condition of aging, insofar as increasing age “is not related directly to stenosis in the neck. “For example, we can have healthier vessels in older age and unhealthy vessels, with high-grade stenosis, in someone aged 30 or 40 years.”
“There are a lot of risk factors, such as smoking, physical activity, and so on. It depends on the individual,” she added.
The study was funded by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
– at huge cost to health care systems and society, an analysis of data from the most recent Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study shows.
“The burden of brain conditions will increase as populations continue to grow and age,” said study presenter Shayla Smith, MPH, an epidemiologist at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, the University of Washington, Seattle, in a press release.
“By 2050, more than 50 million people will be aged 65-79,” she explained, adding that the COVID-19 pandemic “has also influenced the prevalence of mental disorders globally, as people were forced to isolate and social networks broke down.”
Other factors related to brain disorders, she noted, include education level, obesity, and smoking.
“There’s still research to be done on what is the most effective way to maintain brain health, but some literature suggests a healthy brain can be achieved through a healthy lifestyle of managing conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes, limiting alcohol consumption and smoking, prioritizing sleep, eating healthy, and staying physically and mentally active,” said Ms. Smith.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology.
An ‘ambitious exercise’
Coinvestigator Xaviera Steele, also from the IHME, told press conference attendees that the institute was established at the University of Washington in 2007 with the aim of “standardizing the measurement of health outcomes around the world and for all health conditions.”
A central part of that is the GBD study, “which is a very ambitious exercise in descriptive epidemiology in an effort to systematically quantify health loss” due to disease, injury, and risk factors over time, stratified by country, region, age, and sex. In addition, researchers are mapping and projecting trends over the next century and are estimating disease expenditure by country, by type of expense, and by condition “to derive a health care access and quality score for each health system in the world,” Ms. Steele said.
They are also estimating exposure to risk factors, how those risk factors contribute to health burden, and associated health outcomes by race and ethnicity to reflect the “disparities that we know are very prevalent in countries such as the United States.” From that work, Ms. Steele said that brain health and related conditions “do emerge as one of the more pressing challenges of the 21st century.”
Increase in dementia, mental health conditions
The data, which were gathered from 200,000 sources by the IHME, indicate that the number of individuals aged 65 years or older will increase by 350% by 2100. Ms. Steele underlined that “policy action will be needed to help families, who will struggle to provide high-quality care for their loved ones with dementia at a reasonable cost.”
The IHME calculates that in Europe health care spending on Alzheimer’s disease will increase by 226% between 2015 and 2040.
Turning to other conditions, Ms. Steele showed that since 1990, the number of individuals living with anxiety in the European region has increased by 14%, while the number living with depressive disorders has gone up by 13%.
Worldwide, the figures are even starker. Depression is estimated to affect 300 million people across the globe, which represents a 71% increase since 1990. The number of strokes increased by 95% over the same period.
Nevertheless, the “impact of brain conditions such as stroke has decreased since the 1990s due to improved treatments available,” Ms. Smith noted in the press release.
To estimate the toll caused by brain conditions, including neurologic disorders, mental disorders, cerebrovascular disease, brain cancer, brain injuries, and select infectious conditions, the researchers calculated disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
This, Ms. Smith explained in her presentation, “captures the morbidity and mortality associated with brain conditions” and is adjusted for patient location, age, and sex.
The investigators found that, globally, brain conditions accounted for more than 15% of all health loss in 2021, at 406 DALYs – more than the 206 million DALYs that were associated with cancer, and the 402 million that were linked to cardiovascular disease.
This health loss is associated with a $1.22 trillion loss in income for people living with health disorders worldwide and accounts for $1.14 trillion in direct health care costs.
The burden of mental disorders, neurologic conditions, and stroke is expected to increase dramatically between now and 2050, said Ms. Smith, who noted that health loss linked to brain conditions is higher in younger patients. This will create “new challenges for health systems, employers, patients, and families,” she said in the press release.
“Our goal is to see an improved prevention and treatment landscape for other brain conditions and reverse the growing health loss that we are currently forecasting.”
Worrying increase in stroke
Jurgita Valaikiene, MD, PhD, center of neurology, clinic of neurology and neurosurgery, Vilnius (Lithuania) University Faculty of Medicine, who chaired the session, was taken aback by the findings, particularly by the worldwide increase in stroke cases.
“I work in stroke,” she said, and “we spend a lot of time on the diagnosis of stroke” and its prevention. “We try to be faster, to catch asymptomatic stenosis in the neck or head, and to apply the best medical treatment to avoid a stroke. But despite that, the numbers are increasing. I understand the population is getting older ... but still it’s a huge number.”
Dr. Valaikiene pointed out that stroke is not necessarily a condition of aging, insofar as increasing age “is not related directly to stenosis in the neck. “For example, we can have healthier vessels in older age and unhealthy vessels, with high-grade stenosis, in someone aged 30 or 40 years.”
“There are a lot of risk factors, such as smoking, physical activity, and so on. It depends on the individual,” she added.
The study was funded by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PCPs key to heart failure care after discharge
Madeline Sterling, MD, knew something was wrong when she heard her patient’s voice on the phone. The patient was breathing too fast and sounded fatigued. Like many people with heart failure, this patient had several comorbidities: diabetes, high blood pressure, and cancer, which was in remission.
The patient had been in and out of the hospital several times and was afraid of going back, but Dr. Sterling, a primary care physician, advised her that it was the safe thing to do.
During the woman’s stay, the inpatient cardiology team called Dr. Sterling to provide status updates and ask for input. When the patient was discharged, Dr. Sterling received information on what medicines had been changed and scheduled follow-up care within 10 days. Dr. Sterling, who’d cared for the woman for many years, called her family, her home health aide, and another caregiver to discuss the plan.
“When you know these patients really well, it’s helpful,” Dr. Sterling, a professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said. Primary care clinicians have “an appreciation for how all these conditions fit together, how the medicines fit together, and how to put that patient’s priorities at the front of the equation.”
Research has shown that follow-up care within 7-10 days after discharge, especially for patients with heart failure, can prevent hospital readmissions. Patients’ health can change rapidly following discharge: They may start retaining fluid or may not know how to maintain a low-sodium diet, or they might have trouble obtaining medication. Primary care clinicians spot these early warning signs in follow-up visits.
Heart failure affects more than 6 million adults in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The condition is a common cause of hospital readmissions within 30 days of discharge, according to research published by the American Heart Association.
Patients with heart failure are particularly challenging to care for because of comorbidities.
“They’re a very, very sick group of patients that are very difficult to manage,” said Noah Moss, MD, an advanced heart failure and transplant cardiologist at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York.
But patients do not always receive the follow-up care they need, some studies have found.
Right drugs at the right time
Kelly Axsom, MD, a cardiologist at the Columbia University Medical Center, New York, and director of the centralized heart failure management program at the New York–Presbyterian Hospital System, called the primary care clinician the “captain of the ship,” ensuring that medications are reconciled and providing education about what to eat after discharge.
“It’s actually pretty complicated to go from being in the hospital to being at home,” Dr. Axsom said. “There are often many medication changes, there are lots of instructions that are told to you as a patient that are hard to remember.”
A patient’s weight might fluctuate in the days following discharge because the dose of diuretics might be too low or too high and need to be adjusted, according to Ishani Ganguli, MD, MPH, an assistant professor of medicine and a general internist in the Division of General Internal Medicine and Primary Care at Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
K. Melissa Hayes, DNP, ANP-BC, CHFN, an assistant professor in the adult gerontology primary care program at the Vanderbilt University School of Nursing, Nashville, Tenn., recalled one patient who was given a months’ worth of medications following his discharge from the hospital.
“He was given expensive medications he couldn’t afford and not any refills or how to get those medications,” Dr. Hayes said.
Sometimes patients have no way to get to the pharmacy, or their pharmacy doesn’t have the medication they need, or their insurance doesn’t cover the drugs.
“The average patient is on at least six medications for heart failure, maybe even seven, and then that’s not including all their other medications,” Dr. Hayes said. “That can be a lot for people to keep up with.”
Dr. Hayes talks to her patients with heart failure about what drugs they have been prescribed and what medications they require more of, and she deprescribes any that are duplicative.
Helping patients understand why they are taking each drug encourages them to stick to the regimen. Diuretics, for example, can lead to frequent urination. If patients are unable to take regular bathroom breaks, they may be tempted to stop using the medication – a potentially catastrophic mistake.
“Often I have patients say, ‘Nobody ever explained it to me that way,’ ” Dr. Hayes said. “Someone can have a PhD but not understand their medications.”
Clinicians also can alert patients to commonly used medications that can worsen heart failure, such as diabetes drugs and over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen.
Patients should be prescribed a combination of four recommended medications. But several studies have found that clinicians often fail to achieve the target doses for those medications. The use of guideline-directed medications reduces mortality and hospitalization rates, according to multiple clinical trials.
Eyes and ears on the patient
Once home, patients must stick to the right diet, weigh themselves every day, and monitor their blood pressure. But changing behaviors can be a struggle.
“Being seen quickly within a couple of days of discharge, you can catch things,” said Dr. Hayes, who has edited a book on managing patients with heart failure in primary care.
“It’s an opportunity to see how they’re doing at home, make sure they have their medications, make sure there’s been no misunderstanding or miscommunication about what they’re supposed to be doing at home,” says Marc Itskowitz, MD, a primary care physician affiliated with Allegheny General Hospital, Pittsburgh.
Ideally, a record that readily integrates information from wearables – such as blood pressure and weight – would make it easier to spot abnormalities, Dr. Itskowtiz said. “I think we’re still in the infancy of the electronic health record,” he said.
Ensuring that follow-up visits are as accessible as possible for patients is also important. Telehealth makes it easier for patients after they return home from the hospital, Dr. Itskowitz said.
More infrastructure
Another challenge of providing follow-up care for patients with heart failure is completing all the tasks a clinician must do within a 20-minute visit: an examination; education on the condition and medications; counseling on diet and exercise; coordination of medical equipment, such as a blood pressure cuff for home use; and making appointments with specialists.
“In the current system, additional support for primary care is needed so we can do all this,” Dr. Sterling said.
Staff at primary care clinics should be trained to answer calls from patients when they experience changes in their weight or are worried about other potential problems. “A lot of primary care practices are bare bones,” Dr. Hayes said, meaning they might not have the staff to field those calls. Educating patients as to when they should call their physician, especially after experiencing worsening symptoms, is also important.
Dr. Hayes suggests setting aside time in the schedule each week to see patients who have been recently discharged from the hospital. In the Cardiology and Vascular Clinic at Nashville General Hospital, Tenn., where she spends half a day each week, Dr. Hayes requests 30 minutes to see patients who have recently been discharged from hospital.
Even when the process goes smoothly, some patients will return to the hospital because of the progressive nature of heart failure, according to Dr. Hayes. Improving care following their hospitalization can keep these people from rapidly declining.
“Most patients with heart failure want to be taking care of the grandchildren or be able to enjoy family dinners together,” Dr. Axsom said. “I think anything we can do to help improve their quality of life is really important.”
Take-home
- See heart failure patients early after their discharge from hospital, ideally within 7-10 days.
- Make sure patients have access to the right medications at the right dosages and that they know why they’re taking them.
- Educate patients about the diet they should be following.
- Have a system to monitor patients’ symptoms and let them know when they should call.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Madeline Sterling, MD, knew something was wrong when she heard her patient’s voice on the phone. The patient was breathing too fast and sounded fatigued. Like many people with heart failure, this patient had several comorbidities: diabetes, high blood pressure, and cancer, which was in remission.
The patient had been in and out of the hospital several times and was afraid of going back, but Dr. Sterling, a primary care physician, advised her that it was the safe thing to do.
During the woman’s stay, the inpatient cardiology team called Dr. Sterling to provide status updates and ask for input. When the patient was discharged, Dr. Sterling received information on what medicines had been changed and scheduled follow-up care within 10 days. Dr. Sterling, who’d cared for the woman for many years, called her family, her home health aide, and another caregiver to discuss the plan.
“When you know these patients really well, it’s helpful,” Dr. Sterling, a professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said. Primary care clinicians have “an appreciation for how all these conditions fit together, how the medicines fit together, and how to put that patient’s priorities at the front of the equation.”
Research has shown that follow-up care within 7-10 days after discharge, especially for patients with heart failure, can prevent hospital readmissions. Patients’ health can change rapidly following discharge: They may start retaining fluid or may not know how to maintain a low-sodium diet, or they might have trouble obtaining medication. Primary care clinicians spot these early warning signs in follow-up visits.
Heart failure affects more than 6 million adults in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The condition is a common cause of hospital readmissions within 30 days of discharge, according to research published by the American Heart Association.
Patients with heart failure are particularly challenging to care for because of comorbidities.
“They’re a very, very sick group of patients that are very difficult to manage,” said Noah Moss, MD, an advanced heart failure and transplant cardiologist at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York.
But patients do not always receive the follow-up care they need, some studies have found.
Right drugs at the right time
Kelly Axsom, MD, a cardiologist at the Columbia University Medical Center, New York, and director of the centralized heart failure management program at the New York–Presbyterian Hospital System, called the primary care clinician the “captain of the ship,” ensuring that medications are reconciled and providing education about what to eat after discharge.
“It’s actually pretty complicated to go from being in the hospital to being at home,” Dr. Axsom said. “There are often many medication changes, there are lots of instructions that are told to you as a patient that are hard to remember.”
A patient’s weight might fluctuate in the days following discharge because the dose of diuretics might be too low or too high and need to be adjusted, according to Ishani Ganguli, MD, MPH, an assistant professor of medicine and a general internist in the Division of General Internal Medicine and Primary Care at Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
K. Melissa Hayes, DNP, ANP-BC, CHFN, an assistant professor in the adult gerontology primary care program at the Vanderbilt University School of Nursing, Nashville, Tenn., recalled one patient who was given a months’ worth of medications following his discharge from the hospital.
“He was given expensive medications he couldn’t afford and not any refills or how to get those medications,” Dr. Hayes said.
Sometimes patients have no way to get to the pharmacy, or their pharmacy doesn’t have the medication they need, or their insurance doesn’t cover the drugs.
“The average patient is on at least six medications for heart failure, maybe even seven, and then that’s not including all their other medications,” Dr. Hayes said. “That can be a lot for people to keep up with.”
Dr. Hayes talks to her patients with heart failure about what drugs they have been prescribed and what medications they require more of, and she deprescribes any that are duplicative.
Helping patients understand why they are taking each drug encourages them to stick to the regimen. Diuretics, for example, can lead to frequent urination. If patients are unable to take regular bathroom breaks, they may be tempted to stop using the medication – a potentially catastrophic mistake.
“Often I have patients say, ‘Nobody ever explained it to me that way,’ ” Dr. Hayes said. “Someone can have a PhD but not understand their medications.”
Clinicians also can alert patients to commonly used medications that can worsen heart failure, such as diabetes drugs and over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen.
Patients should be prescribed a combination of four recommended medications. But several studies have found that clinicians often fail to achieve the target doses for those medications. The use of guideline-directed medications reduces mortality and hospitalization rates, according to multiple clinical trials.
Eyes and ears on the patient
Once home, patients must stick to the right diet, weigh themselves every day, and monitor their blood pressure. But changing behaviors can be a struggle.
“Being seen quickly within a couple of days of discharge, you can catch things,” said Dr. Hayes, who has edited a book on managing patients with heart failure in primary care.
“It’s an opportunity to see how they’re doing at home, make sure they have their medications, make sure there’s been no misunderstanding or miscommunication about what they’re supposed to be doing at home,” says Marc Itskowitz, MD, a primary care physician affiliated with Allegheny General Hospital, Pittsburgh.
Ideally, a record that readily integrates information from wearables – such as blood pressure and weight – would make it easier to spot abnormalities, Dr. Itskowtiz said. “I think we’re still in the infancy of the electronic health record,” he said.
Ensuring that follow-up visits are as accessible as possible for patients is also important. Telehealth makes it easier for patients after they return home from the hospital, Dr. Itskowitz said.
More infrastructure
Another challenge of providing follow-up care for patients with heart failure is completing all the tasks a clinician must do within a 20-minute visit: an examination; education on the condition and medications; counseling on diet and exercise; coordination of medical equipment, such as a blood pressure cuff for home use; and making appointments with specialists.
“In the current system, additional support for primary care is needed so we can do all this,” Dr. Sterling said.
Staff at primary care clinics should be trained to answer calls from patients when they experience changes in their weight or are worried about other potential problems. “A lot of primary care practices are bare bones,” Dr. Hayes said, meaning they might not have the staff to field those calls. Educating patients as to when they should call their physician, especially after experiencing worsening symptoms, is also important.
Dr. Hayes suggests setting aside time in the schedule each week to see patients who have been recently discharged from the hospital. In the Cardiology and Vascular Clinic at Nashville General Hospital, Tenn., where she spends half a day each week, Dr. Hayes requests 30 minutes to see patients who have recently been discharged from hospital.
Even when the process goes smoothly, some patients will return to the hospital because of the progressive nature of heart failure, according to Dr. Hayes. Improving care following their hospitalization can keep these people from rapidly declining.
“Most patients with heart failure want to be taking care of the grandchildren or be able to enjoy family dinners together,” Dr. Axsom said. “I think anything we can do to help improve their quality of life is really important.”
Take-home
- See heart failure patients early after their discharge from hospital, ideally within 7-10 days.
- Make sure patients have access to the right medications at the right dosages and that they know why they’re taking them.
- Educate patients about the diet they should be following.
- Have a system to monitor patients’ symptoms and let them know when they should call.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Madeline Sterling, MD, knew something was wrong when she heard her patient’s voice on the phone. The patient was breathing too fast and sounded fatigued. Like many people with heart failure, this patient had several comorbidities: diabetes, high blood pressure, and cancer, which was in remission.
The patient had been in and out of the hospital several times and was afraid of going back, but Dr. Sterling, a primary care physician, advised her that it was the safe thing to do.
During the woman’s stay, the inpatient cardiology team called Dr. Sterling to provide status updates and ask for input. When the patient was discharged, Dr. Sterling received information on what medicines had been changed and scheduled follow-up care within 10 days. Dr. Sterling, who’d cared for the woman for many years, called her family, her home health aide, and another caregiver to discuss the plan.
“When you know these patients really well, it’s helpful,” Dr. Sterling, a professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said. Primary care clinicians have “an appreciation for how all these conditions fit together, how the medicines fit together, and how to put that patient’s priorities at the front of the equation.”
Research has shown that follow-up care within 7-10 days after discharge, especially for patients with heart failure, can prevent hospital readmissions. Patients’ health can change rapidly following discharge: They may start retaining fluid or may not know how to maintain a low-sodium diet, or they might have trouble obtaining medication. Primary care clinicians spot these early warning signs in follow-up visits.
Heart failure affects more than 6 million adults in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The condition is a common cause of hospital readmissions within 30 days of discharge, according to research published by the American Heart Association.
Patients with heart failure are particularly challenging to care for because of comorbidities.
“They’re a very, very sick group of patients that are very difficult to manage,” said Noah Moss, MD, an advanced heart failure and transplant cardiologist at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York.
But patients do not always receive the follow-up care they need, some studies have found.
Right drugs at the right time
Kelly Axsom, MD, a cardiologist at the Columbia University Medical Center, New York, and director of the centralized heart failure management program at the New York–Presbyterian Hospital System, called the primary care clinician the “captain of the ship,” ensuring that medications are reconciled and providing education about what to eat after discharge.
“It’s actually pretty complicated to go from being in the hospital to being at home,” Dr. Axsom said. “There are often many medication changes, there are lots of instructions that are told to you as a patient that are hard to remember.”
A patient’s weight might fluctuate in the days following discharge because the dose of diuretics might be too low or too high and need to be adjusted, according to Ishani Ganguli, MD, MPH, an assistant professor of medicine and a general internist in the Division of General Internal Medicine and Primary Care at Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
K. Melissa Hayes, DNP, ANP-BC, CHFN, an assistant professor in the adult gerontology primary care program at the Vanderbilt University School of Nursing, Nashville, Tenn., recalled one patient who was given a months’ worth of medications following his discharge from the hospital.
“He was given expensive medications he couldn’t afford and not any refills or how to get those medications,” Dr. Hayes said.
Sometimes patients have no way to get to the pharmacy, or their pharmacy doesn’t have the medication they need, or their insurance doesn’t cover the drugs.
“The average patient is on at least six medications for heart failure, maybe even seven, and then that’s not including all their other medications,” Dr. Hayes said. “That can be a lot for people to keep up with.”
Dr. Hayes talks to her patients with heart failure about what drugs they have been prescribed and what medications they require more of, and she deprescribes any that are duplicative.
Helping patients understand why they are taking each drug encourages them to stick to the regimen. Diuretics, for example, can lead to frequent urination. If patients are unable to take regular bathroom breaks, they may be tempted to stop using the medication – a potentially catastrophic mistake.
“Often I have patients say, ‘Nobody ever explained it to me that way,’ ” Dr. Hayes said. “Someone can have a PhD but not understand their medications.”
Clinicians also can alert patients to commonly used medications that can worsen heart failure, such as diabetes drugs and over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen.
Patients should be prescribed a combination of four recommended medications. But several studies have found that clinicians often fail to achieve the target doses for those medications. The use of guideline-directed medications reduces mortality and hospitalization rates, according to multiple clinical trials.
Eyes and ears on the patient
Once home, patients must stick to the right diet, weigh themselves every day, and monitor their blood pressure. But changing behaviors can be a struggle.
“Being seen quickly within a couple of days of discharge, you can catch things,” said Dr. Hayes, who has edited a book on managing patients with heart failure in primary care.
“It’s an opportunity to see how they’re doing at home, make sure they have their medications, make sure there’s been no misunderstanding or miscommunication about what they’re supposed to be doing at home,” says Marc Itskowitz, MD, a primary care physician affiliated with Allegheny General Hospital, Pittsburgh.
Ideally, a record that readily integrates information from wearables – such as blood pressure and weight – would make it easier to spot abnormalities, Dr. Itskowtiz said. “I think we’re still in the infancy of the electronic health record,” he said.
Ensuring that follow-up visits are as accessible as possible for patients is also important. Telehealth makes it easier for patients after they return home from the hospital, Dr. Itskowitz said.
More infrastructure
Another challenge of providing follow-up care for patients with heart failure is completing all the tasks a clinician must do within a 20-minute visit: an examination; education on the condition and medications; counseling on diet and exercise; coordination of medical equipment, such as a blood pressure cuff for home use; and making appointments with specialists.
“In the current system, additional support for primary care is needed so we can do all this,” Dr. Sterling said.
Staff at primary care clinics should be trained to answer calls from patients when they experience changes in their weight or are worried about other potential problems. “A lot of primary care practices are bare bones,” Dr. Hayes said, meaning they might not have the staff to field those calls. Educating patients as to when they should call their physician, especially after experiencing worsening symptoms, is also important.
Dr. Hayes suggests setting aside time in the schedule each week to see patients who have been recently discharged from the hospital. In the Cardiology and Vascular Clinic at Nashville General Hospital, Tenn., where she spends half a day each week, Dr. Hayes requests 30 minutes to see patients who have recently been discharged from hospital.
Even when the process goes smoothly, some patients will return to the hospital because of the progressive nature of heart failure, according to Dr. Hayes. Improving care following their hospitalization can keep these people from rapidly declining.
“Most patients with heart failure want to be taking care of the grandchildren or be able to enjoy family dinners together,” Dr. Axsom said. “I think anything we can do to help improve their quality of life is really important.”
Take-home
- See heart failure patients early after their discharge from hospital, ideally within 7-10 days.
- Make sure patients have access to the right medications at the right dosages and that they know why they’re taking them.
- Educate patients about the diet they should be following.
- Have a system to monitor patients’ symptoms and let them know when they should call.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.