User login
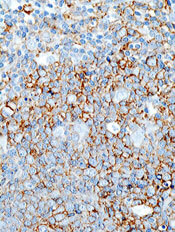
Transplant strategy not viable for aggressive B-NHL
Transplant with radioimmunotherapy (RIT)-based conditioning is a viable treatment option for patients with indolent—but not aggressive—B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs), according to researchers.
Long-term follow-up data showed “excellent” outcomes in patients with indolent B-NHL who received conditioning with 90Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan plus fludarabine and low-dose total body irradiation (TBI) prior to HLA-matched hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
However, long-term outcomes were inferior in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Camille E. Puronen, MD, of the University of Washington in Seattle, and her colleagues reported these results in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The study enrolled 40 patients with high-risk B-NHL. This included DLBCL (n=14), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL; n=10), MCL (n=8), follicular lymphoma (FL; n=6); hairy cell leukemia (HCL; n=1), and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL; n=1).
Patients were treated with 0.4 mCi/kg 90Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan, given 2 weeks prior to HSCT, to a maximum dose of 32 mCi.
Patients also received fludarabine at 30 mg/m2 on day 5, 6, and 7 prior to HSCT and 2 Gy TBI given on the day of transplant.
In an earlier report, the objective response rate (ORR) was 60%, and 35% of patients had a complete response (CR) or unconfirmed CR.
The researchers said early responses were not associated with disease bulk or chemoresistance, as the ORR was 59% in patients with bulky or chemoresistant disease.
However, responses were associated with histology, as the ORR was 38% in patients with DLBCL, 50% in those with MCL, 83% in those with FL, and 90% in those with CLL.
Long-term survival
In the current report, 11 of 40 patients were still alive at a median follow up of 9 years (range, 5.3 to 10.2). Fourteen patients died of disease progression, and 14 died from complications of HSCT.
The 5-year overall survival (OS) was 40%, and the 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 28%.
The best survival rates were in patients with indolent histology. The 5-year PFS was 44% in these patients, and the 5-year OS was 67%.
The researchers said early CR was not associated with long-term survival. However, patients who had at least stable disease (SD) at earlier time points did have the opportunity to achieve long-term survival. All patients who progressed before day 84 were dead by the 1-year mark.
Of the 11 patients who were still alive at a median follow up of 9 years, 4 had a CR or unconfirmed CR at day 84 (FL: 1; CLL: 2; MCL: 1); 6 were in partial response (CLL: 3; FL: 1; MCL: 1; MZL: 1); and 1 patient with FL had SD.
Among the 18 patients with indolent NHL, long-term PFS was observed in 5 of the 7 patients who achieved early CR and 8 of the 11 patients who did not achieve early CR.
Two of the 4 MCL patients who achieved an early CR had long-term PFS, but none of the MCL patients without an early CR had long-term PFS.
Among DLBCL patients, 1 of the 4 who achieved early CR had long-term PFS, but none of the patients without an early CR had long-term PFS. Only 1 DLBCL patient survived beyond 5 years. None survived beyond 8 years.
The researchers said the favorable outcomes in patients with indolent B-NHL are consistent with the known efficacy of RIT and the graft-versus-leukemia effect in these patients.
The team also noted that, since this trial began, several novel agents have been approved for the treatment of indolent B-NHL, which means allogeneic HSCT is often moved to later in the disease course.
The researchers concluded that 90Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan-based conditioning could “continue to play an important role in these settings,” but “improved strategies are needed” for patients with MCL and DLBCL.
Transplant with radioimmunotherapy (RIT)-based conditioning is a viable treatment option for patients with indolent—but not aggressive—B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs), according to researchers.
Long-term follow-up data showed “excellent” outcomes in patients with indolent B-NHL who received conditioning with 90Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan plus fludarabine and low-dose total body irradiation (TBI) prior to HLA-matched hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
However, long-term outcomes were inferior in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Camille E. Puronen, MD, of the University of Washington in Seattle, and her colleagues reported these results in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The study enrolled 40 patients with high-risk B-NHL. This included DLBCL (n=14), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL; n=10), MCL (n=8), follicular lymphoma (FL; n=6); hairy cell leukemia (HCL; n=1), and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL; n=1).
Patients were treated with 0.4 mCi/kg 90Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan, given 2 weeks prior to HSCT, to a maximum dose of 32 mCi.
Patients also received fludarabine at 30 mg/m2 on day 5, 6, and 7 prior to HSCT and 2 Gy TBI given on the day of transplant.
In an earlier report, the objective response rate (ORR) was 60%, and 35% of patients had a complete response (CR) or unconfirmed CR.
The researchers said early responses were not associated with disease bulk or chemoresistance, as the ORR was 59% in patients with bulky or chemoresistant disease.
However, responses were associated with histology, as the ORR was 38% in patients with DLBCL, 50% in those with MCL, 83% in those with FL, and 90% in those with CLL.
Long-term survival
In the current report, 11 of 40 patients were still alive at a median follow up of 9 years (range, 5.3 to 10.2). Fourteen patients died of disease progression, and 14 died from complications of HSCT.
The 5-year overall survival (OS) was 40%, and the 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 28%.
The best survival rates were in patients with indolent histology. The 5-year PFS was 44% in these patients, and the 5-year OS was 67%.
The researchers said early CR was not associated with long-term survival. However, patients who had at least stable disease (SD) at earlier time points did have the opportunity to achieve long-term survival. All patients who progressed before day 84 were dead by the 1-year mark.
Of the 11 patients who were still alive at a median follow up of 9 years, 4 had a CR or unconfirmed CR at day 84 (FL: 1; CLL: 2; MCL: 1); 6 were in partial response (CLL: 3; FL: 1; MCL: 1; MZL: 1); and 1 patient with FL had SD.
Among the 18 patients with indolent NHL, long-term PFS was observed in 5 of the 7 patients who achieved early CR and 8 of the 11 patients who did not achieve early CR.
Two of the 4 MCL patients who achieved an early CR had long-term PFS, but none of the MCL patients without an early CR had long-term PFS.
Among DLBCL patients, 1 of the 4 who achieved early CR had long-term PFS, but none of the patients without an early CR had long-term PFS. Only 1 DLBCL patient survived beyond 5 years. None survived beyond 8 years.
The researchers said the favorable outcomes in patients with indolent B-NHL are consistent with the known efficacy of RIT and the graft-versus-leukemia effect in these patients.
The team also noted that, since this trial began, several novel agents have been approved for the treatment of indolent B-NHL, which means allogeneic HSCT is often moved to later in the disease course.
The researchers concluded that 90Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan-based conditioning could “continue to play an important role in these settings,” but “improved strategies are needed” for patients with MCL and DLBCL.
Transplant with radioimmunotherapy (RIT)-based conditioning is a viable treatment option for patients with indolent—but not aggressive—B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs), according to researchers.
Long-term follow-up data showed “excellent” outcomes in patients with indolent B-NHL who received conditioning with 90Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan plus fludarabine and low-dose total body irradiation (TBI) prior to HLA-matched hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
However, long-term outcomes were inferior in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Camille E. Puronen, MD, of the University of Washington in Seattle, and her colleagues reported these results in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The study enrolled 40 patients with high-risk B-NHL. This included DLBCL (n=14), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL; n=10), MCL (n=8), follicular lymphoma (FL; n=6); hairy cell leukemia (HCL; n=1), and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL; n=1).
Patients were treated with 0.4 mCi/kg 90Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan, given 2 weeks prior to HSCT, to a maximum dose of 32 mCi.
Patients also received fludarabine at 30 mg/m2 on day 5, 6, and 7 prior to HSCT and 2 Gy TBI given on the day of transplant.
In an earlier report, the objective response rate (ORR) was 60%, and 35% of patients had a complete response (CR) or unconfirmed CR.
The researchers said early responses were not associated with disease bulk or chemoresistance, as the ORR was 59% in patients with bulky or chemoresistant disease.
However, responses were associated with histology, as the ORR was 38% in patients with DLBCL, 50% in those with MCL, 83% in those with FL, and 90% in those with CLL.
Long-term survival
In the current report, 11 of 40 patients were still alive at a median follow up of 9 years (range, 5.3 to 10.2). Fourteen patients died of disease progression, and 14 died from complications of HSCT.
The 5-year overall survival (OS) was 40%, and the 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 28%.
The best survival rates were in patients with indolent histology. The 5-year PFS was 44% in these patients, and the 5-year OS was 67%.
The researchers said early CR was not associated with long-term survival. However, patients who had at least stable disease (SD) at earlier time points did have the opportunity to achieve long-term survival. All patients who progressed before day 84 were dead by the 1-year mark.
Of the 11 patients who were still alive at a median follow up of 9 years, 4 had a CR or unconfirmed CR at day 84 (FL: 1; CLL: 2; MCL: 1); 6 were in partial response (CLL: 3; FL: 1; MCL: 1; MZL: 1); and 1 patient with FL had SD.
Among the 18 patients with indolent NHL, long-term PFS was observed in 5 of the 7 patients who achieved early CR and 8 of the 11 patients who did not achieve early CR.
Two of the 4 MCL patients who achieved an early CR had long-term PFS, but none of the MCL patients without an early CR had long-term PFS.
Among DLBCL patients, 1 of the 4 who achieved early CR had long-term PFS, but none of the patients without an early CR had long-term PFS. Only 1 DLBCL patient survived beyond 5 years. None survived beyond 8 years.
The researchers said the favorable outcomes in patients with indolent B-NHL are consistent with the known efficacy of RIT and the graft-versus-leukemia effect in these patients.
The team also noted that, since this trial began, several novel agents have been approved for the treatment of indolent B-NHL, which means allogeneic HSCT is often moved to later in the disease course.
The researchers concluded that 90Y-ibritumomab tiuxetan-based conditioning could “continue to play an important role in these settings,” but “improved strategies are needed” for patients with MCL and DLBCL.
CHMP recommends CAR T for ALL, DLBCL
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended the approval of tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah®, formerly CTL019) for 2 indications.
According to the CHMP, the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy should be approved to treat adults with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who have received 2 or more lines of systemic therapy and patients up to 25 years of age who have B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) that is refractory, in relapse post-transplant, or in second or later relapse.
The CHMP’s recommendation will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to approve medicines for use in the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
The European Commission usually makes a decision within 67 days of the CHMP’s recommendation.
The CHMP’s recommendation is based on results from a pair of phase 2 trials—ELIANA and JULIET.
JULIET trial
Updated results from JULIET were presented at the recent 23rd Annual Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA) as abstract S799.
The trial enrolled 165 adults with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, and 111 of them received a single infusion of tisagenlecleucel. Most of the patients who discontinued before dosing did so due to disease progression or clinical deterioration. The patients’ median age at baseline was 56 (range, 22-76).
Ninety-two percent of patients received bridging therapy, and 93% received lymphodepleting chemotherapy prior to tisagenlecleucel.
The median time from infusion to data cutoff was 13.9 months.
The overall response rate was 52%, and the complete response (CR) rate was 40%. Of the patients in CR at month 3, 83% remained in CR at month 12. The median duration of response was not reached.
At the time of data cutoff, none of the responders had proceeded to stem cell transplant.
For all infused patients (n=111), the 12-month overall survival (OS) rate was 49%, and the median OS was 11.7 months. The median OS was not reached for patients in CR.
Within 8 weeks of tisagenlecleucel infusion, 22% of patients had developed grade 3/4 cytokine release syndrome (CRS). Fifteen percent of patients received tocilizumab for CRS, including 3% of patients with grade 2 CRS and 50% of patients with grade 3 CRS.
Other adverse events (AEs) of interest included grade 3/4 neurologic events (12%), grade 3/4 cytopenias lasting more than 28 days (32%), grade 3/4 infections (20%), and grade 3/4 febrile neutropenia (15%).
ELIANA trial
Updated results from ELIANA were published in NEJM in February.
The trial included 75 children and young adults with relapsed/refractory ALL. The patients’ median age was 11 (range, 3 to 23).
All 75 patients received a single infusion of tisagenlecleucel, and 72 received lymphodepleting chemotherapy.
The median duration of follow-up was 13.1 months. The study’s primary endpoint was overall remission rate, which was defined as the rate of a best overall response of either CR or CR with incomplete hematologic recovery (CRi) within 3 months.
The overall remission rate was 81% (61/75), with 60% of patients (n=45) achieving a CR and 21% (n=16) achieving a CRi.
All patients whose best response was CR/CRi were negative for minimal residual disease. The median duration of response was not met.
Eight patients proceeded to transplant while in remission. At last follow-up, 4 were still in remission, and 4 had unknown disease status.
At 6 months, the event-free survival rate was 73%, and the OS rate was 90%. At 12 months, the rates were 50% and 76%, respectively.
All patients experienced at least 1 AE, and 95% had AEs thought to be related to tisagenlecleucel. The rate of grade 3/4 AEs was 88%, and the rate of related grade 3/4 AEs was 73%.
AEs of special interest included CRS (77%), neurologic events (40%), infections (43%), febrile neutropenia (35%), cytopenias not resolved by day 28 (37%), and tumor lysis syndrome (4%).
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended the approval of tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah®, formerly CTL019) for 2 indications.
According to the CHMP, the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy should be approved to treat adults with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who have received 2 or more lines of systemic therapy and patients up to 25 years of age who have B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) that is refractory, in relapse post-transplant, or in second or later relapse.
The CHMP’s recommendation will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to approve medicines for use in the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
The European Commission usually makes a decision within 67 days of the CHMP’s recommendation.
The CHMP’s recommendation is based on results from a pair of phase 2 trials—ELIANA and JULIET.
JULIET trial
Updated results from JULIET were presented at the recent 23rd Annual Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA) as abstract S799.
The trial enrolled 165 adults with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, and 111 of them received a single infusion of tisagenlecleucel. Most of the patients who discontinued before dosing did so due to disease progression or clinical deterioration. The patients’ median age at baseline was 56 (range, 22-76).
Ninety-two percent of patients received bridging therapy, and 93% received lymphodepleting chemotherapy prior to tisagenlecleucel.
The median time from infusion to data cutoff was 13.9 months.
The overall response rate was 52%, and the complete response (CR) rate was 40%. Of the patients in CR at month 3, 83% remained in CR at month 12. The median duration of response was not reached.
At the time of data cutoff, none of the responders had proceeded to stem cell transplant.
For all infused patients (n=111), the 12-month overall survival (OS) rate was 49%, and the median OS was 11.7 months. The median OS was not reached for patients in CR.
Within 8 weeks of tisagenlecleucel infusion, 22% of patients had developed grade 3/4 cytokine release syndrome (CRS). Fifteen percent of patients received tocilizumab for CRS, including 3% of patients with grade 2 CRS and 50% of patients with grade 3 CRS.
Other adverse events (AEs) of interest included grade 3/4 neurologic events (12%), grade 3/4 cytopenias lasting more than 28 days (32%), grade 3/4 infections (20%), and grade 3/4 febrile neutropenia (15%).
ELIANA trial
Updated results from ELIANA were published in NEJM in February.
The trial included 75 children and young adults with relapsed/refractory ALL. The patients’ median age was 11 (range, 3 to 23).
All 75 patients received a single infusion of tisagenlecleucel, and 72 received lymphodepleting chemotherapy.
The median duration of follow-up was 13.1 months. The study’s primary endpoint was overall remission rate, which was defined as the rate of a best overall response of either CR or CR with incomplete hematologic recovery (CRi) within 3 months.
The overall remission rate was 81% (61/75), with 60% of patients (n=45) achieving a CR and 21% (n=16) achieving a CRi.
All patients whose best response was CR/CRi were negative for minimal residual disease. The median duration of response was not met.
Eight patients proceeded to transplant while in remission. At last follow-up, 4 were still in remission, and 4 had unknown disease status.
At 6 months, the event-free survival rate was 73%, and the OS rate was 90%. At 12 months, the rates were 50% and 76%, respectively.
All patients experienced at least 1 AE, and 95% had AEs thought to be related to tisagenlecleucel. The rate of grade 3/4 AEs was 88%, and the rate of related grade 3/4 AEs was 73%.
AEs of special interest included CRS (77%), neurologic events (40%), infections (43%), febrile neutropenia (35%), cytopenias not resolved by day 28 (37%), and tumor lysis syndrome (4%).
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended the approval of tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah®, formerly CTL019) for 2 indications.
According to the CHMP, the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy should be approved to treat adults with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who have received 2 or more lines of systemic therapy and patients up to 25 years of age who have B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) that is refractory, in relapse post-transplant, or in second or later relapse.
The CHMP’s recommendation will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to approve medicines for use in the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
The European Commission usually makes a decision within 67 days of the CHMP’s recommendation.
The CHMP’s recommendation is based on results from a pair of phase 2 trials—ELIANA and JULIET.
JULIET trial
Updated results from JULIET were presented at the recent 23rd Annual Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA) as abstract S799.
The trial enrolled 165 adults with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, and 111 of them received a single infusion of tisagenlecleucel. Most of the patients who discontinued before dosing did so due to disease progression or clinical deterioration. The patients’ median age at baseline was 56 (range, 22-76).
Ninety-two percent of patients received bridging therapy, and 93% received lymphodepleting chemotherapy prior to tisagenlecleucel.
The median time from infusion to data cutoff was 13.9 months.
The overall response rate was 52%, and the complete response (CR) rate was 40%. Of the patients in CR at month 3, 83% remained in CR at month 12. The median duration of response was not reached.
At the time of data cutoff, none of the responders had proceeded to stem cell transplant.
For all infused patients (n=111), the 12-month overall survival (OS) rate was 49%, and the median OS was 11.7 months. The median OS was not reached for patients in CR.
Within 8 weeks of tisagenlecleucel infusion, 22% of patients had developed grade 3/4 cytokine release syndrome (CRS). Fifteen percent of patients received tocilizumab for CRS, including 3% of patients with grade 2 CRS and 50% of patients with grade 3 CRS.
Other adverse events (AEs) of interest included grade 3/4 neurologic events (12%), grade 3/4 cytopenias lasting more than 28 days (32%), grade 3/4 infections (20%), and grade 3/4 febrile neutropenia (15%).
ELIANA trial
Updated results from ELIANA were published in NEJM in February.
The trial included 75 children and young adults with relapsed/refractory ALL. The patients’ median age was 11 (range, 3 to 23).
All 75 patients received a single infusion of tisagenlecleucel, and 72 received lymphodepleting chemotherapy.
The median duration of follow-up was 13.1 months. The study’s primary endpoint was overall remission rate, which was defined as the rate of a best overall response of either CR or CR with incomplete hematologic recovery (CRi) within 3 months.
The overall remission rate was 81% (61/75), with 60% of patients (n=45) achieving a CR and 21% (n=16) achieving a CRi.
All patients whose best response was CR/CRi were negative for minimal residual disease. The median duration of response was not met.
Eight patients proceeded to transplant while in remission. At last follow-up, 4 were still in remission, and 4 had unknown disease status.
At 6 months, the event-free survival rate was 73%, and the OS rate was 90%. At 12 months, the rates were 50% and 76%, respectively.
All patients experienced at least 1 AE, and 95% had AEs thought to be related to tisagenlecleucel. The rate of grade 3/4 AEs was 88%, and the rate of related grade 3/4 AEs was 73%.
AEs of special interest included CRS (77%), neurologic events (40%), infections (43%), febrile neutropenia (35%), cytopenias not resolved by day 28 (37%), and tumor lysis syndrome (4%).
CHMP recommends CAR T for DLBCL, PMBCL
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval for the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta®, formerly KTE-C19).
The recommendation pertains to axicabtagene ciloleucel as a treatment for adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL) who have received 2 or more lines of systemic therapy.
The CHMP’s recommendation will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to approve medicines for use in the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
The European Commission usually makes a decision within 67 days of the CHMP’s recommendation.
The marketing authorization application for axicabtagene ciloleucel is supported by data from the ZUMA-1 trial.
Results from this phase 2 trial were presented at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting and published simultaneously in NEJM.
The trial enrolled 111 patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas. There were 101 patients who received axicabtagene ciloleucel—77 with DLBCL, 8 with PMBCL, and 16 with transformed follicular lymphoma (TFL).
Patients received conditioning with low-dose cyclophosphamide and fludarabine, followed by axicabtagene ciloleucel.
The objective response rate (ORR) was 82% (n=83), and the complete response (CR) rate was 54% (n=55).
Among the DLBCL patients, the ORR was 82% (63/77), and the CR rate was 49% (38/77). In the patients with PMBCL or TFL, the ORR was 83% (20/24), and the CR rate was 71% (17/24).
With a median follow-up of 15.4 months, 42% of patients retained their response, and 40% retained a CR.
At 18 months, the overall survival was 52%. Most deaths were due to disease progression.
However, 2 patients died of adverse events related to axicabtagene ciloleucel, both cytokine release syndrome (CRS).
The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were neutropenia (78%), anemia (43%), thrombocytopenia (38%), and febrile neutropenia (31%).
Grade 3 or higher CRS occurred in 13% of patients, and grade 3 or higher neurologic events occurred in 28%.
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval for the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta®, formerly KTE-C19).
The recommendation pertains to axicabtagene ciloleucel as a treatment for adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL) who have received 2 or more lines of systemic therapy.
The CHMP’s recommendation will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to approve medicines for use in the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
The European Commission usually makes a decision within 67 days of the CHMP’s recommendation.
The marketing authorization application for axicabtagene ciloleucel is supported by data from the ZUMA-1 trial.
Results from this phase 2 trial were presented at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting and published simultaneously in NEJM.
The trial enrolled 111 patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas. There were 101 patients who received axicabtagene ciloleucel—77 with DLBCL, 8 with PMBCL, and 16 with transformed follicular lymphoma (TFL).
Patients received conditioning with low-dose cyclophosphamide and fludarabine, followed by axicabtagene ciloleucel.
The objective response rate (ORR) was 82% (n=83), and the complete response (CR) rate was 54% (n=55).
Among the DLBCL patients, the ORR was 82% (63/77), and the CR rate was 49% (38/77). In the patients with PMBCL or TFL, the ORR was 83% (20/24), and the CR rate was 71% (17/24).
With a median follow-up of 15.4 months, 42% of patients retained their response, and 40% retained a CR.
At 18 months, the overall survival was 52%. Most deaths were due to disease progression.
However, 2 patients died of adverse events related to axicabtagene ciloleucel, both cytokine release syndrome (CRS).
The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were neutropenia (78%), anemia (43%), thrombocytopenia (38%), and febrile neutropenia (31%).
Grade 3 or higher CRS occurred in 13% of patients, and grade 3 or higher neurologic events occurred in 28%.
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval for the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta®, formerly KTE-C19).
The recommendation pertains to axicabtagene ciloleucel as a treatment for adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL) who have received 2 or more lines of systemic therapy.
The CHMP’s recommendation will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to approve medicines for use in the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
The European Commission usually makes a decision within 67 days of the CHMP’s recommendation.
The marketing authorization application for axicabtagene ciloleucel is supported by data from the ZUMA-1 trial.
Results from this phase 2 trial were presented at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting and published simultaneously in NEJM.
The trial enrolled 111 patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas. There were 101 patients who received axicabtagene ciloleucel—77 with DLBCL, 8 with PMBCL, and 16 with transformed follicular lymphoma (TFL).
Patients received conditioning with low-dose cyclophosphamide and fludarabine, followed by axicabtagene ciloleucel.
The objective response rate (ORR) was 82% (n=83), and the complete response (CR) rate was 54% (n=55).
Among the DLBCL patients, the ORR was 82% (63/77), and the CR rate was 49% (38/77). In the patients with PMBCL or TFL, the ORR was 83% (20/24), and the CR rate was 71% (17/24).
With a median follow-up of 15.4 months, 42% of patients retained their response, and 40% retained a CR.
At 18 months, the overall survival was 52%. Most deaths were due to disease progression.
However, 2 patients died of adverse events related to axicabtagene ciloleucel, both cytokine release syndrome (CRS).
The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were neutropenia (78%), anemia (43%), thrombocytopenia (38%), and febrile neutropenia (31%).
Grade 3 or higher CRS occurred in 13% of patients, and grade 3 or higher neurologic events occurred in 28%.
Doc reports favorable results from trial on hold
STOCKHOLM—Interim trial results suggest the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat can produce durable responses in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL).
In patients with EZH2 mutations, the overall response rate (ORR) was 71%, and the median duration of response (DOR) was 32 weeks.
For patients with wild-type (WT) EZH2, the ORR was 33%, and the median DOR was 76 weeks.
Tazemetostat was considered generally well tolerated in this phase 2 trial, which is currently on partial clinical hold.
Gilles Salles, MD, PhD, of the University Hospital of Lyon France, presented results from the trial at the 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA) as abstract S100.
The trial is sponsored by Epizyme, Inc.
In April, Epizyme announced that all US-based trials of tazemetostat had been placed on partial hold after a pediatric patient on a phase 1 trial developed secondary T-cell lymphoma.
Enrollment was stopped in all the trials, but patients could continue receiving tazemetostat if they had not progressed on the drug.
The phase 2 trial of tazemetostat in non-Hodgkin lymphoma has enrolled 89 adults with relapsed/refractory FL.
At EHA, Dr Salles presented results in 82 of these patients. There were 28 patients with EZH2-mutated FL and 54 with EZH2-WT FL.
The median age was 61 in both cohorts. Forty-three percent of EZH2-mutated and 63% of WT patients were male.
EZH2-mutated patients had a median of 3 prior therapies, and WT patients had a median of 4. Thirty-eight percent and 42%, respectively, were refractory to their last therapy. Eleven percent and 39%, respectively, had received prior transplant.
The median time from diagnosis was 5.1 years for EZH2-mutated patients and 6.4 years for WT patients. The median time from last prior therapy was 18.4 weeks and 28.1 weeks, respectively.
The patients received tazemetostat at 800 mg twice daily until disease progression or withdrawal.
Safety
In all 82 patients, the rate of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) was 95%, and the rate of treatment-related AEs was 78%. The rate of grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs was 17%, and the rate of serious treatment-related AEs was 4%.
Six percent of patients discontinued treatment due to a related AE, 18% had a dose interruption, and 5% had a dose reduction due to a related AE.
Treatment-related AEs included nausea (20%), fatigue (13%), anemia (13%), diarrhea (11%), alopecia (11%), asthenia (10%), thrombocytopenia (10%), muscle spasms (6%), bronchitis (5%), vomiting (5%), headache (5%), abdominal pain (2%), pyrexia (1%), and cough (1%).
Grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs included thrombocytopenia (4%), anemia (4%), fatigue (1%), and asthenia (1%).
Efficacy
In the EZH2-mutated cohort, the ORR was 71% (n=20). Eleven percent of patients (n=3) achieved a complete response, and 61% (n=17) had a partial response.
Twenty-nine percent (n=8) had stable disease as their best response. And 21% (n=6) of patients are still on study with stable disease.
All patients in this cohort experienced a reduction in tumor burden. None of the patients had progressive disease as their best response.
At the time of analysis (May 1, 2018), the median DOR was 32.3 weeks, and 55% of responders (n=11) had an ongoing response.
The median progression-free survival was 48.6 weeks.
In patients with WT EZH2 (n=54), the ORR was 33% (n=18). Six percent of patients (n=3) achieved a complete response, and 28% (n=15) had a partial response.
Thirty-one percent of patients (n=17) had stable disease as their best response, including 1 patient who is still receiving treatment.
Thirty-one percent of patients (n=17) progressed. For 4% (n=2), their response status was unknown.
At the time of analysis, the median DOR was 76 weeks, and 56% of responders (n=10) had an ongoing response.
The median progression-free survival was 29.9 weeks.
“I am impressed by the sustained clinical activity and the good tolerability of tazemetostat in this heavily pretreated patient population,” Dr Salles said. “This is important for patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma, as both the response rates and durations of response usually tend to decrease with each successive line of treatment.”
“I believe tazemetostat has the potential to fill a significant unmet need for these patients, and continued investigation of tazemetostat as a single agent or in combination with other agents is warranted.”
Epizyme’s president and chief executive officer, Robert Bazemore, said the company is still working to resolve the partial clinical hold on tazemetostat trials and is “making good progress.”
STOCKHOLM—Interim trial results suggest the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat can produce durable responses in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL).
In patients with EZH2 mutations, the overall response rate (ORR) was 71%, and the median duration of response (DOR) was 32 weeks.
For patients with wild-type (WT) EZH2, the ORR was 33%, and the median DOR was 76 weeks.
Tazemetostat was considered generally well tolerated in this phase 2 trial, which is currently on partial clinical hold.
Gilles Salles, MD, PhD, of the University Hospital of Lyon France, presented results from the trial at the 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA) as abstract S100.
The trial is sponsored by Epizyme, Inc.
In April, Epizyme announced that all US-based trials of tazemetostat had been placed on partial hold after a pediatric patient on a phase 1 trial developed secondary T-cell lymphoma.
Enrollment was stopped in all the trials, but patients could continue receiving tazemetostat if they had not progressed on the drug.
The phase 2 trial of tazemetostat in non-Hodgkin lymphoma has enrolled 89 adults with relapsed/refractory FL.
At EHA, Dr Salles presented results in 82 of these patients. There were 28 patients with EZH2-mutated FL and 54 with EZH2-WT FL.
The median age was 61 in both cohorts. Forty-three percent of EZH2-mutated and 63% of WT patients were male.
EZH2-mutated patients had a median of 3 prior therapies, and WT patients had a median of 4. Thirty-eight percent and 42%, respectively, were refractory to their last therapy. Eleven percent and 39%, respectively, had received prior transplant.
The median time from diagnosis was 5.1 years for EZH2-mutated patients and 6.4 years for WT patients. The median time from last prior therapy was 18.4 weeks and 28.1 weeks, respectively.
The patients received tazemetostat at 800 mg twice daily until disease progression or withdrawal.
Safety
In all 82 patients, the rate of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) was 95%, and the rate of treatment-related AEs was 78%. The rate of grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs was 17%, and the rate of serious treatment-related AEs was 4%.
Six percent of patients discontinued treatment due to a related AE, 18% had a dose interruption, and 5% had a dose reduction due to a related AE.
Treatment-related AEs included nausea (20%), fatigue (13%), anemia (13%), diarrhea (11%), alopecia (11%), asthenia (10%), thrombocytopenia (10%), muscle spasms (6%), bronchitis (5%), vomiting (5%), headache (5%), abdominal pain (2%), pyrexia (1%), and cough (1%).
Grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs included thrombocytopenia (4%), anemia (4%), fatigue (1%), and asthenia (1%).
Efficacy
In the EZH2-mutated cohort, the ORR was 71% (n=20). Eleven percent of patients (n=3) achieved a complete response, and 61% (n=17) had a partial response.
Twenty-nine percent (n=8) had stable disease as their best response. And 21% (n=6) of patients are still on study with stable disease.
All patients in this cohort experienced a reduction in tumor burden. None of the patients had progressive disease as their best response.
At the time of analysis (May 1, 2018), the median DOR was 32.3 weeks, and 55% of responders (n=11) had an ongoing response.
The median progression-free survival was 48.6 weeks.
In patients with WT EZH2 (n=54), the ORR was 33% (n=18). Six percent of patients (n=3) achieved a complete response, and 28% (n=15) had a partial response.
Thirty-one percent of patients (n=17) had stable disease as their best response, including 1 patient who is still receiving treatment.
Thirty-one percent of patients (n=17) progressed. For 4% (n=2), their response status was unknown.
At the time of analysis, the median DOR was 76 weeks, and 56% of responders (n=10) had an ongoing response.
The median progression-free survival was 29.9 weeks.
“I am impressed by the sustained clinical activity and the good tolerability of tazemetostat in this heavily pretreated patient population,” Dr Salles said. “This is important for patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma, as both the response rates and durations of response usually tend to decrease with each successive line of treatment.”
“I believe tazemetostat has the potential to fill a significant unmet need for these patients, and continued investigation of tazemetostat as a single agent or in combination with other agents is warranted.”
Epizyme’s president and chief executive officer, Robert Bazemore, said the company is still working to resolve the partial clinical hold on tazemetostat trials and is “making good progress.”
STOCKHOLM—Interim trial results suggest the EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat can produce durable responses in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL).
In patients with EZH2 mutations, the overall response rate (ORR) was 71%, and the median duration of response (DOR) was 32 weeks.
For patients with wild-type (WT) EZH2, the ORR was 33%, and the median DOR was 76 weeks.
Tazemetostat was considered generally well tolerated in this phase 2 trial, which is currently on partial clinical hold.
Gilles Salles, MD, PhD, of the University Hospital of Lyon France, presented results from the trial at the 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA) as abstract S100.
The trial is sponsored by Epizyme, Inc.
In April, Epizyme announced that all US-based trials of tazemetostat had been placed on partial hold after a pediatric patient on a phase 1 trial developed secondary T-cell lymphoma.
Enrollment was stopped in all the trials, but patients could continue receiving tazemetostat if they had not progressed on the drug.
The phase 2 trial of tazemetostat in non-Hodgkin lymphoma has enrolled 89 adults with relapsed/refractory FL.
At EHA, Dr Salles presented results in 82 of these patients. There were 28 patients with EZH2-mutated FL and 54 with EZH2-WT FL.
The median age was 61 in both cohorts. Forty-three percent of EZH2-mutated and 63% of WT patients were male.
EZH2-mutated patients had a median of 3 prior therapies, and WT patients had a median of 4. Thirty-eight percent and 42%, respectively, were refractory to their last therapy. Eleven percent and 39%, respectively, had received prior transplant.
The median time from diagnosis was 5.1 years for EZH2-mutated patients and 6.4 years for WT patients. The median time from last prior therapy was 18.4 weeks and 28.1 weeks, respectively.
The patients received tazemetostat at 800 mg twice daily until disease progression or withdrawal.
Safety
In all 82 patients, the rate of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) was 95%, and the rate of treatment-related AEs was 78%. The rate of grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs was 17%, and the rate of serious treatment-related AEs was 4%.
Six percent of patients discontinued treatment due to a related AE, 18% had a dose interruption, and 5% had a dose reduction due to a related AE.
Treatment-related AEs included nausea (20%), fatigue (13%), anemia (13%), diarrhea (11%), alopecia (11%), asthenia (10%), thrombocytopenia (10%), muscle spasms (6%), bronchitis (5%), vomiting (5%), headache (5%), abdominal pain (2%), pyrexia (1%), and cough (1%).
Grade 3 or higher treatment-related AEs included thrombocytopenia (4%), anemia (4%), fatigue (1%), and asthenia (1%).
Efficacy
In the EZH2-mutated cohort, the ORR was 71% (n=20). Eleven percent of patients (n=3) achieved a complete response, and 61% (n=17) had a partial response.
Twenty-nine percent (n=8) had stable disease as their best response. And 21% (n=6) of patients are still on study with stable disease.
All patients in this cohort experienced a reduction in tumor burden. None of the patients had progressive disease as their best response.
At the time of analysis (May 1, 2018), the median DOR was 32.3 weeks, and 55% of responders (n=11) had an ongoing response.
The median progression-free survival was 48.6 weeks.
In patients with WT EZH2 (n=54), the ORR was 33% (n=18). Six percent of patients (n=3) achieved a complete response, and 28% (n=15) had a partial response.
Thirty-one percent of patients (n=17) had stable disease as their best response, including 1 patient who is still receiving treatment.
Thirty-one percent of patients (n=17) progressed. For 4% (n=2), their response status was unknown.
At the time of analysis, the median DOR was 76 weeks, and 56% of responders (n=10) had an ongoing response.
The median progression-free survival was 29.9 weeks.
“I am impressed by the sustained clinical activity and the good tolerability of tazemetostat in this heavily pretreated patient population,” Dr Salles said. “This is important for patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma, as both the response rates and durations of response usually tend to decrease with each successive line of treatment.”
“I believe tazemetostat has the potential to fill a significant unmet need for these patients, and continued investigation of tazemetostat as a single agent or in combination with other agents is warranted.”
Epizyme’s president and chief executive officer, Robert Bazemore, said the company is still working to resolve the partial clinical hold on tazemetostat trials and is “making good progress.”
Group updates guidelines on CLL
Recent advances in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) have prompted an update to the 2008 International Workshop in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (iwCLL) consensus guidelines.
The updated iwCLL guidelines include new information on genomic alterations, the use of clinical staging and prognostic markers/scores, response assessment, minimal residual disease (MRD), and viral diseases in CLL patients.
The update was recently published in Blood.
Diagnosis, prognosis, and staging
To verify CLL diagnosis, the iwCLL guidelines recommend obtaining complete blood counts and differential counts as well as immunophenotyping of peripheral blood lymphocytes. A panel of CD19, CD5, CD20, CD23, κ, and λ typically suffices to establish a diagnosis.
Other tests that may help in prognosis or assessing tumor burden include molecular cytogenetics for del(13q), del(11q), del(17p), and add(12) in peripheral blood lymphocytes and determining TP53 and IGHV mutational status.
These tests can help identify poor-prognosis patients who are not likely to benefit from standard chemotherapy but are likely to benefit from small-molecule inhibitors of BTK, PI3K, or BCL2.
In addition, serum markers such as β2-microglogulin provide insight into overall survival and progression-free survival.
With regard to clinical staging, the guidelines highlight the Binet and Rai systems, which are routinely used in clinical practice and clinical trials.
However, the guidelines also note that “there are a large number of biomarkers that can provide additional prognostic information,” and, recently, “several prognostic scores and stratification systems have been proposed based on multivariate analyses.”
For example, the CLL international prognostic index (CLL-IPI) provides a weighted score that uses clinical stage, age, IGHV mutational status, β2-microglogulin, and the presence of del(17p) and/or TP53 mutations.
Indications for treatment
The guidelines note that active disease must be documented to initiate therapy. At least 1 of the following criteria must be met:
- Evidence of progressive marrow failure
- Massive, progressive, or symptomatic splenomegaly
- Progressive/symptomatic lymphadenopathy or massive nodes
- Progressive lymphocytosis
- Autoimmune complications
- Extranodal involvement
- Disease-related symptoms (unintentional weight loss, significant fatigue, fevers, night sweats for over a month without evidence of infection).
Following relapse, subsequent lines of treatment should follow the same principles as those used for initial treatment decisions.
Response, MRD, and more
The guidelines say 2 groups of parameters must be assessed to determine response to therapy:
- Group A: lymphoid tumor load and constitutional symptoms, including liver and/or spleen size, lymph node evaluation, and circulating lymphocyte count
- Group B: the hematopoietic system (platelet count, hemoglobin, and marrow).
For therapies with a defined treatment duration, response should be assessed at least 2 months after treatment is completed. For continued therapies or maintenance, response should be assessed at a predefined time point or at least 2 months after patients achieve their maximum response.
The guidelines also say MRD should be assessed in clinical trials aimed at maximizing the depth of remission. Furthermore, it “may be important” to confirm MRD negativity in the blood and marrow, as there are therapies that preferentially clear the blood but not the marrow (such as monoclonal antibodies).
In addition to the aforementioned recommendations, the updated iwCLL guidelines also include information on patient eligibility for clinical trials, guidance regarding treatment-related toxicities, and recommendations for supportive care and managing complications.
Recent advances in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) have prompted an update to the 2008 International Workshop in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (iwCLL) consensus guidelines.
The updated iwCLL guidelines include new information on genomic alterations, the use of clinical staging and prognostic markers/scores, response assessment, minimal residual disease (MRD), and viral diseases in CLL patients.
The update was recently published in Blood.
Diagnosis, prognosis, and staging
To verify CLL diagnosis, the iwCLL guidelines recommend obtaining complete blood counts and differential counts as well as immunophenotyping of peripheral blood lymphocytes. A panel of CD19, CD5, CD20, CD23, κ, and λ typically suffices to establish a diagnosis.
Other tests that may help in prognosis or assessing tumor burden include molecular cytogenetics for del(13q), del(11q), del(17p), and add(12) in peripheral blood lymphocytes and determining TP53 and IGHV mutational status.
These tests can help identify poor-prognosis patients who are not likely to benefit from standard chemotherapy but are likely to benefit from small-molecule inhibitors of BTK, PI3K, or BCL2.
In addition, serum markers such as β2-microglogulin provide insight into overall survival and progression-free survival.
With regard to clinical staging, the guidelines highlight the Binet and Rai systems, which are routinely used in clinical practice and clinical trials.
However, the guidelines also note that “there are a large number of biomarkers that can provide additional prognostic information,” and, recently, “several prognostic scores and stratification systems have been proposed based on multivariate analyses.”
For example, the CLL international prognostic index (CLL-IPI) provides a weighted score that uses clinical stage, age, IGHV mutational status, β2-microglogulin, and the presence of del(17p) and/or TP53 mutations.
Indications for treatment
The guidelines note that active disease must be documented to initiate therapy. At least 1 of the following criteria must be met:
- Evidence of progressive marrow failure
- Massive, progressive, or symptomatic splenomegaly
- Progressive/symptomatic lymphadenopathy or massive nodes
- Progressive lymphocytosis
- Autoimmune complications
- Extranodal involvement
- Disease-related symptoms (unintentional weight loss, significant fatigue, fevers, night sweats for over a month without evidence of infection).
Following relapse, subsequent lines of treatment should follow the same principles as those used for initial treatment decisions.
Response, MRD, and more
The guidelines say 2 groups of parameters must be assessed to determine response to therapy:
- Group A: lymphoid tumor load and constitutional symptoms, including liver and/or spleen size, lymph node evaluation, and circulating lymphocyte count
- Group B: the hematopoietic system (platelet count, hemoglobin, and marrow).
For therapies with a defined treatment duration, response should be assessed at least 2 months after treatment is completed. For continued therapies or maintenance, response should be assessed at a predefined time point or at least 2 months after patients achieve their maximum response.
The guidelines also say MRD should be assessed in clinical trials aimed at maximizing the depth of remission. Furthermore, it “may be important” to confirm MRD negativity in the blood and marrow, as there are therapies that preferentially clear the blood but not the marrow (such as monoclonal antibodies).
In addition to the aforementioned recommendations, the updated iwCLL guidelines also include information on patient eligibility for clinical trials, guidance regarding treatment-related toxicities, and recommendations for supportive care and managing complications.
Recent advances in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) have prompted an update to the 2008 International Workshop in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (iwCLL) consensus guidelines.
The updated iwCLL guidelines include new information on genomic alterations, the use of clinical staging and prognostic markers/scores, response assessment, minimal residual disease (MRD), and viral diseases in CLL patients.
The update was recently published in Blood.
Diagnosis, prognosis, and staging
To verify CLL diagnosis, the iwCLL guidelines recommend obtaining complete blood counts and differential counts as well as immunophenotyping of peripheral blood lymphocytes. A panel of CD19, CD5, CD20, CD23, κ, and λ typically suffices to establish a diagnosis.
Other tests that may help in prognosis or assessing tumor burden include molecular cytogenetics for del(13q), del(11q), del(17p), and add(12) in peripheral blood lymphocytes and determining TP53 and IGHV mutational status.
These tests can help identify poor-prognosis patients who are not likely to benefit from standard chemotherapy but are likely to benefit from small-molecule inhibitors of BTK, PI3K, or BCL2.
In addition, serum markers such as β2-microglogulin provide insight into overall survival and progression-free survival.
With regard to clinical staging, the guidelines highlight the Binet and Rai systems, which are routinely used in clinical practice and clinical trials.
However, the guidelines also note that “there are a large number of biomarkers that can provide additional prognostic information,” and, recently, “several prognostic scores and stratification systems have been proposed based on multivariate analyses.”
For example, the CLL international prognostic index (CLL-IPI) provides a weighted score that uses clinical stage, age, IGHV mutational status, β2-microglogulin, and the presence of del(17p) and/or TP53 mutations.
Indications for treatment
The guidelines note that active disease must be documented to initiate therapy. At least 1 of the following criteria must be met:
- Evidence of progressive marrow failure
- Massive, progressive, or symptomatic splenomegaly
- Progressive/symptomatic lymphadenopathy or massive nodes
- Progressive lymphocytosis
- Autoimmune complications
- Extranodal involvement
- Disease-related symptoms (unintentional weight loss, significant fatigue, fevers, night sweats for over a month without evidence of infection).
Following relapse, subsequent lines of treatment should follow the same principles as those used for initial treatment decisions.
Response, MRD, and more
The guidelines say 2 groups of parameters must be assessed to determine response to therapy:
- Group A: lymphoid tumor load and constitutional symptoms, including liver and/or spleen size, lymph node evaluation, and circulating lymphocyte count
- Group B: the hematopoietic system (platelet count, hemoglobin, and marrow).
For therapies with a defined treatment duration, response should be assessed at least 2 months after treatment is completed. For continued therapies or maintenance, response should be assessed at a predefined time point or at least 2 months after patients achieve their maximum response.
The guidelines also say MRD should be assessed in clinical trials aimed at maximizing the depth of remission. Furthermore, it “may be important” to confirm MRD negativity in the blood and marrow, as there are therapies that preferentially clear the blood but not the marrow (such as monoclonal antibodies).
In addition to the aforementioned recommendations, the updated iwCLL guidelines also include information on patient eligibility for clinical trials, guidance regarding treatment-related toxicities, and recommendations for supportive care and managing complications.
CPI-613 receives orphan designation for BL
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted orphan drug designation to CPI-613 for the treatment of Burkitt lymphoma (BL).
CPI-613 is a novel lipoic acid analogue that inhibits multiple enzyme targets within the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
The drug is in development as a treatment for hematologic malignancies and solid tumors.
In a phase 1 trial of patients with advanced hematologic malignancies, CPI-613 produced a response in a patient with relapsed BL.
Now, Rafael Pharmaceuticals, Inc., the company developing CPI-613, is launching a phase 2 trial of the drug in patients with relapsed or refractory BL and high-grade B-cell lymphoma with rearrangements of MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6.
In the phase 1 trial, the patient with relapsed BL achieved a partial response to CPI-613 monotherapy and was ultimately cleared of disease after surgery.
The patient, a 19-year-old female, began taking CPI-613 (2940 mg/m2) after her second relapse. She achieved a radiographic partial response after the third cycle of CPI-613.
The patient completed 17 cycles of CPI-613 over 51 weeks. She decided to stop treatment after the 17th cycle to pursue a surgical resection of residual tumor. The pathology of the surgical specimen revealed BL with extensive necrosis.
Clinical follow-up on the patient showed no evidence of disease more than 36 months later. And CPI-613 was considered well tolerated in this patient.
About orphan designation
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted orphan drug designation to CPI-613 for the treatment of Burkitt lymphoma (BL).
CPI-613 is a novel lipoic acid analogue that inhibits multiple enzyme targets within the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
The drug is in development as a treatment for hematologic malignancies and solid tumors.
In a phase 1 trial of patients with advanced hematologic malignancies, CPI-613 produced a response in a patient with relapsed BL.
Now, Rafael Pharmaceuticals, Inc., the company developing CPI-613, is launching a phase 2 trial of the drug in patients with relapsed or refractory BL and high-grade B-cell lymphoma with rearrangements of MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6.
In the phase 1 trial, the patient with relapsed BL achieved a partial response to CPI-613 monotherapy and was ultimately cleared of disease after surgery.
The patient, a 19-year-old female, began taking CPI-613 (2940 mg/m2) after her second relapse. She achieved a radiographic partial response after the third cycle of CPI-613.
The patient completed 17 cycles of CPI-613 over 51 weeks. She decided to stop treatment after the 17th cycle to pursue a surgical resection of residual tumor. The pathology of the surgical specimen revealed BL with extensive necrosis.
Clinical follow-up on the patient showed no evidence of disease more than 36 months later. And CPI-613 was considered well tolerated in this patient.
About orphan designation
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted orphan drug designation to CPI-613 for the treatment of Burkitt lymphoma (BL).
CPI-613 is a novel lipoic acid analogue that inhibits multiple enzyme targets within the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
The drug is in development as a treatment for hematologic malignancies and solid tumors.
In a phase 1 trial of patients with advanced hematologic malignancies, CPI-613 produced a response in a patient with relapsed BL.
Now, Rafael Pharmaceuticals, Inc., the company developing CPI-613, is launching a phase 2 trial of the drug in patients with relapsed or refractory BL and high-grade B-cell lymphoma with rearrangements of MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6.
In the phase 1 trial, the patient with relapsed BL achieved a partial response to CPI-613 monotherapy and was ultimately cleared of disease after surgery.
The patient, a 19-year-old female, began taking CPI-613 (2940 mg/m2) after her second relapse. She achieved a radiographic partial response after the third cycle of CPI-613.
The patient completed 17 cycles of CPI-613 over 51 weeks. She decided to stop treatment after the 17th cycle to pursue a surgical resection of residual tumor. The pathology of the surgical specimen revealed BL with extensive necrosis.
Clinical follow-up on the patient showed no evidence of disease more than 36 months later. And CPI-613 was considered well tolerated in this patient.
About orphan designation
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
Ibrutinib sNDA receives priority review
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has accepted for priority review a supplemental new drug application (sNDA) for ibrutinib (Imbruvica®) to be used in combination with rituximab in patients with Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
The FDA intends to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
Ibrutinib is a first-in-class Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor jointly developed and commercialized by Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie company, and Janssen Biotech, Inc.
Ibrutinib is already FDA-approved to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, previously treated mantle cell lymphoma, previously treated marginal zone lymphoma, previously treated chronic graft-versus-host disease, and WM.
If the new sNDA is approved, the use of ibrutinib in WM will extend beyond its current approved use as a single agent.
Phase 3 trial
The sNDA for ibrutinib and rituximab in WM is supported by data from the phase 3 iNNOVATE study. Results from this trial were presented at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 8003) and were simultaneously published in NEJM.
iNNOVATE is a placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 study that enrolled 150 patients with relapsed/refractory and treatment-naïve WM.
All patients received rituximab at 375 mg/m2 with weekly infusions at weeks 1 to 4 and 17 to 20. They also received either ibrutinib (420 mg) or placebo once daily continuously until criteria for permanent discontinuation were met.
Overall response rates were significantly higher in the ibrutinib arm than the placebo arm—92% and 47%, respectively (P<0.0001). Complete response rates were 3% and 1%, respectively.
The median time to next treatment was not reached for the ibrutinib arm and was 18 months for the placebo arm (hazard ratio=0.096; P<0.0001). Of the patients randomized to ibrutinib plus rituximab, 75% continued on treatment at last follow-up.
The 30-month progression-free survival rates were 82% in the ibrutinib arm and 28% in the placebo arm. The median progression-free survival was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 20.3 months in the placebo arm (hazard ratio=0.20; P<0.0001).
The 30-month overall survival rates were 94% in the ibrutinib arm and 92% in the placebo arm.
Grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) occurred in 60% of patients in the ibrutinib arm and 61% in the placebo arm.
Serious AEs occurred in 43% and 33% of patients, respectively. There were no fatal AEs in the ibrutinib arm and 3 in the rituximab arm.
Grade 3 or higher AEs that occurred more frequently in the ibrutinib arm than the placebo arm included atrial fibrillation (12% vs 1%) and hypertension (13% vs 4%).
AEs that occurred less frequently in the ibrutinib arm than the placebo arm included grade 3 or higher infusion reactions (1% vs 16%) and any-grade IgM flare (8% vs 47%).
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has accepted for priority review a supplemental new drug application (sNDA) for ibrutinib (Imbruvica®) to be used in combination with rituximab in patients with Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
The FDA intends to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
Ibrutinib is a first-in-class Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor jointly developed and commercialized by Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie company, and Janssen Biotech, Inc.
Ibrutinib is already FDA-approved to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, previously treated mantle cell lymphoma, previously treated marginal zone lymphoma, previously treated chronic graft-versus-host disease, and WM.
If the new sNDA is approved, the use of ibrutinib in WM will extend beyond its current approved use as a single agent.
Phase 3 trial
The sNDA for ibrutinib and rituximab in WM is supported by data from the phase 3 iNNOVATE study. Results from this trial were presented at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 8003) and were simultaneously published in NEJM.
iNNOVATE is a placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 study that enrolled 150 patients with relapsed/refractory and treatment-naïve WM.
All patients received rituximab at 375 mg/m2 with weekly infusions at weeks 1 to 4 and 17 to 20. They also received either ibrutinib (420 mg) or placebo once daily continuously until criteria for permanent discontinuation were met.
Overall response rates were significantly higher in the ibrutinib arm than the placebo arm—92% and 47%, respectively (P<0.0001). Complete response rates were 3% and 1%, respectively.
The median time to next treatment was not reached for the ibrutinib arm and was 18 months for the placebo arm (hazard ratio=0.096; P<0.0001). Of the patients randomized to ibrutinib plus rituximab, 75% continued on treatment at last follow-up.
The 30-month progression-free survival rates were 82% in the ibrutinib arm and 28% in the placebo arm. The median progression-free survival was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 20.3 months in the placebo arm (hazard ratio=0.20; P<0.0001).
The 30-month overall survival rates were 94% in the ibrutinib arm and 92% in the placebo arm.
Grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) occurred in 60% of patients in the ibrutinib arm and 61% in the placebo arm.
Serious AEs occurred in 43% and 33% of patients, respectively. There were no fatal AEs in the ibrutinib arm and 3 in the rituximab arm.
Grade 3 or higher AEs that occurred more frequently in the ibrutinib arm than the placebo arm included atrial fibrillation (12% vs 1%) and hypertension (13% vs 4%).
AEs that occurred less frequently in the ibrutinib arm than the placebo arm included grade 3 or higher infusion reactions (1% vs 16%) and any-grade IgM flare (8% vs 47%).
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has accepted for priority review a supplemental new drug application (sNDA) for ibrutinib (Imbruvica®) to be used in combination with rituximab in patients with Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
The FDA intends to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it, rather than the standard 10 months.
The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that may provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
Ibrutinib is a first-in-class Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor jointly developed and commercialized by Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie company, and Janssen Biotech, Inc.
Ibrutinib is already FDA-approved to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, previously treated mantle cell lymphoma, previously treated marginal zone lymphoma, previously treated chronic graft-versus-host disease, and WM.
If the new sNDA is approved, the use of ibrutinib in WM will extend beyond its current approved use as a single agent.
Phase 3 trial
The sNDA for ibrutinib and rituximab in WM is supported by data from the phase 3 iNNOVATE study. Results from this trial were presented at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 8003) and were simultaneously published in NEJM.
iNNOVATE is a placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 study that enrolled 150 patients with relapsed/refractory and treatment-naïve WM.
All patients received rituximab at 375 mg/m2 with weekly infusions at weeks 1 to 4 and 17 to 20. They also received either ibrutinib (420 mg) or placebo once daily continuously until criteria for permanent discontinuation were met.
Overall response rates were significantly higher in the ibrutinib arm than the placebo arm—92% and 47%, respectively (P<0.0001). Complete response rates were 3% and 1%, respectively.
The median time to next treatment was not reached for the ibrutinib arm and was 18 months for the placebo arm (hazard ratio=0.096; P<0.0001). Of the patients randomized to ibrutinib plus rituximab, 75% continued on treatment at last follow-up.
The 30-month progression-free survival rates were 82% in the ibrutinib arm and 28% in the placebo arm. The median progression-free survival was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 20.3 months in the placebo arm (hazard ratio=0.20; P<0.0001).
The 30-month overall survival rates were 94% in the ibrutinib arm and 92% in the placebo arm.
Grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) occurred in 60% of patients in the ibrutinib arm and 61% in the placebo arm.
Serious AEs occurred in 43% and 33% of patients, respectively. There were no fatal AEs in the ibrutinib arm and 3 in the rituximab arm.
Grade 3 or higher AEs that occurred more frequently in the ibrutinib arm than the placebo arm included atrial fibrillation (12% vs 1%) and hypertension (13% vs 4%).
AEs that occurred less frequently in the ibrutinib arm than the placebo arm included grade 3 or higher infusion reactions (1% vs 16%) and any-grade IgM flare (8% vs 47%).
T-cell therapy induced CMRs with no CRS
CHICAGO—A novel CD19-targeted T-cell therapy induced complete metabolic responses (CMRs) and no cytokine release syndrome (CRS) in patients with B-cell lymphomas in a first-in-human clinical study.
All subjects achieving CMR at the 1-month safety and efficacy assessment continued to show CMR at 3 months, investigators reported at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 3049*).
The therapy is built on a novel platform, ARTEMIS, designed to match the potency of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy but trigger less cytokine release when the target is engaged, investigators explained.
That platform is “potentially a major improvement” over existing CAR-T cell therapy, said Zhi Tao Ying, MD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute in Beijing, China, and coauthors in a poster presented at ASCO.
The treatment, called ET190L1-ARTEMIS, utilizes the T-cell receptor platform and a proprietary human anti-CD19 antibody to target CD19-positive malignancies.
The investigators reported on 21 adults with CD-19 positive relapsed and refractory B-cell lymphomas who had received a median of 4 lines of previous therapy.
Patients received autologous ET190L1-ARTEMIS T cells in 1 of 3 dosing cohorts: 3 patients at 1 x 106/kg, 13 at 3 x 106/kg, and 5 at 6 x 106/kg.
Of 17 patients completing a first-month efficacy assessment, 11 (65%) responded, including 7 CMRs and 3 partial responses. One patient had stable disease.
Seven of the 11 responders completed a third-month efficacy assessment, as of this analysis. Of 5 patients with CMR at month 1, all 5 maintained CMR at month 3. Likewise, 1 patient in partial response and 1 with stable disease at month 1 had the same response status at month 3.
There were no cases of CRS or neurotoxicity in 17 patients who completed the 1-month safety and efficacy assessment reported at ASCO. Grade 3 or greater adverse events in those subjects included lymphopenia in 17 (100%) and neutropenia in 5 (29%).
Eureka Therapeutics Inc., of Emeryville, California, is developing ET190L1-ARTEMIS. Co-investigators in this trial were from Eureka, Xi-An Jiaotong University in China, and Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina.
A phase 1 trial of ET190L1-ARTEMIS in patients with relapsed and refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma has been initiated at Duke University, and investigators say another US phase 1 trial including relapsed and refractory pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients will begin later this year.
Data in the abstract differ from that presented in the poster.
CHICAGO—A novel CD19-targeted T-cell therapy induced complete metabolic responses (CMRs) and no cytokine release syndrome (CRS) in patients with B-cell lymphomas in a first-in-human clinical study.
All subjects achieving CMR at the 1-month safety and efficacy assessment continued to show CMR at 3 months, investigators reported at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 3049*).
The therapy is built on a novel platform, ARTEMIS, designed to match the potency of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy but trigger less cytokine release when the target is engaged, investigators explained.
That platform is “potentially a major improvement” over existing CAR-T cell therapy, said Zhi Tao Ying, MD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute in Beijing, China, and coauthors in a poster presented at ASCO.
The treatment, called ET190L1-ARTEMIS, utilizes the T-cell receptor platform and a proprietary human anti-CD19 antibody to target CD19-positive malignancies.
The investigators reported on 21 adults with CD-19 positive relapsed and refractory B-cell lymphomas who had received a median of 4 lines of previous therapy.
Patients received autologous ET190L1-ARTEMIS T cells in 1 of 3 dosing cohorts: 3 patients at 1 x 106/kg, 13 at 3 x 106/kg, and 5 at 6 x 106/kg.
Of 17 patients completing a first-month efficacy assessment, 11 (65%) responded, including 7 CMRs and 3 partial responses. One patient had stable disease.
Seven of the 11 responders completed a third-month efficacy assessment, as of this analysis. Of 5 patients with CMR at month 1, all 5 maintained CMR at month 3. Likewise, 1 patient in partial response and 1 with stable disease at month 1 had the same response status at month 3.
There were no cases of CRS or neurotoxicity in 17 patients who completed the 1-month safety and efficacy assessment reported at ASCO. Grade 3 or greater adverse events in those subjects included lymphopenia in 17 (100%) and neutropenia in 5 (29%).
Eureka Therapeutics Inc., of Emeryville, California, is developing ET190L1-ARTEMIS. Co-investigators in this trial were from Eureka, Xi-An Jiaotong University in China, and Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina.
A phase 1 trial of ET190L1-ARTEMIS in patients with relapsed and refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma has been initiated at Duke University, and investigators say another US phase 1 trial including relapsed and refractory pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients will begin later this year.
Data in the abstract differ from that presented in the poster.
CHICAGO—A novel CD19-targeted T-cell therapy induced complete metabolic responses (CMRs) and no cytokine release syndrome (CRS) in patients with B-cell lymphomas in a first-in-human clinical study.
All subjects achieving CMR at the 1-month safety and efficacy assessment continued to show CMR at 3 months, investigators reported at the 2018 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 3049*).
The therapy is built on a novel platform, ARTEMIS, designed to match the potency of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy but trigger less cytokine release when the target is engaged, investigators explained.
That platform is “potentially a major improvement” over existing CAR-T cell therapy, said Zhi Tao Ying, MD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute in Beijing, China, and coauthors in a poster presented at ASCO.
The treatment, called ET190L1-ARTEMIS, utilizes the T-cell receptor platform and a proprietary human anti-CD19 antibody to target CD19-positive malignancies.
The investigators reported on 21 adults with CD-19 positive relapsed and refractory B-cell lymphomas who had received a median of 4 lines of previous therapy.
Patients received autologous ET190L1-ARTEMIS T cells in 1 of 3 dosing cohorts: 3 patients at 1 x 106/kg, 13 at 3 x 106/kg, and 5 at 6 x 106/kg.
Of 17 patients completing a first-month efficacy assessment, 11 (65%) responded, including 7 CMRs and 3 partial responses. One patient had stable disease.
Seven of the 11 responders completed a third-month efficacy assessment, as of this analysis. Of 5 patients with CMR at month 1, all 5 maintained CMR at month 3. Likewise, 1 patient in partial response and 1 with stable disease at month 1 had the same response status at month 3.
There were no cases of CRS or neurotoxicity in 17 patients who completed the 1-month safety and efficacy assessment reported at ASCO. Grade 3 or greater adverse events in those subjects included lymphopenia in 17 (100%) and neutropenia in 5 (29%).
Eureka Therapeutics Inc., of Emeryville, California, is developing ET190L1-ARTEMIS. Co-investigators in this trial were from Eureka, Xi-An Jiaotong University in China, and Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina.
A phase 1 trial of ET190L1-ARTEMIS in patients with relapsed and refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma has been initiated at Duke University, and investigators say another US phase 1 trial including relapsed and refractory pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients will begin later this year.
Data in the abstract differ from that presented in the poster.
Inhibitor exhibits activity in B- and T-cell NHLs
STOCKHOLM—The dual SYK/JAK inhibitor cerdulatinib has demonstrated efficacy in a phase 2 trial of patients with heavily pretreated B- and T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs).
There were a few deaths due to sepsis or septic shock that were considered related to cerdulatinib, but investigators have taken steps to prevent additional deaths.
Cerdulatinib produced responses in patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL), cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), follicular lymphoma (FL), and other NHLs.
The 5 deaths due to sepsis or septic shock (3 concomitant with pneumonia) occurred early on in the trial, and dose reductions, monitoring, and antibiotic prophylaxis appeared to be effective in preventing additional deaths.
Results from this trial were presented in a poster (abstract PF437) at the 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA).
The research was sponsored by Portola Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
The trial enrolled 114 patients. They had FL (grade 1-3A; n=39), PTCL (n=25), CTCL (n=5), CLL/SLL (n=28), other indolent NHLs (Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia and marginal zone lymphoma; n=12), or aggressive NHL (defined as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [DLBCL], grade 3B FL, mantle cell lymphoma, and transformed NHL with relapsed disease; n=5).
The patients’ median age was 68 (range, 34-93), and 59% were male. The median number of prior treatment regimens was 3 (range, 1-13), and 37% of patients had refractory disease.
Patients received cerdulatinib at 25, 30, or 35 mg twice daily (BID). A total of 101 patients were evaluable as of May 4, 2018.
Response
The objective response rate (ORR) was 47% in the entire population. Thirteen patients achieved a complete response (CR), and 34 had a partial response (PR). Thirty-four patients remained on cerdulatinib at the data cut-off.
The ORR was 46% in the FL patients, with 3 patients achieving a CR and 13 achieving a PR. Thirteen FL patients remained on cerdulatinib.
In the CLL/SLL patients, the ORR was 61%. Two patients had a CR, and 15 had a PR. Four CLL/SLL patients remained on cerdulatinib.
In PTCL, the ORR was 35%. All 7 responders had a CR. Eleven PTCL patients remained on cerdulatinib.
Only 1 CTCL patient was evaluable, but this patient achieved a CR and remained on cerdulatinib.
The ORR was 42% for patients with other indolent NHLs, with 5 PRs and no CRs. Only 1 patient in this group remained on cerdulatinib.
For aggressive NHL, the ORR was 20%, with 1 PR and no CRs. None of the patients in this group stayed on cerdulatinib.
“Cerdulatinib continues to demonstrate promising results across a wide range of B- and T-cell malignancies, including early indications of the potential for durable responses,” said study investigator Paul Hamlin, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, New York.
“The new signals in relapsed/refractory PTCL and CTCL are particularly compelling when you consider the limited treatment options for patients that fail frontline therapy.”
Safety
Grade 3 or higher adverse events included lipase increase (18%), neutropenia (17%), pneumonia/lung infection (11%), diarrhea (8%), fatigue (6%), amylase increase (5%), sepsis/septic shock (4%), hypertension (4%), anemia (4%), thrombocytopenia (4%), and hypophosphatemia (4%).
The 5 deaths due to sepsis or septic shock (3 of which were concomitant with pneumonia) were considered related to cerdulatinib. Three of the deaths occurred in patients with CLL, 1 in a DLBCL patient, and 1 in an FL patient.
“One of the things we have seen [with CLL patients] is the background infection rate is quite a bit higher,” said John T. Curnutte, MD, PhD, interim co-president and head of research and development at Portola Pharmaceuticals.
“You see this with multiple other agents, so we were not particularly surprised to see [sepsis/septic shock in CLL].”
Dr Curnutte noted that grade 5 sepsis/septic shock tended to occur in patients who were pre-colonized and/or had high plasma levels of cerdulatinib.
So, to prevent these adverse events, the starting dose of cerdulatinib was lowered, investigators began monitoring patients’ plasma levels, and all patients began receiving antibiotic prophylaxis. (Previously, only CLL patients had received this prophylaxis.)
The investigators found that lowering the starting dose from 35 mg BID to 30 mg or even 25 mg BID reduced plasma levels.
“At the 35 mg dose, 1 out of every 4 patients showed accumulation of the drug,” Dr Curnutte said. “In general, the use of the 30 mg BID or step-down 25 mg BID did not result in accumulation of drug.”
Dr Curnutte also noted that enrollment of CLL/SLL patients is complete, and investigators would be “very careful” if the study were to be re-opened to these patients.
For now, Portola is focused on completing enrollment in other patient groups on this phase 2 trial. The company is also hoping to conduct a phase 3 trial of cerdulatinib in PTCL that could begin as early as the end of this year.
STOCKHOLM—The dual SYK/JAK inhibitor cerdulatinib has demonstrated efficacy in a phase 2 trial of patients with heavily pretreated B- and T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs).
There were a few deaths due to sepsis or septic shock that were considered related to cerdulatinib, but investigators have taken steps to prevent additional deaths.
Cerdulatinib produced responses in patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL), cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), follicular lymphoma (FL), and other NHLs.
The 5 deaths due to sepsis or septic shock (3 concomitant with pneumonia) occurred early on in the trial, and dose reductions, monitoring, and antibiotic prophylaxis appeared to be effective in preventing additional deaths.
Results from this trial were presented in a poster (abstract PF437) at the 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA).
The research was sponsored by Portola Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
The trial enrolled 114 patients. They had FL (grade 1-3A; n=39), PTCL (n=25), CTCL (n=5), CLL/SLL (n=28), other indolent NHLs (Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia and marginal zone lymphoma; n=12), or aggressive NHL (defined as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [DLBCL], grade 3B FL, mantle cell lymphoma, and transformed NHL with relapsed disease; n=5).
The patients’ median age was 68 (range, 34-93), and 59% were male. The median number of prior treatment regimens was 3 (range, 1-13), and 37% of patients had refractory disease.
Patients received cerdulatinib at 25, 30, or 35 mg twice daily (BID). A total of 101 patients were evaluable as of May 4, 2018.
Response
The objective response rate (ORR) was 47% in the entire population. Thirteen patients achieved a complete response (CR), and 34 had a partial response (PR). Thirty-four patients remained on cerdulatinib at the data cut-off.
The ORR was 46% in the FL patients, with 3 patients achieving a CR and 13 achieving a PR. Thirteen FL patients remained on cerdulatinib.
In the CLL/SLL patients, the ORR was 61%. Two patients had a CR, and 15 had a PR. Four CLL/SLL patients remained on cerdulatinib.
In PTCL, the ORR was 35%. All 7 responders had a CR. Eleven PTCL patients remained on cerdulatinib.
Only 1 CTCL patient was evaluable, but this patient achieved a CR and remained on cerdulatinib.
The ORR was 42% for patients with other indolent NHLs, with 5 PRs and no CRs. Only 1 patient in this group remained on cerdulatinib.
For aggressive NHL, the ORR was 20%, with 1 PR and no CRs. None of the patients in this group stayed on cerdulatinib.
“Cerdulatinib continues to demonstrate promising results across a wide range of B- and T-cell malignancies, including early indications of the potential for durable responses,” said study investigator Paul Hamlin, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, New York.
“The new signals in relapsed/refractory PTCL and CTCL are particularly compelling when you consider the limited treatment options for patients that fail frontline therapy.”
Safety
Grade 3 or higher adverse events included lipase increase (18%), neutropenia (17%), pneumonia/lung infection (11%), diarrhea (8%), fatigue (6%), amylase increase (5%), sepsis/septic shock (4%), hypertension (4%), anemia (4%), thrombocytopenia (4%), and hypophosphatemia (4%).
The 5 deaths due to sepsis or septic shock (3 of which were concomitant with pneumonia) were considered related to cerdulatinib. Three of the deaths occurred in patients with CLL, 1 in a DLBCL patient, and 1 in an FL patient.
“One of the things we have seen [with CLL patients] is the background infection rate is quite a bit higher,” said John T. Curnutte, MD, PhD, interim co-president and head of research and development at Portola Pharmaceuticals.
“You see this with multiple other agents, so we were not particularly surprised to see [sepsis/septic shock in CLL].”
Dr Curnutte noted that grade 5 sepsis/septic shock tended to occur in patients who were pre-colonized and/or had high plasma levels of cerdulatinib.
So, to prevent these adverse events, the starting dose of cerdulatinib was lowered, investigators began monitoring patients’ plasma levels, and all patients began receiving antibiotic prophylaxis. (Previously, only CLL patients had received this prophylaxis.)
The investigators found that lowering the starting dose from 35 mg BID to 30 mg or even 25 mg BID reduced plasma levels.
“At the 35 mg dose, 1 out of every 4 patients showed accumulation of the drug,” Dr Curnutte said. “In general, the use of the 30 mg BID or step-down 25 mg BID did not result in accumulation of drug.”
Dr Curnutte also noted that enrollment of CLL/SLL patients is complete, and investigators would be “very careful” if the study were to be re-opened to these patients.
For now, Portola is focused on completing enrollment in other patient groups on this phase 2 trial. The company is also hoping to conduct a phase 3 trial of cerdulatinib in PTCL that could begin as early as the end of this year.
STOCKHOLM—The dual SYK/JAK inhibitor cerdulatinib has demonstrated efficacy in a phase 2 trial of patients with heavily pretreated B- and T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs).
There were a few deaths due to sepsis or septic shock that were considered related to cerdulatinib, but investigators have taken steps to prevent additional deaths.
Cerdulatinib produced responses in patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL), cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), follicular lymphoma (FL), and other NHLs.
The 5 deaths due to sepsis or septic shock (3 concomitant with pneumonia) occurred early on in the trial, and dose reductions, monitoring, and antibiotic prophylaxis appeared to be effective in preventing additional deaths.
Results from this trial were presented in a poster (abstract PF437) at the 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA).
The research was sponsored by Portola Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
The trial enrolled 114 patients. They had FL (grade 1-3A; n=39), PTCL (n=25), CTCL (n=5), CLL/SLL (n=28), other indolent NHLs (Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia and marginal zone lymphoma; n=12), or aggressive NHL (defined as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [DLBCL], grade 3B FL, mantle cell lymphoma, and transformed NHL with relapsed disease; n=5).
The patients’ median age was 68 (range, 34-93), and 59% were male. The median number of prior treatment regimens was 3 (range, 1-13), and 37% of patients had refractory disease.
Patients received cerdulatinib at 25, 30, or 35 mg twice daily (BID). A total of 101 patients were evaluable as of May 4, 2018.
Response
The objective response rate (ORR) was 47% in the entire population. Thirteen patients achieved a complete response (CR), and 34 had a partial response (PR). Thirty-four patients remained on cerdulatinib at the data cut-off.
The ORR was 46% in the FL patients, with 3 patients achieving a CR and 13 achieving a PR. Thirteen FL patients remained on cerdulatinib.
In the CLL/SLL patients, the ORR was 61%. Two patients had a CR, and 15 had a PR. Four CLL/SLL patients remained on cerdulatinib.
In PTCL, the ORR was 35%. All 7 responders had a CR. Eleven PTCL patients remained on cerdulatinib.
Only 1 CTCL patient was evaluable, but this patient achieved a CR and remained on cerdulatinib.
The ORR was 42% for patients with other indolent NHLs, with 5 PRs and no CRs. Only 1 patient in this group remained on cerdulatinib.
For aggressive NHL, the ORR was 20%, with 1 PR and no CRs. None of the patients in this group stayed on cerdulatinib.
“Cerdulatinib continues to demonstrate promising results across a wide range of B- and T-cell malignancies, including early indications of the potential for durable responses,” said study investigator Paul Hamlin, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, New York.
“The new signals in relapsed/refractory PTCL and CTCL are particularly compelling when you consider the limited treatment options for patients that fail frontline therapy.”
Safety
Grade 3 or higher adverse events included lipase increase (18%), neutropenia (17%), pneumonia/lung infection (11%), diarrhea (8%), fatigue (6%), amylase increase (5%), sepsis/septic shock (4%), hypertension (4%), anemia (4%), thrombocytopenia (4%), and hypophosphatemia (4%).
The 5 deaths due to sepsis or septic shock (3 of which were concomitant with pneumonia) were considered related to cerdulatinib. Three of the deaths occurred in patients with CLL, 1 in a DLBCL patient, and 1 in an FL patient.
“One of the things we have seen [with CLL patients] is the background infection rate is quite a bit higher,” said John T. Curnutte, MD, PhD, interim co-president and head of research and development at Portola Pharmaceuticals.
“You see this with multiple other agents, so we were not particularly surprised to see [sepsis/septic shock in CLL].”
Dr Curnutte noted that grade 5 sepsis/septic shock tended to occur in patients who were pre-colonized and/or had high plasma levels of cerdulatinib.
So, to prevent these adverse events, the starting dose of cerdulatinib was lowered, investigators began monitoring patients’ plasma levels, and all patients began receiving antibiotic prophylaxis. (Previously, only CLL patients had received this prophylaxis.)
The investigators found that lowering the starting dose from 35 mg BID to 30 mg or even 25 mg BID reduced plasma levels.
“At the 35 mg dose, 1 out of every 4 patients showed accumulation of the drug,” Dr Curnutte said. “In general, the use of the 30 mg BID or step-down 25 mg BID did not result in accumulation of drug.”
Dr Curnutte also noted that enrollment of CLL/SLL patients is complete, and investigators would be “very careful” if the study were to be re-opened to these patients.
For now, Portola is focused on completing enrollment in other patient groups on this phase 2 trial. The company is also hoping to conduct a phase 3 trial of cerdulatinib in PTCL that could begin as early as the end of this year.
Combo proves ‘beneficial’ for ‘unfit’ CLL patients
STOCKHOLM—Obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil (G-Clb) is a “valid and beneficial” frontline treatment option for “unfit” patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to a speaker at the 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA).
Final results from the CLL11 study have revealed additional benefits of G-Clb over rituximab plus chlorambucil (R-Clb) in patients with previously untreated CLL and comorbidities.
Prior results from this study showed that G-Clb produced higher response rates and prolonged progression-fee survival (PFS) compared to R-Clb.
Now, with a median follow-up of 5 years, researchers have found that G-Clb prolongs overall survival (OS) and time to next treatment (TTNT) as well.
Valentin Goede, MD, of the University Hospital Cologne in Germany, presented these results during the Presidential Symposium of the EHA Congress (abstract S151).
The study was sponsored by Hoffmann-La Roche.
CLL11 enrolled patients with previously untreated CLL and coexisting medical conditions. They were randomized to receive six 28-day cycles of Clb alone, G-Clb, or R-Clb.
In stage 1, researchers compared G-Clb (n=238) to Clb alone (n=118) and R-Clb (n=233) to Clb alone (n=118). In stage 2, they compared G-Clb (n=333) and R-Clb (n=330).
“The treatment arms were well-balanced, not just with regard to patient [characteristics] but also with disease characteristics,” Dr Goede said.
Overall, the median age was 73 (range, 39-90), the median Cumulative Illness Rating Scale score was 8, and the median creatinine clearance was 62 mL/min.
Efficacy: G-Clb vs Clb
The median observation time for G-Clb vs Clb was 62.5 months.
The median PFS was 31.1 months in the G-Clb arm and 11.1 months in the Clb arm. The 5-year PFS rates were 25% and 2%, respectively. The hazard ratio (HR) was 0.21 (P<0.0001).
The median OS was not reached in the G-Clb arm and was 66.7 months in the Clb arm. The 5-year OS rates were 66% and 53%, respectively. The HR was 0.68 (P=0.0196).
Thirty-nine percent of the G-Clb arm died, as did 49% of the Clb arm. The main causes of death were adverse events (AEs) and disease progression.
Efficacy: G-Clb vs R-Clb
The median observation time for G-Clb vs R-Clb was 59.4 months.
The median PFS was 28.9 months in the G-Clb arm and 15.7 months in the R-Clb arm. The 5-year PFS rates were 23% and 9%, respectively. The HR was 0.49 (P<0.0001).
“The median PFS was nearly doubled, from approximately 15 months in the rituximab arm to almost 30 months in the obinutuzumab arm,” Dr Goede said. “And this translated into a clinically meaningful prolongation of time to next treatment.”
The median TTNT was 56.4 months in the G-Clb arm and 34.9 months in the R-Clb arm. At 5 years, TTNT rates were 49% and 32%, respectively. The HR was 0.58 (P<0.0001).
“In the rituximab arm, the median time to next treatment was a little greater than 2.5 years, and, in the obinutuzumab arm, it was almost 5 years,” Dr Goede said. “From a clinical perspective, I would consider treatment-free intervals of that duration as highly relevant and beneficial in an elderly population.”
The median OS was not reached in the G-Clb arm and was 73.1 months in the R-Clb arm. The 5-year OS rates were 66% and 57%, respectively. The HR was 0.76 (P=0.0245).
“This difference is clinically meaningful, and it is also remarkable in the context of the long follow-up, given the fact that approximately half of the patients have received at least 1 salvage treatment in the meantime,” Dr Goede said.
In all, 37% of the G-Clb arm died, as did 45% of the R-Clb arm. Again, the main causes of death were AEs and disease progression.
Safety
Dr Goede said no new safety signals or late-onset toxicities were detected.
“Adverse events of any grade, but particularly grade 3-5 and serious adverse events, were more frequent in the obinutuzumab arm compared to the other 2 arms,” he noted. “[This] was mainly driven by more infusion reactions and some greater hematological toxicity.”
“Importantly, the rate of fatal adverse events, during treatment but also during follow-up, was not higher in the obinutuzumab arm. And the most common fatal adverse events were second malignancies.”
G-Clb vs Clb
Ninety-five percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 83% of those in the Clb arm had at least 1 AE. The rates of grade 3-5 AEs were 74% and 51%, respectively. The rates of serious AEs were 47% and 39%, respectively. The rates of fatal AEs were 8% and 11%, respectively.
Seventeen percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 11% of those in the Clb arm had late-onset neutropenia. The rates of prolonged neutropenia were 3% and 9%, respectively.
Fourteen percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 7% of those in the Clb arm had second malignancies (starting 6 months after treatment initiation). The most common of these were squamous cell carcinoma (2% vs 0%) and basal cell carcinoma (2% vs <1%).
G-Clb vs R-Clb
Ninety-four percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 90% of those in the R-Clb arm had at least 1 AE. The rates of grade 3-5 AEs were 72% and 60%, respectively. The rates of serious AEs were 45% and 39%, respectively. The rates of fatal AEs were 7% and 10%, respectively.
Fifteen percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 12% of those in the R-Clb arm had late-onset neutropenia. The rates of prolonged neutropenia were 2% and 4%, respectively.
Eleven percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 10% of those in the Clb arm had second malignancies. Squamous cell carcinoma occurred in 2% of patients in both arms. Basal cell carcinoma occurred in 2% of G-Clb recipients and 1% of R-Clb recipients.
STOCKHOLM—Obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil (G-Clb) is a “valid and beneficial” frontline treatment option for “unfit” patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to a speaker at the 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA).
Final results from the CLL11 study have revealed additional benefits of G-Clb over rituximab plus chlorambucil (R-Clb) in patients with previously untreated CLL and comorbidities.
Prior results from this study showed that G-Clb produced higher response rates and prolonged progression-fee survival (PFS) compared to R-Clb.
Now, with a median follow-up of 5 years, researchers have found that G-Clb prolongs overall survival (OS) and time to next treatment (TTNT) as well.
Valentin Goede, MD, of the University Hospital Cologne in Germany, presented these results during the Presidential Symposium of the EHA Congress (abstract S151).
The study was sponsored by Hoffmann-La Roche.
CLL11 enrolled patients with previously untreated CLL and coexisting medical conditions. They were randomized to receive six 28-day cycles of Clb alone, G-Clb, or R-Clb.
In stage 1, researchers compared G-Clb (n=238) to Clb alone (n=118) and R-Clb (n=233) to Clb alone (n=118). In stage 2, they compared G-Clb (n=333) and R-Clb (n=330).
“The treatment arms were well-balanced, not just with regard to patient [characteristics] but also with disease characteristics,” Dr Goede said.
Overall, the median age was 73 (range, 39-90), the median Cumulative Illness Rating Scale score was 8, and the median creatinine clearance was 62 mL/min.
Efficacy: G-Clb vs Clb
The median observation time for G-Clb vs Clb was 62.5 months.
The median PFS was 31.1 months in the G-Clb arm and 11.1 months in the Clb arm. The 5-year PFS rates were 25% and 2%, respectively. The hazard ratio (HR) was 0.21 (P<0.0001).
The median OS was not reached in the G-Clb arm and was 66.7 months in the Clb arm. The 5-year OS rates were 66% and 53%, respectively. The HR was 0.68 (P=0.0196).
Thirty-nine percent of the G-Clb arm died, as did 49% of the Clb arm. The main causes of death were adverse events (AEs) and disease progression.
Efficacy: G-Clb vs R-Clb
The median observation time for G-Clb vs R-Clb was 59.4 months.
The median PFS was 28.9 months in the G-Clb arm and 15.7 months in the R-Clb arm. The 5-year PFS rates were 23% and 9%, respectively. The HR was 0.49 (P<0.0001).
“The median PFS was nearly doubled, from approximately 15 months in the rituximab arm to almost 30 months in the obinutuzumab arm,” Dr Goede said. “And this translated into a clinically meaningful prolongation of time to next treatment.”
The median TTNT was 56.4 months in the G-Clb arm and 34.9 months in the R-Clb arm. At 5 years, TTNT rates were 49% and 32%, respectively. The HR was 0.58 (P<0.0001).
“In the rituximab arm, the median time to next treatment was a little greater than 2.5 years, and, in the obinutuzumab arm, it was almost 5 years,” Dr Goede said. “From a clinical perspective, I would consider treatment-free intervals of that duration as highly relevant and beneficial in an elderly population.”
The median OS was not reached in the G-Clb arm and was 73.1 months in the R-Clb arm. The 5-year OS rates were 66% and 57%, respectively. The HR was 0.76 (P=0.0245).
“This difference is clinically meaningful, and it is also remarkable in the context of the long follow-up, given the fact that approximately half of the patients have received at least 1 salvage treatment in the meantime,” Dr Goede said.
In all, 37% of the G-Clb arm died, as did 45% of the R-Clb arm. Again, the main causes of death were AEs and disease progression.
Safety
Dr Goede said no new safety signals or late-onset toxicities were detected.
“Adverse events of any grade, but particularly grade 3-5 and serious adverse events, were more frequent in the obinutuzumab arm compared to the other 2 arms,” he noted. “[This] was mainly driven by more infusion reactions and some greater hematological toxicity.”
“Importantly, the rate of fatal adverse events, during treatment but also during follow-up, was not higher in the obinutuzumab arm. And the most common fatal adverse events were second malignancies.”
G-Clb vs Clb
Ninety-five percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 83% of those in the Clb arm had at least 1 AE. The rates of grade 3-5 AEs were 74% and 51%, respectively. The rates of serious AEs were 47% and 39%, respectively. The rates of fatal AEs were 8% and 11%, respectively.
Seventeen percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 11% of those in the Clb arm had late-onset neutropenia. The rates of prolonged neutropenia were 3% and 9%, respectively.
Fourteen percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 7% of those in the Clb arm had second malignancies (starting 6 months after treatment initiation). The most common of these were squamous cell carcinoma (2% vs 0%) and basal cell carcinoma (2% vs <1%).
G-Clb vs R-Clb
Ninety-four percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 90% of those in the R-Clb arm had at least 1 AE. The rates of grade 3-5 AEs were 72% and 60%, respectively. The rates of serious AEs were 45% and 39%, respectively. The rates of fatal AEs were 7% and 10%, respectively.
Fifteen percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 12% of those in the R-Clb arm had late-onset neutropenia. The rates of prolonged neutropenia were 2% and 4%, respectively.
Eleven percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 10% of those in the Clb arm had second malignancies. Squamous cell carcinoma occurred in 2% of patients in both arms. Basal cell carcinoma occurred in 2% of G-Clb recipients and 1% of R-Clb recipients.
STOCKHOLM—Obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil (G-Clb) is a “valid and beneficial” frontline treatment option for “unfit” patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to a speaker at the 23rd Congress of the European Hematology Association (EHA).
Final results from the CLL11 study have revealed additional benefits of G-Clb over rituximab plus chlorambucil (R-Clb) in patients with previously untreated CLL and comorbidities.
Prior results from this study showed that G-Clb produced higher response rates and prolonged progression-fee survival (PFS) compared to R-Clb.
Now, with a median follow-up of 5 years, researchers have found that G-Clb prolongs overall survival (OS) and time to next treatment (TTNT) as well.
Valentin Goede, MD, of the University Hospital Cologne in Germany, presented these results during the Presidential Symposium of the EHA Congress (abstract S151).
The study was sponsored by Hoffmann-La Roche.
CLL11 enrolled patients with previously untreated CLL and coexisting medical conditions. They were randomized to receive six 28-day cycles of Clb alone, G-Clb, or R-Clb.
In stage 1, researchers compared G-Clb (n=238) to Clb alone (n=118) and R-Clb (n=233) to Clb alone (n=118). In stage 2, they compared G-Clb (n=333) and R-Clb (n=330).
“The treatment arms were well-balanced, not just with regard to patient [characteristics] but also with disease characteristics,” Dr Goede said.
Overall, the median age was 73 (range, 39-90), the median Cumulative Illness Rating Scale score was 8, and the median creatinine clearance was 62 mL/min.
Efficacy: G-Clb vs Clb
The median observation time for G-Clb vs Clb was 62.5 months.
The median PFS was 31.1 months in the G-Clb arm and 11.1 months in the Clb arm. The 5-year PFS rates were 25% and 2%, respectively. The hazard ratio (HR) was 0.21 (P<0.0001).
The median OS was not reached in the G-Clb arm and was 66.7 months in the Clb arm. The 5-year OS rates were 66% and 53%, respectively. The HR was 0.68 (P=0.0196).
Thirty-nine percent of the G-Clb arm died, as did 49% of the Clb arm. The main causes of death were adverse events (AEs) and disease progression.
Efficacy: G-Clb vs R-Clb
The median observation time for G-Clb vs R-Clb was 59.4 months.
The median PFS was 28.9 months in the G-Clb arm and 15.7 months in the R-Clb arm. The 5-year PFS rates were 23% and 9%, respectively. The HR was 0.49 (P<0.0001).
“The median PFS was nearly doubled, from approximately 15 months in the rituximab arm to almost 30 months in the obinutuzumab arm,” Dr Goede said. “And this translated into a clinically meaningful prolongation of time to next treatment.”
The median TTNT was 56.4 months in the G-Clb arm and 34.9 months in the R-Clb arm. At 5 years, TTNT rates were 49% and 32%, respectively. The HR was 0.58 (P<0.0001).
“In the rituximab arm, the median time to next treatment was a little greater than 2.5 years, and, in the obinutuzumab arm, it was almost 5 years,” Dr Goede said. “From a clinical perspective, I would consider treatment-free intervals of that duration as highly relevant and beneficial in an elderly population.”
The median OS was not reached in the G-Clb arm and was 73.1 months in the R-Clb arm. The 5-year OS rates were 66% and 57%, respectively. The HR was 0.76 (P=0.0245).
“This difference is clinically meaningful, and it is also remarkable in the context of the long follow-up, given the fact that approximately half of the patients have received at least 1 salvage treatment in the meantime,” Dr Goede said.
In all, 37% of the G-Clb arm died, as did 45% of the R-Clb arm. Again, the main causes of death were AEs and disease progression.
Safety
Dr Goede said no new safety signals or late-onset toxicities were detected.
“Adverse events of any grade, but particularly grade 3-5 and serious adverse events, were more frequent in the obinutuzumab arm compared to the other 2 arms,” he noted. “[This] was mainly driven by more infusion reactions and some greater hematological toxicity.”
“Importantly, the rate of fatal adverse events, during treatment but also during follow-up, was not higher in the obinutuzumab arm. And the most common fatal adverse events were second malignancies.”
G-Clb vs Clb
Ninety-five percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 83% of those in the Clb arm had at least 1 AE. The rates of grade 3-5 AEs were 74% and 51%, respectively. The rates of serious AEs were 47% and 39%, respectively. The rates of fatal AEs were 8% and 11%, respectively.
Seventeen percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 11% of those in the Clb arm had late-onset neutropenia. The rates of prolonged neutropenia were 3% and 9%, respectively.
Fourteen percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 7% of those in the Clb arm had second malignancies (starting 6 months after treatment initiation). The most common of these were squamous cell carcinoma (2% vs 0%) and basal cell carcinoma (2% vs <1%).
G-Clb vs R-Clb
Ninety-four percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 90% of those in the R-Clb arm had at least 1 AE. The rates of grade 3-5 AEs were 72% and 60%, respectively. The rates of serious AEs were 45% and 39%, respectively. The rates of fatal AEs were 7% and 10%, respectively.
Fifteen percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 12% of those in the R-Clb arm had late-onset neutropenia. The rates of prolonged neutropenia were 2% and 4%, respectively.
Eleven percent of patients in the G-Clb arm and 10% of those in the Clb arm had second malignancies. Squamous cell carcinoma occurred in 2% of patients in both arms. Basal cell carcinoma occurred in 2% of G-Clb recipients and 1% of R-Clb recipients.