User login
How AI Is Revolutionizing Drug Repurposing for Faster, Broader Impact
Summary:
In this segment, the speaker discusses how AI is revolutionizing the drug repurposing process. Previously, drug repurposing was limited by manual research on individual diseases and drugs. With AI, scientists can now analyze a vast array of drugs and diseases simultaneously, generating a ranking system based on the likelihood of success. The Center for Cytokine Storm Treatment and Laboratory, along with the platform Every Cure, uses AI to score 3000 drugs against 18,000 diseases. This platform dramatically reduces the time and resources required for drug repurposing, enabling predictions that can be tested in a fraction of the time.
Key Takeaways:
AI is accelerating the drug repurposing process, offering faster and more comprehensive analysis of possible drug-disease matches.
The AI-based platform assigns a likelihood score to each potential match, streamlining the process for testing and validation.
Our Editors Also Recommend:
AI’s Drug Revolution, Part 1: Faster Trials and Approvals
From AI to Obesity Drugs to Soaring Costs: Medscape Hot Topics in the Medical Profession Report 2024
AI Voice Analysis for Diabetes Screening Shows Promise
To see the full event recording, click here.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Summary:
In this segment, the speaker discusses how AI is revolutionizing the drug repurposing process. Previously, drug repurposing was limited by manual research on individual diseases and drugs. With AI, scientists can now analyze a vast array of drugs and diseases simultaneously, generating a ranking system based on the likelihood of success. The Center for Cytokine Storm Treatment and Laboratory, along with the platform Every Cure, uses AI to score 3000 drugs against 18,000 diseases. This platform dramatically reduces the time and resources required for drug repurposing, enabling predictions that can be tested in a fraction of the time.
Key Takeaways:
AI is accelerating the drug repurposing process, offering faster and more comprehensive analysis of possible drug-disease matches.
The AI-based platform assigns a likelihood score to each potential match, streamlining the process for testing and validation.
Our Editors Also Recommend:
AI’s Drug Revolution, Part 1: Faster Trials and Approvals
From AI to Obesity Drugs to Soaring Costs: Medscape Hot Topics in the Medical Profession Report 2024
AI Voice Analysis for Diabetes Screening Shows Promise
To see the full event recording, click here.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Summary:
In this segment, the speaker discusses how AI is revolutionizing the drug repurposing process. Previously, drug repurposing was limited by manual research on individual diseases and drugs. With AI, scientists can now analyze a vast array of drugs and diseases simultaneously, generating a ranking system based on the likelihood of success. The Center for Cytokine Storm Treatment and Laboratory, along with the platform Every Cure, uses AI to score 3000 drugs against 18,000 diseases. This platform dramatically reduces the time and resources required for drug repurposing, enabling predictions that can be tested in a fraction of the time.
Key Takeaways:
AI is accelerating the drug repurposing process, offering faster and more comprehensive analysis of possible drug-disease matches.
The AI-based platform assigns a likelihood score to each potential match, streamlining the process for testing and validation.
Our Editors Also Recommend:
AI’s Drug Revolution, Part 1: Faster Trials and Approvals
From AI to Obesity Drugs to Soaring Costs: Medscape Hot Topics in the Medical Profession Report 2024
AI Voice Analysis for Diabetes Screening Shows Promise
To see the full event recording, click here.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA’s Project Optimus aims to transform early cancer research
SAN DIEGO –
The goal is “to better identify and characterize optimized doses” in early stages of research and move away from the default of the traditional maximum tolerated dose strategy, hematologist-oncologist Marc R. Theoret, MD, deputy director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, said in a presentation at the 2023 Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer annual meeting.
Earlier this year, the FDA released a draft guidance regarding the changes it hopes to see. The agency supported randomized, parallel dose-response trials when feasible, and “strong rationale for choice of dosage should be provided before initiating a registration trial(s) to support a subsequent indication and usage.”
The goal of controlling toxicity is “very highly important” in hematology research since blood cancer drugs can cause significant adverse effects in areas such as the lungs and heart, said Cecilia Yeung, MD, who led the SITC session about Project Optimus. Dr. Yeung is a clinical pathologist who works on investigational trials at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle.
In an interview, Dr. Yeung, who has a subspecialty in hematopathology, explained why the foundations of cancer research are changing and what hematologist-oncologists can expect to see on the horizon.
Q: Project Optimus aims to move beyond the traditional dose-escalation approach to the development of cancer drugs. How does that strategy work?
Dr. Yeung: Prior to Project Optimus, they’d use a 3+3 strategy in phase 1 trials: They’d give a dose to three fairly healthy patients, then they’d go up by escalating doses in more patients. They’d keep going up until two-thirds of patients at a specific dose suffered from bad side effects, then they’d back off to the last dose.
Q: This approach, which aims to identify the “maximum tolerated dose,” seemed to work well over decades of research into chemotherapy drugs. But worries arose as targeted therapies appeared in oncology areas such as blood cancer. Why did things change?
Dr. Yeung: With 3+3, you could tell pretty quickly how toxic chemotherapy was. But in targeted therapy, we were finding that these studies are not representative of actual toxicity. You’re not treating these patients for a very long time in phase 1, while patients on targeted therapy may be on these drugs for years. Concerns actually started with the first targeted drugs to treat leukemias and lymphomas. They were shown to have unexpected toxicity. A 2016 study found that drug developers had to reduce the original phase 1 dose in 45% of phase 3 trials [of small molecule and monoclonal antibody targeted agents] approved by the FDA over 12 years because of toxicity.
Q: What is FDA’s goal for Project Optimus?
Dr. Yeung: They want to have a second piece, to balance that maximum tolerated dose with a safe and tolerable dose for most people.
Q: What kind of resistance is the FDA getting from drug companies?
Dr. Yeung: The FDA makes a good argument that the system wasn’t working. But drug companies say this will drive up the cost of clinical trials and won’t allow them to treat patients with the maximal doses they could give them. I see arguments from both sides. There has to be a balance between the two.
Q: How will all this affect drug development?
Dr. Yeung: Drugs may become more expensive because much more testing will happen during clinical trials.
Q: Could this reduce the number of investigational drugs?
Dr. Yeung: Hopefully not, but this is huge endeavor for smaller companies that are strapped for funding.
Q: What do you think the future holds?
Dr. Yeung: Ultimately, this is a good thing because if everything works out, we’ll have fewer toxic side effects. But we’re going to have to go through a period of growing pains.
SAN DIEGO –
The goal is “to better identify and characterize optimized doses” in early stages of research and move away from the default of the traditional maximum tolerated dose strategy, hematologist-oncologist Marc R. Theoret, MD, deputy director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, said in a presentation at the 2023 Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer annual meeting.
Earlier this year, the FDA released a draft guidance regarding the changes it hopes to see. The agency supported randomized, parallel dose-response trials when feasible, and “strong rationale for choice of dosage should be provided before initiating a registration trial(s) to support a subsequent indication and usage.”
The goal of controlling toxicity is “very highly important” in hematology research since blood cancer drugs can cause significant adverse effects in areas such as the lungs and heart, said Cecilia Yeung, MD, who led the SITC session about Project Optimus. Dr. Yeung is a clinical pathologist who works on investigational trials at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle.
In an interview, Dr. Yeung, who has a subspecialty in hematopathology, explained why the foundations of cancer research are changing and what hematologist-oncologists can expect to see on the horizon.
Q: Project Optimus aims to move beyond the traditional dose-escalation approach to the development of cancer drugs. How does that strategy work?
Dr. Yeung: Prior to Project Optimus, they’d use a 3+3 strategy in phase 1 trials: They’d give a dose to three fairly healthy patients, then they’d go up by escalating doses in more patients. They’d keep going up until two-thirds of patients at a specific dose suffered from bad side effects, then they’d back off to the last dose.
Q: This approach, which aims to identify the “maximum tolerated dose,” seemed to work well over decades of research into chemotherapy drugs. But worries arose as targeted therapies appeared in oncology areas such as blood cancer. Why did things change?
Dr. Yeung: With 3+3, you could tell pretty quickly how toxic chemotherapy was. But in targeted therapy, we were finding that these studies are not representative of actual toxicity. You’re not treating these patients for a very long time in phase 1, while patients on targeted therapy may be on these drugs for years. Concerns actually started with the first targeted drugs to treat leukemias and lymphomas. They were shown to have unexpected toxicity. A 2016 study found that drug developers had to reduce the original phase 1 dose in 45% of phase 3 trials [of small molecule and monoclonal antibody targeted agents] approved by the FDA over 12 years because of toxicity.
Q: What is FDA’s goal for Project Optimus?
Dr. Yeung: They want to have a second piece, to balance that maximum tolerated dose with a safe and tolerable dose for most people.
Q: What kind of resistance is the FDA getting from drug companies?
Dr. Yeung: The FDA makes a good argument that the system wasn’t working. But drug companies say this will drive up the cost of clinical trials and won’t allow them to treat patients with the maximal doses they could give them. I see arguments from both sides. There has to be a balance between the two.
Q: How will all this affect drug development?
Dr. Yeung: Drugs may become more expensive because much more testing will happen during clinical trials.
Q: Could this reduce the number of investigational drugs?
Dr. Yeung: Hopefully not, but this is huge endeavor for smaller companies that are strapped for funding.
Q: What do you think the future holds?
Dr. Yeung: Ultimately, this is a good thing because if everything works out, we’ll have fewer toxic side effects. But we’re going to have to go through a period of growing pains.
SAN DIEGO –
The goal is “to better identify and characterize optimized doses” in early stages of research and move away from the default of the traditional maximum tolerated dose strategy, hematologist-oncologist Marc R. Theoret, MD, deputy director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, said in a presentation at the 2023 Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer annual meeting.
Earlier this year, the FDA released a draft guidance regarding the changes it hopes to see. The agency supported randomized, parallel dose-response trials when feasible, and “strong rationale for choice of dosage should be provided before initiating a registration trial(s) to support a subsequent indication and usage.”
The goal of controlling toxicity is “very highly important” in hematology research since blood cancer drugs can cause significant adverse effects in areas such as the lungs and heart, said Cecilia Yeung, MD, who led the SITC session about Project Optimus. Dr. Yeung is a clinical pathologist who works on investigational trials at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle.
In an interview, Dr. Yeung, who has a subspecialty in hematopathology, explained why the foundations of cancer research are changing and what hematologist-oncologists can expect to see on the horizon.
Q: Project Optimus aims to move beyond the traditional dose-escalation approach to the development of cancer drugs. How does that strategy work?
Dr. Yeung: Prior to Project Optimus, they’d use a 3+3 strategy in phase 1 trials: They’d give a dose to three fairly healthy patients, then they’d go up by escalating doses in more patients. They’d keep going up until two-thirds of patients at a specific dose suffered from bad side effects, then they’d back off to the last dose.
Q: This approach, which aims to identify the “maximum tolerated dose,” seemed to work well over decades of research into chemotherapy drugs. But worries arose as targeted therapies appeared in oncology areas such as blood cancer. Why did things change?
Dr. Yeung: With 3+3, you could tell pretty quickly how toxic chemotherapy was. But in targeted therapy, we were finding that these studies are not representative of actual toxicity. You’re not treating these patients for a very long time in phase 1, while patients on targeted therapy may be on these drugs for years. Concerns actually started with the first targeted drugs to treat leukemias and lymphomas. They were shown to have unexpected toxicity. A 2016 study found that drug developers had to reduce the original phase 1 dose in 45% of phase 3 trials [of small molecule and monoclonal antibody targeted agents] approved by the FDA over 12 years because of toxicity.
Q: What is FDA’s goal for Project Optimus?
Dr. Yeung: They want to have a second piece, to balance that maximum tolerated dose with a safe and tolerable dose for most people.
Q: What kind of resistance is the FDA getting from drug companies?
Dr. Yeung: The FDA makes a good argument that the system wasn’t working. But drug companies say this will drive up the cost of clinical trials and won’t allow them to treat patients with the maximal doses they could give them. I see arguments from both sides. There has to be a balance between the two.
Q: How will all this affect drug development?
Dr. Yeung: Drugs may become more expensive because much more testing will happen during clinical trials.
Q: Could this reduce the number of investigational drugs?
Dr. Yeung: Hopefully not, but this is huge endeavor for smaller companies that are strapped for funding.
Q: What do you think the future holds?
Dr. Yeung: Ultimately, this is a good thing because if everything works out, we’ll have fewer toxic side effects. But we’re going to have to go through a period of growing pains.
AT SITC 2023
Oral cancer drugs requiring prior authorization on the rise
TOPLINE:
with the biggest rise occurring for nonspecialty brand drugs.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used Medicare Part D formulary files to identify insurance companies’ use of prior authorization and quantity limits for each drug-dose-formulary combination for oral cancer drugs.
- Drugs were identified using the 2021 Oncology Care Model drug list.
- Researchers categorized drugs as specialty – when monthly costs were higher than $600 in 2010-2016 and $670 in 2017-2020 – or nonspecialty and brand or generic.
- For each year in the study period, which spanned 2010-2020, researchers estimated the enrollment-weighted proportion of drug-dose-formulary combinations subject to administrative burdens.
- Medicare Part D beneficiaries increased from 28,030,290 in 2010 to 47,337,020 in 2020.
TAKEAWAYS:
- In 2010, 333 formularies covered 62 oral cancer drugs – 26 specialty brands, zero specialty generics, 28 nonspecialty brands, and eight nonspecialty generics – compared with 548 formularies and 249 drugs in 2020 – 139 specialty brands, nine specialty generics, 86 nonspecialty brands, and 15 nonspecialty generics.
- Unique drug-dose-formulary prescribing combinations increased from 19,004 to 122,173 between 2010 and 2020; the proportion of drug-dose-formulary combinations requiring prior authorization also increased in that time.
- For specialty brand drugs, the proportion requiring prior authorization increased from 72.8% to 95.4%; that proportion increased nearly fivefold, from 15.9% to 78.2%, for nonspecialty brand drugs, and eightfold, from 1% to 8%, for nonspecialty generic drugs.
- The proportion of drug-dose-formulary combinations for oral oncology drugs requiring quantity limits for specialty brand drugs doubled over the study period – from 31.4% to 62.5%. That proportion increased from 32.7% to 77.8% for specialty generic drugs between 2016 and 2020; and between 2010 and 2020, from 11.8% to 47.3% for nonspecialty brand drugs and from 9.7% to 18.8% for nonspecialty generic drugs.
IN PRACTICE:
“Utilization management may be appropriate for some oncology drugs, such as those approved with provisional evidence of efficacy,” researchers wrote. “It is less clear why prior authorization is required for highly effective, first-line drugs such as generic imatinib.”
SOURCE:
The analysis, led by Michael Anne Kyle, PhD, RN, was published online July 18 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study focused on Medicare and oral oncology drugs, and future work could expand the scope.
DISCLOSURES:
The research was funded by a National Cancer Institute grant. Coauthors received funding from Arnold Ventures and the Commonwealth Fund.
Authors reported affiliations with the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, Leukemia & Lymphoma Society, Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, West Health, Medicare Payment Advisory Commission, National Cancer Institute, and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
with the biggest rise occurring for nonspecialty brand drugs.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used Medicare Part D formulary files to identify insurance companies’ use of prior authorization and quantity limits for each drug-dose-formulary combination for oral cancer drugs.
- Drugs were identified using the 2021 Oncology Care Model drug list.
- Researchers categorized drugs as specialty – when monthly costs were higher than $600 in 2010-2016 and $670 in 2017-2020 – or nonspecialty and brand or generic.
- For each year in the study period, which spanned 2010-2020, researchers estimated the enrollment-weighted proportion of drug-dose-formulary combinations subject to administrative burdens.
- Medicare Part D beneficiaries increased from 28,030,290 in 2010 to 47,337,020 in 2020.
TAKEAWAYS:
- In 2010, 333 formularies covered 62 oral cancer drugs – 26 specialty brands, zero specialty generics, 28 nonspecialty brands, and eight nonspecialty generics – compared with 548 formularies and 249 drugs in 2020 – 139 specialty brands, nine specialty generics, 86 nonspecialty brands, and 15 nonspecialty generics.
- Unique drug-dose-formulary prescribing combinations increased from 19,004 to 122,173 between 2010 and 2020; the proportion of drug-dose-formulary combinations requiring prior authorization also increased in that time.
- For specialty brand drugs, the proportion requiring prior authorization increased from 72.8% to 95.4%; that proportion increased nearly fivefold, from 15.9% to 78.2%, for nonspecialty brand drugs, and eightfold, from 1% to 8%, for nonspecialty generic drugs.
- The proportion of drug-dose-formulary combinations for oral oncology drugs requiring quantity limits for specialty brand drugs doubled over the study period – from 31.4% to 62.5%. That proportion increased from 32.7% to 77.8% for specialty generic drugs between 2016 and 2020; and between 2010 and 2020, from 11.8% to 47.3% for nonspecialty brand drugs and from 9.7% to 18.8% for nonspecialty generic drugs.
IN PRACTICE:
“Utilization management may be appropriate for some oncology drugs, such as those approved with provisional evidence of efficacy,” researchers wrote. “It is less clear why prior authorization is required for highly effective, first-line drugs such as generic imatinib.”
SOURCE:
The analysis, led by Michael Anne Kyle, PhD, RN, was published online July 18 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study focused on Medicare and oral oncology drugs, and future work could expand the scope.
DISCLOSURES:
The research was funded by a National Cancer Institute grant. Coauthors received funding from Arnold Ventures and the Commonwealth Fund.
Authors reported affiliations with the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, Leukemia & Lymphoma Society, Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, West Health, Medicare Payment Advisory Commission, National Cancer Institute, and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
with the biggest rise occurring for nonspecialty brand drugs.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used Medicare Part D formulary files to identify insurance companies’ use of prior authorization and quantity limits for each drug-dose-formulary combination for oral cancer drugs.
- Drugs were identified using the 2021 Oncology Care Model drug list.
- Researchers categorized drugs as specialty – when monthly costs were higher than $600 in 2010-2016 and $670 in 2017-2020 – or nonspecialty and brand or generic.
- For each year in the study period, which spanned 2010-2020, researchers estimated the enrollment-weighted proportion of drug-dose-formulary combinations subject to administrative burdens.
- Medicare Part D beneficiaries increased from 28,030,290 in 2010 to 47,337,020 in 2020.
TAKEAWAYS:
- In 2010, 333 formularies covered 62 oral cancer drugs – 26 specialty brands, zero specialty generics, 28 nonspecialty brands, and eight nonspecialty generics – compared with 548 formularies and 249 drugs in 2020 – 139 specialty brands, nine specialty generics, 86 nonspecialty brands, and 15 nonspecialty generics.
- Unique drug-dose-formulary prescribing combinations increased from 19,004 to 122,173 between 2010 and 2020; the proportion of drug-dose-formulary combinations requiring prior authorization also increased in that time.
- For specialty brand drugs, the proportion requiring prior authorization increased from 72.8% to 95.4%; that proportion increased nearly fivefold, from 15.9% to 78.2%, for nonspecialty brand drugs, and eightfold, from 1% to 8%, for nonspecialty generic drugs.
- The proportion of drug-dose-formulary combinations for oral oncology drugs requiring quantity limits for specialty brand drugs doubled over the study period – from 31.4% to 62.5%. That proportion increased from 32.7% to 77.8% for specialty generic drugs between 2016 and 2020; and between 2010 and 2020, from 11.8% to 47.3% for nonspecialty brand drugs and from 9.7% to 18.8% for nonspecialty generic drugs.
IN PRACTICE:
“Utilization management may be appropriate for some oncology drugs, such as those approved with provisional evidence of efficacy,” researchers wrote. “It is less clear why prior authorization is required for highly effective, first-line drugs such as generic imatinib.”
SOURCE:
The analysis, led by Michael Anne Kyle, PhD, RN, was published online July 18 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study focused on Medicare and oral oncology drugs, and future work could expand the scope.
DISCLOSURES:
The research was funded by a National Cancer Institute grant. Coauthors received funding from Arnold Ventures and the Commonwealth Fund.
Authors reported affiliations with the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, Leukemia & Lymphoma Society, Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, West Health, Medicare Payment Advisory Commission, National Cancer Institute, and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
FDA approves dasatinib for kids with Ph+ ALL
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a second pediatric indication for dasatinib (Sprycel®).
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor is now approved for use in combination with chemotherapy to treat pediatric patients age 1 year and older who have newly diagnosed, Philadelphia-chromosome-positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Dasatinib is also FDA-approved for use in children age 1 year and older who have chronic phase, Ph+ chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
In adults, dasatinib is FDA-approved to treat:
- Newly diagnosed, Ph+, chronic phase CML
- Chronic, accelerated, or myeloid/lymphoid blast phase, Ph+ CML with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy including imatinib
- Ph+ ALL with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy.
Trial results
The FDA’s approval of dasatinib in children with Ph+ ALL is based on data from a phase 2 study (CA180-372, NCT01460160).
In this trial, researchers evaluated dasatinib in combination with the AIEOP-BFM ALL 2000 chemotherapy protocol in patients (ages 1 to 17) with newly diagnosed, B-cell precursor, Ph+ ALL.
There were 78 patients evaluated for efficacy in cohort 1. They had a median age of 10.4 years (range, 2.6 to 17.9 years). They received dasatinib at a daily dose of 60 mg/m2 for up to 24 months.
Patients with central nervous system 3 disease received cranial irradiation, and patients were assigned to stem cell transplant based on minimal residual disease if they were thought to have a high risk of relapse.
The 3-year event-free survival rate in the 78 patients was 64.1%.
There were 81 patients evaluable for safety who received dasatinib continuously in combination with chemotherapy. Their median duration of treatment was 24 months (range, 2 to 27 months).
The most common adverse events (AEs) in these patients were mucositis (93%), febrile neutropenia (86%), pyrexia (85%), diarrhea (84%), nausea (84%), vomiting (83%), musculoskeletal pain (83%), abdominal pain (78%), cough (78%), headache (77%), rash (68%), fatigue (59%), and constipation (57%).
Eight (10%) patients had AEs leading to treatment discontinuation. These included fungal sepsis, hepatotoxicity in the setting of graft-versus-host disease, thrombocytopenia, cytomegalovirus infection, pneumonia, nausea, enteritis, and drug hypersensitivity.
Three patients (4%) had fatal AEs, all infections.
This trial was sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Additional data are available in the prescribing information for dasatinib.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a second pediatric indication for dasatinib (Sprycel®).
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor is now approved for use in combination with chemotherapy to treat pediatric patients age 1 year and older who have newly diagnosed, Philadelphia-chromosome-positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Dasatinib is also FDA-approved for use in children age 1 year and older who have chronic phase, Ph+ chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
In adults, dasatinib is FDA-approved to treat:
- Newly diagnosed, Ph+, chronic phase CML
- Chronic, accelerated, or myeloid/lymphoid blast phase, Ph+ CML with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy including imatinib
- Ph+ ALL with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy.
Trial results
The FDA’s approval of dasatinib in children with Ph+ ALL is based on data from a phase 2 study (CA180-372, NCT01460160).
In this trial, researchers evaluated dasatinib in combination with the AIEOP-BFM ALL 2000 chemotherapy protocol in patients (ages 1 to 17) with newly diagnosed, B-cell precursor, Ph+ ALL.
There were 78 patients evaluated for efficacy in cohort 1. They had a median age of 10.4 years (range, 2.6 to 17.9 years). They received dasatinib at a daily dose of 60 mg/m2 for up to 24 months.
Patients with central nervous system 3 disease received cranial irradiation, and patients were assigned to stem cell transplant based on minimal residual disease if they were thought to have a high risk of relapse.
The 3-year event-free survival rate in the 78 patients was 64.1%.
There were 81 patients evaluable for safety who received dasatinib continuously in combination with chemotherapy. Their median duration of treatment was 24 months (range, 2 to 27 months).
The most common adverse events (AEs) in these patients were mucositis (93%), febrile neutropenia (86%), pyrexia (85%), diarrhea (84%), nausea (84%), vomiting (83%), musculoskeletal pain (83%), abdominal pain (78%), cough (78%), headache (77%), rash (68%), fatigue (59%), and constipation (57%).
Eight (10%) patients had AEs leading to treatment discontinuation. These included fungal sepsis, hepatotoxicity in the setting of graft-versus-host disease, thrombocytopenia, cytomegalovirus infection, pneumonia, nausea, enteritis, and drug hypersensitivity.
Three patients (4%) had fatal AEs, all infections.
This trial was sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Additional data are available in the prescribing information for dasatinib.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a second pediatric indication for dasatinib (Sprycel®).
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor is now approved for use in combination with chemotherapy to treat pediatric patients age 1 year and older who have newly diagnosed, Philadelphia-chromosome-positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Dasatinib is also FDA-approved for use in children age 1 year and older who have chronic phase, Ph+ chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
In adults, dasatinib is FDA-approved to treat:
- Newly diagnosed, Ph+, chronic phase CML
- Chronic, accelerated, or myeloid/lymphoid blast phase, Ph+ CML with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy including imatinib
- Ph+ ALL with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy.
Trial results
The FDA’s approval of dasatinib in children with Ph+ ALL is based on data from a phase 2 study (CA180-372, NCT01460160).
In this trial, researchers evaluated dasatinib in combination with the AIEOP-BFM ALL 2000 chemotherapy protocol in patients (ages 1 to 17) with newly diagnosed, B-cell precursor, Ph+ ALL.
There were 78 patients evaluated for efficacy in cohort 1. They had a median age of 10.4 years (range, 2.6 to 17.9 years). They received dasatinib at a daily dose of 60 mg/m2 for up to 24 months.
Patients with central nervous system 3 disease received cranial irradiation, and patients were assigned to stem cell transplant based on minimal residual disease if they were thought to have a high risk of relapse.
The 3-year event-free survival rate in the 78 patients was 64.1%.
There were 81 patients evaluable for safety who received dasatinib continuously in combination with chemotherapy. Their median duration of treatment was 24 months (range, 2 to 27 months).
The most common adverse events (AEs) in these patients were mucositis (93%), febrile neutropenia (86%), pyrexia (85%), diarrhea (84%), nausea (84%), vomiting (83%), musculoskeletal pain (83%), abdominal pain (78%), cough (78%), headache (77%), rash (68%), fatigue (59%), and constipation (57%).
Eight (10%) patients had AEs leading to treatment discontinuation. These included fungal sepsis, hepatotoxicity in the setting of graft-versus-host disease, thrombocytopenia, cytomegalovirus infection, pneumonia, nausea, enteritis, and drug hypersensitivity.
Three patients (4%) had fatal AEs, all infections.
This trial was sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Additional data are available in the prescribing information for dasatinib.
EC approves split dosing regimen for daratumumab
The European Commission (EC) has granted marketing authorization for a split dosing regimen for daratumumab (Darzalex®).
The approval provides healthcare professionals with the option to split the first infusion of daratumumab over 2 consecutive days.
“We are hopeful that the availability of this more flexible dosing option will make the first infusion of Darzalex more convenient for European multiple myeloma patients,” said Jan van de Winkel, PhD, chief executive officer of Genmab, which licensed daratumumab to Janssen Biotech, Inc.
Daratumumab is currently EC-approved for the following indications:
- For use in combination with bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone to treat adults with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant
- For use in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, or bortezomib and dexamethasone, for the treatment of adults with MM who have received at least one prior therapy
- As monotherapy for adults with relapsed and refractory MM whose prior therapy included a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent and who have demonstrated disease progression on their last therapy.
The EC’s approval of a split dosing regimen for daratumumab was based on data from the phase 1b EQUULEUS trial (MMY1001, NCT01998971), which was sponsored by Janssen.
This trial was designed to evaluate daratumumab in combination with bortezomib-dexamethasone, bortezomib-melphalan-prednisone, bortezomib-thalidomide-dexamethasone, pomalidomide-dexamethasone, carfilzomib-dexamethasone, and carfilzomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone.
At the 2018 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 1970), researchers presented data from this trial in MM patients who received their first 16 mg/kg daratumumab dose as a split dose of 8 mg/kg on day 1 of cycle 1 and 8 mg/kg on day 2 of cycle 1, compared to patients who received the full 16 mg/kg dose on day 1 of cycle 1.
The researchers said they observed “virtually identical” pharmacokinetics between the dosing groups.
Cmax on the first day of cycle 1 was lower in the split-dose group than in the full-dose group. However, after patients in the split-dose group received the second 8 mg/kg dose on day 2, concentrations were similar between the groups.
The researchers said they do not expect the initial difference they observed to have any impact on clinical outcomes.
The team also pointed out that there was no increase in infusion-related reactions among patients who received the split dose.
The researchers said split dosing of daratumumab is still being investigated in ongoing studies of MM patients, including CANDOR (NCT03158688) and LYRA (NCT02951819).
The European Commission (EC) has granted marketing authorization for a split dosing regimen for daratumumab (Darzalex®).
The approval provides healthcare professionals with the option to split the first infusion of daratumumab over 2 consecutive days.
“We are hopeful that the availability of this more flexible dosing option will make the first infusion of Darzalex more convenient for European multiple myeloma patients,” said Jan van de Winkel, PhD, chief executive officer of Genmab, which licensed daratumumab to Janssen Biotech, Inc.
Daratumumab is currently EC-approved for the following indications:
- For use in combination with bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone to treat adults with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant
- For use in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, or bortezomib and dexamethasone, for the treatment of adults with MM who have received at least one prior therapy
- As monotherapy for adults with relapsed and refractory MM whose prior therapy included a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent and who have demonstrated disease progression on their last therapy.
The EC’s approval of a split dosing regimen for daratumumab was based on data from the phase 1b EQUULEUS trial (MMY1001, NCT01998971), which was sponsored by Janssen.
This trial was designed to evaluate daratumumab in combination with bortezomib-dexamethasone, bortezomib-melphalan-prednisone, bortezomib-thalidomide-dexamethasone, pomalidomide-dexamethasone, carfilzomib-dexamethasone, and carfilzomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone.
At the 2018 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 1970), researchers presented data from this trial in MM patients who received their first 16 mg/kg daratumumab dose as a split dose of 8 mg/kg on day 1 of cycle 1 and 8 mg/kg on day 2 of cycle 1, compared to patients who received the full 16 mg/kg dose on day 1 of cycle 1.
The researchers said they observed “virtually identical” pharmacokinetics between the dosing groups.
Cmax on the first day of cycle 1 was lower in the split-dose group than in the full-dose group. However, after patients in the split-dose group received the second 8 mg/kg dose on day 2, concentrations were similar between the groups.
The researchers said they do not expect the initial difference they observed to have any impact on clinical outcomes.
The team also pointed out that there was no increase in infusion-related reactions among patients who received the split dose.
The researchers said split dosing of daratumumab is still being investigated in ongoing studies of MM patients, including CANDOR (NCT03158688) and LYRA (NCT02951819).
The European Commission (EC) has granted marketing authorization for a split dosing regimen for daratumumab (Darzalex®).
The approval provides healthcare professionals with the option to split the first infusion of daratumumab over 2 consecutive days.
“We are hopeful that the availability of this more flexible dosing option will make the first infusion of Darzalex more convenient for European multiple myeloma patients,” said Jan van de Winkel, PhD, chief executive officer of Genmab, which licensed daratumumab to Janssen Biotech, Inc.
Daratumumab is currently EC-approved for the following indications:
- For use in combination with bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone to treat adults with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant
- For use in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, or bortezomib and dexamethasone, for the treatment of adults with MM who have received at least one prior therapy
- As monotherapy for adults with relapsed and refractory MM whose prior therapy included a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent and who have demonstrated disease progression on their last therapy.
The EC’s approval of a split dosing regimen for daratumumab was based on data from the phase 1b EQUULEUS trial (MMY1001, NCT01998971), which was sponsored by Janssen.
This trial was designed to evaluate daratumumab in combination with bortezomib-dexamethasone, bortezomib-melphalan-prednisone, bortezomib-thalidomide-dexamethasone, pomalidomide-dexamethasone, carfilzomib-dexamethasone, and carfilzomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone.
At the 2018 ASH Annual Meeting (abstract 1970), researchers presented data from this trial in MM patients who received their first 16 mg/kg daratumumab dose as a split dose of 8 mg/kg on day 1 of cycle 1 and 8 mg/kg on day 2 of cycle 1, compared to patients who received the full 16 mg/kg dose on day 1 of cycle 1.
The researchers said they observed “virtually identical” pharmacokinetics between the dosing groups.
Cmax on the first day of cycle 1 was lower in the split-dose group than in the full-dose group. However, after patients in the split-dose group received the second 8 mg/kg dose on day 2, concentrations were similar between the groups.
The researchers said they do not expect the initial difference they observed to have any impact on clinical outcomes.
The team also pointed out that there was no increase in infusion-related reactions among patients who received the split dose.
The researchers said split dosing of daratumumab is still being investigated in ongoing studies of MM patients, including CANDOR (NCT03158688) and LYRA (NCT02951819).
FDA approves first treatment for BPDCN
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved tagraxofusp-erzs (Elzonris) to treat patients age 2 and older who have blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN).
Tagraxofusp-erzs (formerly SL-401) is a CD123-directed cytotoxin that is the first FDA-approved treatment for BPDCN.
Tagraxofusp-erzs will be commercially available in early 2019, according to Stemline Therapeutics, makers of the drug.
The prescribing information for tagraxofusp-erzs contains a boxed warning noting that the drug is associated with an increased risk of capillary leak syndrome (CLS), which may be life-threatening or fatal.
The FDA previously granted tagraxofusp-erzs breakthrough therapy and orphan drug designations and assessed the drug under priority review.
The FDA’s approval of tagraxofusp-erzs was based on a phase 1 trial (STML-401-0114; NCT02113982).
The trial enrolled 47 patients with BPDCN, including 32 who were treatment-naïve and 15 who were previously treated.
Patients received tagraxofusp-erzs intravenously on days 1-5 of a 21-day cycle for multiple consecutive cycles. The trial had a dose-escalation stage (stage 1), an expansion stage (stage 2), a confirmatory stage (stage 3), and a stage that enabled uninterrupted access to tagraxofusp-erzs (stage 4).
In the confirmatory stage, 13 patients with treatment-naïve BPDCN received tagraxofusp-erzs at the recommended dose and schedule—12 mcg/kg daily for 5 days of a 21-day cycle.
Efficacy was based on the rate of complete response (CR) or clinical complete response (CRc). CRc was defined as CR with residual skin abnormality not indicative of active disease.
The CR/CRc rate was 53.8% (7/13), and the median duration of CR/CRc was not reached (range, 3.9 to 12.2 months).
The safety of tagraxofusp-erzs was assessed in 94 adults with treatment-naïve or previously treated myeloid malignancies, including 58 patients with BPDCN, who were treated at the recommended dose and schedule.
There were two fatal adverse events—both CLS. Eleven percent of patients discontinued treatment with tagraxofusp-erzs due to an adverse event. The most common of these were hepatic toxicities and CLS.
The most common adverse events overall were CLS (55%), nausea (49%), fatigue (45%), peripheral edema (43%), pyrexia (43%), and weight increase (31%).
The most common laboratory abnormalities were decreases in albumin (77%), platelets (67%), hemoglobin (60%), calcium (57%), and sodium (50%), as well as increases in glucose (87%), alanine aminotransferase (82%), and aspartate aminotransferase (79%).
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved tagraxofusp-erzs (Elzonris) to treat patients age 2 and older who have blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN).
Tagraxofusp-erzs (formerly SL-401) is a CD123-directed cytotoxin that is the first FDA-approved treatment for BPDCN.
Tagraxofusp-erzs will be commercially available in early 2019, according to Stemline Therapeutics, makers of the drug.
The prescribing information for tagraxofusp-erzs contains a boxed warning noting that the drug is associated with an increased risk of capillary leak syndrome (CLS), which may be life-threatening or fatal.
The FDA previously granted tagraxofusp-erzs breakthrough therapy and orphan drug designations and assessed the drug under priority review.
The FDA’s approval of tagraxofusp-erzs was based on a phase 1 trial (STML-401-0114; NCT02113982).
The trial enrolled 47 patients with BPDCN, including 32 who were treatment-naïve and 15 who were previously treated.
Patients received tagraxofusp-erzs intravenously on days 1-5 of a 21-day cycle for multiple consecutive cycles. The trial had a dose-escalation stage (stage 1), an expansion stage (stage 2), a confirmatory stage (stage 3), and a stage that enabled uninterrupted access to tagraxofusp-erzs (stage 4).
In the confirmatory stage, 13 patients with treatment-naïve BPDCN received tagraxofusp-erzs at the recommended dose and schedule—12 mcg/kg daily for 5 days of a 21-day cycle.
Efficacy was based on the rate of complete response (CR) or clinical complete response (CRc). CRc was defined as CR with residual skin abnormality not indicative of active disease.
The CR/CRc rate was 53.8% (7/13), and the median duration of CR/CRc was not reached (range, 3.9 to 12.2 months).
The safety of tagraxofusp-erzs was assessed in 94 adults with treatment-naïve or previously treated myeloid malignancies, including 58 patients with BPDCN, who were treated at the recommended dose and schedule.
There were two fatal adverse events—both CLS. Eleven percent of patients discontinued treatment with tagraxofusp-erzs due to an adverse event. The most common of these were hepatic toxicities and CLS.
The most common adverse events overall were CLS (55%), nausea (49%), fatigue (45%), peripheral edema (43%), pyrexia (43%), and weight increase (31%).
The most common laboratory abnormalities were decreases in albumin (77%), platelets (67%), hemoglobin (60%), calcium (57%), and sodium (50%), as well as increases in glucose (87%), alanine aminotransferase (82%), and aspartate aminotransferase (79%).
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved tagraxofusp-erzs (Elzonris) to treat patients age 2 and older who have blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN).
Tagraxofusp-erzs (formerly SL-401) is a CD123-directed cytotoxin that is the first FDA-approved treatment for BPDCN.
Tagraxofusp-erzs will be commercially available in early 2019, according to Stemline Therapeutics, makers of the drug.
The prescribing information for tagraxofusp-erzs contains a boxed warning noting that the drug is associated with an increased risk of capillary leak syndrome (CLS), which may be life-threatening or fatal.
The FDA previously granted tagraxofusp-erzs breakthrough therapy and orphan drug designations and assessed the drug under priority review.
The FDA’s approval of tagraxofusp-erzs was based on a phase 1 trial (STML-401-0114; NCT02113982).
The trial enrolled 47 patients with BPDCN, including 32 who were treatment-naïve and 15 who were previously treated.
Patients received tagraxofusp-erzs intravenously on days 1-5 of a 21-day cycle for multiple consecutive cycles. The trial had a dose-escalation stage (stage 1), an expansion stage (stage 2), a confirmatory stage (stage 3), and a stage that enabled uninterrupted access to tagraxofusp-erzs (stage 4).
In the confirmatory stage, 13 patients with treatment-naïve BPDCN received tagraxofusp-erzs at the recommended dose and schedule—12 mcg/kg daily for 5 days of a 21-day cycle.
Efficacy was based on the rate of complete response (CR) or clinical complete response (CRc). CRc was defined as CR with residual skin abnormality not indicative of active disease.
The CR/CRc rate was 53.8% (7/13), and the median duration of CR/CRc was not reached (range, 3.9 to 12.2 months).
The safety of tagraxofusp-erzs was assessed in 94 adults with treatment-naïve or previously treated myeloid malignancies, including 58 patients with BPDCN, who were treated at the recommended dose and schedule.
There were two fatal adverse events—both CLS. Eleven percent of patients discontinued treatment with tagraxofusp-erzs due to an adverse event. The most common of these were hepatic toxicities and CLS.
The most common adverse events overall were CLS (55%), nausea (49%), fatigue (45%), peripheral edema (43%), pyrexia (43%), and weight increase (31%).
The most common laboratory abnormalities were decreases in albumin (77%), platelets (67%), hemoglobin (60%), calcium (57%), and sodium (50%), as well as increases in glucose (87%), alanine aminotransferase (82%), and aspartate aminotransferase (79%).
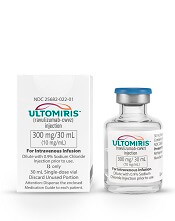
FDA approves ravulizumab for PNH
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved ravulizumab-cwvz (Ultomiris) to treat adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH).
Ravulizumab is a long-acting C5 complement inhibitor, administered every 8 weeks, that has been shown to prevent hemolysis.
The prescribing information for ravulizumab includes a boxed warning stating that meningococcal infections/sepsis have occurred in patients treated with the drug, and these adverse effects can become life-threatening or fatal if not recognized and treated early.
Ravulizumab is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy.
The FDA previously granted the application for ravulizumab priority review, and the product received orphan drug designation from the FDA.
The FDA granted the approval of ravulizumab to Alexion Pharmaceuticals.
The FDA’s approval of ravulizumab is based on results from two phase 3 studies, one in patients who had previously received treatment with a complement inhibitor and one in patients who were complement-inhibitor-naïve. Both studies were recently published in Blood.
Efficacy in inhibitor-experienced patients
In one study (NCT03056040), researchers compared ravulizumab administered every 8 weeks to eculizumab administered every 2 weeks in complement-inhibitor-experienced patients.
The trial included 195 PNH patients who were taking eculizumab for more than 6 months. They were randomized to switch to ravulizumab (n=97) or continue on eculizumab (n=98).
Ravulizumab proved noninferior to eculizumab for all endpoints studied (P<0.0006), including:
- Percentage change in lactate dehydrogenase (LDH): difference, 9.21% (95% CI: -0.42 to 18.84; P=0.058 for superiority)
- Breakthrough hemolysis: difference, 5.1 (95% CI: -8.89 to 18.99)
- Change in FACIT-Fatigue score: difference, 1.47 (95% CI: -0.21 to 3.15)
- Transfusion avoidance: difference, 5.5 (95% CI: -4.27 to 15.68)
- Stabilized hemoglobin: difference, 1.4 (95% CI: -10.41 to 13.31).
Efficacy in inhibitor-naïve patients
In another study (NCT02946463), researchers compared ravulizumab and eculizumab in 246 PNH patients who had not previously received a complement inhibitor.
Ravulizumab was noninferior to eculizumab for all endpoints (P<0.0001), including:
- Transfusion avoidance: 73.6% vs 66.1%; difference of 6.8% (95% CI: -4.66 to 18.14)
- LDH normalization: 53.6% vs 49.4%; odds ratio=1.19 (95% CI: 0.80 to 1.77)
- Percent reduction in LDH: -76.8% vs -76.0%; difference of -0.83% (95% CI: -5.21 to 3.56)
- Change in FACIT-Fatigue score: 7.07 vs 6.40; difference of 0.67 (95% CI: -1.21 to 2.55)
- Breakthrough hemolysis: 4.0% vs 10.7%; difference of -6.7% (95% CI: -14.21 to 0.18)
- Stabilized hemoglobin: 68.0% vs 64.5%; difference of 2.9 (95% CI: -8.80 to 14.64).
Safety in both trials
The safety data from both trials included 441 adults who received ravulizumab (n=222) or eculizumab (n=219) for a median of 6 months.
The most frequent adverse events in both arms (ravulizumab and eculizumab, respectively) were upper respiratory tract infection (39% and 39%) and headache (32% and 26%).
Serious adverse events occurred in 15 (6.8%) patients treated with ravulizumab. These events included hyperthermia and pyrexia.
There was one fatal case of sepsis in a patient treated with ravulizumab.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved ravulizumab-cwvz (Ultomiris) to treat adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH).
Ravulizumab is a long-acting C5 complement inhibitor, administered every 8 weeks, that has been shown to prevent hemolysis.
The prescribing information for ravulizumab includes a boxed warning stating that meningococcal infections/sepsis have occurred in patients treated with the drug, and these adverse effects can become life-threatening or fatal if not recognized and treated early.
Ravulizumab is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy.
The FDA previously granted the application for ravulizumab priority review, and the product received orphan drug designation from the FDA.
The FDA granted the approval of ravulizumab to Alexion Pharmaceuticals.
The FDA’s approval of ravulizumab is based on results from two phase 3 studies, one in patients who had previously received treatment with a complement inhibitor and one in patients who were complement-inhibitor-naïve. Both studies were recently published in Blood.
Efficacy in inhibitor-experienced patients
In one study (NCT03056040), researchers compared ravulizumab administered every 8 weeks to eculizumab administered every 2 weeks in complement-inhibitor-experienced patients.
The trial included 195 PNH patients who were taking eculizumab for more than 6 months. They were randomized to switch to ravulizumab (n=97) or continue on eculizumab (n=98).
Ravulizumab proved noninferior to eculizumab for all endpoints studied (P<0.0006), including:
- Percentage change in lactate dehydrogenase (LDH): difference, 9.21% (95% CI: -0.42 to 18.84; P=0.058 for superiority)
- Breakthrough hemolysis: difference, 5.1 (95% CI: -8.89 to 18.99)
- Change in FACIT-Fatigue score: difference, 1.47 (95% CI: -0.21 to 3.15)
- Transfusion avoidance: difference, 5.5 (95% CI: -4.27 to 15.68)
- Stabilized hemoglobin: difference, 1.4 (95% CI: -10.41 to 13.31).
Efficacy in inhibitor-naïve patients
In another study (NCT02946463), researchers compared ravulizumab and eculizumab in 246 PNH patients who had not previously received a complement inhibitor.
Ravulizumab was noninferior to eculizumab for all endpoints (P<0.0001), including:
- Transfusion avoidance: 73.6% vs 66.1%; difference of 6.8% (95% CI: -4.66 to 18.14)
- LDH normalization: 53.6% vs 49.4%; odds ratio=1.19 (95% CI: 0.80 to 1.77)
- Percent reduction in LDH: -76.8% vs -76.0%; difference of -0.83% (95% CI: -5.21 to 3.56)
- Change in FACIT-Fatigue score: 7.07 vs 6.40; difference of 0.67 (95% CI: -1.21 to 2.55)
- Breakthrough hemolysis: 4.0% vs 10.7%; difference of -6.7% (95% CI: -14.21 to 0.18)
- Stabilized hemoglobin: 68.0% vs 64.5%; difference of 2.9 (95% CI: -8.80 to 14.64).
Safety in both trials
The safety data from both trials included 441 adults who received ravulizumab (n=222) or eculizumab (n=219) for a median of 6 months.
The most frequent adverse events in both arms (ravulizumab and eculizumab, respectively) were upper respiratory tract infection (39% and 39%) and headache (32% and 26%).
Serious adverse events occurred in 15 (6.8%) patients treated with ravulizumab. These events included hyperthermia and pyrexia.
There was one fatal case of sepsis in a patient treated with ravulizumab.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved ravulizumab-cwvz (Ultomiris) to treat adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH).
Ravulizumab is a long-acting C5 complement inhibitor, administered every 8 weeks, that has been shown to prevent hemolysis.
The prescribing information for ravulizumab includes a boxed warning stating that meningococcal infections/sepsis have occurred in patients treated with the drug, and these adverse effects can become life-threatening or fatal if not recognized and treated early.
Ravulizumab is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy.
The FDA previously granted the application for ravulizumab priority review, and the product received orphan drug designation from the FDA.
The FDA granted the approval of ravulizumab to Alexion Pharmaceuticals.
The FDA’s approval of ravulizumab is based on results from two phase 3 studies, one in patients who had previously received treatment with a complement inhibitor and one in patients who were complement-inhibitor-naïve. Both studies were recently published in Blood.
Efficacy in inhibitor-experienced patients
In one study (NCT03056040), researchers compared ravulizumab administered every 8 weeks to eculizumab administered every 2 weeks in complement-inhibitor-experienced patients.
The trial included 195 PNH patients who were taking eculizumab for more than 6 months. They were randomized to switch to ravulizumab (n=97) or continue on eculizumab (n=98).
Ravulizumab proved noninferior to eculizumab for all endpoints studied (P<0.0006), including:
- Percentage change in lactate dehydrogenase (LDH): difference, 9.21% (95% CI: -0.42 to 18.84; P=0.058 for superiority)
- Breakthrough hemolysis: difference, 5.1 (95% CI: -8.89 to 18.99)
- Change in FACIT-Fatigue score: difference, 1.47 (95% CI: -0.21 to 3.15)
- Transfusion avoidance: difference, 5.5 (95% CI: -4.27 to 15.68)
- Stabilized hemoglobin: difference, 1.4 (95% CI: -10.41 to 13.31).
Efficacy in inhibitor-naïve patients
In another study (NCT02946463), researchers compared ravulizumab and eculizumab in 246 PNH patients who had not previously received a complement inhibitor.
Ravulizumab was noninferior to eculizumab for all endpoints (P<0.0001), including:
- Transfusion avoidance: 73.6% vs 66.1%; difference of 6.8% (95% CI: -4.66 to 18.14)
- LDH normalization: 53.6% vs 49.4%; odds ratio=1.19 (95% CI: 0.80 to 1.77)
- Percent reduction in LDH: -76.8% vs -76.0%; difference of -0.83% (95% CI: -5.21 to 3.56)
- Change in FACIT-Fatigue score: 7.07 vs 6.40; difference of 0.67 (95% CI: -1.21 to 2.55)
- Breakthrough hemolysis: 4.0% vs 10.7%; difference of -6.7% (95% CI: -14.21 to 0.18)
- Stabilized hemoglobin: 68.0% vs 64.5%; difference of 2.9 (95% CI: -8.80 to 14.64).
Safety in both trials
The safety data from both trials included 441 adults who received ravulizumab (n=222) or eculizumab (n=219) for a median of 6 months.
The most frequent adverse events in both arms (ravulizumab and eculizumab, respectively) were upper respiratory tract infection (39% and 39%) and headache (32% and 26%).
Serious adverse events occurred in 15 (6.8%) patients treated with ravulizumab. These events included hyperthermia and pyrexia.
There was one fatal case of sepsis in a patient treated with ravulizumab.
FDA approves calaspargase pegol-mknl for ALL
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved calaspargase pegol-mknl (Asparlas) as a component of a multi-agent chemotherapeutic regimen to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in pediatric and young adult patients age 1 month to 21 years.
Calaspargase pegol-mknl is an asparagine-specific enzyme intended to provide a longer interval between doses compared to other available pegaspargase products.
The recommended dosage of calaspargase pegol-mknl is 2,500 U/m2 given no more frequently than every 21 days.
The FDA said it approved calaspargase pegol-mknl because the drug maintained nadir serum asparaginase activity above the level of 0.1 U/mL when given at 2,500 U/m2 every 3 weeks.
Calaspargase pegol-mknl was evaluated in Study DFCI 11-001, a trial of 237 children and adolescents with newly diagnosed ALL or lymphoblastic lymphoma. The patients’ median age was 5 years (range, 1 to 20 years).
They received calaspargase pegol-mknl at 2,500 U/m2 (n=118) or pegaspargase at 2,500 U/m2 (n=119) as part of a Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI) ALL Consortium backbone therapy.
The median duration of exposure was 8 months for both calaspargase pegol-mknl and pegaspargase.
Among the patients with B-cell lineage ALL, the complete remission rate was 98% in the calaspargase pegol-mknl arm and 99% in the pegaspargase arm. Estimated overall survival rates were comparable between the arms.
Common grade 3 or higher adverse events (in the calaspargase pegol-mknl and pegaspargase arms, respectively) included elevated transaminase (52% and 66%), bilirubin increase (20% and 25%), pancreatitis (18% and 24%), and abnormal clotting studies (14% and 21%).
There was one fatal adverse event among patients on calaspargase pegol-mknl—multi-organ failure in the setting of chronic pancreatitis associated with a pancreatic pseudocyst.
The safety of calaspargase pegol-mknl was also evaluated in Study AALL07P4, a trial of patients with newly diagnosed, high-risk B-precursor ALL.
The patients received calaspargase pegol-mknl at 2,500 U/m2 (n=43) or 2,100 U/m2 (n=68) or pegaspargase at 2,500 U/m2 (n=52) as a component of an augmented Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster regimen.
The patients’ median age was 11 years (range, 1 to 26 years). The median duration of exposure was 7 months for both calaspargase pegol-mknl and pegaspargase.
There were three induction deaths among the 111 patients who received calaspargase pegol-mknl (2.8%) but no induction deaths among the 52 patients treated with pegaspargase.
Additional details on these studies and calaspargase pegol-mknl can be found in the drug’s prescribing information.
Calaspargase pegol-mknl is a product of Servier Pharmaceuticals LLC.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved calaspargase pegol-mknl (Asparlas) as a component of a multi-agent chemotherapeutic regimen to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in pediatric and young adult patients age 1 month to 21 years.
Calaspargase pegol-mknl is an asparagine-specific enzyme intended to provide a longer interval between doses compared to other available pegaspargase products.
The recommended dosage of calaspargase pegol-mknl is 2,500 U/m2 given no more frequently than every 21 days.
The FDA said it approved calaspargase pegol-mknl because the drug maintained nadir serum asparaginase activity above the level of 0.1 U/mL when given at 2,500 U/m2 every 3 weeks.
Calaspargase pegol-mknl was evaluated in Study DFCI 11-001, a trial of 237 children and adolescents with newly diagnosed ALL or lymphoblastic lymphoma. The patients’ median age was 5 years (range, 1 to 20 years).
They received calaspargase pegol-mknl at 2,500 U/m2 (n=118) or pegaspargase at 2,500 U/m2 (n=119) as part of a Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI) ALL Consortium backbone therapy.
The median duration of exposure was 8 months for both calaspargase pegol-mknl and pegaspargase.
Among the patients with B-cell lineage ALL, the complete remission rate was 98% in the calaspargase pegol-mknl arm and 99% in the pegaspargase arm. Estimated overall survival rates were comparable between the arms.
Common grade 3 or higher adverse events (in the calaspargase pegol-mknl and pegaspargase arms, respectively) included elevated transaminase (52% and 66%), bilirubin increase (20% and 25%), pancreatitis (18% and 24%), and abnormal clotting studies (14% and 21%).
There was one fatal adverse event among patients on calaspargase pegol-mknl—multi-organ failure in the setting of chronic pancreatitis associated with a pancreatic pseudocyst.
The safety of calaspargase pegol-mknl was also evaluated in Study AALL07P4, a trial of patients with newly diagnosed, high-risk B-precursor ALL.
The patients received calaspargase pegol-mknl at 2,500 U/m2 (n=43) or 2,100 U/m2 (n=68) or pegaspargase at 2,500 U/m2 (n=52) as a component of an augmented Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster regimen.
The patients’ median age was 11 years (range, 1 to 26 years). The median duration of exposure was 7 months for both calaspargase pegol-mknl and pegaspargase.
There were three induction deaths among the 111 patients who received calaspargase pegol-mknl (2.8%) but no induction deaths among the 52 patients treated with pegaspargase.
Additional details on these studies and calaspargase pegol-mknl can be found in the drug’s prescribing information.
Calaspargase pegol-mknl is a product of Servier Pharmaceuticals LLC.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved calaspargase pegol-mknl (Asparlas) as a component of a multi-agent chemotherapeutic regimen to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in pediatric and young adult patients age 1 month to 21 years.
Calaspargase pegol-mknl is an asparagine-specific enzyme intended to provide a longer interval between doses compared to other available pegaspargase products.
The recommended dosage of calaspargase pegol-mknl is 2,500 U/m2 given no more frequently than every 21 days.
The FDA said it approved calaspargase pegol-mknl because the drug maintained nadir serum asparaginase activity above the level of 0.1 U/mL when given at 2,500 U/m2 every 3 weeks.
Calaspargase pegol-mknl was evaluated in Study DFCI 11-001, a trial of 237 children and adolescents with newly diagnosed ALL or lymphoblastic lymphoma. The patients’ median age was 5 years (range, 1 to 20 years).
They received calaspargase pegol-mknl at 2,500 U/m2 (n=118) or pegaspargase at 2,500 U/m2 (n=119) as part of a Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI) ALL Consortium backbone therapy.
The median duration of exposure was 8 months for both calaspargase pegol-mknl and pegaspargase.
Among the patients with B-cell lineage ALL, the complete remission rate was 98% in the calaspargase pegol-mknl arm and 99% in the pegaspargase arm. Estimated overall survival rates were comparable between the arms.
Common grade 3 or higher adverse events (in the calaspargase pegol-mknl and pegaspargase arms, respectively) included elevated transaminase (52% and 66%), bilirubin increase (20% and 25%), pancreatitis (18% and 24%), and abnormal clotting studies (14% and 21%).
There was one fatal adverse event among patients on calaspargase pegol-mknl—multi-organ failure in the setting of chronic pancreatitis associated with a pancreatic pseudocyst.
The safety of calaspargase pegol-mknl was also evaluated in Study AALL07P4, a trial of patients with newly diagnosed, high-risk B-precursor ALL.
The patients received calaspargase pegol-mknl at 2,500 U/m2 (n=43) or 2,100 U/m2 (n=68) or pegaspargase at 2,500 U/m2 (n=52) as a component of an augmented Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster regimen.
The patients’ median age was 11 years (range, 1 to 26 years). The median duration of exposure was 7 months for both calaspargase pegol-mknl and pegaspargase.
There were three induction deaths among the 111 patients who received calaspargase pegol-mknl (2.8%) but no induction deaths among the 52 patients treated with pegaspargase.
Additional details on these studies and calaspargase pegol-mknl can be found in the drug’s prescribing information.
Calaspargase pegol-mknl is a product of Servier Pharmaceuticals LLC.
CHMP recommends treosulfan for allo-HSCT conditioning
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval for treosulfan (Trecondi) as part of conditioning prior to allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HSCT).
The full indication is for treosulfan to be used in combination with fludarabine for conditioning prior to allo-HSCT in adults with malignant and non-malignant diseases and in pediatric patients older than 1 month who have malignant diseases.
The CHMP’s recommendation for treosulfan will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to approve medicines for use in the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
The European Commission usually makes a decision within 67 days of a CHMP recommendation.
The CHMP’s opinion of treosulfan is supported by results from a phase 3 trial (NCT00822393), which were presented at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting.
In this trial, investigators compared two conditioning regimens, treosulfan-fludarabine and busulfan-fludarabine, in elderly or comorbid patients with acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndromes who were undergoing allo-HSCT.
The ASH data included 476 patients from the final analysis.
Investigators said safety results between day -6 and day +28 were similar with the two regimens.
The same was true for trilineage engraftment and the cumulative incidence of relapse/progression at 24 months after allo-HSCT.
However, survival rates were higher in the treosulfan arm.
The event-free survival at 24 months was 64.0% in the treosulfan arm and 50.4% in the busulfan arm (P=0.0000164). The overall survival at 24 months was 72.5% and 56.4%, respectively (P=0.0082).
Transplant-related mortality at 24 months was 11.3% in the treosulfan arm and 28.2% in the busulfan arm (P=0.0201).
This trial was sponsored by medac GmbH.
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval for treosulfan (Trecondi) as part of conditioning prior to allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HSCT).
The full indication is for treosulfan to be used in combination with fludarabine for conditioning prior to allo-HSCT in adults with malignant and non-malignant diseases and in pediatric patients older than 1 month who have malignant diseases.
The CHMP’s recommendation for treosulfan will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to approve medicines for use in the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
The European Commission usually makes a decision within 67 days of a CHMP recommendation.
The CHMP’s opinion of treosulfan is supported by results from a phase 3 trial (NCT00822393), which were presented at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting.
In this trial, investigators compared two conditioning regimens, treosulfan-fludarabine and busulfan-fludarabine, in elderly or comorbid patients with acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndromes who were undergoing allo-HSCT.
The ASH data included 476 patients from the final analysis.
Investigators said safety results between day -6 and day +28 were similar with the two regimens.
The same was true for trilineage engraftment and the cumulative incidence of relapse/progression at 24 months after allo-HSCT.
However, survival rates were higher in the treosulfan arm.
The event-free survival at 24 months was 64.0% in the treosulfan arm and 50.4% in the busulfan arm (P=0.0000164). The overall survival at 24 months was 72.5% and 56.4%, respectively (P=0.0082).
Transplant-related mortality at 24 months was 11.3% in the treosulfan arm and 28.2% in the busulfan arm (P=0.0201).
This trial was sponsored by medac GmbH.
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval for treosulfan (Trecondi) as part of conditioning prior to allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HSCT).
The full indication is for treosulfan to be used in combination with fludarabine for conditioning prior to allo-HSCT in adults with malignant and non-malignant diseases and in pediatric patients older than 1 month who have malignant diseases.
The CHMP’s recommendation for treosulfan will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to approve medicines for use in the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
The European Commission usually makes a decision within 67 days of a CHMP recommendation.
The CHMP’s opinion of treosulfan is supported by results from a phase 3 trial (NCT00822393), which were presented at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting.
In this trial, investigators compared two conditioning regimens, treosulfan-fludarabine and busulfan-fludarabine, in elderly or comorbid patients with acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndromes who were undergoing allo-HSCT.
The ASH data included 476 patients from the final analysis.
Investigators said safety results between day -6 and day +28 were similar with the two regimens.
The same was true for trilineage engraftment and the cumulative incidence of relapse/progression at 24 months after allo-HSCT.
However, survival rates were higher in the treosulfan arm.
The event-free survival at 24 months was 64.0% in the treosulfan arm and 50.4% in the busulfan arm (P=0.0000164). The overall survival at 24 months was 72.5% and 56.4%, respectively (P=0.0082).
Transplant-related mortality at 24 months was 11.3% in the treosulfan arm and 28.2% in the busulfan arm (P=0.0201).
This trial was sponsored by medac GmbH.
CHMP backs lusutrombopag for severe thrombocytopenia
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval for lusutrombopag to treat severe thrombocytopenia in adults with chronic liver disease who are undergoing invasive procedures.
Lusutrombopag is a thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor agonist that acts on the transmembrane domain of TPO receptors to induce proliferation and differentiation of megakaryocyte progenitor cells, thus leading to thrombocytopoiesis.
Lusutrombopag is intended to reduce the need for platelet transfusions before an invasive procedure and for rescue therapy for bleeding in the 7 days after the procedure.
The CHMP’s recommendation for lusutrombopag will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to approve medicines for use in the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
The European Commission usually makes a decision within 67 days of a CHMP recommendation.
Lusutrombopag trials
The efficacy of lusutrombopag was evaluated in two phase 3 trials—L-PLUS1 (1304M0631) and L-PLUS2 (1423M0634, NCT02389621).
The trials included 312 patients with chronic liver disease, severe thrombocytopenia (platelet counts below 50,000/μL), and a scheduled invasive procedure. The patients received lusutrombopag or placebo once daily for up to 7 days.
In L-PLUS1, 78% (38/49) of patients receiving lusutrombopag did not require platelet transfusions prior to the primary invasive procedure. The same was true for 13% (6/48) of patients who received placebo (P<0.0001).
In L-PLUS2 , 65% (70/108) of patients who received lusutrombopag did not require platelet transfusions prior to the primary invasive procedure or rescue therapy for bleeding in the 7 days after the procedure. The same was true for 29% (31/107) of patients receiving placebo (P<0.0001).
The safety of lusutrombopag was evaluated in three trials—L‐PLUS 1, L‐PLUS 2, and M0626 (1208M062).
The most common adverse event (AE) in these trials (n=341) was headache, which occurred in 5% of patients on lusutrombopag and 4% of patients on placebo.
Serious AEs occurred in 5% of patients on lusutrombopag and 7% of patients on placebo. The most common serious AE was portal vein thrombosis, which occurred in 1% of patients in both treatment groups.
None of the patients discontinued lusutrombopag due to AEs.
The trials were sponsored by Shionogi & Co., Ltd.
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval for lusutrombopag to treat severe thrombocytopenia in adults with chronic liver disease who are undergoing invasive procedures.
Lusutrombopag is a thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor agonist that acts on the transmembrane domain of TPO receptors to induce proliferation and differentiation of megakaryocyte progenitor cells, thus leading to thrombocytopoiesis.
Lusutrombopag is intended to reduce the need for platelet transfusions before an invasive procedure and for rescue therapy for bleeding in the 7 days after the procedure.
The CHMP’s recommendation for lusutrombopag will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to approve medicines for use in the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
The European Commission usually makes a decision within 67 days of a CHMP recommendation.
Lusutrombopag trials
The efficacy of lusutrombopag was evaluated in two phase 3 trials—L-PLUS1 (1304M0631) and L-PLUS2 (1423M0634, NCT02389621).
The trials included 312 patients with chronic liver disease, severe thrombocytopenia (platelet counts below 50,000/μL), and a scheduled invasive procedure. The patients received lusutrombopag or placebo once daily for up to 7 days.
In L-PLUS1, 78% (38/49) of patients receiving lusutrombopag did not require platelet transfusions prior to the primary invasive procedure. The same was true for 13% (6/48) of patients who received placebo (P<0.0001).
In L-PLUS2 , 65% (70/108) of patients who received lusutrombopag did not require platelet transfusions prior to the primary invasive procedure or rescue therapy for bleeding in the 7 days after the procedure. The same was true for 29% (31/107) of patients receiving placebo (P<0.0001).
The safety of lusutrombopag was evaluated in three trials—L‐PLUS 1, L‐PLUS 2, and M0626 (1208M062).
The most common adverse event (AE) in these trials (n=341) was headache, which occurred in 5% of patients on lusutrombopag and 4% of patients on placebo.
Serious AEs occurred in 5% of patients on lusutrombopag and 7% of patients on placebo. The most common serious AE was portal vein thrombosis, which occurred in 1% of patients in both treatment groups.
None of the patients discontinued lusutrombopag due to AEs.
The trials were sponsored by Shionogi & Co., Ltd.
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended approval for lusutrombopag to treat severe thrombocytopenia in adults with chronic liver disease who are undergoing invasive procedures.
Lusutrombopag is a thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor agonist that acts on the transmembrane domain of TPO receptors to induce proliferation and differentiation of megakaryocyte progenitor cells, thus leading to thrombocytopoiesis.
Lusutrombopag is intended to reduce the need for platelet transfusions before an invasive procedure and for rescue therapy for bleeding in the 7 days after the procedure.
The CHMP’s recommendation for lusutrombopag will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to approve medicines for use in the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
The European Commission usually makes a decision within 67 days of a CHMP recommendation.
Lusutrombopag trials
The efficacy of lusutrombopag was evaluated in two phase 3 trials—L-PLUS1 (1304M0631) and L-PLUS2 (1423M0634, NCT02389621).
The trials included 312 patients with chronic liver disease, severe thrombocytopenia (platelet counts below 50,000/μL), and a scheduled invasive procedure. The patients received lusutrombopag or placebo once daily for up to 7 days.
In L-PLUS1, 78% (38/49) of patients receiving lusutrombopag did not require platelet transfusions prior to the primary invasive procedure. The same was true for 13% (6/48) of patients who received placebo (P<0.0001).
In L-PLUS2 , 65% (70/108) of patients who received lusutrombopag did not require platelet transfusions prior to the primary invasive procedure or rescue therapy for bleeding in the 7 days after the procedure. The same was true for 29% (31/107) of patients receiving placebo (P<0.0001).
The safety of lusutrombopag was evaluated in three trials—L‐PLUS 1, L‐PLUS 2, and M0626 (1208M062).
The most common adverse event (AE) in these trials (n=341) was headache, which occurred in 5% of patients on lusutrombopag and 4% of patients on placebo.
Serious AEs occurred in 5% of patients on lusutrombopag and 7% of patients on placebo. The most common serious AE was portal vein thrombosis, which occurred in 1% of patients in both treatment groups.
None of the patients discontinued lusutrombopag due to AEs.
The trials were sponsored by Shionogi & Co., Ltd.