User login
Insights From the 2020-2021 Dermatology Residency Match
To the Editor:
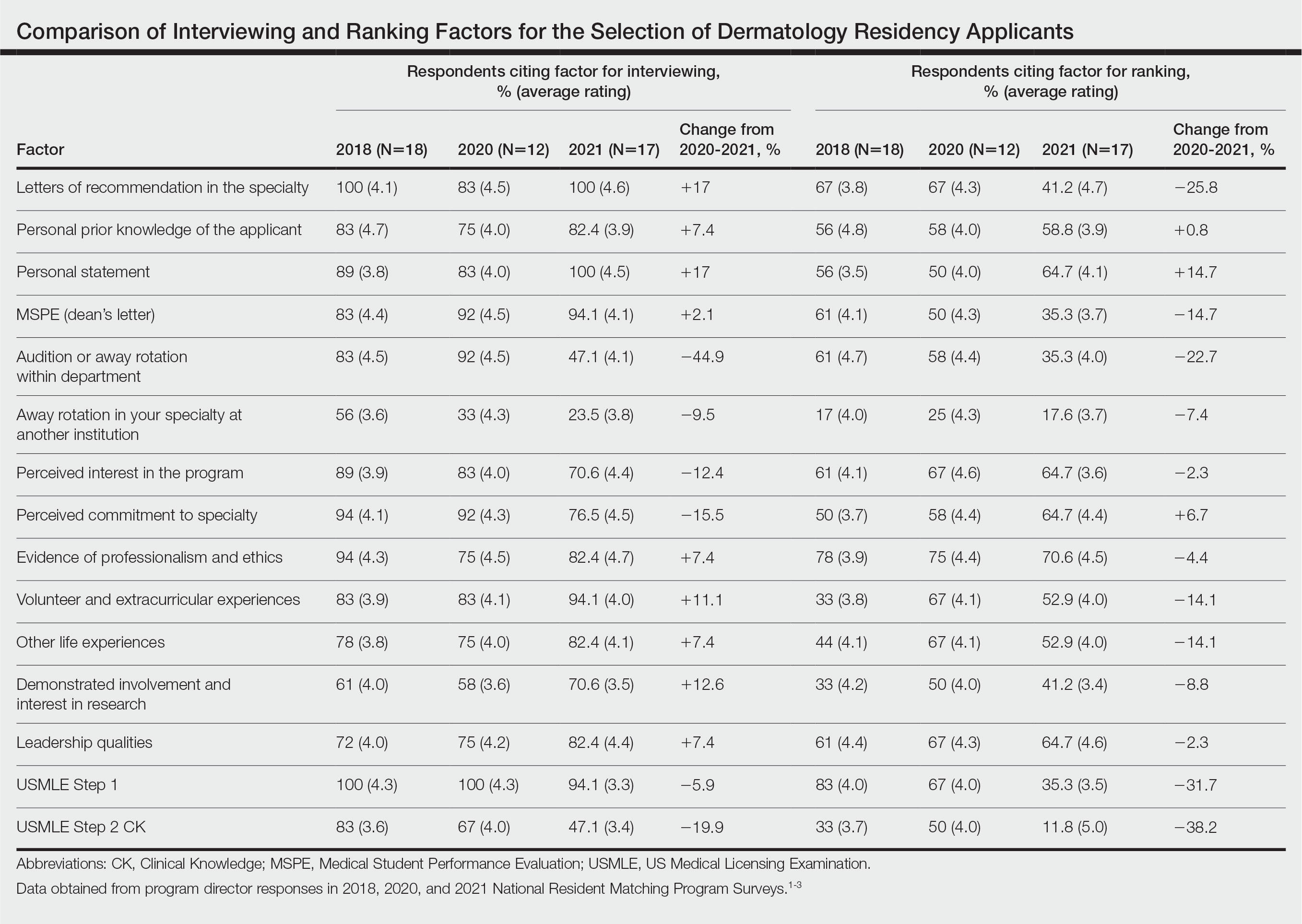
Data from the program director survey of the National Resident Matching Program offer key insights into the 2021 dermatology application process.1,2 Examination of data from the 2020 (N=12) and 2021 (N=17) program director survey regarding interviewing applicants revealed that specialty-specific letters of recommendation (LORs), personal prior knowledge of an applicant, and personal statement increased in importance by 17%, 7.4%, and 17%, respectively, whereas away rotations within the department decreased in importance by 44.9% (Table).1,2 Interestingly, for ranking applicants, programs decreased their emphasis on specialty-specific LORs by 25.8% and away rotations within the department by 22.7% and increased emphasis on personal statements by 14.7% and personal prior knowledge of an applicant by 0.8% from 2020 to 2021 (Table).1,2 These findings align with the prior recommendation to limit away rotations; data are contradictory—when comparing factors for interviewing as compared to ranking applicants—for specialty-specific LORs.
We further compared data from the otolaryngology cycle, which implemented preference signaling by which an applicant can signal their interest in a particular residency program in the 2021 Match, to data from dermatology with no preference signaling. A 90% probability of matching is estimated to require approximately 8 or 9 interviews for dermatology or 12 interviews for otolaryngology for MD senior students in 2020.4 In prior dermatology application cycles, the most highly qualified candidates constituted 7% to 21% of all applicants but were estimated to receive half of all interviews, causing a maldistribution of interviews.5,6
For the 2021 otolaryngology match, the Society of University Otolaryngologists implemented a novel preference signaling system that allowed candidates to show interest in programs by sending 5 preferences, or tokens.7 Recent data reports from the otolaryngology cycle demonstrated at least a 2-fold increase in the rate of receiving an interview invitation for signaled programs compared to the closest nonsignaled program if applicants were provided an additional token.7 Regarding overall applicant competitiveness (ie, dividing participants into quartiles based on their competitiveness), the highest increase in the overall rate of interview invitations (3.5 [total invitations/total applications]) was demonstrated for fourth-quartile (ie, “lowest quartile”) applicants compared with the increase in the overall rate of interview invitations seen in other quartiles (first quartile, an increase of 2.3; second quartile, an increase of 2.6; and third quartile, an increase of 2.4).7 We look forward to seeing the impact of preference signaling on the results of the 2022 dermatology cycle.
Despite changes in the interviewing process to accommodate COVID-19 pandemic safety recommendations, the overall dermatology postgraduate year (PGY) 2 fill rate remained unchanged from 2018 (98.6%) to 2021 (98.7%). Zero PGY-1 positions and 5 PGY-2 positions were unfilled in the 2021 Main Residency Match compared to 1 unfilled PGY-1 position and 4 unfilled PGY-2 positions in 2018.8 The coordinated interview invitation release, holistic review of applications, increased number of rankings, and virtual interviews might have helped offset potential obstacles imparted by inability to complete away rotations, inability to obtain LORs, and conducting interviews virtually.5
A limitation of our analysis is the low response rate of program directors to National Resident Matching Program surveys.
These strategies—holistic application review and coordinated interview release—may be considered in future cycles given their convenience and negligible impact on the dermatology match rate. For example, virtual interviews relieve the financial and time burdens of in-person interviews—approximately $10,000 for each US senior applicant—thus potentially allowing for a more equitable matching process.3 Inversely, in-person interviews allow participants to effectively network and form more meaningful connections while obtaining a better understanding of facilities and surrounding locales. As such, the medical community should continue to come to a consensus on the optimal format to host interviews.
- Results of the 2021 NRMP Program Director Survey. National Resident Matching Program. August 2021. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/2021-PD-Survey-Report-for-WWW.pdf
- Results of the 2020 NRMP Program Director Survey. National Resident Matching Program. August 2020. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/2020-PD-Survey.pdf
- Rojek NW, Shinkai K, Fett N. Dermatology faculty and residents’ perspectives on the dermatology residency application process: a nationwide survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:157-159. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.01.00
- Charting Outcomes in the Match: Senior Students of U.S. MD Medical Schools. National Resident Matching Program. July 2020. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Charting-Outcomes-in-the-Match-2020_MD-Senior_final.pdf
- Thatiparthi A, Martin A, Liu J, et al. Preliminary outcomes of 2020-2021 dermatology residency application cycle and adverse effects of COVID-19. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:e263-e264. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.034
- Hammoud MM, Standiford T, Carmody JB. Potential implications of COVID-19 for the 2020-2021 residency application cycle. JAMA. 2020;324:29-30. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.8911
- Interview offer rate with/without ENTSignaling. Society of University Otolaryngologists. Updated July 19, 2022. Accessed December 12, 2022. https://opdo-hns.org/mpage/signaling-updates
- Results and Data: 2021 Main Residency Match. National Resident Matching Program. May 2021. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/MRM-Results_and-Data_2021.pdf
To the Editor:
Data from the program director survey of the National Resident Matching Program offer key insights into the 2021 dermatology application process.1,2 Examination of data from the 2020 (N=12) and 2021 (N=17) program director survey regarding interviewing applicants revealed that specialty-specific letters of recommendation (LORs), personal prior knowledge of an applicant, and personal statement increased in importance by 17%, 7.4%, and 17%, respectively, whereas away rotations within the department decreased in importance by 44.9% (Table).1,2 Interestingly, for ranking applicants, programs decreased their emphasis on specialty-specific LORs by 25.8% and away rotations within the department by 22.7% and increased emphasis on personal statements by 14.7% and personal prior knowledge of an applicant by 0.8% from 2020 to 2021 (Table).1,2 These findings align with the prior recommendation to limit away rotations; data are contradictory—when comparing factors for interviewing as compared to ranking applicants—for specialty-specific LORs.

We further compared data from the otolaryngology cycle, which implemented preference signaling by which an applicant can signal their interest in a particular residency program in the 2021 Match, to data from dermatology with no preference signaling. A 90% probability of matching is estimated to require approximately 8 or 9 interviews for dermatology or 12 interviews for otolaryngology for MD senior students in 2020.4 In prior dermatology application cycles, the most highly qualified candidates constituted 7% to 21% of all applicants but were estimated to receive half of all interviews, causing a maldistribution of interviews.5,6
For the 2021 otolaryngology match, the Society of University Otolaryngologists implemented a novel preference signaling system that allowed candidates to show interest in programs by sending 5 preferences, or tokens.7 Recent data reports from the otolaryngology cycle demonstrated at least a 2-fold increase in the rate of receiving an interview invitation for signaled programs compared to the closest nonsignaled program if applicants were provided an additional token.7 Regarding overall applicant competitiveness (ie, dividing participants into quartiles based on their competitiveness), the highest increase in the overall rate of interview invitations (3.5 [total invitations/total applications]) was demonstrated for fourth-quartile (ie, “lowest quartile”) applicants compared with the increase in the overall rate of interview invitations seen in other quartiles (first quartile, an increase of 2.3; second quartile, an increase of 2.6; and third quartile, an increase of 2.4).7 We look forward to seeing the impact of preference signaling on the results of the 2022 dermatology cycle.
Despite changes in the interviewing process to accommodate COVID-19 pandemic safety recommendations, the overall dermatology postgraduate year (PGY) 2 fill rate remained unchanged from 2018 (98.6%) to 2021 (98.7%). Zero PGY-1 positions and 5 PGY-2 positions were unfilled in the 2021 Main Residency Match compared to 1 unfilled PGY-1 position and 4 unfilled PGY-2 positions in 2018.8 The coordinated interview invitation release, holistic review of applications, increased number of rankings, and virtual interviews might have helped offset potential obstacles imparted by inability to complete away rotations, inability to obtain LORs, and conducting interviews virtually.5
A limitation of our analysis is the low response rate of program directors to National Resident Matching Program surveys.
These strategies—holistic application review and coordinated interview release—may be considered in future cycles given their convenience and negligible impact on the dermatology match rate. For example, virtual interviews relieve the financial and time burdens of in-person interviews—approximately $10,000 for each US senior applicant—thus potentially allowing for a more equitable matching process.3 Inversely, in-person interviews allow participants to effectively network and form more meaningful connections while obtaining a better understanding of facilities and surrounding locales. As such, the medical community should continue to come to a consensus on the optimal format to host interviews.
To the Editor:
Data from the program director survey of the National Resident Matching Program offer key insights into the 2021 dermatology application process.1,2 Examination of data from the 2020 (N=12) and 2021 (N=17) program director survey regarding interviewing applicants revealed that specialty-specific letters of recommendation (LORs), personal prior knowledge of an applicant, and personal statement increased in importance by 17%, 7.4%, and 17%, respectively, whereas away rotations within the department decreased in importance by 44.9% (Table).1,2 Interestingly, for ranking applicants, programs decreased their emphasis on specialty-specific LORs by 25.8% and away rotations within the department by 22.7% and increased emphasis on personal statements by 14.7% and personal prior knowledge of an applicant by 0.8% from 2020 to 2021 (Table).1,2 These findings align with the prior recommendation to limit away rotations; data are contradictory—when comparing factors for interviewing as compared to ranking applicants—for specialty-specific LORs.

We further compared data from the otolaryngology cycle, which implemented preference signaling by which an applicant can signal their interest in a particular residency program in the 2021 Match, to data from dermatology with no preference signaling. A 90% probability of matching is estimated to require approximately 8 or 9 interviews for dermatology or 12 interviews for otolaryngology for MD senior students in 2020.4 In prior dermatology application cycles, the most highly qualified candidates constituted 7% to 21% of all applicants but were estimated to receive half of all interviews, causing a maldistribution of interviews.5,6
For the 2021 otolaryngology match, the Society of University Otolaryngologists implemented a novel preference signaling system that allowed candidates to show interest in programs by sending 5 preferences, or tokens.7 Recent data reports from the otolaryngology cycle demonstrated at least a 2-fold increase in the rate of receiving an interview invitation for signaled programs compared to the closest nonsignaled program if applicants were provided an additional token.7 Regarding overall applicant competitiveness (ie, dividing participants into quartiles based on their competitiveness), the highest increase in the overall rate of interview invitations (3.5 [total invitations/total applications]) was demonstrated for fourth-quartile (ie, “lowest quartile”) applicants compared with the increase in the overall rate of interview invitations seen in other quartiles (first quartile, an increase of 2.3; second quartile, an increase of 2.6; and third quartile, an increase of 2.4).7 We look forward to seeing the impact of preference signaling on the results of the 2022 dermatology cycle.
Despite changes in the interviewing process to accommodate COVID-19 pandemic safety recommendations, the overall dermatology postgraduate year (PGY) 2 fill rate remained unchanged from 2018 (98.6%) to 2021 (98.7%). Zero PGY-1 positions and 5 PGY-2 positions were unfilled in the 2021 Main Residency Match compared to 1 unfilled PGY-1 position and 4 unfilled PGY-2 positions in 2018.8 The coordinated interview invitation release, holistic review of applications, increased number of rankings, and virtual interviews might have helped offset potential obstacles imparted by inability to complete away rotations, inability to obtain LORs, and conducting interviews virtually.5
A limitation of our analysis is the low response rate of program directors to National Resident Matching Program surveys.
These strategies—holistic application review and coordinated interview release—may be considered in future cycles given their convenience and negligible impact on the dermatology match rate. For example, virtual interviews relieve the financial and time burdens of in-person interviews—approximately $10,000 for each US senior applicant—thus potentially allowing for a more equitable matching process.3 Inversely, in-person interviews allow participants to effectively network and form more meaningful connections while obtaining a better understanding of facilities and surrounding locales. As such, the medical community should continue to come to a consensus on the optimal format to host interviews.
- Results of the 2021 NRMP Program Director Survey. National Resident Matching Program. August 2021. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/2021-PD-Survey-Report-for-WWW.pdf
- Results of the 2020 NRMP Program Director Survey. National Resident Matching Program. August 2020. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/2020-PD-Survey.pdf
- Rojek NW, Shinkai K, Fett N. Dermatology faculty and residents’ perspectives on the dermatology residency application process: a nationwide survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:157-159. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.01.00
- Charting Outcomes in the Match: Senior Students of U.S. MD Medical Schools. National Resident Matching Program. July 2020. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Charting-Outcomes-in-the-Match-2020_MD-Senior_final.pdf
- Thatiparthi A, Martin A, Liu J, et al. Preliminary outcomes of 2020-2021 dermatology residency application cycle and adverse effects of COVID-19. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:e263-e264. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.034
- Hammoud MM, Standiford T, Carmody JB. Potential implications of COVID-19 for the 2020-2021 residency application cycle. JAMA. 2020;324:29-30. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.8911
- Interview offer rate with/without ENTSignaling. Society of University Otolaryngologists. Updated July 19, 2022. Accessed December 12, 2022. https://opdo-hns.org/mpage/signaling-updates
- Results and Data: 2021 Main Residency Match. National Resident Matching Program. May 2021. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/MRM-Results_and-Data_2021.pdf
- Results of the 2021 NRMP Program Director Survey. National Resident Matching Program. August 2021. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/2021-PD-Survey-Report-for-WWW.pdf
- Results of the 2020 NRMP Program Director Survey. National Resident Matching Program. August 2020. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/2020-PD-Survey.pdf
- Rojek NW, Shinkai K, Fett N. Dermatology faculty and residents’ perspectives on the dermatology residency application process: a nationwide survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:157-159. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.01.00
- Charting Outcomes in the Match: Senior Students of U.S. MD Medical Schools. National Resident Matching Program. July 2020. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Charting-Outcomes-in-the-Match-2020_MD-Senior_final.pdf
- Thatiparthi A, Martin A, Liu J, et al. Preliminary outcomes of 2020-2021 dermatology residency application cycle and adverse effects of COVID-19. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:e263-e264. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.034
- Hammoud MM, Standiford T, Carmody JB. Potential implications of COVID-19 for the 2020-2021 residency application cycle. JAMA. 2020;324:29-30. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.8911
- Interview offer rate with/without ENTSignaling. Society of University Otolaryngologists. Updated July 19, 2022. Accessed December 12, 2022. https://opdo-hns.org/mpage/signaling-updates
- Results and Data: 2021 Main Residency Match. National Resident Matching Program. May 2021. Accessed December 6, 2021. https://www.nrmp.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/MRM-Results_and-Data_2021.pdf
PRACTICE POINTS
- Although there have been numerous changes to the dermatology interview process due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the overall fill rate for postgraduate year 2 positions remained unchanged from 2018 (prepandemic) to 2021 (postpandemic).
- Strategies to accommodate new safety recommendations for interviews may reduce the financial burden (approximately $10,000 for each senior applicant) and time constraints on applicants. These strategies should be considered for implementation in future cycles.