User login
Distinguishing cellulitis from its mimics
More than 10% of patients labeled as having cellulitis do not have cellulitis.1 This is unfortunate, as it leads to excessive and incorrect use of antibiotics and to delays in appropriate therapy.2 However, it is not surprising, given the number of conditions that bear a striking similarity to cellulitis. A familiarity with the features of true cellulitis and with the handful of conditions that can bear a striking similarity to it is the way out of this potential diagnostic quagmire.
WHAT CELLULITIS IS—AND IS NOT
The key characteristics of cellulitis are redness, warmth, tenderness, and swelling of the skin. A history of trauma and pain in the affected area and evidence of leukocytosis3 suggest cellulitis. A symmetric or diffusely scattered pattern indicates a condition other than cellulitis, which is overwhelmingly unilateral, with smooth, indistinct borders4,5 Other factors pointing to cellulitis are underlying immunosuppression, a more rapid progression, previous episodes, systemic symptoms (eg, fever, leukocytosis), new medications, new travel or outdoor exposure, and comorbidities such as diabetes and peripheral vascular disease. A long-standing, slowly progressive course and a history of unsuccessful treatment with antibiotics are strong indicators of a condition other than cellulitis.
Consultation with a dermatologist is recommended to narrow the differential diagnosis. The dermatologist can determine if biopsy is necessary, as many dermatoses that mimic cellulitis can be diagnosed by visual recognition alone.
STASIS DERMATITIS
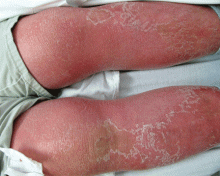
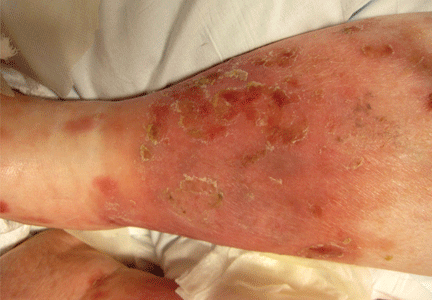
The most common mimic of cellulitis is stasis dermatitis (Figure 1).2 Patients can present with ill-defined, bilateral, pitting edema of the lower extremities, typically with erythema, hyperpigmentation, serous drainage, and superficial desquamation.3,6,7
The inciting factor is chronic venous insufficiency, leading to interstitial edema, extravasation of red blood cells, and decreased tissue oxygenation. This process causes micro-vascular changes and microthrombi that up-regulate transforming growth factor beta and fibroblastic growth factor.7 If the process is allowed to continue, stasis dermatitis may progress to lipodermatosclerosis.
Tip: Stasis dermatitis is generally bilateral, the process will have been ongoing for years, there is often pitting edema, and the legs should be nontender.
LIPODERMATOSCLEROSIS
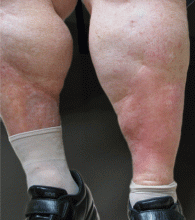
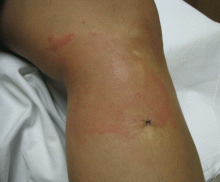
Lipodermatosclerosis is a sclerosing panniculitis classically described as an “inverted champagne bottle” or “inverted bowling pin” appearance of the leg, ie, the diameter of the leg is sharply narrowed directly below the calf (Figure 2).
There is an acute and a chronic phase. The acute phase is characterized by inflammation and erythema, and the chronic phase is characterized by fibrosis.8 The acute phase presents with severe lower-extremity pain above the medial malleolus, erythema, edema, and warmth; there is no sharp demarcation between affected and unaffected skin.9,10 This phase can be difficult to distinguish from cellulitis, so the history plays a key role. Known venous insufficiency, cutaneous changes of stasis dermatitis, and the absence of systemic symptoms all point to lipodermatosclerosis.
The chronic phase is characterized by unilateral or bilateral, indurated, sclerotic plaques with a “bound-down” appearance (ie, they appear as if tethered—or bound—to the subcutaneous tissue) affecting the skin from below the knee to the ankle; there is a sharp demarcation between affected and unaffected skin.9–11 The skin is often bronze or brown secondary to hemosiderin deposits. There can be prominent varicosities and scattered ulcerations depending on the course of the disease.
This condition is thought to be the result of long-standing chronic venous insufficiency.7,8,9,11 It is proposed that venous incompetence leads to extravasation of interstitial fluid and red blood cells, decreased diffusion of oxygen to the tissues, and eventual tissue and endothelial damage. As the endothelium is damaged, microthrombi formation and infarction ensue, stimulating fibroblasts to form granulation tissue.
Tip: The history helps to distinguish acute lipodermatosclerosis from cellulitis. Chroniclipodermatoslcerosis will have been ongoing for years, the legs should be nontender, the skin will be bound-down, and the diameter of the leg will sharply decrease from knee to ankle.
CONTACT DERMATITIS
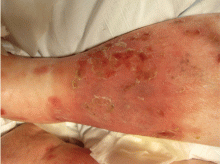
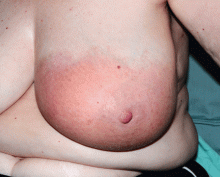
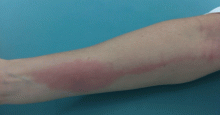
Allergic and irritant forms of contact dermatitis are often mistaken for cellulitis. Irritant contact dermatitis (Figure 3) presents with erythematous patches and plaques with well-defined borders, often in a geometric distribution where the skin was exposed to an irritant.12 Allergic contact dermatitis is a delayed hypersensitivity dermatitis that can be secondary to something ingested, applied to the skin, or airborne (Figure 4). It presents as erythematous macules, papules, and plaques that may have serous drainage or vesiculation. Lesions of allergic contact dermatitis are usually confined to the site of contact with the allergen, but they can infrequently be found at distant sites, in which case it is considered systemic contact dermatitis.3,5 Depending on the severity of the allergy, patients may complain of intense pain and pruritus.3
Additionally, chronic, nonhealing leg ulcers may have a confounding allergic contact dermatitis.7 Although patients may believe they are helping the ulcer heal by applying topical antibiotics or other lubricants, they may in fact be impeding the healing process. Always inquire as to what the patient is applying if he or she has leg ulceration with surrounding edema and erythema that has not resolved with conventional treatments.13,14
Tip: The key to distinguishing contact dermatitis from cellulitis is the history. For example, ask about recent changes in medications, soaps, and laundry detergents, new hobbies, or recent surgeries. The involved site is often confined to the area where the allergen contacted the skin, except in cases of exposure to an airborne allergen.
LYMPHEDEMA
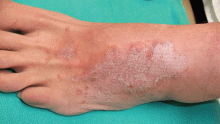
Lymphedema is characterized by localized edema of an affected extremity, with induration, erythema, and secondary cutaneous changes such as hyperkeratosis, dyspigmentation, and wart-like architecture (Figure 5).
Primary lymphedema appears in the setting of congenital abnormalities, whereas secondary lymphedema results from an interruption of a previously functioning lymphatic system (eg, after radical mastectomy).
Patients often present with unilateral nonpitting edema and erythema in the absence of systemic symptoms.12 Many patients presenting with lower-extremity lymphedema are overweight or obese, as the weight they carry causes obstruction of the inguinal lymphatics.6
The pathophysiology is not clearly delineated but is thought to be a consequence of decreased oxygenation of tissue secondary to extravasated lymph. As the oxygen is compromised, macrophages and fibroblasts are recruited, resulting in fibrosis.6
Patients with lymphedema are more susceptible to superficial and deep skin infections, as the natural defense system in the epidermis and papillary dermis is compromised by impaired lymphatic drainage.15
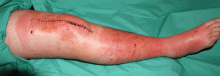
To differentiate uncomplicated lymphedema from a secondary cutaneous infection, the clinician should take into account the presence or absence of warmth, pain, increased erythema, and systemic symptoms (Figure 6).
Tip: Primary lymphedema will most likely present in childhood with no inciting factors and will require a full workup. Obtaining a history should make secondary lymphedema a relatively straightforward diagnosis: Has the patient undergone lymph node dissection? Has the patient had an injury in the affected leg? Lymphedema is overwhelmingly unilateral and nonpitting, and is often seen in overweight people (if no precipitating factor is present).
EOSINOPHILIC CELLULITIS
Eosinophilic cellulitis, or Wells syndrome, was first described in 1971 as a granulomatous dermatitis.16 It is a recurrent hypersensitivity reaction to a drug, to a vaccine, or to an insect bite, or to a viral or fungal infection that presents on the extremities as localized erythema, edema, and induration with sharp borders and a green or gray hue (Figure 7).17–19 The lesions commonly progress to firm, indurated plaques that resemble morphea. The plaques may take weeks or years to resolve, but they do so without scarring.12,17,20,21
As patients tend to have recurrent bouts of eosinophilic cellulitis, they may have lesions in different stages of healing. Patients tend to report itching and burning that precedes the onset of plaques.22 The complete blood count typically shows a transient hypereosinophilia.12,16,17,23–25
Tip: This diagnosis often requires biopsy for confirmation, but helpful clues are a history of recurrent episodes, the color of the lesions, and peripheral eosinophilia.
PAPULAR URTICARIA
Papular urticaria is a dermal hypersensitivity reaction to an insect bite, most commonly from a flea or mosquito.26 Patients are often children, as their immune system may be hypersensitive. But children often develop tolerance before puberty.27
The presentation may vary, from numerous urticarial papules near the site of a bite, to generalized, large, indurated, erythematous plaques reminiscent of cellulitis (Figure 8).5,26 The lesions usually develop within hours of a bite and persist for an average of 1 to 2 weeks.28 The areas typically affected are the head and neck or the upper or lower extremities; the palms, soles, and trunk are usually spared.27
Patients most often complain of intense itching.12 The pathogenesis is proposed to be mediated by the immune complex, and tissue biopsy study shows increased eosinophils. The eosinophils stimulate mast cells, causing release of histamine, leading to increased vascular permeability, edema, and erythema.28,29
Tip: Biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis, though often the history may be sufficient. The patient may or may not recall a bite, so probe into recent activities such as outdoor sports or contact with a new pet. The papules and plaques are generally very pruritic but not painful.
DERMATOLOGY CONSULT
If the clinical presentation and history do not correlate, or if the skin condition has been treated with antibiotics yet has failed to respond, the possibility of other cutaneous dermatoses should be entertained. A dermatology consult can help determine the diagnosis, the need for further evaluation, and the best treatment course.
- Hepburn MJ, Dooley DP, Ellis MW. Alternative diagnoses that often mimic cellulitis. Am Fam Physician 2003; 67:2471.
- David CV, Chira S, Eells SJ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy in patients admitted to hospitals with cellulitis. Dermatol Online J 2011; 17:1.
- Bailey E, Kroshinsky D. Cellulitis: diagnosis and management. Dermatol Ther 2011; 24:229–239.
- Stevens DL, Bisno AL, Chambers HF, et al; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft-tissue infections. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 41:1373–1406.
- Lio PA. The many faces of cellulitis. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed 2009; 94:50–54.
- Yosipovitch G, DeVore A, Dawn A. Obesity and the skin: skin physiology and skin manifestations of obesity. J Am Acad Dermatol 2007; 56:901–916.
- Farage MA, Miller KW, Berardesca E, Maibach HI. Clinical implications of aging skin: cutaneous disorders in the elderly. Am J Clin Dermatol 2009; 10:73–86.
- Kirsner RS, Pardes JB, Eaglstein WH, Falanga V. The clinical spectrum of lipodermatosclerosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 1993; 28:623–627.
- Miteva M, Romanelli P, Kirsner RS. Lipodermatosclerosis. Dermatol Ther 2010; 23:375–388.
- Barron GS, Jacob SE, Kirsner RS. Dermatologic complications of chronic venous disease: medical management and beyond. Ann Vasc Surg 2007; 21:652–662.
- Bruce AJ, Bennett DD, Lohse CM, Rooke TW, Davis MD. Lipodermatosclerosis: review of cases evaluated at Mayo Clinic. J Am Acad Dermatol 2002; 46:187–192.
- Falagas ME, Vergidis PI. Narrative review: diseases that masquerade as infectious cellulitis. Ann Intern Med 2005; 142:47–55.
- Wilson CL, Cameron J, Powell SM, Cherry G, Ryan TJ. High incidence of contact dermatitis in leg-ulcer patients—implications for management. Clin Exp Dermatol 1991; 16:250–253.
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology 1996; 192:198–202.
- Keeley VL. Lymphoedema and cellulitis: chicken or egg? Br J Dermatol 2008; 158:1175–1176.
- Wells GC. Recurrent granulomatous dermatitis with eosinophilia. Trans St Johns Hosp Dermatol Soc 1971; 57:46–56.
- Ferreli C, Pinna AL, Atzori L, Aste N. Eosinophilic cellulitis (Well’s syndrome): a new case description. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 1999; 13:41–45.
- Ladoyanni E, Vlachou C, Thushara R, Snead D. A patient with Wells’ syndrome. Clin Exp Dermatol 2010; 35:e3–e4.
- Moon HS, Park K, Lee JH, Son SJ. Eosinophilic cellulitis in an infant. Int J Dermatol 2010; 49:592–593.
- Walker P, Long D, James C, Marshman G. Exaggerated insect bite reaction exacerbated by a pyogenic infection in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Australas J Dermatol 2007; 48:165–169.
- Laliwala NM, Kulshrestha R, Singh R, Balasubramaniam P. A case of eosinophilic cellulitis of the hand mimicking bacterial cellulitis. J Hand Surg Eur Vol 2009; 34:410–411.
- Chung CL, Cusack CA. Wells syndrome: an enigmatic and therapeutically challenging disease. J Drugs Dermatol 2006; 5:908–911.
- Melski JW. Wells’ syndrome, insect bites, and eosinophils. Dermatol Clin 1990; 8:287–293.
- Spigel GT, Winkelmann RK. Wells’ syndrome. Recurrent granulomatous dermatitis with eosinophilia. Arch Dermatol 1979; 115:611–613.
- Clark DP, Anderson PC. Eosinophilic cellulitis caused by arthropod bites. Int J Dermatol 1988; 27:411–412.
- Howard R, Frieden IJ. Papular urticaria in children. Pediatr Dermatol 1996; 13:246–249.
- Hernandez RG, Cohen BA. Insect bite-induced hypersensitivity and the SCRATCH principles: a new approach to papular urticaria. Pediatrics 2006; 118:e189–e196.
- Heng MC, Kloss SG, Haberfelde GC. Pathogenesis of papular urticaria. J Am Acad Dermatol 1984; 10:1030–1034.
- Kossard S, Hamann I, Wilkinson B. Defining urticarial dermatitis: a subset of dermal hypersensitivity reaction pattern. Arch Dermatol 2006; 142:29–34.
More than 10% of patients labeled as having cellulitis do not have cellulitis.1 This is unfortunate, as it leads to excessive and incorrect use of antibiotics and to delays in appropriate therapy.2 However, it is not surprising, given the number of conditions that bear a striking similarity to cellulitis. A familiarity with the features of true cellulitis and with the handful of conditions that can bear a striking similarity to it is the way out of this potential diagnostic quagmire.
WHAT CELLULITIS IS—AND IS NOT
The key characteristics of cellulitis are redness, warmth, tenderness, and swelling of the skin. A history of trauma and pain in the affected area and evidence of leukocytosis3 suggest cellulitis. A symmetric or diffusely scattered pattern indicates a condition other than cellulitis, which is overwhelmingly unilateral, with smooth, indistinct borders4,5 Other factors pointing to cellulitis are underlying immunosuppression, a more rapid progression, previous episodes, systemic symptoms (eg, fever, leukocytosis), new medications, new travel or outdoor exposure, and comorbidities such as diabetes and peripheral vascular disease. A long-standing, slowly progressive course and a history of unsuccessful treatment with antibiotics are strong indicators of a condition other than cellulitis.
Consultation with a dermatologist is recommended to narrow the differential diagnosis. The dermatologist can determine if biopsy is necessary, as many dermatoses that mimic cellulitis can be diagnosed by visual recognition alone.
STASIS DERMATITIS
The most common mimic of cellulitis is stasis dermatitis (Figure 1).2 Patients can present with ill-defined, bilateral, pitting edema of the lower extremities, typically with erythema, hyperpigmentation, serous drainage, and superficial desquamation.3,6,7
The inciting factor is chronic venous insufficiency, leading to interstitial edema, extravasation of red blood cells, and decreased tissue oxygenation. This process causes micro-vascular changes and microthrombi that up-regulate transforming growth factor beta and fibroblastic growth factor.7 If the process is allowed to continue, stasis dermatitis may progress to lipodermatosclerosis.
Tip: Stasis dermatitis is generally bilateral, the process will have been ongoing for years, there is often pitting edema, and the legs should be nontender.
LIPODERMATOSCLEROSIS
Lipodermatosclerosis is a sclerosing panniculitis classically described as an “inverted champagne bottle” or “inverted bowling pin” appearance of the leg, ie, the diameter of the leg is sharply narrowed directly below the calf (Figure 2).
There is an acute and a chronic phase. The acute phase is characterized by inflammation and erythema, and the chronic phase is characterized by fibrosis.8 The acute phase presents with severe lower-extremity pain above the medial malleolus, erythema, edema, and warmth; there is no sharp demarcation between affected and unaffected skin.9,10 This phase can be difficult to distinguish from cellulitis, so the history plays a key role. Known venous insufficiency, cutaneous changes of stasis dermatitis, and the absence of systemic symptoms all point to lipodermatosclerosis.
The chronic phase is characterized by unilateral or bilateral, indurated, sclerotic plaques with a “bound-down” appearance (ie, they appear as if tethered—or bound—to the subcutaneous tissue) affecting the skin from below the knee to the ankle; there is a sharp demarcation between affected and unaffected skin.9–11 The skin is often bronze or brown secondary to hemosiderin deposits. There can be prominent varicosities and scattered ulcerations depending on the course of the disease.
This condition is thought to be the result of long-standing chronic venous insufficiency.7,8,9,11 It is proposed that venous incompetence leads to extravasation of interstitial fluid and red blood cells, decreased diffusion of oxygen to the tissues, and eventual tissue and endothelial damage. As the endothelium is damaged, microthrombi formation and infarction ensue, stimulating fibroblasts to form granulation tissue.
Tip: The history helps to distinguish acute lipodermatosclerosis from cellulitis. Chroniclipodermatoslcerosis will have been ongoing for years, the legs should be nontender, the skin will be bound-down, and the diameter of the leg will sharply decrease from knee to ankle.
CONTACT DERMATITIS
Allergic and irritant forms of contact dermatitis are often mistaken for cellulitis. Irritant contact dermatitis (Figure 3) presents with erythematous patches and plaques with well-defined borders, often in a geometric distribution where the skin was exposed to an irritant.12 Allergic contact dermatitis is a delayed hypersensitivity dermatitis that can be secondary to something ingested, applied to the skin, or airborne (Figure 4). It presents as erythematous macules, papules, and plaques that may have serous drainage or vesiculation. Lesions of allergic contact dermatitis are usually confined to the site of contact with the allergen, but they can infrequently be found at distant sites, in which case it is considered systemic contact dermatitis.3,5 Depending on the severity of the allergy, patients may complain of intense pain and pruritus.3
Additionally, chronic, nonhealing leg ulcers may have a confounding allergic contact dermatitis.7 Although patients may believe they are helping the ulcer heal by applying topical antibiotics or other lubricants, they may in fact be impeding the healing process. Always inquire as to what the patient is applying if he or she has leg ulceration with surrounding edema and erythema that has not resolved with conventional treatments.13,14
Tip: The key to distinguishing contact dermatitis from cellulitis is the history. For example, ask about recent changes in medications, soaps, and laundry detergents, new hobbies, or recent surgeries. The involved site is often confined to the area where the allergen contacted the skin, except in cases of exposure to an airborne allergen.
LYMPHEDEMA
Lymphedema is characterized by localized edema of an affected extremity, with induration, erythema, and secondary cutaneous changes such as hyperkeratosis, dyspigmentation, and wart-like architecture (Figure 5).
Primary lymphedema appears in the setting of congenital abnormalities, whereas secondary lymphedema results from an interruption of a previously functioning lymphatic system (eg, after radical mastectomy).
Patients often present with unilateral nonpitting edema and erythema in the absence of systemic symptoms.12 Many patients presenting with lower-extremity lymphedema are overweight or obese, as the weight they carry causes obstruction of the inguinal lymphatics.6
The pathophysiology is not clearly delineated but is thought to be a consequence of decreased oxygenation of tissue secondary to extravasated lymph. As the oxygen is compromised, macrophages and fibroblasts are recruited, resulting in fibrosis.6
Patients with lymphedema are more susceptible to superficial and deep skin infections, as the natural defense system in the epidermis and papillary dermis is compromised by impaired lymphatic drainage.15
To differentiate uncomplicated lymphedema from a secondary cutaneous infection, the clinician should take into account the presence or absence of warmth, pain, increased erythema, and systemic symptoms (Figure 6).
Tip: Primary lymphedema will most likely present in childhood with no inciting factors and will require a full workup. Obtaining a history should make secondary lymphedema a relatively straightforward diagnosis: Has the patient undergone lymph node dissection? Has the patient had an injury in the affected leg? Lymphedema is overwhelmingly unilateral and nonpitting, and is often seen in overweight people (if no precipitating factor is present).
EOSINOPHILIC CELLULITIS
Eosinophilic cellulitis, or Wells syndrome, was first described in 1971 as a granulomatous dermatitis.16 It is a recurrent hypersensitivity reaction to a drug, to a vaccine, or to an insect bite, or to a viral or fungal infection that presents on the extremities as localized erythema, edema, and induration with sharp borders and a green or gray hue (Figure 7).17–19 The lesions commonly progress to firm, indurated plaques that resemble morphea. The plaques may take weeks or years to resolve, but they do so without scarring.12,17,20,21
As patients tend to have recurrent bouts of eosinophilic cellulitis, they may have lesions in different stages of healing. Patients tend to report itching and burning that precedes the onset of plaques.22 The complete blood count typically shows a transient hypereosinophilia.12,16,17,23–25
Tip: This diagnosis often requires biopsy for confirmation, but helpful clues are a history of recurrent episodes, the color of the lesions, and peripheral eosinophilia.
PAPULAR URTICARIA
Papular urticaria is a dermal hypersensitivity reaction to an insect bite, most commonly from a flea or mosquito.26 Patients are often children, as their immune system may be hypersensitive. But children often develop tolerance before puberty.27
The presentation may vary, from numerous urticarial papules near the site of a bite, to generalized, large, indurated, erythematous plaques reminiscent of cellulitis (Figure 8).5,26 The lesions usually develop within hours of a bite and persist for an average of 1 to 2 weeks.28 The areas typically affected are the head and neck or the upper or lower extremities; the palms, soles, and trunk are usually spared.27
Patients most often complain of intense itching.12 The pathogenesis is proposed to be mediated by the immune complex, and tissue biopsy study shows increased eosinophils. The eosinophils stimulate mast cells, causing release of histamine, leading to increased vascular permeability, edema, and erythema.28,29
Tip: Biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis, though often the history may be sufficient. The patient may or may not recall a bite, so probe into recent activities such as outdoor sports or contact with a new pet. The papules and plaques are generally very pruritic but not painful.
DERMATOLOGY CONSULT
If the clinical presentation and history do not correlate, or if the skin condition has been treated with antibiotics yet has failed to respond, the possibility of other cutaneous dermatoses should be entertained. A dermatology consult can help determine the diagnosis, the need for further evaluation, and the best treatment course.
More than 10% of patients labeled as having cellulitis do not have cellulitis.1 This is unfortunate, as it leads to excessive and incorrect use of antibiotics and to delays in appropriate therapy.2 However, it is not surprising, given the number of conditions that bear a striking similarity to cellulitis. A familiarity with the features of true cellulitis and with the handful of conditions that can bear a striking similarity to it is the way out of this potential diagnostic quagmire.
WHAT CELLULITIS IS—AND IS NOT
The key characteristics of cellulitis are redness, warmth, tenderness, and swelling of the skin. A history of trauma and pain in the affected area and evidence of leukocytosis3 suggest cellulitis. A symmetric or diffusely scattered pattern indicates a condition other than cellulitis, which is overwhelmingly unilateral, with smooth, indistinct borders4,5 Other factors pointing to cellulitis are underlying immunosuppression, a more rapid progression, previous episodes, systemic symptoms (eg, fever, leukocytosis), new medications, new travel or outdoor exposure, and comorbidities such as diabetes and peripheral vascular disease. A long-standing, slowly progressive course and a history of unsuccessful treatment with antibiotics are strong indicators of a condition other than cellulitis.
Consultation with a dermatologist is recommended to narrow the differential diagnosis. The dermatologist can determine if biopsy is necessary, as many dermatoses that mimic cellulitis can be diagnosed by visual recognition alone.
STASIS DERMATITIS
The most common mimic of cellulitis is stasis dermatitis (Figure 1).2 Patients can present with ill-defined, bilateral, pitting edema of the lower extremities, typically with erythema, hyperpigmentation, serous drainage, and superficial desquamation.3,6,7
The inciting factor is chronic venous insufficiency, leading to interstitial edema, extravasation of red blood cells, and decreased tissue oxygenation. This process causes micro-vascular changes and microthrombi that up-regulate transforming growth factor beta and fibroblastic growth factor.7 If the process is allowed to continue, stasis dermatitis may progress to lipodermatosclerosis.
Tip: Stasis dermatitis is generally bilateral, the process will have been ongoing for years, there is often pitting edema, and the legs should be nontender.
LIPODERMATOSCLEROSIS
Lipodermatosclerosis is a sclerosing panniculitis classically described as an “inverted champagne bottle” or “inverted bowling pin” appearance of the leg, ie, the diameter of the leg is sharply narrowed directly below the calf (Figure 2).
There is an acute and a chronic phase. The acute phase is characterized by inflammation and erythema, and the chronic phase is characterized by fibrosis.8 The acute phase presents with severe lower-extremity pain above the medial malleolus, erythema, edema, and warmth; there is no sharp demarcation between affected and unaffected skin.9,10 This phase can be difficult to distinguish from cellulitis, so the history plays a key role. Known venous insufficiency, cutaneous changes of stasis dermatitis, and the absence of systemic symptoms all point to lipodermatosclerosis.
The chronic phase is characterized by unilateral or bilateral, indurated, sclerotic plaques with a “bound-down” appearance (ie, they appear as if tethered—or bound—to the subcutaneous tissue) affecting the skin from below the knee to the ankle; there is a sharp demarcation between affected and unaffected skin.9–11 The skin is often bronze or brown secondary to hemosiderin deposits. There can be prominent varicosities and scattered ulcerations depending on the course of the disease.
This condition is thought to be the result of long-standing chronic venous insufficiency.7,8,9,11 It is proposed that venous incompetence leads to extravasation of interstitial fluid and red blood cells, decreased diffusion of oxygen to the tissues, and eventual tissue and endothelial damage. As the endothelium is damaged, microthrombi formation and infarction ensue, stimulating fibroblasts to form granulation tissue.
Tip: The history helps to distinguish acute lipodermatosclerosis from cellulitis. Chroniclipodermatoslcerosis will have been ongoing for years, the legs should be nontender, the skin will be bound-down, and the diameter of the leg will sharply decrease from knee to ankle.
CONTACT DERMATITIS
Allergic and irritant forms of contact dermatitis are often mistaken for cellulitis. Irritant contact dermatitis (Figure 3) presents with erythematous patches and plaques with well-defined borders, often in a geometric distribution where the skin was exposed to an irritant.12 Allergic contact dermatitis is a delayed hypersensitivity dermatitis that can be secondary to something ingested, applied to the skin, or airborne (Figure 4). It presents as erythematous macules, papules, and plaques that may have serous drainage or vesiculation. Lesions of allergic contact dermatitis are usually confined to the site of contact with the allergen, but they can infrequently be found at distant sites, in which case it is considered systemic contact dermatitis.3,5 Depending on the severity of the allergy, patients may complain of intense pain and pruritus.3
Additionally, chronic, nonhealing leg ulcers may have a confounding allergic contact dermatitis.7 Although patients may believe they are helping the ulcer heal by applying topical antibiotics or other lubricants, they may in fact be impeding the healing process. Always inquire as to what the patient is applying if he or she has leg ulceration with surrounding edema and erythema that has not resolved with conventional treatments.13,14
Tip: The key to distinguishing contact dermatitis from cellulitis is the history. For example, ask about recent changes in medications, soaps, and laundry detergents, new hobbies, or recent surgeries. The involved site is often confined to the area where the allergen contacted the skin, except in cases of exposure to an airborne allergen.
LYMPHEDEMA
Lymphedema is characterized by localized edema of an affected extremity, with induration, erythema, and secondary cutaneous changes such as hyperkeratosis, dyspigmentation, and wart-like architecture (Figure 5).
Primary lymphedema appears in the setting of congenital abnormalities, whereas secondary lymphedema results from an interruption of a previously functioning lymphatic system (eg, after radical mastectomy).
Patients often present with unilateral nonpitting edema and erythema in the absence of systemic symptoms.12 Many patients presenting with lower-extremity lymphedema are overweight or obese, as the weight they carry causes obstruction of the inguinal lymphatics.6
The pathophysiology is not clearly delineated but is thought to be a consequence of decreased oxygenation of tissue secondary to extravasated lymph. As the oxygen is compromised, macrophages and fibroblasts are recruited, resulting in fibrosis.6
Patients with lymphedema are more susceptible to superficial and deep skin infections, as the natural defense system in the epidermis and papillary dermis is compromised by impaired lymphatic drainage.15
To differentiate uncomplicated lymphedema from a secondary cutaneous infection, the clinician should take into account the presence or absence of warmth, pain, increased erythema, and systemic symptoms (Figure 6).
Tip: Primary lymphedema will most likely present in childhood with no inciting factors and will require a full workup. Obtaining a history should make secondary lymphedema a relatively straightforward diagnosis: Has the patient undergone lymph node dissection? Has the patient had an injury in the affected leg? Lymphedema is overwhelmingly unilateral and nonpitting, and is often seen in overweight people (if no precipitating factor is present).
EOSINOPHILIC CELLULITIS
Eosinophilic cellulitis, or Wells syndrome, was first described in 1971 as a granulomatous dermatitis.16 It is a recurrent hypersensitivity reaction to a drug, to a vaccine, or to an insect bite, or to a viral or fungal infection that presents on the extremities as localized erythema, edema, and induration with sharp borders and a green or gray hue (Figure 7).17–19 The lesions commonly progress to firm, indurated plaques that resemble morphea. The plaques may take weeks or years to resolve, but they do so without scarring.12,17,20,21
As patients tend to have recurrent bouts of eosinophilic cellulitis, they may have lesions in different stages of healing. Patients tend to report itching and burning that precedes the onset of plaques.22 The complete blood count typically shows a transient hypereosinophilia.12,16,17,23–25
Tip: This diagnosis often requires biopsy for confirmation, but helpful clues are a history of recurrent episodes, the color of the lesions, and peripheral eosinophilia.
PAPULAR URTICARIA
Papular urticaria is a dermal hypersensitivity reaction to an insect bite, most commonly from a flea or mosquito.26 Patients are often children, as their immune system may be hypersensitive. But children often develop tolerance before puberty.27
The presentation may vary, from numerous urticarial papules near the site of a bite, to generalized, large, indurated, erythematous plaques reminiscent of cellulitis (Figure 8).5,26 The lesions usually develop within hours of a bite and persist for an average of 1 to 2 weeks.28 The areas typically affected are the head and neck or the upper or lower extremities; the palms, soles, and trunk are usually spared.27
Patients most often complain of intense itching.12 The pathogenesis is proposed to be mediated by the immune complex, and tissue biopsy study shows increased eosinophils. The eosinophils stimulate mast cells, causing release of histamine, leading to increased vascular permeability, edema, and erythema.28,29
Tip: Biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis, though often the history may be sufficient. The patient may or may not recall a bite, so probe into recent activities such as outdoor sports or contact with a new pet. The papules and plaques are generally very pruritic but not painful.
DERMATOLOGY CONSULT
If the clinical presentation and history do not correlate, or if the skin condition has been treated with antibiotics yet has failed to respond, the possibility of other cutaneous dermatoses should be entertained. A dermatology consult can help determine the diagnosis, the need for further evaluation, and the best treatment course.
- Hepburn MJ, Dooley DP, Ellis MW. Alternative diagnoses that often mimic cellulitis. Am Fam Physician 2003; 67:2471.
- David CV, Chira S, Eells SJ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy in patients admitted to hospitals with cellulitis. Dermatol Online J 2011; 17:1.
- Bailey E, Kroshinsky D. Cellulitis: diagnosis and management. Dermatol Ther 2011; 24:229–239.
- Stevens DL, Bisno AL, Chambers HF, et al; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft-tissue infections. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 41:1373–1406.
- Lio PA. The many faces of cellulitis. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed 2009; 94:50–54.
- Yosipovitch G, DeVore A, Dawn A. Obesity and the skin: skin physiology and skin manifestations of obesity. J Am Acad Dermatol 2007; 56:901–916.
- Farage MA, Miller KW, Berardesca E, Maibach HI. Clinical implications of aging skin: cutaneous disorders in the elderly. Am J Clin Dermatol 2009; 10:73–86.
- Kirsner RS, Pardes JB, Eaglstein WH, Falanga V. The clinical spectrum of lipodermatosclerosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 1993; 28:623–627.
- Miteva M, Romanelli P, Kirsner RS. Lipodermatosclerosis. Dermatol Ther 2010; 23:375–388.
- Barron GS, Jacob SE, Kirsner RS. Dermatologic complications of chronic venous disease: medical management and beyond. Ann Vasc Surg 2007; 21:652–662.
- Bruce AJ, Bennett DD, Lohse CM, Rooke TW, Davis MD. Lipodermatosclerosis: review of cases evaluated at Mayo Clinic. J Am Acad Dermatol 2002; 46:187–192.
- Falagas ME, Vergidis PI. Narrative review: diseases that masquerade as infectious cellulitis. Ann Intern Med 2005; 142:47–55.
- Wilson CL, Cameron J, Powell SM, Cherry G, Ryan TJ. High incidence of contact dermatitis in leg-ulcer patients—implications for management. Clin Exp Dermatol 1991; 16:250–253.
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology 1996; 192:198–202.
- Keeley VL. Lymphoedema and cellulitis: chicken or egg? Br J Dermatol 2008; 158:1175–1176.
- Wells GC. Recurrent granulomatous dermatitis with eosinophilia. Trans St Johns Hosp Dermatol Soc 1971; 57:46–56.
- Ferreli C, Pinna AL, Atzori L, Aste N. Eosinophilic cellulitis (Well’s syndrome): a new case description. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 1999; 13:41–45.
- Ladoyanni E, Vlachou C, Thushara R, Snead D. A patient with Wells’ syndrome. Clin Exp Dermatol 2010; 35:e3–e4.
- Moon HS, Park K, Lee JH, Son SJ. Eosinophilic cellulitis in an infant. Int J Dermatol 2010; 49:592–593.
- Walker P, Long D, James C, Marshman G. Exaggerated insect bite reaction exacerbated by a pyogenic infection in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Australas J Dermatol 2007; 48:165–169.
- Laliwala NM, Kulshrestha R, Singh R, Balasubramaniam P. A case of eosinophilic cellulitis of the hand mimicking bacterial cellulitis. J Hand Surg Eur Vol 2009; 34:410–411.
- Chung CL, Cusack CA. Wells syndrome: an enigmatic and therapeutically challenging disease. J Drugs Dermatol 2006; 5:908–911.
- Melski JW. Wells’ syndrome, insect bites, and eosinophils. Dermatol Clin 1990; 8:287–293.
- Spigel GT, Winkelmann RK. Wells’ syndrome. Recurrent granulomatous dermatitis with eosinophilia. Arch Dermatol 1979; 115:611–613.
- Clark DP, Anderson PC. Eosinophilic cellulitis caused by arthropod bites. Int J Dermatol 1988; 27:411–412.
- Howard R, Frieden IJ. Papular urticaria in children. Pediatr Dermatol 1996; 13:246–249.
- Hernandez RG, Cohen BA. Insect bite-induced hypersensitivity and the SCRATCH principles: a new approach to papular urticaria. Pediatrics 2006; 118:e189–e196.
- Heng MC, Kloss SG, Haberfelde GC. Pathogenesis of papular urticaria. J Am Acad Dermatol 1984; 10:1030–1034.
- Kossard S, Hamann I, Wilkinson B. Defining urticarial dermatitis: a subset of dermal hypersensitivity reaction pattern. Arch Dermatol 2006; 142:29–34.
- Hepburn MJ, Dooley DP, Ellis MW. Alternative diagnoses that often mimic cellulitis. Am Fam Physician 2003; 67:2471.
- David CV, Chira S, Eells SJ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy in patients admitted to hospitals with cellulitis. Dermatol Online J 2011; 17:1.
- Bailey E, Kroshinsky D. Cellulitis: diagnosis and management. Dermatol Ther 2011; 24:229–239.
- Stevens DL, Bisno AL, Chambers HF, et al; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft-tissue infections. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 41:1373–1406.
- Lio PA. The many faces of cellulitis. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed 2009; 94:50–54.
- Yosipovitch G, DeVore A, Dawn A. Obesity and the skin: skin physiology and skin manifestations of obesity. J Am Acad Dermatol 2007; 56:901–916.
- Farage MA, Miller KW, Berardesca E, Maibach HI. Clinical implications of aging skin: cutaneous disorders in the elderly. Am J Clin Dermatol 2009; 10:73–86.
- Kirsner RS, Pardes JB, Eaglstein WH, Falanga V. The clinical spectrum of lipodermatosclerosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 1993; 28:623–627.
- Miteva M, Romanelli P, Kirsner RS. Lipodermatosclerosis. Dermatol Ther 2010; 23:375–388.
- Barron GS, Jacob SE, Kirsner RS. Dermatologic complications of chronic venous disease: medical management and beyond. Ann Vasc Surg 2007; 21:652–662.
- Bruce AJ, Bennett DD, Lohse CM, Rooke TW, Davis MD. Lipodermatosclerosis: review of cases evaluated at Mayo Clinic. J Am Acad Dermatol 2002; 46:187–192.
- Falagas ME, Vergidis PI. Narrative review: diseases that masquerade as infectious cellulitis. Ann Intern Med 2005; 142:47–55.
- Wilson CL, Cameron J, Powell SM, Cherry G, Ryan TJ. High incidence of contact dermatitis in leg-ulcer patients—implications for management. Clin Exp Dermatol 1991; 16:250–253.
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology 1996; 192:198–202.
- Keeley VL. Lymphoedema and cellulitis: chicken or egg? Br J Dermatol 2008; 158:1175–1176.
- Wells GC. Recurrent granulomatous dermatitis with eosinophilia. Trans St Johns Hosp Dermatol Soc 1971; 57:46–56.
- Ferreli C, Pinna AL, Atzori L, Aste N. Eosinophilic cellulitis (Well’s syndrome): a new case description. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 1999; 13:41–45.
- Ladoyanni E, Vlachou C, Thushara R, Snead D. A patient with Wells’ syndrome. Clin Exp Dermatol 2010; 35:e3–e4.
- Moon HS, Park K, Lee JH, Son SJ. Eosinophilic cellulitis in an infant. Int J Dermatol 2010; 49:592–593.
- Walker P, Long D, James C, Marshman G. Exaggerated insect bite reaction exacerbated by a pyogenic infection in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Australas J Dermatol 2007; 48:165–169.
- Laliwala NM, Kulshrestha R, Singh R, Balasubramaniam P. A case of eosinophilic cellulitis of the hand mimicking bacterial cellulitis. J Hand Surg Eur Vol 2009; 34:410–411.
- Chung CL, Cusack CA. Wells syndrome: an enigmatic and therapeutically challenging disease. J Drugs Dermatol 2006; 5:908–911.
- Melski JW. Wells’ syndrome, insect bites, and eosinophils. Dermatol Clin 1990; 8:287–293.
- Spigel GT, Winkelmann RK. Wells’ syndrome. Recurrent granulomatous dermatitis with eosinophilia. Arch Dermatol 1979; 115:611–613.
- Clark DP, Anderson PC. Eosinophilic cellulitis caused by arthropod bites. Int J Dermatol 1988; 27:411–412.
- Howard R, Frieden IJ. Papular urticaria in children. Pediatr Dermatol 1996; 13:246–249.
- Hernandez RG, Cohen BA. Insect bite-induced hypersensitivity and the SCRATCH principles: a new approach to papular urticaria. Pediatrics 2006; 118:e189–e196.
- Heng MC, Kloss SG, Haberfelde GC. Pathogenesis of papular urticaria. J Am Acad Dermatol 1984; 10:1030–1034.
- Kossard S, Hamann I, Wilkinson B. Defining urticarial dermatitis: a subset of dermal hypersensitivity reaction pattern. Arch Dermatol 2006; 142:29–34.
KEY POINTS
- Cellulitis is rarely bilateral.
- Patients with cellulitis often have systemic symptoms, such as fever and leukocytosis.
- A chronic course points to a diagnosis other than cellulitis.
- Plaques with a “bound-down” appearance or dark pigmentation point to a chronic disease rather than cellulitis.
- Stasis dermatitis is the most common mimic of cellulitis.