User login
Photosensitivity Reaction From Dronedarone for Atrial Fibrillation
To the Editor:
A 61-year-old woman with a history of atrial fibrillation, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hyperlipidemia presented with an erythematous, edematous, pruritic eruption on the chest, neck, and arms of 2 weeks’ duration. The patient had no history of considerable sun exposure or reports of photosensitivity. One month prior to presentation she had started taking dronedarone for improved control of atrial fibrillation. She had no known history of drug allergies. Other medications included valsartan, digoxin, pioglitazone, simvastatin, aspirin, hydrocodone, and zolpidem, all of which were unchanged for years. There were no changes in topical products used.
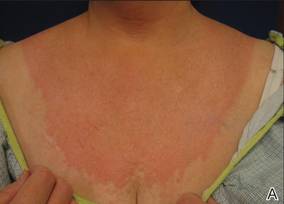
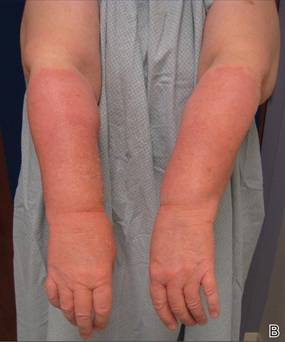
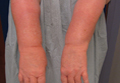
Physical examination revealed confluent, well-demarcated, erythematous and edematous papules and plaques over the anterior aspect of the neck, bilateral forearms, and dorsal aspect of the hands, with a v-shaped distribution on the chest (Figure). There was notable sparing of the submental region, upper arms, abdomen, back, and legs. Dronedarone was discontinued and she was started on fluocinonide ointment 0.05% and oral hydroxyzine for pruritus. Her rash resolved within the following few weeks.
|
|
| Confluent, well-demarcated, erythematous and edematous papules and plaques in a v-shaped distribution on the chest (A) and dorsal aspect of the hands (B). |
Dronedarone is a noniodinated benzofuran derivative. It is structurally similar to and shares the antiarrhythmic properties of amiodarone,1 and thus it is used in the treatment of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter. However, the pulmonary and thyroid toxicities sometimes associated with amiodarone have not been observed with dronedarone. The primary side effect of dronedarone is gastrointestinal distress, specifically nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Dronedarone has been associated with severe liver injury and hepatic failure.2 Cutaneous reactions appear to be an uncommon side effect of dronedarone therapy. Across 5 clinical studies (N=6285), adverse events involving skin and subcutaneous tissue including eczema, allergic dermatitis, pruritus, and nonspecific rash occurred in 5% of dronedarone and 3% of placebo patients. Photosensitivity reactions occurred in less than 1% of dronedarone recipients.3
Although the lack of a biopsy leaves the possibility of a contact or photocontact dermatitis, our patient demonstrated the potential for dronedarone to cause a photodistributed drug eruption that resolved after cessation of the medication.
1. Hoy SM, Keam SJ. Dronedarone. Drugs. 2009;69:1647-1663.
2. In brief: FDA warning on dronedarone (Multaq). Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2011;53:17.
3. Multaq [package insert]. Bridgewater, NJ: sanofi-aventis; 2009.
To the Editor:
A 61-year-old woman with a history of atrial fibrillation, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hyperlipidemia presented with an erythematous, edematous, pruritic eruption on the chest, neck, and arms of 2 weeks’ duration. The patient had no history of considerable sun exposure or reports of photosensitivity. One month prior to presentation she had started taking dronedarone for improved control of atrial fibrillation. She had no known history of drug allergies. Other medications included valsartan, digoxin, pioglitazone, simvastatin, aspirin, hydrocodone, and zolpidem, all of which were unchanged for years. There were no changes in topical products used.
Physical examination revealed confluent, well-demarcated, erythematous and edematous papules and plaques over the anterior aspect of the neck, bilateral forearms, and dorsal aspect of the hands, with a v-shaped distribution on the chest (Figure). There was notable sparing of the submental region, upper arms, abdomen, back, and legs. Dronedarone was discontinued and she was started on fluocinonide ointment 0.05% and oral hydroxyzine for pruritus. Her rash resolved within the following few weeks.
|
|
| Confluent, well-demarcated, erythematous and edematous papules and plaques in a v-shaped distribution on the chest (A) and dorsal aspect of the hands (B). |
Dronedarone is a noniodinated benzofuran derivative. It is structurally similar to and shares the antiarrhythmic properties of amiodarone,1 and thus it is used in the treatment of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter. However, the pulmonary and thyroid toxicities sometimes associated with amiodarone have not been observed with dronedarone. The primary side effect of dronedarone is gastrointestinal distress, specifically nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Dronedarone has been associated with severe liver injury and hepatic failure.2 Cutaneous reactions appear to be an uncommon side effect of dronedarone therapy. Across 5 clinical studies (N=6285), adverse events involving skin and subcutaneous tissue including eczema, allergic dermatitis, pruritus, and nonspecific rash occurred in 5% of dronedarone and 3% of placebo patients. Photosensitivity reactions occurred in less than 1% of dronedarone recipients.3
Although the lack of a biopsy leaves the possibility of a contact or photocontact dermatitis, our patient demonstrated the potential for dronedarone to cause a photodistributed drug eruption that resolved after cessation of the medication.
To the Editor:
A 61-year-old woman with a history of atrial fibrillation, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hyperlipidemia presented with an erythematous, edematous, pruritic eruption on the chest, neck, and arms of 2 weeks’ duration. The patient had no history of considerable sun exposure or reports of photosensitivity. One month prior to presentation she had started taking dronedarone for improved control of atrial fibrillation. She had no known history of drug allergies. Other medications included valsartan, digoxin, pioglitazone, simvastatin, aspirin, hydrocodone, and zolpidem, all of which were unchanged for years. There were no changes in topical products used.
Physical examination revealed confluent, well-demarcated, erythematous and edematous papules and plaques over the anterior aspect of the neck, bilateral forearms, and dorsal aspect of the hands, with a v-shaped distribution on the chest (Figure). There was notable sparing of the submental region, upper arms, abdomen, back, and legs. Dronedarone was discontinued and she was started on fluocinonide ointment 0.05% and oral hydroxyzine for pruritus. Her rash resolved within the following few weeks.
|
|
| Confluent, well-demarcated, erythematous and edematous papules and plaques in a v-shaped distribution on the chest (A) and dorsal aspect of the hands (B). |
Dronedarone is a noniodinated benzofuran derivative. It is structurally similar to and shares the antiarrhythmic properties of amiodarone,1 and thus it is used in the treatment of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter. However, the pulmonary and thyroid toxicities sometimes associated with amiodarone have not been observed with dronedarone. The primary side effect of dronedarone is gastrointestinal distress, specifically nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Dronedarone has been associated with severe liver injury and hepatic failure.2 Cutaneous reactions appear to be an uncommon side effect of dronedarone therapy. Across 5 clinical studies (N=6285), adverse events involving skin and subcutaneous tissue including eczema, allergic dermatitis, pruritus, and nonspecific rash occurred in 5% of dronedarone and 3% of placebo patients. Photosensitivity reactions occurred in less than 1% of dronedarone recipients.3
Although the lack of a biopsy leaves the possibility of a contact or photocontact dermatitis, our patient demonstrated the potential for dronedarone to cause a photodistributed drug eruption that resolved after cessation of the medication.
1. Hoy SM, Keam SJ. Dronedarone. Drugs. 2009;69:1647-1663.
2. In brief: FDA warning on dronedarone (Multaq). Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2011;53:17.
3. Multaq [package insert]. Bridgewater, NJ: sanofi-aventis; 2009.
1. Hoy SM, Keam SJ. Dronedarone. Drugs. 2009;69:1647-1663.
2. In brief: FDA warning on dronedarone (Multaq). Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2011;53:17.
3. Multaq [package insert]. Bridgewater, NJ: sanofi-aventis; 2009.