User login
Increase in message volume begs the question: ‘Should we be compensated for our time?’
The American Gastroenterological Association and other gastrointestinal-specific organizations have excellent resources available to members that focus on optimizing reimbursement in your clinical and endoscopic practice.
During the COVID-19 pandemic and public health emergency (PHE), many previously noncovered services were now covered under rules of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. During the pandemic, patient portal messages increased by 157%, meaning more work for health care teams, negatively impacting physician satisfaction, and increasing burnout.1 Medical burnout has been associated with increased time spent on electronic health records, with some subspeciality gastroenterology (GI) groups having a high EHR burden, according to a recently published article in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.2
This topic is a timely discussion as several large health systems have implemented processes to bill for non–face-to-face services (termed “asynchronous care”), some of which have not been well received in the lay media. It is important to note that despite these implementations, studies have shown only 1% of all incoming portal messages would meet criteria to be submitted for reimbursement. This impact might be slightly higher in chronic care management practices.
Providers and practices have several options when considering billing for non–face-to-face encounters, which we outline in Table 1.3
The focus of this article will be to review the more common non–face-to-face evaluation and management services, such as telephone E/M (patient phone call) and e-visits (patient portal messages) as these have recently generated the most interest and discussion amongst health care providers.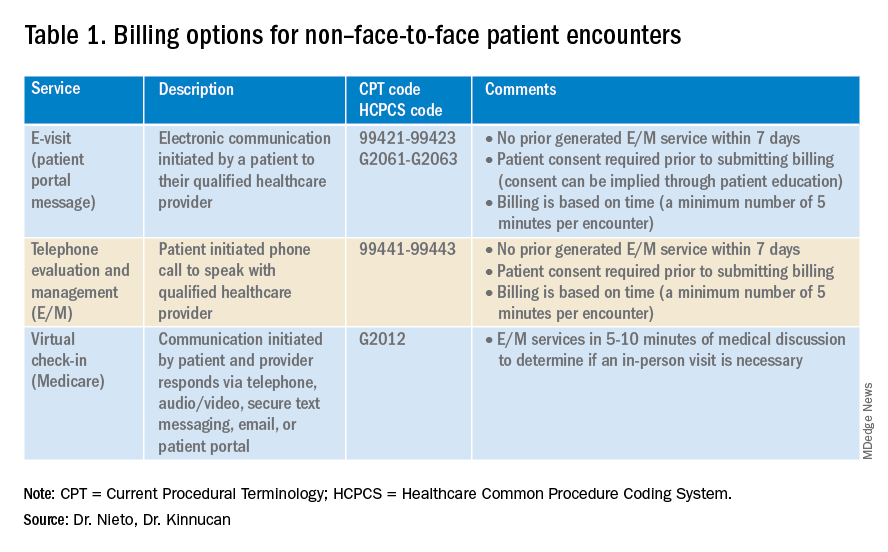
Telemedicine after COVID-19 pandemic
During the beginning of the pandemic, a web-based survey study found that almost all providers in GI practices implemented some form of telemedicine to continue to provide care for patients, compared to 32% prior to the pandemic.4,5 The high demand and essential requirement for telehealth evaluation facilitated its reimbursement, eliminating the primary barrier to previous use.6
One of the new covered benefits by CMS was asynchronous telehealth care.7 The PHE ended in May 2023, and since then a qualified health care provider (QHCP) does not have the full flexibility to deliver telemedicine services across state lines. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has considered some telehealth policy changes after the COVID-19 PHE and many of those will be extended, at least through 2024.8 As during the pandemic, where the U.S. national payer network (CMS, state Medicaid, and private payers) and state health agencies assisted to ensure patients get the care they need by authorizing providers to be compensated for non–face-to-face services, we believe this service will continue to be part of our clinical practice.
We recommend you stay informed about local and federal laws, regulations, and alternatives for reimbursement as they may be modified at the beginning of a new calendar year. Remember, you can always talk with your revenue cycle team to clarify any query.
Telephone evaluation and management services
The patient requests to speak with you.
Telephone evaluation and management services became more widely used after the pandemic and were recognized by CMS as a covered medical service under PHE. As outlined in Table 1, there are associated codes with this service and it can only apply to an established patient in your practice. The cumulative time spent over a 7-day period without generating an immediate follow-up visit could qualify for this CPT code. However, for a patient with a high-complexity diagnosis and/or decisions being made about care, it might be better to consider a virtual office visit as this would value the complex care at a higher level than the time spent during the telephone E/M encounter.
A common question comes up: Can my nurse or support team bill for telephone care? No, only QHCP can, which means physicians and advanced practice providers can bill for this E/M service, and it does not include time spent by other members of clinical staff in patient care. However, there are CPT codes for chronic care management, which is not covered in this article.
Virtual evaluation and management services
You respond to a patient-initiated portal message.
Patient portal messages increased exponentially during the pandemic with 2.5 more minutes spent per message, resulting in more EHR work by practitioners, compared with prior to the pandemic. One study showed an immediate postpandemic increase in EHR patient-initiated messages with no return to prepandemic baseline.1
Although studies evaluating postpandemic telemedicine services are needed, we believe that this trend will continue, and for this reason, it is important to create sustainable workflows to continue to provide this patient driven avenue of care.9
E-visits are asynchronous patient or guardian portal messages that require a minimum of 5 minutes to provide medical decision-making without prior E/M services in the last 7 days. To obtain reimbursement for this service, it cannot be initiated by the provider, and patient consent must be obtained. Documentation should include this information and the time spent in the encounter. The associated CPT codes with this e-service are outlined in Table 1.
A common question is, “Are there additional codes I should use if a portal message E/M visit lasts more than 30 minutes?” No. If an e-visit lasts more than 30 minutes, the QHCP should bill the CPT code 99423. However, we would advise that, if this care requires more than 30 minutes, then either virtual or face-to-face E/M be considered for the optimal reimbursement for provider time spent. Another common question is around consent for services, and we advise providers to review this requirement with their compliance colleagues as each institution has different policies.
Virtual check-in
Medicare also covers brief communication technology–based services also known as virtual check-ins, where patients can communicate with their provider after having established care. During this brief conversation that can be via telephone, audio/video, secure text messaging, email, or patient portal, providers will determine if an in-person visit is necessary. CMS has designed G codes for these virtual check-ins that are from the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS). Two codes are available for this E/M service: G2012, which is outlined in Table 1, and G2010, which covers the evaluation of images and/or recorded videos. In order to be reimbursed for a G2010 code, providers need at least a 5-minute response to make a clinical determination or give the patient a medical impression.
Patient satisfaction, physician well-being and quality of care outcomes
Large health care systems like Kaiser Permanente implemented secure message patient-physician communication (the patient portal) even before the pandemic, showing promising results in 2010 with reduction in office visits, improvement in measurable quality outcomes, and high level of patient satisfaction.10 Post pandemic, several large health care centers opted to announce the billing implementation for patient-initiated portal messages.11 A focus was placed on educating their patients about when a message will and will not be billed. Using this type of strategy can help to improve patient awareness about potential billing without affecting patient satisfaction and care outcomes. Studies have shown the EHR has contributed to physician burnout and some physicians reducing their clinical time or leaving medicine; a reduction in messaging might have a positive impact on physician well-being.
The challenge is that medical billing is not routinely included as a curriculum topic in many residency and fellowship programs; however, trainees are part of E/M services and have limited knowledge of billing processes. Unfortunately, at this time, trainees cannot submit for reimbursement for asynchronous care as described above. We hope that this brief article will help junior gastroenterologists optimize their outpatient billing practices.
Dr. Nieto is an internal medicine chief resident with WellStar Cobb Medical Center, Austell, Ga. Dr. Kinnucan is a gastroenterologist with Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla. The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose for this article. The authors certify that no financial and grant support has been received for this article.
References
1. Holmgren AJ et al. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2021 Dec 9. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocab268.
2. Bali AS et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2023 Apr 24. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002254.
3. AAFP. Family Physician. “Coding Scenario: Coding for Virtual-Digital Visits”
4. Keihanian T. et al. Telehealth Utilization in Gastroenterology Clinics Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic: Impact on Clinical Practice and Gastroenterology Training. Gastroenterology. 2020 Jun 20. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.040.
5. Lewin S et al. J Crohns Colitis. 2020 Oct 21. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaa140.
6. Perisetti A and H Goyal. Dig Dis Sci. 2021 Mar 3. doi: 10.1007/s10620-021-06874-x.
7. Telehealth.HHS.gov. Medicaid and Medicare billing for asynchronous telehealth. Updated: 2022 May 4.
8. Telehealth.HHS.gov. Telehealth policy changes after the COVID-19 public health emergency. Last updated: 2023 Jan 23.
9. Fox B and Sizemore JO. Telehealth: Fad or the future. Epic Health Research Network. 2020 Aug 18.
10. Baer D. Patient-physician e-mail communication: the kaiser permanente experience. J Oncol Pract. 2011 Jul. doi: 10.1200/JOP.2011.000323.
11. Myclevelandclinic.org. MyChart Messaging.
12. Sinsky CA et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2022 Aug 29. doi: 10.1007/s11606-022-07766-0.
The American Gastroenterological Association and other gastrointestinal-specific organizations have excellent resources available to members that focus on optimizing reimbursement in your clinical and endoscopic practice.
During the COVID-19 pandemic and public health emergency (PHE), many previously noncovered services were now covered under rules of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. During the pandemic, patient portal messages increased by 157%, meaning more work for health care teams, negatively impacting physician satisfaction, and increasing burnout.1 Medical burnout has been associated with increased time spent on electronic health records, with some subspeciality gastroenterology (GI) groups having a high EHR burden, according to a recently published article in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.2
This topic is a timely discussion as several large health systems have implemented processes to bill for non–face-to-face services (termed “asynchronous care”), some of which have not been well received in the lay media. It is important to note that despite these implementations, studies have shown only 1% of all incoming portal messages would meet criteria to be submitted for reimbursement. This impact might be slightly higher in chronic care management practices.
Providers and practices have several options when considering billing for non–face-to-face encounters, which we outline in Table 1.3
The focus of this article will be to review the more common non–face-to-face evaluation and management services, such as telephone E/M (patient phone call) and e-visits (patient portal messages) as these have recently generated the most interest and discussion amongst health care providers.
Telemedicine after COVID-19 pandemic
During the beginning of the pandemic, a web-based survey study found that almost all providers in GI practices implemented some form of telemedicine to continue to provide care for patients, compared to 32% prior to the pandemic.4,5 The high demand and essential requirement for telehealth evaluation facilitated its reimbursement, eliminating the primary barrier to previous use.6
One of the new covered benefits by CMS was asynchronous telehealth care.7 The PHE ended in May 2023, and since then a qualified health care provider (QHCP) does not have the full flexibility to deliver telemedicine services across state lines. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has considered some telehealth policy changes after the COVID-19 PHE and many of those will be extended, at least through 2024.8 As during the pandemic, where the U.S. national payer network (CMS, state Medicaid, and private payers) and state health agencies assisted to ensure patients get the care they need by authorizing providers to be compensated for non–face-to-face services, we believe this service will continue to be part of our clinical practice.
We recommend you stay informed about local and federal laws, regulations, and alternatives for reimbursement as they may be modified at the beginning of a new calendar year. Remember, you can always talk with your revenue cycle team to clarify any query.
Telephone evaluation and management services
The patient requests to speak with you.
Telephone evaluation and management services became more widely used after the pandemic and were recognized by CMS as a covered medical service under PHE. As outlined in Table 1, there are associated codes with this service and it can only apply to an established patient in your practice. The cumulative time spent over a 7-day period without generating an immediate follow-up visit could qualify for this CPT code. However, for a patient with a high-complexity diagnosis and/or decisions being made about care, it might be better to consider a virtual office visit as this would value the complex care at a higher level than the time spent during the telephone E/M encounter.
A common question comes up: Can my nurse or support team bill for telephone care? No, only QHCP can, which means physicians and advanced practice providers can bill for this E/M service, and it does not include time spent by other members of clinical staff in patient care. However, there are CPT codes for chronic care management, which is not covered in this article.
Virtual evaluation and management services
You respond to a patient-initiated portal message.
Patient portal messages increased exponentially during the pandemic with 2.5 more minutes spent per message, resulting in more EHR work by practitioners, compared with prior to the pandemic. One study showed an immediate postpandemic increase in EHR patient-initiated messages with no return to prepandemic baseline.1
Although studies evaluating postpandemic telemedicine services are needed, we believe that this trend will continue, and for this reason, it is important to create sustainable workflows to continue to provide this patient driven avenue of care.9
E-visits are asynchronous patient or guardian portal messages that require a minimum of 5 minutes to provide medical decision-making without prior E/M services in the last 7 days. To obtain reimbursement for this service, it cannot be initiated by the provider, and patient consent must be obtained. Documentation should include this information and the time spent in the encounter. The associated CPT codes with this e-service are outlined in Table 1.
A common question is, “Are there additional codes I should use if a portal message E/M visit lasts more than 30 minutes?” No. If an e-visit lasts more than 30 minutes, the QHCP should bill the CPT code 99423. However, we would advise that, if this care requires more than 30 minutes, then either virtual or face-to-face E/M be considered for the optimal reimbursement for provider time spent. Another common question is around consent for services, and we advise providers to review this requirement with their compliance colleagues as each institution has different policies.
Virtual check-in
Medicare also covers brief communication technology–based services also known as virtual check-ins, where patients can communicate with their provider after having established care. During this brief conversation that can be via telephone, audio/video, secure text messaging, email, or patient portal, providers will determine if an in-person visit is necessary. CMS has designed G codes for these virtual check-ins that are from the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS). Two codes are available for this E/M service: G2012, which is outlined in Table 1, and G2010, which covers the evaluation of images and/or recorded videos. In order to be reimbursed for a G2010 code, providers need at least a 5-minute response to make a clinical determination or give the patient a medical impression.
Patient satisfaction, physician well-being and quality of care outcomes
Large health care systems like Kaiser Permanente implemented secure message patient-physician communication (the patient portal) even before the pandemic, showing promising results in 2010 with reduction in office visits, improvement in measurable quality outcomes, and high level of patient satisfaction.10 Post pandemic, several large health care centers opted to announce the billing implementation for patient-initiated portal messages.11 A focus was placed on educating their patients about when a message will and will not be billed. Using this type of strategy can help to improve patient awareness about potential billing without affecting patient satisfaction and care outcomes. Studies have shown the EHR has contributed to physician burnout and some physicians reducing their clinical time or leaving medicine; a reduction in messaging might have a positive impact on physician well-being.
The challenge is that medical billing is not routinely included as a curriculum topic in many residency and fellowship programs; however, trainees are part of E/M services and have limited knowledge of billing processes. Unfortunately, at this time, trainees cannot submit for reimbursement for asynchronous care as described above. We hope that this brief article will help junior gastroenterologists optimize their outpatient billing practices.
Dr. Nieto is an internal medicine chief resident with WellStar Cobb Medical Center, Austell, Ga. Dr. Kinnucan is a gastroenterologist with Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla. The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose for this article. The authors certify that no financial and grant support has been received for this article.
References
1. Holmgren AJ et al. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2021 Dec 9. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocab268.
2. Bali AS et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2023 Apr 24. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002254.
3. AAFP. Family Physician. “Coding Scenario: Coding for Virtual-Digital Visits”
4. Keihanian T. et al. Telehealth Utilization in Gastroenterology Clinics Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic: Impact on Clinical Practice and Gastroenterology Training. Gastroenterology. 2020 Jun 20. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.040.
5. Lewin S et al. J Crohns Colitis. 2020 Oct 21. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaa140.
6. Perisetti A and H Goyal. Dig Dis Sci. 2021 Mar 3. doi: 10.1007/s10620-021-06874-x.
7. Telehealth.HHS.gov. Medicaid and Medicare billing for asynchronous telehealth. Updated: 2022 May 4.
8. Telehealth.HHS.gov. Telehealth policy changes after the COVID-19 public health emergency. Last updated: 2023 Jan 23.
9. Fox B and Sizemore JO. Telehealth: Fad or the future. Epic Health Research Network. 2020 Aug 18.
10. Baer D. Patient-physician e-mail communication: the kaiser permanente experience. J Oncol Pract. 2011 Jul. doi: 10.1200/JOP.2011.000323.
11. Myclevelandclinic.org. MyChart Messaging.
12. Sinsky CA et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2022 Aug 29. doi: 10.1007/s11606-022-07766-0.
The American Gastroenterological Association and other gastrointestinal-specific organizations have excellent resources available to members that focus on optimizing reimbursement in your clinical and endoscopic practice.
During the COVID-19 pandemic and public health emergency (PHE), many previously noncovered services were now covered under rules of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. During the pandemic, patient portal messages increased by 157%, meaning more work for health care teams, negatively impacting physician satisfaction, and increasing burnout.1 Medical burnout has been associated with increased time spent on electronic health records, with some subspeciality gastroenterology (GI) groups having a high EHR burden, according to a recently published article in the American Journal of Gastroenterology.2
This topic is a timely discussion as several large health systems have implemented processes to bill for non–face-to-face services (termed “asynchronous care”), some of which have not been well received in the lay media. It is important to note that despite these implementations, studies have shown only 1% of all incoming portal messages would meet criteria to be submitted for reimbursement. This impact might be slightly higher in chronic care management practices.
Providers and practices have several options when considering billing for non–face-to-face encounters, which we outline in Table 1.3
The focus of this article will be to review the more common non–face-to-face evaluation and management services, such as telephone E/M (patient phone call) and e-visits (patient portal messages) as these have recently generated the most interest and discussion amongst health care providers.
Telemedicine after COVID-19 pandemic
During the beginning of the pandemic, a web-based survey study found that almost all providers in GI practices implemented some form of telemedicine to continue to provide care for patients, compared to 32% prior to the pandemic.4,5 The high demand and essential requirement for telehealth evaluation facilitated its reimbursement, eliminating the primary barrier to previous use.6
One of the new covered benefits by CMS was asynchronous telehealth care.7 The PHE ended in May 2023, and since then a qualified health care provider (QHCP) does not have the full flexibility to deliver telemedicine services across state lines. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has considered some telehealth policy changes after the COVID-19 PHE and many of those will be extended, at least through 2024.8 As during the pandemic, where the U.S. national payer network (CMS, state Medicaid, and private payers) and state health agencies assisted to ensure patients get the care they need by authorizing providers to be compensated for non–face-to-face services, we believe this service will continue to be part of our clinical practice.
We recommend you stay informed about local and federal laws, regulations, and alternatives for reimbursement as they may be modified at the beginning of a new calendar year. Remember, you can always talk with your revenue cycle team to clarify any query.
Telephone evaluation and management services
The patient requests to speak with you.
Telephone evaluation and management services became more widely used after the pandemic and were recognized by CMS as a covered medical service under PHE. As outlined in Table 1, there are associated codes with this service and it can only apply to an established patient in your practice. The cumulative time spent over a 7-day period without generating an immediate follow-up visit could qualify for this CPT code. However, for a patient with a high-complexity diagnosis and/or decisions being made about care, it might be better to consider a virtual office visit as this would value the complex care at a higher level than the time spent during the telephone E/M encounter.
A common question comes up: Can my nurse or support team bill for telephone care? No, only QHCP can, which means physicians and advanced practice providers can bill for this E/M service, and it does not include time spent by other members of clinical staff in patient care. However, there are CPT codes for chronic care management, which is not covered in this article.
Virtual evaluation and management services
You respond to a patient-initiated portal message.
Patient portal messages increased exponentially during the pandemic with 2.5 more minutes spent per message, resulting in more EHR work by practitioners, compared with prior to the pandemic. One study showed an immediate postpandemic increase in EHR patient-initiated messages with no return to prepandemic baseline.1
Although studies evaluating postpandemic telemedicine services are needed, we believe that this trend will continue, and for this reason, it is important to create sustainable workflows to continue to provide this patient driven avenue of care.9
E-visits are asynchronous patient or guardian portal messages that require a minimum of 5 minutes to provide medical decision-making without prior E/M services in the last 7 days. To obtain reimbursement for this service, it cannot be initiated by the provider, and patient consent must be obtained. Documentation should include this information and the time spent in the encounter. The associated CPT codes with this e-service are outlined in Table 1.
A common question is, “Are there additional codes I should use if a portal message E/M visit lasts more than 30 minutes?” No. If an e-visit lasts more than 30 minutes, the QHCP should bill the CPT code 99423. However, we would advise that, if this care requires more than 30 minutes, then either virtual or face-to-face E/M be considered for the optimal reimbursement for provider time spent. Another common question is around consent for services, and we advise providers to review this requirement with their compliance colleagues as each institution has different policies.
Virtual check-in
Medicare also covers brief communication technology–based services also known as virtual check-ins, where patients can communicate with their provider after having established care. During this brief conversation that can be via telephone, audio/video, secure text messaging, email, or patient portal, providers will determine if an in-person visit is necessary. CMS has designed G codes for these virtual check-ins that are from the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS). Two codes are available for this E/M service: G2012, which is outlined in Table 1, and G2010, which covers the evaluation of images and/or recorded videos. In order to be reimbursed for a G2010 code, providers need at least a 5-minute response to make a clinical determination or give the patient a medical impression.
Patient satisfaction, physician well-being and quality of care outcomes
Large health care systems like Kaiser Permanente implemented secure message patient-physician communication (the patient portal) even before the pandemic, showing promising results in 2010 with reduction in office visits, improvement in measurable quality outcomes, and high level of patient satisfaction.10 Post pandemic, several large health care centers opted to announce the billing implementation for patient-initiated portal messages.11 A focus was placed on educating their patients about when a message will and will not be billed. Using this type of strategy can help to improve patient awareness about potential billing without affecting patient satisfaction and care outcomes. Studies have shown the EHR has contributed to physician burnout and some physicians reducing their clinical time or leaving medicine; a reduction in messaging might have a positive impact on physician well-being.
The challenge is that medical billing is not routinely included as a curriculum topic in many residency and fellowship programs; however, trainees are part of E/M services and have limited knowledge of billing processes. Unfortunately, at this time, trainees cannot submit for reimbursement for asynchronous care as described above. We hope that this brief article will help junior gastroenterologists optimize their outpatient billing practices.
Dr. Nieto is an internal medicine chief resident with WellStar Cobb Medical Center, Austell, Ga. Dr. Kinnucan is a gastroenterologist with Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla. The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose for this article. The authors certify that no financial and grant support has been received for this article.
References
1. Holmgren AJ et al. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2021 Dec 9. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocab268.
2. Bali AS et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2023 Apr 24. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002254.
3. AAFP. Family Physician. “Coding Scenario: Coding for Virtual-Digital Visits”
4. Keihanian T. et al. Telehealth Utilization in Gastroenterology Clinics Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic: Impact on Clinical Practice and Gastroenterology Training. Gastroenterology. 2020 Jun 20. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.040.
5. Lewin S et al. J Crohns Colitis. 2020 Oct 21. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaa140.
6. Perisetti A and H Goyal. Dig Dis Sci. 2021 Mar 3. doi: 10.1007/s10620-021-06874-x.
7. Telehealth.HHS.gov. Medicaid and Medicare billing for asynchronous telehealth. Updated: 2022 May 4.
8. Telehealth.HHS.gov. Telehealth policy changes after the COVID-19 public health emergency. Last updated: 2023 Jan 23.
9. Fox B and Sizemore JO. Telehealth: Fad or the future. Epic Health Research Network. 2020 Aug 18.
10. Baer D. Patient-physician e-mail communication: the kaiser permanente experience. J Oncol Pract. 2011 Jul. doi: 10.1200/JOP.2011.000323.
11. Myclevelandclinic.org. MyChart Messaging.
12. Sinsky CA et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2022 Aug 29. doi: 10.1007/s11606-022-07766-0.


