User login
Defending access to reproductive health care
The 1973 Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) decision in Roe v Wade was a landmark ruling,1 establishing that the United States Constitution provides a fundamental “right to privacy,” protecting pregnant people’s freedom to access all available reproductive health care options. Recognizing that the right to abortion was not absolute, the majority of justices supported a trimester system. In the first trimester, decisions about abortion care are fully controlled by patients and clinicians, and no government could place restrictions on access to abortion. In the second trimester, SCOTUS ruled that states may choose to regulate abortion to protect maternal health. (As an example of such state restrictions, in Massachusetts, for many years, but no longer, the state required that abortions occur in a hospital when the patient was between 18 and 24 weeks’ gestation in order to facilitate comprehensive emergency care for complications.) Beginning in the third trimester, a point at which a fetus could be viable, the Court ruled that a government could prohibit abortion except when an abortion was necessary to protect the life or health of the pregnant person. In 1992, the SCOTUS decision in Planned Parenthood v Casey2 rejected the trimester system, reaffirming the right to an abortion before fetal viability, and adopting a new standard that states may not create an undue burden on a person seeking an abortion b
If, as anticipated, the 2022 SCOTUS decision in Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization3 overturns the precedents set in Roe v Wade and Planned Parenthood v Casey, decisions on abortion law will be relegated to elected legislators and state courts.4 It is expected that at least 26 state legislatures and governors will enact stringent new restrictions on access to abortion. This cataclysmic reversal of judicial opinion creates a historic challenge to obstetrician-gynecologists and their patients and could threaten access to other vital reproductive services beyond abortion, like contraception. We will be fighting, state by state, for people’s right to access all available reproductive health procedures. This will also significantly affect the ability for providers in women’s reproductive health to obtain appropriate and necessary education and training in a critical skills. If access to safe abortion is restricted, we fear patients may be forced to consider unsafe abortion, raising the specter of a return to the 1960s, when an epidemic of unsafe abortion caused countless injuries and deaths.5,6
How do we best prepare for these challenges?
- We will need to be flexible and continually evolve our clinical practices to be adherent with state and local legislation and regulation.
- To reduce unintended pregnancies, we need to strengthen our efforts to ensure that every patient has ready access to all available contraceptive options with no out-of-pocket cost.
- When a contraceptive is desired, we will focus on educating people about effectiveness, and offering them highly reliable contraception, such as the implant or intrauterine devices.
- We need to ensure timely access to abortion if state-based laws permit abortion before 6 or 7 weeks’ gestation. Providing medication abortion without an in-person visit using a telehealth option would be one option to expand rapid access to early first trimester abortion.
- Clinicians in states with access to abortion services will need to collaborate with colleagues in states with restrictions on abortion services to improve patient access across state borders.
On a national level, advancing our effective advocacy in Congress may lead to national legislation passed and signed by the President. This could supersede most state laws prohibiting access to comprehensive women’s reproductive health and create a unified, national approach to abortion care, allowing for the appropriate training of all obstetrician-gynecologists. We will also need to develop teams in every state capable of advocating for laws that ensure access to all reproductive health care options. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has leaders trained and tasked with legislative advocacy in every state.7 This network will be a foundation upon which to build additional advocacy efforts.
As women’s health care professionals, our responsibility to our patients, is to work to ensure universal access to safe and effective comprehensive reproductive options, and to ensure that our workforce is prepared to meet the needs of our patients by defending the patient-clinician relationship. Abortion care saves lives of pregnant patients and reduces maternal morbidity.8 Access to safe abortion care as part of comprehensive reproductive services is an important component of health care. ●
- Roe v Wade, 410 U.S. 113 (1973).
- Planned Parenthood v Casey, 505 U.S. 833 (1992).
- Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization, 19-1392. https://www.supremecourt.gov/search .aspx?filename=/docket/docketfiles/html /public/19-1392.html. Accessed May 18, 2022.
- Gerstein J, Ward A. Supreme Court has voted to overturn abortion rights, draft opinion shows. Politico. May 5, 2022. Updated May 3, 2022.
- Gold RB. Lessons from before Roe: will past be prologue? Guttmacher Institute. March 1, 2003. https://www.guttmacher.org/gpr/2003/03 /lessons-roe-will-past-be-prologue. Accessed May 18, 2022.
- Edelin KC. Broken Justice: A True Story of Race, Sex and Revenge in a Boston Courtroom. Pond View Press; 2007.
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Get involved in your state. ACOG web site. https://www.acog.org/advocacy /get-involved/get-involved-in-your-state. Accessed May 18, 2022.
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Improving Birth Outcomes. Bale JR, Stoll BJ, Lucas AO, eds. Reducing maternal mortality and morbidity. In: Improving Birth Outcomes: Meeting the Challenge in the Developing World. Washington, DC: National Academies Press (US); 2003.
The 1973 Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) decision in Roe v Wade was a landmark ruling,1 establishing that the United States Constitution provides a fundamental “right to privacy,” protecting pregnant people’s freedom to access all available reproductive health care options. Recognizing that the right to abortion was not absolute, the majority of justices supported a trimester system. In the first trimester, decisions about abortion care are fully controlled by patients and clinicians, and no government could place restrictions on access to abortion. In the second trimester, SCOTUS ruled that states may choose to regulate abortion to protect maternal health. (As an example of such state restrictions, in Massachusetts, for many years, but no longer, the state required that abortions occur in a hospital when the patient was between 18 and 24 weeks’ gestation in order to facilitate comprehensive emergency care for complications.) Beginning in the third trimester, a point at which a fetus could be viable, the Court ruled that a government could prohibit abortion except when an abortion was necessary to protect the life or health of the pregnant person. In 1992, the SCOTUS decision in Planned Parenthood v Casey2 rejected the trimester system, reaffirming the right to an abortion before fetal viability, and adopting a new standard that states may not create an undue burden on a person seeking an abortion b
If, as anticipated, the 2022 SCOTUS decision in Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization3 overturns the precedents set in Roe v Wade and Planned Parenthood v Casey, decisions on abortion law will be relegated to elected legislators and state courts.4 It is expected that at least 26 state legislatures and governors will enact stringent new restrictions on access to abortion. This cataclysmic reversal of judicial opinion creates a historic challenge to obstetrician-gynecologists and their patients and could threaten access to other vital reproductive services beyond abortion, like contraception. We will be fighting, state by state, for people’s right to access all available reproductive health procedures. This will also significantly affect the ability for providers in women’s reproductive health to obtain appropriate and necessary education and training in a critical skills. If access to safe abortion is restricted, we fear patients may be forced to consider unsafe abortion, raising the specter of a return to the 1960s, when an epidemic of unsafe abortion caused countless injuries and deaths.5,6
How do we best prepare for these challenges?
- We will need to be flexible and continually evolve our clinical practices to be adherent with state and local legislation and regulation.
- To reduce unintended pregnancies, we need to strengthen our efforts to ensure that every patient has ready access to all available contraceptive options with no out-of-pocket cost.
- When a contraceptive is desired, we will focus on educating people about effectiveness, and offering them highly reliable contraception, such as the implant or intrauterine devices.
- We need to ensure timely access to abortion if state-based laws permit abortion before 6 or 7 weeks’ gestation. Providing medication abortion without an in-person visit using a telehealth option would be one option to expand rapid access to early first trimester abortion.
- Clinicians in states with access to abortion services will need to collaborate with colleagues in states with restrictions on abortion services to improve patient access across state borders.
On a national level, advancing our effective advocacy in Congress may lead to national legislation passed and signed by the President. This could supersede most state laws prohibiting access to comprehensive women’s reproductive health and create a unified, national approach to abortion care, allowing for the appropriate training of all obstetrician-gynecologists. We will also need to develop teams in every state capable of advocating for laws that ensure access to all reproductive health care options. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has leaders trained and tasked with legislative advocacy in every state.7 This network will be a foundation upon which to build additional advocacy efforts.
As women’s health care professionals, our responsibility to our patients, is to work to ensure universal access to safe and effective comprehensive reproductive options, and to ensure that our workforce is prepared to meet the needs of our patients by defending the patient-clinician relationship. Abortion care saves lives of pregnant patients and reduces maternal morbidity.8 Access to safe abortion care as part of comprehensive reproductive services is an important component of health care. ●
The 1973 Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) decision in Roe v Wade was a landmark ruling,1 establishing that the United States Constitution provides a fundamental “right to privacy,” protecting pregnant people’s freedom to access all available reproductive health care options. Recognizing that the right to abortion was not absolute, the majority of justices supported a trimester system. In the first trimester, decisions about abortion care are fully controlled by patients and clinicians, and no government could place restrictions on access to abortion. In the second trimester, SCOTUS ruled that states may choose to regulate abortion to protect maternal health. (As an example of such state restrictions, in Massachusetts, for many years, but no longer, the state required that abortions occur in a hospital when the patient was between 18 and 24 weeks’ gestation in order to facilitate comprehensive emergency care for complications.) Beginning in the third trimester, a point at which a fetus could be viable, the Court ruled that a government could prohibit abortion except when an abortion was necessary to protect the life or health of the pregnant person. In 1992, the SCOTUS decision in Planned Parenthood v Casey2 rejected the trimester system, reaffirming the right to an abortion before fetal viability, and adopting a new standard that states may not create an undue burden on a person seeking an abortion b
If, as anticipated, the 2022 SCOTUS decision in Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization3 overturns the precedents set in Roe v Wade and Planned Parenthood v Casey, decisions on abortion law will be relegated to elected legislators and state courts.4 It is expected that at least 26 state legislatures and governors will enact stringent new restrictions on access to abortion. This cataclysmic reversal of judicial opinion creates a historic challenge to obstetrician-gynecologists and their patients and could threaten access to other vital reproductive services beyond abortion, like contraception. We will be fighting, state by state, for people’s right to access all available reproductive health procedures. This will also significantly affect the ability for providers in women’s reproductive health to obtain appropriate and necessary education and training in a critical skills. If access to safe abortion is restricted, we fear patients may be forced to consider unsafe abortion, raising the specter of a return to the 1960s, when an epidemic of unsafe abortion caused countless injuries and deaths.5,6
How do we best prepare for these challenges?
- We will need to be flexible and continually evolve our clinical practices to be adherent with state and local legislation and regulation.
- To reduce unintended pregnancies, we need to strengthen our efforts to ensure that every patient has ready access to all available contraceptive options with no out-of-pocket cost.
- When a contraceptive is desired, we will focus on educating people about effectiveness, and offering them highly reliable contraception, such as the implant or intrauterine devices.
- We need to ensure timely access to abortion if state-based laws permit abortion before 6 or 7 weeks’ gestation. Providing medication abortion without an in-person visit using a telehealth option would be one option to expand rapid access to early first trimester abortion.
- Clinicians in states with access to abortion services will need to collaborate with colleagues in states with restrictions on abortion services to improve patient access across state borders.
On a national level, advancing our effective advocacy in Congress may lead to national legislation passed and signed by the President. This could supersede most state laws prohibiting access to comprehensive women’s reproductive health and create a unified, national approach to abortion care, allowing for the appropriate training of all obstetrician-gynecologists. We will also need to develop teams in every state capable of advocating for laws that ensure access to all reproductive health care options. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has leaders trained and tasked with legislative advocacy in every state.7 This network will be a foundation upon which to build additional advocacy efforts.
As women’s health care professionals, our responsibility to our patients, is to work to ensure universal access to safe and effective comprehensive reproductive options, and to ensure that our workforce is prepared to meet the needs of our patients by defending the patient-clinician relationship. Abortion care saves lives of pregnant patients and reduces maternal morbidity.8 Access to safe abortion care as part of comprehensive reproductive services is an important component of health care. ●
- Roe v Wade, 410 U.S. 113 (1973).
- Planned Parenthood v Casey, 505 U.S. 833 (1992).
- Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization, 19-1392. https://www.supremecourt.gov/search .aspx?filename=/docket/docketfiles/html /public/19-1392.html. Accessed May 18, 2022.
- Gerstein J, Ward A. Supreme Court has voted to overturn abortion rights, draft opinion shows. Politico. May 5, 2022. Updated May 3, 2022.
- Gold RB. Lessons from before Roe: will past be prologue? Guttmacher Institute. March 1, 2003. https://www.guttmacher.org/gpr/2003/03 /lessons-roe-will-past-be-prologue. Accessed May 18, 2022.
- Edelin KC. Broken Justice: A True Story of Race, Sex and Revenge in a Boston Courtroom. Pond View Press; 2007.
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Get involved in your state. ACOG web site. https://www.acog.org/advocacy /get-involved/get-involved-in-your-state. Accessed May 18, 2022.
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Improving Birth Outcomes. Bale JR, Stoll BJ, Lucas AO, eds. Reducing maternal mortality and morbidity. In: Improving Birth Outcomes: Meeting the Challenge in the Developing World. Washington, DC: National Academies Press (US); 2003.
- Roe v Wade, 410 U.S. 113 (1973).
- Planned Parenthood v Casey, 505 U.S. 833 (1992).
- Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization, 19-1392. https://www.supremecourt.gov/search .aspx?filename=/docket/docketfiles/html /public/19-1392.html. Accessed May 18, 2022.
- Gerstein J, Ward A. Supreme Court has voted to overturn abortion rights, draft opinion shows. Politico. May 5, 2022. Updated May 3, 2022.
- Gold RB. Lessons from before Roe: will past be prologue? Guttmacher Institute. March 1, 2003. https://www.guttmacher.org/gpr/2003/03 /lessons-roe-will-past-be-prologue. Accessed May 18, 2022.
- Edelin KC. Broken Justice: A True Story of Race, Sex and Revenge in a Boston Courtroom. Pond View Press; 2007.
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Get involved in your state. ACOG web site. https://www.acog.org/advocacy /get-involved/get-involved-in-your-state. Accessed May 18, 2022.
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Improving Birth Outcomes. Bale JR, Stoll BJ, Lucas AO, eds. Reducing maternal mortality and morbidity. In: Improving Birth Outcomes: Meeting the Challenge in the Developing World. Washington, DC: National Academies Press (US); 2003.
Stress and infertility – is it a proven cause and effect?
“Just relax, stop thinking about it and, more than likely, it will happen.” If ever there was a controversial subject in medicine, especially in reproduction, the relationship between stress and infertility would be high on the list. Who among us has not overheard or even personally shared with an infertility patient that they should try and reduce their stress to improve fertility? The theory is certainly not new. Hippocrates, back in the 5th century B.C., was one of the first to associate a woman’s psychological state with her reproductive potential. His contention was that a physical sign of psychological stress in women (which scholars later dubbed “hysteria”) could result in sterility. In medieval times, a German abbess and mystic named Hildegard of Bingen posited women suffering from melancholy – a condition that we today might call depression – were infertile as a result.
The deeper meaning behind the flippant advice to relax is implicit blame; that is, a woman interprets the link of stress and infertility as a declaration that she is sabotaging reproduction. Not only is this assumption flawed, but it does further damage to a woman’s emotional fragility. To provide the presumption of stress affecting reproduction, a recent survey of over 5,000 infertility patients found, remarkably, 98% considered emotional stress as either a cause or a contributor to infertility, and 31% believed stress was a cause of miscarriage, although racial differences existed (J Assist Reprod Genet. 2021 Apr;38[4]:877-87). This relationship was mostly seen in women who used complementary and alternative medicine, Black women, and those who frequented Internet search engines. Whereas women who had a professional degree, had more infertility insurance coverage, and were nonreligious were less likely to attribute stress to infertility. Intriguingly, the more engaged the physicians, the less patients linked stress with infertility, while the contrary also applied.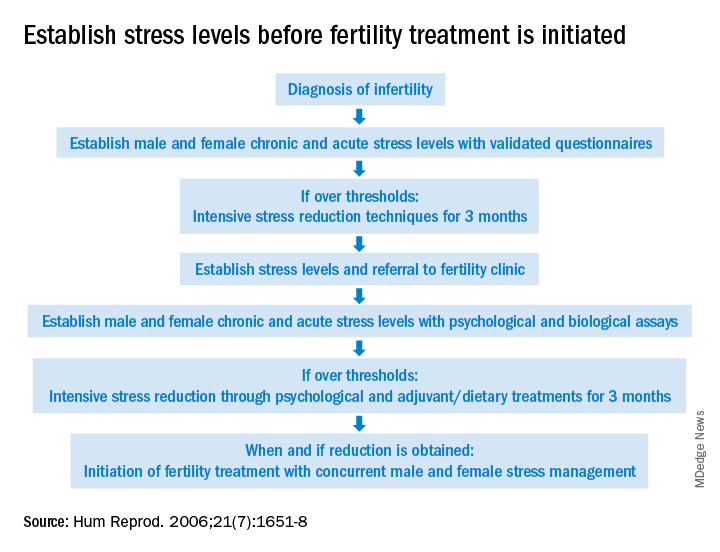
The power of stress can be exemplified by the pathophysiology of amenorrhea. Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea is the most common cause of the female athlete triad of secondary amenorrhea in women of childbearing age. It is a reversible disorder caused by stress related to weight loss, excessive exercise and/or traumatic mental experiences (Endocrines. 2021;2:203-11). Stress of infertility has also been demonstrated to be equivalent to a diagnosis of cancer and other major medical morbidities (J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. 1993;14[Suppl]:45-52).
A definitive link between stress and infertility is evasive because of the lack of controlled, prospective longitudinal studies and the challenge of reducing variables in the analysis. The question remains which developed initially – the stress or the infertility? Infertility treatment is a physical, emotional, and financial investment. Stress and the duration of infertility are correlative. The additive factor is that poor insurance coverage for costly fertility treatment can not only heighten stress but, concurrently, subject the patient to the risk of exploitation driven by desperation whereby they accept unproven “add-ons” offered with assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
Both acute and chronic stress affect the number of oocytes retrieved and fertilized with ART as well as live birth delivery and birth weights (Fertil Steril. 2001;76:675-87). Men are also affected by stress, which is manifested by decreased libido and impaired semen, further compromised as the duration of infertility continues. The gut-derived hormone ghrelin appears to play a role with stress and reproduction (Endocr Rev. 2017;38:432-67).
As the relationship between stress and infertility is far from proven, there are conflicting study results. Two meta-analyses failed to show any association between stress and the outcomes of ART cycles (Hum Reprod. 2011;26:2763-76; BMJ. 2011;342:d223). In contrast, a recent study suggested stress during infertility treatment was contributed by the variables of low spousal support, financial constraints, and social coercion in the early years of marriage (J Hum Reprod Sci. 2018;11:172-9). Emotional distress was found to be three times greater in women whose families had unrealistic expectations from treatments.
Fortunately, psychotherapy during the ART cycle has demonstrated a benefit in outcomes. Domar revealed psychological support and cognitive behavior therapy resulted in higher pregnancy rates than in the control group (Fertil Steril. 2000;73:805-12). Another recent study appears to support stress reduction improving reproductive potential (Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018;20[1]:41-7).
Given the evidence provided in this article, it behooves infertility clinics to address baseline (chronic) stress and acute stress (because of infertility) prior to initiating treatment (see Figure). While the definitive answer addressing the impact of stress on reproduction remains unknown, we may share with our patients a definition in which they may find enlightenment, “Stress is trying to control an event in which one is incapable.”
Dr. Mark P Trolice is director of Fertility CARE: The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
“Just relax, stop thinking about it and, more than likely, it will happen.” If ever there was a controversial subject in medicine, especially in reproduction, the relationship between stress and infertility would be high on the list. Who among us has not overheard or even personally shared with an infertility patient that they should try and reduce their stress to improve fertility? The theory is certainly not new. Hippocrates, back in the 5th century B.C., was one of the first to associate a woman’s psychological state with her reproductive potential. His contention was that a physical sign of psychological stress in women (which scholars later dubbed “hysteria”) could result in sterility. In medieval times, a German abbess and mystic named Hildegard of Bingen posited women suffering from melancholy – a condition that we today might call depression – were infertile as a result.
The deeper meaning behind the flippant advice to relax is implicit blame; that is, a woman interprets the link of stress and infertility as a declaration that she is sabotaging reproduction. Not only is this assumption flawed, but it does further damage to a woman’s emotional fragility. To provide the presumption of stress affecting reproduction, a recent survey of over 5,000 infertility patients found, remarkably, 98% considered emotional stress as either a cause or a contributor to infertility, and 31% believed stress was a cause of miscarriage, although racial differences existed (J Assist Reprod Genet. 2021 Apr;38[4]:877-87). This relationship was mostly seen in women who used complementary and alternative medicine, Black women, and those who frequented Internet search engines. Whereas women who had a professional degree, had more infertility insurance coverage, and were nonreligious were less likely to attribute stress to infertility. Intriguingly, the more engaged the physicians, the less patients linked stress with infertility, while the contrary also applied.
The power of stress can be exemplified by the pathophysiology of amenorrhea. Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea is the most common cause of the female athlete triad of secondary amenorrhea in women of childbearing age. It is a reversible disorder caused by stress related to weight loss, excessive exercise and/or traumatic mental experiences (Endocrines. 2021;2:203-11). Stress of infertility has also been demonstrated to be equivalent to a diagnosis of cancer and other major medical morbidities (J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. 1993;14[Suppl]:45-52).
A definitive link between stress and infertility is evasive because of the lack of controlled, prospective longitudinal studies and the challenge of reducing variables in the analysis. The question remains which developed initially – the stress or the infertility? Infertility treatment is a physical, emotional, and financial investment. Stress and the duration of infertility are correlative. The additive factor is that poor insurance coverage for costly fertility treatment can not only heighten stress but, concurrently, subject the patient to the risk of exploitation driven by desperation whereby they accept unproven “add-ons” offered with assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
Both acute and chronic stress affect the number of oocytes retrieved and fertilized with ART as well as live birth delivery and birth weights (Fertil Steril. 2001;76:675-87). Men are also affected by stress, which is manifested by decreased libido and impaired semen, further compromised as the duration of infertility continues. The gut-derived hormone ghrelin appears to play a role with stress and reproduction (Endocr Rev. 2017;38:432-67).
As the relationship between stress and infertility is far from proven, there are conflicting study results. Two meta-analyses failed to show any association between stress and the outcomes of ART cycles (Hum Reprod. 2011;26:2763-76; BMJ. 2011;342:d223). In contrast, a recent study suggested stress during infertility treatment was contributed by the variables of low spousal support, financial constraints, and social coercion in the early years of marriage (J Hum Reprod Sci. 2018;11:172-9). Emotional distress was found to be three times greater in women whose families had unrealistic expectations from treatments.
Fortunately, psychotherapy during the ART cycle has demonstrated a benefit in outcomes. Domar revealed psychological support and cognitive behavior therapy resulted in higher pregnancy rates than in the control group (Fertil Steril. 2000;73:805-12). Another recent study appears to support stress reduction improving reproductive potential (Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018;20[1]:41-7).
Given the evidence provided in this article, it behooves infertility clinics to address baseline (chronic) stress and acute stress (because of infertility) prior to initiating treatment (see Figure). While the definitive answer addressing the impact of stress on reproduction remains unknown, we may share with our patients a definition in which they may find enlightenment, “Stress is trying to control an event in which one is incapable.”
Dr. Mark P Trolice is director of Fertility CARE: The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
“Just relax, stop thinking about it and, more than likely, it will happen.” If ever there was a controversial subject in medicine, especially in reproduction, the relationship between stress and infertility would be high on the list. Who among us has not overheard or even personally shared with an infertility patient that they should try and reduce their stress to improve fertility? The theory is certainly not new. Hippocrates, back in the 5th century B.C., was one of the first to associate a woman’s psychological state with her reproductive potential. His contention was that a physical sign of psychological stress in women (which scholars later dubbed “hysteria”) could result in sterility. In medieval times, a German abbess and mystic named Hildegard of Bingen posited women suffering from melancholy – a condition that we today might call depression – were infertile as a result.
The deeper meaning behind the flippant advice to relax is implicit blame; that is, a woman interprets the link of stress and infertility as a declaration that she is sabotaging reproduction. Not only is this assumption flawed, but it does further damage to a woman’s emotional fragility. To provide the presumption of stress affecting reproduction, a recent survey of over 5,000 infertility patients found, remarkably, 98% considered emotional stress as either a cause or a contributor to infertility, and 31% believed stress was a cause of miscarriage, although racial differences existed (J Assist Reprod Genet. 2021 Apr;38[4]:877-87). This relationship was mostly seen in women who used complementary and alternative medicine, Black women, and those who frequented Internet search engines. Whereas women who had a professional degree, had more infertility insurance coverage, and were nonreligious were less likely to attribute stress to infertility. Intriguingly, the more engaged the physicians, the less patients linked stress with infertility, while the contrary also applied.
The power of stress can be exemplified by the pathophysiology of amenorrhea. Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea is the most common cause of the female athlete triad of secondary amenorrhea in women of childbearing age. It is a reversible disorder caused by stress related to weight loss, excessive exercise and/or traumatic mental experiences (Endocrines. 2021;2:203-11). Stress of infertility has also been demonstrated to be equivalent to a diagnosis of cancer and other major medical morbidities (J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. 1993;14[Suppl]:45-52).
A definitive link between stress and infertility is evasive because of the lack of controlled, prospective longitudinal studies and the challenge of reducing variables in the analysis. The question remains which developed initially – the stress or the infertility? Infertility treatment is a physical, emotional, and financial investment. Stress and the duration of infertility are correlative. The additive factor is that poor insurance coverage for costly fertility treatment can not only heighten stress but, concurrently, subject the patient to the risk of exploitation driven by desperation whereby they accept unproven “add-ons” offered with assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
Both acute and chronic stress affect the number of oocytes retrieved and fertilized with ART as well as live birth delivery and birth weights (Fertil Steril. 2001;76:675-87). Men are also affected by stress, which is manifested by decreased libido and impaired semen, further compromised as the duration of infertility continues. The gut-derived hormone ghrelin appears to play a role with stress and reproduction (Endocr Rev. 2017;38:432-67).
As the relationship between stress and infertility is far from proven, there are conflicting study results. Two meta-analyses failed to show any association between stress and the outcomes of ART cycles (Hum Reprod. 2011;26:2763-76; BMJ. 2011;342:d223). In contrast, a recent study suggested stress during infertility treatment was contributed by the variables of low spousal support, financial constraints, and social coercion in the early years of marriage (J Hum Reprod Sci. 2018;11:172-9). Emotional distress was found to be three times greater in women whose families had unrealistic expectations from treatments.
Fortunately, psychotherapy during the ART cycle has demonstrated a benefit in outcomes. Domar revealed psychological support and cognitive behavior therapy resulted in higher pregnancy rates than in the control group (Fertil Steril. 2000;73:805-12). Another recent study appears to support stress reduction improving reproductive potential (Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018;20[1]:41-7).
Given the evidence provided in this article, it behooves infertility clinics to address baseline (chronic) stress and acute stress (because of infertility) prior to initiating treatment (see Figure). While the definitive answer addressing the impact of stress on reproduction remains unknown, we may share with our patients a definition in which they may find enlightenment, “Stress is trying to control an event in which one is incapable.”
Dr. Mark P Trolice is director of Fertility CARE: The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
