Article
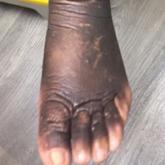
Treatment of Elephantiasic Pretibial Myxedema With Rituximab Therapy
- Author:
- Shaan Patel, MD, MBA
- David Choi, MD
- Stratos Christianakis, MD
- Ashley Wysong, MD
- Ashley Crew, MD
Rituximab may be an effective therapy to consider in the treatment of elephantiasic pretibial myxedema.
Article
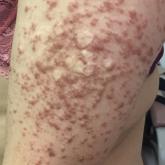
Management of Refractory Pain From Hereditary Cutaneous Leiomyomas With Nifedipine and Gabapentin
- Author:
- Shaan Patel, MD, MBA
- David Choi, MD
- Iris Ahronowitz, MD
Cutaneous leiomyomas may be a source of considerable pain, which may respond to treatment with nifedipine in combination with gabapentin.
