User login
Severe tophaceous gout
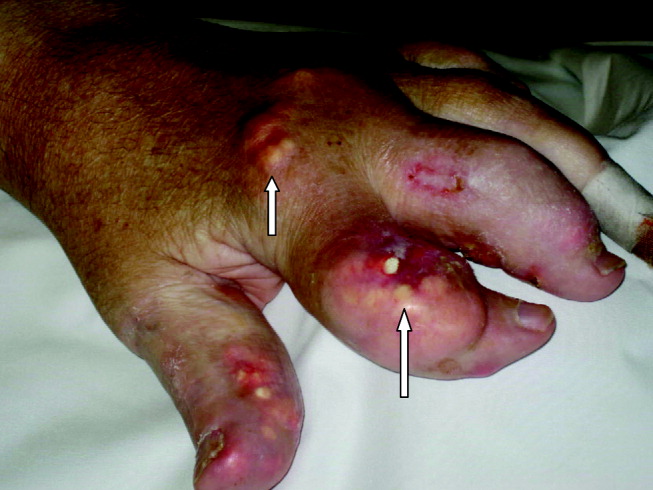
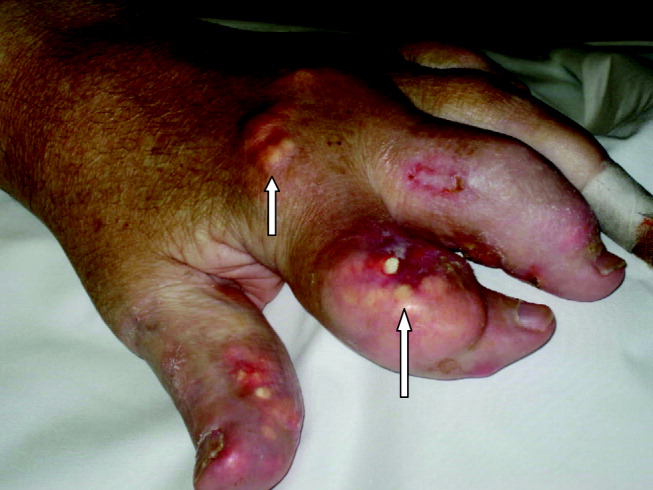
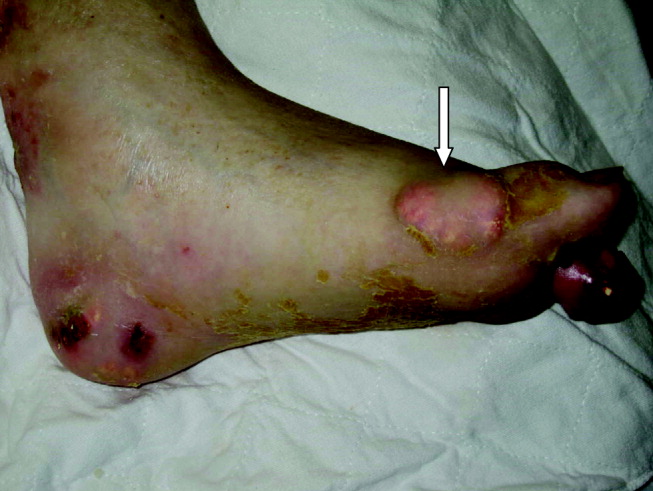
A 55‐year‐old man was admitted to the hospital for amputation of multiple toes secondarily infected in the setting of severe tophaceous gout. He had been wheelchair bound for several years because of severe gouty arthritis. His medical history was remarkable for previous arthroscopies of his hands, knees, and Achilles tendons to remove uric acid deposits, in addition to multiple episodes of nephrolithiasis from uric acid stones. His family history was remarkable for severe, debilitating gout in multiple first‐degree relatives. On further examination he was noted to have severe tophaceous gouty involvement of numerous joints (arrows in Figs. 1 and 2). His uric acid level was 11.6 mg/dL despite receiving 900 mg of allopurinol daily. Because his creatinine was 1.7 mg/dL on admission, his dose of allopurinol was reduced. Renal ultrasound revealed multiple bilateral renal stones (arrows in Fig. 3).

He underwent surgery, and was subsequently transferred to a skilled nursing facility for wound care and physical therapy, where he recuperated uneventfully.
A 55‐year‐old man was admitted to the hospital for amputation of multiple toes secondarily infected in the setting of severe tophaceous gout. He had been wheelchair bound for several years because of severe gouty arthritis. His medical history was remarkable for previous arthroscopies of his hands, knees, and Achilles tendons to remove uric acid deposits, in addition to multiple episodes of nephrolithiasis from uric acid stones. His family history was remarkable for severe, debilitating gout in multiple first‐degree relatives. On further examination he was noted to have severe tophaceous gouty involvement of numerous joints (arrows in Figs. 1 and 2). His uric acid level was 11.6 mg/dL despite receiving 900 mg of allopurinol daily. Because his creatinine was 1.7 mg/dL on admission, his dose of allopurinol was reduced. Renal ultrasound revealed multiple bilateral renal stones (arrows in Fig. 3).



He underwent surgery, and was subsequently transferred to a skilled nursing facility for wound care and physical therapy, where he recuperated uneventfully.
A 55‐year‐old man was admitted to the hospital for amputation of multiple toes secondarily infected in the setting of severe tophaceous gout. He had been wheelchair bound for several years because of severe gouty arthritis. His medical history was remarkable for previous arthroscopies of his hands, knees, and Achilles tendons to remove uric acid deposits, in addition to multiple episodes of nephrolithiasis from uric acid stones. His family history was remarkable for severe, debilitating gout in multiple first‐degree relatives. On further examination he was noted to have severe tophaceous gouty involvement of numerous joints (arrows in Figs. 1 and 2). His uric acid level was 11.6 mg/dL despite receiving 900 mg of allopurinol daily. Because his creatinine was 1.7 mg/dL on admission, his dose of allopurinol was reduced. Renal ultrasound revealed multiple bilateral renal stones (arrows in Fig. 3).



He underwent surgery, and was subsequently transferred to a skilled nursing facility for wound care and physical therapy, where he recuperated uneventfully.