Article
2023 Update on minimally invasive gynecologic surgery
- Author:
- Sierra J. Seaman, MD
- Jessica Chaoul, MD
- Arnold P. Advincula, MD
Focused guidance on treating cesarean scar pregnancy, preventing complications from laparoscopic hysterectomy for endometriosis,...
Video
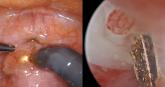
Isthmocele repair: Simultaneous hysteroscopy and robotic-assisted laparoscopy
- Author:
- Sierra J. Seaman, MD
- Chetna Arora, MD
- Arnold P. Advincula, MD
An isthmocele is a pouch-like anterior uterine wall defect at the site of a previous cesarean scar. The incidence is not well known, but it is...
Video
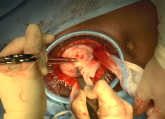
Minilaparotomy: Minimally invasive approach to abdominal myomectomy
- Author:
- Sierra J. Seaman, MD
- Patricia J. Mattingly, MD
- Arnold P. Advincula, MD
Technique for removing symptomatic fibroids in a nulliparous 37-year-old patient seeking fertility
