User login
Recognizing granulosa cell ovarian tumors
Granulosa cell tumors arise from ovarian sex cords and make up an estimated 1% of all ovarian cancer cases but comprise more than 70% of all sex cord stromal tumors.
Granulosa cell tumors (GCTs) can be divided into adult and juvenile types. Adult GCTs are much more common, representing 95% of all GCTs. Women diagnosed with adult GCTs are typically younger as compared with those with epithelial ovarian cancer. The average age of diagnosis for adult GCTs is 50 years, and for women with juvenile GCTs, the average age at diagnosis is 20 years.
Granulosa cell tumors have been shown to be more common in nonwhite women, those with a high body mass index, and a family history of breast or ovarian cancer.1
Adult GCTs can be associated with Peutz-Jeghers and Potter syndromes. Juvenile GCTs are exceedingly rare but can also be associated with mesodermal dysplastic syndromes characterized by the presence of enchondromatosis and hemangioma formation, such as Ollier disease or Maffucci syndrome.
Adult granulosa cell tumors are large, hormonally active tumors; typically secreting estrogen and associated with symptoms of hyperestrogenism. In one study, 55% of women with GCTs were reported to have hyperestrogenic findings such as breast tenderness, virulism, abnormal or postmenopausal bleeding, and hyperplasia, and those with juvenile GCTs may present with precocious puberty.2,3
In pregnancy, hormonal symptoms are temporized, thus the most common presentation is acute rupture. Initial evaluation of women with adult GCTs will reveal a palpable unilateral pelvic mass typically larger than 10cm. Juvenile and adult GCTs are unilateral in 95% of cases.4
In women presenting with a large adnexal mass, the appropriate initial clinical evaluation includes radiographic and laboratory studies. Endovaginal ultrasound typically reveals a large adnexal mass with heterogeneous solid and cystic components, areas of hemorrhage or necrosis and increased vascularity on Doppler. Juvenile GCTs have a more distinct appearance of solid growth with focal areas of follicular formation.
Laboratory findings suggestive of GCT include elevated inhibin-A, inhibin-B, anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH), and CA-125. Inhibin-B is the most commonly used tumor marker for the clinical monitoring of adult GCTs, but AMH may be the most specific.5 Lastly, an endometrial biopsy should be considered in all patients with abnormal uterine bleeding and in all postmenopausal women with an adnexal mass and an endometrial stripe greater than 5mm.6
Surgical staging for adult GCTs is the standard of care. For women who do not desire fertility, this includes total hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and removal of all gross disease. Comprehensive nodal dissection is not indicated except when necessary for complete cytoreduction. In contrast to epithelial ovarian cancer, approximately 80% of women with adult GCTs are diagnosed with stage I disease. For stage IA disease, treatment with surgery alone is sufficient, yet in women with stage II-IV disease or with tumors that are ruptured intraoperatively, platinum-based chemotherapy is recommended. The most common regimen is bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin, though there is increasing experience with an outpatient regimen of paclitaxel and carboplatin.
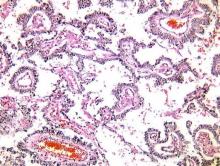
The gross appearance of both adult and juvenile GCTs are of a large, tan-yellow tumor with cystic, solid, and hemorrhagic components. Microscopically, juvenile GCTs are more distinct than that of adult GCTs. Whereas adult GCTs comprise diffuse cords or trabeculae and small follicles termed Call-Exner bodies of rounded cells with scant cytoplasm and pale “coffee-bean” nuclei, juvenile GCTs have nuclei that are rounded, hyperchromatic with moderate to abundant eosinophilic or vacuolated cytoplasm.
The prognosis of GCTs is largely dependent on the stage at diagnosis and presence of residual disease after debulking. Negative prognostic factors for recurrence include tumor size, rupture, atypia and increased mitotic activity.
There are distinct clinical, radiographic, and laboratory characteristics that may raise the suspicion of the practicing gynecologist for a GCT. In such cases, expedient referral for surgical exploration to a gynecologic oncologist is warranted. If the tumor is encountered inadvertently, intraoperative consultation from a gynecologic oncologist should be requested. If a gynecologic oncologist is not available, it is paramount to optimize surgical exposure to clearly document any abnormal pelvic or intra-abdominal findings, take care to prevent surgical spillage, and preserve fertility if indicated.
If referred appropriately and completely resected, the 5-year overall survival of stage IA disease can be upward of 90%. Recurrences are stage dependent with an average time to recurrence of just under 5 years. When recurrences occur, they tend to happen in the pelvis. All women with a history of GCT will require surveillance and monitoring.
References
1. Gynecol Oncol. 2005 May;97(2):519-23.
2. “Rare and Uncommon Gynecological Cancers: A Clinical Guide” (Heidelberg: Springer, 2011): Reed N.
3. Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Feb;55(2):231-8.
4. “Principles and Practice of Gynecologic Oncology” (Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013): Barakat R.
5. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2013 Mar;4(1):37-47.
6. “Uncommon Gynecologic Cancers” (Indianapolis: Wiley-Blackwell, 2014): Del Carmen M.
Dr. Gehrig is professor and director of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Castellano is a resident physician in the obstetrics and gynecology program at the university. They reported having no relevant financial disclosures. To comment, email them at obnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Granulosa cell tumors arise from ovarian sex cords and make up an estimated 1% of all ovarian cancer cases but comprise more than 70% of all sex cord stromal tumors.
Granulosa cell tumors (GCTs) can be divided into adult and juvenile types. Adult GCTs are much more common, representing 95% of all GCTs. Women diagnosed with adult GCTs are typically younger as compared with those with epithelial ovarian cancer. The average age of diagnosis for adult GCTs is 50 years, and for women with juvenile GCTs, the average age at diagnosis is 20 years.
Granulosa cell tumors have been shown to be more common in nonwhite women, those with a high body mass index, and a family history of breast or ovarian cancer.1
Adult GCTs can be associated with Peutz-Jeghers and Potter syndromes. Juvenile GCTs are exceedingly rare but can also be associated with mesodermal dysplastic syndromes characterized by the presence of enchondromatosis and hemangioma formation, such as Ollier disease or Maffucci syndrome.
Adult granulosa cell tumors are large, hormonally active tumors; typically secreting estrogen and associated with symptoms of hyperestrogenism. In one study, 55% of women with GCTs were reported to have hyperestrogenic findings such as breast tenderness, virulism, abnormal or postmenopausal bleeding, and hyperplasia, and those with juvenile GCTs may present with precocious puberty.2,3
In pregnancy, hormonal symptoms are temporized, thus the most common presentation is acute rupture. Initial evaluation of women with adult GCTs will reveal a palpable unilateral pelvic mass typically larger than 10cm. Juvenile and adult GCTs are unilateral in 95% of cases.4
In women presenting with a large adnexal mass, the appropriate initial clinical evaluation includes radiographic and laboratory studies. Endovaginal ultrasound typically reveals a large adnexal mass with heterogeneous solid and cystic components, areas of hemorrhage or necrosis and increased vascularity on Doppler. Juvenile GCTs have a more distinct appearance of solid growth with focal areas of follicular formation.
Laboratory findings suggestive of GCT include elevated inhibin-A, inhibin-B, anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH), and CA-125. Inhibin-B is the most commonly used tumor marker for the clinical monitoring of adult GCTs, but AMH may be the most specific.5 Lastly, an endometrial biopsy should be considered in all patients with abnormal uterine bleeding and in all postmenopausal women with an adnexal mass and an endometrial stripe greater than 5mm.6
Surgical staging for adult GCTs is the standard of care. For women who do not desire fertility, this includes total hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and removal of all gross disease. Comprehensive nodal dissection is not indicated except when necessary for complete cytoreduction. In contrast to epithelial ovarian cancer, approximately 80% of women with adult GCTs are diagnosed with stage I disease. For stage IA disease, treatment with surgery alone is sufficient, yet in women with stage II-IV disease or with tumors that are ruptured intraoperatively, platinum-based chemotherapy is recommended. The most common regimen is bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin, though there is increasing experience with an outpatient regimen of paclitaxel and carboplatin.
The gross appearance of both adult and juvenile GCTs are of a large, tan-yellow tumor with cystic, solid, and hemorrhagic components. Microscopically, juvenile GCTs are more distinct than that of adult GCTs. Whereas adult GCTs comprise diffuse cords or trabeculae and small follicles termed Call-Exner bodies of rounded cells with scant cytoplasm and pale “coffee-bean” nuclei, juvenile GCTs have nuclei that are rounded, hyperchromatic with moderate to abundant eosinophilic or vacuolated cytoplasm.
The prognosis of GCTs is largely dependent on the stage at diagnosis and presence of residual disease after debulking. Negative prognostic factors for recurrence include tumor size, rupture, atypia and increased mitotic activity.
There are distinct clinical, radiographic, and laboratory characteristics that may raise the suspicion of the practicing gynecologist for a GCT. In such cases, expedient referral for surgical exploration to a gynecologic oncologist is warranted. If the tumor is encountered inadvertently, intraoperative consultation from a gynecologic oncologist should be requested. If a gynecologic oncologist is not available, it is paramount to optimize surgical exposure to clearly document any abnormal pelvic or intra-abdominal findings, take care to prevent surgical spillage, and preserve fertility if indicated.
If referred appropriately and completely resected, the 5-year overall survival of stage IA disease can be upward of 90%. Recurrences are stage dependent with an average time to recurrence of just under 5 years. When recurrences occur, they tend to happen in the pelvis. All women with a history of GCT will require surveillance and monitoring.
References
1. Gynecol Oncol. 2005 May;97(2):519-23.
2. “Rare and Uncommon Gynecological Cancers: A Clinical Guide” (Heidelberg: Springer, 2011): Reed N.
3. Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Feb;55(2):231-8.
4. “Principles and Practice of Gynecologic Oncology” (Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013): Barakat R.
5. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2013 Mar;4(1):37-47.
6. “Uncommon Gynecologic Cancers” (Indianapolis: Wiley-Blackwell, 2014): Del Carmen M.
Dr. Gehrig is professor and director of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Castellano is a resident physician in the obstetrics and gynecology program at the university. They reported having no relevant financial disclosures. To comment, email them at obnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Granulosa cell tumors arise from ovarian sex cords and make up an estimated 1% of all ovarian cancer cases but comprise more than 70% of all sex cord stromal tumors.
Granulosa cell tumors (GCTs) can be divided into adult and juvenile types. Adult GCTs are much more common, representing 95% of all GCTs. Women diagnosed with adult GCTs are typically younger as compared with those with epithelial ovarian cancer. The average age of diagnosis for adult GCTs is 50 years, and for women with juvenile GCTs, the average age at diagnosis is 20 years.
Granulosa cell tumors have been shown to be more common in nonwhite women, those with a high body mass index, and a family history of breast or ovarian cancer.1
Adult GCTs can be associated with Peutz-Jeghers and Potter syndromes. Juvenile GCTs are exceedingly rare but can also be associated with mesodermal dysplastic syndromes characterized by the presence of enchondromatosis and hemangioma formation, such as Ollier disease or Maffucci syndrome.
Adult granulosa cell tumors are large, hormonally active tumors; typically secreting estrogen and associated with symptoms of hyperestrogenism. In one study, 55% of women with GCTs were reported to have hyperestrogenic findings such as breast tenderness, virulism, abnormal or postmenopausal bleeding, and hyperplasia, and those with juvenile GCTs may present with precocious puberty.2,3
In pregnancy, hormonal symptoms are temporized, thus the most common presentation is acute rupture. Initial evaluation of women with adult GCTs will reveal a palpable unilateral pelvic mass typically larger than 10cm. Juvenile and adult GCTs are unilateral in 95% of cases.4
In women presenting with a large adnexal mass, the appropriate initial clinical evaluation includes radiographic and laboratory studies. Endovaginal ultrasound typically reveals a large adnexal mass with heterogeneous solid and cystic components, areas of hemorrhage or necrosis and increased vascularity on Doppler. Juvenile GCTs have a more distinct appearance of solid growth with focal areas of follicular formation.
Laboratory findings suggestive of GCT include elevated inhibin-A, inhibin-B, anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH), and CA-125. Inhibin-B is the most commonly used tumor marker for the clinical monitoring of adult GCTs, but AMH may be the most specific.5 Lastly, an endometrial biopsy should be considered in all patients with abnormal uterine bleeding and in all postmenopausal women with an adnexal mass and an endometrial stripe greater than 5mm.6
Surgical staging for adult GCTs is the standard of care. For women who do not desire fertility, this includes total hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and removal of all gross disease. Comprehensive nodal dissection is not indicated except when necessary for complete cytoreduction. In contrast to epithelial ovarian cancer, approximately 80% of women with adult GCTs are diagnosed with stage I disease. For stage IA disease, treatment with surgery alone is sufficient, yet in women with stage II-IV disease or with tumors that are ruptured intraoperatively, platinum-based chemotherapy is recommended. The most common regimen is bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin, though there is increasing experience with an outpatient regimen of paclitaxel and carboplatin.
The gross appearance of both adult and juvenile GCTs are of a large, tan-yellow tumor with cystic, solid, and hemorrhagic components. Microscopically, juvenile GCTs are more distinct than that of adult GCTs. Whereas adult GCTs comprise diffuse cords or trabeculae and small follicles termed Call-Exner bodies of rounded cells with scant cytoplasm and pale “coffee-bean” nuclei, juvenile GCTs have nuclei that are rounded, hyperchromatic with moderate to abundant eosinophilic or vacuolated cytoplasm.
The prognosis of GCTs is largely dependent on the stage at diagnosis and presence of residual disease after debulking. Negative prognostic factors for recurrence include tumor size, rupture, atypia and increased mitotic activity.
There are distinct clinical, radiographic, and laboratory characteristics that may raise the suspicion of the practicing gynecologist for a GCT. In such cases, expedient referral for surgical exploration to a gynecologic oncologist is warranted. If the tumor is encountered inadvertently, intraoperative consultation from a gynecologic oncologist should be requested. If a gynecologic oncologist is not available, it is paramount to optimize surgical exposure to clearly document any abnormal pelvic or intra-abdominal findings, take care to prevent surgical spillage, and preserve fertility if indicated.
If referred appropriately and completely resected, the 5-year overall survival of stage IA disease can be upward of 90%. Recurrences are stage dependent with an average time to recurrence of just under 5 years. When recurrences occur, they tend to happen in the pelvis. All women with a history of GCT will require surveillance and monitoring.
References
1. Gynecol Oncol. 2005 May;97(2):519-23.
2. “Rare and Uncommon Gynecological Cancers: A Clinical Guide” (Heidelberg: Springer, 2011): Reed N.
3. Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Feb;55(2):231-8.
4. “Principles and Practice of Gynecologic Oncology” (Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013): Barakat R.
5. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2013 Mar;4(1):37-47.
6. “Uncommon Gynecologic Cancers” (Indianapolis: Wiley-Blackwell, 2014): Del Carmen M.
Dr. Gehrig is professor and director of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Castellano is a resident physician in the obstetrics and gynecology program at the university. They reported having no relevant financial disclosures. To comment, email them at obnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Understanding ovarian germ cell neoplasms
Germ cell neoplasms arise from primordial germ cells of the gonad that differentiate to embryonic and extraembryonic tissues. Approximately 20%-25% of ovarian neoplasms are germ cell in origin but they account for only 3%-5% of ovarian malignancies. Importantly, germ cell neoplasms encompass 70% of the ovarian neoplasms among girls and young women aged 10-30 years, of which approximately one-third are malignant.
Unlike epithelial ovarian cancers, malignant germ cell neoplasms are typically diagnosed at early stages. They can present as a palpable mass or cause acute abdominal pain secondary to their rapid growth, penchant for necrosis, torsion, hemorrhage, infection, or rupture. Since malignant germ cell neoplasms can excrete hormonally-active tumor markers, such as human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), many women present with menstrual irregularities.
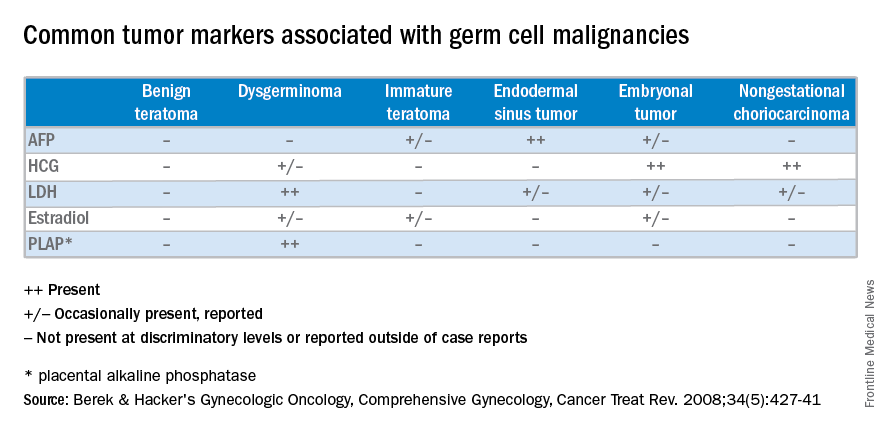
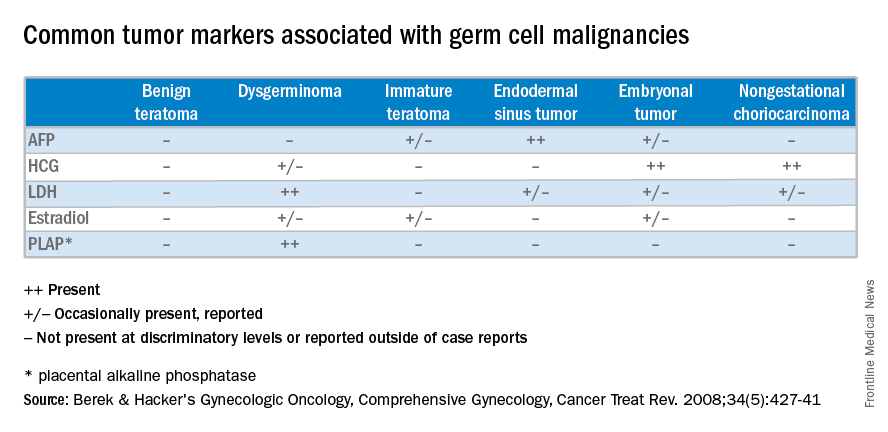
Management of malignant germ cell neoplasms generally includes fertility-sparing surgery – with or without neoadjuvant combination bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin (BEP) – and is typically associated with a favorable prognosis (Cancer Treat Rev. 2008 Aug;34[5]:427-41).
Teratomas
Benign teratomas represent about a quarter of all ovarian neoplasms. Benign teratomas can be solid or cystic, and contain components representing all three cell layers: endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. Due to the presence of differentiated adult tissues, benign teratomas have a characteristic radiographic appearance. They can appear as cystic echogenic masses with intense acoustic shadowing, homogenous nodules or bands, and rounded protuberances called “Rokitansky nodules.”
Treatment of benign teratomas in reproductive-age women includes ovarian cystectomy and careful inspection of the contralateral ovary as 10%-15% may be bilateral. In postmenopausal women, there is less than a 2% risk for malignant transformation of the associated cell lines, most commonly a squamous cell carcinoma. In these cases, spread beyond the ovarian capsule is associated with a poor prognosis and chemotherapy and/or radiation are indicated (Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2006 Jan-Feb;16[1]:140-4). Malignant monodermal teratomas are composed of single cell lines with malignant transformations of that tissue type; struma ovarii composed of thyroid tissue, for example, is exceedingly rare.
Dysgerminoma
Dysgerminomas are the most common malignant germ cell neoplasms, accounting for about one-third of cases. They typically present in girls and young women between 10 and 30 years of age, and rarely occur after 50 years of age. As a result, a quarter of cases are identified during pregnancy and another 5% are found in patients presenting with amenorrhea secondary to gonadal dysgenesis, such as is associated with Turner’s syndrome.
At diagnosis, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) may be elevated and 10% may have an elevation of HCG. Ultrasound findings include a solid, mostly echoic, but heterogeneous mass with apparent lobulations. About two-thirds are stage I at the time of diagnosis, and 10%-15% are bilateral, making dysgerminomas the only malignant germ cell neoplasm with significant risk for bilaterality.
Treatment for early stage dysgerminoma is surgical; young women should have at least unilateral oophorectomy performed; if the contralateral ovary is spared there’s a 10% risk for recurrence over the next 2 years. Comprehensive fertility-sparing surgery is recommended with pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy. Women with gonadal dysgenesis should have a bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and those beyond childbearing should undergo a total hysterectomy, with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and appropriate staging. BEP should be added for patients with advanced disease.
Other malignant germ cell neoplasms
Uncommon malignant germ cell neoplasms include immature teratomas and endodermal sinus tumors. Though uncommon, the majority of immature teratomas present between the ages of 10 and 20 years and account for nearly 30% of the ovarian cancer deaths in this age group. Immature teratomas usually have negative serum markers, though about one-third will excrete HCG. Immature teratomas are graded by the proportion of neuro-epithelium. Treatment includes unilateral oophorectomy, and surgical staging with adjuvant chemotherapy (BEP) for patients with greater than stage 1A grade 1 disease.
Endodermal sinus tumors are derived from the primitive yolk sac, are unilateral, and most will secrete alpha-fetoprotein (AFP). The median age of diagnosis of an endodermal sinus tumor is 18 years, thus treatment includes unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and comprehensive fertility-sparing surgical staging followed by BEP.
Embryonal and nongestational choriocarcinomas are rare malignant germ cell neoplasms found in prepubertal girls to young women. Embryonal carcinomas can secrete estrogens, HCG and/or AFP, so patients may present with precocious puberty. Treatment is similar to that of endodermal sinus tumors. Nongestational choriocarcinomas, like the gestational forms, have a poor prognosis and are monitored and treated similarly.
Understanding presentation and treatments for malignant germ cell neoplasms is important in the evaluation of a young patient with a pelvic mass and should prompt the practicing gynecologist to test for AFP and HCG, with or without LDH and CA-125. If encountered inadvertently, every attempt should be made to preserve fertility in these young patients and expedient referral to a gynecologic oncologist, pediatric gynecologist, and/or a reproductive endocrinologist is warranted. Rarely, a second look laparotomy is indicated without obvious intraperitoneal spread and reproductive potential is preserved even in those requiring BEP. If managed appropriately, the overall prognosis remains good for these young women.
Dr. Gehrig is professor and director of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Castellano is a resident physician in the obstetrics and gynecology program at the university. They reported having no relevant financial disclosures. To comment, email them at obnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Germ cell neoplasms arise from primordial germ cells of the gonad that differentiate to embryonic and extraembryonic tissues. Approximately 20%-25% of ovarian neoplasms are germ cell in origin but they account for only 3%-5% of ovarian malignancies. Importantly, germ cell neoplasms encompass 70% of the ovarian neoplasms among girls and young women aged 10-30 years, of which approximately one-third are malignant.
Unlike epithelial ovarian cancers, malignant germ cell neoplasms are typically diagnosed at early stages. They can present as a palpable mass or cause acute abdominal pain secondary to their rapid growth, penchant for necrosis, torsion, hemorrhage, infection, or rupture. Since malignant germ cell neoplasms can excrete hormonally-active tumor markers, such as human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), many women present with menstrual irregularities.

Management of malignant germ cell neoplasms generally includes fertility-sparing surgery – with or without neoadjuvant combination bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin (BEP) – and is typically associated with a favorable prognosis (Cancer Treat Rev. 2008 Aug;34[5]:427-41).
Teratomas
Benign teratomas represent about a quarter of all ovarian neoplasms. Benign teratomas can be solid or cystic, and contain components representing all three cell layers: endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. Due to the presence of differentiated adult tissues, benign teratomas have a characteristic radiographic appearance. They can appear as cystic echogenic masses with intense acoustic shadowing, homogenous nodules or bands, and rounded protuberances called “Rokitansky nodules.”
Treatment of benign teratomas in reproductive-age women includes ovarian cystectomy and careful inspection of the contralateral ovary as 10%-15% may be bilateral. In postmenopausal women, there is less than a 2% risk for malignant transformation of the associated cell lines, most commonly a squamous cell carcinoma. In these cases, spread beyond the ovarian capsule is associated with a poor prognosis and chemotherapy and/or radiation are indicated (Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2006 Jan-Feb;16[1]:140-4). Malignant monodermal teratomas are composed of single cell lines with malignant transformations of that tissue type; struma ovarii composed of thyroid tissue, for example, is exceedingly rare.
Dysgerminoma
Dysgerminomas are the most common malignant germ cell neoplasms, accounting for about one-third of cases. They typically present in girls and young women between 10 and 30 years of age, and rarely occur after 50 years of age. As a result, a quarter of cases are identified during pregnancy and another 5% are found in patients presenting with amenorrhea secondary to gonadal dysgenesis, such as is associated with Turner’s syndrome.
At diagnosis, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) may be elevated and 10% may have an elevation of HCG. Ultrasound findings include a solid, mostly echoic, but heterogeneous mass with apparent lobulations. About two-thirds are stage I at the time of diagnosis, and 10%-15% are bilateral, making dysgerminomas the only malignant germ cell neoplasm with significant risk for bilaterality.
Treatment for early stage dysgerminoma is surgical; young women should have at least unilateral oophorectomy performed; if the contralateral ovary is spared there’s a 10% risk for recurrence over the next 2 years. Comprehensive fertility-sparing surgery is recommended with pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy. Women with gonadal dysgenesis should have a bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and those beyond childbearing should undergo a total hysterectomy, with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and appropriate staging. BEP should be added for patients with advanced disease.
Other malignant germ cell neoplasms
Uncommon malignant germ cell neoplasms include immature teratomas and endodermal sinus tumors. Though uncommon, the majority of immature teratomas present between the ages of 10 and 20 years and account for nearly 30% of the ovarian cancer deaths in this age group. Immature teratomas usually have negative serum markers, though about one-third will excrete HCG. Immature teratomas are graded by the proportion of neuro-epithelium. Treatment includes unilateral oophorectomy, and surgical staging with adjuvant chemotherapy (BEP) for patients with greater than stage 1A grade 1 disease.
Endodermal sinus tumors are derived from the primitive yolk sac, are unilateral, and most will secrete alpha-fetoprotein (AFP). The median age of diagnosis of an endodermal sinus tumor is 18 years, thus treatment includes unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and comprehensive fertility-sparing surgical staging followed by BEP.
Embryonal and nongestational choriocarcinomas are rare malignant germ cell neoplasms found in prepubertal girls to young women. Embryonal carcinomas can secrete estrogens, HCG and/or AFP, so patients may present with precocious puberty. Treatment is similar to that of endodermal sinus tumors. Nongestational choriocarcinomas, like the gestational forms, have a poor prognosis and are monitored and treated similarly.
Understanding presentation and treatments for malignant germ cell neoplasms is important in the evaluation of a young patient with a pelvic mass and should prompt the practicing gynecologist to test for AFP and HCG, with or without LDH and CA-125. If encountered inadvertently, every attempt should be made to preserve fertility in these young patients and expedient referral to a gynecologic oncologist, pediatric gynecologist, and/or a reproductive endocrinologist is warranted. Rarely, a second look laparotomy is indicated without obvious intraperitoneal spread and reproductive potential is preserved even in those requiring BEP. If managed appropriately, the overall prognosis remains good for these young women.
Dr. Gehrig is professor and director of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Castellano is a resident physician in the obstetrics and gynecology program at the university. They reported having no relevant financial disclosures. To comment, email them at obnews@frontlinemedcom.com.
Germ cell neoplasms arise from primordial germ cells of the gonad that differentiate to embryonic and extraembryonic tissues. Approximately 20%-25% of ovarian neoplasms are germ cell in origin but they account for only 3%-5% of ovarian malignancies. Importantly, germ cell neoplasms encompass 70% of the ovarian neoplasms among girls and young women aged 10-30 years, of which approximately one-third are malignant.
Unlike epithelial ovarian cancers, malignant germ cell neoplasms are typically diagnosed at early stages. They can present as a palpable mass or cause acute abdominal pain secondary to their rapid growth, penchant for necrosis, torsion, hemorrhage, infection, or rupture. Since malignant germ cell neoplasms can excrete hormonally-active tumor markers, such as human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), many women present with menstrual irregularities.

Management of malignant germ cell neoplasms generally includes fertility-sparing surgery – with or without neoadjuvant combination bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin (BEP) – and is typically associated with a favorable prognosis (Cancer Treat Rev. 2008 Aug;34[5]:427-41).
Teratomas
Benign teratomas represent about a quarter of all ovarian neoplasms. Benign teratomas can be solid or cystic, and contain components representing all three cell layers: endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. Due to the presence of differentiated adult tissues, benign teratomas have a characteristic radiographic appearance. They can appear as cystic echogenic masses with intense acoustic shadowing, homogenous nodules or bands, and rounded protuberances called “Rokitansky nodules.”
Treatment of benign teratomas in reproductive-age women includes ovarian cystectomy and careful inspection of the contralateral ovary as 10%-15% may be bilateral. In postmenopausal women, there is less than a 2% risk for malignant transformation of the associated cell lines, most commonly a squamous cell carcinoma. In these cases, spread beyond the ovarian capsule is associated with a poor prognosis and chemotherapy and/or radiation are indicated (Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2006 Jan-Feb;16[1]:140-4). Malignant monodermal teratomas are composed of single cell lines with malignant transformations of that tissue type; struma ovarii composed of thyroid tissue, for example, is exceedingly rare.
Dysgerminoma
Dysgerminomas are the most common malignant germ cell neoplasms, accounting for about one-third of cases. They typically present in girls and young women between 10 and 30 years of age, and rarely occur after 50 years of age. As a result, a quarter of cases are identified during pregnancy and another 5% are found in patients presenting with amenorrhea secondary to gonadal dysgenesis, such as is associated with Turner’s syndrome.
At diagnosis, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) may be elevated and 10% may have an elevation of HCG. Ultrasound findings include a solid, mostly echoic, but heterogeneous mass with apparent lobulations. About two-thirds are stage I at the time of diagnosis, and 10%-15% are bilateral, making dysgerminomas the only malignant germ cell neoplasm with significant risk for bilaterality.
Treatment for early stage dysgerminoma is surgical; young women should have at least unilateral oophorectomy performed; if the contralateral ovary is spared there’s a 10% risk for recurrence over the next 2 years. Comprehensive fertility-sparing surgery is recommended with pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy. Women with gonadal dysgenesis should have a bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and those beyond childbearing should undergo a total hysterectomy, with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and appropriate staging. BEP should be added for patients with advanced disease.
Other malignant germ cell neoplasms
Uncommon malignant germ cell neoplasms include immature teratomas and endodermal sinus tumors. Though uncommon, the majority of immature teratomas present between the ages of 10 and 20 years and account for nearly 30% of the ovarian cancer deaths in this age group. Immature teratomas usually have negative serum markers, though about one-third will excrete HCG. Immature teratomas are graded by the proportion of neuro-epithelium. Treatment includes unilateral oophorectomy, and surgical staging with adjuvant chemotherapy (BEP) for patients with greater than stage 1A grade 1 disease.
Endodermal sinus tumors are derived from the primitive yolk sac, are unilateral, and most will secrete alpha-fetoprotein (AFP). The median age of diagnosis of an endodermal sinus tumor is 18 years, thus treatment includes unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and comprehensive fertility-sparing surgical staging followed by BEP.
Embryonal and nongestational choriocarcinomas are rare malignant germ cell neoplasms found in prepubertal girls to young women. Embryonal carcinomas can secrete estrogens, HCG and/or AFP, so patients may present with precocious puberty. Treatment is similar to that of endodermal sinus tumors. Nongestational choriocarcinomas, like the gestational forms, have a poor prognosis and are monitored and treated similarly.
Understanding presentation and treatments for malignant germ cell neoplasms is important in the evaluation of a young patient with a pelvic mass and should prompt the practicing gynecologist to test for AFP and HCG, with or without LDH and CA-125. If encountered inadvertently, every attempt should be made to preserve fertility in these young patients and expedient referral to a gynecologic oncologist, pediatric gynecologist, and/or a reproductive endocrinologist is warranted. Rarely, a second look laparotomy is indicated without obvious intraperitoneal spread and reproductive potential is preserved even in those requiring BEP. If managed appropriately, the overall prognosis remains good for these young women.
Dr. Gehrig is professor and director of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Castellano is a resident physician in the obstetrics and gynecology program at the university. They reported having no relevant financial disclosures. To comment, email them at obnews@frontlinemedcom.com.