User login
Lesions on the Thigh After an Organ Transplant
The Diagnosis: Microcystic Lymphatic Malformation
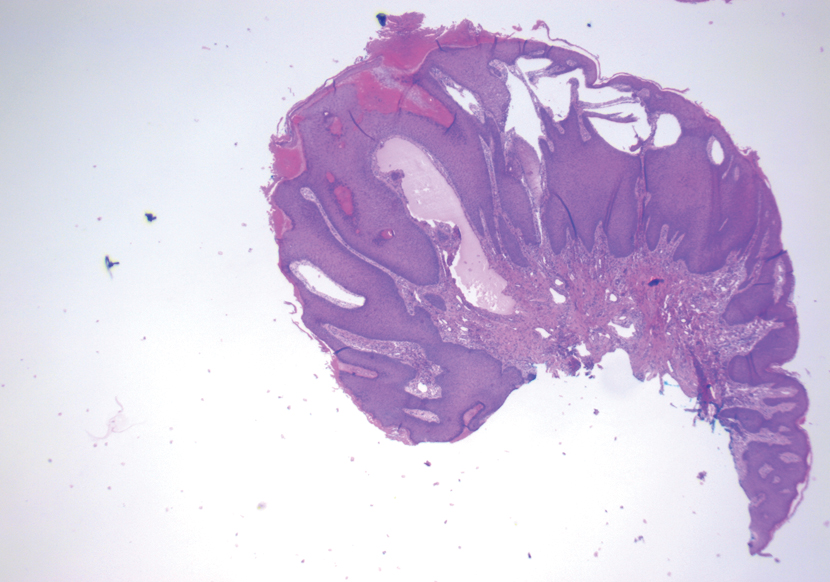
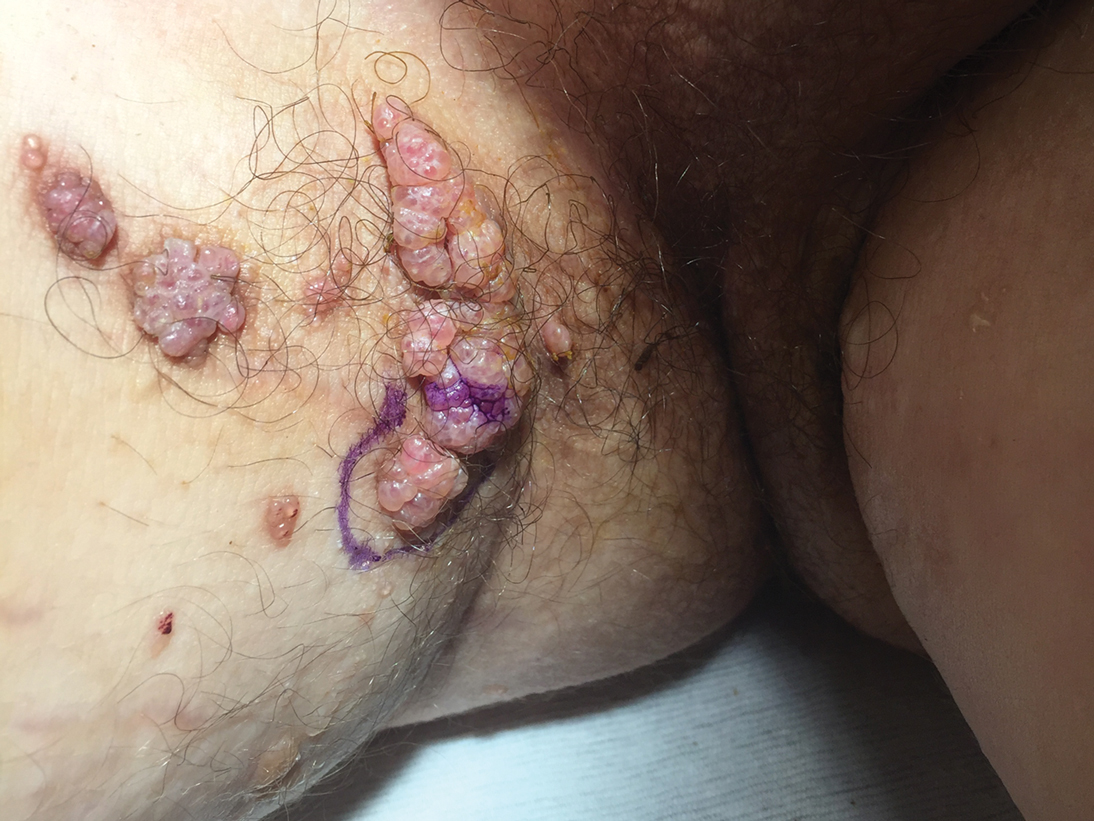
The shave biopsy demonstrated numerous thin-walled vascular spaces filled with lymphatic fluid within the dermis (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of microcystic lymphatic malformation (LM). Lymphatic malformations represent a class of benign vascular lesions consisting of anomalous or dilated lymphatic vessels, which can be broadly categorized as macrocystic (formerly cavernous lymphangioma or cystic hygroma), microcystic (formerly lymphangioma circumscriptum), or mixed.1 Patients often will present with pruritus, crusting, secondary infection, edema, or oozing.2 The superficial blebs of microcystic LMs resemble frog spawn and range in color from clear to pink, brawny, or deep maroon.3 Although the lymphatic vessels involved in microcystic LMs appear disconnected from the major lymphatic circulation,3 systemic fluid overload could plausibly promote lesional swelling and tenderness; we attributed our patient's worsening symptoms to the cumulative 7.8 L of intravenous fluid he received intraoperatively during his cardiac transplant. The excess fluid allowed communication between lymphatic cisterns and thin-walled vesicles on the skin surface through dilated channels. Overall, LMs represent roughly 26% of pediatric benign vascular tumors and approximately 4% of all vascular tumors.4
Although microcystic LMs may appear especially vascular or verrucous, the differential diagnosis for our patient's LM included condyloma acuminatum,5,6 condyloma lata,7 epidermal nevus, and lymphangiosarcoma. Epidermal nevi are congenital lesions, varying in appearance from velvety to verrucous patches and plaques that often evolve during puberty and become thicker, more verrucous, and hyperpigmented. Keratinocytic epidermal nevus syndromes and other entities such as nevus sebaceous have been associated with somatic mutations affecting proteins in the fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway (eg, FGFR3, HRAS).8 Although the clinical appearance alone may be similar, lymphangiosarcoma can be distinguished from LM via biopsy.
There are several methods to diagnose LM. Duplex sonography is possibly the best noninvasive method to identify the flow between venous valves. Magnetic resonance imaging can detect larger occurrences of LM, and lymphangiography can be utilized to confirm a normal or abnormal lymphatic network.4 Treatment options are broad, including surgical excision, laser ablation, and topical sirolimus. Hypertonic saline sclerotherapy can be injected into the afflicted lymphatic channels to decrease inflammation, erythema, and hyperpigmentation without further treatment or major side effects.4
However, the benefits of sclerotherapy alone in the treatment of LM often come gradually, and radiofrequency ablation may need to be utilized to achieve more immediate results.2 Overall, outcomes are highly variable, but favorable outcomes often can be difficult to obtain due to a high recurrence rate.2,8 Our patient's symptoms improved during his postoperative recovery, and he declined further intervention.
- Elluru RG, Balakrishnan K, Padua HM. Lymphatic malformations: diagnosis and management. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014;23:178-185. doi:10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2014.07.002
- Niti K, Manish P. Microcystic lymphatic malformation (lymphangioma circumscriptum) treated using a minimally invasive technique of radiofrequency ablation and sclerotherapy. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1711-1717. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2010.01723.x
- Patel GA, Schwartz RA. Cutaneous lymphangioma circumscriptum: frog spawn on the skin. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1290-1295. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2009.04226.x
- Bikowski JB, Dumont AM. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: treatment with hypertonic saline sclerotherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:442-444. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.04.086
- Costa-Silva M, Fernandes I, Rodrigues AG, et al. Anogenital warts in pediatric population. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:675-681. doi:10.1590 /abd1806-4841.201756411
- Darmstadt GL. Perianal lymphangioma circumscriptum mistaken for genital warts. Pediatrics 1996;98;461.
- Bruins FG, van Deudekom FJA, de Vries HJC. Syphilitic condylomata lata mimicking anogenital warts. BMJ. 2015;350:h1259. doi:10.1136 /bmj.h1259
- Asch S, Sugarman JL. Epidermal nevus syndromes: new insights into whorls and swirls. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:21-29. doi:10.1111 /pde.13273
The Diagnosis: Microcystic Lymphatic Malformation
The shave biopsy demonstrated numerous thin-walled vascular spaces filled with lymphatic fluid within the dermis (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of microcystic lymphatic malformation (LM). Lymphatic malformations represent a class of benign vascular lesions consisting of anomalous or dilated lymphatic vessels, which can be broadly categorized as macrocystic (formerly cavernous lymphangioma or cystic hygroma), microcystic (formerly lymphangioma circumscriptum), or mixed.1 Patients often will present with pruritus, crusting, secondary infection, edema, or oozing.2 The superficial blebs of microcystic LMs resemble frog spawn and range in color from clear to pink, brawny, or deep maroon.3 Although the lymphatic vessels involved in microcystic LMs appear disconnected from the major lymphatic circulation,3 systemic fluid overload could plausibly promote lesional swelling and tenderness; we attributed our patient's worsening symptoms to the cumulative 7.8 L of intravenous fluid he received intraoperatively during his cardiac transplant. The excess fluid allowed communication between lymphatic cisterns and thin-walled vesicles on the skin surface through dilated channels. Overall, LMs represent roughly 26% of pediatric benign vascular tumors and approximately 4% of all vascular tumors.4
Although microcystic LMs may appear especially vascular or verrucous, the differential diagnosis for our patient's LM included condyloma acuminatum,5,6 condyloma lata,7 epidermal nevus, and lymphangiosarcoma. Epidermal nevi are congenital lesions, varying in appearance from velvety to verrucous patches and plaques that often evolve during puberty and become thicker, more verrucous, and hyperpigmented. Keratinocytic epidermal nevus syndromes and other entities such as nevus sebaceous have been associated with somatic mutations affecting proteins in the fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway (eg, FGFR3, HRAS).8 Although the clinical appearance alone may be similar, lymphangiosarcoma can be distinguished from LM via biopsy.
There are several methods to diagnose LM. Duplex sonography is possibly the best noninvasive method to identify the flow between venous valves. Magnetic resonance imaging can detect larger occurrences of LM, and lymphangiography can be utilized to confirm a normal or abnormal lymphatic network.4 Treatment options are broad, including surgical excision, laser ablation, and topical sirolimus. Hypertonic saline sclerotherapy can be injected into the afflicted lymphatic channels to decrease inflammation, erythema, and hyperpigmentation without further treatment or major side effects.4
However, the benefits of sclerotherapy alone in the treatment of LM often come gradually, and radiofrequency ablation may need to be utilized to achieve more immediate results.2 Overall, outcomes are highly variable, but favorable outcomes often can be difficult to obtain due to a high recurrence rate.2,8 Our patient's symptoms improved during his postoperative recovery, and he declined further intervention.
The Diagnosis: Microcystic Lymphatic Malformation
The shave biopsy demonstrated numerous thin-walled vascular spaces filled with lymphatic fluid within the dermis (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of microcystic lymphatic malformation (LM). Lymphatic malformations represent a class of benign vascular lesions consisting of anomalous or dilated lymphatic vessels, which can be broadly categorized as macrocystic (formerly cavernous lymphangioma or cystic hygroma), microcystic (formerly lymphangioma circumscriptum), or mixed.1 Patients often will present with pruritus, crusting, secondary infection, edema, or oozing.2 The superficial blebs of microcystic LMs resemble frog spawn and range in color from clear to pink, brawny, or deep maroon.3 Although the lymphatic vessels involved in microcystic LMs appear disconnected from the major lymphatic circulation,3 systemic fluid overload could plausibly promote lesional swelling and tenderness; we attributed our patient's worsening symptoms to the cumulative 7.8 L of intravenous fluid he received intraoperatively during his cardiac transplant. The excess fluid allowed communication between lymphatic cisterns and thin-walled vesicles on the skin surface through dilated channels. Overall, LMs represent roughly 26% of pediatric benign vascular tumors and approximately 4% of all vascular tumors.4
Although microcystic LMs may appear especially vascular or verrucous, the differential diagnosis for our patient's LM included condyloma acuminatum,5,6 condyloma lata,7 epidermal nevus, and lymphangiosarcoma. Epidermal nevi are congenital lesions, varying in appearance from velvety to verrucous patches and plaques that often evolve during puberty and become thicker, more verrucous, and hyperpigmented. Keratinocytic epidermal nevus syndromes and other entities such as nevus sebaceous have been associated with somatic mutations affecting proteins in the fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway (eg, FGFR3, HRAS).8 Although the clinical appearance alone may be similar, lymphangiosarcoma can be distinguished from LM via biopsy.
There are several methods to diagnose LM. Duplex sonography is possibly the best noninvasive method to identify the flow between venous valves. Magnetic resonance imaging can detect larger occurrences of LM, and lymphangiography can be utilized to confirm a normal or abnormal lymphatic network.4 Treatment options are broad, including surgical excision, laser ablation, and topical sirolimus. Hypertonic saline sclerotherapy can be injected into the afflicted lymphatic channels to decrease inflammation, erythema, and hyperpigmentation without further treatment or major side effects.4
However, the benefits of sclerotherapy alone in the treatment of LM often come gradually, and radiofrequency ablation may need to be utilized to achieve more immediate results.2 Overall, outcomes are highly variable, but favorable outcomes often can be difficult to obtain due to a high recurrence rate.2,8 Our patient's symptoms improved during his postoperative recovery, and he declined further intervention.
- Elluru RG, Balakrishnan K, Padua HM. Lymphatic malformations: diagnosis and management. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014;23:178-185. doi:10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2014.07.002
- Niti K, Manish P. Microcystic lymphatic malformation (lymphangioma circumscriptum) treated using a minimally invasive technique of radiofrequency ablation and sclerotherapy. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1711-1717. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2010.01723.x
- Patel GA, Schwartz RA. Cutaneous lymphangioma circumscriptum: frog spawn on the skin. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1290-1295. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2009.04226.x
- Bikowski JB, Dumont AM. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: treatment with hypertonic saline sclerotherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:442-444. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.04.086
- Costa-Silva M, Fernandes I, Rodrigues AG, et al. Anogenital warts in pediatric population. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:675-681. doi:10.1590 /abd1806-4841.201756411
- Darmstadt GL. Perianal lymphangioma circumscriptum mistaken for genital warts. Pediatrics 1996;98;461.
- Bruins FG, van Deudekom FJA, de Vries HJC. Syphilitic condylomata lata mimicking anogenital warts. BMJ. 2015;350:h1259. doi:10.1136 /bmj.h1259
- Asch S, Sugarman JL. Epidermal nevus syndromes: new insights into whorls and swirls. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:21-29. doi:10.1111 /pde.13273
- Elluru RG, Balakrishnan K, Padua HM. Lymphatic malformations: diagnosis and management. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014;23:178-185. doi:10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2014.07.002
- Niti K, Manish P. Microcystic lymphatic malformation (lymphangioma circumscriptum) treated using a minimally invasive technique of radiofrequency ablation and sclerotherapy. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1711-1717. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2010.01723.x
- Patel GA, Schwartz RA. Cutaneous lymphangioma circumscriptum: frog spawn on the skin. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1290-1295. doi:10.1111 /j.1365-4632.2009.04226.x
- Bikowski JB, Dumont AM. Lymphangioma circumscriptum: treatment with hypertonic saline sclerotherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:442-444. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.04.086
- Costa-Silva M, Fernandes I, Rodrigues AG, et al. Anogenital warts in pediatric population. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:675-681. doi:10.1590 /abd1806-4841.201756411
- Darmstadt GL. Perianal lymphangioma circumscriptum mistaken for genital warts. Pediatrics 1996;98;461.
- Bruins FG, van Deudekom FJA, de Vries HJC. Syphilitic condylomata lata mimicking anogenital warts. BMJ. 2015;350:h1259. doi:10.1136 /bmj.h1259
- Asch S, Sugarman JL. Epidermal nevus syndromes: new insights into whorls and swirls. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:21-29. doi:10.1111 /pde.13273
A 17-year-old adolescent boy presented with increasingly painful genital warts on the right thigh, groin, and scrotum that had been present since birth. The patient had a medical history of cardiac transplantation in the months prior to presentation and was on immunosuppressive therapy. The lesions had become more swollen and bothersome in the weeks following the transplantation and now prevented him from ambulating due to discomfort. He denied any history of sexual contact or oral lesions. Physical examination revealed numerous translucent and hemorrhagic vesicles clustered and linearly distributed on the right medial thigh. A shave biopsy of a vesicle was performed.
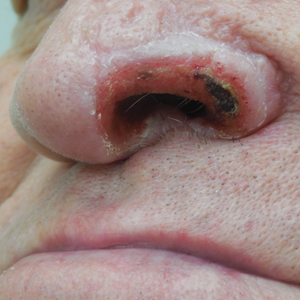
Unilateral Alar Ulceration
The Diagnosis: Trigeminal Trophic Syndrome (Self-induced Trauma)
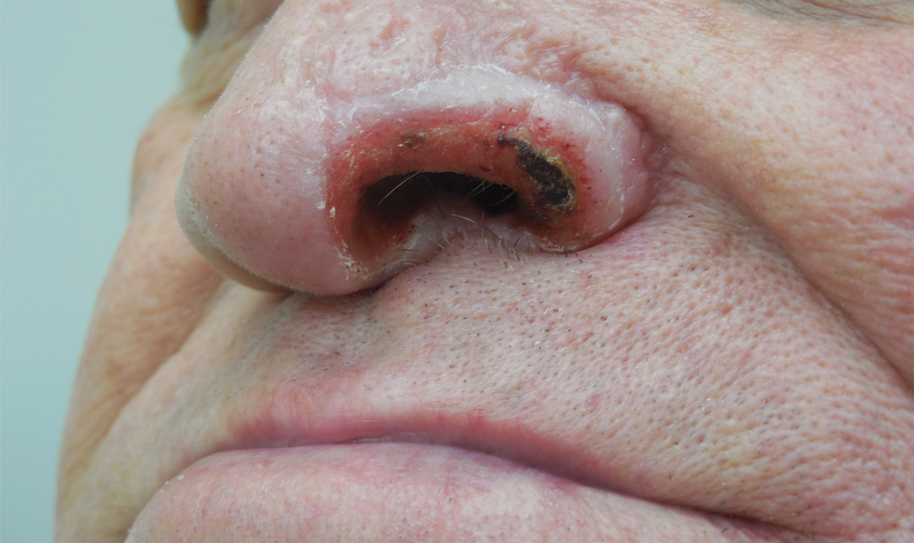
The patient admitted to manipulation of the ala in response to persistent pain despite resolution of the herpes zoster, for which he recently had completed a course of oral acyclovir. A preliminary diagnosis of trigeminal trophic syndrome (TTS) was made, and a subsequent punch biopsy revealed no evidence of malignancy. Topical antibiotic prophylaxis was prescribed, and he was instructed to avoid manipulation of the affected area. Treatment was initiated in consultation with pain specialists, and over the following 3 years our patient experienced a waxing and waning course of persistent pain complicated by new scalp and oral ulcers as well as alar impetigo. His condition eventually stabilized with tolerable pain on oral gabapentin and doxepin cream 5% applied up to 4 times daily. The alar lesion healed following sufficient abstinence from manipulation, leaving a crescent-shaped rim defect.
Trigeminal trophic syndrome classically is characterized by a triad of cutaneous anesthesia, paresthesia and/or pain, and ulceration secondary to pathology of trigeminal nerve sensory branches. Ulceration arises primarily through excoriation in response to paresthetic pruritus or pain. The differential diagnosis for TTS includes ulcerating cutaneous neoplasms (eg, basal cell carcinoma); mycobacterial, fungal, and viral infections (especially herpetic lesions); and cutaneous involvement of systemic vasculitides (eg, granulomatosis with polyangiitis).1 Biopsy is necessary to exclude malignancy, and ulcers may be scraped for viral diagnosis. Complete blood cell count and serologic testing also may help to exclude immunodeficiencies or disorders. Apart from viral neuropathy, common etiologies of TTS include iatrogenic trigeminal injury (eg, in ablation treatment for trigeminal neuralgia) and stroke (eg, lateral medullary syndrome).
- Khan AU, Khachemoune A. Trigeminal trophic syndrome: an updated review. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:530-537.
The Diagnosis: Trigeminal Trophic Syndrome (Self-induced Trauma)
The patient admitted to manipulation of the ala in response to persistent pain despite resolution of the herpes zoster, for which he recently had completed a course of oral acyclovir. A preliminary diagnosis of trigeminal trophic syndrome (TTS) was made, and a subsequent punch biopsy revealed no evidence of malignancy. Topical antibiotic prophylaxis was prescribed, and he was instructed to avoid manipulation of the affected area. Treatment was initiated in consultation with pain specialists, and over the following 3 years our patient experienced a waxing and waning course of persistent pain complicated by new scalp and oral ulcers as well as alar impetigo. His condition eventually stabilized with tolerable pain on oral gabapentin and doxepin cream 5% applied up to 4 times daily. The alar lesion healed following sufficient abstinence from manipulation, leaving a crescent-shaped rim defect.
Trigeminal trophic syndrome classically is characterized by a triad of cutaneous anesthesia, paresthesia and/or pain, and ulceration secondary to pathology of trigeminal nerve sensory branches. Ulceration arises primarily through excoriation in response to paresthetic pruritus or pain. The differential diagnosis for TTS includes ulcerating cutaneous neoplasms (eg, basal cell carcinoma); mycobacterial, fungal, and viral infections (especially herpetic lesions); and cutaneous involvement of systemic vasculitides (eg, granulomatosis with polyangiitis).1 Biopsy is necessary to exclude malignancy, and ulcers may be scraped for viral diagnosis. Complete blood cell count and serologic testing also may help to exclude immunodeficiencies or disorders. Apart from viral neuropathy, common etiologies of TTS include iatrogenic trigeminal injury (eg, in ablation treatment for trigeminal neuralgia) and stroke (eg, lateral medullary syndrome).
The Diagnosis: Trigeminal Trophic Syndrome (Self-induced Trauma)
The patient admitted to manipulation of the ala in response to persistent pain despite resolution of the herpes zoster, for which he recently had completed a course of oral acyclovir. A preliminary diagnosis of trigeminal trophic syndrome (TTS) was made, and a subsequent punch biopsy revealed no evidence of malignancy. Topical antibiotic prophylaxis was prescribed, and he was instructed to avoid manipulation of the affected area. Treatment was initiated in consultation with pain specialists, and over the following 3 years our patient experienced a waxing and waning course of persistent pain complicated by new scalp and oral ulcers as well as alar impetigo. His condition eventually stabilized with tolerable pain on oral gabapentin and doxepin cream 5% applied up to 4 times daily. The alar lesion healed following sufficient abstinence from manipulation, leaving a crescent-shaped rim defect.
Trigeminal trophic syndrome classically is characterized by a triad of cutaneous anesthesia, paresthesia and/or pain, and ulceration secondary to pathology of trigeminal nerve sensory branches. Ulceration arises primarily through excoriation in response to paresthetic pruritus or pain. The differential diagnosis for TTS includes ulcerating cutaneous neoplasms (eg, basal cell carcinoma); mycobacterial, fungal, and viral infections (especially herpetic lesions); and cutaneous involvement of systemic vasculitides (eg, granulomatosis with polyangiitis).1 Biopsy is necessary to exclude malignancy, and ulcers may be scraped for viral diagnosis. Complete blood cell count and serologic testing also may help to exclude immunodeficiencies or disorders. Apart from viral neuropathy, common etiologies of TTS include iatrogenic trigeminal injury (eg, in ablation treatment for trigeminal neuralgia) and stroke (eg, lateral medullary syndrome).
- Khan AU, Khachemoune A. Trigeminal trophic syndrome: an updated review. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:530-537.
- Khan AU, Khachemoune A. Trigeminal trophic syndrome: an updated review. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:530-537.
A 68-year-old man presented with a new left nasal alar ulcer following a recent episode of primary herpes zoster. Physical examination revealed erythema, erosion, and necrosis of the left naris with partial loss of the alar rim. Additional erythema was present without vesicles around the left eye and on the forehead.