DISCUSSIONIt is not uncommon for a woman to miscarry a very early pregnancy and not realize she had been pregnant.1 Many attribute it to a “heavy” or unusual period. In one study, 11% of patients who denied the possibility of pregnancy were, in fact, pregnant.2
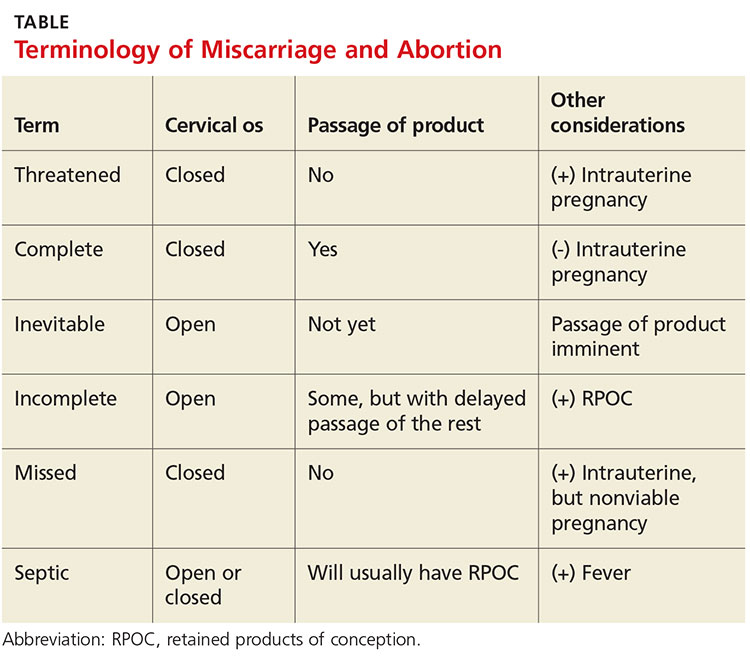
Miscarriage is a frequent outcome of early pregnancy; it is estimated that 11% to 20% of early pregnancies result in a spontaneous miscarriage.3-5 Most resolve without complications, but risk increases with gestational age. When they do occur, complications include RPOC, heavy prolonged bleeding, and endometritis. RPOC refers to placental or fetal tissue that remains in the uterus after a miscarriage, surgical abortion, or preterm/term delivery (see Table for additional terminology related to miscarriage and abortion). Because of increased morbidity, it is important to suspect RPOC after a known miscarriage or an induced abortion, or in a pregnant patient with bleeding.
Incidence and pathophysiologySeptic abortion is a relatively rare complication of miscarriage. It can refer to a spontaneous miscarriage complicated by a subsequent intrauterine infection, often caused by RPOC. Septic abortion is much more common after an induced abortion, in which there is instrumentation of the uterus.
The infection after a spontaneous miscarriage usually begins as endometritis. It involves the necrotic RPOC, which are prone to infection by the cervical and vaginal flora. It may spread further into the parametrium/myometrium and the peritoneal cavity. The infection may then progress to bacteremia and sepsis. Typical causative organisms include Escherichia coli, Enterobacter aerogenes, Proteus vulgaris, hemolytic streptococci, staphylococci, and some anaerobic organisms, including Clostridium perfringens.3
Death, although rare in developed countries, is usually secondary to the sequela of sepsis, including septic shock, renal failure, adult respiratory distress syndrome, and disseminated intravascular coagulation.3,6,7 Pelvic adhesions and hysterectomy are also possible outcomes of a septic abortion.
Continue for clinical presentation and evaluation >>