Noncyclical
Noncyclical breast pain is not associated with the menstrual cycle and can be unilateral or bilateral. Providers should perform a good history of patients presenting with noncyclicalbreast pain, to include character, onset, duration, location, radiation, alleviating, and aggravating factors. A physical examination may elicit point tenderness at the chest by pushing the breast tissue off of the chest wall while the patient is in supine position and pressing directly over the ribs. Lack of tenderness on palpation of the breast parenchyma, but pain on the chest wall, points to a musculoskeletal etiology. Chest wall pain may be related to muscle spasm or muscle strain, trauma, rib fracture, or costochondritis (Tietze syndrome). Finally, based on history of review of systems and physical examination, referred pain from biliary or cardiac etiology should be considered.
When breast pain occurs with skin changes
Skin changes usually have an underlying pathology. Infectious processes, such as infected epidermal inclusion cyst, hidradenitis of the cleavage and inframammary crease, or breast abscess will present with pain and induration with an acute onset of 5 to 10 days. Large pendulous breasts may develop yeast infection at the inframammary crease. Chronic infectious irritation can lead to hyperpigmentation of that area. Eczema or contact dermatitis frequently can affect the areola and become confused with Paget disease (ductal carcinoma in situ of the nipple). With Paget, the excoriation always starts at the nipple and can then spread to the areola. However, with dermatitis, the rash begins on the peri-areolar skin, without affecting the nipple itself.
When breast pain occurs with nipple discharge
Breast pain with nipple discharge usually is bilateral and more common in patients with significant fibrocystic changes who smoke. If the nipple discharge is bilateral, serous and non-bloody, and multiduct, it is considered benign and physiologic. Physiologic nipple discharge can be multifactorial and hormonal. It may be related to thyroid disorders or medications such as antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), mood stabilizers, or antipsychotics. The only nipple discharge that is considered pathologic is unilateral spontaneous bloody discharge for which diagnostic imaging and breast surgeon referral is indicated. Women should be discouraged from self-expressing their nipples, as 80% will experience serous nipple discharge upon manual self-expression.
Breast pain is not associated with breast cancer. Most breast cancers do not hurt; they present as firm, painless masses. However, when a woman notices pain in her breast, her first concern is breast cancer. This concern is re-enforced by the medical provider whose first impulse is to order diagnostic imaging. Yet less than 3% of breast cancers are associated with breast pain.
There have been multiple published retrospective and prospective radiologic studies about the utility of breast imaging in women with breast pain without a palpable mass. All of the studies have demonstrated that breast imaging with mammography and ultrasonography in these patients yields mostly negative or benign findings. The incidence of breast cancer during imaging work-up in women with breast pain and no clinical abnormality is only 0.4% to 1.8%.1-3 Some patients may develop future subsequent breast cancer in the symptomatic breast. But this is considered incidental and possibly related to increased cell turnover related to fibrocystic changes. Breast imaging for evaluation of breast pain only provides reassurance to the physician. The patient's reassurance will come from a medical explanation for the symptoms and advice on symptom management from the provider.
Researchers from MD Anderson Cancer Center reported imaging findings and cost analysis for 799 patients presenting with breast pain from 3 large network community-based breast imaging centers in 2014. Breast ultrasound was the initial imaging modality for women younger than age 30. Digital mammography (sometimes with tomosynthesis) was used for those older than age 30 that had not had a mammogram in the last 6 months. Breast magnetic resonance imaging was performed only when ordered by the referring physician. Most of the patients presented for diagnostic imaging, and 95% had negative findings and 5% had a benign finding. Only 1 patient was found to have an incidental cancer in the contralateral breast, which was detected by tomosynthesis. The cost of breast imaging was $87,322 in younger women and $152,732 in women older than age 40, representing overutilization of health care resources and no association between breast pain and breast cancer.4
References
- Chetlan AL, Kapoor MM, Watts MR. Mastalgia: imaging work-up appropriateness. Acad Radiol. 2017;24:345-349.
- Arslan M, Kücükerdem HS, Can H, et al. Retrospective analysis of women with only mastalgia. J Breast Health. 2016;12:151-154.
- Noroozian M, Stein LF, Gaetke-Udager K, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes in women with breast pain in the absence of additional clinical findings: Mammography remains indicated. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015;149:417-424.
- Kushwaha AC, Shin K, Kalambo M, et al. Overutilization of health care resources for breast pain. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2018; 211:217-223.
Management of mastalgia
Appropriate breast pain management begins with a good history and physical examination. The decision to perform imaging should depend on clinical exam findings and not on symptoms of breast pain. If there is a palpable mass, then breast imaging and possible biopsy is appropriate. However, if clinical exam is normal, there is no indication for breast imaging in low-risk women under the age of 40 whose only symptom is breast pain. Women older than age 40 can undergo diagnostic imaging, if they have not had a negative screening mammogram in the past year.
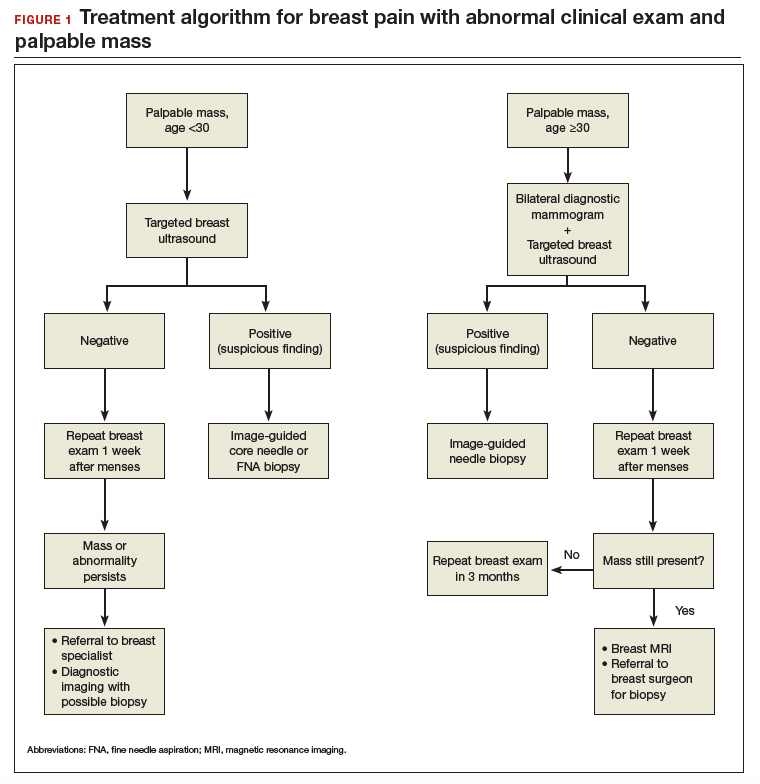
Breast pain with abnormal clinical exam
In the patient who is younger than age 30 with a palpable mass. For this patient order targeted breast ultrasound (US) (FIGURE 1). If results are negative, repeat the clinical examination 1 week after menses. If the mass is persistent, refer the patient to a breast surgeon. If diagnostic imaging results are negative, consider breast MRI, especially if there is a strong family history of breast cancer.
In the patient who is aged 30 and older with a palpable mass. For this patient, bilateral diagnostic mammogram and US are in order. The testing is best performed 1 week after menses to reduce false-positive findings. If imaging is negative and the patient still has a clinically suspicious finding or mass, refer her to a breast surgeon and consider breast MRI. At this point if there is a persistent firm dominant mass, a biopsy is indicated as part of the triple test. If the mass resolves with menses, the patient can be reassured that the cause is most likely benign, with clinical examination repeated in 3 months.
Continue to: Breast pain and normal clinical exam...