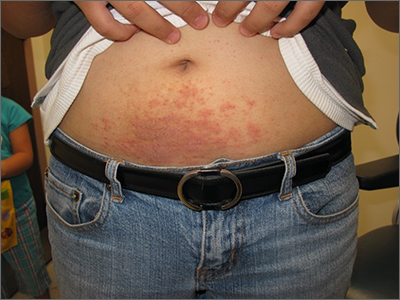
Examination revealed diffusely bordered periumbilical pink to violet scaly plaques consistent with nickel allergic contact dermatitis (Ni-ACD). The patient was wearing a belt with a buckle containing nickel, which had begun dispersing nickel. Her earlobes were also pierced and had similar scale and erythema around the metal earring studs
Ni-ACD is the most common, delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction worldwide. It affects 10% of people in the United States with a strong female predominance and a 4-fold increase in the last 30 years.1 The induction of nickel delayed-type hypersensitivity has been well-studied and includes nickel corrosion dissolving into a solution and exceeding an immunogenic threshold. Piercing practices, sweat, and friction facilitate this process.
Gold jewelry that’s less than 24 karat, “white gold,” and stainless steel all contain nickel and may cause allergy in sensitized individuals. It’s wise to assume that any shiny metal fashion accessory contains nickel, unless proven otherwise. Items can be tested for the presence of nickel with an inexpensive kit containing dimethylglyoxime.
Symptoms of Ni-ACD may range from mild erythema to thickened and weepy lichenified plaques. Distribution is often present at the site of exposure but may also be seen on the eyelids or hands from nickel transfer. A systematized reaction or id reaction is uncommon but can occur. Allergic contact dermatitis can be distinguished from psoriasis by a fading border rather than a sharp, well-demarcated border.
The patient in this case switched to a nonmetallic belt and earrings with plastic studs. She was prescribed topical triamcinolone cream 0.1% bid for 3 weeks, which led to clearance of her rash.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).