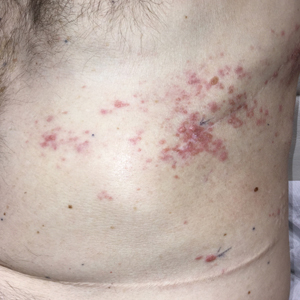
THE DIAGNOSIS:
Cutaneous Metastatic Mesothelioma
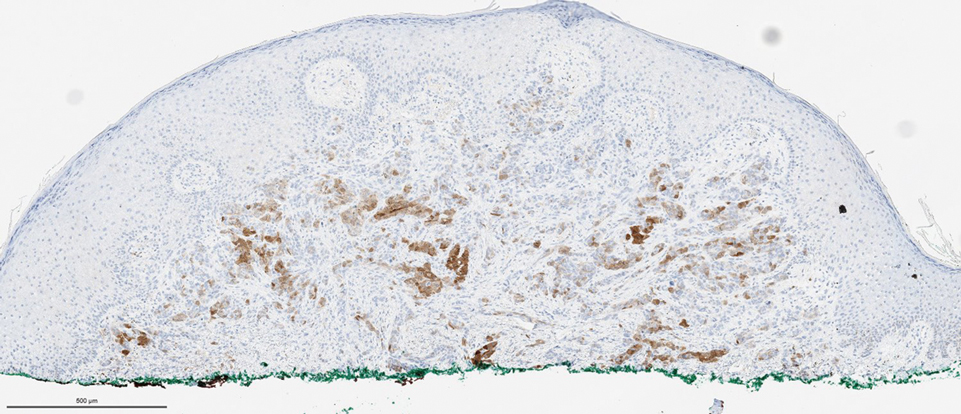
Biopsies of the larger erythematous papules revealed an infiltrate of atypical tumor cells with mitoses (Figure 1) that were immunoreactive for calretinin (Figure 2) and lacked nuclear BRCA1 associated protein-1, BAP1, expression (not shown). The patient’s prior mesothelioma was re-reviewed, and the cutaneous tumor cells were similar to the primary mesothelioma. A diagnosis of cutaneous metastatic mesothelioma (CMM) was made.
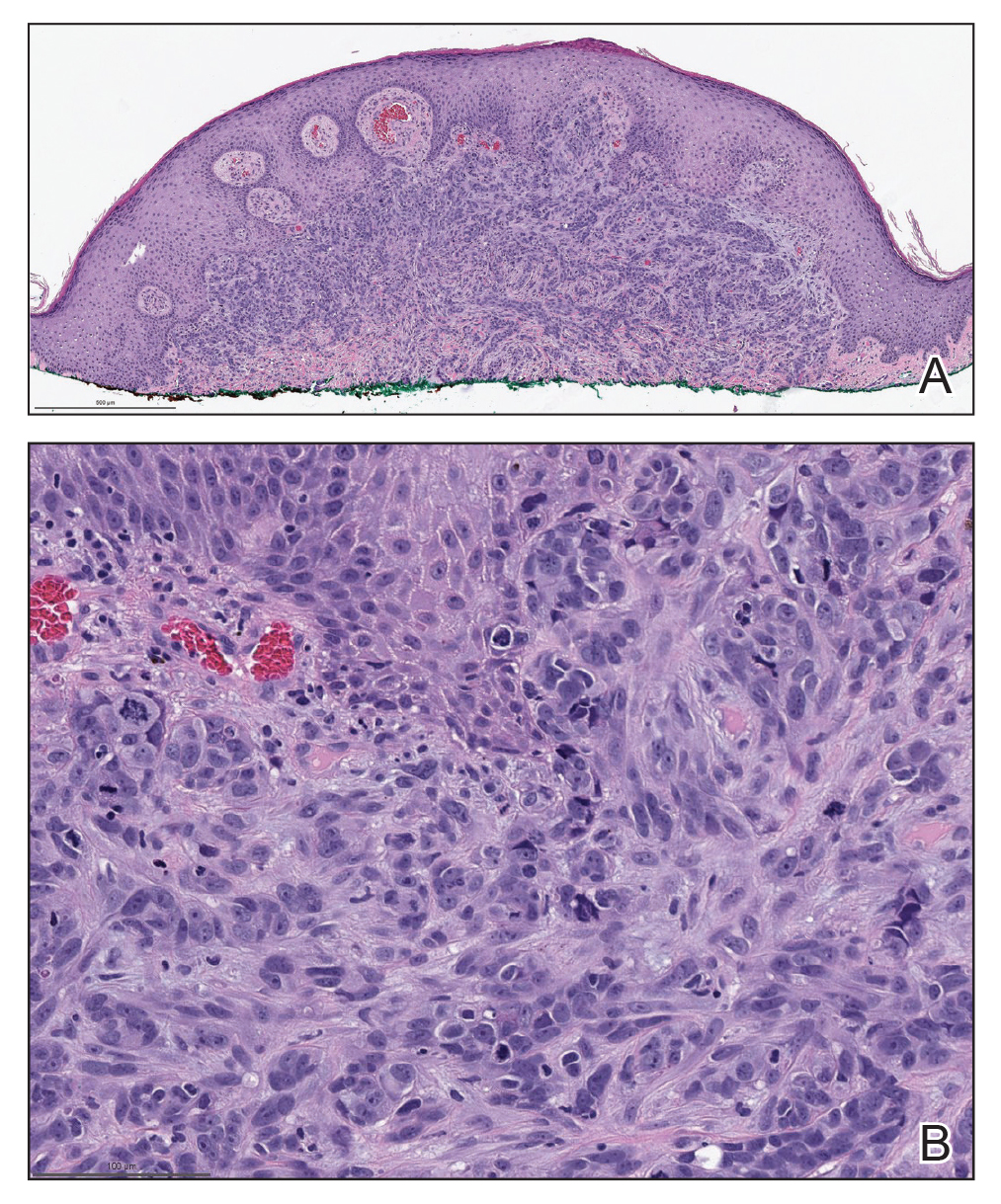
FIGURE 1. A, A shave biopsy of the left chest revealed infiltration of the dermis by a proliferation of spindle and epithelioid cells (H&E, original magnification ×40). Reference bar indicates 500 μm. B, The tumor cells showed marked nuclear atypia, and several mitoses were seen with calretinin staining (original magnification ×40). Reference bar indicates 100 μm.
Mesothelioma is a rare neoplasm arising from the pleura, pericardium, peritoneum, and tunica vaginalis,1 with an estimated annual incidence of 2500 cases.2 The predominant risk factor for the development of pleural mesothelioma is asbestos exposure, which has been identified in up to 90% of cases. Mesothelioma can give rise to local and less frequently distant hematogenous metastases. Cutaneous involvement of mesothelioma is rare.3 More than 80% of CMM cases are attributed to seeding the skin at procedure sites or by direct infiltration of scars. Distant CMM is rare and typically presents as subcutaneous nodules.4 Few cases of inflammatory CMM have been published,1,4,5 with even fewer mimicking herpes zoster infection (HZI), as seen in our patient.
The most specific stain for mesothelioma is calretinin, which strongly and diffusely stains both the nucleus and cytoplasm. Other markers include Wilms tumor 1, cytokeratin 5/6, thrombomodulin, and HBME-1. Immunohistochemistry to detect the loss of BAP1 staining in the nucleus is important for differentiating between mesothelioma and mesothelial hyperplasia.3
Cutaneous metastases occur in 0.7% to 9% of patients with internal malignant disease. Most commonly, cutaneous metastases present as cutaneous nodules, though other reported inflammatory presentations include erysipeloides, generalized erythematous patches, telangiectasia, and zosteriform distributions.6 Zosteriform distributions are particularly rare and most commonly are due to breast carcinomas or lymphomas. The mechanism of zosteriform metastasis is unknown, but theories include tumoral spread along vessels, invasion of the thoracic perineural sheaths, localized spread of tumor cells from a surgical site, or a Koebner-like reaction at the site of an existing HZI. Regardless of primary tumor type or presentation, cutaneous metastasis is a poor prognostic sign, with survival rates varying based on primary tumor type.7
Other differential diagnoses include herpes zoster granulomatous dermatitis, radiation recall dermatitis, cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease, and zosteriform lichen planus, all of which have been reported after HZI.8-10 Herpes zoster granulomatous dermatitis typically presents weeks to years after acute HZI with erythematous to violaceous papules and plaques at the site of the prior HZI. A biopsy reveals interstitial granulomatous dermatitis and multinucleated giant cells.8 Radiation recall dermatitis is a cutaneous inflammatory reaction limited to regions of prior radiation exposure after the administration of a triggering medication. Radiation recall dermatitis can present days to many years after the completion of treatment.9 Although the eruption in our patient was at the site of prior radiation, the pathologic and clinical presentation was not consistent with radiation recall dermatitis. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease is a non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis that may present as either solitary or numerous papules, plaques, or nodules and has been reported to occur after HZI. Biopsy reveals a diffuse dermal histiocytic infiltration with plasma cells and lymphocytes. In contrast to metastatic disease, mitoses and nuclear atypia are rare in cutaneous RosaiDorfman disease.11 Lichen planus is an inflammatory disease of unknown etiology presenting as flat-topped, violaceous, pruritic papules12 that may present in a zosteriform pattern.13
Although it is uncommon, metastatic spread should be considered in patients with known malignancy presenting with zosteriform eruptions.2 Our patient remained on treatment with immunotherapy, as he was unable to undergo additional radiation and had failed multiple other lines of therapy. He died 3 months after presentation.