FAIRFAX, VIRGINIA — Nearly 30 years ago, in a 1995 paper, the British physician-epidemiologist David Barker, MD, PhD, wrote about his fetal origins hypothesis — the idea that fetal undernutrition and low birth weight "programs" later coronary heart disease (BMJ 1995;311:171-4).
His hypothesis and subsequent research led to the concept of adult diseases of fetal origins, which today extends beyond low birth weight and implicates the in utero environment as a significant determinant of risk for adverse childhood and adult metabolic outcomes and for major chronic diseases, including diabetes and obesity. Studies have shown that the offspring of pregnant mothers with diabetes have a higher risk of developing obesity and diabetes themselves.
“It’s a whole discipline [of research],” E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, of the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), said in an interview. “But what we’ve never quite understood is the ‘how’ and ‘why’? What are the mechanisms driving the fetal origins of such adverse outcomes in offspring?
At the biennial meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (DPSG), investigators described studies underway that are digging deeper into the associations between the intrauterine milieu and longer-term offspring health — and that are searching for biological and molecular processes that may be involved.
The studies are like “branches of the Barker hypothesis,” said Dr. Reece, former dean of UMSOM and current director of the UMSOM Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation, who co-organized the DPSG meeting. “They’re taking the hypothesis and dissecting it by asking, for instance, it is possible that transgenerational obesity may align with the Barker hypothesis? Is it possible that it involves epigenetics regulation? Could we find biomarkers?”
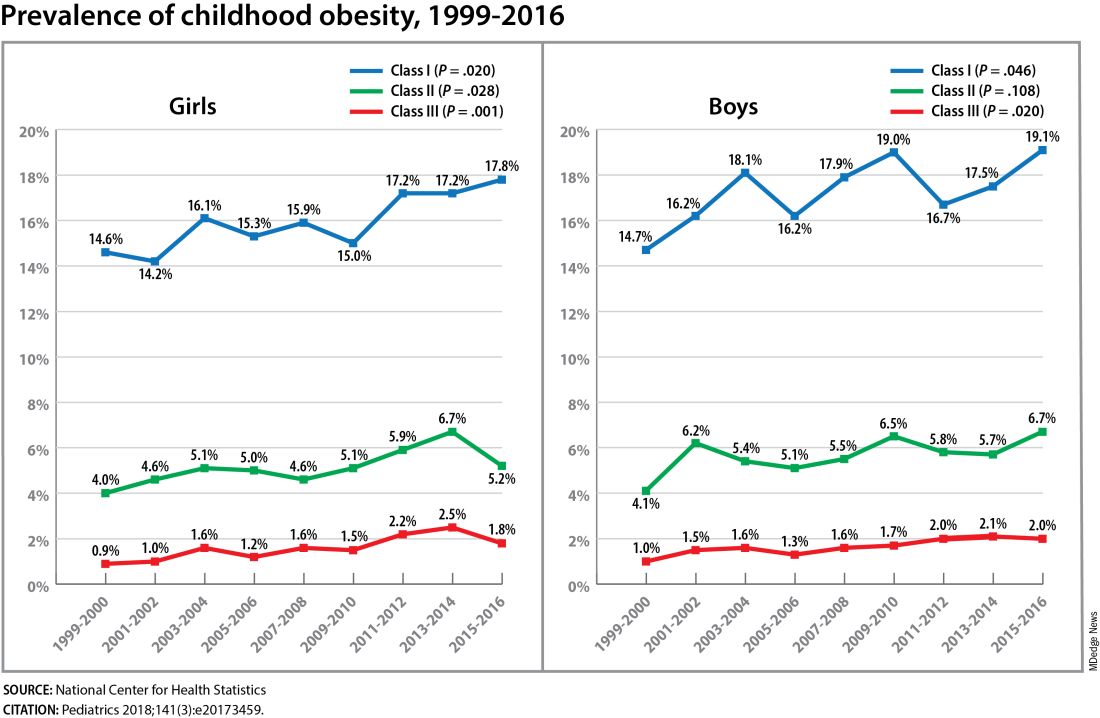
The need for a better understanding of the fetal origins framework — and its subsequent transgenerational impact — is urgent. From 2000 to 2018, the prevalence of childhood obesity increased from 14.7% to 19.2% (a 31% increase) and the prevalence of severe childhood obesity rose from 3.9% to 6.1% (a 56% increase), according to data from the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (Obes Facts. 2022;15[4]:560-9).
Children aged 2-5 years have had an especially sharp increase in obesity (Pediatrics 2018;141[3]:e20173459), Christine Wey Hockett, PhD, of the University of South Dakota School of Medicine, said at the DPSG meeting (Figure 1).
Also notable, she said, is that one-quarter of today’s pediatric diabetes cases are type 2 diabetes, which “is significant as there is a higher prevalence of early complications and comorbidities in youth with type 2 diabetes compared to type 1 diabetes.”
Moreover, recent projections estimate that 57% of today’s children will be obese at 35 years of age (N Engl J Med. 2017;377[22]:2145-53) and that 45% will have diabetes or prediabetes by 2030 (Popul Health Manag. 2017;20[1]:6-12), said Dr. Hockett, assistant professor in the university’s department of pediatrics. An investigator of the Exploring Perinatal Outcomes Among Children (EPOCH) study, which looked at gestational diabetes (GDM) and offspring cardiometabolic risks, she said more chronic disease “at increasingly younger ages [points toward] prebirth influences.”
She noted that there are critical periods postnatally — such as infancy and puberty — that can “impact or further shift the trajectory of chronic disease.” The developmental origins theory posits that life events and biological and environmental processes during the lifespan can modify the effects of intrauterine exposures.
The transgenerational implications “are clear,” she said. “As the number of reproductive-aged individuals with chronic diseases rises, the number of exposed offspring also rises ... It leads to a vicious cycle.”