ANSWER
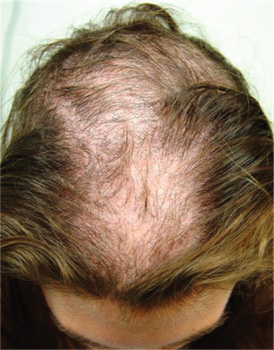
The correct answer is trichotillomania (choice “c”). See Discussion for more information.
Alopecia mucinosa (choice “a”) is a rare cause of focal hair loss that can occur in children. However, it usually presents with papules or plaques, unlike the smooth skin surface seen here.
Alopecia areata (choice “b”), common in children, typically entails complete hair loss in a given area—or, as hair regrows, with hairs of equal length. The uneven hairs seen in trichotillomania help a great deal in distinguishing it from alopecia areata.
Traction alopecia (choice “d”) is focal hair loss caused by chronic tension related to hairstyling. Most common in African-American women, and typically affecting the frontal periphery of the scalp, it is an unlikely explanation for hair loss in a 10-year-old boy.
DISCUSSION
Trichotillomania (TT) means, literally, “hair-pulling madness.” But in reality, there’s little actual plucking of hairs in this common condition. Instead, patients habitually manipulate hair by twirling and tugging, which weakens the shafts and follicles and renders them more susceptible to everyday wear and tear. In some cases, individual hairs speed through their growth phases and others break off in mid-shaft. All of this contributes to the classic “uneven” look of TT.
Patients with TT tend to be in the 4-to-17 age range, and most have issues with unresolved anxiety that manifest in part with manipulation of the hair. Officially considered an impulse control disorder, TT in most cases belongs to the psychiatrist’s domain.
In this case, it was enormously helpful to have corroboration from the patient and his mother regarding his role in creating and perpetuating the problem. Had that not been the case—or in the event of other doubts as to the correct diagnosis—biopsy could have been performed to rule out most of the other items in the differential, particularly alopecia areata.
Interestingly enough, studies have shown that the more sharply defined the area of hair loss, the more likely the patient is to admit his/her role in its creation. However, as is often the case with scientific research, contradictory findings have also been made.
TREATMENT
Treatment of TT is problematic, since no medications have proven to be completely helpful. Psychiatrists use a combination of medication, cognitive behavioral therapy, and other behavior modifications that are designed to overcome the habitual component of the problem. Most cases of TT resolve on their own, but in severe cases that persist for years, permanent hair loss can result.
In this case, there was enough insight and motivation on the part of the patient and his family to stop the offending behavior and allow the hair to regrow.