User login
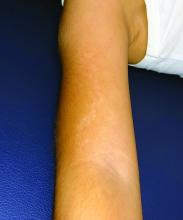
Lichen striatus (LS) is a common benign skin condition that presents in children between the ages of 5 and 15 years.1 The rash is typically unilateral and most frequently on the extremities, although it may appear on the face, trunk, or buttocks. The lesions start as pink or skin-colored asymptomatic papules in a linear orientation following the lines of Blaschko. There may be residual postinflammatory hypo- or hyperpigmentation which often improves within a few years.
Of note, there are subsets of lichen striatus: Hypopigmented lichen striatus with minimal papules has been termed “lichen striatus albus.” Nail lichen striatus may present as onycholysis or fissuring of nails, present as an isolated finding, or more commonly in association with concurrent affected skin. Nail lichen striatus typically resolves on its own, however there are case reports of improvement with intralesional steroids.2
There is no established etiology for LS. Autoimmune disease, viruses, immunizations, medications, and hypersensitivity reactions have been associated with triggering LS in various case reports, although strength of the associations is low. Children have been reported to have LS following scarlet fever and Candida vulvitis.3 Diagnosis usually is clinical, although biopsy may be helpful for histopathologic confirmation. No work-up for associated infections or conditions is warranted.
The differential for linear papular lesions includes inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN), blaschkitis, or linear morphea. ILVEN is a hamartoma that usually is congenital or presents in early childhood; presents with linear or whorled, hyperkeratotic papules and plaque in similar linear “line of Blaschko” patterns; and represents cutaneous mosaicism. It is often difficult to differentiate between lichen striatus and ILVEN, however lichen striatus is not congenital, and is a self-limited condition. Under dermoscopy (polarized light systems) findings of LS more frequently demonstrate gray granular pigmentation. ILVEN is more frequently associated with cerebriform pattern.4 Blaschkitis is a term for a blaschkoid inflammation of the skin that presents with more eczematous findings and histology of spongiosis, unlike the lichenoid findings of LS. It is typically accompanied by noticeable pruritus and broader bands of involved area, and has older age of onset than LS. Linear morphea is a deeper inflammatory process of the dermis or subcutaneous fat, presenting with sclerotic skin, and typically has associated atrophy.
Treatment need not be pursued for lichen striatus because it is a benign condition. The lesions typically self-resolve without any residual scarring. If patients have associated pruritus then low- to midpotency topical steroids can be used for symptomatic relief.
Dr. Kaushik is with the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital-San Diego, and Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. There are no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures for Dr. Kaushik or Dr. Eichenfield. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Gupta D, Mathes E. Lichen Striatus. (Levy ML ed.) 2019: UpToDate.
2. Dermatol Ther. 2018 Nov;31(6):e12713.
3. Int J Dermatol. 2018 Sep;57(9):1118-9.
4. J Dermatol. 2017 Dec;44(12):e355-6.
Lichen striatus (LS) is a common benign skin condition that presents in children between the ages of 5 and 15 years.1 The rash is typically unilateral and most frequently on the extremities, although it may appear on the face, trunk, or buttocks. The lesions start as pink or skin-colored asymptomatic papules in a linear orientation following the lines of Blaschko. There may be residual postinflammatory hypo- or hyperpigmentation which often improves within a few years.
Of note, there are subsets of lichen striatus: Hypopigmented lichen striatus with minimal papules has been termed “lichen striatus albus.” Nail lichen striatus may present as onycholysis or fissuring of nails, present as an isolated finding, or more commonly in association with concurrent affected skin. Nail lichen striatus typically resolves on its own, however there are case reports of improvement with intralesional steroids.2
There is no established etiology for LS. Autoimmune disease, viruses, immunizations, medications, and hypersensitivity reactions have been associated with triggering LS in various case reports, although strength of the associations is low. Children have been reported to have LS following scarlet fever and Candida vulvitis.3 Diagnosis usually is clinical, although biopsy may be helpful for histopathologic confirmation. No work-up for associated infections or conditions is warranted.
The differential for linear papular lesions includes inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN), blaschkitis, or linear morphea. ILVEN is a hamartoma that usually is congenital or presents in early childhood; presents with linear or whorled, hyperkeratotic papules and plaque in similar linear “line of Blaschko” patterns; and represents cutaneous mosaicism. It is often difficult to differentiate between lichen striatus and ILVEN, however lichen striatus is not congenital, and is a self-limited condition. Under dermoscopy (polarized light systems) findings of LS more frequently demonstrate gray granular pigmentation. ILVEN is more frequently associated with cerebriform pattern.4 Blaschkitis is a term for a blaschkoid inflammation of the skin that presents with more eczematous findings and histology of spongiosis, unlike the lichenoid findings of LS. It is typically accompanied by noticeable pruritus and broader bands of involved area, and has older age of onset than LS. Linear morphea is a deeper inflammatory process of the dermis or subcutaneous fat, presenting with sclerotic skin, and typically has associated atrophy.
Treatment need not be pursued for lichen striatus because it is a benign condition. The lesions typically self-resolve without any residual scarring. If patients have associated pruritus then low- to midpotency topical steroids can be used for symptomatic relief.
Dr. Kaushik is with the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital-San Diego, and Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. There are no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures for Dr. Kaushik or Dr. Eichenfield. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Gupta D, Mathes E. Lichen Striatus. (Levy ML ed.) 2019: UpToDate.
2. Dermatol Ther. 2018 Nov;31(6):e12713.
3. Int J Dermatol. 2018 Sep;57(9):1118-9.
4. J Dermatol. 2017 Dec;44(12):e355-6.
Lichen striatus (LS) is a common benign skin condition that presents in children between the ages of 5 and 15 years.1 The rash is typically unilateral and most frequently on the extremities, although it may appear on the face, trunk, or buttocks. The lesions start as pink or skin-colored asymptomatic papules in a linear orientation following the lines of Blaschko. There may be residual postinflammatory hypo- or hyperpigmentation which often improves within a few years.
Of note, there are subsets of lichen striatus: Hypopigmented lichen striatus with minimal papules has been termed “lichen striatus albus.” Nail lichen striatus may present as onycholysis or fissuring of nails, present as an isolated finding, or more commonly in association with concurrent affected skin. Nail lichen striatus typically resolves on its own, however there are case reports of improvement with intralesional steroids.2
There is no established etiology for LS. Autoimmune disease, viruses, immunizations, medications, and hypersensitivity reactions have been associated with triggering LS in various case reports, although strength of the associations is low. Children have been reported to have LS following scarlet fever and Candida vulvitis.3 Diagnosis usually is clinical, although biopsy may be helpful for histopathologic confirmation. No work-up for associated infections or conditions is warranted.
The differential for linear papular lesions includes inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN), blaschkitis, or linear morphea. ILVEN is a hamartoma that usually is congenital or presents in early childhood; presents with linear or whorled, hyperkeratotic papules and plaque in similar linear “line of Blaschko” patterns; and represents cutaneous mosaicism. It is often difficult to differentiate between lichen striatus and ILVEN, however lichen striatus is not congenital, and is a self-limited condition. Under dermoscopy (polarized light systems) findings of LS more frequently demonstrate gray granular pigmentation. ILVEN is more frequently associated with cerebriform pattern.4 Blaschkitis is a term for a blaschkoid inflammation of the skin that presents with more eczematous findings and histology of spongiosis, unlike the lichenoid findings of LS. It is typically accompanied by noticeable pruritus and broader bands of involved area, and has older age of onset than LS. Linear morphea is a deeper inflammatory process of the dermis or subcutaneous fat, presenting with sclerotic skin, and typically has associated atrophy.
Treatment need not be pursued for lichen striatus because it is a benign condition. The lesions typically self-resolve without any residual scarring. If patients have associated pruritus then low- to midpotency topical steroids can be used for symptomatic relief.
Dr. Kaushik is with the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital-San Diego, and Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. There are no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures for Dr. Kaushik or Dr. Eichenfield. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Gupta D, Mathes E. Lichen Striatus. (Levy ML ed.) 2019: UpToDate.
2. Dermatol Ther. 2018 Nov;31(6):e12713.
3. Int J Dermatol. 2018 Sep;57(9):1118-9.
4. J Dermatol. 2017 Dec;44(12):e355-6.