To the Editor:
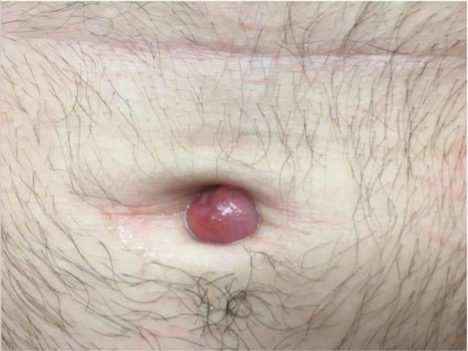
An otherwise healthy 26-year-old man presented to our outpatient clinic with a 15- to 20-mm, shiny, friable-appearing, red umbilical nodule with clear malodorous discharge (Figure 1). The lesion developed 2 weeks prior and gradually increased in size and discomfort. The patient reported mild associated abdominal pain. He had no fever, changes in urination or bowel movements, or prior history of umbilical growths or drainage. The abdomen was tender to palpation.
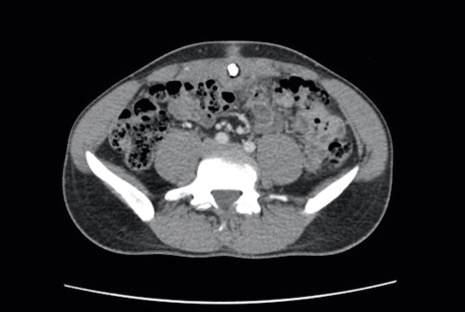
Differential diagnoses included pyogenic granuloma, umbilical hernia, epidermoid cyst or abscess, and malignancy (low suspicion). A biopsy was not performed due to concern for bleeding or communication with the bowel. A complete blood cell count, comprehensive metabolic panel, and urinalysis were unremarkable except for mild leukocytosis and elevated C-reactive protein. Ultrasonography revealed a 1.4×1.3-cm inflammatory umbilical mass with no communication with the bowel. The patient was referred to the emergency department (ED) for further evaluation. Computed tomography (CT) revealed periumbilical inflammation and an associated 1-cm calcification that appeared to be connected to a potential tract from the bladder, suggestive of a urachal remnant calcification (Figure 2). The patient was diagnosed with a persistent urachal remnant, discharged home with ciprofloxacin, and scheduled for a follow-up with urology.
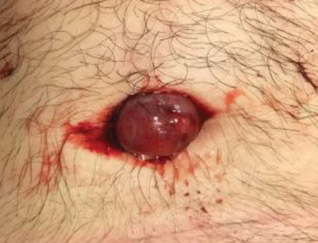
The patient returned to the ED 3 days later with painful umbilical bleeding (Figure 3). While there, the patient extracted a 1-cm stone from the lesion, consistent with the calcification visualized on CT scan. Computed tomographic virtual cystoscopy showed no connection between the bladder and umbilicus. He was diagnosed with an umbilical-urachal sinus. Complete surgical excision was recommended and performed by urology without complication.
We report an unusual presentation of a symptomatic urachal remnant in an adult. During embryogenesis, the urachus connects the umbilicus to the developing bladder and normally involutes during development. Incomplete regression can cause rare pathological urachal anomalies. The clinical presentation is nonspecific and differs between children and adults, with most cases presenting during infancy or childhood.1 Pediatric urachal abnormalities often present with umbilical drainage, abdominal pain, a palpable mass, an abnormal appearance of the umbilicus, or urinary tract infections.2,3 In adults, the most common symptoms include hematuria, pain, or dysuria. Alternatively, they may be asympomatic3 or present with periumbilical dermatitis4 or abscess. Rodrigues and Gandhi5 reported another case of a symptomatic calculus formed within a urachal remnant. Calcifications in urachal remnants are rare and usually are reported as incidental radiologic findings.
Overall, visible umbilical masses occur infrequently. In addition to urachal anomalies, the differential diagnosis includes several benign and malignant pathologies. Benign causes include epidermoid cysts, foreign body granulomas, pyogenic granulomas, abscesses, hamartomas, nevi, hemangiomas, dermatofibromas, neurofibromas, lipomas, granular cell tumors, desmoid tumors, keloid scars, omphaliths, hernias, or omphalomesenteric duct remnants.6 Primary malignancies (eg, skin cancers, urachal adenocarcinoma, mesenchymal tumors) or metastasis (ie, Sister Mary Joseph nodule) also can present as umbilical nodules.
The wide range of clinical presentations of urachal anomalies combined with the rarity make diagnosis difficult. Thus, it is essential to have a high index of suspicion and awareness of how they can present. Ultrasonography and CT scan are useful tools in making the diagnosis. Urachal anomalies are prone to infection or can be associated with malignancy; therefore, timely and correct diagnosis is critical. Although surgical removal is the primary treatment for urachal anomalies, it may not be the primary treatment of the other entities included in the differential diagnosis of umbilical nodules. For example, the Sister Mary Joseph nodule can be associated with various primary malignancies, which should be treated accordingly.