User login
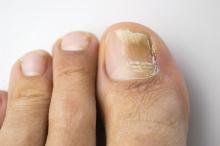
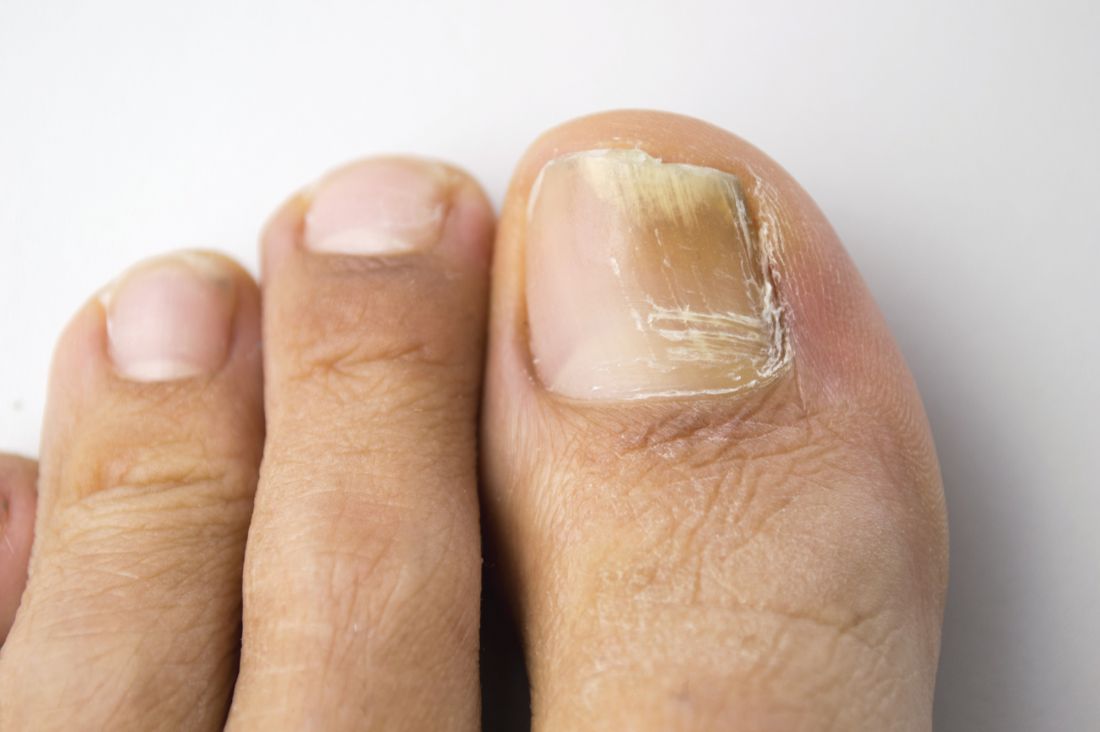
In the absence of a typical presentation, combining direct microscopy plus nail clipping histopathology – two diagnostic tests with different sensitivities and specificities – raises the likelihood of correctly diagnosing onychomycosis, according to a report published in Mycoses.
It is often difficult to diagnose nail diseases based solely on clinical features, and laboratory techniques for diagnosing onychomycoses in particular “remain a challenge,” said Fernanda G. Lavorato, MD, of Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, and her associates.
Isolating filamentous fungi in cultures is considered the preferred method for diagnosing the disorder, but this method lacks sensitivity and is not always accessible, since some dermatologic centers don’t have a mycology laboratory with personnel trained in sample collection and fungal processing.
The mean patient age was 58.8 years (range, 27-86 years). Most study participants (77.8%) had more than 1 affected nail. Many (29.7%) also had symptoms or signs of cutaneous lesions on the palm, sole, or interdigital region.
Direct microscopy was the most sensitive diagnostic test, correctly identifying 100% of the 122 cases of onychomycosis. In contrast, cultures identified only 34.4% of cases. This low sensitivity for culture testing was expected, and was “likely due to the rapid growth of fungi and bacteria comprising the local microbiota, which often prevents the growth of pathogenic fungi, particularly of slow-growing dermatophytes,” Dr. Lavorato and her associates said (Mycoses. 2017 May 15. doi:10.1111/myc.12633).
Histopathology of nail clippings was the most specific diagnostic test, correctly identifying 77% of cases. “Nail clipping histopathologic analysis complements the [microscopic] examination, particularly in cases of strong clinical suspicion but repeatedly negative mycological tests,” the investigators noted.
Direct microscopy showed greater accuracy with nondermatophytes, while nail clipping showed greater accuracy for dermatophytes, they added.
In this study, Trichophyton rubrum and T. mentagrophytes were the most frequently isolated dermatophytes, found in 70% and 23% of cases, respectively. Neoscytalidium dimidatum and Fusarium species were the most frequently isolated nondermatophytes, found in 44% and 28% of cases, respectively. In addition, Candida yeasts were isolated in samples from 14% of patients, and bacterial colonies were isolated in 70%.
The Mycology Laboratory at Pedro Ernesto University Hospital supported the study. Dr. Lavorato and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
In the absence of a typical presentation, combining direct microscopy plus nail clipping histopathology – two diagnostic tests with different sensitivities and specificities – raises the likelihood of correctly diagnosing onychomycosis, according to a report published in Mycoses.
It is often difficult to diagnose nail diseases based solely on clinical features, and laboratory techniques for diagnosing onychomycoses in particular “remain a challenge,” said Fernanda G. Lavorato, MD, of Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, and her associates.
Isolating filamentous fungi in cultures is considered the preferred method for diagnosing the disorder, but this method lacks sensitivity and is not always accessible, since some dermatologic centers don’t have a mycology laboratory with personnel trained in sample collection and fungal processing.
The mean patient age was 58.8 years (range, 27-86 years). Most study participants (77.8%) had more than 1 affected nail. Many (29.7%) also had symptoms or signs of cutaneous lesions on the palm, sole, or interdigital region.
Direct microscopy was the most sensitive diagnostic test, correctly identifying 100% of the 122 cases of onychomycosis. In contrast, cultures identified only 34.4% of cases. This low sensitivity for culture testing was expected, and was “likely due to the rapid growth of fungi and bacteria comprising the local microbiota, which often prevents the growth of pathogenic fungi, particularly of slow-growing dermatophytes,” Dr. Lavorato and her associates said (Mycoses. 2017 May 15. doi:10.1111/myc.12633).
Histopathology of nail clippings was the most specific diagnostic test, correctly identifying 77% of cases. “Nail clipping histopathologic analysis complements the [microscopic] examination, particularly in cases of strong clinical suspicion but repeatedly negative mycological tests,” the investigators noted.
Direct microscopy showed greater accuracy with nondermatophytes, while nail clipping showed greater accuracy for dermatophytes, they added.
In this study, Trichophyton rubrum and T. mentagrophytes were the most frequently isolated dermatophytes, found in 70% and 23% of cases, respectively. Neoscytalidium dimidatum and Fusarium species were the most frequently isolated nondermatophytes, found in 44% and 28% of cases, respectively. In addition, Candida yeasts were isolated in samples from 14% of patients, and bacterial colonies were isolated in 70%.
The Mycology Laboratory at Pedro Ernesto University Hospital supported the study. Dr. Lavorato and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
In the absence of a typical presentation, combining direct microscopy plus nail clipping histopathology – two diagnostic tests with different sensitivities and specificities – raises the likelihood of correctly diagnosing onychomycosis, according to a report published in Mycoses.
It is often difficult to diagnose nail diseases based solely on clinical features, and laboratory techniques for diagnosing onychomycoses in particular “remain a challenge,” said Fernanda G. Lavorato, MD, of Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, and her associates.
Isolating filamentous fungi in cultures is considered the preferred method for diagnosing the disorder, but this method lacks sensitivity and is not always accessible, since some dermatologic centers don’t have a mycology laboratory with personnel trained in sample collection and fungal processing.
The mean patient age was 58.8 years (range, 27-86 years). Most study participants (77.8%) had more than 1 affected nail. Many (29.7%) also had symptoms or signs of cutaneous lesions on the palm, sole, or interdigital region.
Direct microscopy was the most sensitive diagnostic test, correctly identifying 100% of the 122 cases of onychomycosis. In contrast, cultures identified only 34.4% of cases. This low sensitivity for culture testing was expected, and was “likely due to the rapid growth of fungi and bacteria comprising the local microbiota, which often prevents the growth of pathogenic fungi, particularly of slow-growing dermatophytes,” Dr. Lavorato and her associates said (Mycoses. 2017 May 15. doi:10.1111/myc.12633).
Histopathology of nail clippings was the most specific diagnostic test, correctly identifying 77% of cases. “Nail clipping histopathologic analysis complements the [microscopic] examination, particularly in cases of strong clinical suspicion but repeatedly negative mycological tests,” the investigators noted.
Direct microscopy showed greater accuracy with nondermatophytes, while nail clipping showed greater accuracy for dermatophytes, they added.
In this study, Trichophyton rubrum and T. mentagrophytes were the most frequently isolated dermatophytes, found in 70% and 23% of cases, respectively. Neoscytalidium dimidatum and Fusarium species were the most frequently isolated nondermatophytes, found in 44% and 28% of cases, respectively. In addition, Candida yeasts were isolated in samples from 14% of patients, and bacterial colonies were isolated in 70%.
The Mycology Laboratory at Pedro Ernesto University Hospital supported the study. Dr. Lavorato and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM MYCOSES
Key clinical point: In the absence of a typical clinical presentation, combining direct microscopy plus nail clipping histopathology – two diagnostic tests with different sensitivities and specificities – raises the likelihood of correctly diagnosing onychomycosis.
Major finding: Direct microscopy was the most sensitive diagnostic test, correctly identifying 100% of the 122 cases of onychomycosis, while histopathology of nail clippings was the most specific diagnostic test, correctly identifying 77% of cases.
Data source: A single-center prospective cross-sectional study involving 212 adults suspected of having onychomycosis during a 2-year period.
Disclosures: The Mycology Laboratory at Pedro Ernesto University Hospital supported the study. Dr. Lavorato and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.