User login
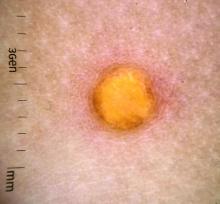
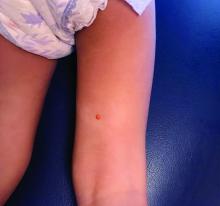
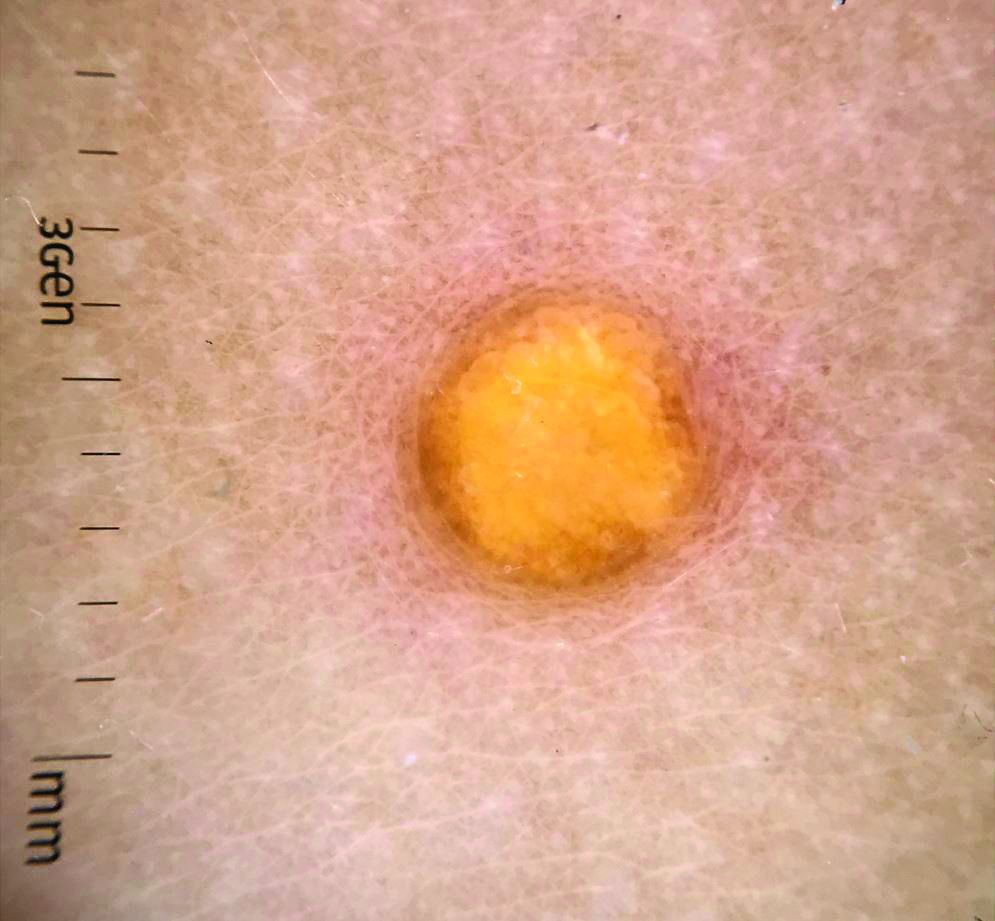
Juvenile xanthogranuloma (JXG) is a benign disorder presenting as firm, yellow-red skin papules or nodules, usually in infancy or early childhood. It derives its name based on its yellowish color and the histologic finding of lipid-filled histiocytes. In fact, it is a form of non-Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis. It most commonly presents on the head, neck, and trunk, but can arise anywhere on the body as demonstrated by this case. While often pink to reddish early on, the characteristic yellow or orange, brown appearance over time is common, occasionally with overlying telangiectasia, and ranging in size from 1 mm to 2 cm. While typically asymptomatic, it is possible for lesions to itch. JXG is usually self-limiting, and spontaneously resolves over several years. On dermoscopy (with polarized light), it has a characteristic “setting sun” appearance because of its central yellow area surrounded by a reddish periphery.
JXGs have been associated with neurofibromatosis-1 and a “triple association” of NF-1, JXG, and juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) has been debated. Many cases are diagnosed on clinical grounds without histologic confirmation, so while the absolute incidence is unknown, they are not uncommon.
What is on the differential?
Spitz nevus is a melanocytic lesion which typically presents as a sharply circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papule or nodule, and is composed of large epithelioid and/or spindled cells. These nevi can present with a spectrum of morphology and biologic activity; commonly with benign melanocytic proliferations and a symmetric appearance or, rarely, with atypical tumors or lesions, characterized as Spitzoid melanomas. The yellowish color of JXG is distinct from the appearance of Spitz tumors.
Molluscum contagiosum is a common pox viral infection seen in children that presents with round, flat-topped firm papules on the skin and distinctive whitish centers with or without umbilication. Like JXG, molluscum contagiosum papules may grow over time and cause pruritus. However, this diagnosis is less likely given the absence of other lesions on the skin, lack of known contacts with similar lesions, and yellowish color without a more typical appearance of molluscum.
Dermatofibromas occur in people of all ages, although more commonly between the ages of 20 and 40 and in those with a history of trauma at the lesion. Like JXGs, dermatofibromas tend to be firm, solitary papules or nodules. They usually are hyperpigmented, and classically “dimple when pinched” as they are fixed to the subcutaneous tissue. However, this patient’s age, lack of trauma, and the lesion morphology are not consistent with dermatofibromas.
Like XJGs, mastocytomas commonly present in the first 2 years of life with maculopapular or nodular lesions that itch. However, the history of new-onset itch in recent months as the lesion grew larger and the yellow color on dermoscopy are more consistent with JXG.
Eruptive xanthomas typically appear suddenly as multiple erythematous yellow, dome-shaped papules on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, buttocks, and hands. They are usually present with hypertriglyceridemia and are very rare in young children. The presence of a solitary lesion in a 6-month-old patient without a history of lipid abnormalities favors the diagnosis of XJG.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield and Ms. Kleinman have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
Hernandez-Martin A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997 Mar;36(3 Pt 1):355-67.
Prendiville J. Lumps, bumps and hamartomas in “Neonatal and Infant Dermatology,” 3rd ed. (Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2015).
Püttgen KB. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. UpToDate, 2021.
Schaffer JV. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021 Mar;22(2):205-20.
Juvenile xanthogranuloma (JXG) is a benign disorder presenting as firm, yellow-red skin papules or nodules, usually in infancy or early childhood. It derives its name based on its yellowish color and the histologic finding of lipid-filled histiocytes. In fact, it is a form of non-Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis. It most commonly presents on the head, neck, and trunk, but can arise anywhere on the body as demonstrated by this case. While often pink to reddish early on, the characteristic yellow or orange, brown appearance over time is common, occasionally with overlying telangiectasia, and ranging in size from 1 mm to 2 cm. While typically asymptomatic, it is possible for lesions to itch. JXG is usually self-limiting, and spontaneously resolves over several years. On dermoscopy (with polarized light), it has a characteristic “setting sun” appearance because of its central yellow area surrounded by a reddish periphery.
JXGs have been associated with neurofibromatosis-1 and a “triple association” of NF-1, JXG, and juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) has been debated. Many cases are diagnosed on clinical grounds without histologic confirmation, so while the absolute incidence is unknown, they are not uncommon.
What is on the differential?
Spitz nevus is a melanocytic lesion which typically presents as a sharply circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papule or nodule, and is composed of large epithelioid and/or spindled cells. These nevi can present with a spectrum of morphology and biologic activity; commonly with benign melanocytic proliferations and a symmetric appearance or, rarely, with atypical tumors or lesions, characterized as Spitzoid melanomas. The yellowish color of JXG is distinct from the appearance of Spitz tumors.
Molluscum contagiosum is a common pox viral infection seen in children that presents with round, flat-topped firm papules on the skin and distinctive whitish centers with or without umbilication. Like JXG, molluscum contagiosum papules may grow over time and cause pruritus. However, this diagnosis is less likely given the absence of other lesions on the skin, lack of known contacts with similar lesions, and yellowish color without a more typical appearance of molluscum.
Dermatofibromas occur in people of all ages, although more commonly between the ages of 20 and 40 and in those with a history of trauma at the lesion. Like JXGs, dermatofibromas tend to be firm, solitary papules or nodules. They usually are hyperpigmented, and classically “dimple when pinched” as they are fixed to the subcutaneous tissue. However, this patient’s age, lack of trauma, and the lesion morphology are not consistent with dermatofibromas.
Like XJGs, mastocytomas commonly present in the first 2 years of life with maculopapular or nodular lesions that itch. However, the history of new-onset itch in recent months as the lesion grew larger and the yellow color on dermoscopy are more consistent with JXG.
Eruptive xanthomas typically appear suddenly as multiple erythematous yellow, dome-shaped papules on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, buttocks, and hands. They are usually present with hypertriglyceridemia and are very rare in young children. The presence of a solitary lesion in a 6-month-old patient without a history of lipid abnormalities favors the diagnosis of XJG.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield and Ms. Kleinman have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
Hernandez-Martin A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997 Mar;36(3 Pt 1):355-67.
Prendiville J. Lumps, bumps and hamartomas in “Neonatal and Infant Dermatology,” 3rd ed. (Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2015).
Püttgen KB. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. UpToDate, 2021.
Schaffer JV. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021 Mar;22(2):205-20.
Juvenile xanthogranuloma (JXG) is a benign disorder presenting as firm, yellow-red skin papules or nodules, usually in infancy or early childhood. It derives its name based on its yellowish color and the histologic finding of lipid-filled histiocytes. In fact, it is a form of non-Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis. It most commonly presents on the head, neck, and trunk, but can arise anywhere on the body as demonstrated by this case. While often pink to reddish early on, the characteristic yellow or orange, brown appearance over time is common, occasionally with overlying telangiectasia, and ranging in size from 1 mm to 2 cm. While typically asymptomatic, it is possible for lesions to itch. JXG is usually self-limiting, and spontaneously resolves over several years. On dermoscopy (with polarized light), it has a characteristic “setting sun” appearance because of its central yellow area surrounded by a reddish periphery.
JXGs have been associated with neurofibromatosis-1 and a “triple association” of NF-1, JXG, and juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) has been debated. Many cases are diagnosed on clinical grounds without histologic confirmation, so while the absolute incidence is unknown, they are not uncommon.
What is on the differential?
Spitz nevus is a melanocytic lesion which typically presents as a sharply circumscribed, dome-shaped, pink-red or brown papule or nodule, and is composed of large epithelioid and/or spindled cells. These nevi can present with a spectrum of morphology and biologic activity; commonly with benign melanocytic proliferations and a symmetric appearance or, rarely, with atypical tumors or lesions, characterized as Spitzoid melanomas. The yellowish color of JXG is distinct from the appearance of Spitz tumors.
Molluscum contagiosum is a common pox viral infection seen in children that presents with round, flat-topped firm papules on the skin and distinctive whitish centers with or without umbilication. Like JXG, molluscum contagiosum papules may grow over time and cause pruritus. However, this diagnosis is less likely given the absence of other lesions on the skin, lack of known contacts with similar lesions, and yellowish color without a more typical appearance of molluscum.
Dermatofibromas occur in people of all ages, although more commonly between the ages of 20 and 40 and in those with a history of trauma at the lesion. Like JXGs, dermatofibromas tend to be firm, solitary papules or nodules. They usually are hyperpigmented, and classically “dimple when pinched” as they are fixed to the subcutaneous tissue. However, this patient’s age, lack of trauma, and the lesion morphology are not consistent with dermatofibromas.
Like XJGs, mastocytomas commonly present in the first 2 years of life with maculopapular or nodular lesions that itch. However, the history of new-onset itch in recent months as the lesion grew larger and the yellow color on dermoscopy are more consistent with JXG.
Eruptive xanthomas typically appear suddenly as multiple erythematous yellow, dome-shaped papules on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, buttocks, and hands. They are usually present with hypertriglyceridemia and are very rare in young children. The presence of a solitary lesion in a 6-month-old patient without a history of lipid abnormalities favors the diagnosis of XJG.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Ms. Kleinman is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield and Ms. Kleinman have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
Hernandez-Martin A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997 Mar;36(3 Pt 1):355-67.
Prendiville J. Lumps, bumps and hamartomas in “Neonatal and Infant Dermatology,” 3rd ed. (Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2015).
Püttgen KB. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. UpToDate, 2021.
Schaffer JV. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021 Mar;22(2):205-20.