User login
Contact dermatitis is an eczematous, pruritic eruption caused by direct contact with a substance and an irritant or allergic reaction. While it may not be contagious or life-threatening, contact dermatitis may be tremendously uncomfortable and impactful. Contact dermatitis may occur from exposure to chemicals in soaps, shampoos, cosmetics, metals, plants and topical products, and medications. The hallmark of contact dermatitis is localized eczematous reactions on the portion of the body that has been directly exposed to the reaction-causing substance. – often with oozing and crusting.
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type, which occurs when a substance damages the skin’s outer protective layer and does not require prior exposure or sensitization. Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can develop after exposure and sensitization, with an external allergen triggering an acute inflammatory response.1 Common causes of ACD include nickel, cobalt, gold, chromium, poison ivy/oak/sumac, cosmetics/personal care products that contain formaldehyde, fragrances, topical medications (anesthetics, antibiotics, corticosteroids), baby wipes, sunscreens, latex materials, protective equipment, soap/cleansers, resins, and acrylics. Among children, nickel sulfate, ammonium persulfate, gold sodium thiosulfate, thimerosal, and toluene-2,5-diamine are the most common sensitizers. Rarely, ACD can be triggered by something that enters the body through foods, flavorings, medicine, or medical or dental procedures (systemic contact dermatitis).
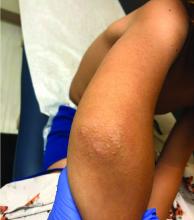
An Id reaction, or autoeczematization, is a generalized acute cutaneous reaction to a variety of stimuli, including infectious and inflammatory skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, or other eczematous dermatitis.3 Id reactions usually are preceded by a preexisting dermatitis. Lesions are, by definition, at a site distant from the primary infection or dermatitis. They often are distributed symmetrically. Papular or papular-vesicular lesions of the extremities and or trunk are common in children.
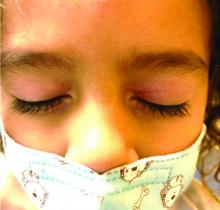
Our patient had evidence of a localized periocular contact dermatitis reaction that preceded the symmetric papular, eczematous eruption consistent with an id reaction. Our patient was prescribed hydrocortisone 2.5 % ointment for the eyes and triamcinolone 0.1% ointment for the rash on the body, which resulted in significant improvement.
Rosacea is a chronic and relapsing inflammatory skin disorder that primarily involves the central face. Common clinical features include facial erythema, telangiectasias, and inflammatory papules or pustules. Ocular involvement may occur in the presence or absence of cutaneous manifestations. Patients may report the presence of ocular foreign body sensation, burning, photophobia, blurred vision, redness, and tearing. Ocular disease is usually bilateral and is not proportional to the severity of the skin disease.4 Common skin findings are blepharitis, lid margin telangiectasia, tear abnormalities, meibomian gland inflammation, frequent chalazion, bilateral hordeolum, conjunctivitis, and, rarely, corneal ulcers and vascularization. Our patient initially did have bilateral hordeolum in what may seem to be ocular rosacea. However, given the use of a recent topical antibiotic with subsequent eczematous rash of the eyelids and then resulting distant rash on the body 1week later made the rash likely allergic contact dermatitis with id reaction.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing, and usually mild form of dermatitis that occurs in infants and in adults. The severity may vary from minimal, asymptomatic scaliness of the scalp (dandruff) to more widespread involvement. It is usually characterized by well-demarcated, erythematous plaques with greasy-looking, yellowish scales distributed on areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, the external ear, the center of the face, the upper part of the trunk, and the intertriginous areas.
Psoriasis typically affects the outside of the elbows, knees, or scalp, although it can appear on any location. It tends to go through cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding for a while or going into remission. Ocular involvement is a well known manifestation of psoriasis.5 Psoriatic lesions of the eyelid are rare, even in the erythrodermic variant of the disease. Occasionally, pustular psoriasis may involve the eyelids, with typical psoriatic lesions visible on the skin and lid margin. The reason for the relative sparing of the eyelid skin in patients with psoriasis is unknown. Other manifestations include meibomian gland dysfunction, decreased tear film break-up time, a nonspecific conjunctivitis, and corneal disease secondary to lid disease such as trichiasis.
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome (GCS), also known as papular acrodermatitis, papular acrodermatitis of childhood, and infantile papular acrodermatitis, is a self-limited skin disorder that most often occurs in young children. Viral infections are common GCS precipitating factors . GCS typically manifests as a symmetric, papular eruption, often with larger (3- to 10-mm) flat topped papulovesicles. Classic sites of involvement include the cheeks, buttocks, and extensor surfaces of the forearms and legs. GCS may be pruritic or asymptomatic, and papules typically resolve spontaneously within 2 months. Occasionally, GCS persists for longer periods. The eyelid lesions and localized pattern, with the absence of larger symmetric papules of the buttocks and legs, was not consistent with papular acrodermatitis of childhood.
Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. They had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016 Jun; 74(6):1043-54.
2. Pediatr Dermatol 2016 Jul; 33(4):399-404.
3. Evans M & Bronson D. (2019) Id Reaction (Autoeczematization). Retrieved from emedicine.medscape.com/article/1049760-overview.
4. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004 Dec;15(6):499-502.
5. Clin Dermatol. Mar-Apr 2016;34(2):146-50.
Contact dermatitis is an eczematous, pruritic eruption caused by direct contact with a substance and an irritant or allergic reaction. While it may not be contagious or life-threatening, contact dermatitis may be tremendously uncomfortable and impactful. Contact dermatitis may occur from exposure to chemicals in soaps, shampoos, cosmetics, metals, plants and topical products, and medications. The hallmark of contact dermatitis is localized eczematous reactions on the portion of the body that has been directly exposed to the reaction-causing substance. – often with oozing and crusting.
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type, which occurs when a substance damages the skin’s outer protective layer and does not require prior exposure or sensitization. Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can develop after exposure and sensitization, with an external allergen triggering an acute inflammatory response.1 Common causes of ACD include nickel, cobalt, gold, chromium, poison ivy/oak/sumac, cosmetics/personal care products that contain formaldehyde, fragrances, topical medications (anesthetics, antibiotics, corticosteroids), baby wipes, sunscreens, latex materials, protective equipment, soap/cleansers, resins, and acrylics. Among children, nickel sulfate, ammonium persulfate, gold sodium thiosulfate, thimerosal, and toluene-2,5-diamine are the most common sensitizers. Rarely, ACD can be triggered by something that enters the body through foods, flavorings, medicine, or medical or dental procedures (systemic contact dermatitis).
An Id reaction, or autoeczematization, is a generalized acute cutaneous reaction to a variety of stimuli, including infectious and inflammatory skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, or other eczematous dermatitis.3 Id reactions usually are preceded by a preexisting dermatitis. Lesions are, by definition, at a site distant from the primary infection or dermatitis. They often are distributed symmetrically. Papular or papular-vesicular lesions of the extremities and or trunk are common in children.
Our patient had evidence of a localized periocular contact dermatitis reaction that preceded the symmetric papular, eczematous eruption consistent with an id reaction. Our patient was prescribed hydrocortisone 2.5 % ointment for the eyes and triamcinolone 0.1% ointment for the rash on the body, which resulted in significant improvement.
Rosacea is a chronic and relapsing inflammatory skin disorder that primarily involves the central face. Common clinical features include facial erythema, telangiectasias, and inflammatory papules or pustules. Ocular involvement may occur in the presence or absence of cutaneous manifestations. Patients may report the presence of ocular foreign body sensation, burning, photophobia, blurred vision, redness, and tearing. Ocular disease is usually bilateral and is not proportional to the severity of the skin disease.4 Common skin findings are blepharitis, lid margin telangiectasia, tear abnormalities, meibomian gland inflammation, frequent chalazion, bilateral hordeolum, conjunctivitis, and, rarely, corneal ulcers and vascularization. Our patient initially did have bilateral hordeolum in what may seem to be ocular rosacea. However, given the use of a recent topical antibiotic with subsequent eczematous rash of the eyelids and then resulting distant rash on the body 1week later made the rash likely allergic contact dermatitis with id reaction.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing, and usually mild form of dermatitis that occurs in infants and in adults. The severity may vary from minimal, asymptomatic scaliness of the scalp (dandruff) to more widespread involvement. It is usually characterized by well-demarcated, erythematous plaques with greasy-looking, yellowish scales distributed on areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, the external ear, the center of the face, the upper part of the trunk, and the intertriginous areas.
Psoriasis typically affects the outside of the elbows, knees, or scalp, although it can appear on any location. It tends to go through cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding for a while or going into remission. Ocular involvement is a well known manifestation of psoriasis.5 Psoriatic lesions of the eyelid are rare, even in the erythrodermic variant of the disease. Occasionally, pustular psoriasis may involve the eyelids, with typical psoriatic lesions visible on the skin and lid margin. The reason for the relative sparing of the eyelid skin in patients with psoriasis is unknown. Other manifestations include meibomian gland dysfunction, decreased tear film break-up time, a nonspecific conjunctivitis, and corneal disease secondary to lid disease such as trichiasis.
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome (GCS), also known as papular acrodermatitis, papular acrodermatitis of childhood, and infantile papular acrodermatitis, is a self-limited skin disorder that most often occurs in young children. Viral infections are common GCS precipitating factors . GCS typically manifests as a symmetric, papular eruption, often with larger (3- to 10-mm) flat topped papulovesicles. Classic sites of involvement include the cheeks, buttocks, and extensor surfaces of the forearms and legs. GCS may be pruritic or asymptomatic, and papules typically resolve spontaneously within 2 months. Occasionally, GCS persists for longer periods. The eyelid lesions and localized pattern, with the absence of larger symmetric papules of the buttocks and legs, was not consistent with papular acrodermatitis of childhood.
Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. They had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016 Jun; 74(6):1043-54.
2. Pediatr Dermatol 2016 Jul; 33(4):399-404.
3. Evans M & Bronson D. (2019) Id Reaction (Autoeczematization). Retrieved from emedicine.medscape.com/article/1049760-overview.
4. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004 Dec;15(6):499-502.
5. Clin Dermatol. Mar-Apr 2016;34(2):146-50.
Contact dermatitis is an eczematous, pruritic eruption caused by direct contact with a substance and an irritant or allergic reaction. While it may not be contagious or life-threatening, contact dermatitis may be tremendously uncomfortable and impactful. Contact dermatitis may occur from exposure to chemicals in soaps, shampoos, cosmetics, metals, plants and topical products, and medications. The hallmark of contact dermatitis is localized eczematous reactions on the portion of the body that has been directly exposed to the reaction-causing substance. – often with oozing and crusting.
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type, which occurs when a substance damages the skin’s outer protective layer and does not require prior exposure or sensitization. Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can develop after exposure and sensitization, with an external allergen triggering an acute inflammatory response.1 Common causes of ACD include nickel, cobalt, gold, chromium, poison ivy/oak/sumac, cosmetics/personal care products that contain formaldehyde, fragrances, topical medications (anesthetics, antibiotics, corticosteroids), baby wipes, sunscreens, latex materials, protective equipment, soap/cleansers, resins, and acrylics. Among children, nickel sulfate, ammonium persulfate, gold sodium thiosulfate, thimerosal, and toluene-2,5-diamine are the most common sensitizers. Rarely, ACD can be triggered by something that enters the body through foods, flavorings, medicine, or medical or dental procedures (systemic contact dermatitis).
An Id reaction, or autoeczematization, is a generalized acute cutaneous reaction to a variety of stimuli, including infectious and inflammatory skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, or other eczematous dermatitis.3 Id reactions usually are preceded by a preexisting dermatitis. Lesions are, by definition, at a site distant from the primary infection or dermatitis. They often are distributed symmetrically. Papular or papular-vesicular lesions of the extremities and or trunk are common in children.
Our patient had evidence of a localized periocular contact dermatitis reaction that preceded the symmetric papular, eczematous eruption consistent with an id reaction. Our patient was prescribed hydrocortisone 2.5 % ointment for the eyes and triamcinolone 0.1% ointment for the rash on the body, which resulted in significant improvement.
Rosacea is a chronic and relapsing inflammatory skin disorder that primarily involves the central face. Common clinical features include facial erythema, telangiectasias, and inflammatory papules or pustules. Ocular involvement may occur in the presence or absence of cutaneous manifestations. Patients may report the presence of ocular foreign body sensation, burning, photophobia, blurred vision, redness, and tearing. Ocular disease is usually bilateral and is not proportional to the severity of the skin disease.4 Common skin findings are blepharitis, lid margin telangiectasia, tear abnormalities, meibomian gland inflammation, frequent chalazion, bilateral hordeolum, conjunctivitis, and, rarely, corneal ulcers and vascularization. Our patient initially did have bilateral hordeolum in what may seem to be ocular rosacea. However, given the use of a recent topical antibiotic with subsequent eczematous rash of the eyelids and then resulting distant rash on the body 1week later made the rash likely allergic contact dermatitis with id reaction.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing, and usually mild form of dermatitis that occurs in infants and in adults. The severity may vary from minimal, asymptomatic scaliness of the scalp (dandruff) to more widespread involvement. It is usually characterized by well-demarcated, erythematous plaques with greasy-looking, yellowish scales distributed on areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, the external ear, the center of the face, the upper part of the trunk, and the intertriginous areas.
Psoriasis typically affects the outside of the elbows, knees, or scalp, although it can appear on any location. It tends to go through cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding for a while or going into remission. Ocular involvement is a well known manifestation of psoriasis.5 Psoriatic lesions of the eyelid are rare, even in the erythrodermic variant of the disease. Occasionally, pustular psoriasis may involve the eyelids, with typical psoriatic lesions visible on the skin and lid margin. The reason for the relative sparing of the eyelid skin in patients with psoriasis is unknown. Other manifestations include meibomian gland dysfunction, decreased tear film break-up time, a nonspecific conjunctivitis, and corneal disease secondary to lid disease such as trichiasis.
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome (GCS), also known as papular acrodermatitis, papular acrodermatitis of childhood, and infantile papular acrodermatitis, is a self-limited skin disorder that most often occurs in young children. Viral infections are common GCS precipitating factors . GCS typically manifests as a symmetric, papular eruption, often with larger (3- to 10-mm) flat topped papulovesicles. Classic sites of involvement include the cheeks, buttocks, and extensor surfaces of the forearms and legs. GCS may be pruritic or asymptomatic, and papules typically resolve spontaneously within 2 months. Occasionally, GCS persists for longer periods. The eyelid lesions and localized pattern, with the absence of larger symmetric papules of the buttocks and legs, was not consistent with papular acrodermatitis of childhood.
Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. They had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016 Jun; 74(6):1043-54.
2. Pediatr Dermatol 2016 Jul; 33(4):399-404.
3. Evans M & Bronson D. (2019) Id Reaction (Autoeczematization). Retrieved from emedicine.medscape.com/article/1049760-overview.
4. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004 Dec;15(6):499-502.
5. Clin Dermatol. Mar-Apr 2016;34(2):146-50.
A 4-year-old healthy male with no significant prior medical history presents for evaluation of "itchy bumps" on the face and extremities of 2 weeks' duration.
The child was well until around 2 and a half weeks ago when he presented for evaluation of two lesions on the lower eyelids, diagnosed as hordeolum (a stye). He was prescribed ofloxacin ophthalmic solution.
One week later he developed bilateral itchy red eyes with red, thickened areas on the upper lids, followed several days later by pruritic papules on the ears, wrists, elbows, knees, and ankles. His mother used Vaseline for the eyelids for 1 week with no improvement. Physical exam at the dermatologist's office showed mild erythema, induration, and lichenification of the upper eyelids, and bilateral periocular eczematous patches with overlying scale. Subtle papules were evident on the elbows and feet.