User login
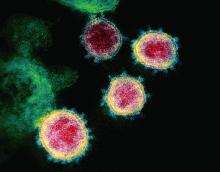
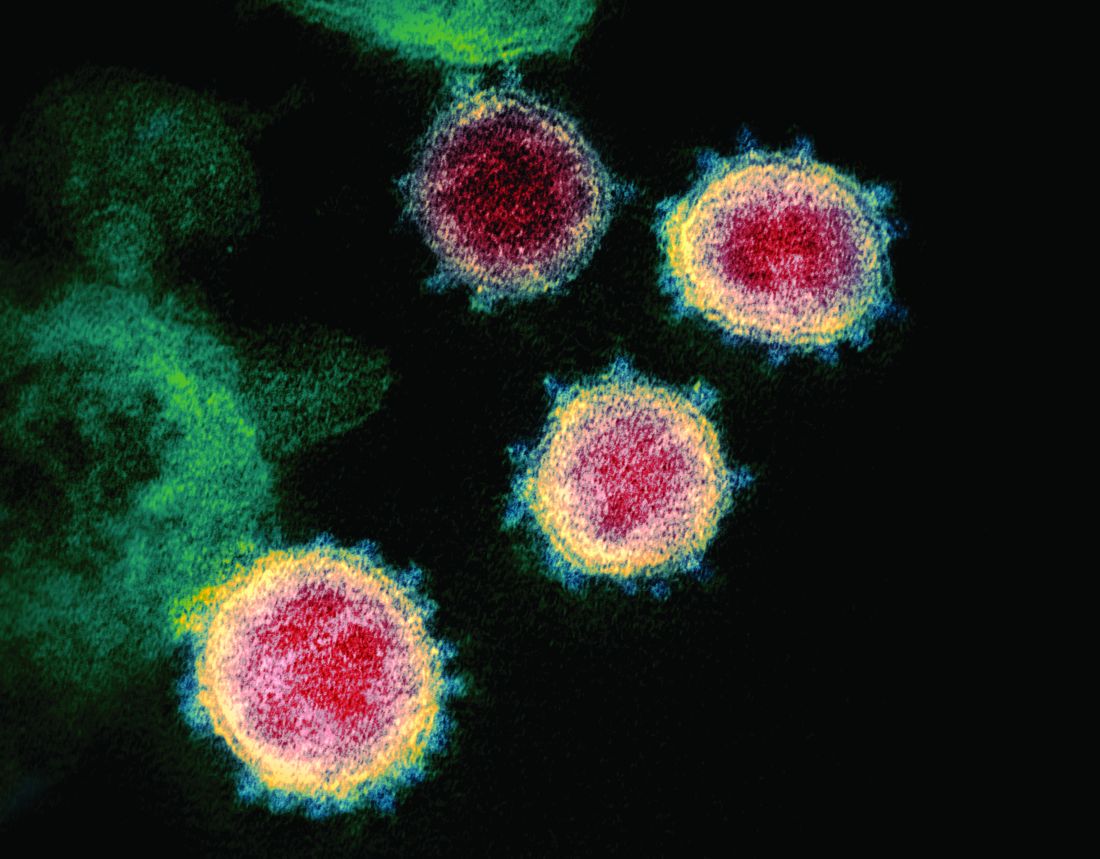
Coming up with a moniker for the new coronavirus shows the perils of naming names.
There is no Baby Book of Names or hurricane alphabet to readily name diseases and their causal entities. Throughout history and even in the modern era, a host of considerations have intruded on the decision as to what to call these blights upon humanity. Names have varied from inflammatory to misleading, from colloquial to scientific. And when it concerns a new epidemiological entity such as the latest coronavirus outbreak originating in China, health organizations, media, politicians, scientific taxonomy commissions, and the public at large all have a stake in the naming.
From “Wuhan virus” to “novel coronavirus-2019” to “COVID-19 virus,” the name of the new coronavirus that first appeared in China has been evolving to its now official designation: SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2). But where did the final name come from, how does such a name become official, and who makes it so?
Virus taxonomy
The Coronavirus Study Group (CSG) of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) named the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 based upon its genetic relationship to the original SARS-CoV that caused an outbreak of disease in 2002–2003.
According to the ICTV website, the first internationally organized attempts to introduce order into the bewildering variety of viruses took place at the International Congress of Microbiology held in Moscow in 1966 where a committee was created that later became the ICTV and was given the task of developing a single, universal taxonomic scheme for all the viruses infecting animals, plants, fungi, bacteria, and archaea. The ICTV was created as a committee of the virology division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies and is governed by statutes approved by the virology division. Virus classification and nomenclature are subject to rules set out in an International Code.
These designate that: “The universal virus classification system shall employ the hierarchical levels of realm, subrealm, kingdom, subkingdom, phylum, subphylum, class, subclass, order, suborder, family, subfamily, genus, subgenus and species.”
Many of the topmost areas of classification are based on whether the viruses are DNA or RNA, single or double stranded, and have a simple protein shell or a complex lipoprotein envelope. Other levels of classification include host species, type of replication, and type of diseases they cause, the later exemplified in the SARS designation for this virus.
There are 98 international study groups (SGs) covering all major virus orders, families, and genera that are part of the ICTV, and it was the one dedicated to the single-stranded RNA coronaviruses, the CSG, that came up with the SARS-CoV-2 name and first referenced it in their Feb 11 publication in the Cold Springs Harbor preprint journal bioRxiv.
“Based on phylogeny, taxonomy and established practice, the CSG formally recognizes this virus as a sister to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronaviruses (SARS-CoVs) of the species severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus and designates it as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2),” they wrote.
According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information Taxonomy Browser, with respect to the original SARS CoV virus, of which this is a relative, the full taxonomic designation is: Viruses, Riboviria, Nidovirales, Cornidovirineae, Coronaviridae, Orthocoronavirinae, Betacoronavirus, Sarbecovirus.
The problem with naming names
The World Health Organization currently is not using the official scientific name of the virus, but rather is merely labeling it with regard to the disease: COVID-19, which simply refers to coronavirus disease 2019.
They are following a modern standard by which disease names avoid inflammatory connotations with people and places. Too often in the past from syphilis as the “French pox,” the 1918 influenza as the “Spanish flu,” AIDS as the “gay plague,” Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS), and the currently named “WuFlu,” which made an appearance early in the new outbreak and which is symbolic of a sudden wave of anti-Asian, and specifically Chinese, prejudice.
Chinatown districts even in the United States are being affected economically through unwarranted fear associated with the virus. And there have been equivalently virulent outbreaks of hate speech against Asian individuals in places untouched by the new virus.
However, although SARS-CoV-2 as a name avoids such problems, different considerations led the WHO to reject it in its discussions, determining that its use ties it to tightly to the much more deadly SARS-CoV-1 virus in the public mind, risking greater fear and panic, especially in Asia, where SARS-CoV-1 had the biggest impact.
Back in 1896, William Sykes, MD, writing in the first flush of the triumph of germ theory in modern medicine, attempted to give some guidance to how medical science should best come up with new names of diseases by merging the demands of common parlance with those of taxonomic legitimacy. His “On the Origin and History of Disease-Names,” published in the Lancet, had clearcut advice: “It is vain to attempt to replace a folk name or one widely adopted by the people by a new one deliberately coined by scholars, and this for the following reasons: first, whatever names may be accepted by medical men must be translated by them into the vernacular of their patients, and by a resulting reaction the vernacular name comes to be the commoner one with themselves; and, secondly, there is no continuity or unchangeableness in the terms invented by savants, which are amended, improved upon, and displaced by the next writer on the subject, or, even more absurdly still, by the very inventors themselves in a subsequent publication.”
This is the reason that virus taxonomy provides names based upon unchangeable scientific descriptors of the actual disease causing entity, as illustrated by the decisions of the ICTV. In addition, the genomic sequences being provided by the scientific community are all being organized under the SARS-CoV-2 name and thus are cementing that moniker as the only acceptable scientific one.
Whether the rest of the world universally adopts SARS-CoV-2 as a name is still in question. If the outbreak spreads significantly beyond its current limits, fear and confusion – and simply the need for a more familiar-sounding label – may lead the general public to adopt more colloquial designations than those that science attempts to impose, as Dr. Sykes suggested back in 1896. That remains to be seen.
mlesney@mdedge.com
Mark Lesney is the managing editor of MDedge.com/IDPractioner. He has a PhD in plant virology and a PhD in the history of science, with a focus on the history of biotechnology and medicine. He has served as an adjunct assistant professor of the department of biochemistry and molecular & cellular biology at Georgetown University, Washington.
Coming up with a moniker for the new coronavirus shows the perils of naming names.
Coming up with a moniker for the new coronavirus shows the perils of naming names.
There is no Baby Book of Names or hurricane alphabet to readily name diseases and their causal entities. Throughout history and even in the modern era, a host of considerations have intruded on the decision as to what to call these blights upon humanity. Names have varied from inflammatory to misleading, from colloquial to scientific. And when it concerns a new epidemiological entity such as the latest coronavirus outbreak originating in China, health organizations, media, politicians, scientific taxonomy commissions, and the public at large all have a stake in the naming.
From “Wuhan virus” to “novel coronavirus-2019” to “COVID-19 virus,” the name of the new coronavirus that first appeared in China has been evolving to its now official designation: SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2). But where did the final name come from, how does such a name become official, and who makes it so?
Virus taxonomy
The Coronavirus Study Group (CSG) of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) named the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 based upon its genetic relationship to the original SARS-CoV that caused an outbreak of disease in 2002–2003.
According to the ICTV website, the first internationally organized attempts to introduce order into the bewildering variety of viruses took place at the International Congress of Microbiology held in Moscow in 1966 where a committee was created that later became the ICTV and was given the task of developing a single, universal taxonomic scheme for all the viruses infecting animals, plants, fungi, bacteria, and archaea. The ICTV was created as a committee of the virology division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies and is governed by statutes approved by the virology division. Virus classification and nomenclature are subject to rules set out in an International Code.
These designate that: “The universal virus classification system shall employ the hierarchical levels of realm, subrealm, kingdom, subkingdom, phylum, subphylum, class, subclass, order, suborder, family, subfamily, genus, subgenus and species.”
Many of the topmost areas of classification are based on whether the viruses are DNA or RNA, single or double stranded, and have a simple protein shell or a complex lipoprotein envelope. Other levels of classification include host species, type of replication, and type of diseases they cause, the later exemplified in the SARS designation for this virus.
There are 98 international study groups (SGs) covering all major virus orders, families, and genera that are part of the ICTV, and it was the one dedicated to the single-stranded RNA coronaviruses, the CSG, that came up with the SARS-CoV-2 name and first referenced it in their Feb 11 publication in the Cold Springs Harbor preprint journal bioRxiv.
“Based on phylogeny, taxonomy and established practice, the CSG formally recognizes this virus as a sister to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronaviruses (SARS-CoVs) of the species severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus and designates it as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2),” they wrote.
According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information Taxonomy Browser, with respect to the original SARS CoV virus, of which this is a relative, the full taxonomic designation is: Viruses, Riboviria, Nidovirales, Cornidovirineae, Coronaviridae, Orthocoronavirinae, Betacoronavirus, Sarbecovirus.
The problem with naming names
The World Health Organization currently is not using the official scientific name of the virus, but rather is merely labeling it with regard to the disease: COVID-19, which simply refers to coronavirus disease 2019.
They are following a modern standard by which disease names avoid inflammatory connotations with people and places. Too often in the past from syphilis as the “French pox,” the 1918 influenza as the “Spanish flu,” AIDS as the “gay plague,” Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS), and the currently named “WuFlu,” which made an appearance early in the new outbreak and which is symbolic of a sudden wave of anti-Asian, and specifically Chinese, prejudice.
Chinatown districts even in the United States are being affected economically through unwarranted fear associated with the virus. And there have been equivalently virulent outbreaks of hate speech against Asian individuals in places untouched by the new virus.
However, although SARS-CoV-2 as a name avoids such problems, different considerations led the WHO to reject it in its discussions, determining that its use ties it to tightly to the much more deadly SARS-CoV-1 virus in the public mind, risking greater fear and panic, especially in Asia, where SARS-CoV-1 had the biggest impact.
Back in 1896, William Sykes, MD, writing in the first flush of the triumph of germ theory in modern medicine, attempted to give some guidance to how medical science should best come up with new names of diseases by merging the demands of common parlance with those of taxonomic legitimacy. His “On the Origin and History of Disease-Names,” published in the Lancet, had clearcut advice: “It is vain to attempt to replace a folk name or one widely adopted by the people by a new one deliberately coined by scholars, and this for the following reasons: first, whatever names may be accepted by medical men must be translated by them into the vernacular of their patients, and by a resulting reaction the vernacular name comes to be the commoner one with themselves; and, secondly, there is no continuity or unchangeableness in the terms invented by savants, which are amended, improved upon, and displaced by the next writer on the subject, or, even more absurdly still, by the very inventors themselves in a subsequent publication.”
This is the reason that virus taxonomy provides names based upon unchangeable scientific descriptors of the actual disease causing entity, as illustrated by the decisions of the ICTV. In addition, the genomic sequences being provided by the scientific community are all being organized under the SARS-CoV-2 name and thus are cementing that moniker as the only acceptable scientific one.
Whether the rest of the world universally adopts SARS-CoV-2 as a name is still in question. If the outbreak spreads significantly beyond its current limits, fear and confusion – and simply the need for a more familiar-sounding label – may lead the general public to adopt more colloquial designations than those that science attempts to impose, as Dr. Sykes suggested back in 1896. That remains to be seen.
mlesney@mdedge.com
Mark Lesney is the managing editor of MDedge.com/IDPractioner. He has a PhD in plant virology and a PhD in the history of science, with a focus on the history of biotechnology and medicine. He has served as an adjunct assistant professor of the department of biochemistry and molecular & cellular biology at Georgetown University, Washington.
There is no Baby Book of Names or hurricane alphabet to readily name diseases and their causal entities. Throughout history and even in the modern era, a host of considerations have intruded on the decision as to what to call these blights upon humanity. Names have varied from inflammatory to misleading, from colloquial to scientific. And when it concerns a new epidemiological entity such as the latest coronavirus outbreak originating in China, health organizations, media, politicians, scientific taxonomy commissions, and the public at large all have a stake in the naming.
From “Wuhan virus” to “novel coronavirus-2019” to “COVID-19 virus,” the name of the new coronavirus that first appeared in China has been evolving to its now official designation: SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2). But where did the final name come from, how does such a name become official, and who makes it so?
Virus taxonomy
The Coronavirus Study Group (CSG) of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) named the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 based upon its genetic relationship to the original SARS-CoV that caused an outbreak of disease in 2002–2003.
According to the ICTV website, the first internationally organized attempts to introduce order into the bewildering variety of viruses took place at the International Congress of Microbiology held in Moscow in 1966 where a committee was created that later became the ICTV and was given the task of developing a single, universal taxonomic scheme for all the viruses infecting animals, plants, fungi, bacteria, and archaea. The ICTV was created as a committee of the virology division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies and is governed by statutes approved by the virology division. Virus classification and nomenclature are subject to rules set out in an International Code.
These designate that: “The universal virus classification system shall employ the hierarchical levels of realm, subrealm, kingdom, subkingdom, phylum, subphylum, class, subclass, order, suborder, family, subfamily, genus, subgenus and species.”
Many of the topmost areas of classification are based on whether the viruses are DNA or RNA, single or double stranded, and have a simple protein shell or a complex lipoprotein envelope. Other levels of classification include host species, type of replication, and type of diseases they cause, the later exemplified in the SARS designation for this virus.
There are 98 international study groups (SGs) covering all major virus orders, families, and genera that are part of the ICTV, and it was the one dedicated to the single-stranded RNA coronaviruses, the CSG, that came up with the SARS-CoV-2 name and first referenced it in their Feb 11 publication in the Cold Springs Harbor preprint journal bioRxiv.
“Based on phylogeny, taxonomy and established practice, the CSG formally recognizes this virus as a sister to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronaviruses (SARS-CoVs) of the species severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus and designates it as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2),” they wrote.
According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information Taxonomy Browser, with respect to the original SARS CoV virus, of which this is a relative, the full taxonomic designation is: Viruses, Riboviria, Nidovirales, Cornidovirineae, Coronaviridae, Orthocoronavirinae, Betacoronavirus, Sarbecovirus.
The problem with naming names
The World Health Organization currently is not using the official scientific name of the virus, but rather is merely labeling it with regard to the disease: COVID-19, which simply refers to coronavirus disease 2019.
They are following a modern standard by which disease names avoid inflammatory connotations with people and places. Too often in the past from syphilis as the “French pox,” the 1918 influenza as the “Spanish flu,” AIDS as the “gay plague,” Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS), and the currently named “WuFlu,” which made an appearance early in the new outbreak and which is symbolic of a sudden wave of anti-Asian, and specifically Chinese, prejudice.
Chinatown districts even in the United States are being affected economically through unwarranted fear associated with the virus. And there have been equivalently virulent outbreaks of hate speech against Asian individuals in places untouched by the new virus.
However, although SARS-CoV-2 as a name avoids such problems, different considerations led the WHO to reject it in its discussions, determining that its use ties it to tightly to the much more deadly SARS-CoV-1 virus in the public mind, risking greater fear and panic, especially in Asia, where SARS-CoV-1 had the biggest impact.
Back in 1896, William Sykes, MD, writing in the first flush of the triumph of germ theory in modern medicine, attempted to give some guidance to how medical science should best come up with new names of diseases by merging the demands of common parlance with those of taxonomic legitimacy. His “On the Origin and History of Disease-Names,” published in the Lancet, had clearcut advice: “It is vain to attempt to replace a folk name or one widely adopted by the people by a new one deliberately coined by scholars, and this for the following reasons: first, whatever names may be accepted by medical men must be translated by them into the vernacular of their patients, and by a resulting reaction the vernacular name comes to be the commoner one with themselves; and, secondly, there is no continuity or unchangeableness in the terms invented by savants, which are amended, improved upon, and displaced by the next writer on the subject, or, even more absurdly still, by the very inventors themselves in a subsequent publication.”
This is the reason that virus taxonomy provides names based upon unchangeable scientific descriptors of the actual disease causing entity, as illustrated by the decisions of the ICTV. In addition, the genomic sequences being provided by the scientific community are all being organized under the SARS-CoV-2 name and thus are cementing that moniker as the only acceptable scientific one.
Whether the rest of the world universally adopts SARS-CoV-2 as a name is still in question. If the outbreak spreads significantly beyond its current limits, fear and confusion – and simply the need for a more familiar-sounding label – may lead the general public to adopt more colloquial designations than those that science attempts to impose, as Dr. Sykes suggested back in 1896. That remains to be seen.
mlesney@mdedge.com
Mark Lesney is the managing editor of MDedge.com/IDPractioner. He has a PhD in plant virology and a PhD in the history of science, with a focus on the history of biotechnology and medicine. He has served as an adjunct assistant professor of the department of biochemistry and molecular & cellular biology at Georgetown University, Washington.