User login
The tortured road to successful treatment
It is rare in this modern era for medicine to confront an infectious disease for which there is no cure. Today, there are comparatively few infectious diseases (in the developed world and in places where money is no object) for which medicine cannot offer at least a glimmer of hope to infected patients. Even at its most futile, modern medicine has achieved vast improvements in the efficacy of palliative care. But it wasn’t that long ago that HIV infection was a nearly inevitable death sentence from the complications of AIDS, with no available treatments. And however monstrous that suffering and death, which still continues in many areas of the developing world, it was decades rather than centuries before modern medicine came up with effective treatments. Recently, there is even significant hope on the Ebola virus front that curative treatments may soon become available.
Medicine has always been in the business of hope, even when true cures were not available. Today that hope is less often misplaced. But in previous centuries, the need to offer hope to – and perhaps to make money from – desperate patients was a hallmark of the doctor’s trade.
It was this need to give patients hope and for doctors to feel that they were being effective that led to some highly dubious and desperate efforts to cure syphilis throughout history. These efforts meant centuries of fruitless torture for countless patients until the rise of modern antibiotics.
For the most part, what we now look upon as horrors and insanity in treatment were the result of misguided scientific theories, half-baked folk wisdom, and the generally well-intentioned efforts of medical practitioners at a cure. There were the charlatans as well, seeking a quick buck from the truly hopeless.
However, the social stigma of syphilis as a venereal disease played a role in the courses of treatment.
By the 15th century, syphilis was recognized as being spread by sexual intercourse, and in a situation analogous with the early AIDS epidemic, “16th- and 17th-century writers and physicians were divided on the moral aspects of syphilis. Some thought it was a divine punishment for sin – and as such only harsh treatments would cure it – or that people with syphilis shouldn’t be treated at all.”
Mercury rising
In its earliest manifestations, syphilis was considered untreatable. In 1496, Sebastian Brandt, wrote a poem entitled “De pestilentiali Scorra sive mala de Franzos” detailing the disease’s early spread across Europe and how doctors had no remedy for it.
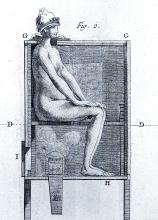
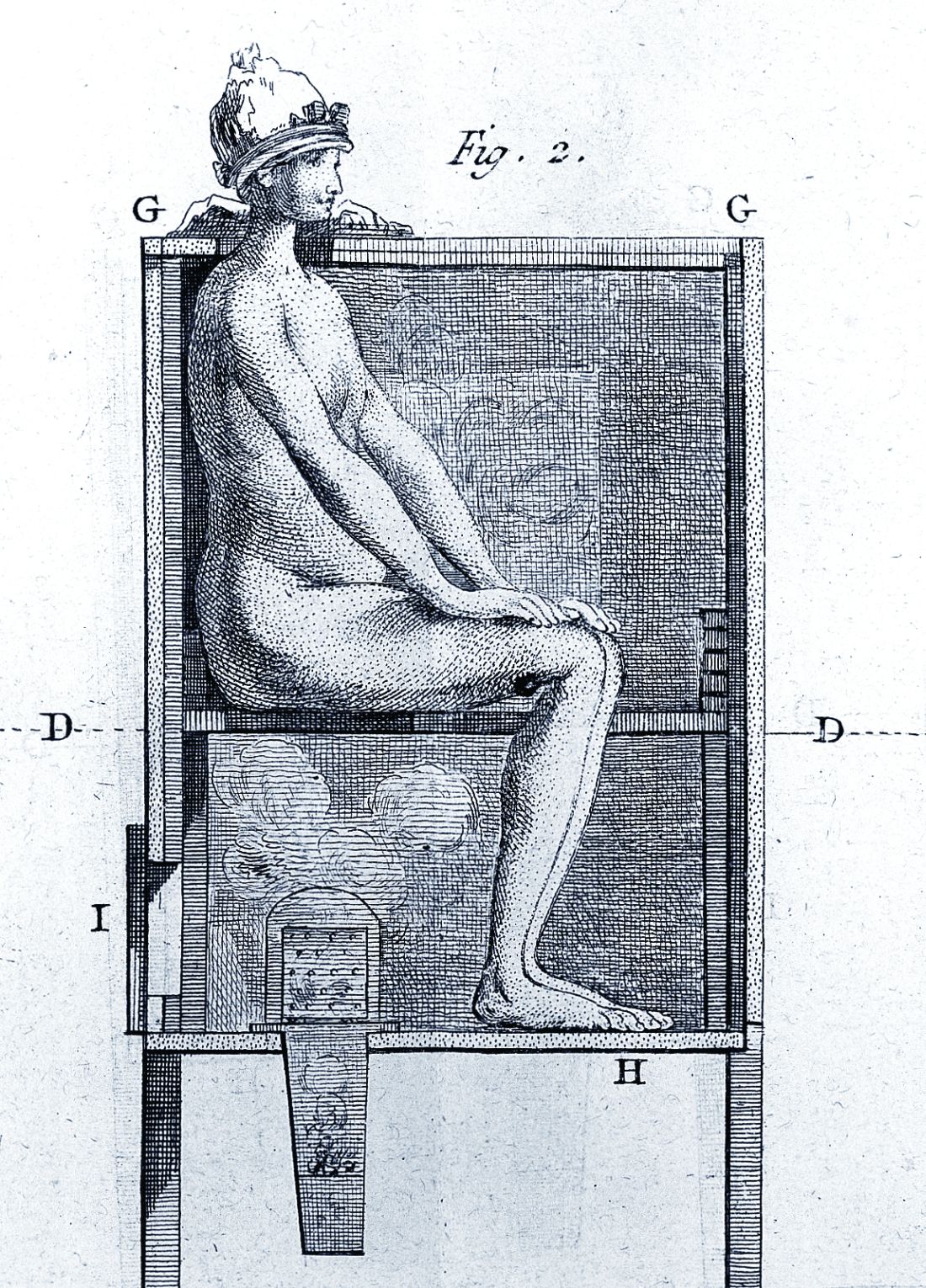
However, it wasn’t long before desperate physicians turned their quest for a cure to a reliable old standby treatment of the period – mercury, which had a history of being used for skin diseases. Mercury salves had been in use in the Arab world for leprosy and eczema, among other skin afflictions, and had been brought to Europe with the return of the medieval crusaders. Another way elemental mercury was administered was through the use of heated cinnabar (HgS), which gave off mercury vapors that could be absorbed by breathing and through the skin. In the 16th century, doctors would place a syphilis-infected individual inside an ovenlike chamber over pans of cinnabar, which were then heated at the person’s feet.
Oral mercury treatments were promoted by Paracelsus (1493?-1541), an alchemist and physician who prescribed calomel (HgCl), or mercury chloride, pills. Mercury treatment, administered at almost inevitably toxic doses, led to ulcerations of the lips, tongue, palate, and jaw; tooth loss; and fetid breath and excessive salivation. This last symptom was, in fact, considered the endpoint in mercury therapy for syphilis, which was “originally judged to be a copious secretion of saliva – ‘some few liters per diem.’ ” Even as recent as the late 19th century and early 20th century, syphilitic patients such as Oscar Wilde (whose teeth were blackened by the treatment), were prescribed calomel.
Looking to the “holy wood”
By 1519, an alternative treatment to mercury was available. In that year, Ulrich von Hutton, a German scholar who suffered from the “great pox,” described its treatment with guaiacum sanctum, or holy wood, in “De Morbo Gallico.” Four years later, despite such treatment, he was dead from the disease himself. But the lack of efficacy did not stop the faith that doctors placed in this botanical cure.
Holy wood was an herbal treatment derived from the bark of trees from the Guaiacum family. It was brought back on trading ships from the Caribbean and South America, the origin of syphilis’s foothold in Europe and the rest of the world. The use of holy wood matched a then-current theory that the cure to a disease could be found in the area from which it came. Other botanicals from around the world were also tried, but never came into routine use.
Guaiacum was the first treatment given to sufferers of syphilis in the Blatterhaus (pox hospital) in Augsburg after 1522, according to information from the archives at the Edward Worth Library in Dublin. The botanical therapy was given as a hot drink and followed by a sweating cure. Guaiacum extract acted as a sudorific, a compound which induces sweating when ingested. Even though the use of Guaiacum was initially popular, it was replaced almost exclusively by the use of mercury.
“Give me fever”
In the late 1800s, Julius Wagner von Jauregg (1857-1940), a Viennese neurologist, observed that Austrian army officers with neurosyphilis did not become partially paralyzed if they had also contracted malaria or relapsing fever. He initiated clinical trials in which he induced fever in syphilitics with tuberculin (1-10 mg) and observed in many the remissions their neuropsychiatric symptoms and signs. He also injected neurosyphilitic patients with a mild form of malaria to induce fever, which could then be suppressed with quinine treatment.
“Other physicians soon began using malariotherapy in uncontrolled studies of neurosyphilitics and reported clinical success rates of 33%-51% and only a 5% mortality. Persons with tabes dorsalis (the “wasting” paralysis of neurosyphilis) were hospitalized for 3 weeks of alternate-day fever therapy involving 5-hour long hot baths and extended periods wrapped in heavy blankets,” according to C.T. Ambrose, MD, of the University of Kentucky, Lexington.
A 1931 medical text summarizes in 35 studies involving 2,356 cases of general paresis treated with malaria and reported a 27.5% “full remission,” he added. A bacterial treatment developed in this period used a course of 18-23 injections of killed typhoid cells administered every 2-3 days in order to produce a fever of 103°–104°F. Animal studies of rabbits infected with syphilis showed that high temperatures could be curative.
Dr. Ambrose suggests that 16th-century syphilitics who had been subjected to mercury fumigation in ovenlike chambers endured severe sweating conditions and – for those who survived – the prolonged elevated body temperature (not the mercury) may have proved curative. Fever “was the common therapeutic denominator in the cinnabar-oven treatment, botanical sudorifics (guaiacum, China root), malarial infections (natural and iatrogenic), and bacterial (tuberculin) vaccine therapy.”
Prelude to modern antibiotics
German bacteriologist/immunologist Paul Ehrlich, MD, (1854-1915) investigated the use of atoxyl (sodium arsanilate) in syphilis, but the metallic drug had severe side effects, injuring the optic nerve and causing blindness. To overcome this problem, Ehrlich and his coworkers synthesized and tested related organic arsenicals. The antisyphilitic activity of arsphenamine (compound 606) was discovered by Sahachiro Hata, MD, (1879-1938) in 1909. This compound, known as Salvarsan, became “Dr. Ehrlich’s Magic Bullet,” for the treatment of syphilis in the 1910s, and it, and later, the less-toxic compound neoarsphenamine (compound 914) became mainstays of successful clinical treatment until the development and use of penicillin in the 1940s.
Selected sources
Ambrose, CT. Pre-antibiotic therapy of syphilis. NESSA J Infect Dis Immunology. 2016. 1(1);1-20.
Frith J. Syphilis: Its early history and treatment until penicillin and the debate on its origins. J Mil Veterans Health. 2012;20(4):49-58.
Tognotti B. The rise and fall of syphilis in Renaissance Italy. J Med Humanit. 2009 Jun;30(2):99-113.
Mark Lesney is the managing editor of MDedge.com/IDPractioner. He has a PhD in plant virology and a PhD in the history of science, with a focus on the history of biotechnology and medicine. He has served as an adjunct assistant professor in the department of biochemistry and molecular & cellular biology at Georgetown University, Washington.
The tortured road to successful treatment
The tortured road to successful treatment
It is rare in this modern era for medicine to confront an infectious disease for which there is no cure. Today, there are comparatively few infectious diseases (in the developed world and in places where money is no object) for which medicine cannot offer at least a glimmer of hope to infected patients. Even at its most futile, modern medicine has achieved vast improvements in the efficacy of palliative care. But it wasn’t that long ago that HIV infection was a nearly inevitable death sentence from the complications of AIDS, with no available treatments. And however monstrous that suffering and death, which still continues in many areas of the developing world, it was decades rather than centuries before modern medicine came up with effective treatments. Recently, there is even significant hope on the Ebola virus front that curative treatments may soon become available.
Medicine has always been in the business of hope, even when true cures were not available. Today that hope is less often misplaced. But in previous centuries, the need to offer hope to – and perhaps to make money from – desperate patients was a hallmark of the doctor’s trade.
It was this need to give patients hope and for doctors to feel that they were being effective that led to some highly dubious and desperate efforts to cure syphilis throughout history. These efforts meant centuries of fruitless torture for countless patients until the rise of modern antibiotics.
For the most part, what we now look upon as horrors and insanity in treatment were the result of misguided scientific theories, half-baked folk wisdom, and the generally well-intentioned efforts of medical practitioners at a cure. There were the charlatans as well, seeking a quick buck from the truly hopeless.
However, the social stigma of syphilis as a venereal disease played a role in the courses of treatment.
By the 15th century, syphilis was recognized as being spread by sexual intercourse, and in a situation analogous with the early AIDS epidemic, “16th- and 17th-century writers and physicians were divided on the moral aspects of syphilis. Some thought it was a divine punishment for sin – and as such only harsh treatments would cure it – or that people with syphilis shouldn’t be treated at all.”
Mercury rising
In its earliest manifestations, syphilis was considered untreatable. In 1496, Sebastian Brandt, wrote a poem entitled “De pestilentiali Scorra sive mala de Franzos” detailing the disease’s early spread across Europe and how doctors had no remedy for it.
However, it wasn’t long before desperate physicians turned their quest for a cure to a reliable old standby treatment of the period – mercury, which had a history of being used for skin diseases. Mercury salves had been in use in the Arab world for leprosy and eczema, among other skin afflictions, and had been brought to Europe with the return of the medieval crusaders. Another way elemental mercury was administered was through the use of heated cinnabar (HgS), which gave off mercury vapors that could be absorbed by breathing and through the skin. In the 16th century, doctors would place a syphilis-infected individual inside an ovenlike chamber over pans of cinnabar, which were then heated at the person’s feet.
Oral mercury treatments were promoted by Paracelsus (1493?-1541), an alchemist and physician who prescribed calomel (HgCl), or mercury chloride, pills. Mercury treatment, administered at almost inevitably toxic doses, led to ulcerations of the lips, tongue, palate, and jaw; tooth loss; and fetid breath and excessive salivation. This last symptom was, in fact, considered the endpoint in mercury therapy for syphilis, which was “originally judged to be a copious secretion of saliva – ‘some few liters per diem.’ ” Even as recent as the late 19th century and early 20th century, syphilitic patients such as Oscar Wilde (whose teeth were blackened by the treatment), were prescribed calomel.
Looking to the “holy wood”
By 1519, an alternative treatment to mercury was available. In that year, Ulrich von Hutton, a German scholar who suffered from the “great pox,” described its treatment with guaiacum sanctum, or holy wood, in “De Morbo Gallico.” Four years later, despite such treatment, he was dead from the disease himself. But the lack of efficacy did not stop the faith that doctors placed in this botanical cure.
Holy wood was an herbal treatment derived from the bark of trees from the Guaiacum family. It was brought back on trading ships from the Caribbean and South America, the origin of syphilis’s foothold in Europe and the rest of the world. The use of holy wood matched a then-current theory that the cure to a disease could be found in the area from which it came. Other botanicals from around the world were also tried, but never came into routine use.
Guaiacum was the first treatment given to sufferers of syphilis in the Blatterhaus (pox hospital) in Augsburg after 1522, according to information from the archives at the Edward Worth Library in Dublin. The botanical therapy was given as a hot drink and followed by a sweating cure. Guaiacum extract acted as a sudorific, a compound which induces sweating when ingested. Even though the use of Guaiacum was initially popular, it was replaced almost exclusively by the use of mercury.
“Give me fever”
In the late 1800s, Julius Wagner von Jauregg (1857-1940), a Viennese neurologist, observed that Austrian army officers with neurosyphilis did not become partially paralyzed if they had also contracted malaria or relapsing fever. He initiated clinical trials in which he induced fever in syphilitics with tuberculin (1-10 mg) and observed in many the remissions their neuropsychiatric symptoms and signs. He also injected neurosyphilitic patients with a mild form of malaria to induce fever, which could then be suppressed with quinine treatment.
“Other physicians soon began using malariotherapy in uncontrolled studies of neurosyphilitics and reported clinical success rates of 33%-51% and only a 5% mortality. Persons with tabes dorsalis (the “wasting” paralysis of neurosyphilis) were hospitalized for 3 weeks of alternate-day fever therapy involving 5-hour long hot baths and extended periods wrapped in heavy blankets,” according to C.T. Ambrose, MD, of the University of Kentucky, Lexington.
A 1931 medical text summarizes in 35 studies involving 2,356 cases of general paresis treated with malaria and reported a 27.5% “full remission,” he added. A bacterial treatment developed in this period used a course of 18-23 injections of killed typhoid cells administered every 2-3 days in order to produce a fever of 103°–104°F. Animal studies of rabbits infected with syphilis showed that high temperatures could be curative.
Dr. Ambrose suggests that 16th-century syphilitics who had been subjected to mercury fumigation in ovenlike chambers endured severe sweating conditions and – for those who survived – the prolonged elevated body temperature (not the mercury) may have proved curative. Fever “was the common therapeutic denominator in the cinnabar-oven treatment, botanical sudorifics (guaiacum, China root), malarial infections (natural and iatrogenic), and bacterial (tuberculin) vaccine therapy.”
Prelude to modern antibiotics
German bacteriologist/immunologist Paul Ehrlich, MD, (1854-1915) investigated the use of atoxyl (sodium arsanilate) in syphilis, but the metallic drug had severe side effects, injuring the optic nerve and causing blindness. To overcome this problem, Ehrlich and his coworkers synthesized and tested related organic arsenicals. The antisyphilitic activity of arsphenamine (compound 606) was discovered by Sahachiro Hata, MD, (1879-1938) in 1909. This compound, known as Salvarsan, became “Dr. Ehrlich’s Magic Bullet,” for the treatment of syphilis in the 1910s, and it, and later, the less-toxic compound neoarsphenamine (compound 914) became mainstays of successful clinical treatment until the development and use of penicillin in the 1940s.
Selected sources
Ambrose, CT. Pre-antibiotic therapy of syphilis. NESSA J Infect Dis Immunology. 2016. 1(1);1-20.
Frith J. Syphilis: Its early history and treatment until penicillin and the debate on its origins. J Mil Veterans Health. 2012;20(4):49-58.
Tognotti B. The rise and fall of syphilis in Renaissance Italy. J Med Humanit. 2009 Jun;30(2):99-113.
Mark Lesney is the managing editor of MDedge.com/IDPractioner. He has a PhD in plant virology and a PhD in the history of science, with a focus on the history of biotechnology and medicine. He has served as an adjunct assistant professor in the department of biochemistry and molecular & cellular biology at Georgetown University, Washington.
It is rare in this modern era for medicine to confront an infectious disease for which there is no cure. Today, there are comparatively few infectious diseases (in the developed world and in places where money is no object) for which medicine cannot offer at least a glimmer of hope to infected patients. Even at its most futile, modern medicine has achieved vast improvements in the efficacy of palliative care. But it wasn’t that long ago that HIV infection was a nearly inevitable death sentence from the complications of AIDS, with no available treatments. And however monstrous that suffering and death, which still continues in many areas of the developing world, it was decades rather than centuries before modern medicine came up with effective treatments. Recently, there is even significant hope on the Ebola virus front that curative treatments may soon become available.
Medicine has always been in the business of hope, even when true cures were not available. Today that hope is less often misplaced. But in previous centuries, the need to offer hope to – and perhaps to make money from – desperate patients was a hallmark of the doctor’s trade.
It was this need to give patients hope and for doctors to feel that they were being effective that led to some highly dubious and desperate efforts to cure syphilis throughout history. These efforts meant centuries of fruitless torture for countless patients until the rise of modern antibiotics.
For the most part, what we now look upon as horrors and insanity in treatment were the result of misguided scientific theories, half-baked folk wisdom, and the generally well-intentioned efforts of medical practitioners at a cure. There were the charlatans as well, seeking a quick buck from the truly hopeless.
However, the social stigma of syphilis as a venereal disease played a role in the courses of treatment.
By the 15th century, syphilis was recognized as being spread by sexual intercourse, and in a situation analogous with the early AIDS epidemic, “16th- and 17th-century writers and physicians were divided on the moral aspects of syphilis. Some thought it was a divine punishment for sin – and as such only harsh treatments would cure it – or that people with syphilis shouldn’t be treated at all.”
Mercury rising
In its earliest manifestations, syphilis was considered untreatable. In 1496, Sebastian Brandt, wrote a poem entitled “De pestilentiali Scorra sive mala de Franzos” detailing the disease’s early spread across Europe and how doctors had no remedy for it.
However, it wasn’t long before desperate physicians turned their quest for a cure to a reliable old standby treatment of the period – mercury, which had a history of being used for skin diseases. Mercury salves had been in use in the Arab world for leprosy and eczema, among other skin afflictions, and had been brought to Europe with the return of the medieval crusaders. Another way elemental mercury was administered was through the use of heated cinnabar (HgS), which gave off mercury vapors that could be absorbed by breathing and through the skin. In the 16th century, doctors would place a syphilis-infected individual inside an ovenlike chamber over pans of cinnabar, which were then heated at the person’s feet.
Oral mercury treatments were promoted by Paracelsus (1493?-1541), an alchemist and physician who prescribed calomel (HgCl), or mercury chloride, pills. Mercury treatment, administered at almost inevitably toxic doses, led to ulcerations of the lips, tongue, palate, and jaw; tooth loss; and fetid breath and excessive salivation. This last symptom was, in fact, considered the endpoint in mercury therapy for syphilis, which was “originally judged to be a copious secretion of saliva – ‘some few liters per diem.’ ” Even as recent as the late 19th century and early 20th century, syphilitic patients such as Oscar Wilde (whose teeth were blackened by the treatment), were prescribed calomel.
Looking to the “holy wood”
By 1519, an alternative treatment to mercury was available. In that year, Ulrich von Hutton, a German scholar who suffered from the “great pox,” described its treatment with guaiacum sanctum, or holy wood, in “De Morbo Gallico.” Four years later, despite such treatment, he was dead from the disease himself. But the lack of efficacy did not stop the faith that doctors placed in this botanical cure.
Holy wood was an herbal treatment derived from the bark of trees from the Guaiacum family. It was brought back on trading ships from the Caribbean and South America, the origin of syphilis’s foothold in Europe and the rest of the world. The use of holy wood matched a then-current theory that the cure to a disease could be found in the area from which it came. Other botanicals from around the world were also tried, but never came into routine use.
Guaiacum was the first treatment given to sufferers of syphilis in the Blatterhaus (pox hospital) in Augsburg after 1522, according to information from the archives at the Edward Worth Library in Dublin. The botanical therapy was given as a hot drink and followed by a sweating cure. Guaiacum extract acted as a sudorific, a compound which induces sweating when ingested. Even though the use of Guaiacum was initially popular, it was replaced almost exclusively by the use of mercury.
“Give me fever”
In the late 1800s, Julius Wagner von Jauregg (1857-1940), a Viennese neurologist, observed that Austrian army officers with neurosyphilis did not become partially paralyzed if they had also contracted malaria or relapsing fever. He initiated clinical trials in which he induced fever in syphilitics with tuberculin (1-10 mg) and observed in many the remissions their neuropsychiatric symptoms and signs. He also injected neurosyphilitic patients with a mild form of malaria to induce fever, which could then be suppressed with quinine treatment.
“Other physicians soon began using malariotherapy in uncontrolled studies of neurosyphilitics and reported clinical success rates of 33%-51% and only a 5% mortality. Persons with tabes dorsalis (the “wasting” paralysis of neurosyphilis) were hospitalized for 3 weeks of alternate-day fever therapy involving 5-hour long hot baths and extended periods wrapped in heavy blankets,” according to C.T. Ambrose, MD, of the University of Kentucky, Lexington.
A 1931 medical text summarizes in 35 studies involving 2,356 cases of general paresis treated with malaria and reported a 27.5% “full remission,” he added. A bacterial treatment developed in this period used a course of 18-23 injections of killed typhoid cells administered every 2-3 days in order to produce a fever of 103°–104°F. Animal studies of rabbits infected with syphilis showed that high temperatures could be curative.
Dr. Ambrose suggests that 16th-century syphilitics who had been subjected to mercury fumigation in ovenlike chambers endured severe sweating conditions and – for those who survived – the prolonged elevated body temperature (not the mercury) may have proved curative. Fever “was the common therapeutic denominator in the cinnabar-oven treatment, botanical sudorifics (guaiacum, China root), malarial infections (natural and iatrogenic), and bacterial (tuberculin) vaccine therapy.”
Prelude to modern antibiotics
German bacteriologist/immunologist Paul Ehrlich, MD, (1854-1915) investigated the use of atoxyl (sodium arsanilate) in syphilis, but the metallic drug had severe side effects, injuring the optic nerve and causing blindness. To overcome this problem, Ehrlich and his coworkers synthesized and tested related organic arsenicals. The antisyphilitic activity of arsphenamine (compound 606) was discovered by Sahachiro Hata, MD, (1879-1938) in 1909. This compound, known as Salvarsan, became “Dr. Ehrlich’s Magic Bullet,” for the treatment of syphilis in the 1910s, and it, and later, the less-toxic compound neoarsphenamine (compound 914) became mainstays of successful clinical treatment until the development and use of penicillin in the 1940s.
Selected sources
Ambrose, CT. Pre-antibiotic therapy of syphilis. NESSA J Infect Dis Immunology. 2016. 1(1);1-20.
Frith J. Syphilis: Its early history and treatment until penicillin and the debate on its origins. J Mil Veterans Health. 2012;20(4):49-58.
Tognotti B. The rise and fall of syphilis in Renaissance Italy. J Med Humanit. 2009 Jun;30(2):99-113.
Mark Lesney is the managing editor of MDedge.com/IDPractioner. He has a PhD in plant virology and a PhD in the history of science, with a focus on the history of biotechnology and medicine. He has served as an adjunct assistant professor in the department of biochemistry and molecular & cellular biology at Georgetown University, Washington.