User login
The 2019-2020 flu season continues its unusually early rise in activity, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimating that 3.7 million cases have occurred through Dec. 14.
which is up from 3.2% the previous week and is the sixth consecutive week that the United States has been at or above the national baseline of 2.4%, the CDC reported Dec. 20. This year’s 3.9% is the highest mid-December rate recorded since 2003, when it reached almost 7.4%.
Most of the influenza activity so far this season is being driven by influenza B/Victoria viruses. Nationwide testing puts influenza B prevalence at 68.5% of all positive specimens, exactly the same as last week, but A(H1N1) viruses “are increasing in proportion relative to other influenza viruses in some regions,” the CDC’s influenza division said.
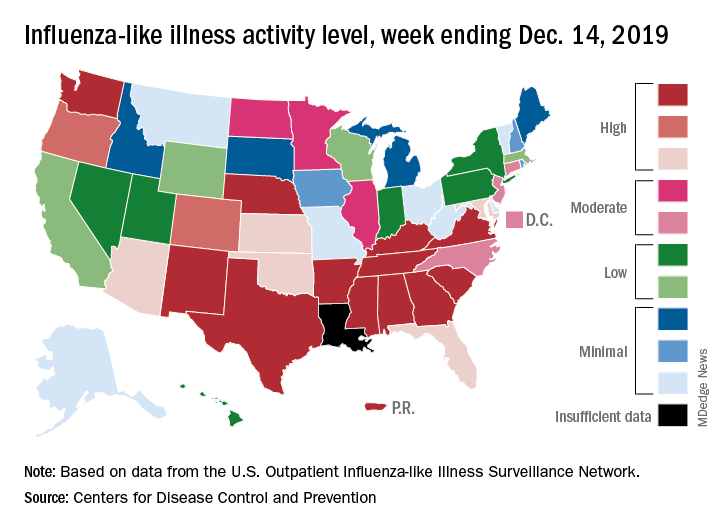
A look at this week’s activity map shows that 21 states, compared with 12 last week, were in the “high” range of activity – that’s levels 8-10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale. Twelve of those states, along with Puerto Rico, were at level 10, which was up from nine a week earlier, the CDC said.
The overall hospitalization rate through the week of Dec. 8-14 (5.5 per 100,000 population) “is similar to what has been seen at this time during recent seasons,” the CDC noted. The highest rates are occurring among adults over age 65 years (12.7 per 100,000) and children aged 0-4 years (10.9 per 100,000).
Three ILI-related deaths among children that occurred last week were reported, which brings the total for the 2019-2020 season to 19, the CDC said.
The 2019-2020 flu season continues its unusually early rise in activity, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimating that 3.7 million cases have occurred through Dec. 14.

which is up from 3.2% the previous week and is the sixth consecutive week that the United States has been at or above the national baseline of 2.4%, the CDC reported Dec. 20. This year’s 3.9% is the highest mid-December rate recorded since 2003, when it reached almost 7.4%.
Most of the influenza activity so far this season is being driven by influenza B/Victoria viruses. Nationwide testing puts influenza B prevalence at 68.5% of all positive specimens, exactly the same as last week, but A(H1N1) viruses “are increasing in proportion relative to other influenza viruses in some regions,” the CDC’s influenza division said.
A look at this week’s activity map shows that 21 states, compared with 12 last week, were in the “high” range of activity – that’s levels 8-10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale. Twelve of those states, along with Puerto Rico, were at level 10, which was up from nine a week earlier, the CDC said.
The overall hospitalization rate through the week of Dec. 8-14 (5.5 per 100,000 population) “is similar to what has been seen at this time during recent seasons,” the CDC noted. The highest rates are occurring among adults over age 65 years (12.7 per 100,000) and children aged 0-4 years (10.9 per 100,000).
Three ILI-related deaths among children that occurred last week were reported, which brings the total for the 2019-2020 season to 19, the CDC said.
The 2019-2020 flu season continues its unusually early rise in activity, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimating that 3.7 million cases have occurred through Dec. 14.

which is up from 3.2% the previous week and is the sixth consecutive week that the United States has been at or above the national baseline of 2.4%, the CDC reported Dec. 20. This year’s 3.9% is the highest mid-December rate recorded since 2003, when it reached almost 7.4%.
Most of the influenza activity so far this season is being driven by influenza B/Victoria viruses. Nationwide testing puts influenza B prevalence at 68.5% of all positive specimens, exactly the same as last week, but A(H1N1) viruses “are increasing in proportion relative to other influenza viruses in some regions,” the CDC’s influenza division said.
A look at this week’s activity map shows that 21 states, compared with 12 last week, were in the “high” range of activity – that’s levels 8-10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale. Twelve of those states, along with Puerto Rico, were at level 10, which was up from nine a week earlier, the CDC said.
The overall hospitalization rate through the week of Dec. 8-14 (5.5 per 100,000 population) “is similar to what has been seen at this time during recent seasons,” the CDC noted. The highest rates are occurring among adults over age 65 years (12.7 per 100,000) and children aged 0-4 years (10.9 per 100,000).
Three ILI-related deaths among children that occurred last week were reported, which brings the total for the 2019-2020 season to 19, the CDC said.