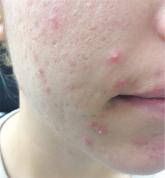
The correct answer is pyogenic granuloma (choice “d”), further discussion of which follows. Bacillary angiomatosis (choice “a”) is a lesion caused by infection with a species of Bartonella—a distinctly unusual problem. While a retained foreign body (choice “b”), such as a splinter, could trigger a similar lesion, there was no relevant history to suggest this was the case here. The most concerning differential item, melanoma (choice “c”), can present as a glistening red nodule, especially in children, but this too would be quite unusual.
Pyogenic granuloma (PG) was the name originally given to these common lesions, which are neither pyogenic (pus producing) nor truly granulomatous (demonstrating a classic histologic pattern). Rather, they are the body’s frustrated attempt to lay down new blood supply in a healing but oft-traumatized lesion (eg, acne lesion, tag, nevus, or wart).
Other names for them include sclerosing hemangioma and lobular capillary hemangioma. Their appearance can vary from the classic look seen in this case to older lesions that tend to be drier and more warty.
PGs are far more common in children than in adults and greatly favor females over males. Pregnancy appears to trigger them, especially in the mouth, but they can appear on fingers, nipples, or even the scalp. Certain drugs, such as isotretinoin and certain chemotherapy agents, predispose to their formation.
PGs removed from children (by shave technique, followed by electrodesiccation and curettage) must be sent for pathologic examination to rule out nodular melanoma. That’s what was done in this case, with the pathology report confirming the expected vascular nature of the lesion.