Photo Challenge
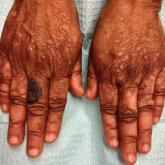
Hyperkeratotic Papules and Black Macules on the Hands
An elderly woman with a long history of hyperkeratotic papules on the abdomen, forearms, dorsal hands, and skinfolds presented with new lesions on...
From the Department of Dermatology, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore.
The authors have no relevant financial disclosures to report.
Correspondence: Shealinna Ge, MD, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Department of Dermatology, 419 W Redwood St, Ste 235, Baltimore, MD 21201 (shealinnage@gmail.com).
Cutis. 2024 November;114(5):140,144. doi:10.12788/cutis.1120

A healthy 13-year-old boy presented to the dermatology department with dystrophy of the right thumbnail of 3 to 4 years’ duration. A 5-mm-wide, depressed median longitudinal groove with a fir tree pattern was noted on the central nail plate. The patient noted that the groove had been gradually deepening. There was erythema, edema, and lichenification of the proximal nailfold without vascular changes, and the lunula was enlarged. No hyperkeratosis, subungual debris, erythematous nail folds, or inward curvature of the lateral aspects of the nail were noted. The patient denied any pruritus, pain, discomfort, or bleeding; he also denied any recent illness or trauma to the nail. None of the other nails were affected, and no other lesions or rashes were observed elsewhere on the body. The patient was unsure if he picked at the nail but acknowledged that he may have done so subconsciously. He had no history of eczema, psoriasis, or autoimmune connective tissue disorders.
Habit-tic deformity is a cause of nail dystrophy that commonly arises in children and adults due to subconscious repetitive and self-injurious manipulation of the nail bed or cuticle, which ultimately damages the nail matrix.1,2 It can be considered a variant of onychotillomania.1
Characteristic features of habit-tic deformity include a longitudinal depression on the central nail plate with transverse ridges,1 which can be more prominent on the dominant hand.3 Patients typically note a long duration of nail deformity, often without insight into its etiology.2 Diagnosis relies on careful assessment of the clinical presentation and the patient’s history to rule out other differential diagnoses. Based on our patient’s clinical presentation and history, we excluded wart, squamous cell carcinoma, eczema, psoriasis, lichen planus, autoimmune connective tissue disease, onychomycosis, paronychia, pincer nail deformity, and Beau line as potential diagnoses. Biopsy also can be performed to exclude these diagnoses from the differential if the cause is unclear following clinical examination.
Treatment for habit-tic deformity involves identifying and addressing the underlying habit. Barrier methods such as bandages and cyanoacrylate adhesives that prevent further manipulation of the nail matrix are effective treatments for habit-tic deformity.2 A multidisciplinary approach with psychiatry may be optimal to identify underlying psychological comorbidities and break the habit through behavior interventions and medications.4 Nail dystrophy generally improves once the habit is disrupted; however, a younger age of onset may carry a worse prognosis.3 Patients should be counseled that the affected nail may never grow normally.
Our patient was advised to use fluocinonide ointment 0.05% to reduce inflammation of the proximal nail fold and to cover the thumbnail with a bandage to prevent picking. He also was counseled that the nail may show ongoing abnormal growth. Minimal improvement was noted after 6 months.

An elderly woman with a long history of hyperkeratotic papules on the abdomen, forearms, dorsal hands, and skinfolds presented with new lesions on...
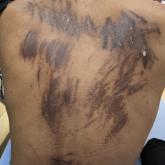
A 28-year-old man presented for evaluation of an intensely itchy rash of 5 days’ duration involving the face, trunk, arms, and legs.
