User login
In this column, I will describe the results of a recently published study from my group.1 We sought to profile Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), Haemophilus influenzae (Hflu) and Moraxella catarrhalis (Mcat) in the nasopharynx among 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13)-immunized children, with a focus on the first 6 months of life. The rationale was to provide heretofore unreported contemporary data in a highly PCV13-immunized, community-based child population in the United States. A secondary objective was to assess nasopharyngeal bacterial density because higher density associates with greater likelihood of progression to infection. Thirdly, the serotype distribution and antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci among children seen in primary care settings in the United States had not been evaluated for strains circulating among infants less than 6 months old and they may differ from strains recovered from older children. Therefore, comparisons were made within the same cohort of children to later child age time points.
Risk factors identified
The study was prospective and collected from a cohort of 101 children in Rochester, N.Y., during 2018-2020. Nasopharyngeal swabs were taken for study at age 1, 2 and 3 weeks, then 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. All children had received PCV13 vaccine according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended schedule.
We found two significant risk factors in the first 6 months of life for detection of nasopharyngeal colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat. They were daycare attendance and one or more siblings aged 1-5 years at home.
Colonization by one or more of the three bacteria was detected in only 5% of infants before age 2 months. None of the five children attended daycare but all five had young siblings at home. Pneumococcal colonization was detected in 12%, Hflu in 3%, and Mcat in 21% of nasopharyngeal swabs collected during the first 6 months of life. Nasopharyngeal colonization with the bacteria increased rapidly between age 4 and 6 months of life, coincident with infants going to daycare and other social interaction opportunities. Bacterial density of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat during the first 6 months of life was significantly lower in the nasopharynx compared with bacterial density when samples were collected during child age 7-24 months.
The prevalent pneumococcal serotypes in children up to 6 months old were 23B (17%), 22F (13%), 15B/C (11%), 16F (9%), and 21 (7%), 19F (7%), which differed from those isolated from children age 7-24 months, where serotypes 35B (15%), 21 (10%), 15B (9%), and 23B (7%), 23A (7%) were most commonly observed. Antibiotic resistance among isolates did not significantly differ in comparisons between infants younger than 6 months versus 7- to 24-month-olds.
What is the clinical significance?
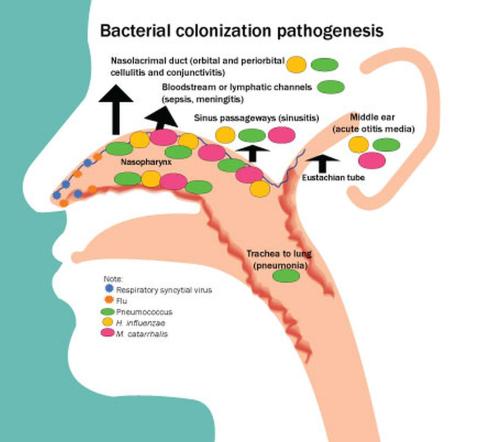
Colonization of the nasopharynx is a necessary first step in infection pathogenesis (Figure).
Prevalence of colonization varies among settings and countries, with generally much higher prevalence soon after birth and persisting at high rates in children living in low/middle-income countries versus high-income countries. This is one explanation for higher respiratory infection rates in low/middle-income countries compared with the United States, Europe, and other high-income countries. Environmental risk factors for early life colonization include household crowding, young siblings, no breastfeeding, daycare attendance, antibiotic usage, and passive exposure to smoke.
In a prior study of a different cohort of 358 prospectively-enrolled children, we sought associations between physician-attended illness visits and bacterial colonization in the first 5 years of life.2 We showed that early age of first colonization with pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat was associated with respiratory infection proneness and asthma among the children.
Multiple demographic and risk factors may contribute to early life and high-density colonization that in turn may increase risk of infections. High densities and early life pneumococcal colonization in low/middle-income countries might impact PCV responses by induction of immunity tolerance. While it is appealing to study new vaccines in low/middle-income populations with high infection incidence, there are reasons that infection incidence is higher compared with high-income countries like the United States, among them may be early life nasopharyngeal colonization and density of colonization.
Prevalent pneumococcal serotype appear to differ with age. The most common serotypes in the first 6 months of life for the children were 23B> 22F> 16F and 21=19F, but in children 7-24 months, serotypes 35B> 21>15B>23A=23B were most commonly observed. This difference might be due to the impact of antibiotics.3 Pneumococci expressing serotypes 22F and 16F were oxacillin susceptible and antibiotic exposure in the first 6 months of life is very uncommon in our study cohorts. In contrast, all pneumococci expressing 35B capsule were oxacillin resistant and in our cohorts antibiotic exposures are common among 7- to 24-month-olds.
In conclusion, we determined that children in the first 6 months of life seen in pediatric primary care settings in Rochester, N.Y., have very low prevalence and low-density colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat compared with 7- to 24-month olds. Our results may explain the significantly lower rates of infections caused by pneumococci, Hflu, and Mcat in infants younger than 6 months old compared with low/middle-income countries.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Kaur R and Pichichero M. Colonization, density, and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis among PCV13 vaccinated infants in the first six months of life in Rochester, New York. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2023 Apr 18;12(3):135-42.
2. Chapman T et al. Nasopharyngeal colonization with pathobionts is associated with susceptibility to respiratory illnesses in young children. PLoS One. 2020 Dec 11;15(12):e0243942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243942.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Antibiotic use and vaccine antibody levels. Pediatrics 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.
In this column, I will describe the results of a recently published study from my group.1 We sought to profile Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), Haemophilus influenzae (Hflu) and Moraxella catarrhalis (Mcat) in the nasopharynx among 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13)-immunized children, with a focus on the first 6 months of life. The rationale was to provide heretofore unreported contemporary data in a highly PCV13-immunized, community-based child population in the United States. A secondary objective was to assess nasopharyngeal bacterial density because higher density associates with greater likelihood of progression to infection. Thirdly, the serotype distribution and antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci among children seen in primary care settings in the United States had not been evaluated for strains circulating among infants less than 6 months old and they may differ from strains recovered from older children. Therefore, comparisons were made within the same cohort of children to later child age time points.
Risk factors identified
The study was prospective and collected from a cohort of 101 children in Rochester, N.Y., during 2018-2020. Nasopharyngeal swabs were taken for study at age 1, 2 and 3 weeks, then 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. All children had received PCV13 vaccine according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended schedule.
We found two significant risk factors in the first 6 months of life for detection of nasopharyngeal colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat. They were daycare attendance and one or more siblings aged 1-5 years at home.
Colonization by one or more of the three bacteria was detected in only 5% of infants before age 2 months. None of the five children attended daycare but all five had young siblings at home. Pneumococcal colonization was detected in 12%, Hflu in 3%, and Mcat in 21% of nasopharyngeal swabs collected during the first 6 months of life. Nasopharyngeal colonization with the bacteria increased rapidly between age 4 and 6 months of life, coincident with infants going to daycare and other social interaction opportunities. Bacterial density of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat during the first 6 months of life was significantly lower in the nasopharynx compared with bacterial density when samples were collected during child age 7-24 months.
The prevalent pneumococcal serotypes in children up to 6 months old were 23B (17%), 22F (13%), 15B/C (11%), 16F (9%), and 21 (7%), 19F (7%), which differed from those isolated from children age 7-24 months, where serotypes 35B (15%), 21 (10%), 15B (9%), and 23B (7%), 23A (7%) were most commonly observed. Antibiotic resistance among isolates did not significantly differ in comparisons between infants younger than 6 months versus 7- to 24-month-olds.
What is the clinical significance?
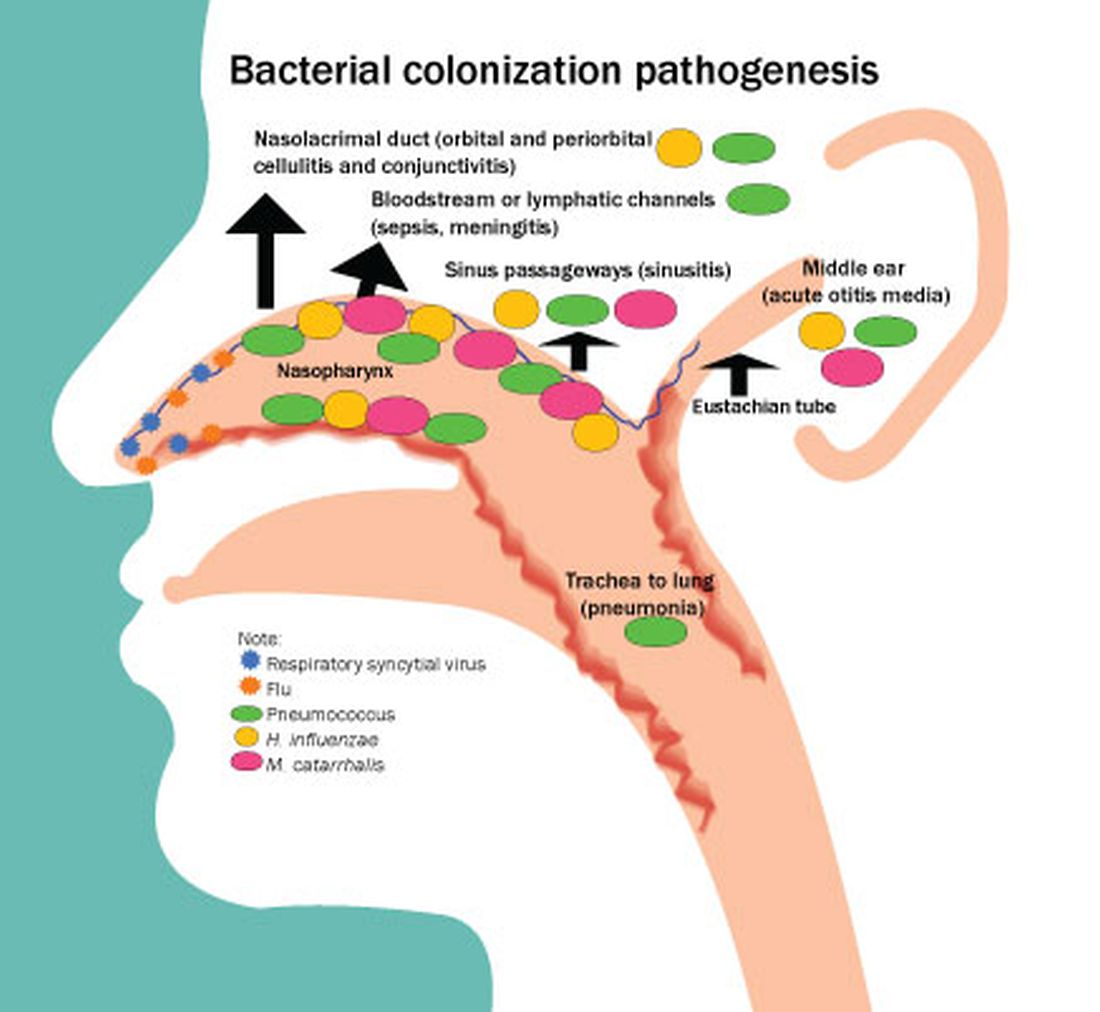
Colonization of the nasopharynx is a necessary first step in infection pathogenesis (Figure).
Prevalence of colonization varies among settings and countries, with generally much higher prevalence soon after birth and persisting at high rates in children living in low/middle-income countries versus high-income countries. This is one explanation for higher respiratory infection rates in low/middle-income countries compared with the United States, Europe, and other high-income countries. Environmental risk factors for early life colonization include household crowding, young siblings, no breastfeeding, daycare attendance, antibiotic usage, and passive exposure to smoke.
In a prior study of a different cohort of 358 prospectively-enrolled children, we sought associations between physician-attended illness visits and bacterial colonization in the first 5 years of life.2 We showed that early age of first colonization with pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat was associated with respiratory infection proneness and asthma among the children.
Multiple demographic and risk factors may contribute to early life and high-density colonization that in turn may increase risk of infections. High densities and early life pneumococcal colonization in low/middle-income countries might impact PCV responses by induction of immunity tolerance. While it is appealing to study new vaccines in low/middle-income populations with high infection incidence, there are reasons that infection incidence is higher compared with high-income countries like the United States, among them may be early life nasopharyngeal colonization and density of colonization.
Prevalent pneumococcal serotype appear to differ with age. The most common serotypes in the first 6 months of life for the children were 23B> 22F> 16F and 21=19F, but in children 7-24 months, serotypes 35B> 21>15B>23A=23B were most commonly observed. This difference might be due to the impact of antibiotics.3 Pneumococci expressing serotypes 22F and 16F were oxacillin susceptible and antibiotic exposure in the first 6 months of life is very uncommon in our study cohorts. In contrast, all pneumococci expressing 35B capsule were oxacillin resistant and in our cohorts antibiotic exposures are common among 7- to 24-month-olds.
In conclusion, we determined that children in the first 6 months of life seen in pediatric primary care settings in Rochester, N.Y., have very low prevalence and low-density colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat compared with 7- to 24-month olds. Our results may explain the significantly lower rates of infections caused by pneumococci, Hflu, and Mcat in infants younger than 6 months old compared with low/middle-income countries.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Kaur R and Pichichero M. Colonization, density, and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis among PCV13 vaccinated infants in the first six months of life in Rochester, New York. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2023 Apr 18;12(3):135-42.
2. Chapman T et al. Nasopharyngeal colonization with pathobionts is associated with susceptibility to respiratory illnesses in young children. PLoS One. 2020 Dec 11;15(12):e0243942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243942.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Antibiotic use and vaccine antibody levels. Pediatrics 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.
In this column, I will describe the results of a recently published study from my group.1 We sought to profile Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), Haemophilus influenzae (Hflu) and Moraxella catarrhalis (Mcat) in the nasopharynx among 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13)-immunized children, with a focus on the first 6 months of life. The rationale was to provide heretofore unreported contemporary data in a highly PCV13-immunized, community-based child population in the United States. A secondary objective was to assess nasopharyngeal bacterial density because higher density associates with greater likelihood of progression to infection. Thirdly, the serotype distribution and antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci among children seen in primary care settings in the United States had not been evaluated for strains circulating among infants less than 6 months old and they may differ from strains recovered from older children. Therefore, comparisons were made within the same cohort of children to later child age time points.
Risk factors identified
The study was prospective and collected from a cohort of 101 children in Rochester, N.Y., during 2018-2020. Nasopharyngeal swabs were taken for study at age 1, 2 and 3 weeks, then 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. All children had received PCV13 vaccine according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended schedule.
We found two significant risk factors in the first 6 months of life for detection of nasopharyngeal colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat. They were daycare attendance and one or more siblings aged 1-5 years at home.
Colonization by one or more of the three bacteria was detected in only 5% of infants before age 2 months. None of the five children attended daycare but all five had young siblings at home. Pneumococcal colonization was detected in 12%, Hflu in 3%, and Mcat in 21% of nasopharyngeal swabs collected during the first 6 months of life. Nasopharyngeal colonization with the bacteria increased rapidly between age 4 and 6 months of life, coincident with infants going to daycare and other social interaction opportunities. Bacterial density of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat during the first 6 months of life was significantly lower in the nasopharynx compared with bacterial density when samples were collected during child age 7-24 months.
The prevalent pneumococcal serotypes in children up to 6 months old were 23B (17%), 22F (13%), 15B/C (11%), 16F (9%), and 21 (7%), 19F (7%), which differed from those isolated from children age 7-24 months, where serotypes 35B (15%), 21 (10%), 15B (9%), and 23B (7%), 23A (7%) were most commonly observed. Antibiotic resistance among isolates did not significantly differ in comparisons between infants younger than 6 months versus 7- to 24-month-olds.
What is the clinical significance?
Colonization of the nasopharynx is a necessary first step in infection pathogenesis (Figure).
Prevalence of colonization varies among settings and countries, with generally much higher prevalence soon after birth and persisting at high rates in children living in low/middle-income countries versus high-income countries. This is one explanation for higher respiratory infection rates in low/middle-income countries compared with the United States, Europe, and other high-income countries. Environmental risk factors for early life colonization include household crowding, young siblings, no breastfeeding, daycare attendance, antibiotic usage, and passive exposure to smoke.
In a prior study of a different cohort of 358 prospectively-enrolled children, we sought associations between physician-attended illness visits and bacterial colonization in the first 5 years of life.2 We showed that early age of first colonization with pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat was associated with respiratory infection proneness and asthma among the children.
Multiple demographic and risk factors may contribute to early life and high-density colonization that in turn may increase risk of infections. High densities and early life pneumococcal colonization in low/middle-income countries might impact PCV responses by induction of immunity tolerance. While it is appealing to study new vaccines in low/middle-income populations with high infection incidence, there are reasons that infection incidence is higher compared with high-income countries like the United States, among them may be early life nasopharyngeal colonization and density of colonization.
Prevalent pneumococcal serotype appear to differ with age. The most common serotypes in the first 6 months of life for the children were 23B> 22F> 16F and 21=19F, but in children 7-24 months, serotypes 35B> 21>15B>23A=23B were most commonly observed. This difference might be due to the impact of antibiotics.3 Pneumococci expressing serotypes 22F and 16F were oxacillin susceptible and antibiotic exposure in the first 6 months of life is very uncommon in our study cohorts. In contrast, all pneumococci expressing 35B capsule were oxacillin resistant and in our cohorts antibiotic exposures are common among 7- to 24-month-olds.
In conclusion, we determined that children in the first 6 months of life seen in pediatric primary care settings in Rochester, N.Y., have very low prevalence and low-density colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat compared with 7- to 24-month olds. Our results may explain the significantly lower rates of infections caused by pneumococci, Hflu, and Mcat in infants younger than 6 months old compared with low/middle-income countries.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Kaur R and Pichichero M. Colonization, density, and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis among PCV13 vaccinated infants in the first six months of life in Rochester, New York. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2023 Apr 18;12(3):135-42.
2. Chapman T et al. Nasopharyngeal colonization with pathobionts is associated with susceptibility to respiratory illnesses in young children. PLoS One. 2020 Dec 11;15(12):e0243942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243942.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Antibiotic use and vaccine antibody levels. Pediatrics 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.