User login
with targeted messages and images, a study of e-cigarette promotion has found.
In 2018, the JUUL company declared a commitment to support efforts to raise the age of legal purchase of tobacco to age 21 years in all U.S. states. In addition, JUUL deleted its official Facebook and Instagram accounts in November 2018, but the promotion of these products has continued through affiliated marketing campaigns from other online vendors.
Vaping among teens has shot up in popularity in recent years. The prevalence of vaping among young people aged 16-19 years has been estimated at 16% in 2018, up from 11% in 2017 (BMJ. 2019 Jun 19. doi: 10.1136/bmj.12219. A study published in JAMA Pediatrics (2019;173[7]:690-92) found that an estimated 81% of users following a popular Twitter account (@JUULvapor) were aged 13-20 years, with 45% in the 13-17 year age range.
Elizabeth C. Hair, PhD, senior vice president of the Truth Initiative Schroeder Institute, and a team of investigators conducted a study of the “proliferation of JUUL-related content across four themes over a 3-month period: overt promotional content, nicotine and addiction-related content, lifestyle content, and content related to youth culture.” The study appeared online in Tobacco Control (2019 Jul 2; doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2018-054824).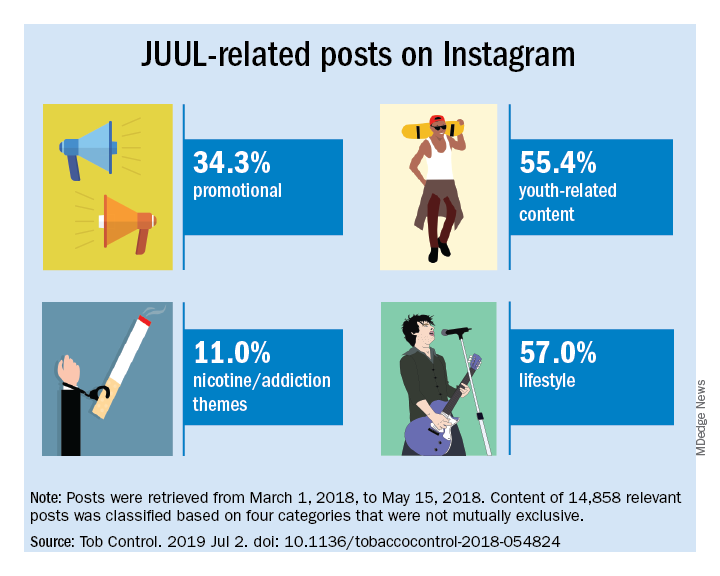
The investigators did a content analysis of social media posts on Instagram related to JUUL and JUUL-like products from March 1 to May 15, 2018. Hash-tag keyword queries of JUUL-related posts on Instagram were collected from the Instagram application programming interface through NUVI, a licensed syndicator of the Instagram firehose. The researchers used 50 hashtags to capture and enumerate individual posts. Examples of the hashtags used are #juul, #juuling, #juulvapor, #juulpod, #switchtojuul, and #juulgang. All posts were included from the official JUUL account and JUUL-related accounts with the highest number of followers at the time of data collection (e.g., @juulcentral, @juulnation, @juul_university, @juul.girls).
The search identified 14,838 posts by 5,201 unique users that featured content relating to product promotion, nicotine and addiction messages, youth culture, and lifestyle themes. Posts were rated promotional incluced branded content, URLs linking to commercial websites, and hashtags indicating affiliations with commercial sites.
Nicotine/addiction posts contained “references to nicotine, including compatible pod-related brand names and nicotine content, as well as any references to addiction or nicotine dependence (e.g., daily use, being an addict, junkie, “nichead,” fiend, maniac), or effects of nicotine use (e.g., “buzz”).
Youth-themed posts included stylistic features such as jargon or slang, acronyms common among youth (e.g., di4j, doit4juul), youth-oriented cartoons, JUUL wrap imagery, youth entertainment, and music. Posts with references to school, the classroom, and other places frequented by youth and youth social networks, family, and peers were included in the youth-themed category.
Lifestyle content referenced "social norms and acceptability-related messages contained any mentions of online or offline communitiesand peer groups (eg, collegelife, juulgirls, juulgang, vapeusa, collegedaily, vapelyfe hashtags) as well as JUUL use during social activities, events, social acceptance of JUULing and any mentions of JUULing as a characteristic of cultural or social identity."
Content analysis of the posts found that 34.3% were promotional, 11% referenced nicotine and addiction themes, and 55.4% featured youth-oriented cultural themes, and 57% featured lifestyle themes. There was overlap among the categories, for example, the 71.9% of the promotional posts had lifestyle messages included and 86.3% of the nicotine/addiction posts contained lifestyle elements. The promotional posts also contained some hashtags referencing cannabis (#420, #710).
An additional feature of the promotional posts is the incentivizing messages. “More than more than a third of JUUL-related posts containing overt promotional content that highlights ways to obtain products at reduced cost, such as giveaways and incentivized friend-tagging. This finding is consistent with previous research which found that Twitter users employed person-tagging (e.g., @username) when purchasing JUUL, suggesting friend-tagging plays an important role in motivating product use,” the researchers wrote.
The study was limited by the short time frame, the analysis of Instagram postings only, and the limitation of only 50 hashtags. These limitations may result in underreporting of the amount of JUUL-related social media messaging that targets youth. In addition, the investigators did not analyze the origin of accounts or the identity of the individuals creating the content.
“The results of this study demonstrate the reach of organic posts that contain JUUL-related content, and posts by third-party vendors of vaping products, who continue to push explicitly youth-targeted advertisements for JUUL and similar e-cigarette products under JUUL-related hashtags,” Dr. Hair wrote. “Our research and studies done by others in the field are one way to build the evidence base to advocate for stricter social media marketing restrictions on tobacco products that are applicable to all players in the field.”
She added that the Food and Drug Administration should use its power to restrict e-cigarette manufacturers from using social media to market to young people. “We also think that social media platforms should do more to adopt and enforce strong and well-enforced policies against the promotion of any tobacco products to young adults,” she concluded.
The study was sponsored by the Truth Initiative. The Truth Initiative was created as a part of the Master Settlement Agreement (MSA) that was negotiated between the tobacco industry and 46 states and the District of Columbia in 1998. The MSA created the American Legacy Foundation (now known as the Truth Initiative), a nonprofit research and educational organization that focuses its efforts on preventing teen smoking and encouraging smokers to quit.
SOURCE: Czaplicki L et al. Tob Control. 2019 Jul 2; doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2018-054824.
This article was updated 7/17/2019.
with targeted messages and images, a study of e-cigarette promotion has found.
In 2018, the JUUL company declared a commitment to support efforts to raise the age of legal purchase of tobacco to age 21 years in all U.S. states. In addition, JUUL deleted its official Facebook and Instagram accounts in November 2018, but the promotion of these products has continued through affiliated marketing campaigns from other online vendors.
Vaping among teens has shot up in popularity in recent years. The prevalence of vaping among young people aged 16-19 years has been estimated at 16% in 2018, up from 11% in 2017 (BMJ. 2019 Jun 19. doi: 10.1136/bmj.12219. A study published in JAMA Pediatrics (2019;173[7]:690-92) found that an estimated 81% of users following a popular Twitter account (@JUULvapor) were aged 13-20 years, with 45% in the 13-17 year age range.
Elizabeth C. Hair, PhD, senior vice president of the Truth Initiative Schroeder Institute, and a team of investigators conducted a study of the “proliferation of JUUL-related content across four themes over a 3-month period: overt promotional content, nicotine and addiction-related content, lifestyle content, and content related to youth culture.” The study appeared online in Tobacco Control (2019 Jul 2; doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2018-054824).
The investigators did a content analysis of social media posts on Instagram related to JUUL and JUUL-like products from March 1 to May 15, 2018. Hash-tag keyword queries of JUUL-related posts on Instagram were collected from the Instagram application programming interface through NUVI, a licensed syndicator of the Instagram firehose. The researchers used 50 hashtags to capture and enumerate individual posts. Examples of the hashtags used are #juul, #juuling, #juulvapor, #juulpod, #switchtojuul, and #juulgang. All posts were included from the official JUUL account and JUUL-related accounts with the highest number of followers at the time of data collection (e.g., @juulcentral, @juulnation, @juul_university, @juul.girls).
The search identified 14,838 posts by 5,201 unique users that featured content relating to product promotion, nicotine and addiction messages, youth culture, and lifestyle themes. Posts were rated promotional incluced branded content, URLs linking to commercial websites, and hashtags indicating affiliations with commercial sites.
Nicotine/addiction posts contained “references to nicotine, including compatible pod-related brand names and nicotine content, as well as any references to addiction or nicotine dependence (e.g., daily use, being an addict, junkie, “nichead,” fiend, maniac), or effects of nicotine use (e.g., “buzz”).
Youth-themed posts included stylistic features such as jargon or slang, acronyms common among youth (e.g., di4j, doit4juul), youth-oriented cartoons, JUUL wrap imagery, youth entertainment, and music. Posts with references to school, the classroom, and other places frequented by youth and youth social networks, family, and peers were included in the youth-themed category.
Lifestyle content referenced "social norms and acceptability-related messages contained any mentions of online or offline communitiesand peer groups (eg, collegelife, juulgirls, juulgang, vapeusa, collegedaily, vapelyfe hashtags) as well as JUUL use during social activities, events, social acceptance of JUULing and any mentions of JUULing as a characteristic of cultural or social identity."
Content analysis of the posts found that 34.3% were promotional, 11% referenced nicotine and addiction themes, and 55.4% featured youth-oriented cultural themes, and 57% featured lifestyle themes. There was overlap among the categories, for example, the 71.9% of the promotional posts had lifestyle messages included and 86.3% of the nicotine/addiction posts contained lifestyle elements. The promotional posts also contained some hashtags referencing cannabis (#420, #710).
An additional feature of the promotional posts is the incentivizing messages. “More than more than a third of JUUL-related posts containing overt promotional content that highlights ways to obtain products at reduced cost, such as giveaways and incentivized friend-tagging. This finding is consistent with previous research which found that Twitter users employed person-tagging (e.g., @username) when purchasing JUUL, suggesting friend-tagging plays an important role in motivating product use,” the researchers wrote.
The study was limited by the short time frame, the analysis of Instagram postings only, and the limitation of only 50 hashtags. These limitations may result in underreporting of the amount of JUUL-related social media messaging that targets youth. In addition, the investigators did not analyze the origin of accounts or the identity of the individuals creating the content.
“The results of this study demonstrate the reach of organic posts that contain JUUL-related content, and posts by third-party vendors of vaping products, who continue to push explicitly youth-targeted advertisements for JUUL and similar e-cigarette products under JUUL-related hashtags,” Dr. Hair wrote. “Our research and studies done by others in the field are one way to build the evidence base to advocate for stricter social media marketing restrictions on tobacco products that are applicable to all players in the field.”
She added that the Food and Drug Administration should use its power to restrict e-cigarette manufacturers from using social media to market to young people. “We also think that social media platforms should do more to adopt and enforce strong and well-enforced policies against the promotion of any tobacco products to young adults,” she concluded.
The study was sponsored by the Truth Initiative. The Truth Initiative was created as a part of the Master Settlement Agreement (MSA) that was negotiated between the tobacco industry and 46 states and the District of Columbia in 1998. The MSA created the American Legacy Foundation (now known as the Truth Initiative), a nonprofit research and educational organization that focuses its efforts on preventing teen smoking and encouraging smokers to quit.
SOURCE: Czaplicki L et al. Tob Control. 2019 Jul 2; doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2018-054824.
This article was updated 7/17/2019.
with targeted messages and images, a study of e-cigarette promotion has found.
In 2018, the JUUL company declared a commitment to support efforts to raise the age of legal purchase of tobacco to age 21 years in all U.S. states. In addition, JUUL deleted its official Facebook and Instagram accounts in November 2018, but the promotion of these products has continued through affiliated marketing campaigns from other online vendors.
Vaping among teens has shot up in popularity in recent years. The prevalence of vaping among young people aged 16-19 years has been estimated at 16% in 2018, up from 11% in 2017 (BMJ. 2019 Jun 19. doi: 10.1136/bmj.12219. A study published in JAMA Pediatrics (2019;173[7]:690-92) found that an estimated 81% of users following a popular Twitter account (@JUULvapor) were aged 13-20 years, with 45% in the 13-17 year age range.
Elizabeth C. Hair, PhD, senior vice president of the Truth Initiative Schroeder Institute, and a team of investigators conducted a study of the “proliferation of JUUL-related content across four themes over a 3-month period: overt promotional content, nicotine and addiction-related content, lifestyle content, and content related to youth culture.” The study appeared online in Tobacco Control (2019 Jul 2; doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2018-054824).
The investigators did a content analysis of social media posts on Instagram related to JUUL and JUUL-like products from March 1 to May 15, 2018. Hash-tag keyword queries of JUUL-related posts on Instagram were collected from the Instagram application programming interface through NUVI, a licensed syndicator of the Instagram firehose. The researchers used 50 hashtags to capture and enumerate individual posts. Examples of the hashtags used are #juul, #juuling, #juulvapor, #juulpod, #switchtojuul, and #juulgang. All posts were included from the official JUUL account and JUUL-related accounts with the highest number of followers at the time of data collection (e.g., @juulcentral, @juulnation, @juul_university, @juul.girls).
The search identified 14,838 posts by 5,201 unique users that featured content relating to product promotion, nicotine and addiction messages, youth culture, and lifestyle themes. Posts were rated promotional incluced branded content, URLs linking to commercial websites, and hashtags indicating affiliations with commercial sites.
Nicotine/addiction posts contained “references to nicotine, including compatible pod-related brand names and nicotine content, as well as any references to addiction or nicotine dependence (e.g., daily use, being an addict, junkie, “nichead,” fiend, maniac), or effects of nicotine use (e.g., “buzz”).
Youth-themed posts included stylistic features such as jargon or slang, acronyms common among youth (e.g., di4j, doit4juul), youth-oriented cartoons, JUUL wrap imagery, youth entertainment, and music. Posts with references to school, the classroom, and other places frequented by youth and youth social networks, family, and peers were included in the youth-themed category.
Lifestyle content referenced "social norms and acceptability-related messages contained any mentions of online or offline communitiesand peer groups (eg, collegelife, juulgirls, juulgang, vapeusa, collegedaily, vapelyfe hashtags) as well as JUUL use during social activities, events, social acceptance of JUULing and any mentions of JUULing as a characteristic of cultural or social identity."
Content analysis of the posts found that 34.3% were promotional, 11% referenced nicotine and addiction themes, and 55.4% featured youth-oriented cultural themes, and 57% featured lifestyle themes. There was overlap among the categories, for example, the 71.9% of the promotional posts had lifestyle messages included and 86.3% of the nicotine/addiction posts contained lifestyle elements. The promotional posts also contained some hashtags referencing cannabis (#420, #710).
An additional feature of the promotional posts is the incentivizing messages. “More than more than a third of JUUL-related posts containing overt promotional content that highlights ways to obtain products at reduced cost, such as giveaways and incentivized friend-tagging. This finding is consistent with previous research which found that Twitter users employed person-tagging (e.g., @username) when purchasing JUUL, suggesting friend-tagging plays an important role in motivating product use,” the researchers wrote.
The study was limited by the short time frame, the analysis of Instagram postings only, and the limitation of only 50 hashtags. These limitations may result in underreporting of the amount of JUUL-related social media messaging that targets youth. In addition, the investigators did not analyze the origin of accounts or the identity of the individuals creating the content.
“The results of this study demonstrate the reach of organic posts that contain JUUL-related content, and posts by third-party vendors of vaping products, who continue to push explicitly youth-targeted advertisements for JUUL and similar e-cigarette products under JUUL-related hashtags,” Dr. Hair wrote. “Our research and studies done by others in the field are one way to build the evidence base to advocate for stricter social media marketing restrictions on tobacco products that are applicable to all players in the field.”
She added that the Food and Drug Administration should use its power to restrict e-cigarette manufacturers from using social media to market to young people. “We also think that social media platforms should do more to adopt and enforce strong and well-enforced policies against the promotion of any tobacco products to young adults,” she concluded.
The study was sponsored by the Truth Initiative. The Truth Initiative was created as a part of the Master Settlement Agreement (MSA) that was negotiated between the tobacco industry and 46 states and the District of Columbia in 1998. The MSA created the American Legacy Foundation (now known as the Truth Initiative), a nonprofit research and educational organization that focuses its efforts on preventing teen smoking and encouraging smokers to quit.
SOURCE: Czaplicki L et al. Tob Control. 2019 Jul 2; doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2018-054824.
This article was updated 7/17/2019.
FROM TOBACCO CONTROL